1. Introduction
Screen-printed carbon electrode (SPCE) is a useful technique that has been widely used in the practical application of biosensors oriented toward point-of-care testing (POCT) [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5]. Many researchers have reported electrochemical biosensors that use SPCE to detect hormones [
6,
7,
8], ions [
9,
10], metals [
11], nucleic acid [
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17] and proteins [
18,
19,
20,
21]. Although the sensitivity of the electrochemical biosensor is controlled by surface conditions, such as the diffusion coefficient and electron transfer rate [
22], these are altered by the modification of molecular recognition elements and blocking materials on the electrode surface. We previously reported biosensors that use redox reactions of gold nanoparticles and found that antibodies and blocking materials modified on the electrode reduced the diffusion coefficient and electron transfer rate [
23]. As it is necessary to measure very small amounts of biomarkers to achieve POCT, electrochemical biosensors with higher sensitivity and selectivity are required. Therefore, a more efficient method for modifying molecular recognition elements, such as antibodies, without degrading their electrochemical properties is required. However, compared to gold or platinum electrodes, surface modification of SPCEs is difficult because the carbon surface is chemically or physically stable [
24]. For gold or platinum electrodes, self-assembled monolayer (SAM) is a popular method for modifying antibodies [
25,
26], aptamers [
27], and others [
28,
29,
30,
31]. In addition, drop-casted biopolymers and nano-materials do not depend on the electrode material [
14,
32,
33,
34,
35,
36,
37,
38,
39]
For the carbon electrode, direct production of a carboxyl group, which is acts as a scaffold of covalent bonds, on the carbon surface using electrochemical activation has been reported [
40,
41,
42]. For example, the SPCE surface was activated to produce a carboxyl group by applying a potential of 0.9 V for 60 s in 0.5 M acetate buffer (ABS, pH 4.80) [
43] or 1.0 V for 50 s in 0.10 M sulfuric acid solution [
44]. Oxygen plasma (O
2-plasma) treatment is an efficient technique for producing carboxyl groups on the surface [
45,
46,
47]. However, regarding SPCE, there have been no reports of antibody modification by generating carboxyl groups using O
2-plasma treatment, and only improvements in electrochemical performance have been discussed. For example, O
2 plasma is used to remove the binder from carbon inks and control the surface roughness of SPCE [
48,
49,
50,
51,
52,
53].
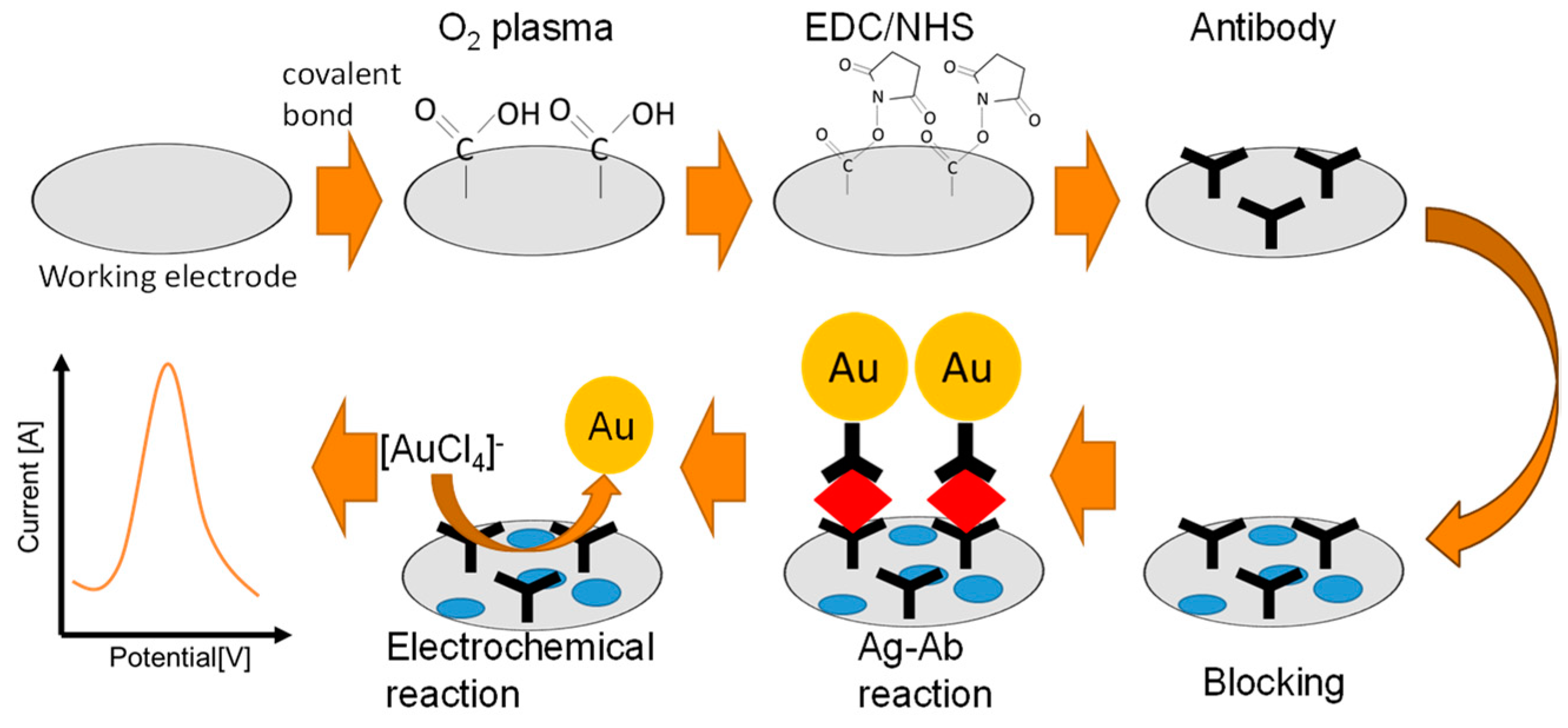
In this study, we compared the antibody modification by O
2-plasma treatment and physical adsorption using our original immunosensor, which is a gold-linked electrochemical immunoassay (GLEIA). This biosensor is based on a sandwich-type immunoassay applied directly on the electrode and detects the antigen concentration through the redox current of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) modified with a secondary antibody [
5,
23,
54,
55,
56,
57,
58]. Specifically, the AuNPs on the electrode are oxidized at a high potential to produce gold ions, and the concentration of nanoparticles is quantified by measuring the reduction current of gold ions. The chemical reaction is Au + Cl
4 ⇄AuCl
4 +3e (E
0= 0.803 V, vs Ag/AgCl sat). We previously reported that physically adsorbed antibodies decrease the electrochemical reaction rate because they act as a resistance on the electrode [
23]. Thus, O
2-plasma and covalent bonding reagents can be used asan alternative antibody modification method to physical adsorption. We investigated the plasma-treated surface by cyclic voltammetry, scanning electron microscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and contact angle analysis. Consequently, the generation of carboxyl groups on the electrode surface, changes in the surface charge, increased capacitance, and hydrophilicity were observed. These changes can be explained by the generation of carboxyl groups on the electrode surface, indicating that O
2-plasma treatment is a simple and effective surface modification method. We also observed that the O
2-plasma treated electrode shows higher sensitivity than without O
2-plasma because the covalently bonded antibody inhibited nonspecific adsorption with the abovementioned changes in the surface.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
All reagents used were of guaranteed grade and used without further purification. All inorganic salts, gold tetrachloride tetrahydrate (Au complex), 1-Ethyl-3-(3dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide ·HCl (EDC), N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS), polyethylene glycol (Mw is 20,000), trehalose dihydrate, and pH 7.5 D-PBS (-) were purchased from Fujifilm Wako Pure Chemicals (Osaka, Japan). AuNPs with diameters of 60 nm were purchased from BBI Solutions (Cardiff, UK). Anti-IgA (α), Human, Goat-Poly, A80-102A, and Purified Human IgA, P80-102 were purchased from Bethyl Laboratory (Montgomery, USA). Bovine serum albumin (BSA) was purchased from Jackson Immunoresearch (Pennsylvania, USA). All water used in this study was Milli-Q water (18.3 MΩ cm).
