1. Introduction
Prostate-specific antigen (PSA or KLK3) serves as a crucial indicator in the detection and control of prostate cancer. It is a glycoprotein belonging to the kallikrein-related protease family, regulated by androgens, and is secreted by the epithelial cells of the prostate gland [
1,
2].
Prostate cancer is a type of cancer that develops in the prostate, a small gland that produces seminal fluid in men. It is one of the most common cancers among men. Prostate cancer usually grows slowly and may not cause noticeable symptoms in its early stages. However, as the cancer advances, it can lead to symptoms such as difficulty urinating, blood in the urine or semen, pelvic discomfort, and erectile dysfunction. Screening for prostate cancer often involves the measurement of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels in the blood, as elevated levels may indicate the presence of cancer. Diagnosis is typically confirmed through a biopsy, where a small sample of prostate tissue is examined under a microscope [
3,
4,
5].
The current study is focused on conducting molecular docking simulations [
6,
7,
8] to investigate the binding interactions of various natural compounds with Human prostate-specific antigen (PSA or KLK3). Molecular docking is a computational technique used to predict and analyze the binding affinity and orientation of small molecules, such as natural compounds, within the binding site of a target protein—in this case, the PSA.The objective is to understand how these natural compounds interact with the PSA at a molecular level, potentially revealing insights into their ability to modulate or inhibit the activity of PSA. Such findings could have implications for the diagnosis and management of prostate cancer, as PSA is a significant marker in the context of this disease.
2. Material and Methods
Structure of Crystal Human
Prostate-specific antigen was taken from Protein Data Bank (PDB Code:
2ZCH). The docking investigation was meticulously prepared and was executed by Autodock Vina [
6] with Pyrx program, using: Grid box Coordinates of binding Center X (-31.3121), Y(-33.4163), Z(-17.7042); size_x = 44.8086516953; size_y = 50.3861114502; size_z = 45.3239394379.
3. Results and Discussion
In this investigation, molecular docking simulations [
6,
7,
8] were conducted to predict the binding modes and energies of various natural compounds with Human prostate-specific antigen (PSA). The acquired results could offer valuable insights for subsequent experimental validation and show promise for the potential development of innovative therapeutic approaches.
A noteworthy observation derived from the docking results is the identification of molecules that assume their most favorable poses, characterized by the highest negative binding energies during interaction with the target. This observation suggests a robust and effective binding affinity between the natural compounds and PSA.
The docking results, assessed using Autodock Vina [
6] with the Pyrx program, indicate that Amentoflavone, Ginketin, Rutin, and Hypericin have exhibited outstanding binding energy values, approximately reaching -10 kcal/mol.
Table 1.
Comparison best binding energies scores (kcal/mol) of natural compounds in complex with Human prostate-specific antigen (PSA), evaluated by Blind Docking method with Pyrx program.
Table 1.
Comparison best binding energies scores (kcal/mol) of natural compounds in complex with Human prostate-specific antigen (PSA), evaluated by Blind Docking method with Pyrx program.
