Submitted:
04 February 2024
Posted:
05 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
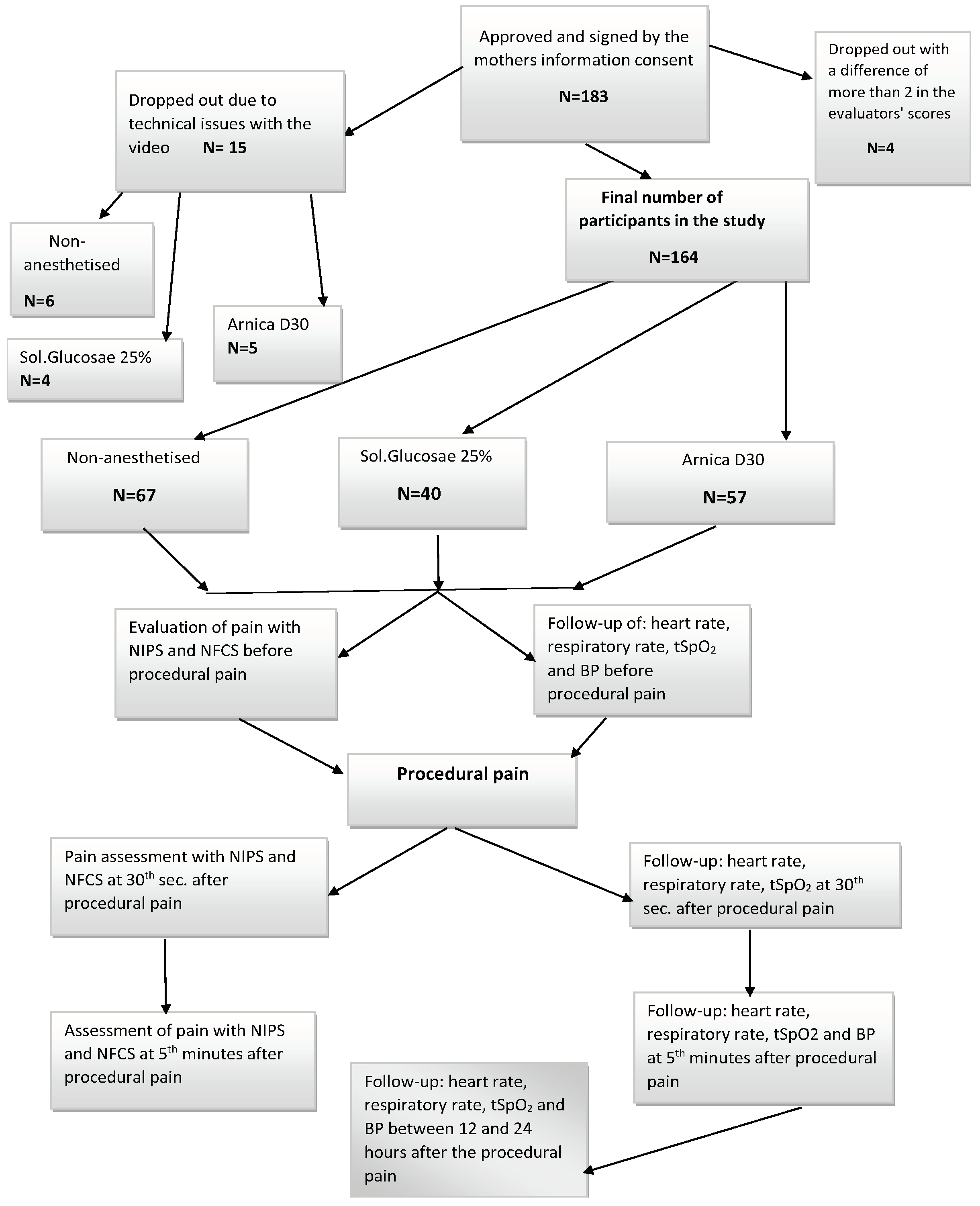
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.1.1. Inclusion Criteria
2.1.2. Exclusion Criteria
2.2. Statistical Methods
3. Results
| NIPS -5th min | Groups | Groups | Mean Difference | Sig. |
| Breathing patterns | Arnica D30 Sol. Glucose 25% |
Sol.Glucose 25% Arnica D30 |
-,334* ,334* |
0,0001 0,0001 |
| Arms | Arnica D30 Sol. Glucose 25% |
Sol.Glucose 25% Arnica D30 |
-,239* ,239* |
0,016 0,016 |
| Overall Assesment |
Arnica D30 Sol. Glucose 25% |
Sol.Glucose 25% Arnica D30 |
-1,181* 1,181* |
0,037 0,037 |
| NFCS-5th min. | Groups | N | Mean | Std.Deviation | F | Sig. level |
| Brow bulge | without analgesia Arnica D30 Sol. Glucose 25% |
67 57 40 |
,41 ,32 ,34 |
,492 ,469 ,490 |
0,571 | 0,566 |
| Eye squeeze | without analgesia Arnica D30 Sol. Glucose 25% |
67 57 40 |
,54 ,30 ,52 |
,502 ,481 ,490 |
4,306 | 0,015* |
| Nasolabial furrow | without analgesia Arnica D30 Sol. Glucose 25% |
67 57 40 |
,48 ,30 ,36 |
,503 ,462 ,496 |
2,367 | 0,097 |
| Open mouth | without analgesia Arnica D30 Sol. Glucose 25% |
67 57 40 |
,87 ,70 ,75 |
,336 ,453 ,304 |
4,095 | 0,018* |
| Taut tongue | without analgesia Arnica D30 Sol. Glucose 25% |
67 57 40 |
,29 ,16 ,23 |
,456 ,368 ,452 |
1,608 | 0,204 |
| Chin quiver | without analgesia Arnica D30 Sol. Glucose 25% |
67 57 40 |
,29 ,11 ,22 |
,456 ,310 ,439 |
3,704 | 0,027* |
| Tongue sticking out | without analgesia Arnica D30 Sol. Glucose 25% |
67 57 40 |
,20 ,15 ,17 |
,404 ,368 ,423 |
,360 | 0,698 |
| Stretch mouth | without analgesia Arnica D30 Sol. Glucose 25% |
67 57 40 |
,54 ,32 ,37 |
,503 ,471 ,506 |
3,183 | 0,045 |
| Overall Assesment |
without analgesia Arnica D30 Sol. Glucose 25% |
67 57 40 |
3,85 2,35 2,95 |
2,502 2,443 2,469 |
