1. Introduction
KIBRA is a multifunctional protein that plays important roles in cellular signaling pathways and may have implications for various physiological processes, including brain function and memory [
1,
2] KIBRA (also known as WWC1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WWC1 gene. The term "KIBRA" originates from the acronym kidney and brain expressed protein. It is primarily expressed in the brain and kidneys, but it is also found in other tissues.
KIBRA has been implicated in various cellular processes, including cell growth, cell polarity, and cell migration. It plays a role in regulating the Hippo signaling pathway, which is involved in controlling organ size and tissue homeostasis [
3,
4,
5,
6].
Specifically, KIBRA engages with other proteins within the Hippo pathway to modulate the function of transcriptional coactivators like YAP (Yes-associated protein) and TAZ (transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding motif), crucial for governing cell proliferation and organ size [
7,
8,
9,
10].
Recent research by Kauwe et al. has underscored the critical importance of Kibra in synaptic plasticity and memory formation. Studies have indicated a correlation between reduced levels of Kibra in the brain and the severity of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Moreover, increased levels of Kibra in cerebrospinal fluid have been linked to AD progression, suggesting its potential as a biomarker for synaptic dysfunction and cognitive decline. Kauwe et al. have suggested that Kibra holds promise as a target for AD treatment; however, further research is necessary to fully understand its mechanisms of action and to develop effective therapeutic approaches [
11].
Some monoclonal antibodies such as Lecanemab, Aducanumab, and Donanemab that target amyloid have already been approved by the FDA in the United States and are currently in use.
However, therapies targeting amyloid remain controversial as the biological benefits, such as the reduction of beta-amyloid and tau plaques, do not yet translate into clinical benefits with tangible effects on patients.
Additionally, the side effects of these monoclonal antibodies can be significant [
12,
13,
14].
The present study utilizes Virtual Screening and Docking techniques [
15,
16] to investigate natural compounds' interactions with the KIBRA protein. The Autodock Vina program [
15,
16], along with the Pyrx software, is employed for this purpose.
These methods aim to identify small molecules that exhibit the highest binding energy with the KIBRA protein, potentially uncovering novel compounds for further research and drug development.
2. Material and Methods
Structure of Crystal Human Crystal structure of C2 domain of KIBRA protein was taken from Protein Data Bank (PDB Code:2Z0U). Docking investigation was performed by Autodock Vina with Pyrx program, using : Grid box Coordinates of binding Center X ( 24.1947), Y( 13.3255), Z(35.4581); size_x = 49.051660105; size_y = 31.9303591943; size_z = 36.2286488724.
3. Results and Discussion
Some monoclonal antibodies, including Lecanemab, Aducanumab, and Donanemab, have received approval from the FDA in the United States and are currently in clinical use to target amyloid. However, the efficacy of amyloid-targeting therapies remains controversial, as the observed biological benefits, such as the reduction of beta-amyloid and tau plaques, have not translated into tangible clinical benefits for patients. Furthermore, these monoclonal antibodies can have significant side effects [
12,
13,
14].
This study employs Virtual Screening and Docking techniques [
15,
16] to explore the interactions of natural compounds with the KIBRA protein. The Autodock Vina program [
15,
16], in conjunction with Pyrx software, is utilized for this investigation. These methodologies are aimed at identifying small molecules with the highest binding energy to the KIBRA protein, potentially unveiling novel compounds for further research and drug development.
Based on the docking results, Hypericin demonstrated the lowest binding energy among the 50 natural molecules investigated, with a value of approximately -9 kcal/mol.
Previous studies have consistently highlighted Hypericin's potential to effectively bind with ABAD and BACE1 targets involved in Alzheimer's Disease Pathogenesis.
This suggests that Hypericin may hold promise as a natural therapeutic agent for Alzheimer's disease due to its strong binding affinity with relevant protein targets [
17,
18].
