Submitted:
01 February 2024
Posted:
02 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- Evaluating the effects of video advertisements on QoE; here, the reliable measurement of QoE is a fundamental step in multimedia communication. Considering all the influencing factors in QoE experiments is important.
- Compare and analyze the experimental results based on the ITU-T P.1203 standard and existing studies [6].
- Propose an accurate machine learning model that can estimate QoE by considering advertisements and user expressions.
- Obtaining subjective QoE is expensive in terms of money, effort, and time. Therefore, we attempted to offer an alternative solution to this problem.
- The ITU-T P.1203 standard QoE measurement did not anticipate some significant factors, leading to inaccurate results. We hope to alleviate this issue using our proposed model.
- Excessive video advertisements during a video streaming session may weaken user engagement and negatively impact user QoE. We attempted to devise a method wherein a viewing session can coexist with several advertisements if a specific threshold is met.
-
How can machine learning be used to infer QoE from different data sources, such as viewers’ emotions, bitrates, resolutions, and advertisements?
- We conducted a preliminary experiment and obtained ITU-T P.1203 results with low accuracy.
- We investigated the reasons for the low accuracy of ITU-T P.1203 results.
- We hypothesized that the low accuracy of the ITU-T P.1203 result is because the features considered for building the model are irrelevant to recent conditions, that is, advertisement data and users’ facial emotions.
- We proposed video QoE inference by developing an ML model that considers ITU-T standard results, facial expression, gaze behavior, and advertising data.
- We compared various ML models and state-of-the-art algorithms with our proposed model to determine the accuracy of our proposed model.
-
How can high-quality data be collected and prepared to yield an effective ML model for QoE estimations?
- We created and circulated two websites to collect facial and YouTube stats-for-nerds video information.
- We designed more than 100 questions for participants to answer to ensure the accuracy of the obtained data. We asked many questions to make sure that the participants have the same answer about the topic and to minimize the random answer by participant. If we found it random answer or the answer not aligned with the other answer, we simply did not use them.
- We collected 50 video face recordings and metadata from 122 questionnaires from 661 survey participants from 114 countries and cities using an online platform.
- We intended to collect as much complete data as possible from individuals of various ethnicities and nations.
-
How to improve data quality for ML?
- We applied feature extraction and attribute selection to improve the supervised learning methods.
- We preprocessed the data to improve the data quality and thereby improve the ML performance.