| Ligand |
Binding Energy (kcal/mol) |
| Amentoflavone |
-9.8 |
| Ginketin |
-9.9 |
| Rutin |
-9.6 |
| Hypericin |
-9.6 |
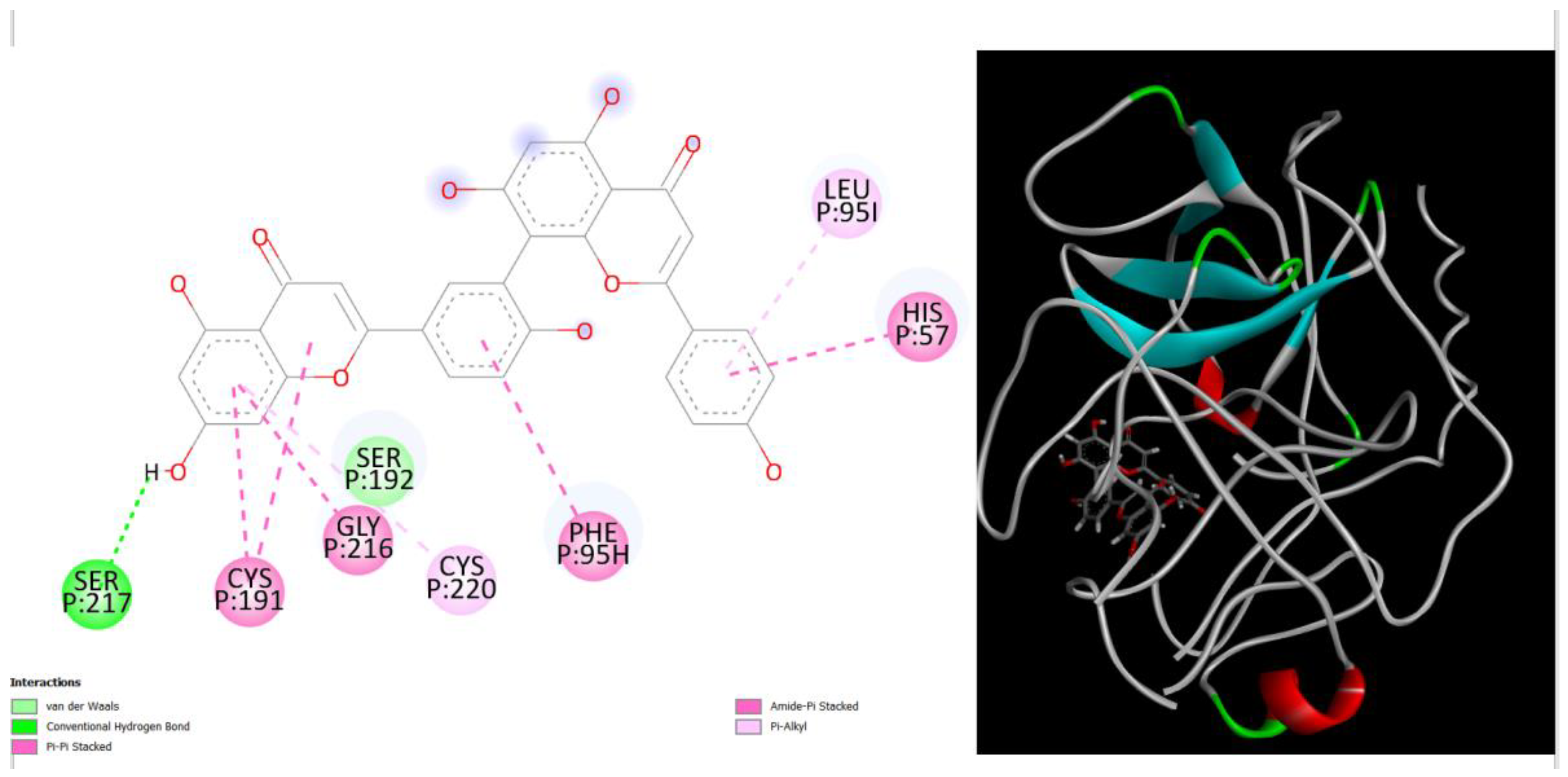
Figure 1.
displays the docking outcomes of Structure of Crystal Human Human prostate-specific antigen (PSA) in conjunction with docked amentoflavone -9.8 kcal mol, within the Ligand Binding Site, as analyzed by Autodock Vina with pyrx program. On the left side, 2D diagrams illustrate the residue interactions between the protein and amentoflavone. Meanwhile, the right side exhibits the Ligand Binding Site of the protein, highlighting the specific location of amentoflavone.
Figure 1.
displays the docking outcomes of Structure of Crystal Human Human prostate-specific antigen (PSA) in conjunction with docked amentoflavone -9.8 kcal mol, within the Ligand Binding Site, as analyzed by Autodock Vina with pyrx program. On the left side, 2D diagrams illustrate the residue interactions between the protein and amentoflavone. Meanwhile, the right side exhibits the Ligand Binding Site of the protein, highlighting the specific location of amentoflavone.