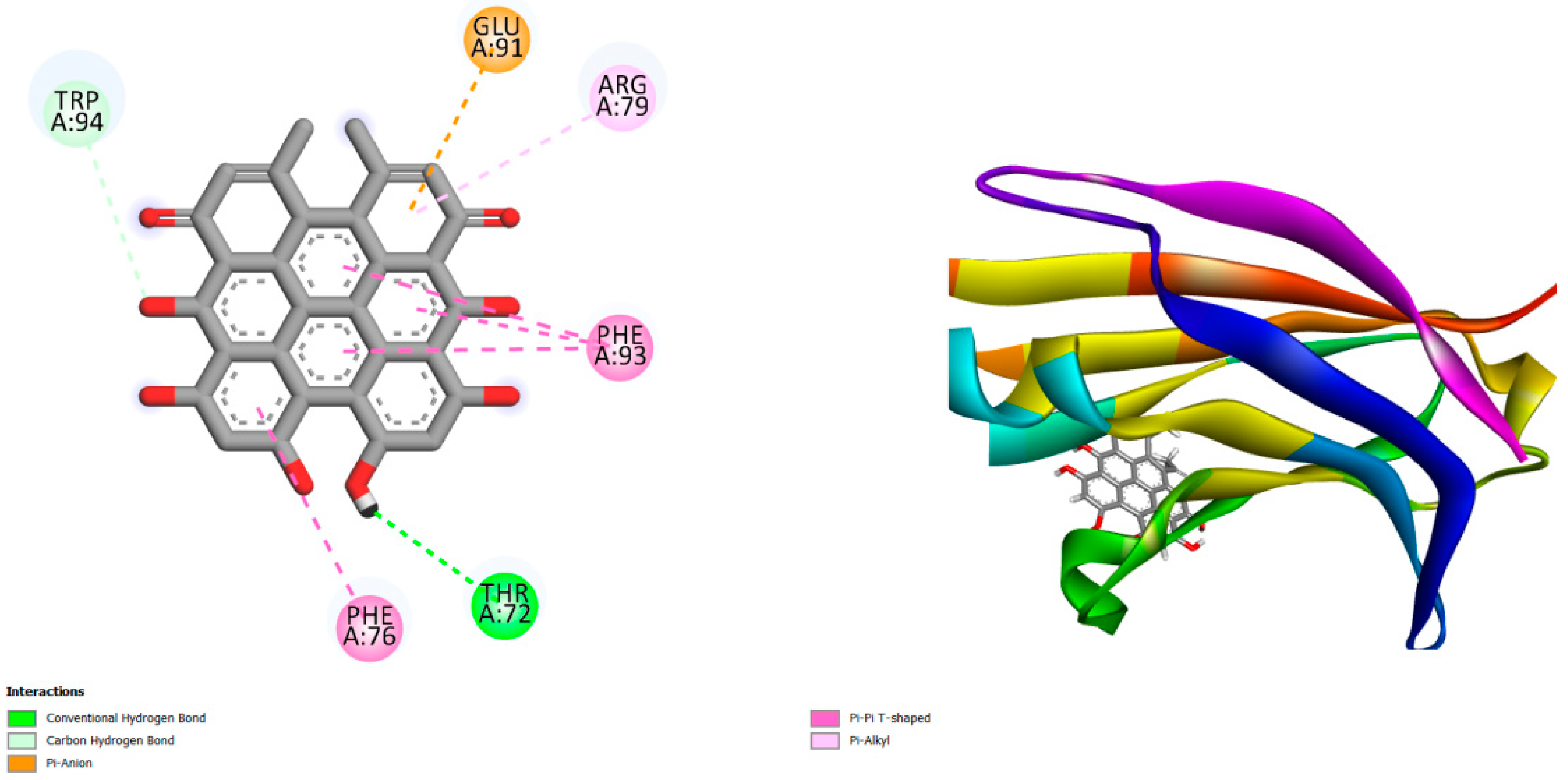
Figure 1.
This figure displays the docking outcomes of Structure of Crystal structure of C2 domain of KIBRA protein in conjunction with docked Hypericin -9 kcal mol analyzed by Autodock Vina with pyrx program. On the left side, 2D diagrams illustrate the residue interactions between the protein and Hypericin . Meanwhile, the right side exhibits the Ligand Binding Site of the protein, highlighting the specific location of Hypericin .
Figure 1.
This figure displays the docking outcomes of Structure of Crystal structure of C2 domain of KIBRA protein in conjunction with docked Hypericin -9 kcal mol analyzed by Autodock Vina with pyrx program. On the left side, 2D diagrams illustrate the residue interactions between the protein and Hypericin . Meanwhile, the right side exhibits the Ligand Binding Site of the protein, highlighting the specific location of Hypericin .
4. Conclusion
In conclusion, the study has shed light on the potential of Hypericin as a promising therapeutic agent for Alzheimer's Disease. By employing Virtual Screening and Docking techniques, we identified Hypericin as having the lowest binding energy with the KIBRA protein, a key biomarker for synaptic dysfunction and cognitive decline.Previous research has highlighted Hypericin's strong affinity for Alzheimer's Disease-associated targets like ABAD and BACE1, further supporting its potential therapeutic utility in Alzheimer's Disease pathogenesis.