- We obtained training data from various sources to enrich the model’s accuracy.
- We performed numerous ML experiments and made the necessary modifications to train the model.
-
How can we propose better advertisement duration and placement during video playback to preserve the advertiser budget and boost user QoE?
- We conducted questionnaire research to gather cultural patterns on how, what, and where advertisers can manage their budgets while efficiently promoting products.
- We provided insight into how to compromise video QoE, user engagement, and advertisement efficacy to optimize the budget.
2. Background and Related Work
2.1. Quality of Experience
| Reference | Influence Factors | Considered Features |
|---|---|---|
| Amour et al. [23] | Resolution, bandwidth, delay | Face emotion |
| Bhattacharya et al. [24] | Delay, packet loss, bandwidth | Acoustic feature |
| Porcu et al. [15] | Delay, stalling | Face and gaze tracking information |
| Porcu et al. [26] | Blurring | Face and gaze tracking information |
| Antons et al. [27] | Noise signal | EEG |
| Arndt et al. [29] | Low bitrate encoding | EEG and EOG |
| Kroupi et al. [28] | High quantization attribute | EEG |
| Arndt et al. [30] | Low bitrate encoding | EEG and gaze movement information |
| Rai et al. [32] | High quantization attribute | Gaze movement information |
| Rai et al. [33] | Packet loss | Gaze movement information |
| Engelke et al. [31] | Packet loss | Gaze movement information |
| Bailenson et al. [34] | Provoked delight and anxiety | Face emotion and 15 physiological features |
| Our Proposed Work | Video advertisement | Face emotion, video metadata and advertisement information |
2.2. ITU-T P.1203 Standard
2.3. Face Emotion Recognition (FER)
2.4. HTTP Adaptive Streaming (HAS)
2.5. QoE Influence Factors
2.6. QoE Metrics
- Source video quality: Content quality may be affected by the characteristics of the original video, such as codec type and video bitrate.
- QoS: mainly the consideration of how the packet or video traffic chunks travel in the network from the source to the destination; alternately, technical details include packet loss, jitter, delay, and throughput.
- MOS or subjective QoE measurement: this involves the human perception or satisfaction level.
- Objective QoE measurement: This denotes assessment models for estimating/predicting subjective video quality services by extracting important QoE metrics, for example, by examining the stalling frequency and stalling period.
2.7. QoE Assessment Types
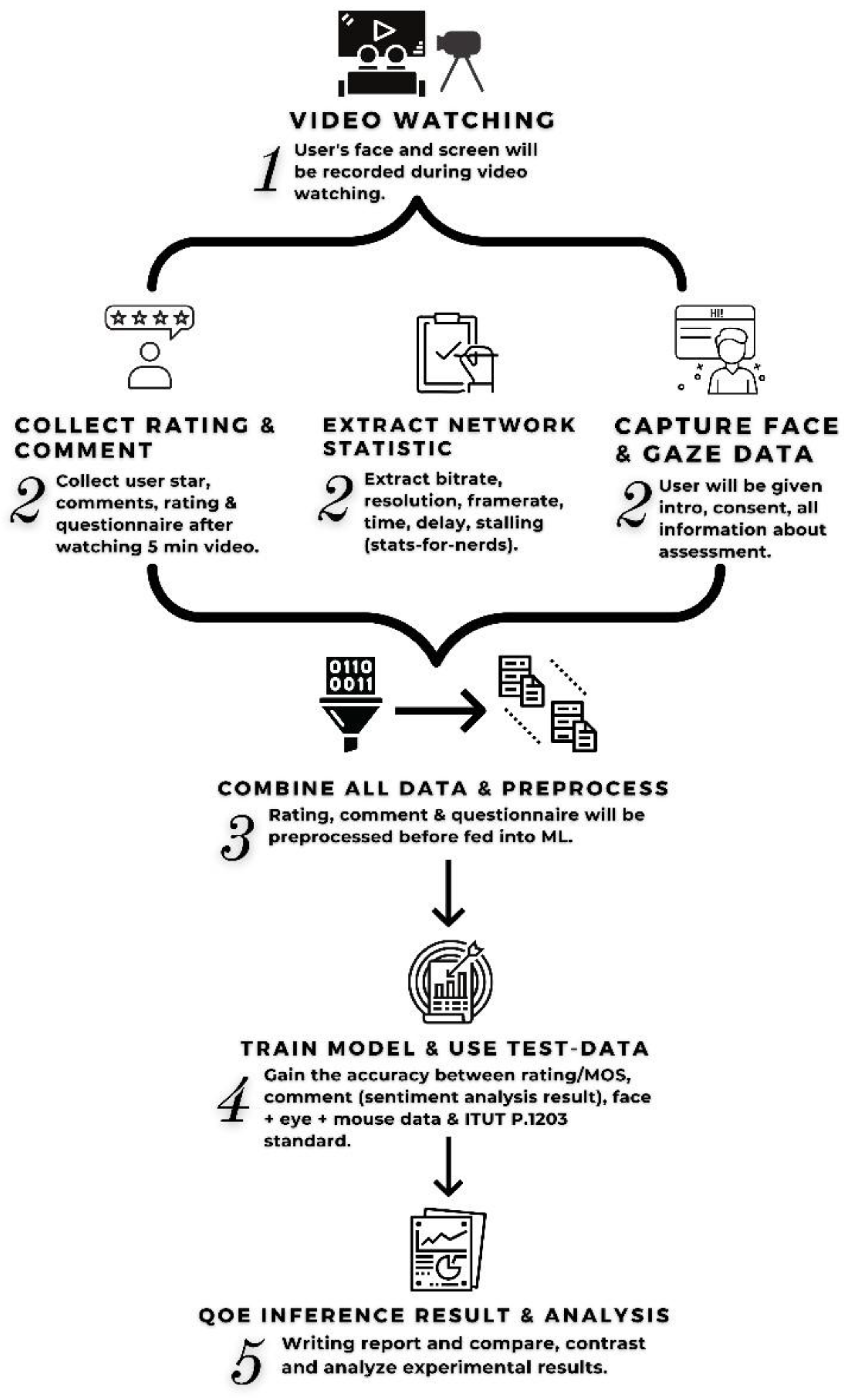
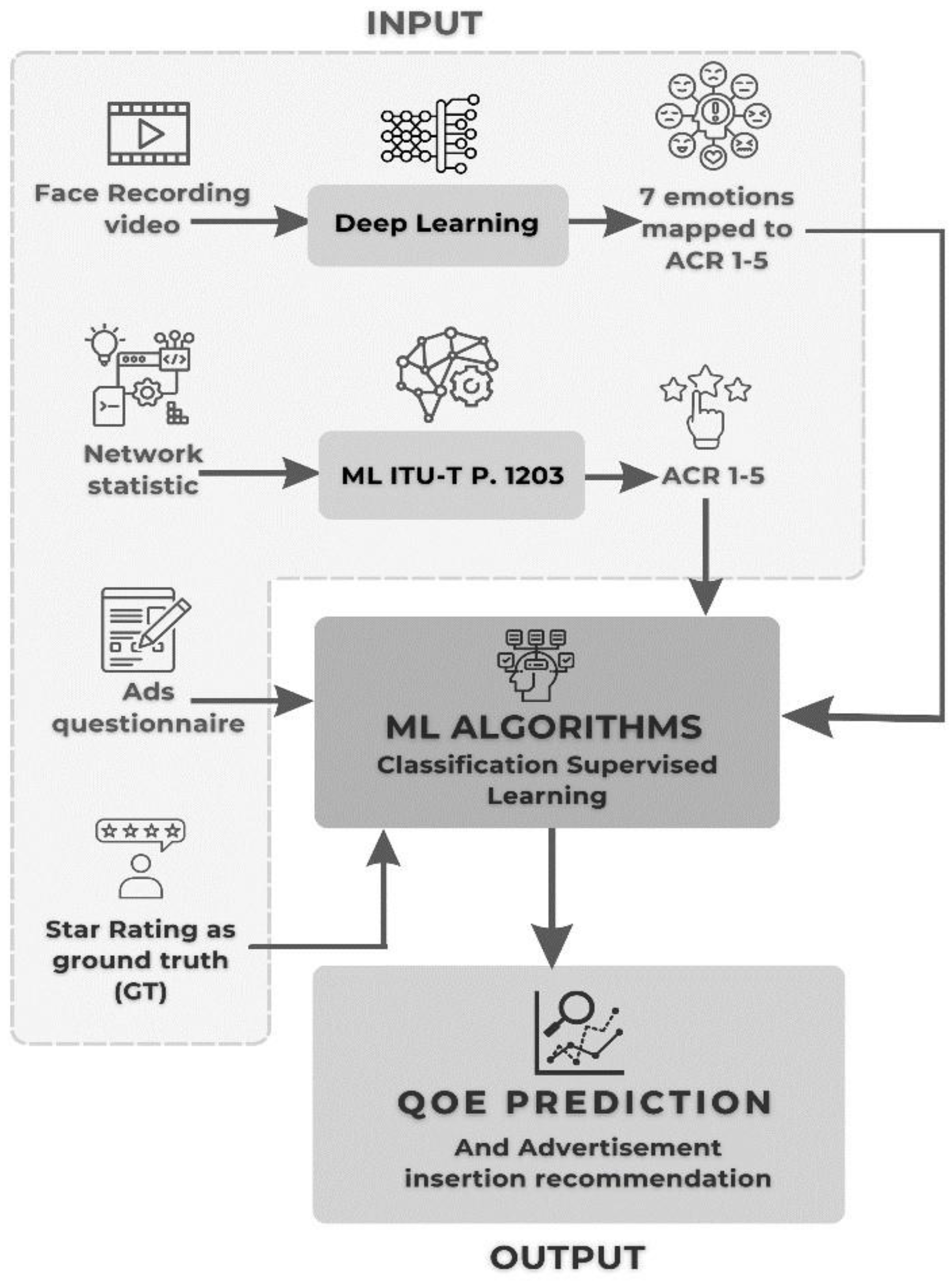
3. Methodology
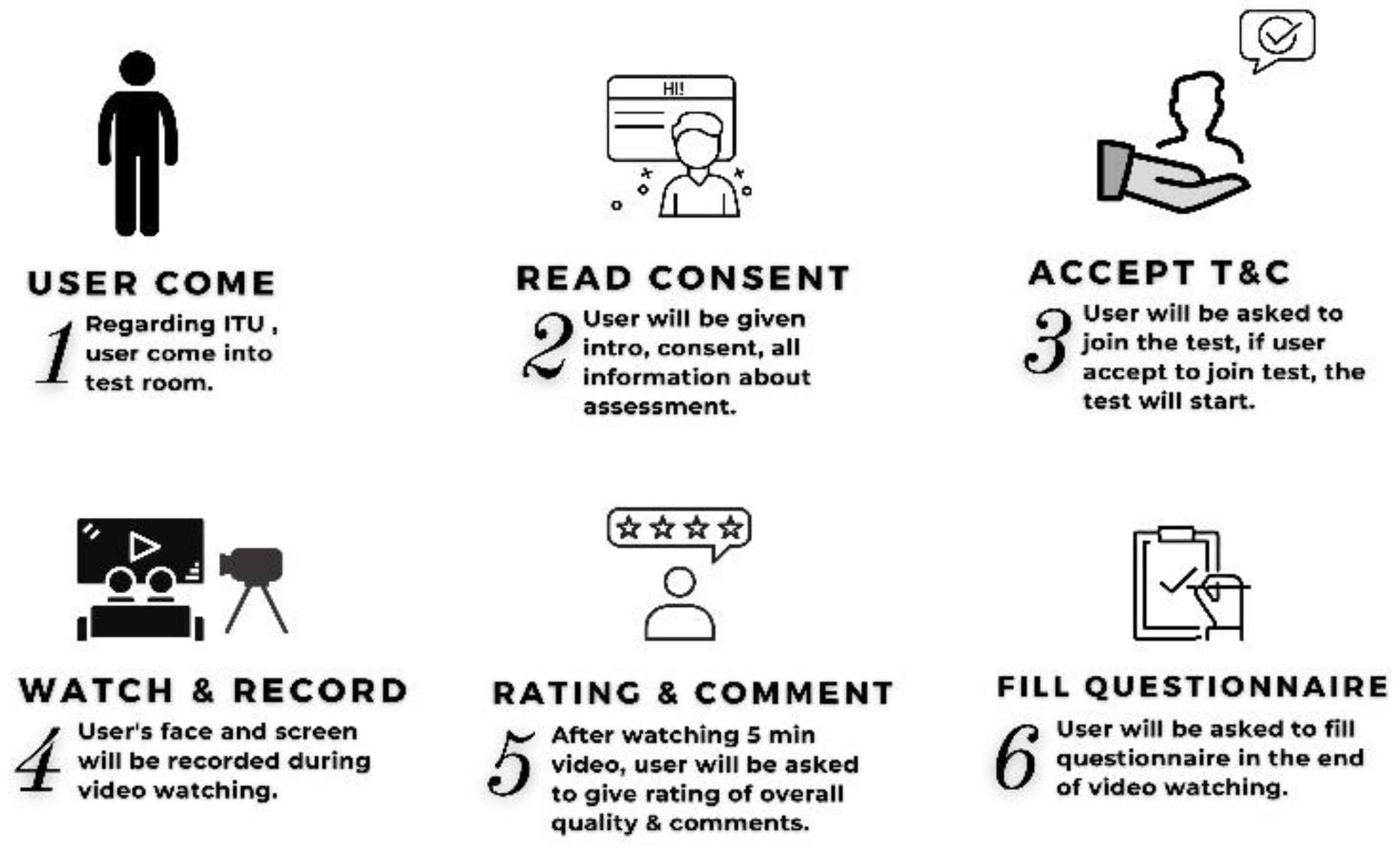
3.1. Video Watching Session
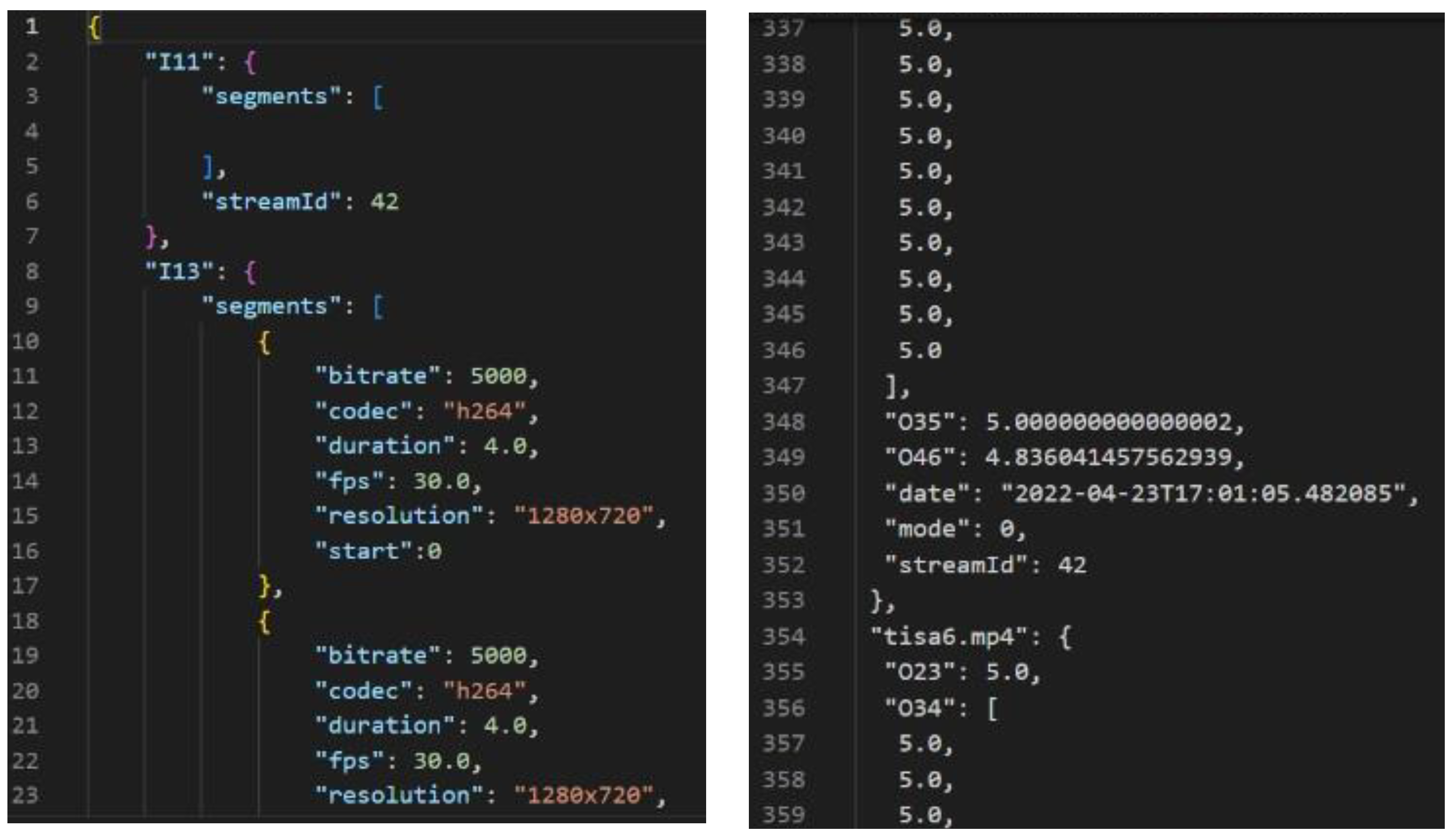
3.2. Data Collection and Storing
3.3. Combine All Data Approach
- P.1203 (ITU-T): Parametric bitstream-based quality evaluation of progressive download and adaptive audiovisual streaming services over dependable transport.
