Submitted:
04 February 2024
Posted:
05 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Note
2.2. Animal mantainance
2.3. Experimental design
2.3.1. Novel Tank Test
2.3.2. Social Preference Test
2.3.3. Aggressivity Test
2.3.4. Oxidative stress analysis
2.4. Statistical analysis
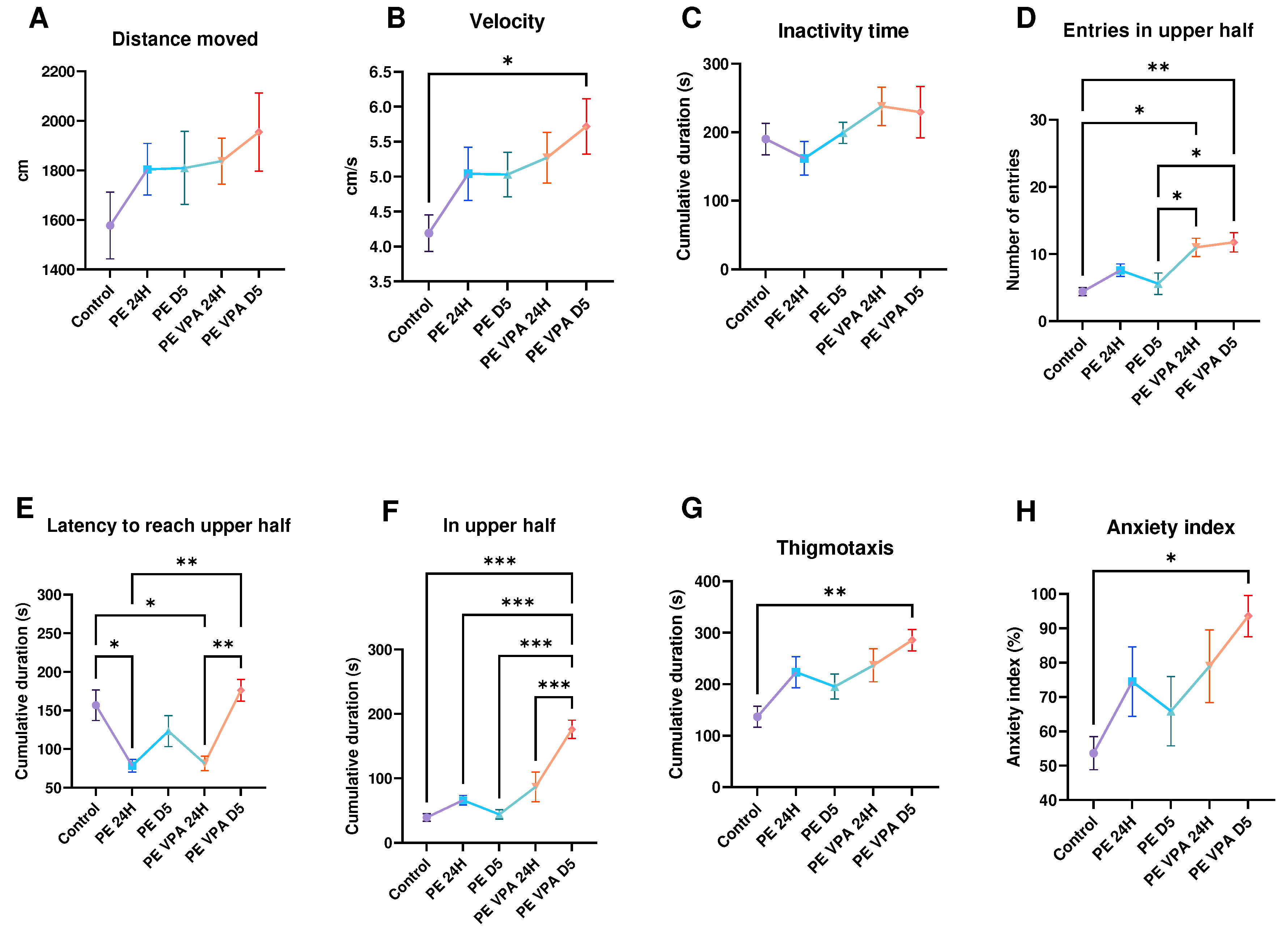
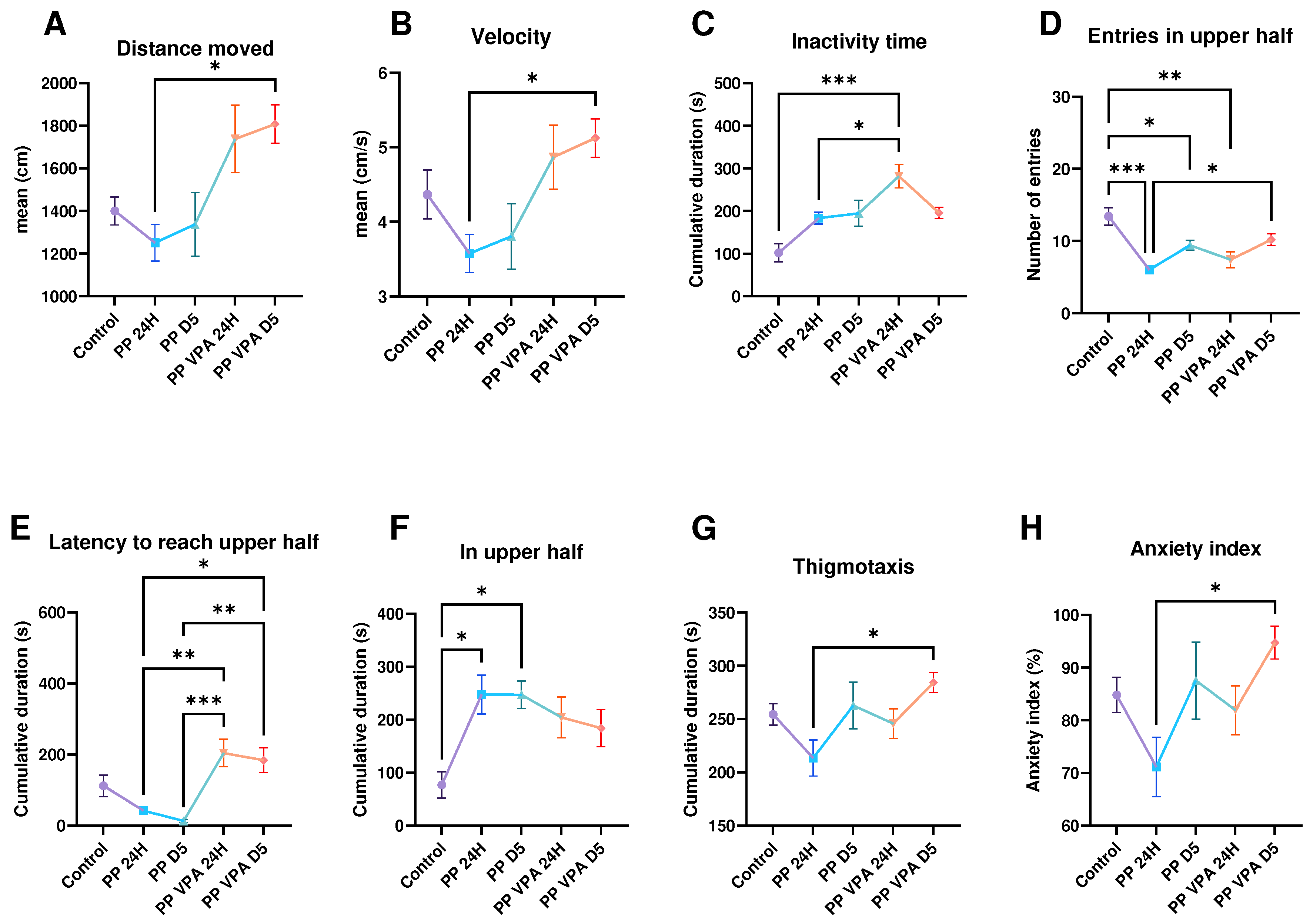
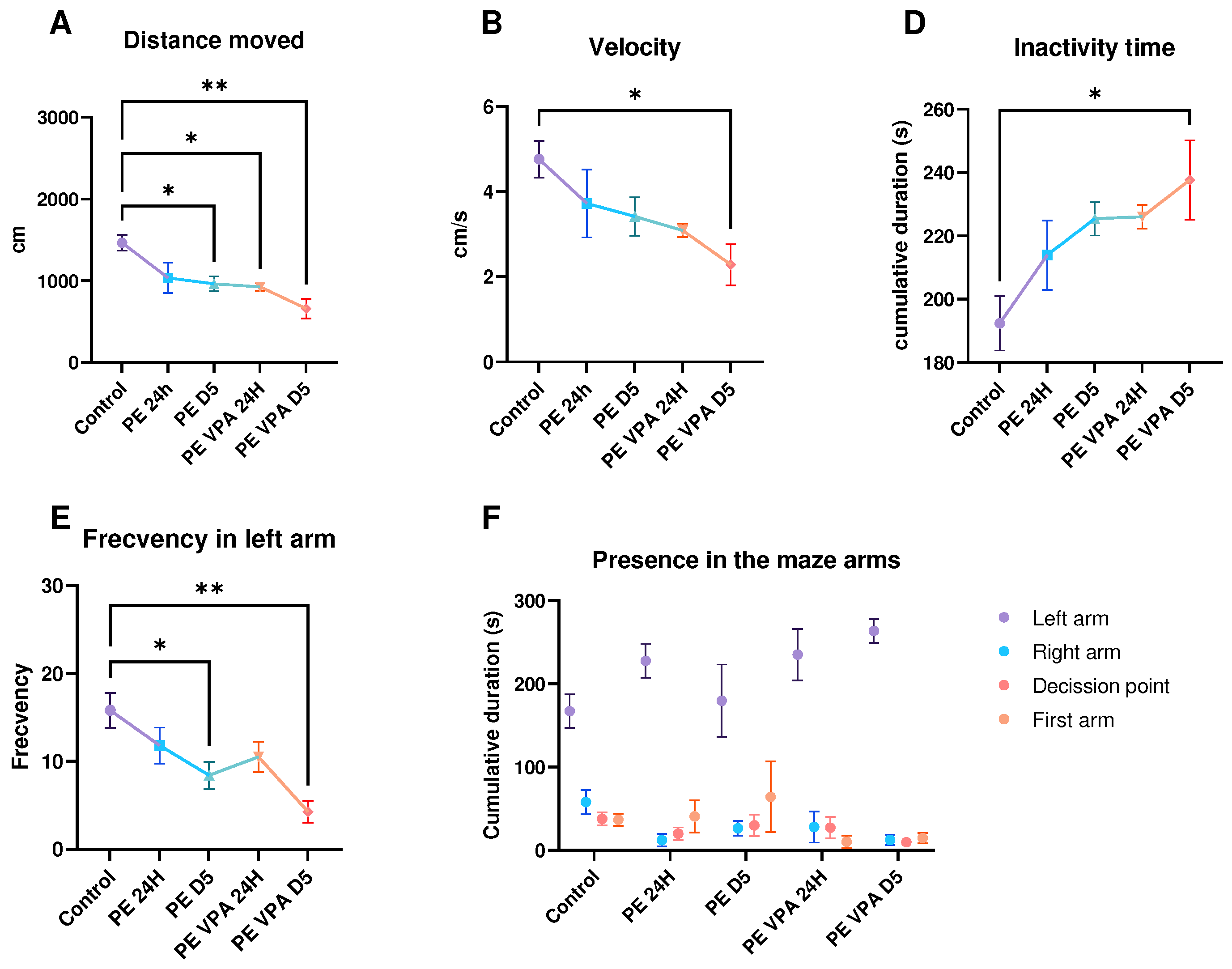
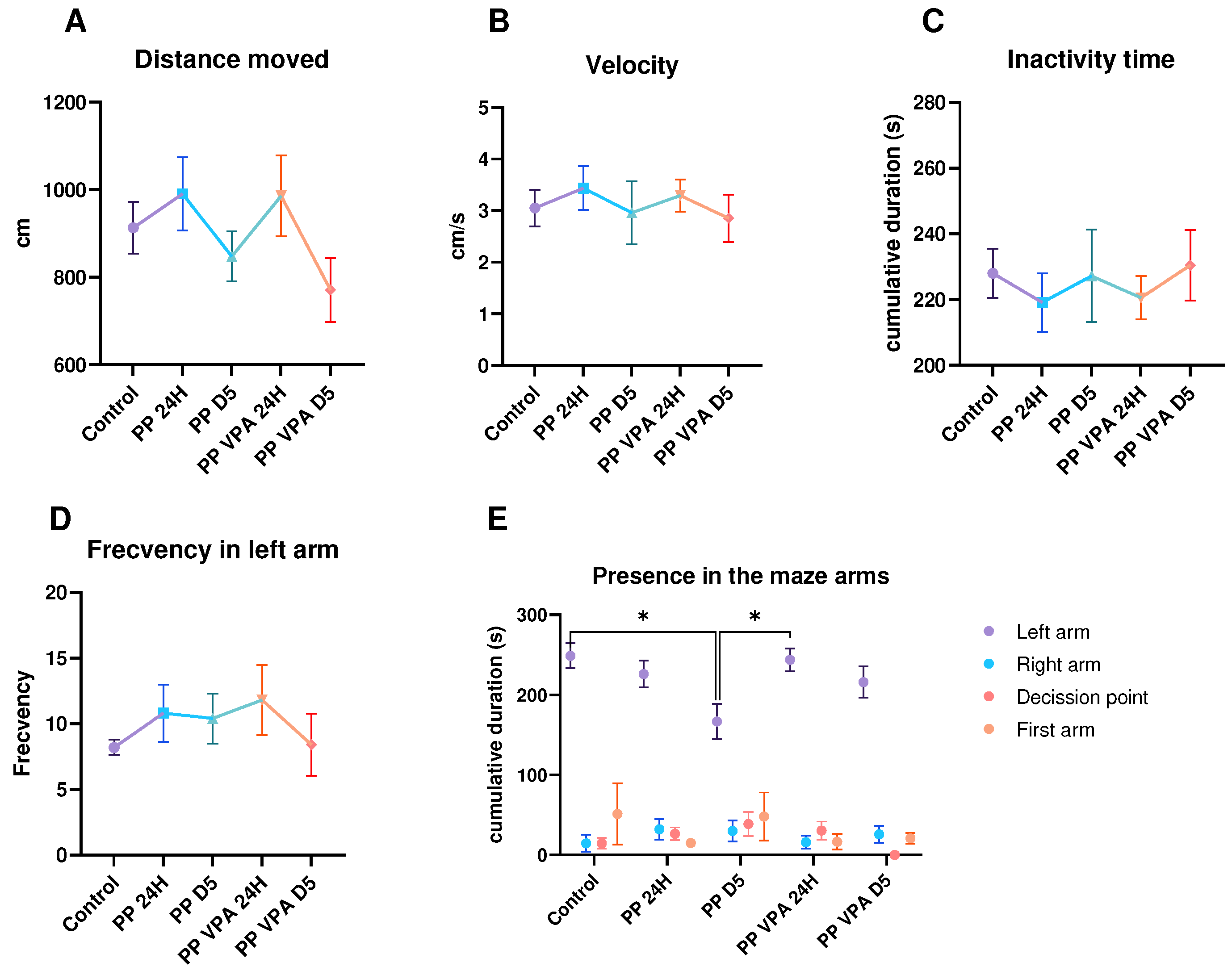
3. Results
3.1. Behavior analysis
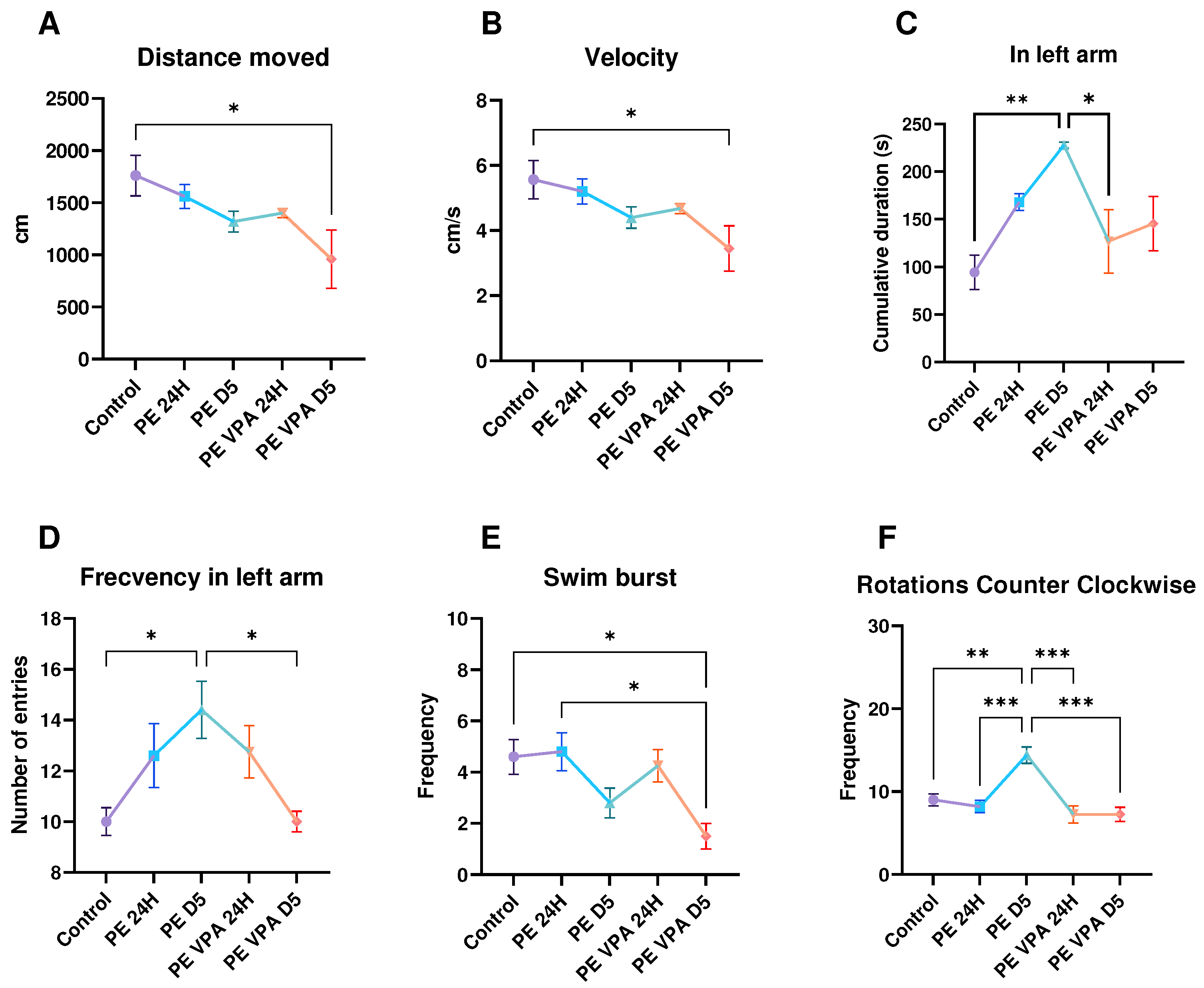
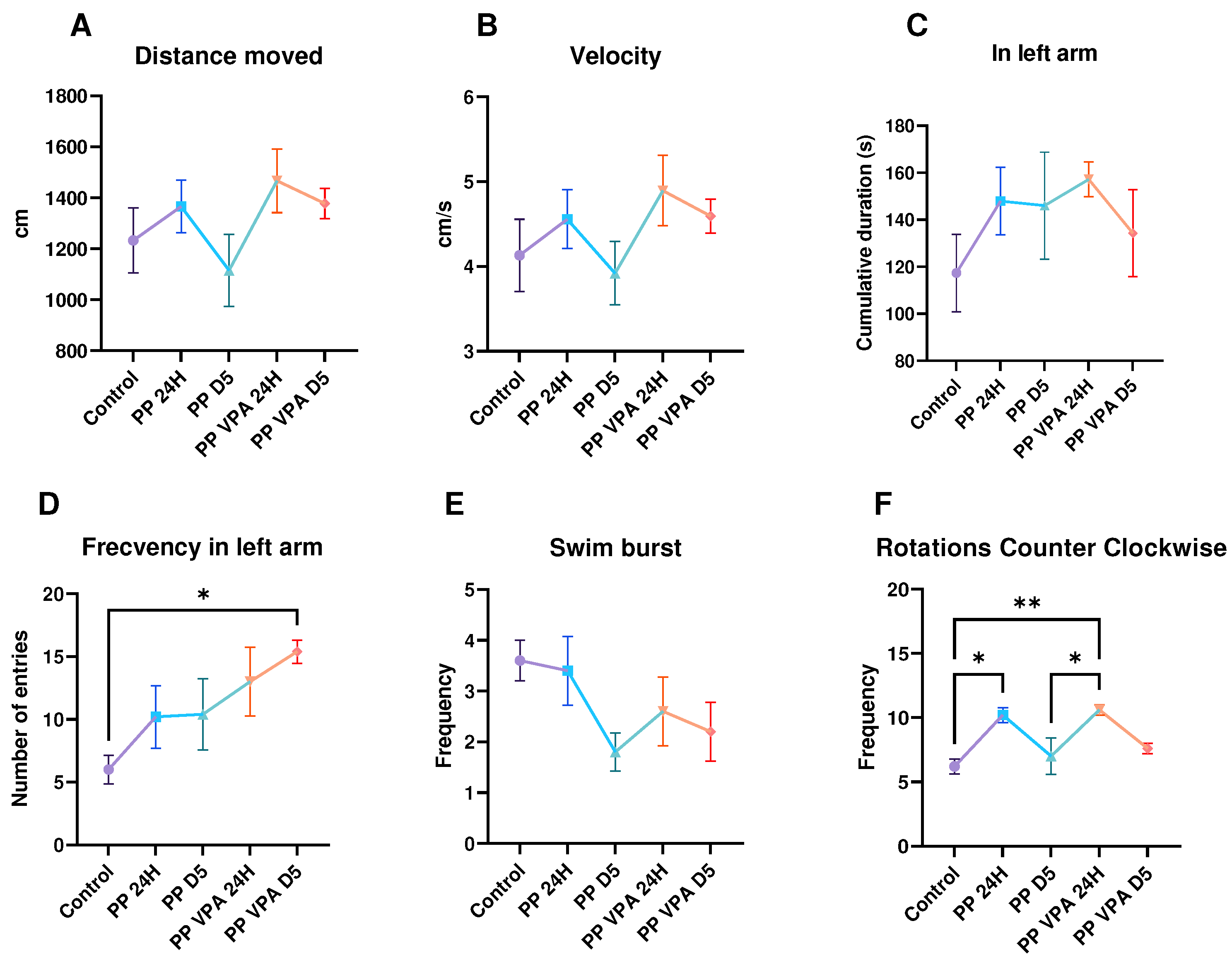
3.1.1. Novel Tank Test
3.1.2. Social Preference Test
3.1.3. Aggressivity Test
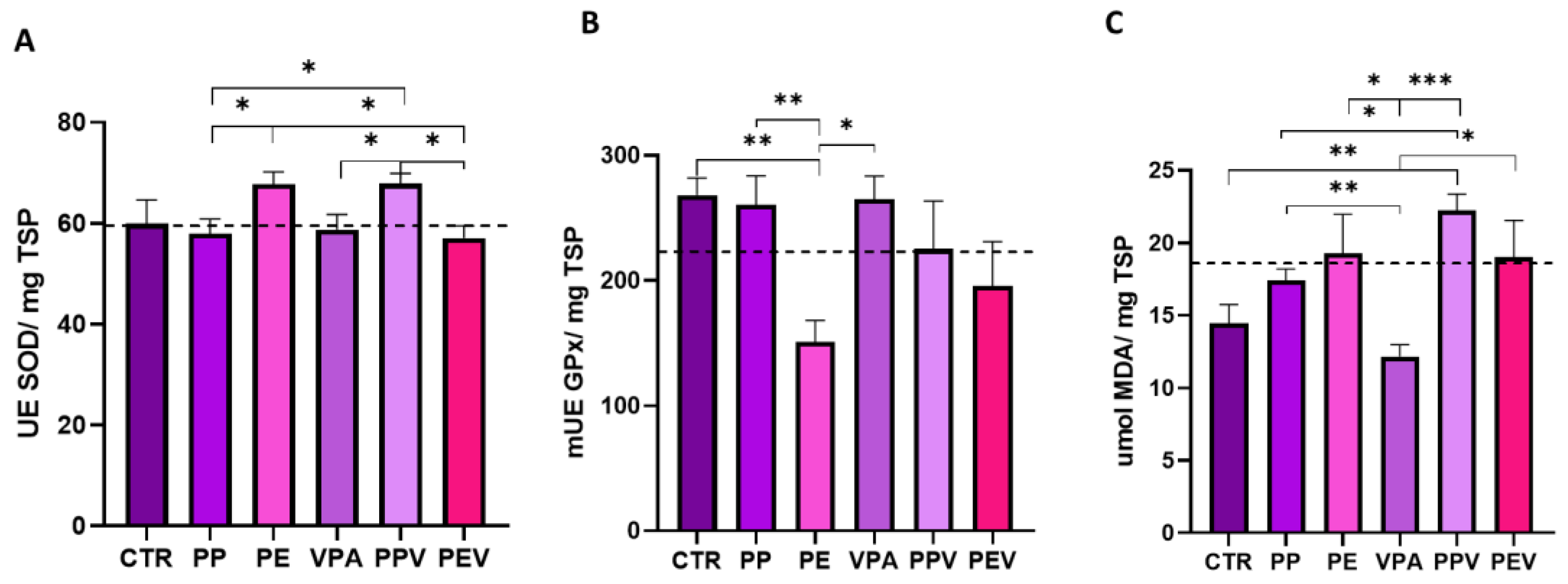
3.2. Oxidative stress analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Henderson, L.; Green, C. Making Sense of Microplastics? Public Understandings of Plastic Pollution. Mar Pollut Bull 2020, 152, 110908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, L.; Chao, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, Q. Research Progress of Microplastics in Freshwater Sediments in China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2020, 27, 31046–31060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanthini Devi, K.; Raju, P.; Santhanam, P.; Dinesh Kumar, S.; Krishnaveni, N.; Roopavathy, J.; Perumal, P. Biodegradation of Low-Density Polyethylene and Polypropylene by Microbes Isolated from Vaigai River, Madurai, India. Arch Microbiol 2021, 203, 6253–6265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, J.L.; Boxall, A.B.A.; Kolpin, D.W.; Leung, K.M.Y.; Lai, R.W.S.; Galbán-Malagón, C.; Adell, A.D.; Mondon, J.; Metian, M.; Marchant, R.A.; et al. Pharmaceutical Pollution of the World’s Rivers. