1. Introduction
Plastic products entered the market in the 1950s. The production of plastics in Europe reached 58 million tons in 2014. More than 40% of plastic is single-use packaging. It is predicted that the amount of plastic waste will reach 13% by 2060 and will continue to increase. It is estimated that by 2040, about 250 million metric tons of plastic waste will enter the water system and about 460 million metric tons will enter the soil system. It is very difficult to imagine life without plastics, which have become part of our everyday life [
1]. They are used in a lot of applications such as packaging, automotive, aquaculture, fisheries, agriculture, building, furniture, transportation, personal care products, textiles, clothing, etc. [
2]. Important environmental challenges include the necessity to reduce the amount of contaminants in the environment, eliminate and suppress their effects. Plastic pollution in all components of the environment such as water, air, soil, biota and their negative impact on human health is a still misunderstood and researched area [
3,
4]. Plastics are often used materials in various industries due to their low production costs, easy transportation, low weight and high resistance.
The huge consumption of plastics and the associated large amount of plastic waste causes their constant release into the environment, where they can degrade into smaller pieces, microplastics, which are considered contaminants [
5,
6]. Microplastics are a synthetic material that contains a high proportion of polymers [
7].
The constant increase of plastics and their degradation products leads to their presence in the components of the environment, including the food chain [
8,
9]. Pollution by microplastics is a large concern, because they can be transported over long distances and spread into soil, air, water, but they are also found in various foods such as tap water, bottled water, seafood, honey, salt. Air, indoor dust, contaminated food and water were considered the main sources of MP exposure. Recently, information about other possible sources of exposure to MP, such as baby bottles, has been increasingly emerging, while studies of human stool, placenta, fetus provide evidence of exposure to MP in infants and children. However, research in this area is still insufficient [
10,
11].
Microplastics come from multiple sources, interact with different components of the environment and have different routes of transport and transformation. Currently, microplastic pollution is an urgent worldwide problem due to environmental pollution. Statistics show that about 3 million tons of plastic is produced annually, and most of it is waste. Due to the influence of various external factors (UV radiation, weather effects, etc.), plastics degrade into smaller particles, microplastics. Concerning fact that they are highly persistent substances that are not biodegradable and accumulate in various environments, they represent a potential risk to human health. However, it should be kept in mind that microplastics also serve as carriers of heavy metals, persistent organic pollutants that can have toxic effects on the human body [
4,
11].
Scientific studies deal with their presence, distribution and potential effects on the environment and living organisms. Monitoring and understanding the sources and pathways of microplastics are key to developing strategies for their negative impact on the life of organisms on the planet.
2. Characterization of Microplastics
A large amount of plastics, such as cosmetic products, personal care products, clothes, plastic bags, bottles, enters the environment through various routes, for example from households, from hospitals, industrial, from human and agricultural activities. These products gradually degrade in the environment and turn into microplastics whereas it depends on molecular weight, chemical structure, crystallinity, additives, and functional groups. Although, degradation is difficult proccess according to their properties, it is effective in the fight against plastic pollution [
12,
13,
14]. Microplastics (MPs) are usually defined as plastic particles and fibres smaller than 5000 µm. They are small enough to be easily overlooked, but they can have significant environmental and potential health consequences MPs are divided into primary and secondary.
Primary MP in the environment arise from plastic pellets or balls. Primary used for commercial pur poses and created by industrial activity in the production of personal care products, for example shampoos, soaps, toothpaste, hair gel etc. [
15,
16,
17]. They are secondary to the degradation of plastic products by physical, chemical and biological processes.
Secondary MPs arise as a result of the degradation of plastics (packaging, paints from various types of plastic products, fibers from textiles, etc.) by various physical, chemical and biological processes including erosion, corrosion, photooxidation and biological transformation. The most common way of MP formation is photodegradation [
18,
19]. Due to their small size, MPs can be consumed by marine animals, terrestrial organisms and humans, which leads to concerns about their impact on ecosystems and human health.