- P.1203.1, ITU-T: Parametric bitstream-based quality evaluation of progressive download and adaptive audio-visual streaming services over dependable transport–video quality estimate module.
- ITU-T Rec. P.1203.2: Audio quality estimate module for metric bitstream-based quality evaluation of progressive download and adaptive audiovisual streaming services over dependable transport.
- ITU-T Rec. P.1203.3: Quality integration module for metric bitstream-based quality evaluation of progressive download and adaptive audiovisual streaming services over dependable transport.
3.4. Pre-processing, Data Cleaning, Model Training and Evaluation
3.5. QoE Evaluation Result and Analysis
3.7. Analysis on Machine Learning Methodologies, Features Importance, and QoE Perceptions
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Survey Results and Statistics
- a.
- Competing Approaches
4.3. Hardware and Software Setup
4.4. Evaluation
- Massive intense ads may impact QoE and increase ITU results (i.e., higher bitrate, frame rate, and resolution); this does not signify that star review from participants will be high.
- Possible QoE IFs: For acceptable general video content, the advertisement factors, ad length, number of ads, ad location, related ad with content, repeated ad, and maximum ad acceptance are the QoE IFs.
- The most impaired QoE was in mid-roll and unskippable ads (approximately 36.2% and 31.9%, respectively). The QoE that the user can accept to watch an ad of less than 10 seconds is approximately 41.67.
- Massive intense ads may impact QoE Even ITU results is high (bitrate, framerate, and resolution are high), it does not mean that star review from participants will also be high.
- Possible QoE influence factors: Advertisement After the acceptable general video content, it can be advertisement factors: ad length, number of ads, ad location, related ad with content, repeated ad, and maximum ad acceptance.
- The most impaired QoE was in the mid-long ad and unskippable ads at approximately 36.2% and 31.9%, respectively. The limitation that a user can accept to watch an ad is less than 10 s (approximately 41.67%).
5. Discussions and Future Directions
- Real live FER system: We have tried the real time live system face emotion recognition in the wild and it works effectively although the emotion results do not drive the shape of traffic yet. Our proposed method uses emotion-aware advertisement insertion. Shaping the traffic based on emotion to improve QoE will be our future work.
- Computational complexity of the system: the computational complexity of the proposed method is dominated by the process of facial emotion recognition (FER). The FER process involves several steps, including: first, face detection: This step involves identifying the location of the face in the video frame. The computational complexity of face detection depends on the DeepFace algorithm. The complexity is O(n), where n is the number of pixels in the video frame. Second, feature extraction: This step involves extracting features from the face. The computational complexity of feature extraction depends on the specific feature used. Therefore, the complexity of the compound becomes O(f), where f is the number of extracted features. Third, motion classification: This step involves classifying the extracted features into one of seven basic emotions (happiness, sadness, anger, fear, surprise, disgust, and neutrality). The computational complexity of emotion classification depends on the specific classifier used. However, in general, it can be thought of as O (c), where c is the sum of emotion classes.
- Therefore, the overall computational complexity of the FER process can be thought of as O ( n ⋅ f ⋅ c ). In the context of the proposed method, the FER process is carried out on each frame of the video. Therefore, the overall computational complexity of the proposed method is O ( T ⋅ n ⋅ f ⋅ c), where T is the total number of video frames. For a video that is 30 seconds long and has a frame rate of 30 frames per second, then T = 30 × 30 = 900. If the video frame is 640 × 480 pixels, then n = 640 × 480 = 307200. For f = 100 features are extracted from each face, and c = 7 emotions are classified, then the overall computational complexity of the proposed method is O (900 ⋅ 307200 ⋅ 100 ⋅ 7) = 1.6 × 1012. This is a relatively high computational complexity. However, it is important to note that the FER process can be parallelized with the GPU to significantly reduce the computational costs of the proposed method. In addition, it is important to note that the proposed method is used only to select the most relevant ads for a particular user. Once the most relevant ad is selected, including the place, type, time of the ad. Then these types of ads can be provided to users without the need for further facial emotion recognition. Therefore, the overall computational impact of the proposed method is relatively small.
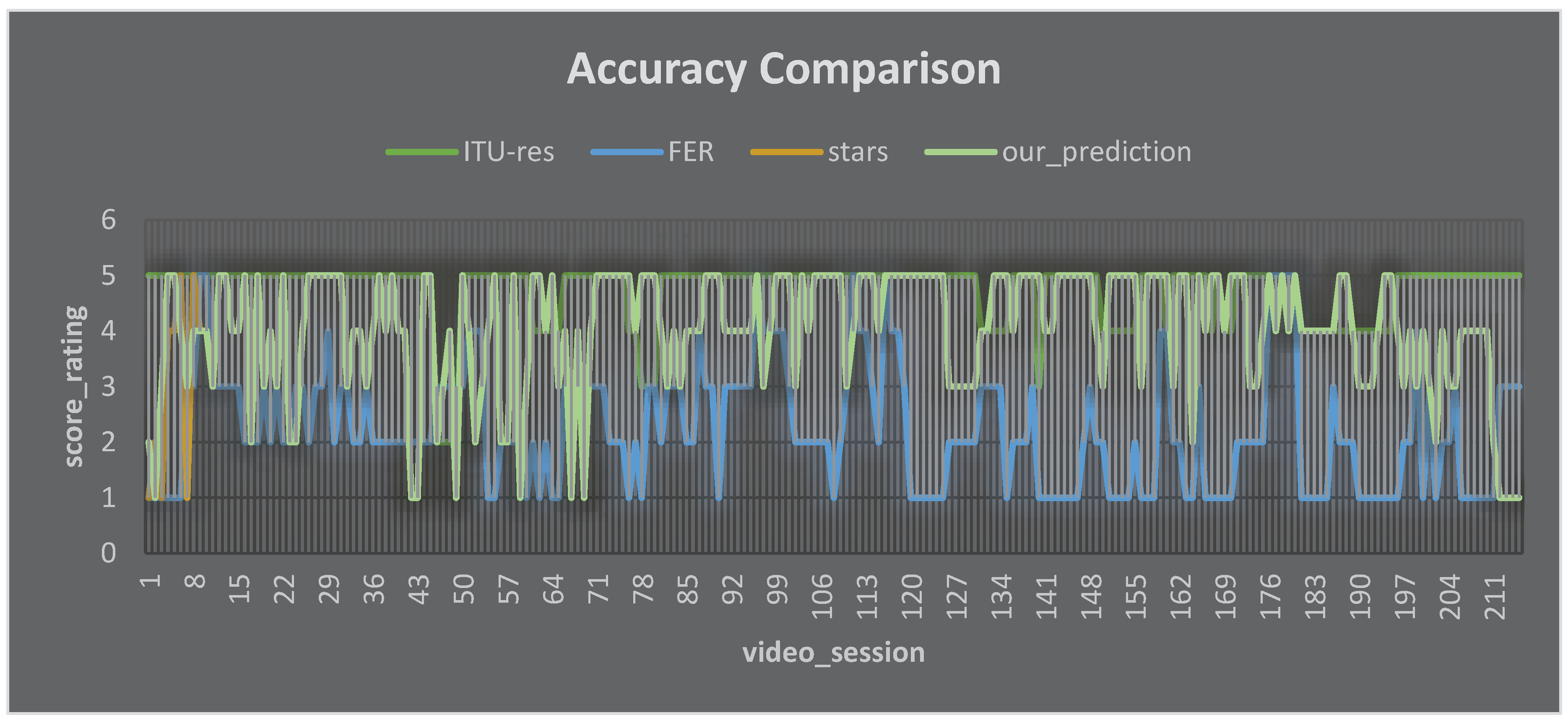
- Theoretical analysis of our proposed model: for the theoretical analysis of our proposed model, we can see the explanation as follows. The proposed Machine Learning (ML) model for Video Quality of Experience (QoE) inference, incorporating face emotion recognition, user feedback on ad insertion, and network conditions, was evaluated on a dataset of 50 recorded video streaming sessions. This dataset included face videos of viewers, network traffic logs, user feedback on ad insertion, and subjective QoE scores. The model's accuracy was compared against two baseline models: one utilizing only network conditions for QoE inference, ITU-T P.1203 and another employing solely user feedback on ad insertion. The proposed model consistently achieved lower Mean Absolute Error (MAE) and Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE) compared to the baseline models, indicating superior accuracy in inferring QoE. It can be seen in Figure 8 and Table 9.