However, it is important to acknowledge that the present study is theoretical, and further experimental validation is necessary to confirm the efficacy and safety of Hypericin for clinical use.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Meliambro, K., Yang, Y., de Cos, M., Ballestas, E. R., Malkin, C., Haydak, J., ... & Campbell, K. N. (2023). KIBRA upregulation increases susceptibility to podocyte injury and glomerular disease progression. JCI insight, 8(7). [CrossRef]
- Nagashima, Y., Mitsunari, K., Matsuo, T., Nakamura, Y., Miyata, Y., & Ohba, K. (2023). Pathological Significance of Kidney and Brain Expressed Protein (KIBRA) in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Anticancer Research, 43(1), 45-51. [CrossRef]
- Kauwe, G., Pareja-Navarro, K. A., Yao, L., Chen, J. H., Wong, I., Saloner, R., ... & Tracy, T. E. (2023). KIBRA repairs synaptic plasticity and promotes resilience to tauopathy-related memory loss. bioRxiv. [CrossRef]
- Homayouni, R., Daugherty, A. M., Yu, Q., Raz, N., & Ofen, N. (2023). KIBRA single nucleotide polymorphism is associated with hippocampal subfield volumes and cognition across development. Brain Structure and Function, 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Homayouni, R., Daugherty, A. M., Yu, Q., Raz, N., & Ofen, N. (2023). KIBRA single nucleotide polymorphism is associated with hippocampal subfield volumes and cognition across development. Brain Structure and Function, 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Meliambro, K., Yang, Y., de Cos, M., Rodriguez-Ballestas, E., Malkin, C., Haydak, J. C., ... & Campbell, K. N. (2023). KIBRA upregulation increases susceptibility to glomerular injury and correlates with kidney function decline. JCI Insight, e165002-e165002.
- Krahn, M., Wellenberg, L., John, J., Maximowitsch, V., Stiewe, M., Dickmann, K., ... & Kremerskothen, J. (2023). Phosphorylation of Kibra by RSK regulates binding to Cdk4 to control cell cycle progression and organ growth independently of the Hippo-pathway. (2021): 132-134. [CrossRef]
- Tokamov, S. A., Nouri, N., Rich, A., Buiter, S., Glotzer, M., & Fehon, R. G. (2023). Apical polarity and actomyosin dynamics control Kibra subcellular localization and function in Drosophila Hippo signaling. Developmental Cell, 58(19), 1864-1879. [CrossRef]
- Tokamov, S. A., Nouri, N., Rich, A., Buiter, S., Glotzer, M., & Fehon, R. G. (2023). Apical polarity and actomyosin dynamics control Kibra subcellular localization and function in Drosophila Hippo signaling. Developmental Cell, 58(19), 1864-1879. [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, R. B., Ashayeri, N., Baghaie, L., Sambi, M., Satari, K., Baluch, N., ... & Chakraborty, S. (2023). The hippo pathway effectors YAP/TAZ-TEAD oncoproteins as emerging therapeutic targets in the tumor microenvironment. Cancers, 15(13), 3468. [CrossRef]
- Kauwe, G., Pareja-Navarro, K. A., Yao, L., Chen, J. H., Wong, I., Saloner, R., ... & Tracy, T. E. (2023). KIBRA repairs synaptic plasticity and promotes resilience to tauopathy-related memory loss. bioRxiv. [CrossRef]
- Terao, I., & Kodama, W. (2024). Comparative efficacy, tolerability and acceptability of donanemab, lecanemab, aducanumab and lithium on cognitive function in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Ageing Research Reviews, 102203. [CrossRef]
- Ebell, M. H., Barry, H. C., Baduni, K., & Grasso, G. (2024). Clinically Important Benefits and Harms of Monoclonal Antibodies Targeting Amyloid for the Treatment of Alzheimer Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. The Annals of Family Medicine, 22(1), 50-62. [CrossRef]
- Söderberg, L., Johannesson, M., Nygren, P., Laudon, H., Eriksson, F., Osswald, G., ... & Lannfelt, L. (2023). Lecanemab, aducanumab, and gantenerumab—binding profiles to different forms of amyloid-beta might explain efficacy and side effects in clinical trials for Alzheimer's disease. Neurotherapeutics, 20(1), 195-206. [CrossRef]
- Muhammed, M. T., & Aki-Yalcin, E. (2024). Molecular docking: principles, advances, and its applications in drug discovery. Letters in Drug Design & Discovery, 21(3), 480-495. [CrossRef]
- Che, X., Liu, Q., & Zhang, L. (2023). An accurate and universal protein-small molecule batch docking solution using Autodock Vina. Results in Engineering, 19, 101335. [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, I. V. (2023). Exploring the Therapeutic Potential of Hypericin: Molecular Docking with ABAD and BACE1 targets in Alzheimer's Disease Pathogenesis.Preprints.org.
- Ferrari, I. V. (2023). Hypericin As A Possible Natural Molecule For The Treatment Of Alzheimer's Disease: Computationa Studies Focused On Beta-Secretase-1 (or BACE1). Int. J. Sci. Res. in Biological Sciences Vol, 10(5).
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).