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2022, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, M.; Njoku, A.; Nimo-Sefah, L. Comparing Environmental Policies to Reduce Pharmaceutical Pollution and Address Disparities. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022, 19, 8292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onesios-Barry, K.M.; Berry, D.; Proescher, J.B.; Sivakumar, I.K.A.; Bouwer, E.J. Removal of Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products during Water Recycling: Microbial Community Structure and Effects of Substrate Concentration. Appl Environ Microbiol 2014, 80, 2440–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada, H.B.; Baptista, A.T.A.; Cusioli, L.F.; Seibert, D.; de Oliveira Bezerra, C.; Bergamasco, R. Surface Water Pollution by Pharmaceuticals and an Alternative of Removal by Low-Cost Adsorbents: A Review. Chemosphere 2019, 222, 766–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimaszyk, P.; Rzymski, P. Water and Aquatic Fauna on Drugs: What Are the Impacts of Pharmaceutical Pollution? In; 2018; pp. 255–278. [CrossRef]
- Vatovec, C.; Van Wagoner, E.; Evans, C. Investigating Sources of Pharmaceutical Pollution: Survey of over-the-Counter and Prescription Medication Purchasing, Use, and Disposal Practices among University Students. J Environ Manage 2017, 198, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjanapriya, S.; SulaimanMumtaz, M.; Mohideen, M.H.A.K.; Radha, A.; Sasirekha, N.; Sawicka, B.; Tamizhazhagan, V. Pharmaceutical Pollution Crisis in the World: A Menace to Ecosystem. Entomology and Applied Science Letters 2021, 8, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.-C.; Tseng, H.-K.; Wang, S.-C.; Wang, Y.