- Qualitative analysis revealed the model's sensitivity to facial expressions of viewers, particularly joy, surprise, and frustration, known indicators of positive and negative QoE, respectively. It also learned to identify ad placements perceived as disruptive by users, adjusting its QoE predictions accordingly. Moreover, the model effectively utilized network bandwidth as a critical indicator of potential rebuffering and stalling, which negatively impacts QoE. These experimental results convincingly demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed ML model in accurately inferring video QoE. Its ability to integrate face emotion recognition, user feedback on ad insertion, and network conditions provides a comprehensive understanding of QoE, holding significant promise for improving user satisfaction and network performance in video streaming systems.
- Our hypothesis by mapping the extracted emotion to ACR and MOS are based on two studies by Porcu et al. [40] and Martinez-Caro & Cano [52]. Porcu et al. [40] analyzing the facial expression and gaze direction achieved 93.9% accuracy leveraging k-NN classifier which investigates the possibility to estimate perceived QoE by using face emotion and gaze movement. Moreover, the work by Martinez-Caro & Cano [52] utilizing the ITU-T P.1203 model to estimate MOS value and uses variational algorithms to predict QoE to give insight on emotional impact of video quality.
6. Conclusions
- Users get more annoyed when an advertisement is placed in the middle of the content.
- The maximum tolerable advertisement length is 10 s.
- The most annoying advertisement is an unskippable one.
- The most degraded QoE was obtained for a mid-roll advertisement.
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Abbreviation | Stands For |
|---|---|
| CCI CNN |
Correctly Classified Instances Convolutional neural network |
| CV | Cross Validation |
| DL | Deep learning |
| FER | Face Emotion Recognition |
| HAS | HTTP Adaptive Streaming |
| HTTP ICI |
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Incorrectly Classified Instances |
| ITU-T | International Telecommunication Union - Telecommunication |
| Mid-roll | Video advertisement at the middle of content playback |
| MSE | Mean squared error |
| Post-roll | Video advertisement at the end of content playback |
| Pre-roll | Video advertisement before content playback started |
| QoE | Quality of Experience |
| QoS | Quality of Service |
| UE | User Experience |
| Weka | Waikato Environment for Knowledge Analysis |
| MSE | Mean squared error |
Appendix B
| 1. What do you think about the frequency of advertisement in pre-roll |
| 2. What do you think about the frequency of advertisement in mid-roll |
| 3. What do you think about the frequency of advertisement in post-roll |
| 4. How bodily relaxed / aroused are you after watching first video (Title: How This Guy Found a Stolen Car!)? [(A) Relaxed - (B) Stimulated] |
| 5. How bodily relaxed / aroused are you after watching first video (Title: How This Guy Found a Stolen Car!)? [(A) Calm - (B) Excited] |
| 6. How bodily relaxed / aroused are you after watching first video (Title: How This Guy Found a Stolen Car!)? [(A) Sluggish - (B) Frenzied] |
| 7. How bodily relaxed / aroused are you after watching first video (Title: How This Guy Found a Stolen Car!)? [(A) Dull - (B) Jittery] |
| 8. How bodily relaxed / aroused are you after watching first video (Title: How This Guy Found a Stolen Car!)? [(A) Sleepy - (B) Wide Awake] |
| 9. How bodily relaxed / aroused are you after watching first video (Title: How This Guy Found a Stolen Car!)? [(A) Unaroused - (B) Aroused] |
| 10. How bodily relaxed / aroused are you after watching second video (Title: First Underwater Farm)? [(A) Relaxed - (B) Stimulated] |
| 11. How bodily relaxed / aroused are you after watching second video (Title: First Underwater Farm)? [(A) Calm - (B) Excited] |
| 12. How bodily relaxed / aroused are you after watching second video (Title: First Underwater Farm)? [(A) Sluggish - (B) Frenzied] |
| 13. How bodily relaxed / aroused are you after watching second video (Title: First Underwater Farm)? [(A) Dull - (B) Jittery] |
| 14. How bodily relaxed / aroused are you after watching second video (Title: First Underwater Farm)? [(A) Sleepy - (B) Wide Awake] |
| 15. How bodily relaxed / aroused are you after watching second video (Title: First Underwater Farm)? [(A) Unaroused - (B) Aroused] |
| 16. How bodily relaxed / aroused are you after watching third video (Title: Most Beautiful Building In The World)? [(A) Relaxed - (B) Stimulated] |
| 17. How bodily relaxed / aroused are you after watching third video (Title: Most Beautiful Building In The World)? [(A) Calm - (B) Excited] |
| 18. How bodily relaxed / aroused are you after watching third video (Title: Most Beautiful Building In The World)? [(A) Sluggish - (B) Frenzied] |
| 19. How bodily relaxed / aroused are you after watching third video (Title: Most Beautiful Building In The World)? [(A) Dull - (B) Jittery] |
| 20. How bodily relaxed / aroused are you after watching third video (Title: Most Beautiful Building In The World)? [(A) Sleepy - (B) Wide Awake] |
| 21. How bodily relaxed / aroused are you after watching third video (Title: Most Beautiful Building In The World)? [(A) Unaroused - (B) Aroused] |
| 22. How bodily relaxed / aroused are you after watching fourth video (Title: This is Made of...PEE?!)? [(A) Relaxed - (B) Stimulated] |
| 23. How bodily relaxed / aroused are you after watching fourth video (Title: This is Made of...PEE?!)? [(A) Calm - (B) Excited] |
| 24. How bodily relaxed / aroused are you after watching fourth video (Title: This is Made of...PEE?!)? [(A) Sluggish - (B) Frenzied] |
| 25. How bodily relaxed / aroused are you after watching fourth video (Title: This is Made of...PEE?!)? [(A) Dull - (B) Jittery] |
| 26. How bodily relaxed / aroused are you after watching fourth video (Title: This is Made of...PEE?!)? [(A) Sleepy - (B) Wide Awake] |
| 27. How bodily relaxed / aroused are you after watching fourth video (Title: This is Made of...PEE?!)? [(A) Unaroused - (B) Aroused] |
| 28. How bodily relaxed / aroused are you after watching fifth video (Title: The Most Unexplored Place In The World)? [(A) Relaxed - (B) Stimulated] |
| 29. How bodily relaxed / aroused are you after watching fifth video (Title: The Most Unexplored Place In The World)? [(A) Calm - (B) Excited] |
| 30. How bodily relaxed / aroused are you after watching fifth video (Title: The Most Unexplored Place In The World)? [(A) Sluggish - (B) Frenzied] |
| 31. How bodily relaxed / aroused are you after watching fifth video (Title: The Most Unexplored Place In The World)? [(A) Dull - (B) Jittery] |
| 32. How bodily relaxed / aroused are you after watching fifth video (Title: The Most Unexplored Place In The World)? [(A) Sleepy - (B) Wide Awake] |
| 33. How bodily relaxed / aroused are you after watching fifth video (Title: The Most Unexplored Place In The World)? [(A) Unaroused - (B) Aroused] |
| 34. How emotionally controlled / uncontrolled are you after watching first video (Title: How This Guy Found a Stolen Car!)? [(A) Controlled - (B) Controlling] |
| 35. How emotionally controlled / uncontrolled are you after watching first video (Title: How This Guy Found a Stolen Car!)? [(A) Influenced - (B) Influential] |
| 36. How emotionally controlled / uncontrolled are you after watching first video (Title: How This Guy Found a Stolen Car!)? [(A) Cared for - (B) In control] |
| 37. How emotionally controlled / uncontrolled are you after watching first video (Title: How This Guy Found a Stolen Car!)? [(A) Awed - (B) Important] |
| 38. How emotionally controlled / uncontrolled are you after watching first video (Title: How This Guy Found a Stolen Car!)? [(A) Submissive - (B) Dominant] |
| 39. How emotionally controlled / uncontrolled are you after watching first video (Title: How This Guy Found a Stolen Car!)? [(A) Guided - (B) Autonomous] |
| 40. How emotionally controlled / uncontrolled are you after watching second video (Title: First Underwater Farm)? [(A) Controlled - (B) Controlling] |
| 41. How emotionally controlled / uncontrolled are you after watching second video (Title: First Underwater Farm)? [(A) Influenced - (B) Influential] |