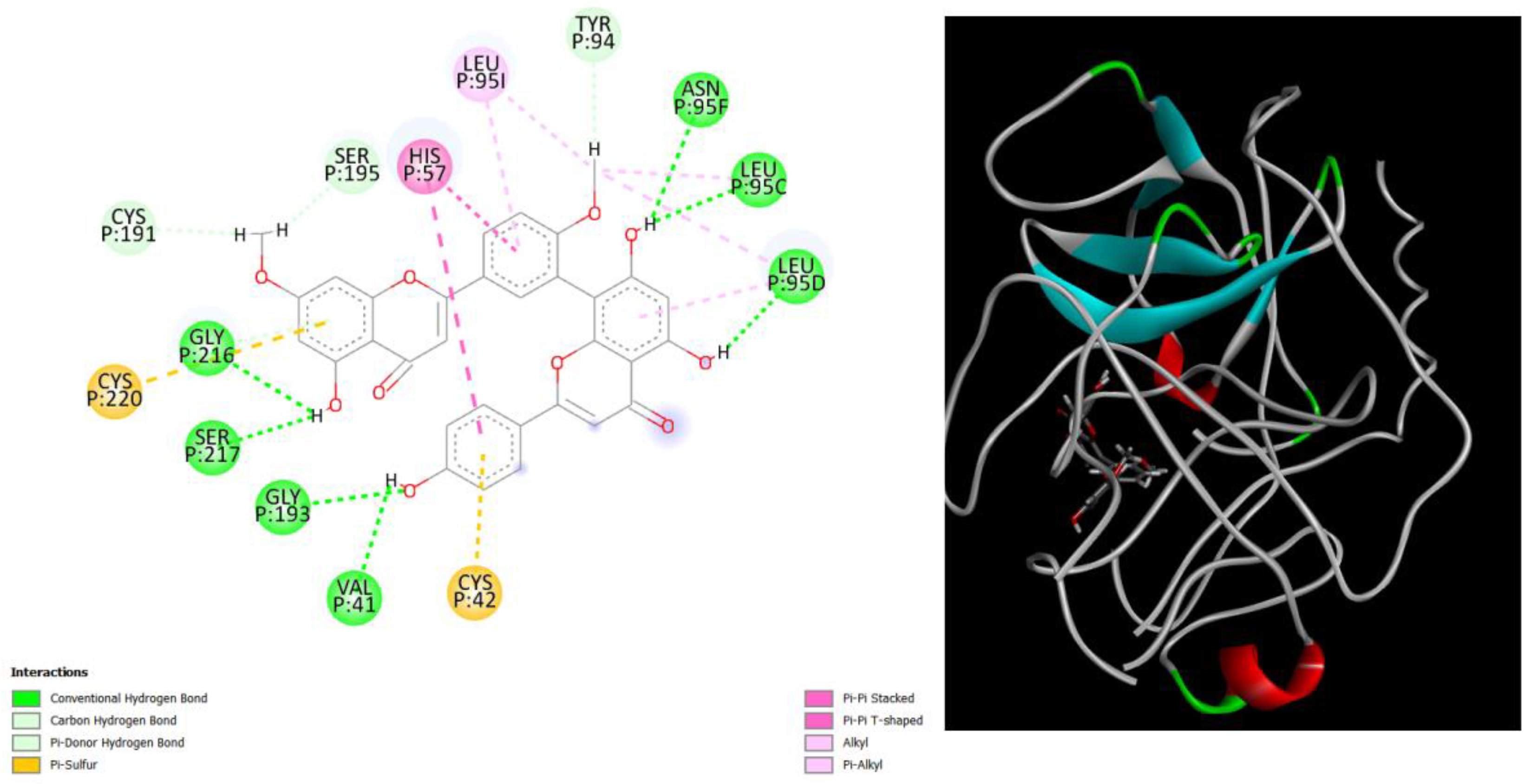
Figure 2.
displays the docking outcomes of Structure of Crystal Human Human prostate-specific antigen (PSA) in conjunction with docked Ginkgetin -9.9 kcal mol, within the Ligand Binding Site, as analyzed by Autodock Vina with pyrx program. On the left side, 2D diagrams illustrate the residue interactions between the protein and Ginkgetin. Meanwhile, the right side exhibits the Ligand Binding Site of the protein, highlighting the specific location of Ginkgetin.