-Y. Valproic Acid-Induced Agranulocytosis. Int J Gerontol 2009, 3, 137–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terbach, N.; Shah, R.; Kelemen, R.; Klein, P.S.; Gordienko, D.; Brown, N.A.; Wilkinson, C.J.; Williams, R.S.B. Identifying an Uptake Mechanism for the Antiepileptic and Bipolar Disorder Treatment Valproic Acid Using the Simple Biomedical Model Dictyostelium. J Cell Sci 2011, 124, 2267–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triyasakorn, K.; Ubah, U.D.B.; Roan, B.; Conlin, M.; Aho, K.; Awale, P.S. The Antiepileptic Drug and Toxic Teratogen Valproic Acid Alters Microglia in an Environmental Mouse Model of Autism. Toxics 2022, 10, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, Y.-H.; Yun, J.-S.; Lee, C.-J. Valproic Acid Decreases the Proliferation of Telencephalic Cells in Zebrafish Larvae. Neurotoxicol Teratol 2013, 39, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kus, K.; Burda, K.; Nowakowska, E.; Czubak, A.; Metelska, J.; Łancucki, M.; Brodowska, K.; Nowakowska, A. Effect of Valproic Acid and Environmental Enrichment on Behavioral Functions in Rats. Arzneimittelforschung 2011, 60, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brotzmann, K.; Escher, S.E.; Walker, P.; Braunbeck, T. Potential of the Zebrafish (Danio Rerio) Embryo Test to Discriminate between Chemicals of Similar Molecular Structure—a Study with Valproic Acid and 14 of Its Analogues. Arch Toxicol 2022, 96, 3033–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romoli, M.; Mazzocchetti, P.; D’Alonzo, R.; Siliquini, S.; Rinaldi, V.E.; Verrotti, A.; Calabresi, P.; Costa, C. Valproic Acid and Epilepsy: From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical Evidences. Curr Neuropharmacol 2019, 17, 926–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Chun, H.-S.; Lee, J.; Park, H.-J.; Kim, K.