Concerns about human health are growing, as people are constantly exposed to MP in particular through the animal or plant food chain, through food additives, beverages, plastic packaging for food [
18,
19,
20].
The mechanism of degradation of primary microplastics to secondary ones is still not well known, but both groups have harmful effects on the environment and human health [
21]. About 80% of microplastics in the environment correspond to fibers and fragments. The most common primary microplastics include polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polystyrene (PS), polyester (PE), polyamide (PA), polyacrylonitrile (PAN), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polyphthalamide (PPA), polycarbonate (PC), polyurethane (PU), PLA- polylactic acid and poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) [
3,
13,
14,
22,
23]. Each type of polymer has different properties, and thus, they can be applied in various applications. Microplastics have a different polymer structure on which physical or chemical properties depend [
24]. The most commonly used is PE, which is commonly used in packaging films, garbage and food bags, and many household items for a long time. PET is used for the production of water bottles, and caps is usually from PP. Beverage cartons are usually made from PE, while PS is suitable for disposable food packaging with insulating properties [
20]. According to Directive 2019/904 of the European Parliament and the Council, food and beverage containers made from PS has been restricted since 2021 [
25]. Microplastics are present not only in the environment, but also in households. Various disposable or reusable food containers, bottles, jars, cups, caps and other plastic packaging are often used, which are usually made of PET, PP, PVC, PS. Chemically, microplastics have a polymeric structure and contain 2 main elements, carbon and hydrogen. Some other substances may contain bromide, chlorine and oxygen. Chemical additives are typical for microplastics. Their toxicity is related to the size of microplastics. It is true that the smaller the MP, the more toxic it is.
Exposure of the human body can occur through various routes, such as inhalation, through the skin, or ingestion of contaminated food [
6,
17]. Ingestion of contaminated food most often occurs through the gastrointestinal tract, where dangerous substances such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon – PAH or polychlorinated biphenyl – PCB) [
26]. Some MPs are excreted from the body through stool, in which PET has been proven. Its concentration in infant feces was 10 times higher than in adult samples [
27].