Figure 2.
displays the docking outcomes of Structure of Crystal Human Human prostate-specific antigen (PSA) in conjunction with docked Ginkgetin -9.9 kcal mol, within the Ligand Binding Site, as analyzed by Autodock Vina with pyrx program. On the left side, 2D diagrams illustrate the residue interactions between the protein and Ginkgetin. Meanwhile, the right side exhibits the Ligand Binding Site of the protein, highlighting the specific location of Ginkgetin.
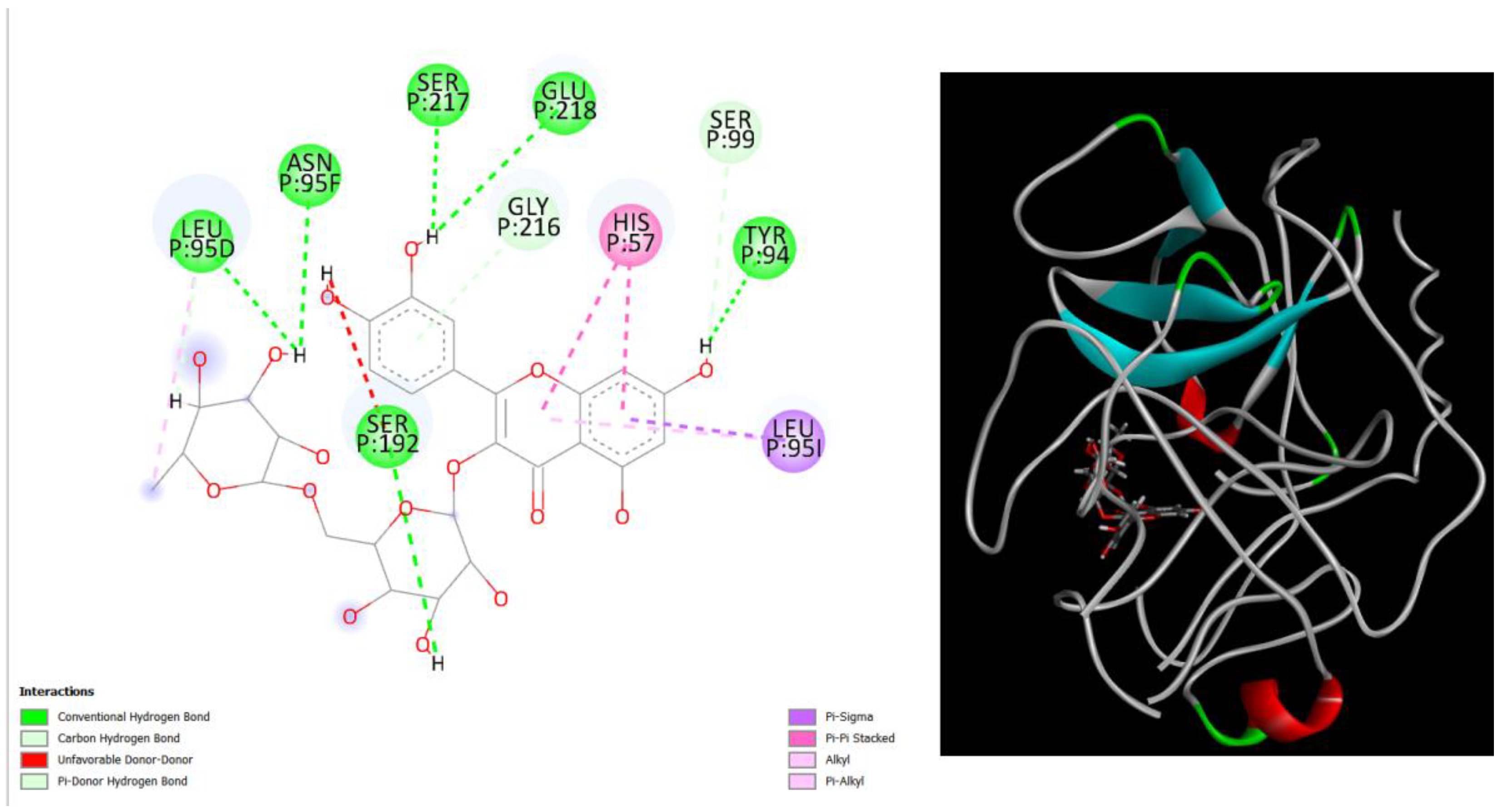
Figure 3.