2.2. Instruments
A miniSTAT400 potentiostat was purchased from BioDevice Technology (Ishikawa, Japan). A screen-printed carbon electrode (DEP-EP-PP) with an integrated working electrode (surface area: 2.64 mm2), counter electrode, and Ag/AgCl reference electrode, with a total length of 11 mm, was also purchased from BioDevice Technology. All electrochemical measurements were performed by dropping 20 μL of sample onto the printed electrode unless otherwise stated. A UV-visible spectrometer (DS-11+) was purchased from Denovix (Delaware, USA). A micro-high-speed cooling centrifuge (kitman-24) was purchased from Tomy Seiko (Tokyo, Japan). An O2-plasma cleaner (PDC210) was purchased from Yamato Scientific (Tokyo, Japan). Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) was performed using an S-4800 (Hitachi High-Tech, Tokyo, Japan). X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) analysis was performed by Toray Research Center (Tokyo, Japan) using a Quantera SXM (Ulvac-PHI). Contact angle analysis was performed using a DMo-602 instrument obtained from Kyowa Interface Science (Saitama, Japan).
2.3. Electrochemical analysis of O2-plasma treated electrodes
O2-plasma treatment was performed in a 13.56 MHz ratio frequency (RF) plasma reactor. The SPCE with a cyclo olefin polymer (COP) film covering the connector part and reference electrode was placed in the reactor. After the reactor was first evacuated to a base pressure of less than 10−3 Pa, 200 cc O2 gas was introduced. The O2-plasma treatment of SPCE was performed at 75 W plasma power for a period of 5 s. The O2-plasma treated electrode was evaluated using cyclic voltammetry (CV) with the standard electrochemical mediators: potassium ferricyanide and Hexaammineruthenium(III) chloride, each containing 100 mM of Na2SO4 as the electrolyte,. For the ferricyanide, the sweep rates were 10 to 250 mV/s, and the sweep range was -400 to 600 mV. For the ruthenium, the sweep rates were 10 to 200 mV/s, and the sweep range was 700 to -700 mV. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) was also used to evaluate the kinetic parameters within the frequency range of 100 kHz to 0.1 Hz applied potential, superimposed on a DC potential of 0.1 V, with an AC of 10 mV peak-to-peak amplitude under 5 mM ferricyanide and 100 mM Na2SO4.
2.4. Surface analysis of O2-plasma treated electrodes
The electrode surface was analyzed by SEM, XPS, and contact angle measurement. SEM was used to observe the electrode surface after the antigen–antibody reaction to evaluate the AuNPs present on the surface. For this purpose, X-rays (monochromatic Al K∝ ray) of 200 μm diameter were irradiated on the electrode. O2-plasma treatment electrodes were stored in light-shielded vacuum gauges prior to XPS analysis. The contact angle measurement was conducted using water drops (2 μL). The drops were placed on the working electrode, the needle was pulsed back, and the drop shape was immediately captured using the camera. The obtained images were analyzed using FAMAS software to determine the contact angle by circle fitting. The contact angle was evaluated at each plasma treatment time and elapsed time.
2.5. Antibody modification
The antibody was modified on the electrode via physical adsorption and covalent bonding to compare the response of the sensor to the antibody modification process. For the physical adsorption, 2 µL of 50 µg/mL antibody in PBS was dropped onto the working electrode and incubated at 4°C for 1 h to adsorb the antibody. Next, 20 µL of 1% BSA in
Scheme 1.
PBS solution was dropped onto the entire electrode and incubated at room temperature for 1 h. For covalent bonding, 50:50 mM of EDC/NHS solution was dropped onto the O2-plasma treated working electrode and incubated for 30 min. Next, 2 uL of 50 ug/mL antibody in PBS was placed on the electrodes. Finally, 20 µL of 1% BSA in PBS solution was dropped onto the entire electrode and incubated at room temperature for 1 h (see
Scheme 1). The protein-modified electrode was stored at 4°C until use.
2.6. Preparing secondary antibody modified gold nanoparticles
Secondary antibody-modified AuNPs were prepared using a reported method [
5]. Then, the 0.9 mL of AuNP solution was mixed with the 0.1 mL of phosphate buffer (Na2HPO4/NaH2PO4, 50 mM, pH 7.5). 50 μg/mL of Anti-IgA was added to the Au nanoparticle solution to dissolve the 5 mM of phosphate buffer (pH 7.5) and kept for 10 min at room temperature. Hereinafter, this is referred to as the Au conjugate. Then, 0.1 mL of 10% BSA in PBS buffer and 0.05 mL of 1% PEG in PBS buffer were added to the Au conjugate. Au and Anti-IgA conjugate was collected by centrifugal operation (4000 g for 20 min at 4℃). After centrifugation, the Au Anti-IgA conjugate was suspended in 1 mL of preservation solution (1% BSA, 0.05% PEG 20000, 0.1% NaN3, and 150 mM NaCl in 20 mM Tris-HCl buffer, pH 8.2) and collected again in the same manner. For the stock solution, the Au and Anti-IgA conjugate was suspended in the preservation solution, and the optical density was adjusted to OD520 = 6. The Au Anti-IgA conjugate was diluted by 3 times with 50 w/v of trehalose (OD520 = 2) and dripping 5µL of this solution in the 96 well. Then, the 96 well was dried in a vacuum condition for 5 min. Dried wells were stored at 4℃ until use.
2.7. Immunosensor fabrication using O2 plasma treated SPCE
A sandwich type antigen-antibody (Ab-Ag) reaction occurred directly on the working electrode. The primary antibody-modified electrode was prepared by the method described above (
Scheme 1). IgA antigen solution (100 ng/mL) was prepared by diluting in PBS. For the Ab-Ag reaction, 10 µL of IgA solution was dropped in the prepared 96 well and mixed for 10 s. After 1 min, 2.0 µL of the solution was placed on the working electrode to incubate for 1 h at room temperature in the closed box with damped cotton (to maintain humidity to prevent the sample from drying). After rinsing with PBS and eliminating the PBS solution with N2 air, the direct redox reaction was performed in 2M KCl solution (20 µL) covering the entire electrode at room temperature. The pre-oxidation and DPV parameters were as follows: the beginning and end potentials were 800 and 200 mV, respectively, step potential was 4 mV, pulse amplitude (pulse potential) was 100 mV, pulse period was 200 ms, pulse width was 50 ms, and sampling width was set to 16 ms. All conditions were optimized through our further work.