The problem of MP food contamination cannot be solved without taking environmental pollution into account. Accumulation of MP has been detected in seas, oceans, surface and groundwater, soils, arctic snow and antarctic ice, and beaches. They are commonly spread through wastewater treatment plants, from which they can enter natural waters, groundwater, or terrestrial ecosystems [
28,
29,
30].
People are in close contact with plastics and their degradation products, especially microplastics, which have a negative impact on human health due to their complex physical and chemical properties (e.g., polymer, size, shape, charge) [
31]. The vulnerability of children and pregnant women to these exposures must be taken into account.
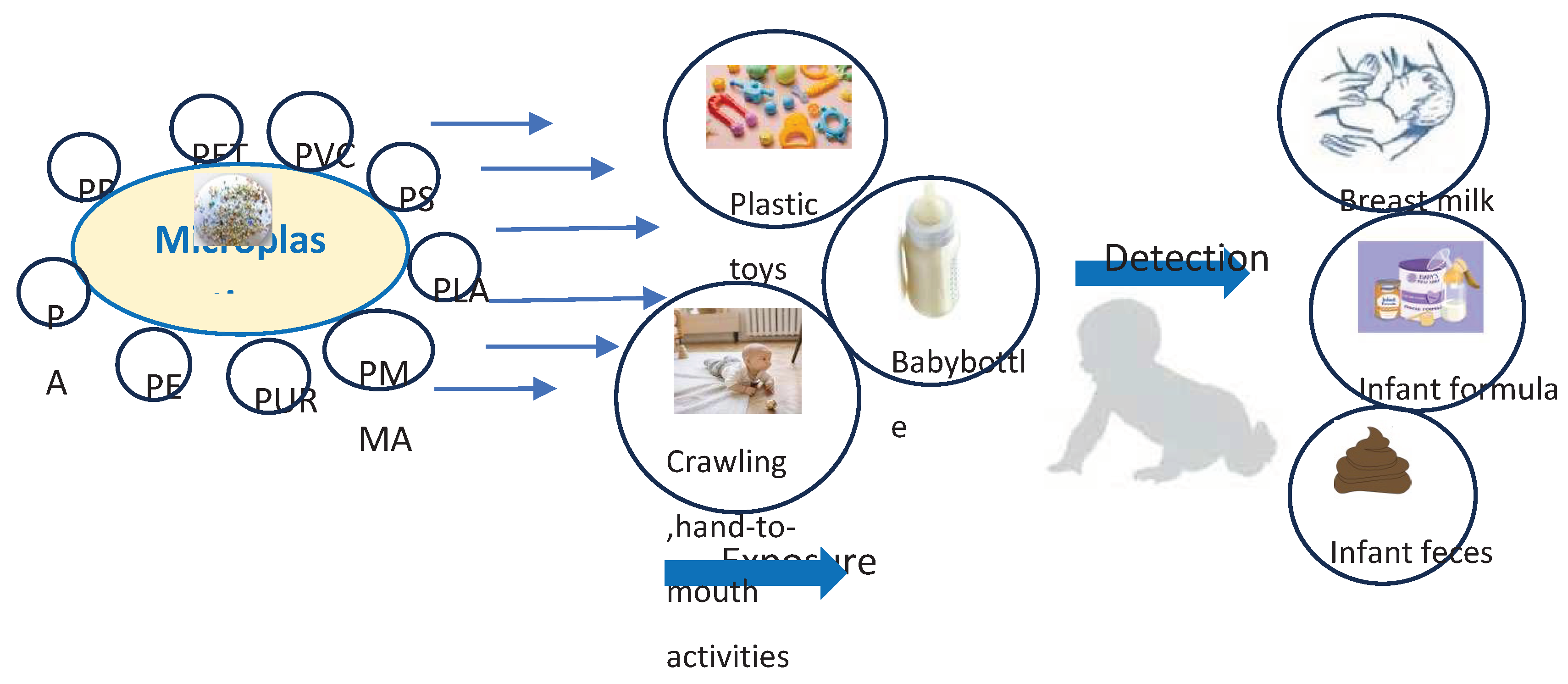
It is very important to monitor the group (fetus, newborns, infants, children) that is very sensitive to exposure to toxic substances, because they do not have sufficiently developed metabolizing enzymes, have a lower ability to remove them, high sensitivity of target organs. who, have highly sensitive target organs and have a lower ability to remove these compounds are particularly sensitive to exposure to toxic substances [
1]. MPs most often enter children's bodies through toys, pacifiers, contaminated food, but also by crawling on carpets and floors made of plastic. Baby bottles are an important source of MP [
32].
3. Analytical Methods for Identification and Quantification of Microplastics
Considering that microplastics represent a great risk, it is necessary to put into practice developed general standard protocols (currently they do not exist) that include collection, characterization and quantification of MPs. Analytical techniques relate mainly to sample collection and preparation, identification and quantification of microplastics. In the research field, there is still a deficit of standardized methods for the extraction of MP from different samples, especially from sediment, air and biological tissues.
Analytical methods for identification and detection of microplastics are described in various studies [
11,
33,
34]. Visual observation using a microscope is the most commonly used method because it does not require complex technique and is based on the observation of particle size, shape, color, surface and transparency. But it appears to be an ineffective method of identification, as the results obtained were often overestimated or underestimated.
Infrared spectroscopy with Fourier transform (FTIR) is the most popular and widespread technique to identify the type of plastic from which the microplast found in the environment. It is very precise, clean and a reliable method in which they can be easily distinguished plastics from natural materials thanks to specific are that show in the spectra. Single clean plastics they have a specific structure and therefore two different pure plastics they do not have the same infrared spectra, which allows them unambiguous identification. FTIR is more sensitive for polar groups [
33,
34].