displays the docking outcomes of Structure of Crystal Human Human prostate-specific antigen (PSA) in conjunction with docked Rutin -9.6 kcal mol, within the Ligand Binding Site, as analyzed by Autodock Vina with pyrx program. On the left side, 2D diagrams illustrate the residue interactions between the protein and Rutin. Meanwhile, the right side exhibits the Ligand Binding Site of the protein, highlighting the specific location of Rutin.
Figure 3.
displays the docking outcomes of Structure of Crystal Human Human prostate-specific antigen (PSA) in conjunction with docked Rutin -9.6 kcal mol, within the Ligand Binding Site, as analyzed by Autodock Vina with pyrx program. On the left side, 2D diagrams illustrate the residue interactions between the protein and Rutin. Meanwhile, the right side exhibits the Ligand Binding Site of the protein, highlighting the specific location of Rutin.
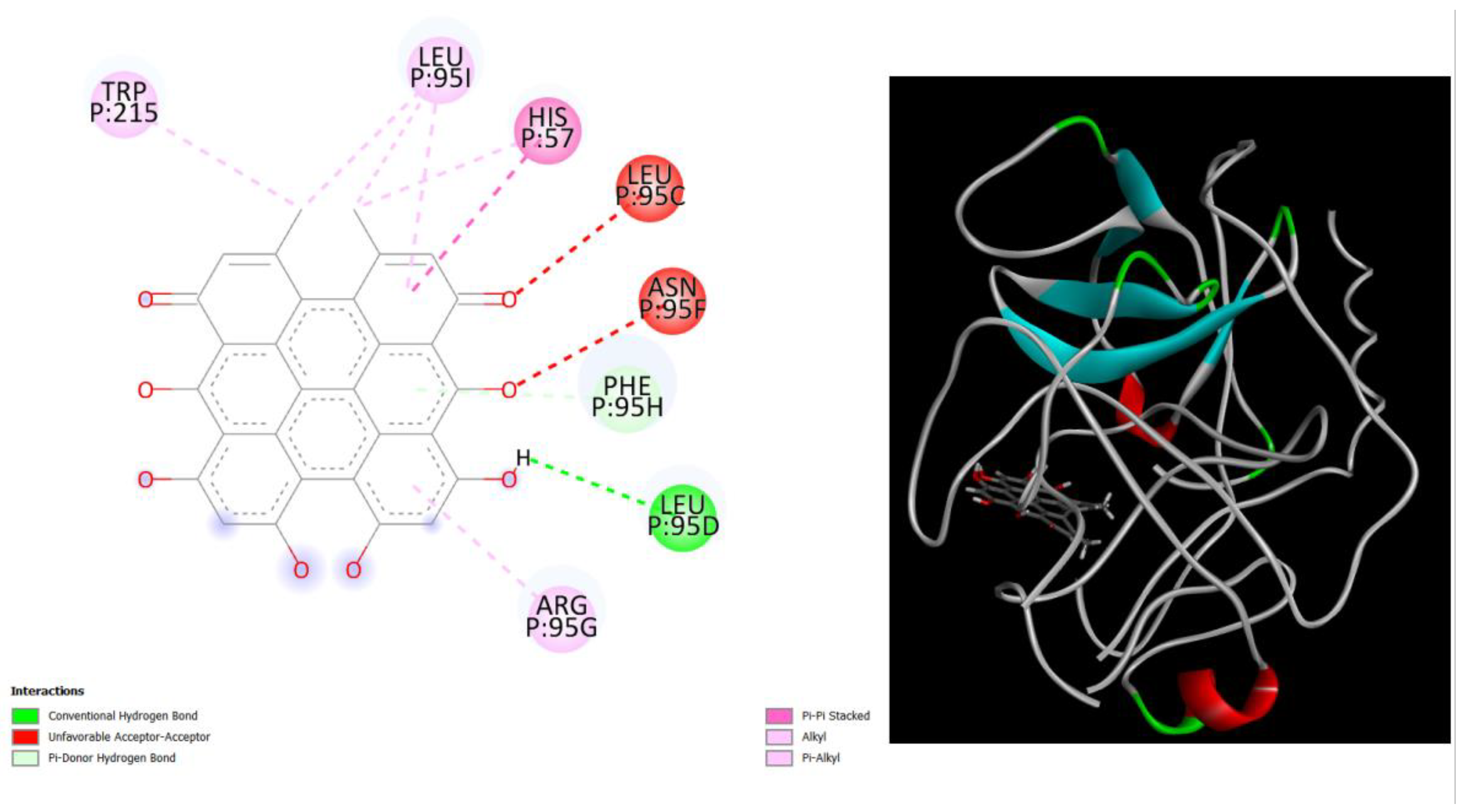
Figure 4.