| 42. How emotionally controlled / uncontrolled are you after watching second video (Title: First Underwater Farm)? [(A) Cared for - (B) In control] |
| 43. How emotionally controlled / uncontrolled are you after watching second video (Title: First Underwater Farm)? [(A) Awed - (B) Important] |
| 44. How emotionally controlled / uncontrolled are you after watching second video (Title: First Underwater Farm)? [(A) Submissive - (B) Dominant] |
| 45. How emotionally controlled / uncontrolled are you after watching second video (Title: First Underwater Farm)? [(A) Guided - (B) Autonomous] |
| 46. How emotionally controlled / uncontrolled are you after watching third video (Title: Most Beautiful Building In The World)? [(A) Controlled - (B) Controlling] |
| 47. How emotionally controlled / uncontrolled are you after watching third video (Title: Most Beautiful Building In The World)? [(A) Influenced - (B) Influential] |
| 48. How emotionally controlled / uncontrolled are you after watching third video (Title: Most Beautiful Building In The World)? [(A) Cared for - (B) In control] |
| 49. How emotionally controlled / uncontrolled are you after watching third video (Title: Most Beautiful Building In The World)? [(A) Awed - (B) Important] |
| 50. How emotionally controlled / uncontrolled are you after watching third video (Title: Most Beautiful Building In The World)? [(A) Submissive - (B) Dominant] |
| 51. How emotionally controlled / uncontrolled are you after watching third video (Title: Most Beautiful Building In The World)? [(A) Guided - (B) Autonomous] |
| 52. How emotionally controlled / uncontrolled are you after watching fourth video (Title: This is Made of...PEE?!)? [(A) Controlled - (B) Controlling] |
| 53. How emotionally controlled / uncontrolled are you after watching fourth video (Title: This is Made of...PEE?!)? [(A) Influenced - (B) Influential] |
| 54. How emotionally controlled / uncontrolled are you after watching fourth video (Title: This is Made of...PEE?!)? [(A) Cared for - (B) In control] |
| 55. How emotionally controlled / uncontrolled are you after watching fourth video (Title: This is Made of...PEE?!)? [(A) Awed - (B) Important] |
| 56. How emotionally controlled / uncontrolled are you after watching fourth video (Title: This is Made of...PEE?!)? [(A) Submissive - (B) Dominant] |
| 57. How emotionally controlled / uncontrolled are you after watching fourth video (Title: This is Made of...PEE?!)? [(A) Guided - (B) Autonomous] |
| 58. How emotionally controlled / uncontrolled are you after watching fifth video (Title: The Most Unexplored Place In The World)? [(A) Controlled - (B) Controlling] |
| 59. How emotionally controlled / uncontrolled are you after watching fifth video (Title: The Most Unexplored Place In The World)? [(A) Influenced - (B) Influential] |
| 60. How emotionally controlled / uncontrolled are you after watching fifth video (Title: The Most Unexplored Place In The World)? [(A) Cared for - (B) In control] |
| 61. How emotionally controlled / uncontrolled are you after watching fifth video (Title: The Most Unexplored Place In The World)? [(A) Awed - (B) Important] |
| 62. How emotionally controlled / uncontrolled are you after watching fifth video (Title: The Most Unexplored Place In The World)? [(A) Submissive - (B) Dominant] |
| 63. How emotionally controlled / uncontrolled are you after watching fifth video (Title: The Most Unexplored Place In The World)? [(A) Guided - (B) Autonomous] |
| 64. How pleasant / unpleasant do you feel after watching first video (Title: How This Guy Found a Stolen Car!)? [(A) Unhappy - (B) Happy] |
| 65. How pleasant / unpleasant do you feel after watching first video (Title: How This Guy Found a Stolen Car!)? [(A) Annoyed - (B) Pleased] |
| 66. How pleasant / unpleasant do you feel after watching first video (Title: How This Guy Found a Stolen Car!)? [(A) Unsatisfied - (B) Satisfied] |
| 67. How pleasant / unpleasant do you feel after watching first video (Title: How This Guy Found a Stolen Car!)? [(A) Melancholic - (B) Contented] |
| 68. How pleasant / unpleasant do you feel after watching first video (Title: How This Guy Found a Stolen Car!)? [(A) Despairing - (B) Hopeful] |
| 69. How pleasant / unpleasant do you feel after watching first video (Title: How This Guy Found a Stolen Car!)? [(A) Bored - (B) Relaxed] |
| 70. How pleasant / unpleasant do you feel after watching second video (Title: First Underwater Farm)? [(A) Unhappy - (B) Happy] |
| 71. How pleasant / unpleasant do you feel after watching second video (Title: First Underwater Farm)? [(A) Annoyed - (B) Pleased] |
| 72. How pleasant / unpleasant do you feel after watching second video (Title: First Underwater Farm)? [(A) Unsatisfied - (B) Satisfied] |
| 73. How pleasant / unpleasant do you feel after watching second video (Title: First Underwater Farm)? [(A) Melancholic - (B) Contented] |
| 74. How pleasant / unpleasant do you feel after watching second video (Title: First Underwater Farm)? [(A) Despairing - (B) Hopeful] |
| 75. How pleasant / unpleasant do you feel after watching second video (Title: First Underwater Farm)? [(A) Bored - (B) Relaxed] |
| 76. How pleasant / unpleasant do you feel after watching third video (Title: Most Beautiful Building In The World)? [(A) Unhappy - (B) Happy] |
| 77. How pleasant / unpleasant do you feel after watching third video (Title: Most Beautiful Building In The World)? [(A) Annoyed - (B) Pleased] |
| 78. How pleasant / unpleasant do you feel after watching third video (Title: Most Beautiful Building In The World)? [(A) Unsatisfied - (B) Satisfied] |
| 79. How pleasant / unpleasant do you feel after watching third video (Title: Most Beautiful Building In The World)? [(A) Melancholic - (B) Contented] |
| 80. How pleasant / unpleasant do you feel after watching third video (Title: Most Beautiful Building In The World)? [(A) Despairing - (B) Hopeful] |
| 81. How pleasant / unpleasant do you feel after watching third video (Title: Most Beautiful Building In The World)? [(A) Bored - (B) Relaxed] |
| 82. How pleasant / unpleasant do you feel after watching fourth video (Title: This is Made of...PEE?!)? [(A) Unhappy - (B) Happy] |
| 83. How pleasant / unpleasant do you feel after watching fourth video (Title: This is Made of...PEE?!)? [(A) Annoyed - (B) Pleased] |
| 84. How pleasant / unpleasant do you feel after watching fourth video (Title: This is Made of...PEE?!)? [(A) Unsatisfied - (B) Satisfied] |
| 85. How pleasant / unpleasant do you feel after watching fourth video (Title: This is Made of...PEE?!)? [(A) Melancholic - (B) Contented] |
| 86. How pleasant / unpleasant do you feel after watching fourth video (Title: This is Made of...PEE?!)? [(A) Despairing - (B) Hopeful] |
| 87. How pleasant / unpleasant do you feel after watching fourth video (Title: This is Made of...PEE?!)? [(A) Bored - (B) Relaxed] |
| 88. How pleasant / unpleasant do you feel after watching fifth video (Title: The Most Unexplored Place In The World)? [(A) Unhappy - (B) Happy] |
| 89. How pleasant / unpleasant do you feel after watching fifth video (Title: The Most Unexplored Place In The World)? [(A) Annoyed - (B) Pleased] |
| 90. How pleasant / unpleasant do you feel after watching fifth video (Title: The Most Unexplored Place In The World)? [(A) Unsatisfied - (B) Satisfied] |
| 91. How pleasant / unpleasant do you feel after watching fifth video (Title: The Most Unexplored Place In The World)? [(A) Melancholic - (B) Contented] |
| 92. How pleasant / unpleasant do you feel after watching fifth video (Title: The Most Unexplored Place In The World)? [(A) Despairing - (B) Hopeful] |
| 93. How pleasant / unpleasant do you feel after watching fifth video (Title: The Most Unexplored Place In The World)? [(A) Bored - (B) Relaxed] |
| 94. Reduction of service experience due to pre-roll advertisement |
| 95. What do you think about the reduction of service experience due to mid-roll advertisement |
| 96. What do you think about the reduction of service experience due to post-roll advertisement |
| 97. How do you feel about the annoyance due to pre-roll advertisement |
| 98. How do you feel about the annoyance due to mid-roll advertisement |
| 99. How do you feel about the annoyance due to post-roll advertisement |
| 100. What is your opinion about maximum acceptable advertisement length period |