Raman spectroscopy is together with infrared spectroscopy, the most widely used technique for the characterization of microplastics. It can be analyzed by Raman spectroscopy samples larger than 1 μm and allows tracking very small differences in molecular conformation of polymers, in degree crystallinity with respect to amorphous regions and in tracking stereoregularity of the polymer. Compared to FTIR spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy achieves a better response of non-polar symmetric bonds [
11,
30,
35].
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) is suitable for microplastics identification and it is able to provide clear images of the vital physical properties of the particle. There is also a combination of SEM and X-ray dispersion spectroscopy (SEM-EDS), which is appropriate for determining the content of additives in plastics [
36,
37].
Pyrolysis-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (Pyro-GC-MS) is a method for characterization of microplastics from the point of view of analysis of the degradation products of the given polymer. It consists of thermal degradation up to pyrolysis of the polymer, which takes place in an inert atmosphere and breaks the chemical bonds of the polymer. Molecules with a lower molecular weight are formed, which are further separated by gas chromatography and detected by mass spectrometry [
35,
38,
39]. The sample is fragmented at a temperature between 500 and 1400 °C, in the presence of helium and at low pressure, creating fragments that are introduced into the GC system. No sample pretreatment is required and the amount of sample is within range 5–200 μg.
The methodology makes it possible to simultaneously identify the type of polymer and organic filler. With this method, it is possible to determine the chemical composition of MP using spectral libraries and databases. It provides quantitative results with high accuracy, high sensitivity and selectivity are achieved. A small amount of sample is required and allows analyzing the entire MP particle, not just its surface.
The main disadvantage of this technique is that it is destructive and no information can be obtained about the color, number, size and shape of the particle. It is not possible to analyze more MP simultaneously, the analysis time is extended. Although this technique is highly effective in identifying different types of polymers, it is unable to distinguish between low- and high-density MPs.
NMR spectroscopy provides the data on the chemical structure of the polymer chain of plastics, information on crystallinity, on monomers in copolymer compounds and about branching [
11,
35,
39].
4. Sources of Exposure to Microplastics
Research on plastics is mostly focused on the main sources of exposure, namely water and food, and the transfer of MP to humans through the food chain, but there is little information on direct microplastic exposure to plastic product. Monitoring and understanding the sources and pathways of microplastics are key to developing strategies for their negative impact on the life of organisms on the planet. Microplastics can enter food and drink from a variety of sources, including the environment, food packaging and the manufacturing process. Some studies have shown that microplastics can be present in food that is packed in plastic packaging, or in the production process they can come into contact with plastic materials. Organizations such as the World Health Organization (WHO) [
40] and the European Food Safety Agency (EFSA) [
41] monitor this issue and carry out scientific studies to assess the possible risks associated with the presence of microplastics in food. However, few studies have evaluated exposure to microplastics in infants and pregnant women.
Review article by Kadac-Czapska et al. [
14] deals in detail with current knowledge in the field of microplastics and their impact on human health. It characterizes the routes of exposure, defines the sources of pollution, points out the most frequently occurring microplastics in food and identifies the types of food contaminated with microplastics.
Ragusa et al. [
42] were the first to address the issue of the presence of microplastics in the human placenta. They examined 6 placentas, 4 of which contained 12 microplastics of various shapes. Based on these results in their research, Liu et al. [
43] who tested not only placentas, but also infant feces, meconium, breast milk, and baby formula.
Exposure of fetuses to microplastics through pregnant mothers poses a potential risk to nborn children. Aghaei et al. [
44] investigated the effect of polystyrene microspheres to the fetus and placenta in laboratory mice, with microplastic particles 50 nm-5 μm in size causing growth problems.
Hu et al. [
45] also investigated the effects of exposure to polystyrene microparticles in mice and found that these particles can adversely affect pregnancy by disrupting the immune system.