5,273 | 0,006* |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, M.; El Chaar, G. Reducing pain from heel lances in neonates following education on oral sucrose. Int Clin Pharm 2015, 37,529-536. [CrossRef]
- Rennie, J.M.; & Kendall, G.A. Manual of Neonatal Intensive Care (5th ed.). CRC Press 2013; London; pp382-383.
- Anand, K.J.S. Assessment of neonatal pain.UpToDate 2018.
- American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Fetus and Newborn; American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Аnesthesiology and Pain medicine. Prevention and Management of Procedural Pain in the Neonate: An Update; Pediatrics. January 2016.
- Hall, R.W.; Anand, K.J.S. Pain Management in Newborns. Clin Perinatol. 2014; 41(4); 895–924. [CrossRef]
- Roué, Jean-Michel. Assessment of neonatal pain. UpToDate 2023.
- Lawrence, J.; Alcock, D.; Mc Grath, P.; Kay, J.; Mac Murray,S.B.; Dulberg, C. The Development of a Tool to Assess Neonatal Pain. Neonatal Network 1993; 12;59-66.
- da Paixão Freitas, Z.M.; Pereira C.U.; da Paixão Oliveira D.M. Pain Scale: When the Training Influences Its Use. Open Journal of Nursing 2018; 8:130-138. [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, G.; Riccitelli, M.; Sordino, D.; Giordano, M.; Piccolo, S.; Buonocore, G.; Perrone, S. Oral 24% sucrose associated with non-nutritive sucking for pain control in healthy term newborns receiving venepuncture beyond the first week of life. Journal of Pain Research. 2019;12: 299-305.
- de Cassia Pinheiro da Motta, G., Machado Schardosim, J.; Chollopetz da Cunha M.L. Neonatal Infant Pain Scale: Cross-Cultural Adaptation and Validation in Brazil. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management 2015;50(3): 394-401. [CrossRef]
- Grunau, R.V.E.; Craig, K.D. Pain expression in neonates: facial action and cry. Pain. 1987; 28:395–410. [CrossRef]
- Grunau R.V.E.; Craig K.D. Facial activity as a measure of neonatal pain expression. Advances in Pain Research and Therapy. Raven Press. 1990; 15:147-155.