101. Please reorder from the most annoying to the least:.
|
Appendix C
| ITU-res | FER | Star (ground truth) | Our Prediction |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| 5 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| 5 | 1 | 4 | 5 |
| 5 | 1 | 4 | 5 |
| 5 | 1 | 5 | 4 |
| 5 | 3 | 1 | 3 |
| 5 | 3 | 5 | 4 |
| 5 | 5 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 5 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| 5 | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 2 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 5 | 2 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| 5 | 2 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| 5 | 2 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 5 | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| 5 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 2 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 2 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| 5 | 2 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 2 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| 5 | 2 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 2 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 2 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 2 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 2 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 2 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 5 | 2 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 2 | 5 | 5 |
| 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| 5 | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 |
| 5 | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 5 | 2 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 5 | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| 4 | 2 | 5 | 5 |
| 4 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| 4 | 2 | 4 | 4 |
| 4 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| 4 | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| 5 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| 5 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| 5 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 2 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 2 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 2 | 5 | 5 |
| 4 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| 4 | 2 | 4 | 4 |
| 3 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| 3 | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| 3 | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 2 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| 5 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| 5 | 2 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 2 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 |
| 5 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| 5 | 2 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 2 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 2 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 2 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 2 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 2 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| 5 | 5 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 2 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| 5 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| 5 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| 5 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| 5 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| 4 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| 4 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| 4 | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| 4 | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| 4 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 2 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 2 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 2 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| 3 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 2 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 2 | 4 | 4 |
| 4 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| 4 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| 4 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| 4 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| 4 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| 4 | 2 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| 5 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| 5 | 2 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 5 | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| 4 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| 4 | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| 4 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 2 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 2 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| 5 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| 5 | 2 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 5 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 5 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| 4 | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| 4 | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| 4 | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| 4 | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| 4 | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| 4 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| 4 | 2 | 5 | 5 |
| 4 | 2 | 5 | 5 |
| 4 | 2 | 4 | 4 |
| 4 | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| 4 | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| 4 | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| 4 | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| 4 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| 4 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| 5 | 2 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 |
| 5 | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| 5 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 5 | 2 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| 5 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| 5 | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 5 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| 5 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| 5 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| 5 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
References
- Gutterman, C.; et al. Requet: Real-Time Quantitative Detection for Encrypted YouTube Traffic. In Proceedings of the 10th ACM Multimedia System Conference, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Izima, O.; de Fréin, R.; Malik, A. A survey of machine learning techniques for video quality prediction from quality of delivery metrics. Electronics 2021, 10 (22), 2851. [CrossRef]
- Agboma, F.; Liotta, A. "QoE-Aware QoS Management." Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Advances in Mobile Computing and Multimedia 2008. [CrossRef]
- Streijl, R. C.; Winkler, S.; Hands, D. S. "Mean Opinion Score (MOS) Revisited: Methods and Applications, Limitations and Alternatives." Multimedia Systems 2016, 22 (2), 213-227. [CrossRef]
- Engelke, U.; Darcy, D. P.; Mulliken, G. H.; Bosse, S.; Martini, M. G.; Arndt, S.; Antons, J. N.; Chan, K. Y.; Ramzan, N.; Brunnström, K. "Psychophysiology-Based QoE Assessment: A Survey." IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing 2016, 11 (1), 6-21. [CrossRef]
- Raake, A.; et al. "A Bitstream-Based, Scalable Video-Quality Model for HTTP Adaptive Streaming: ITU-T P. 1203.1." 2017 Ninth International Conference on Quality of Multimedia Experience (QoMEX). IEEE, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.-N.; Dytko, D.; Raake, A. Quality Impact Due to Initial Loading, Stalling, and Video Bitrate in Progressive Download Video Services. 2014 Sixth International Workshop on Quality of Multimedia Experience (QoMEX) 2014, pp. 129–134. [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M. N.; Dytko, D.; Raake, A. "Quality Impact Due to Initial Loading, Stalling, and Video Bitrate in Progressive Download Video Services." 2014 Sixth International Workshop on Quality of Multimedia Experience (QoMEX). IEEE, 2014, 129-134. [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.; Pereira, E. G. "Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP and Progressive Download: Comparative Considerations." 2014 28th International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications Workshops. IEEE, 2014, 905-909. [CrossRef]
- Sackl, A.; Zwickl, P.; Reichl, P. The trouble with choice: An empirical study to investigate the influence of charging strategies and content selection on QoE. Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Network and Service Management (CNSM 2013) 2013, 298–303. [CrossRef]
- Hoßfeld, T.; Seufert, M.; Hirth, M.; Zinner, T.; Tran-Gia, P.; Schatz, R. Quantification of YouTube QoE via crowdsourcing. 2011 IEEE International Symposium on Multimedia 2011, 494–499. [CrossRef]
- Oyman, O.; Singh, S. Quality of experience for HTTP adaptive streaming services. IEEE Communications Magazine 2012, 50 (4), 20–27. [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Kanhere, S. S.; Hossain, I.; Hassan, M. Empirical evaluation of HTTP adaptive streaming under vehicular mobility. International Conference on Research in Networking 2011, 92–105. [CrossRef]
- Ghani, R. F.; Ajrash, A. S. Quality of Experience Metric of Streaming Video: A Survey. Iraqi Journal of Science 2018, 59 (3B), 1531–1537. [CrossRef]
- Porcu, S.; Floris, A.; Atzori, L. Towards the Prediction of the Quality of Experience from Facial Expression and Gaze Direction. 2019 22nd Conference on Innovation in Clouds, Internet and Networks and Workshops (ICIN). IEEE 2019, pp. 82–87. [CrossRef]
- Akhshabi, S.; Anantakrishnan, L.; Begen, A. C.; Dovrolis, C. What happens when adaptive streaming players compete for bandwidth? Proceedings of the 22nd International Workshop on Network and Operating System Support for Digital Audio and Video 2012, 9–14. [CrossRef]
- Zinner, T.; Hossfeld, T.; Minhas, T. N.; Fiedler, M. Controlled vs. uncontrolled degradations of QoE: The provisioning-delivery hysteresis in case of video. EuroITV 2010 Workshop: Quality of Experience for Multimedia Content Sharing 2010.
- Cohen, W. W. Fast Effective Rule Induction. In Machine Learning Proceedings 1995. Elsevier 1995, pp. 115–123. [CrossRef]
- Landis, J. R.; Koch, G. G. An Application of Hierarchical Kappa-Type Statistics in the Assessment of Majority Agreement among Multiple Observers. Biometrics 1977, pp. 363–374. [CrossRef]
- Bermudez, H.-F.; et al. Live Video-Streaming Evaluation Using the ITU-T P. 1203 QoE Model in LTE Networks. Computer Network 2019, 165, 106967. [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lu, Y. Analysis of the Mean Absolute Error (MAE) and the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) in Assessing Rounding Model. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering 2018, 324 (1), 012049. [CrossRef]
- Seshadrinathan, K.; Soundararajan, R.; Bovik, A. C. Study of Subjective and Objective Quality Assessment of Video. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2010, 19 (6), 1427–1441. [CrossRef]
- Amour, L.; Lamine, et al. "An Improved QoE Estimation Method Based on QoS and Affective Computing." 2018 Int. Symp. Program. Syst. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Wu, W.; Yang, Z. "Quality of Experience Evaluation of Voice Communication: An Affect-Based Approach." Hum.-Centric Comput. Inf. Sci. 2012, 2 (1), 1-18. [CrossRef]
- Callet, P.; Möller, S.; Perkis, A. "Qualinet White Paper on Definitions of Quality of Experience (2012)." Eur. Network Qual. Exp. Multimedia Syst. and Serv. 2013.
- Porcu, S.; et al. "Emotional Impact of Video Quality: Self-Assessment and Facial Expression Recognition." 2019 11th Int. Conf. Qual. Multimedia Exp. (QoMEX). 2019. [CrossRef]
- Antons, J.-N.; et al. "Analyzing Speech Quality Perception Using Electroencephalography." IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2012, 6 (6), 721-731. [CrossRef]
- Kroupi, E.; et al. "EEG Correlates During Video Quality Perception." 2014 22nd Eur. Signal Process. Conf. (EUSIPCO). 2014.
- Arndt, S.; et al. "Using Electroencephalography to Analyze Sleepiness Due to Low-Quality Audiovisual Stimuli." Signal Process. Image Commun. 2016, 42, 120-129. [CrossRef]
- Arndt, S.; et al. "Using Eye-Tracking and Correlates of Brain Activity to Predict Quality Scores." 2014 Sixth Int. Workshop Qual. Multimedia Exp. (QoMEX). 2014. [CrossRef]
- Engelke, U.; et al. "Linking Distortion Perception and Visual Saliency in H. 264/AVC Coded Video Containing Packet Loss." Visual Commun. Image Process. 2010, 7744. [CrossRef]
- Rai, Y.; Le Callet, P. "Do Gaze Disruptions Indicate the Perceived Quality of Nonuniformly Coded Natural Scenes?." Electron. Imaging 2017, 14, 104-109. [CrossRef]
- Rai, Y.; Barkowsky, M.; Le Callet, P. "Role of Spatio-Temporal Distortions in the Visual Periphery in Disrupting Natural Attention Deployment." Electron. Imaging 2016, 16, 1-6. [CrossRef]
- Bailenson, J. N.; et al. "Real-time Classification of Evoked Emotions Using Facial Feature Tracking and Physiological Responses." Int. J. Hum.-Comput. Stud. 2008, 66(5), 303-317. [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.; Pereira, E. G. "Dynamic Adaptive Streaming Over HTTP and Progressive Download: Comparative Considerations." 28th International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications Workshops 2014, 905–909. [CrossRef]
- Robitza, W.; Göring, S.; Raake, A.; Lindegren, D.; Heikkilä, G.; Gustafsson, J.; List, P.; Feiten, B.; Wüstenhagen, U.; Garcia, M. N.; et al. "HTTP Adaptive Streaming QoE Estimation with ITU-T Rec. P. 1203: Open Databases and Software." Proceedings of the 9th ACM Multimedia Systems Conference 2018, 466-471. [CrossRef]
- International Telecommunication Union. "Recommendation ITU-T P. 1203.3, Parametric Bitstream-Based Quality Assessment of Progressive Download and Adaptive Audiovisual Streaming Services over Reliable Transport-Quality Integration Module." 2017.
- Raake, A.; Garcia, M. N.; Robitza, W.; List, P.; Göring, S.; Feiten, B. "A Bitstream-Based, Scalable Video-Quality Model for HTTP Adaptive Streaming: ITU-T P. 1203.1." 2017 Ninth International Conference on Quality of Multimedia Experience (QoMEX). IEEE, 2017, 1-6. [CrossRef]
- Bentaleb, A.; Taani, B.; Begen, A. C.; Timmerer, C.; Zimmermann, R. A survey on bitrate adaptation schemes for streaming media over HTTP. IEEE Communications Surveys Tutorials 2018, 21 (1), 562–585. [CrossRef]
- Porcu, S. Estimation of the QoE for Video Streaming Services Based on Facial Expressions and Gaze Direction. 2021.
- Roettgers, J. Don’t touch that dial: How YouTube is bringing adaptive streaming to mobile, TVs. 2013.