Studies in animal models have found that nanopolystyrene particles can translocate from the maternal lung across the placenta to the fetus in its kidneys, heart, lungs, liver and brain in late pregnancy [
46,
47,
48]. In addition, using an ex vivo placental perfusion system, nanopolystyrene particles were found to be able to pass from the maternal uterine circulation to the fetal circulation via the placenta [
49]. Recently, several microplastic fragments (5 to 10 μm in size) were found for the first time in 4 human placentas, suggesting that these microplastics can pass into the placental tissue [
50]. Based on these findings, there is growing concern about the potential risks of microplastics to the embryo during pregnancy. However, there is the potential for translocation of microplastics from mother to fetus and storage or accumulation of microplastics in the fetus/embryo.
Infants, children and pregnant women constantly come into contact with plastics. The most studied areas of occurrence of microplastics are primarily air, food and beverages, although exposure in infants can also occur through the placenta and breast milk and materials that come into contact with food. These sources of exposure are still not well studied (
Figure 1).
In addition to the human placenta (49), microplastics have also been detected in children's stool [
51], but the sources of these plastics are relatively difficult to detect. Early exposures can occur through the placenta, during breastfeeding and infant formula, the child breathes dust, licks and chews plastic toys and textiles as well as from baby bottles etc. [
32].
According to review by Calatayud Arroyo et al. [
1] describing the interplay between the microbiota of the mother and the child - xenobiotics - diet during pregnancy and in the perinatal period. Maternal exposure to metals, persistent organic substances, food additives can cause changes in the microbiota of infants, and exposure can also result in modulation of mother-to-child transmission of microorganisms during childbirth and breastfeeding [
10].
A study [
52] focused on the first evidence of microplastics and additives in human amniotic fluid and placenta samples. The identified materials were chlorinated polyethylene and calcium zinc PVC stabilizer. The placenta acted as a partial barrier against the entry of microplastics into the amniotic fluid and the fetus.
Similarly, tea bags are among the sources of exposure to microplastics. During 5 minutes of exposing a tea bag to hot water (95ºC), 11.6 trillion microplastics were released per one cup of tea [
50].
Given the high exposure and to avoid potential adverse effects, it is important to identify the main sources of microplastics to reduce exposure.
4.1. Microplastics in Baby Feeding Bottle
Polypropylene (PP)-based plastic products are often used for food preparation and storage. Such products also include lunch boxes and baby feeding bottles [
53]. Baby feeding bottles and plastic packaging for baby food must be considered as potential sources of MP. In the work [
54] the possible exposure of infants to MP during the contamination of infant formula in PP feeding bottles was investigated. A 21-day test was conducted on infants up to 12 months of age and in 48 regions in the central Amazon. The effects of water temperature, sterilization, and repeated use over a 21-day period on MP release levels were assessed.
Plastics are heat sensitive materials and repeated use under high temperature conditions can accelerate degradation and release MP. During the preparation of infant formula, feeding bottles are exposed to temperatures up to 100°C in accordance with WHO guidelines. To assess the effect of temperature on MP release, we exposed bottles to deionized water at temperatures of 25, 40, 70 and 95°C. The measured values of MP released were in the range of 14.600–4.550.000 particles per capita per day, depending on the region. Sterilization of bottles and exposure to high temperature water during sterilization significantly increased the release of microplastics. As a result of the prevalence of PP products used in the preparation of infant formula, the exposure of infants is higher than expected and therefore it is necessary to assess whether exposure to MP at this level posess a risk to the health of infants [
54].
Microplastics of irregular shapes released from baby bottles can cause increased cytotoxicity. A study by Xu et al. [
55] dealt with the analysis of the thermal-oxidative processes of aging of plastics, as well as the research of what kind of inflammatory response in human intestinal cells (Caco-2) can be induced by these irregular MPs. Exposure of intestinal cells to PP from a baby bottle triggered oxidative stress, which caused a decrease in glutathione levels, increased lipid peroxidation, and release of reactive oxygen species. The levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6 and TNFα), which are markers of the inflammatory process, increased and were even more intense during the disinfection of bottles with boiling water or when using microwave heating.