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Comparing the surface change by electrochemical kinetics parameters
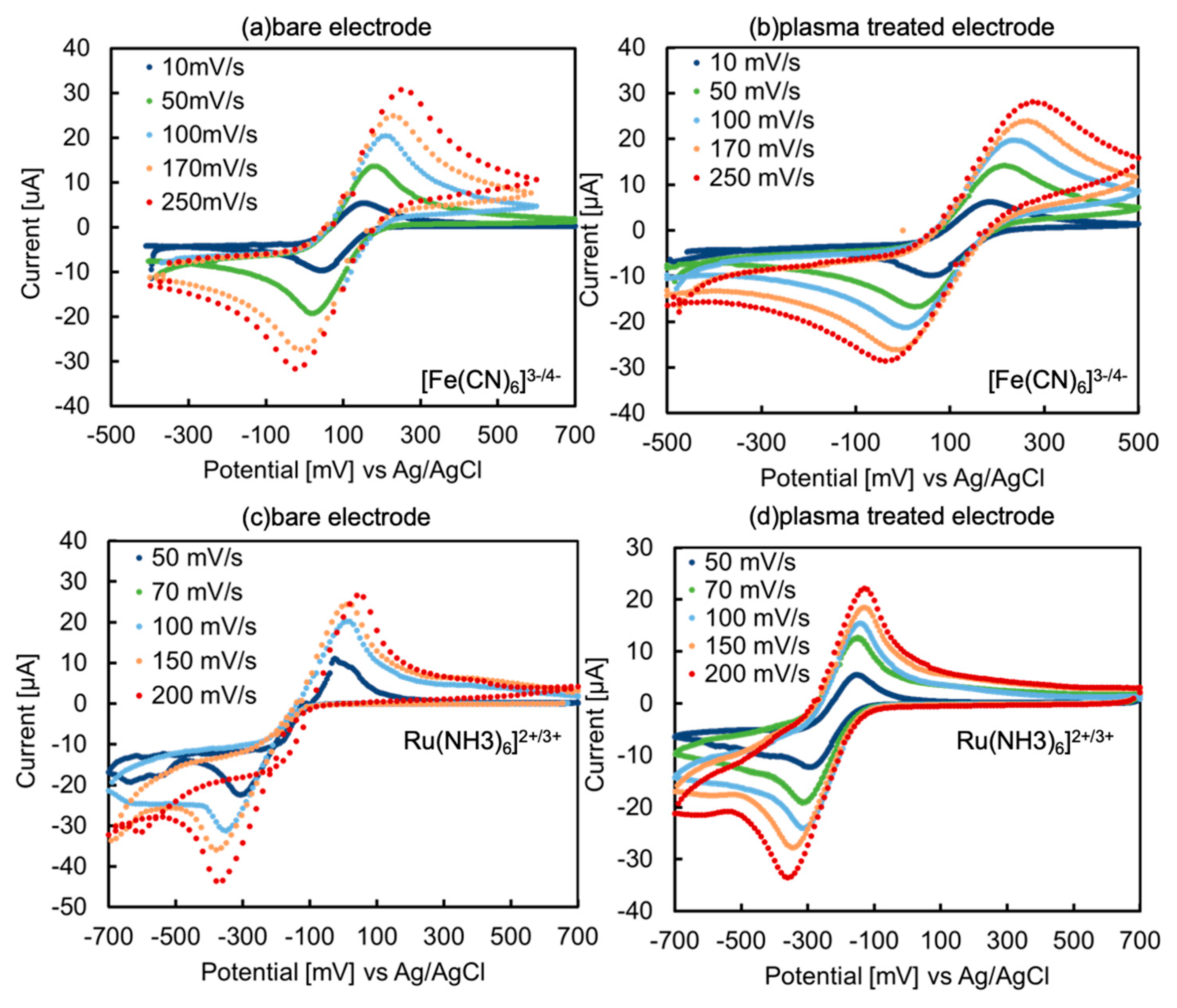
Figure 1a–d shows the cyclic voltammograms of 5 mM ferricyanide and ruthenium complex on the bare and O
2-plasma treated electrodes. Among these voltammograms, the electrochemical reaction is a reversible process because of the peak separations at the 50 mV/s scan rate of 152, 190, 286, and 178 mV.
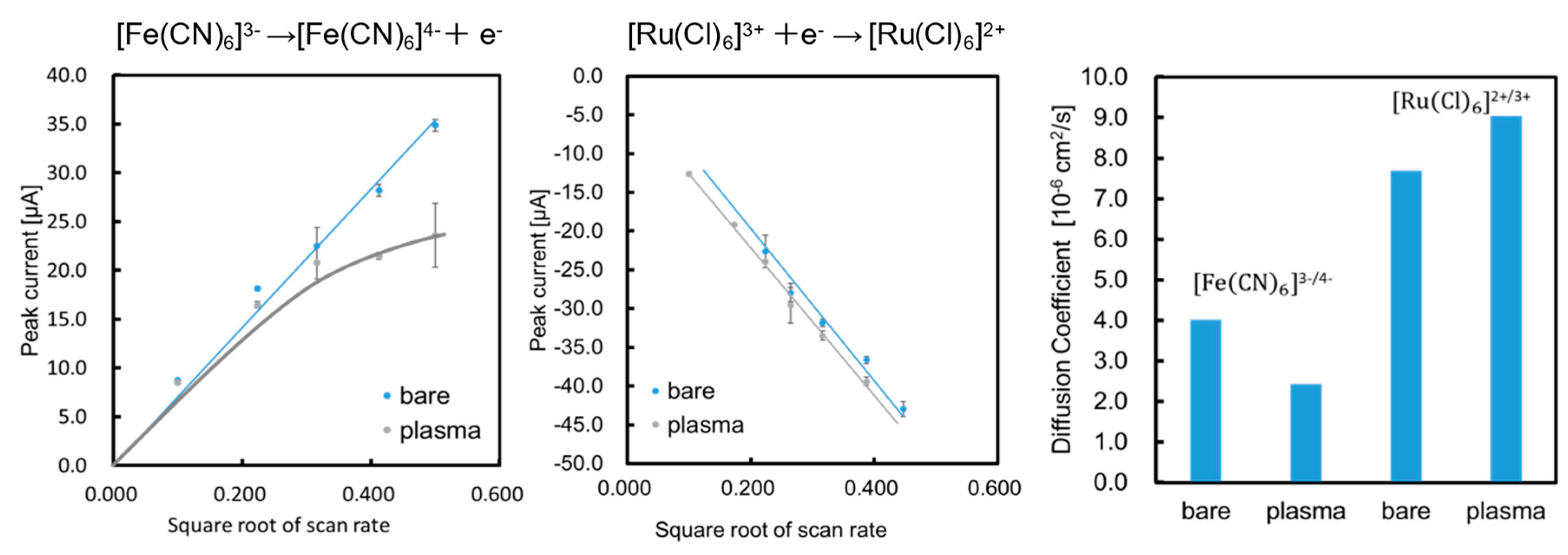
Figure 2a,b shows the relationship between peak current intensity and the square root of the scan rate. The diffusion coefficient for the reversible process was calculated using the following equation:
where
n is the number of electrons in the reaction,
A is the electrode area,
Cbulk is the concentration of the electrochemical mediators, and
v is the scan rate.