- Seufert, M.; Egger, S.; Slanina, M.; Zinner, T.; Hoßfeld, T.; Tran-Gia, P. A survey on quality of experience of HTTP adaptive streaming. IEEE Communications Surveys Tutorials 2014, 17 (1), 469–492. [CrossRef]
- Barman, N.; Martini, M. G. "QoE Modeling for HTTP Adaptive Video Streaming–A Survey and Open Challenges." IEEE Access 2019, 7, 30831–30859. [CrossRef]
- Barakovic´, S.; Skorin-Kapov, L. "Survey of Research on Quality of Experience Modelling for Web Browsing." Quality and User Experience 2017, 2(1), 1–31. [CrossRef]
- Cofano, G.; De Cicco, L.; Zinner, T.; Nguyen-Ngoc, A.; Tran-Gia, P.; Mascolo, S. Design and experimental evaluation of network-assisted strategies for HTTP adaptive streaming. Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Multimedia Systems 2016, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, Z.; Falk, T. H. Audio-Visual Multimedia Quality Assessment: A Comprehensive Survey. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 21 090–21 117. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Liu, Q.; Chen, C. W. "QoE in Video Transmission: A User Experience-Driven Strategy." IEEE Communications Surveys Tutorials 2016, 19 (1), 285-302. [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Yu, L. "A Variance Reduction Framework for Stable Feature Selection." Statistical Analysis and Data Mining: The ASA Data Science Journal 2012, 5(5), 428-445. [CrossRef]
- Strobl, C.; et al. "Conditional Variable Importance for Random Forests." BMC Bioinformatics 2008, 9(1). [CrossRef]
- Altmann, A.; Toloşi, L.; Sander, O.; Lengauer, T. "Permutation Importance: A Corrected Feature Importance Measure." Bioinformatics 2010, 26(10), 1340-1347. [CrossRef]
- Menze, B.; et al. "A Comparison of Random Forest and Its Gini Importance with Standard Chemometric Methods for the Feature Selection and Classification of Spectral Data." BMC Bioinformatics 2009, 10(1). [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Caro, J.-M.; Cano, M.-D. On the Identification and Prediction of Stalling Events to Improve QoE in Video Streaming. Electronics 2021, 10, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
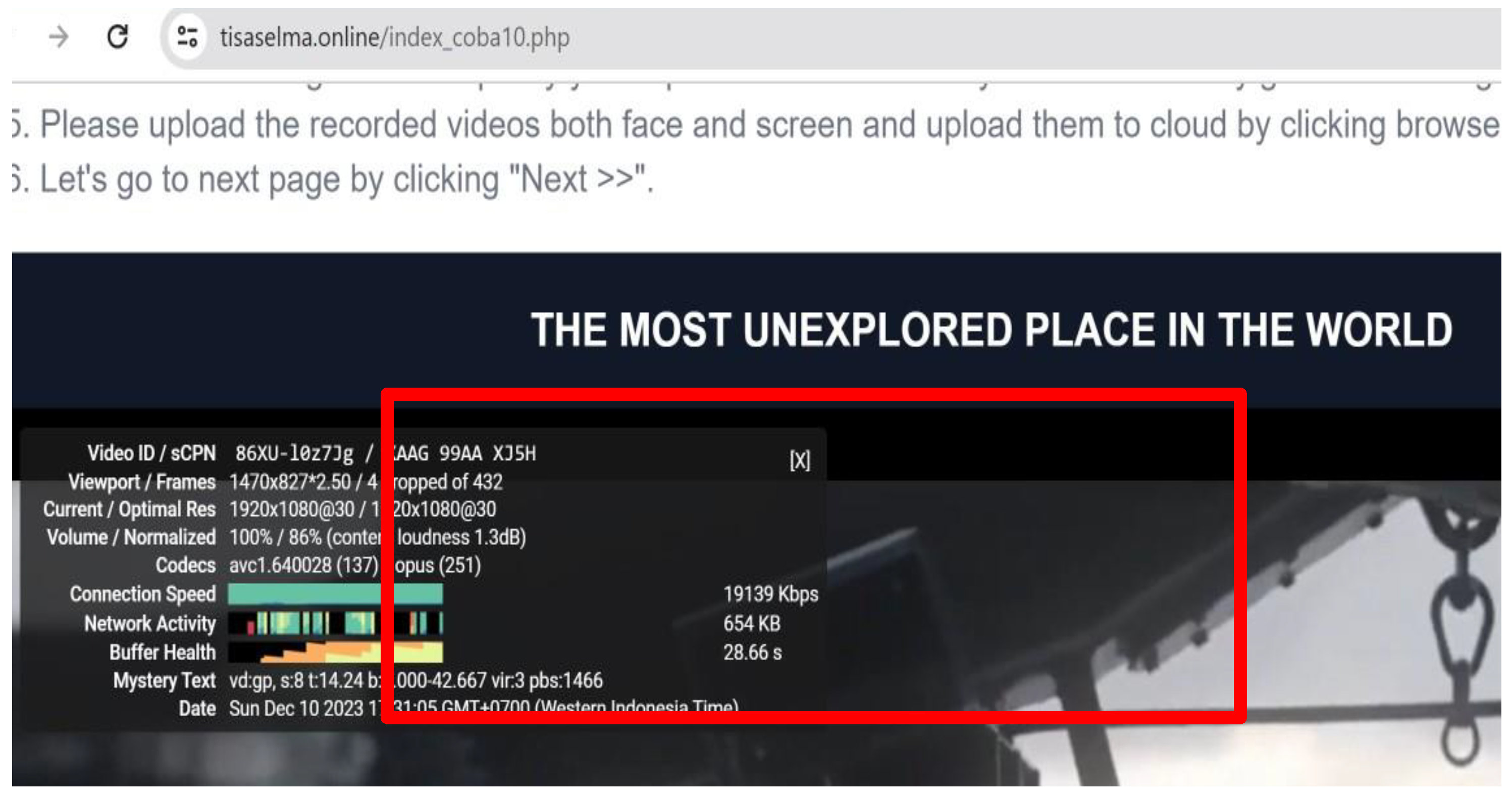
| Content Title | Content Length (s) | Number of Ad | Length of Ad | Position of Ad |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Expo 2020 Dubai | 280 | 1 | 18 | Post-roll |
| Squid game2 | 113 | 1 | 30 | Pre-roll |
| Every death game SG | 375 | 1 | 18 | Mid-roll |
| 5 metaverse | 461 | 3 | 75 | Pre-roll, mid-roll, post-roll |
| Created Light from Trash | 297 | 2 | 45 | Pre-roll |
| How this guy found a stolen car! | 171 | 6 | 288 | Pre-roll, mid-roll, post-roll |
| First underwater farm | 233 | 6 | 198 | Pre-roll, mid-roll, post-roll |
| Most beautiful building in the world | 166 | 6 | 292 | Mid-roll |
| This is made of...pee?! | 78 | 4 | 418 | Pre-roll |
| The most unexplored place in the world | 256 | 5 | 391 | Post-roll |
| Jeda Rodja 1 | 387 | 8 | 279 | Pre-roll |
| Jeda Rodja 2 | 320 | 8 | 440 | Pre-roll, mid-roll, post-roll |
| Jeda Rodja 3 | 415 | 6 | 272 | Pre-roll, mid-roll, post-roll |
| Jeda Rodja 4 | 371 | 6 | 311 | Post-roll |
| Jeda Rodja 5 | 376 | 6 | 311 | Mid-roll |
| Grading Value | Emotion |
|---|---|
| 5 | Happy |
| 4 | Surprised |
| 3 | Neutral |
| 2 | Sad, fear |
| 1 | disgust, anger |
| Resolution | Bitrate | ITU-T P.1203 Results | Video Content Length | Star Review | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1080 | 8000 | 5 | 301 | 1 | |
| 1080 | 8000 | 5 | 301 | 2 | |
| 1080 | 8000 | 5 | 301 | 1 | |
| 1080 | 8000 | 5 | 301 | 4 | |
| 1080 | 8000 | 5 | 301 | 4 | |
| 720 | 5000 | 5 | 301 | 5 | |
| 720 | 5000 | 5 | 303 | 1 | |
| Grade | Estimated Quality | Estimated Emotion |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | Excellent | Happy |
| 4 | Good | Surprise |
| 3 | Fair | Neutral |
| 2 | Poor | Sad |
| 1 | Bad | Disgust, Anger, Fear |
| The Most Annoying Advertisement Type From 122 Participants | ||
|---|---|---|
| Case | Participants | Percentage (%) |
| Many repeated advertisements in 1 point of time in mid-roll | 22 | 18.03% |
| Single 5 minutes advertisement long in mid-roll | 22 | 18.03% |
| In 5 minutes of video content, every 1 minute there is one repeated ad. | 21 | 17.21% |
| The same advertisement is repeated in pre, mid, and post-roll. | 18 | 14.75% |
| There is no skippable advertisement. | 39 | 31.97% |
| Total | 122 | 100% |
| Amount | Types |
|---|---|
| 661 | Total participants from around the world |
| 114 | Countries and cities |
| 125 | Completed questionnaires |
| 30 | Questionnaires completed with video recordings |
| The Maximum Acceptable Advert Length Period | |
|---|---|
| Time | Participants |
| < 10 second | 41.67% |
| 10 – 30 second | 37.5% |
| Title | Res | Bitrate | ITU | FER | Cont. length |