In a Chinese study [
56] they tested the release of microplastics during the opening/closing process of a baby bottle, finding that 53-393 particles.mL
-1 were released during 100 opening and closing cycles. In addition, they found that the type and brand of bottles, whether plastic or glass, affected the release of microparticles, suggesting that high-quality plastic and glass bottles release fewer microparticles and are more suitable for the health of infants and children.
Considering the results of this study, there is a growing need to focus more intensively on the potential for possible health risks arising from the use of baby bottles with PP content.
4.2. Microplastics in Human Feces
Due to the properties of microplastics, such as their persistence and slow degradation in the environment, their bioavailability for various organisms increases. The presence of microplastics in an organism can cause the growth and reproduction of other organisms and achieve entry into the food chain. Most organisms use the process of excretion in feces to remove indigestible microplastics. A study by Perez-Guevara et al. from 2018 [
51] was the first study to identify microplastics in human feces. Studies that dealt with the extent of contamination of feces with microplastics began to appear more often. Schwabl et al. [
57]. published a study where they assigned microplastics to 9 different types of polymers in human feces. Currently, there is still little knowledge about the consequences of the behavior of microplastics in feces that enter the environment. Research on microplastics in feces continues to grow and it is important to understand the analytical methods available to identify and quantify microplastics.
There are few studies that address the toxic effects of MP on humans, although some studies on laboratory animals have shown adverse health effects [
58,
59]. It is known that humans are exposed to MP, the degree of exposure is poorly understood. Some studies provide a dose range of exposure to MP calculated using controversial empirical models, others report MP intake through various sources and pathways. But research describing the burden of MP on the human body is still lacking. A limitation is also the lack of reliable analytical methods for determining MP in biological matrices. Since particles larger than 150 µm are reported to be excreted in feces, determination of MP in the stool could indicate the degree of burden. The occurrence of MP in the placenta has been proven, but there is no information about the presence of MP in meconium and in the child's stool. A USA study measured PET and PC, which are mainly used in the production of textile fibers, water bottles, mobile phones, in samples of meconium and infant and adult feces [
43]. The depolymerization method followed by LC-MS/MS was used, with PET and PC doses assessed from fece concentrations. A depolymerization method followed by LC-MS/MS was used, with PET and PC doses assessed from fece concentrations. A concentration of 36.000 ng.g
-1 PET and 78 ng.g
-1 PC was detected in feces of six infants. In stool samples from 8 adults, values of 2600 ng.g
-1 for PET and 110 ng.g
-1 of PC were detected in 10 stool samples. The concentration of PET in adults was an order of magnitude lower than in infants, PC were approximately the same. High concentrations of MPs in the infant feces can come from several sources of exposure: use of plastic products, such as baby feeding bottles, tableware, plastic teethers and toys, plastic containers with baby food. A one-year-old child often puts plastic products in his mouth, sucks cloths, crawls on carpeted surfaces [
43].
In the study [
43], there was observed a higher content of MP in infant feces than in adults. The first reason they cited was the possibility of transmission of MP from mother to child. Infants who consumed more than 600 mL of breast milk had higher MP content than those who received a mixed diet. Infants who received a complementary diet (more than 50 g per day) had lower MP content. From which it follows that exposure to MP probably occurs through breast milk. However, there may be more reasons. Some women use a breast pump and store their milk in breast milk storage bags, which can lead to milk contamination. Another source of exposure can be the use of baby bottles. MP contamination was detected in infants who consumed infant formula 5 times a day and in infants who also received breast milk from a bottle. Since MP content was detected in both milk and infant formula, the bottle was probably the potential source of exposure.
4.3. Microplastics in Breast Milk and Infant Formula
Nutrition plays an important role in the first months of a child's life for his physical and cognitive development. According to the WHO, a child should be exclusively breastfed for at least the first 6 months of life, because breast milk is unique, complex, optimal and irreplaceable in its composition. It represents the ideal form of nutrition for a newborn and adapts to its needs. However, if the mother cannot breastfeed, it is necessary to replace breast milk with artificial milk intended for the initial feeding of infants. Although all breast milk substitutes differ from it, it is necessary that these products provide a comparable rate of growth and metabolism observed in exclusively breastfed infants [
32].