-T.; Kim, C.-H.; Yoon, S.; Kim, W.-K. Plausibility of the Zebrafish Embryos/Larvae as an Alternative Animal Model for Autism: A Comparison Study of Transcriptome Changes. PLoS One 2018, 13, e0203543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khazrajy, O.S.A.; Boxall, A.B.A. Risk-Based Prioritization of Pharmaceuticals in the Natural Environment in Iraq. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2016, 23, 15712–15726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perazzolo, C.; Morasch, B.; Kohn, T.; Magnet, A.; Thonney, D.; Chèvre, N. Occurrence and Fate of Micropollutants in the Vidy Bay of Lake Geneva, Switzerland. Part I: Priority List for Environmental Risk Assessment of Pharmaceuticals. Environ Toxicol Chem 2010, 29, 1649–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.T.; Bisceglia, K.J.; Bouwer, E.J.; Roberts, A.L.; Coelhan, M. Determination of Pharmaceuticals and Antiseptics in Water by Solid-Phase Extraction and Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry: Analysis via Pentafluorobenzylation and Stable Isotope Dilution. Anal Bioanal Chem 2012, 403, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.T.; Bouwer, E.J.; Coelhan, M. Occurrence and Biodegradability Studies of Selected Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in Sewage Effluent. Agric Water Manag 2006, 86, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, A.D.; Khan, K.M.; Caramillo, E.M.; Mohn, R.S.; Echevarria, D.J. Zebrafish and Conditioned Place Preference: A Translational Model of Drug Reward. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2014, 55, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Abreu, M.S.; Costa, F.; Giacomini, A.C.V. V.; Demin, K.A.; Zabegalov, K.N.; Maslov, G.O.; Kositsyn, Y.M.; Petersen, E.V.; Strekalova, T.; Rosemberg, D.B.; et al. Towards Modeling Anhedonia and Its Treatment in Zebrafish. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology 2022, 25, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cueto-Escobedo, J.; German-Ponciano, L.J.; Guillén-Ruiz, G.; Soria-Fregozo, C.; Herrera-Huerta, E.V. Zebrafish as a Useful Tool in the Research of Natural Products With Potential Anxiolytic Effects. Front Behav Neurosci 2022, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, Í.N.; Dourado, A.V.; Araújo, A.P.d.C.; de Souza, S.S.; da Luz, T.M.; Guimarães, A.T.B.; Gomes, A.R.; Islam, A.R.M.T.; Rahman, M.M.; Arias, A.H.; et al. Toxicity Assessment of SARS-CoV-2-Derived Peptides in Combination with a Mix of Pollutants on Zebrafish Adults: A Perspective Study of Behavioral, Biometric, Mutagenic, and Biochemical Toxicity. Science of The Total Environment 2023, 858, 159838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilie, O.-D.; Duta, R.; Jijie, R.; Nita, I.-B.; Nicoara, M.; Faggio, C.; Dobrin, R.; Mavroudis, I.; Ciobica, A.; Doroftei, B. Assessing Anti-Social and Aggressive Behavior in a Zebrafish (Danio Rerio) Model of Parkinson’s Disease Chronically Exposed to Rotenone. Brain Sci 2022, 12, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balmus, I.-M.; Lefter, R.; Ciobica, A.; Cojocaru, S.; Guenne, S.; Timofte, D.; Stanciu, C.; Trifan, A.; Hritcu, L. Preliminary Biochemical Description of Brain Oxidative Stress Status in Irritable Bowel Syndrome Contention-Stress Rat Model. Medicina (B Aires) 2019, 55, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meshalkina, D.A.; Kizlyk, M.N.; Kysil, E.V.; Collier, A.D.; Echevarria, D.J.; Abreu, M.S.; Barcellos, L.J.G.; Song, C.; Warnick, J.E.; Kyzar, E.J.; et