Ad. count | Long. ad | Ad. loc | repeat | 5min. len.ad | Ad.each.min | p/m/p same ad | No skip ad | Star | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stolen_car | 720 | 5000 | 5 | 3 | 459 | 6 | 288 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Underwater_farm | 720 | 5000 | 5 | 3 | 431 | 6 | 198 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| beautiful_building | 720 | 5000 | 5 | 3 | 608 | 6 | 442 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Made_of_pee | 720 | 5000 | 5 | 3 | 496 | 4 | 418 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4 | |
| Unexplored_place | 720 | 5000 | 5 | 3 | 433 | 4 | 177 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4 | |
| ML Method | Tree SPAARC | Random Forest | Tree Optimized Forest | ||||||||
| Test Types | 80:20 | 50 CV | Train Set | 80:20 | 50 CV | Train Set | 80:20 | 50 CV | Train Set | ||
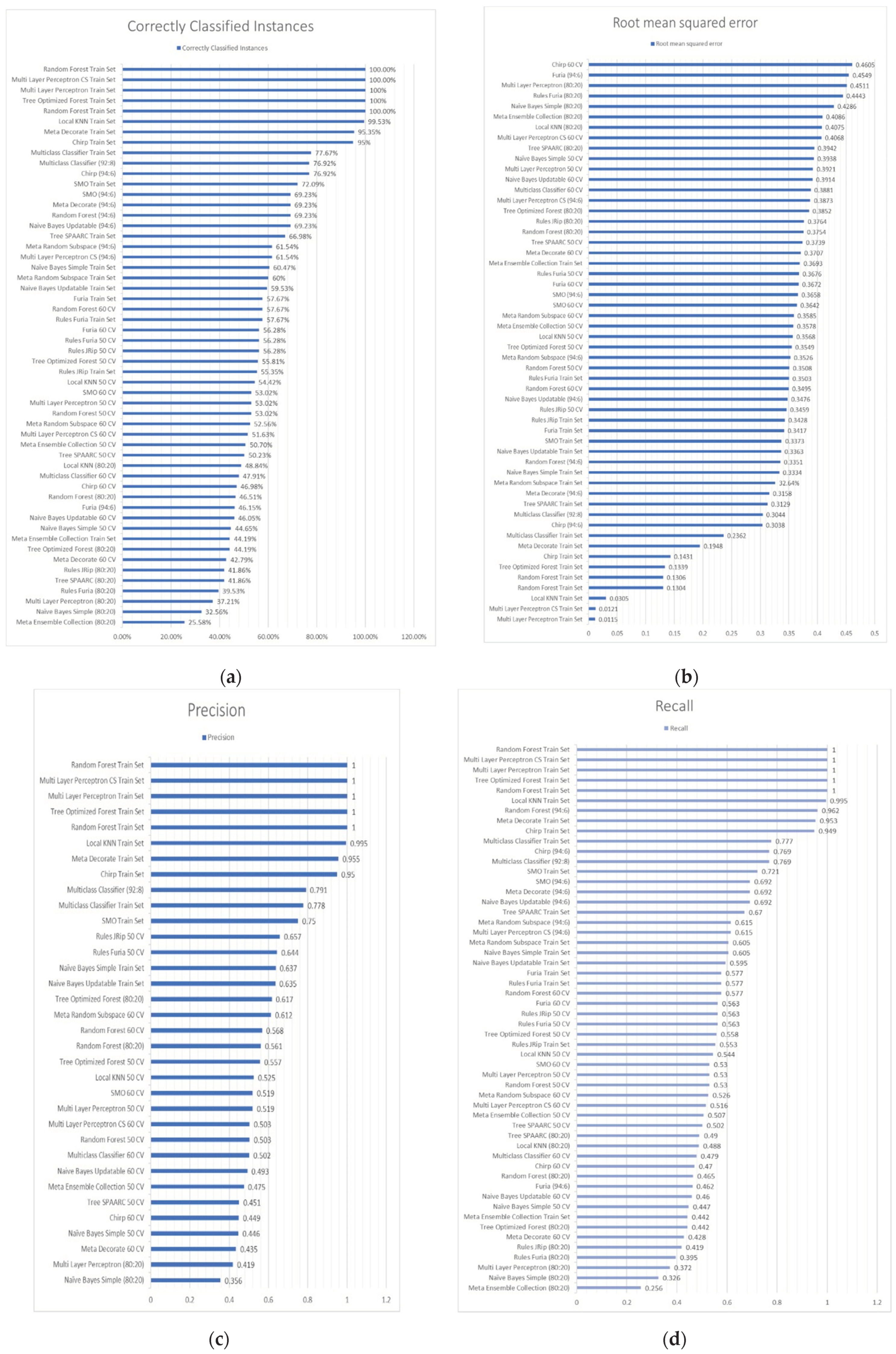
| CCI | 41.86% | 50.23% | 66.98% | 46.51% | 53.02% | 100.00% | 44.19% | 55.81% | 100% | ||
| ICI | 58.14% | 49.77% | 33.02% | 53.49% | 46.98% | 0.00% | 55.81% | 44.19% | 0% | ||
| RMSE | 0.3942 | 0.3739 | 0.3129 | 0.3754 | 0.3508 | 0.1304 | 0.3852 | 0.3549 | 0.1339 | ||
| Total Instances | 43 | 215 | 215 | 43 | 215 | 215 | 43 | 215 | 215 | ||
| Precision | N/A | 0.451 | N/A | 0.561 | 0.503 | 1 | 0.617 | 0.557 | 1 | ||
| Recall | 0.49 | 0.502 | 0.67 | 0.465 | 0.53 | 1 | 0.442 | 0.558 | 1 | ||
| ML Method | Local KNN | Multi Layer Perceptron | Naïve Bayes Simple | ||||||||
| Test Types | 80:20 | 50 CV | Train Set | 80:20 | 50 CV | Train Set | 80:20 | 50 CV | Train Set | ||
| CCI | 48.84% | 54.42% | 99.53% | 37.21% | 53.02% | 100% | 32.56% | 44.65% | 60.47% | ||
| ICI | 51.16% | 45.58% | 0.47% | 62.79% | 46.98% | 0% | 67.44% | 55.35% | 39.53% | ||
| RMSE | 0.4075 | 0.3568 | 0.0305 | 0.4511 | 0.3921 | 0.0115 | 0.4286 | 0.3938 | 0.3334 | ||
| Total Instances | 43 | 215 | 215 | 43 | 215 | 215 | 43 | 215 | 215 | ||
| Precision | N/A | 0.525 | 0.995 | 0.419 | 0.519 | 1 | 0.356 | 0.446 | 0.637 | ||
| Recall | 0.488 | 0.544 | 0.995 | 0.372 | 0.53 | 1 | 0.326 | 0.447 | 0.605 | ||
| ML Method | Meta Ensemble Collection | Rules JRip | Rules Furia | ||||||||
| Test Types | 80:20 | 50 CV | Train Set | 80:20 | 50 CV | Train Set | 80:20 | 50 CV | Train Set | ||
| CCI | 25.58% | 50.70% | 44.19% | 41.86% | 56.28% | 55.35% | 39.53% | 56.28% | 57.67% | ||
| ICI | 74.42% | 49.30% | 55.81% | 58.14% | 43.72% | 44.65% | 60.47% | 43.72% | 42.33% | ||
| RMSE | 0.4086 | 0.3578 | 0.3693 | 0.3764 | 0.3459 | 0.3428 | 0.4443 | 0.3676 | 0.3503 | ||
| Total Instances | 43 | 215 | 215 | 43 | 215 | 215 | 43 | 215 | 215 | ||
| Precision | N/A | 0.475 | N/A | N/A | 0.657 | N/A | N/A | 0.644 | N/A | ||
| Recall | 0.256 | 0.507 | 0.442 | 0.419 | 0.563 | 0.553 | 0.395 | 0.563 | 0.577 | ||
| ML Method | Naive Bayes Updatable | Multi Layer Perceptron CS | Meta Random Subspace | ||||||||
| Test Types | 94:6 | 60 CV | Train Set | 94:6 | 60 CV | Train Set | 94:6 | 60 CV | Train Set | ||
| CCI | 69.23% | 46.05% | 59.53% | 61.54% | 51.63% | 100.00% | 61.54% | 52.56% | 60% | ||
| ICI | 30.77% | 53.95% | 40.47% | 38.46% | 48.37% | 0.00% | 38.46% | 47.44% | 39.53% | ||
| RMSE | 0.3476 | 0.3914 | 0.3363 | 0.3873 | 0.4068 | 0.0121 | 0.3526 | 0.3585 | 32.64% | ||
| Total Instances | 13 | 215 | 215 | 13 | 215 | 215 | 13 | 215 | 215 | ||
| Precision | N/A | 0.493 | 0.635 | N/A | 0.503 | 1 | N/A | 0.612 | N/A | ||
| Recall | 0.692 | 0.46 | 0.595 | 0.615 | 0.516 | 1 | 0.615 | 0.526 | 0.605 | ||
| ML Method | Random Forest | Chirp | Multiclass Classifier | ||||||||
| Test Types | 94:6 | 60 CV | Train Set | 94:6 | 60 CV | Train Set | 92:8 | 60 CV | Train Set | ||
| CCI | 69.23% | 57.67% | 100.00% | 76.92% | 46.98% | 95% | 76.92% | 47.91% | 77.67% | ||
| ICI | 30.77% | 42.33% | 0.00% | 23.08% | 53.02% | 5% | 23.08% | 52.09% | 22.33% | ||
| RMSE | 0.3351 | 0.3495 | 0.1306 | 0.3038 | 0.4605 | 0.1431 | 0.3044 | 0.3881 | 0.2362 | ||
| Total Instances | 13 | 215 | 215 | 13 | 215 | 215 | 13 | 215 | 215 | ||
| Precision | N/A | 0.568 | 1 | N/A | 0.449 | 0.95 | 0.791 | 0.502 | 0.778 | ||
| Recall | 0.962 | 0.577 | 1 | 0.769 | 0.47 | 0.949 | 0.769 | 0.479 | 0.777 | ||
| ML Method | Meta Decorate | SMO | Furia | ||||||||
| Test Types | 94:6 | 60 CV | Train Set | 94:6 | 60 CV | Train Set | 94:6 | 60 CV | Train Set | ||
| CCI | 69.23% | 42.79% | 95.35% | 69.23% | 53.02% | 72.09% | 46.15% | 56.28% | 57.67% | ||
| ICI | 30.77% | 57.21% | 4.65% | 30.77% | 46.98% | 27.91% | 53.85% | 43.72% | 42.33% | ||
| RMSE | 0.3158 | 0.3707 | 0.1948 | 0.3658 | 0.3642 | 0.3373 | 0.4549 | 0.3672 | 0.3417 | ||
| Total Instances | 13 | 215 | 215 | 13 | 215 | 215 | 13 | 215 | 215 | ||
| Precision | N/A | 0.435 | 0.955 | N/A | 0.519 | 0.75 | N/A | N/A | N/A | ||
| Recall | 0.692 | 0.428 | 0.953 | 0.692 | 0.53 | 0.721 | 0.462 | 0.563 | 0.577 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