For infants with specific health problems, formula must be adapted to eliminate or at least minimize the health problems.
Bisphenol analogues were detected in 62 breastmilk samples and 54 infant formula samples.The median concentration (0.56 ng.g
-1) of bisphenol (BPF) was the highest in infant formula, while in breast milk, there was the median concentration (0.01 ng.mL
-1) of bisphenol S (BPS) the highest [
60].
A study by Liu [
61] investigated the presence of microplastics in 18 mother-infant pairs and assessed exposure in the placenta, meconium, infant feces, breast milk, and infant formula. Infant feces, breast milk, and infant formula samples were collected in the first 6 months of age. More than 74% of microplastics had dimensions of 20-50 μm and PA and PU dominated. In women, the sources of exposure could be cleaning products or toothpaste, while baby bottles and plastic toys could be the sources in infant. The total amount of released PA, PU, PE in infants who also received complementary food > 50 g per day was significantly lower than in infants who did not. An interesting finding was that the way plastic toys were washed affected the amount of PET and PVC in the infants' feces. In addition, higher consumption of breast milk in infants, higher frequency of use of baby bottles caused an increase in the number of released MP particles. The amount of MP in feces was also higher in infants who sucked plastic toys.
Infant formula is packaged in plastic materials, which represent additional sources of MP exposure through dietary intake [
62] or oral activities in infants [
63]. Sealable disposable plastic bags, which are sterile, are often used to store freshly expressed breast milk. The U.S. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend storing the maternal medicine in these bags for 4 hours at room temperature of 25º C or 4 days in the refrigerator (4º C). Given that these products are now often used and come into direct contact with breast milk, more detailed research on the risk of infant exposure is necessary. For the study [
64] 6 most commonly used baby food packaging were selected and the aim was to characterize the size, amount, and composition of microplastic particles released from the products. Large amounts of microparticles (<300 μm) and fragments (1–50 μm) were released, which were identified as polyethylene (PE). PET and nylon-6 using Raman spectroscopy. The amount of released microplastics was in the range of 0.61-0.89 mg.day
-1 due to the average daily intake of breast milk and infants.
Baby food can be contaminated with various substances, such as inorganic and organic substances, drug residues, pesticides and even microplastics. Given that few studies are known on the extent of food contamination with microplastics, there are knowledge gaps that prevent effective action on plastics. In a Mexican study [
64] they found a MP concentration in a milk sample of 6.5 ± 2.3 MPs.L
-1. For example, a study conducted in Mexico found the presence of MP in 23 samples of branded milk with an average 6.5 ± 2.3 particles.L
−1. Evidence on children's exposure to microplastics is quite limited. It is very important to know which products are contaminated and to what extent children are exposed to MP. The most vulnerable period for MP exposure is the first months of a child's life, because immunological, metabolic, cardiovascular and neurobehavioral developmental processes are taking place. Children are more exposed to the environment than adults (crawling, hand-to-mouth activities), eat and drink more per unit of body weight, which again increases exposure to environmental contaminants.
In Polish study [
32], 30 types of infant formula from pharmacies, drugstores and supermarkets were tested. The products were intended for healthy babies as well as for infants with digestive problems. The infant formula samples came from 6 manufacturers. Contamination of infant formula is incompatible with food safety standards, the results of this study point to the presence of MP in infant formula. Daily consumption in infants from birth to 6 months of age was 49 ± 32 MP particles.100 g
-1. They assumed that one of the reasons for the high concentration of plastic particles in products is the type of packaging. The most common polymers identified were polyethylene (63% of packaging) and polypropylene (37% of packaging). Sources to which infants may be exposed are breastfeeding, use of plastic baby bottles, plastic toys and disposable breast milk storage bags. In canned infant formula from the Chinese market, it was detected an order of magnitude less particles (4 ± 3 MPs.100 g
-1) than in products from the Polish market (51 ± 8 MP.100 g
-1).