- Hardeep, K.; Gaurav M. A Comprehensive analysis of Neonatal pain and measures to reduce pain. Journal of Pediatric Critical Care.2019; 6;1: 43-48.
- Roué, J.M.; Rioualen, S.; Gendras, J.; Misery, L.; Gouillou, M.; Sizun, J. Multi-modal painassessment: are near-infrared spectroscopy, skin conductance, salivary cortisol, physiologic parameters, and neonatal Facial coding system interrelated during venepuncture in healthy, term neonates? Journal of Pain Research 2018;11:2257-2267. [CrossRef]
- Sposito, N.P.B.; Rossato, L.M.; Bueno, M.; Kimura, A.F.; Costa, T.; Guedes, D.M.B. Assessment and management of pain in newborns hospitalized in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit: a cross-sectional study. Rev Lat Am Enfermagem. 2017; 12;25: e2931. [CrossRef]
- Bueno, M.; Yamada, J.; Harrison, D.; Khan, S.; Ohlsson, A.; Adams-Webber, T. et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of non-sweetened solutions to relieve pain in neonates. Pain Res Manag.2013;18 (3): 153-161.
- Liu, Y.; Huang, X.; Luo, B.; Peng W. Effects of combined oral sucrose and nonnutritive sucking (NNS) on procedural pain of NICU newborns, 2001 to 2016: A PRISMA-compliant systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(6):e6108. [CrossRef]
- Bhalla, T.; Shepherd, E.; Tobias, J. Neonatal pain management. Saudi J Anaesth. 2014; 8(Suppl 1): S89–S97.
- Messerer, B.; Krauss-Stoisser, B.; Urlesberger, B. Nichtmedikamentöse Maßnahmen sowie topische Analgetika und orale Zuckerstoffe im Schmerzmanagement. Der Schmerz 2014; 28: 31–42. [CrossRef]
- Yamada, J.; Bueno, M.; Santos, L.; Haliburton, S.; Campbell-Yeo, M,; Stevens, B. Sucrose analgesia for heel-lance procedures in neonates. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023; 30;8(8):CD014806. [CrossRef]
- Stevens, B.; Yamada, J.; Ohlsson, A.; Haliburton, S.; Shorkey, A. Sucrose for analgesia in newborn infants undergoing painful procedures. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;16;7:CD001069.
- Ahn, H.Y.; Jang, M.Y.; Hur, M.H. The effect of oral glucose on pain relief in newborns. Taehan Kanho Hakhoe Chi. 2006;36:992–1001. [CrossRef]
- Bonetto, G.; Salvatico, E.; Varela, N.; Cometto, C.; Gomez, P.F.; Calvo, B. Pain prevention in term neonates: Randomized trial for three methods. Arch Argent Pediatr.2008; 106:392–6. [CrossRef]
- Brovedani, P.; Montico, M.; Shardlow, A.; et al. Suckling and sugar for pain reduction in babies. Lancet 2007; 369:1429. [CrossRef]
- Bellieni, C.V.; Bagnoli, F.; Perrone, S.; Nenci, A.; Cordelli, D.M.; Fusi, M.; Ceccarelli, S.; Buonocore, G. Effect of multisensory stimulation on analgesia in term neonates: a randomized controlled trial.Pediatr Res. 2002;51(4):460-3. [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, S.; Ogihara, T.; Fujiwara, E.; Ito, K.; Nakano, M.; Nakayama, S.; Hachiya, T.; Fujimoto, N.; Abe, H.; Ban, S.; Ikeda, E.; Tamai, H. Venepuncture is preferable to heel lance for blood sampling in term neonates. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2005; 90(5): F432-6. [CrossRef]
- Okan, F.; Coban, A.; Ince, Z.; Yapici, Z.; Can, G. Analgesia in preterm newborns: The comparative effects of sucrose and glucose. Eur J Pediatr. 2007; 166:1017–24. [CrossRef]
- Jatana, S.K.; Dalal, S.S.; Wilson, C.G. Analgesic Effect of Oral Glucose in Neonates Med J Armed Forces India. 2003; 59(2); 100–104.