al. Zebrafish Models of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Exp Neurol 2018, 299, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, P. Zebrafish as a Pharmacological Tool: The How, Why and When. Curr Opin Pharmacol 2004, 4, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belo, M.A.A.; Oliveira, M.F.; Oliveira, S.L.; Aracati, M.F.; Rodrigues, L.F.; Costa, C.C.; Conde, G.; Gomes, J.M.M.; Prata, M.N.L.; Barra, A.; et al. Zebrafish as a Model to Study Inflammation: A Tool for Drug Discovery. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2021, 144, 112310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, F.F.; Gaspary, K.V.; Leite, C.E.; De Paula Cognato, G.; Bonan, C.D. Embryological Exposure to Valproic Acid Induces Social Interaction Deficits in Zebrafish (Danio Rerio): A Developmental Behavior Analysis. Neurotoxicol Teratol 2015, 52, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robea, M.A.; Ciobica, A.; Curpan, A.-S.; Plavan, G.; Strungaru, S.; Lefter, R.; Nicoara, M. Preliminary Results Regarding Sleep in a Zebrafish Model of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Brain Sci 2021, 11, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, T.P.; Zhou, F.; Sai, L.Y.; Chen, H.; Lin, S.L.; Schachner, M. Duloxetine Ameliorates Valproic <scp>acid-induced</Scp> Hyperactivity, Anxiety-like Behavior, and Social Interaction Deficits in Zebrafish. Autism Research 2022, 15, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Bonneton, F.; Tohme, M.; Bernard, L.; Chen, X.Y.; Laudet, V. In Vivo Screening Using Transgenic Zebrafish Embryos Reveals New Effects of HDAC Inhibitors Trichostatin A and Valproic Acid on Organogenesis. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0149497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, J.M.; Oliveri, A.N.; Karbhari, N.; Brooks, R.A.J.; De La Rocha, A.J.; Janardhan, S.; Levin, E.D. Persistent Behavioral Effects Following Early Life Exposure to Retinoic Acid or Valproic Acid in Zebrafish. Neurotoxicology 2016, 52, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helinski, O.K.; Poor, C.J.; Wolfand, J.M. Ridding Our Rivers of Plastic: A Framework for Plastic Pollution Capture Device Selection. Mar Pollut Bull 2021, 165, 112095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, H.; Li, T.; Yu, L.; Qi, Y.; Tian, G.; He, F.; Li, X.; Sun, N.; Liu, R. Size-Dependent Effects of Nanoplastics on Structure and Function of Superoxide Dismutase. Chemosphere 2022, 309, 136768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.; Tong, L.; Zhang, W. Microplastics in Freshwater Environments: Sources, Fates and Toxicity. Water Air Soil Pollut 2021, 232, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuppasamy, P.K.; Ravi, A.; Vasudevan, L.; Elangovan, M.P.; Dyana Mary, P.; Vincent, S.G.T.; Palanisami, T. Baseline Survey of Micro and Mesoplastics in the Gastro-Intestinal Tract of Commercial Fish from Southeast Coast of the Bay of Bengal. Mar Pollut Bull 2020, 153, 110974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olexová, L.; Štefánik, P.; Kršková, L. Increased Anxiety-like Behaviour and Altered GABAergic System in the Amygdala and Cerebellum of VPA Rats—An Animal Model of Autism. Neurosci Lett 2016, 629, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, J.; Xia, Q.; Guo, N.; Li, Q. Social Preference Deficits in Juvenile Zebrafish Induced by Early Chronic Exposure to Sodium Valproate. Front Behav Neurosci 2016, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younus, H. Therapeutic Potentials of Superoxide Dismutase. Int J Health Sci (Qassim) 2018, 12, 88–93. [Google Scholar]