The diffusion coefficients of the two types of electrodes (bare and plasma) were calculated using Equation (1) for the oxidation of ferricyanide and reduction of the ruthenium complex. The results were
,
,
, and
, as summarized in
Figure 2c. These results indicate that the diffusion coefficient for the negatively charged ferricyanide decreased and that for the positively charged ruthenium complexes slightly increased. The formation of carboxyl groups changed the surface charge of the electrode to negative, which may lead to electrostatic interactions between the mediators and the surface. Next, charge transfer resistance (
Rct) and capacitance (
Cdl) were evaluated using EIS.
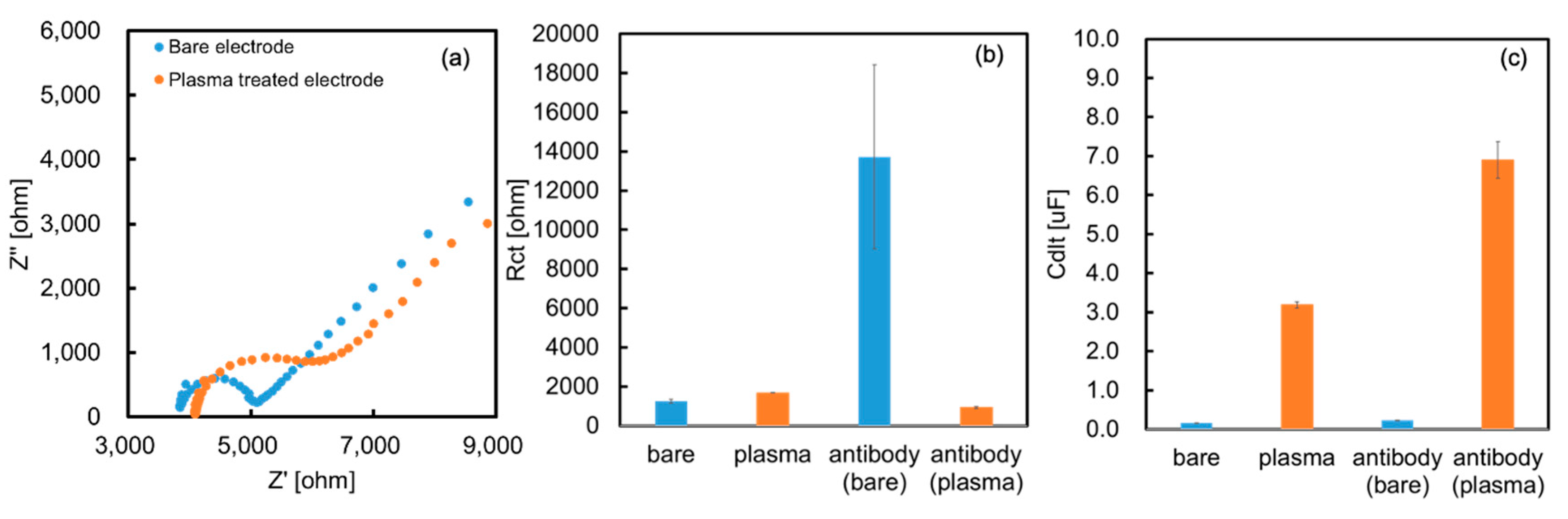
Figure 3a shows the Cole–Cole plots of both electrodes in 5 mM of ferricyanide. The bare electrode showed a clear semicircle, while the O
2-plasma treated electrode showed partial disappearance of the semicircle. Based on these results, Cdl and Rct were obtained by fitting using the equivalent circuit. Plasma treatment did not change Rct, but increased Cdl (
Figure 3b,c). This result supports the aforementioned surface charge change.
Therefore, the O
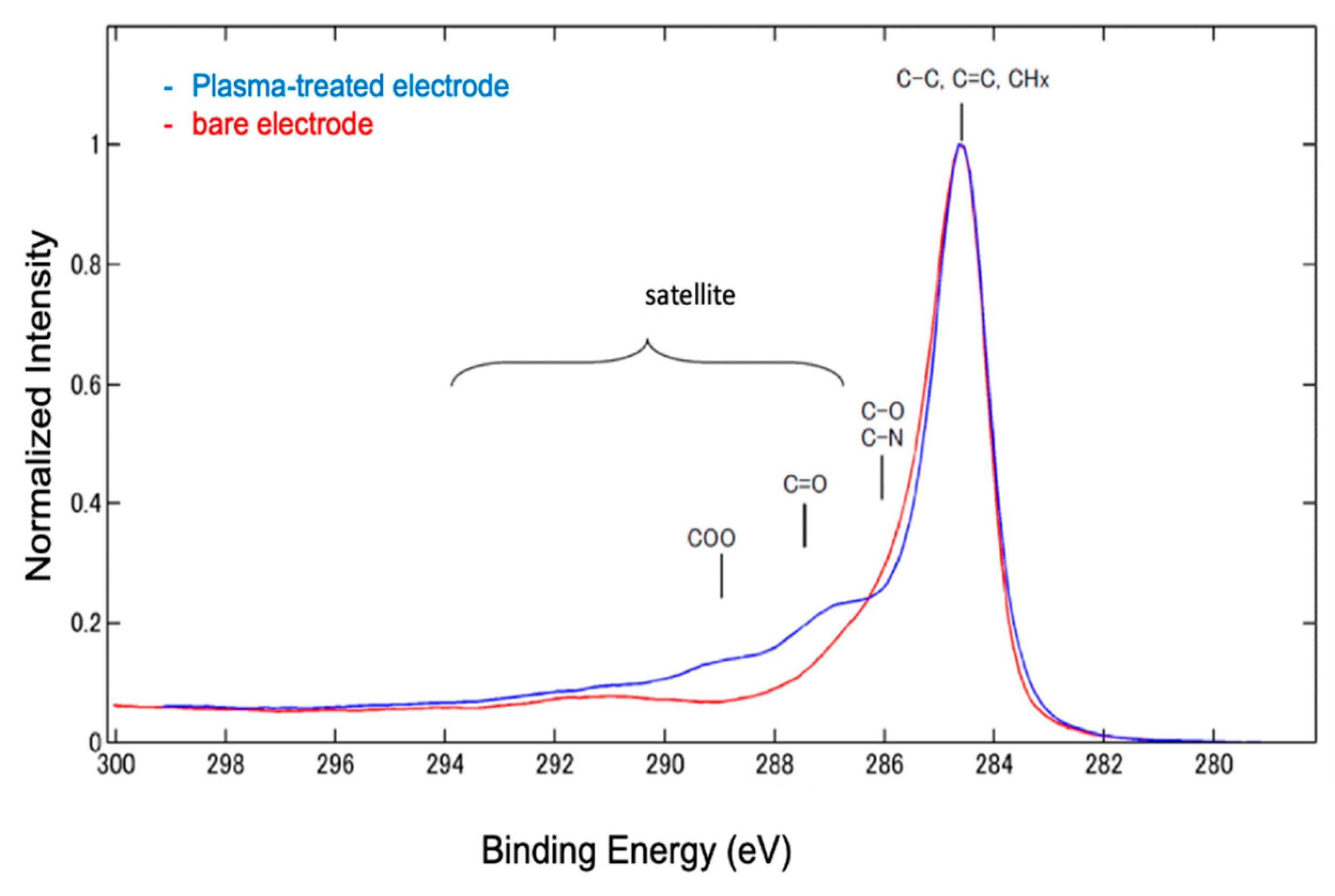
2-plasma treatment changes the surface charge of the electrode and alters its electrochemical properties. Surface analysis using XPS suggested that this change in surface charge was due to the formation of carboxyl groups (
Figure 4). Our results did not show any improvement in the electrode performance owing to the removal of impurities or binders in the SPCE. On the contrary, electrostatic interactions with reactive species and improvement in hydrophilicity were observed due to the generation of carboxyl groups. These results depend on the electrode materials and plasma irradiation conditions, indicating that individual optimization is required.