- Guala, A.; Pastore, G.; Liverani, M.E. et al. Glucose or sucrose as an analgesic for newborns: A randomised controlled blind trial. Minerva Pediatr. 2001;53:271–4.
- Slater, R. et al. Oral sucrose as an analgesic drug for procedural pain in newborn infants: a randomised controlled trial. 2010; Lancet 376(9748):1225–1232. [CrossRef]
- Akcam, M. Oral fructose solution as an analgesic in the newborn: A randomized, placebo-controlled and masked study. Pediatr Int 2004;46:459–462. [CrossRef]
- Isik, U.; Ozek, E.; Bilgen, H.; Cebeci, D. Comparison of oral glucose and sucrose solutions on pain response in neonates. Journal of Pain 2000;1:275-8. [CrossRef]
- Suhrabi, Z.; Taghinejad, H.; Valian, K.; Sayehmiri, K.; Taheri. S. A comparative study on the efficacy of glucose and sucrose on the vaccination pain: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research 2014; 8(10): PC01-03.
- Kumari, S.; Datta, V.; Rehan, H. Comparison of the efficacy of oral 25% glucose with oral 24% sucrose for pain relief during heel lance in preterm neonates: a double blind rando-mized controlled trial. J Trop Pediatr 2016. 63(1):30–35.
- Tutag Lehr, V.; Cortez, J.; Grever, W.; Cepeda, E.; Thomas, R.; Aranda, J.V. Randomized placebo controlled trial of sucrose analgesia on neonatal skin blood flow and pain response during heel lance. The Clinical Journal of Pain 2015;31(5):451-8. [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.F.; Lin, K.C.; Chou, Y.H.; Lee, T.Y. Using non-nutritive sucking and oral glucose solution with neonates to relieve pain: a randomised controlled trial. J Clin Nurs. 2010;19(11-12):1604-11. [CrossRef]
- Gray, L.; Garza, E.; Zageris, D. et al. Sucrose and warmth for analgesia in healthy newborns: an RCT. Pediatrics 2015;135: e607. [CrossRef]
- Gaspardo, C.M.; Miyase, C.I.; Chimello, J.T.; Martinez, F.E.; Martins Linhares, M.B. Is pain relief equally efficacious and free of side effects with repeated doses of oral sucrose in preterm neonates? Pain 2008; 137:16-25. [CrossRef]
- Asmerom, Y.; Slater, L.; Boskovic, D.S.; Bahjri, K.; Holden, M.S.; Phillips, R. et al. Oral sucrose for heel lance increases adenosine triphosphate use and oxidative stress in preterm neonates. The Journal of Pediatrics 2013;163(1):29-35.e1. [CrossRef]
- Milazzo, W.; Fielder, J.; Bittel, A.; Coil, J.; McClure, M.; Tobin, P. et al. Oral sucrose to decrease pain associated with arterial puncture in infants 30 to 36 weeks’ gestation. A randomized clinical trial. Advances in Neonatal Care 2011;11(6):406-11. [CrossRef]
- Montoya, I.G.; Gázquez, M.A.R.; Cadavid, L.A.M.; Jaramillo, A.Q. The use of sucrose for the prevention of pain during venipuncture in neonates. Enfermería Clínica 2009;19:267-74.
- Liaw, J.J.; Zeng, W.P.; Yang, L.; Yuh, Y.S.; Yin, T.; Yang, M.H. Nonnutritive sucking and oral sucrose relieve neonatal pain during intramuscular injection of hepatitis vaccine. J Pain Symptom Manage 2011;42(6):918-30. [CrossRef]
- Burke, L. Homeopathy for Pain Management. Alternative and complementary therapies. 2017; 23:176-183.
- Martin, P. Аrnica and Aconite - homeopathic newborn care -Midwifery Today- Summer 2009:30-66.
- Burgari, R. Homeopathic treatment of newborn and infant children. (1st ed.). Similia;Russia; 2002:17-40.