- Félix, L.; Carreira, P.; Peixoto, F. Effects of Chronic Exposure of Naturally Weathered Microplastics on Oxidative Stress Level, Behaviour, and Mitochondrial Function of Adult Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). Chemosphere 2023, 310, 136895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubos, E.; Loscalzo, J.; Handy, D.E. Glutathione Peroxidase-1 in Health and Disease: From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Opportunities. Antioxid Redox Signal 2011, 15, 1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, C.W.; Ching-Fong Yeung, K.; Chan, K.M. Acute Toxic Effects of Polyethylene Microplastic on Adult Zebrafish. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 2019, 182, 109442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Rio, D.; Stewart, A.J.; Pellegrini, N. A Review of Recent Studies on Malondialdehyde as Toxic Molecule and Biological Marker of Oxidative Stress. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2005, 15, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y. The Influence of Different Polymer Types of Microplastics on Adsorption, Accumulation, and Toxicity of Triclosan in Zebrafish. J Hazard Mater 2021, 402, 123733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobori, D.C.; Feidantsis, K.; Dimitriadi, A.; Datsi, N.; Ripis, P.; Kalogiannis, S.; Sampsonidis, I.; Kastrinaki, G.; Ainali, N.M.; Lambropoulou, D.A.; et al. Dose-Dependent Cytotoxicity of Polypropylene Microplastics (PP-MPs) in Two Freshwater Fishes. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23, 13878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