We also performed EIS measurements on the electrode after antibody modification. The results are shown in
Figure 3b,c, where Rct increased when the antibody was modified by physical adsorption, and Cdl increased when it was modified by covalent bonding. These contrasting results are interesting and may indicate differences in the orientation and adsorption conditions of the antibody on each electrode. The antibody simply functions as an insulator because it is physically adsorbed on the bare electrodes and increases Rct. However, a gap occurs between the antibody and electrode because the antibody is modified by covalent bonding at the O
2-plasma treated electrode. Consequently, electrode resistance did not occur; instead, the electric double layer capacitance was altered by the electric charge of the antibody.
3.2. Sensor characteristics
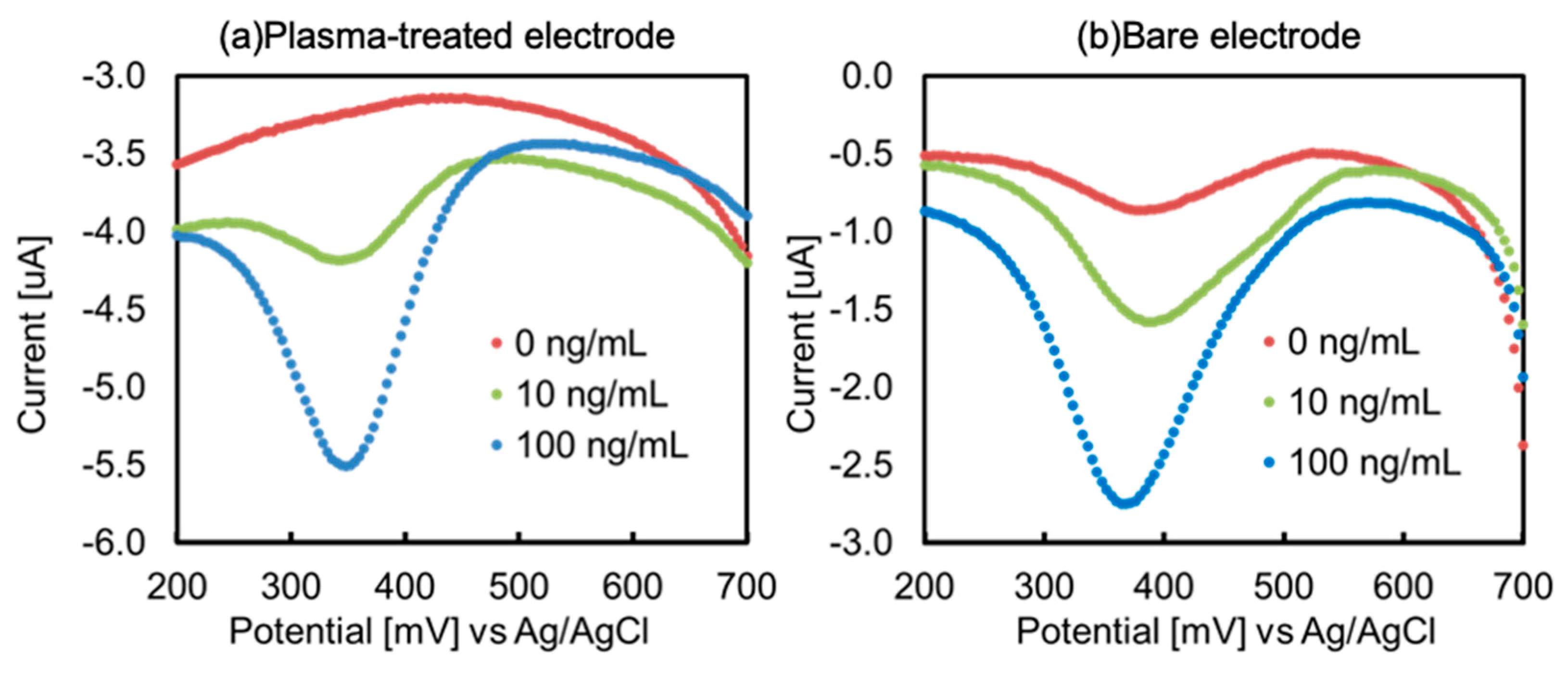
Figure 5 shows differential pulse voltammograms of the biosensor using the O
2-plasma-treated electrode (a) and the bare electrode (b). Comparing both voltammograms, the O
2-plasma treated electrode did not show much peak current intensity compared to the blank sample, indicating that non-specific adsorption was suppressed. This was attributed to the increased affinity with antigenic proteins owing to the increased hydrophilicity, and the generation of carboxylate by plasma treatment contributed to surface improvement. This increase in surface hydrophilicity is supported by the results of the contact angle measurements (
Figure S1), which show that the surface condition changes sufficiently even after 5 s of treatment, and there is no change in contact angle after 9 h of treatment. Therefore, O
2-plasma treatment not only generates carboxylate but also suppresses non-specific adsorption by improving hydrophilicity. The voltammograms also showed an increase in the background current at the O
2-plasma treated electrode. This may have been due to an increase in the charging current. In general, the charge current (
) is given by Equation (2).
where
E is applied potential,
Rs is solution resistance, and
t is potential applied time.
In other words, the increase in background current is associated with an increase in Cdl. In addition, because DPV was used in this study, the Faraday current could be detected even when the charge current was increased. The biosensor measurement results correlated with the electrode surface evaluation results, highlighting the relationship between the surface conditions and sensor sensitivity.