displays the docking outcomes of Structure of Crystal Human Human prostate-specific antigen (PSA) in conjunction with docked Hypericin -9.6 kcal mol, within the Ligand Binding Site, as analyzed by Autodock Vina with pyrx program. On the left side, 2D diagrams illustrate the residue interactions between the protein and Hypericin. Meanwhile, the right side exhibits the Ligand Binding Site of the protein, highlighting the specific location of Hypericin.
Figure 4.
displays the docking outcomes of Structure of Crystal Human Human prostate-specific antigen (PSA) in conjunction with docked Hypericin -9.6 kcal mol, within the Ligand Binding Site, as analyzed by Autodock Vina with pyrx program. On the left side, 2D diagrams illustrate the residue interactions between the protein and Hypericin. Meanwhile, the right side exhibits the Ligand Binding Site of the protein, highlighting the specific location of Hypericin.
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, these molecular docking simulations employing Autodock Vina with the Pyrx program have demonstrated promising interactions between Human prostate-specific antigen (PSA) and natural compounds, specifically Amentoflavone, Ginketin, Rutin, and Hypericin. The consistently excellent binding energy values of approximately -10 kcal/mol suggest a strong potential for these compounds in modulating PSA activity. These findings present a foundation for further experimental validation to confirm the observed interactions and explore the practical applications of these natural compounds in prostate cancer treatment or management.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Duffy, M.J. (2020). Biomarkers for prostate cancer: prostate-specific antigen and beyond. Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine (CCLM), 58(3), 326-339. [CrossRef]
- Nik-Ahd, F., Jarjour, A., Figueiredo, J., Anger, J.T., Garcia, M., Carroll, P.R., ... & Freedland, S.J. (2023). Prostate-specific antigen screening in transgender patients. European Urology, 83(1), 48-54. [CrossRef]
- Freedland, S.J., de Almeida Luz, M., De Giorgi, U., Gleave, M., Gotto, G.T., Pieczonka, C.M., ... & Shore, N.D. (2023). Improved outcomes with enzalutamide in biochemically recurrent prostate cancer. New England Journal of Medicine, 389(16), 1453-1465. [CrossRef]
- Crowley, F., Mihalopoulos, M., Gaglani, S., Tewari, A.K., Tsao, C.K., Djordjevic, M., ... & Lundon, D.J. (2023). Prostate cancer in transgender women: considerations for screening, diagnosis and management. British Journal of Cancer, 128(2), 177-189. [CrossRef]
- Pozdnyakov, A., Kulanthaivelu, R., Bauman, G., Ortega, C., Veit-Haibach, P., & Metser, U. (2023). The impact of PSMA PET on the treatment and outcomes of men with biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases, 26(2), 240-248. [CrossRef]
- Trott, O., & Olson, A.J. (2010). AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. Journal of computational chemistry, 31(2), 455-461. [CrossRef]
- Muhammed, M.T., & Aki-Yalcin, E. (2024). Molecular docking: principles, advances, and its applications in drug discovery. Letters in Drug Design & Discovery, 21(3), 480-495. [CrossRef]
- Asiamah, I., Obiri, S.A., Tamekloe, W., Armah, F.A., & Borquaye, L.S. (2023). Applications of molecular docking in natural products-based drug discovery. Scientific African, e01593. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).