- Castro, F.C.; Magre, A.; Cherpinski, R.; Zelante, P.M.; Neves; L.M.; Esquisatto, M.A. et al. Effects of microcurrent application alone or in combination with topical Hypericum perforatum L. and Arnica montana L. on surgically induced wound healing in Wistar rats. Homeopathy 2012;101(3):147-53. [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.G.; Miles, V.N.; Holmes, D.T.; Chen, X.; Lei, W. Clinical Trials, Potential Mechanisms, and Adverse Effects of Arnica as an Adjunct Medication for Pain Management. Medicines (Basel). 2021; 9;8(10):58. [CrossRef]
- Iannitti, T.; Morales-Medina, J.C.; Bellavite, P.; Rottigni, V.; Palmieri, B. Effectiveness and Safety of Arnica montana in Post-Surgical Setting, Pain and Inflammation. Am J Ther. 2016;23(1):e184-97. [CrossRef]
- Olioso, D.; Marzotto, M.; Bonafini, C.; Brizzi, M.; Bellavite, P. Arnica montana effects on gene expression in a human macrophage cell line. Evaluation by quantitative Real-Time PCR. Homeopathy 2016;105 (2): 131-47. [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, A.P.; Sato, C.; Cardoso, T.N.; Bonamin, L.V. Inflammatory Process Modulation by Homeopathic Arnica montana 6CH: The Role of Individual Variation. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011; 2011:917541. [CrossRef]
| Рain rating scales | Groups | before the procedure | SD | F | Sig. level | at the 30th sec. | SD | F | Sig. level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NIPS – Overall Assesment |
Without anesthesia -/А/ | 1,79±0,18 | 1,46 | 1,227 | 0,296 | 6,73±0,11 | 0,898 | 1,702 | 0,186 |
| Arnica D30-/В/ | 1,35±0,22 | 1,65 | 6,89±0,09 | 0,673 | |||||
| Sol.Glucosae 25%- /С/ | 1,50±0,28 | 1,70 | 6,98±0,03 | 0,158 | |||||
| NFCS – Overall Assesment |
Without anesthesia -/А/ | 1,24±0,15 | 1,24 | 0,408 | 0,666 | 6,85±0,09 | 0,751 | 2,499 | 0,085 |
| Arnica D30–/В/ | 1,04±0,18 | 1,04 | 6,28±0,10 | 0,959 | |||||
| Sol.Glucosae 25%-/С/ | 1,24±0,20 | 1,24 | 6,88±0,05 | 0,335 |
| NIPS -5th min | Groups | N | Mean | Std.Deviation | F | Sig. level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Face expression | without analgesia Arnica D30 Sol. Glucose 25% |
67 57 40 |
,74 ,40 ,60 |
,441 ,495 ,496 |
7,834 | 0,001** |
| Cry | without analgesia Arnica D30 Sol. Glucose 25% |
67 57 40 |
,91 ,47 ,68 |
,830 ,758 ,859 |
4,471 | 0,013* |
| Breathing patterns | without analgesia Arnica D30 Sol. Glucose 25% |
67 57 40 |
,75 ,49 ,83 |
,438 ,504 ,385 |
7,789 | 0,001** |
| Arms | without analgesia Arnica D30 Sol. Glucose 25% |
67 57 40 |
,88 ,56 ,80 |
,327 ,501 ,405 |
9,580 | 0,000*** |
| Legs | without analgesia Arnica D30 Sol. Glucose 25% |
67 57 40 |
,85 ,60 ,70 |
,359 ,495 ,464 |
5,324 | 0,006** |
| State of arousal | without analgesia Arnica D30 Sol. Glucose 25% |
67 57 40 |
,35 ,21 ,28 |
,480 ,411 ,452 |
1,443 | 0,239 |
| OverallAssesment | without analgesia Arnica D30 Sol. Glucose 25% |
67 57 40 |
4,46 3,00 3,28 |
2,127 2,699 2,552 |
8,989 | 0,000*** |
| Groups | Groups | Mean Difference | Sig. |
| Arnica D30 | Sol.Glucose 25% | -,274* | 0,021 |
| Sol. Glucose 25% | Arnica D30 | ,274* | 0,021 |