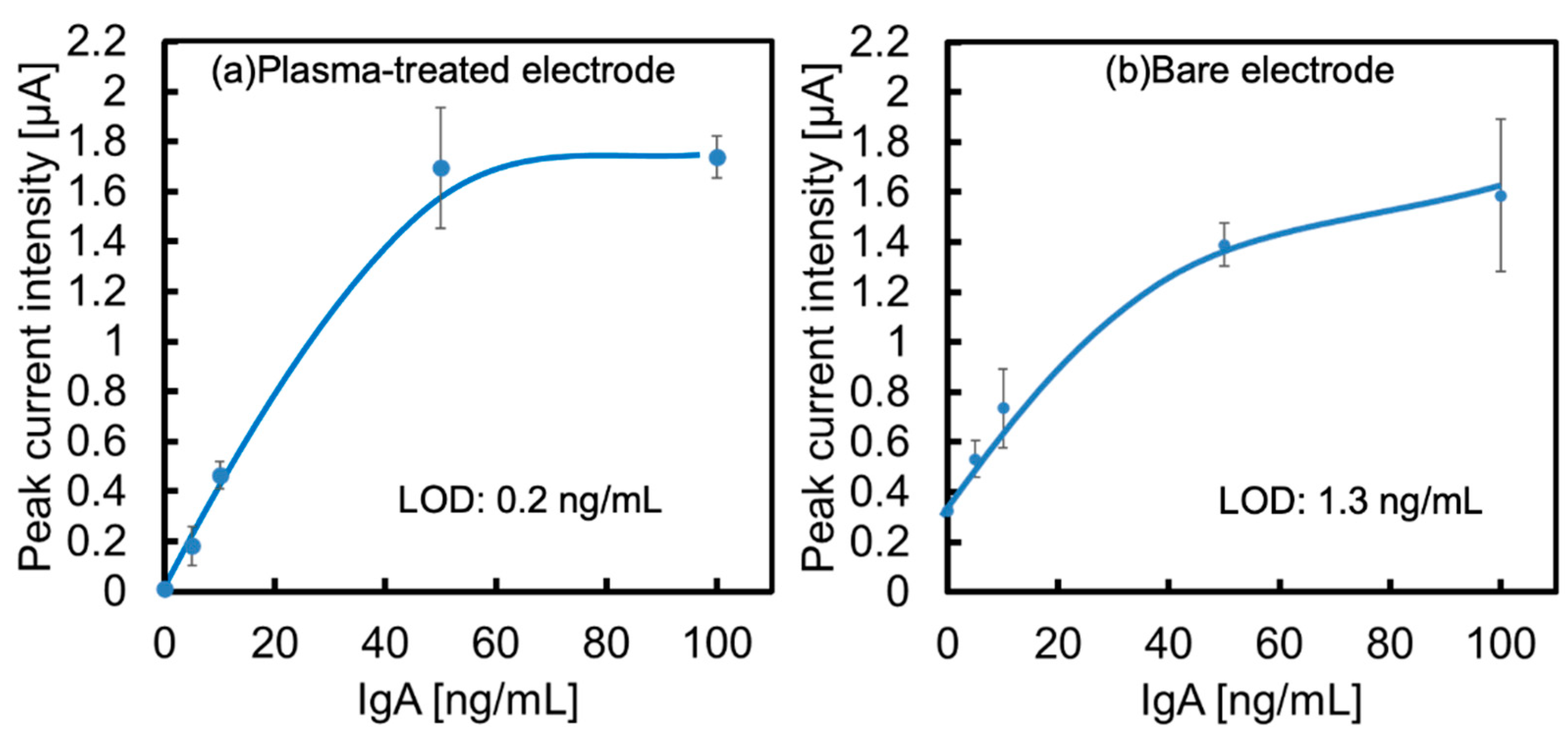
The calibration curves obtained from each voltammogram are shown in
Figure 6a,b. The limit of the detection (LOD) of both electrodes at this time was calculated from 3σ to be 0.2 ng/mL for the O
2-plasma treated electrode (
Figure 6a) and 3.9 ng/mL for the bare electrode (
Figure 6b). Based on these results, we succeeded in increasing the sensitivity by a factor of 20 using an O
2-plasma treated electrode.
This is due to the aforementioned improvement in the surface conditions of the electrode and the suppression of non-specific adsorption by plasma treatment, which is effective.
Table S1 lists the signal values, averages, and standard deviations of each calibration curve used in the LOD calculations. The O
2-plasma treated electrode reduced the blank signal.
We observed the electrode surface immediately after reaction with 100 ng/mL IgA using SEM and found the presence of nanoparticles on the electrode (
Figure S2). The number of AuNPs present on the electrode surface after the antigen–antibody reaction was counted: 195 ± 47 for the O
2-plasma treated electrode and 95 ± 24 for the bare electrode. These results also suggest an increase in antibody activity at the O
2-plasma treated electrode. This is because the modification of the antibody with an amide bond improves the orientation of the Fab fragments. This indicates that the DPV conditions were not optimized for the O
2-plasma treated electrode, suggesting that further work is required. However, the results obtained in this study show a close relationship between the surface conditions and sensor sensitivity, and the importance of surface design becomes clear.
4. Conclusion
We investigated the modification of SPCE using O2-plasma to develop highly sensitive electrochemical biosensors. XPS analysis and contact angle measurements of the O2-plasma treated electrode confirmed the generation of carboxyl groups and improved hydrophilicity. We also investigated the electrode surface using electrochemical methods such as CV and EIS. The results of both methods support the XPS and contact angle measurements, and the electrode surface was successfully modified. Therefore, we modified antibodies with common covalent bonding reagents, such as EDC/NHS, to develop an electrochemical biosensor with improved sensitivity compared to conventional methods, such as the physical adsorption of antibodies. The increased sensitivity was attributed to the suppression of nonspecific adsorption owing to improved hydrophilicity and antibody orientation. Furthermore, the O2-plasma treated SPCE did not show an improvement in electrochemical performance, as shown in previous studies. The reactivity with gold AuNPs appeared to decrease. As a results, we found a close relationship between the substituents, charge, and hydrophilicity of the electrode surface and electrochemical activity, which affects sensor sensitivity. Our findings relate to the relationship between the electrode surface conditions and sensor sensitivity, and we might identify important factors in the discussion of antibody modification methods.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on
Preprints.org. Figure S1: Contact angle measurement of plasma treated electrode. Figure S2 : Scanning electron microscopy images observed from after antigen–antibody reaction on plasma-treated electrode (a) and bare electrode (b). Table S1: Signal values used in the calibration curves.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, SO and ET; analysis, SO, MS and ET; writing-original draft preparation, SO; review and editing, MS, HN and ET; supervision, ET; funding acquisition, SO, HN and ET. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI (Grant Number JP15H05769) and operating expenses from AIST.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- N. Thiyagarajan, J.-L. Chang, K. Senthilkumar, and J.-M. Zen, "Disposable electrochemical sensors: A mini review," Electrochemistry Communications, vol. 38, pp. 86-90, 2014. [CrossRef]
- K. Omidfar, A. Dehdast, H. Zarei, B. K. Sourkohi, and B. Larijani, "Development of urinary albumin immunosensor based on colloidal AuNP and PVA," Biosens Bioelectron, vol. 26, no. 10, pp. 4177-83, Jun 15 2011. [CrossRef]
- J. Su et al., "A Carbon-Based DNA Framework Nano-Bio Interface for Biosensing with High Sensitivity and a High Signal-to-Noise Ratio," ACS Sens, vol. 5, no. 12, pp. 3979-3987, Dec 24 2020. [CrossRef]
- Y. W. Hartati et al., "An aptasensor using ceria electrodeposited-screen-printed carbon electrode for detection of epithelial sodium channel protein as a hypertension biomarker," R Soc Open Sci, vol. 8, no. 2, p. 202040, Feb 17 2021. [CrossRef]
- S. Osaki, S. I. Wakida, M. Saito, and E. Tamiya, "Towards On-site Determination of Secretory IgA in Artificial Saliva with Gold-Linked Electrochemical Immunoassay (GLEIA) Using Portable Potentiostat and Disposable Printed Electrode," Appl Biochem Biotechnol, vol. 193, no. 5, pp. 1311-1320, May 2021. [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, K. C. Lin, S. Muthukumar, and S. Prasad, "Autonomous, Real-Time Monitoring Electrochemical Aptasensor for Circadian Tracking of Cortisol Hormone in Sub-microliter Volumes of Passively Eluted Human Sweat," ACS Sens, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 63-72, Jan 22 2021. [CrossRef]
- P. Pusomjit, P. Teengam, N. Thepsuparungsikul, S. Sanongkiet, and O. Chailapakul, "Impedimetric determination of cortisol using screen-printed electrode with aptamer-modified magnetic beads," Mikrochim Acta, vol. 188, no. 2, p. 41, Jan 15 2021. [CrossRef]
- W. Tang, L. Yin, J. R. Sempionatto, J. M. Moon, H. Teymourian, and J. Wang, "Touch-Based Stressless Cortisol Sensing," Adv Mater, vol. 33, no. 18, p. e2008465, May 2021. [CrossRef]
- B. M. Gunasekaran, G. K. Rajendran, J. B. B. Rayappan, J. R. Sivanesan, N. Nesakumar, and A. W. Paulraj, "Covalently Grafted 4-Aminopyridine-Reduced Graphene Oxide-Modified Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode for Electrochemical Sensing of Lead Ions," Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, vol. 48, no. 6, pp. 7721-7738, Jun 2023. [CrossRef]
- J. H. Hwang, D. Fox, J. Stanberry, V. Anagnostopoulos, L. Zhai, and W. H. Lee, "Direct Mercury Detection in Landfill Leachate Using a Novel AuNP-Biopolymer Carbon Screen-Printed Electrode Sensor," Micromachines (Basel), vol. 12, no. 6, Jun 1 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. Biyani et al., "DEP-On-Go for Simultaneous Sensing of Multiple Heavy Metals Pollutants in Environmental Samples," Sensors (Basel), vol. 17, no. 1, Dec 27 2016. [CrossRef]
- K. Yamanaka et al., "Rapid detection for primary screening of influenza A virus: microfluidic RT-PCR chip and electrochemical DNA sensor," Analyst, vol. 136, no. 10, pp. 2064-8, May 21 2011. [CrossRef]
- P. A. Rasheed and N. Sandhyarani, "Electrochemical DNA sensors based on the use of gold nanoparticles: a review on recent developments," Microchimica Acta, vol. 184, no. 4, pp. 981-1000, 2017. [CrossRef]
- S. Gupta, C. N. Murthy, and C. R. Prabha, "Recent advances in carbon nanotube based electrochemical biosensors," (in English), International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, Review vol. 108, pp. 687-703, Mar 2018. [CrossRef]
- H. Yang, "Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Biosensor Assembled by Au Nanoparticle /MOF-5 Composite Electrode for DNA Detection," International Journal of Electrochemical Science, pp. 5491-5507, 2019. [CrossRef]
- M. Z. H. Khan, M. R. Hasan, S. I. Hossain, M. S. Ahommed, and M. Daizy, "Ultrasensitive detection of pathogenic viruses with electrochemical biosensor: State of the art," Biosens Bioelectron, vol. 166, p. 112431, Oct 15 2020. [CrossRef]
- D. Feng et al., "DNA tetrahedron-mediated immune-sandwich assay for rapid and sensitive detection of PSA through a microfluidic electrochemical detection system," Microsyst Nanoeng, vol. 7, p. 33, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, H. Shirazi, N. Pourbagher, A. Akbarzadeh, and K. Omidfar, "An electrochemical immunosensor for digoxin using core-shell gold coated magnetic nanoparticles as labels," Mol Biol Rep, vol. 41, no. 3, pp. 1659-68, Mar 2014. [CrossRef]
- P. Duangkaew et al., "Ultrasensitive electrochemical immunosensor based on dual signal amplification process for p16(INK4a) cervical cancer detection in clinical samples," Biosens Bioelectron, vol. 74, pp. 673-9, Dec 15 2015. [CrossRef]
- K. Yamanaka, M. C. Vestergaard, and E. Tamiya, "Printable Electrochemical Biosensors: A Focus on Screen-Printed Electrodes and Their Application," Sensors (Basel), vol. 16, no. 10, Oct 21 2016. [CrossRef]
- Vasilescu, G. Nunes, A. Hayat, U. Latif, and J. L. Marty, "Electrochemical Affinity Biosensors Based on Disposable Screen-Printed Electrodes for Detection of Food Allergens," Sensors (Basel), vol. 16, no. 11, Nov 5 2016. [CrossRef]
- M. H. Yang, B. G. Choi, H. Park, W. H. Hong, S. Y. Lee, and T. J. Park, "Development of a Glucose Biosensor Using Advanced Electrode Modified by Nanohybrid Composing Chemically Modified Graphene and Ionic Liquid," Electroanalysis, vol. 22, no. 11, pp. 1223-1228, Jun 2010. [CrossRef]
- S. Osaki, W. V. Espulgar, S. Wakida, M. Saito, and E. Tamiya, "Optimization of electrochemical analysis for signal amplification in gold nanoparticle-probed immunoassays," (in English), Electrochimica Acta, Article vol. 432, p. 8, Nov 2022, Art no. 141180. [CrossRef]
- N. M. Nor, N. H. Ramli, H. Poobalan, K. Q. Tan, and K. A. Razak, "Recent Advancement in Disposable Electrode Modified with Nanomaterials for Electrochemical Heavy Metal Sensors," (in English), Critical Reviews in Analytical Chemistry, Review vol. 53, no. 2, pp. 253-288, Feb 2023. [CrossRef]
- R. K. Shervedani and A. Hatefi-Mehrjardi, "Electrochemical characterization of directly immobilized glucose oxidase on gold mercaptosuccinic anhydride self-assembled monolayer," (in English), Sensors and Actuators B-Chemical, Article vol. 126, no. 2, pp. 415-423, Oct 2007. [CrossRef]
- Tricase et al., "Electrochemical Investigation of Self-Assembling Monolayers toward Ultrasensitive Sensing," in 2022 IEEE International Conference on Flexible and Printable Sensors and Systems (FLEPS), Vienna, AUSTRIA, Jul 10-13 2022, NEW YORK: Ieee, 2022. [CrossRef]
- T. Goda and Y. Miyahara, "Label-free and reagent-less protein biosensing using aptamer-modified extended-gate field-effect transistors," Biosens Bioelectron, vol. 45, pp. 89-94, Jul 15 2013. [CrossRef]
- T. Wink, S. J. vanZuilen, A. Bult, and W. P. vanBennekom, "Self-assembled monolayers for biosensors," Analyst, vol. 122, no. 4, pp. R43-R50, Apr 1997. [CrossRef]
- S. Campuzano, M. Pedrero, C. Montemayor, E. Fatás, and J. M. Pingarrón, "Characterization of alkanethiol-self-assembled monolayers-modified gold electrodes by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy," Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, vol. 586, no. 1, pp. 112-121, 2006. [CrossRef]
- V. Ganesh, S. K. Pal, S. Kumar, and V. Lakshminarayanan, "Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) of alkoxycyanobiphenyl thiols on gold--a study of electron transfer reaction using cyclic voltammetry and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy," J Colloid Interface Sci, vol. 296, no. 1, pp. 195-203, Apr 1 2006. [CrossRef]
- D. Mandler and S. Kraus-Ophir, "Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) for electrochemical sensing," Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, vol. 15, no. 7-8, pp. 1535-1558, Jul 2011. [CrossRef]
- Y. Zeng, Z.-H. Zhu, R.-X. Wang, and G.-H. Lu, "Electrochemical determination of bromide at a multiwall carbon nanotubes-chitosan modified electrode," Electrochimica Acta, vol. 51, no. 4, pp. 649-654, 2005. [CrossRef]
- Q. Wang, B. Zhang, X. Lin, and W. Weng, "Hybridization biosensor based on the covalent immobilization of probe DNA on chitosan–mutiwalled carbon nanotubes nanocomposite by using glutaraldehyde as an arm linker," Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, vol. 156, no. 2, pp. 599-605, 2011. [CrossRef]
- G. Lai, L. Wang, J. Wu, H. Ju, and F. Yan, "Electrochemical stripping analysis of nanogold label-induced silver deposition for ultrasensitive multiplexed detection of tumor markers," Anal Chim Acta, vol. 721, pp. 1-6, Apr 6 2012. [CrossRef]