| Arnica D30 | Sol.Glucose 25% | -,181* | 0,049 |
| Sol. Glucose 25% | Arnica D30 | ,181* | 0,049 |
| Arnica D30 | Sol.Glucose 25% | -1,234* | 0,041 |
| Sol. Glucose 25% | Arnica D30 | 1,234* | 0,041 |
| Indicators | Groups | before the procedure | Std. | Sig. level | |
| Deviation | F | ||||
| Heartbeat | not anesthetised/А/ | 136,85±2,74 | 22,456 | 0,377 | 0,687 |
| ArnicaD30/В/ | 141.00±2,77 | 18,664 | |||
| Sol.Glucose 25%/С/ | 139,50±3,36 | 21,281 | |||
| Oxygen saturation | not anesthetised | 97,04±0,57 | 4,637 | 7,275 | ,001** |
| Arnica D30 | 97,33±0,56 | 2,754 | |||
| Sol.Glucose 25% | 94,58±0,81 | 5,103 | |||
| Breathing frequency | not anesthetized | 43,29±1,16 | 9,444 | 18,285 | ,000*** |
| Arnica D30 | 42,45±1,38 | 10,21 | |||
| Sol.Glucose 25% | 30,15±2,51 | 15,858 | |||
| Systolic blood pressure | not anesthetised | 79,46±2,12 | 15,853 | 4,91 | ,009** |
| Arnica D30 | 81,44±1,95 | 13,802 | |||
| Sol.Glucose 25% | 90,03±3,17 | 18,218 | |||
| Diastolic blood pressure | not anesthetised | 46,20±1,48 | 11,082 | 2,483 | 0,087 |
| Arnica D30 | 47,80±1,70 | 12,151 | |||
| Sol.Glucose25% | 52,27±2,65 | 15,195 |
| Indicators | Groups | Std. | F | Sig. Level | Std. | Sig. level | |||
| at the 30th sec. | Deviation | on the 5th min. | Deviation | F | |||||
| Heartbeat | not anesthetised/А/ | 158,07±3,49 | 28,557 | 4,569 | ,012* | 143,99±3,67 | 30,017 | 1,358 | 0,26 |
| ArnicaD30 /В/ | 162,37±3,21 | 27,369 | 141,35±3,57 | 23,579 | |||||
| Sol.Glucose 25%/С/ | 170,70±4,01 | 25,341 | 137,18±4,89 | 30,937 | |||||
| Oxygen saturation | not anesthetised | 88,13±1,09 | 8,881 | 1,777 | 0,173 | 94,12±1,08 | 8,845 | 2,675 | 0,072 |
| Arnica D30 | 89,93±0,81 | 5,812 | 97,00±0,50 | 4,767 | |||||
| Sol.Glucose 25% | 86,08±1,75 | 10,781 | 93,08±1,09 | 6,776 | |||||
| Breathing frequency | not anesthetized | 30,47±1,19 | 9,67 | 0,256 | 0,774 | 45,34±1,68 | 13,749 | 5,143 | ,007** |
| Arnica D30 | 29,61±2,09 | 15,391 | 40,13±1,81 | 13,433 | |||||
| Sol.Glucose 25% | 31,54±2,17 | 13,553 | 35,03±3,58 | 22,668 | |||||
| Systolic blood pressure | not anesthetised | - | - | 93,16±1,98 | 14,68 | 8,503 | ,000*** | ||
| Arnica D30 | - | - | 86,35±2,38 | 17,013 | |||||
| Sol.Glucose 25% | 101,10±2,64 | 14,211 | |||||||
| Diastolic blood pressure | not anesthetised | - | - | 53,45±1,89 | 14,004 | 0,941 | 0,393 | ||
| ArnicaD30 | - | - | 53,75±1,88 | 13,409 | |||||
| Sol.Glucose 25% | 57,62±2,82 | 15,197 |
| Physiological markers | Groups | Groups | Mean Difference | Sig. |
| Respiratory rate - before the procedure | Arnica D30/В/ | Sol.Glucose 25% | 12,305* | 0,00 |
| Sol. Glucose 25%/С/ | Arnica D30 | -12,305* | 0,00 | |
| Systolic blood pressure- before the procedure | Arnica D30 | Sol.Glucose 25% | -8,590* | 0,043 |
| Sol. Glucose 25% | Arnica D30 | 8,590* | 0,043 | |
| Heartbeat- at the 30th sec. | Arnica D30 | Sol.Glucose 25% | -16,682* | 0,010 |
| Sol. Glucose 25% | Arnica D30 | 16,682* | 0,010 | |
| Systolic blood pressure-at the 5th min. | Arnica D30 | Sol.Glucose 25% | -14,751* | 0,00 |
| Sol. Glucose 25% | Arnica D30 | 14,751* | 0,00 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