- H. Shirazi, A. Ahmadi, M. Darzianiazizi, S. Kashanian, S. Kashanian, and K. Omidfar, "Signal amplification strategy using gold/N-trimethyl chitosan/iron oxide magnetic composite nanoparticles as a tracer tag for high-sensitive electrochemical detection," IET Nanobiotechnol, vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 20-7, Feb 2016. [CrossRef]
- J. Kitikul, S. Satienperakul, A. Preechaworapun, P. Pookmanee, and T. Tangkuaram, "A Simple Flow Amperometric Electrochemical Biosensor Based on Chitosan Scaffolds and Gold Nanowires Modified on a Glassy Carbon Electrode for Detection of Glutamate in Food Products," Electroanalysis, vol. 29, no. 1, pp. 264-271, 2017. [CrossRef]
- S. Muniandy et al., "Carbon Nanomaterial-Based Electrochemical Biosensors for Foodborne Bacterial Detection," (in English), Critical Reviews in Analytical Chemistry, Review vol. 49, no. 6, pp. 510-533, Nov 2019. [CrossRef]
- N. X. Viet, N. X. Hoan, and Y. Takamura, "Development of highly sensitive electrochemical immunosensor based on single-walled carbon nanotube modified screen-printed carbon electrode," Materials Chemistry and Physics, vol. 227, pp. 123-129, 2019. [CrossRef]
- K. Torres-Rivero, A. Florido, and J. Bastos-Arrieta, "Recent Trends in the Improvement of the Electrochemical Response of Screen-Printed Electrodes by Their Modification with Shaped Metal Nanoparticles," (in English), Sensors, Review vol. 21, no. 8, p. 20, Apr 2021, Art no. 2596. [CrossRef]
- J. Wang, M. Pedrero, H. Sakslund, O. Hammerich, and J. Pingarron, "Electrochemical activation of screen-printed carbon strips," , Analyst, Article vol. 121, no. 3, pp. 345-350, Mar 1996. [CrossRef]
- P. Sundaresan, T. W. Chen, S. M. Chen, T. W. Tseng, and X. H. Liu, "Electrochemical Activation of Screen Printed Carbon Electrode for the Determination of Antibiotic Drug Metronidazole," International Journal of Electrochemical Science, vol. 13, no. 2, pp. 1441-1451, Feb 2018. [CrossRef]
- Y. Lu, C. Q. Bao, J. Zou, J. L. Xiao, W. Zhong, and Y. S. Gao, "Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Sensor for Sunset Yellow Based on Electrochemically Activated Glassy Carbon Electrode," Molecules, vol. 27, no. 16, Aug 2022, Art no. 5221. [CrossRef]
- Erdem, H. Senturk, E. Yildiz, and M. Maral, "Amperometric immunosensor developed for sensitive detection of SARS-CoV-2 spike S1 protein in combined with portable device," Talanta, vol. 244, Jul 2022, Art no. 123422. [CrossRef]
- M. Saito, M. Kitsunai, M. U. Ahmed, S. Sugiyama, and E. Tamiya, "Label-free electrochemical detection for food allergen using screen printed carbon electrode," Electrochemistry, vol. 76, no. 8, pp. 606-609, Aug 2008. [CrossRef]
- W. J. Kim et al., "Enhanced protein immobilization efficiency on a TiO2 surface modified with a hydroxyl functional group," Langmuir, vol. 25, no. 19, pp. 11692-7, Oct 6 2009. [CrossRef]
- R. Daum et al., "Fibronectin adsorption on oxygen plasma-treated polyurethane surfaces modulates endothelial cell response," J Mater Chem B, vol. 9, no. 6, pp. 1647-1660, Feb 14 2021. [CrossRef]
- J. Raj et al., "Surface immobilisation of antibody on cyclic olefin copolymer for sandwich immunoassay," Biosens Bioelectron, vol. 24, no. 8, pp. 2654-8, Apr 15 2009. [CrossRef]
- B. Garcia, A. Martinez-Alonso, C. A. Leon y Leon, and J. M. D. Tascon, "Modification of the surface properties of an activated carbon by oxygen plasma treatment," (in English), Fuel, Article; Proceedings Paper vol. 77, no. 6, pp. 613-624, May 1998. [CrossRef]
- K. Sudhakara Prasad, G. Muthuraman, and J.-M. Zen, "The role of oxygen functionalities and edge plane sites on screen-printed carbon electrodes for simultaneous determination of dopamine, uric acid and ascorbic acid," Electrochemistry Communications, vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 559-563, 2008. [CrossRef]
- P. Hojati-Talemi, L. D. Zou, M. Fabretto, and R. D. Short, "Using oxygen plasma treatment to improve the performance of electrodes for capacitive water deionization," Electrochimica Acta, vol. 106, pp. 494-499, Sep 2013. [CrossRef]
- X. Yuan, L. Ma, J. Zhang, and Y. Zheng, "Simple pre-treatment by low-level oxygen plasma activates screen-printed carbon electrode: Potential for mass production," Applied Surface Science, vol. 544, 2021. [CrossRef]
- J. Wang, S. K. Xu, P. C. Sun, H. Y. Du, and L. D. Wang, "Enhanced electrochemical performance of screen-printed carbon electrode by RF-plasma-assisted polypyrrole modification," Journal of Materials Science-Materials in Electronics, vol. 33, no. 25, pp. 19923-19936, Sep 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. Ardhaoui, M. Zheng, J. Pulpytel, D. Dowling, C. Jolivalt, and F. A. Khonsari, "Plasma functionalized carbon electrode for laccase-catalyzed oxygen reduction by direct electron transfer," Bioelectrochemistry, vol. 91, pp. 52-61, Jun 2013. [CrossRef]
- K. Idegami et al., "Gold Nanoparticle-Based Redox Signal Enhancement for Sensitive Detection of Human Chorionic Gonadotropin Hormone," Electroanalysis, vol. 20, no. 1, pp. 14-21, 2008. [CrossRef]
- N. Xuan Viet et al., "Gold-linked electrochemical immunoassay on single-walled carbon nanotube for highly sensitive detection of human chorionic gonadotropin hormone," Biosens Bioelectron, vol. 42, pp. 592-7, Apr 15 2013. [CrossRef]
- S. A. Lim, H. Yoshikawa, E. Tamiya, H. M. Yasin, and M. U. Ahmed, "A highly sensitive gold nanoparticle bioprobe based electrochemical immunosensor using screen printed graphene biochip," RSC Adv., vol. 4, no. 102, pp. 58460-58466, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Y. Gondoh-Noda et al., "Feasibility of a Novel Mobile C-Reactive Protein-Testing Device Using Gold-Linked Electrochemical Immunoassay: Clinical Performance Study," JMIR Mhealth Uhealth, vol. 8, no. 9, p. e18782, Sep 7 2020. [CrossRef]
- E. Tamiya, S. Osaki, T. Tsuchihashi, H. Ushijima, and K. Tsukinoki, "Point-of-Care Diagnostic Biosensors to Monitor Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing IgG/sIgA Antibodies and Antioxidant Activity in Saliva," (in English), Biosensors-Basel, Article vol. 13, no. 2, p. 13, Feb 2023, Art no. 167. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).