Compared to the well-studied MP food contamination, the presence of MP in baby food packaging is still not well studied. A study by Liu et al. [
62] reported the release of large amounts of micro and submicron particles, flakes (<300 μm) and fragments (1–50 μm) when using commercially available disposable breast milk storage bags. Among the released particles, PE, PET and nylon-6 predominated, which were identified by Raman spectroscopy. The weight of MP released from the bags was 0.61-0.89 mg.day
-1 with an average intake of breast milk. Infant formula is packaged in plastic material, which can be another source of MP exposure for infants through eating or through food sources.
In a study by Li et al. [
63] it is stated that infant formula prepared in a PP bottle will release up to millions of MP. PET and PC were quantified in the feces of infants, the concentrations of which were significantly higher than in adults [
28,
63]. In infants who consumed complementary food more than 50 g per day, the amount of total MP, PA and PU was significantly lower than in infants who did not receive complementary food. The method of washing plastic toys influenced the amount of released PET and PVC in infant feces The more breast milk the infants drank, the greater the amount of MP was released into the feces. The amount of released MP increases with increasing frequency of drinking milk in feeding bottles. The amount of MP in feces was higher in children who had a habit of sucking plastic toys The study by Liu [
62] was the first study to comprehensively examine MP exposure in pregnant women, fetuses, and infants. The presence of MP in breast milk and infant formula was detected. In children at an early age, exposure to MP occurred through breastfeeding, use of baby bottles and plastic toys. The content of PA was higher in meconium than in placentas. Experimental studies investigating how MPs reach the embryo and fetus are still lacking. The increased content of MP in meconium may be related to the long-term accumulation of MP in meconium, which accumulates in the fetus from the 16th week of pregnancy and is not excreted until delivery [
65]. Apart from the mentioned study, only one other study found MP contamination of breast milk.
Infants' exposure to microplastics, especially PET and PC, in their daily diet is higher than that of adults. Children are more susceptible and come into contact with various plastic objects, such as plastic feeding bottles, toys, plastic dishes, etc. However, there is still a lack of information on neonatal exposure. Estimates so far are based on general food intake assumptions but do not take into account exposure in children with specific requirements. For infants who cannot be breastfed, the main component of the diet is powdered milk, which is packed in special packaging. However, there is no research to determine if powdered milk contains microplastics. Contamination with microplastics in milk powder does not only come from the milk powder, but can also be released from the baby bottle and when the milk powder is brewing. In addition, they are commonly found in the air and from clothing. Few studies have correctly understood the need to consider all sources of exposure that may contaminate milk powder. The authors Zhang et al. [
63] in their work focused on a comprehensive study of potential sources of contamination of powdered infant milk: namely, whether it comes from the packaging, from powdered milk, from the baby bottle or from the preparation of the milk itself. They studied 13 different types of powdered milk with different packaging, milk preparation and milk sources. There were more microplastics in the milk in the box than in the can. They assumed that the main source is the inner packaging of the box, which consists of three layers: the outer special cardboard, the middle aluminum foil and the inner PE layer. The exposure from powdered milk itself was low, from baby bottles it was 6.8 times higher and the exposure from milk preparation was 1.7 times higher.
5. Conclusions
The production of plastics was originally aimed at simplifying and improving human life, whether in industry, agriculture or home. However, over the course of decades, this production got out of control and we started to face unwanted consequences in the form of microplastics. These microparticles, created by the degradation of plastics, have spread to all areas of the environment, with a negative impact on human health and the overall ecosystem. Our review, based on scientific studies, clarified the extent of the presence of microplastics in various aspects of life, including breast milk, baby bottles, toys and milk forms. Based on these findings, it is necessary to carry out further research and systematically monitor the sources of microplastics. Only in this way will we be able to create the foundations for the development of effective strategies and minimize the negative impact of these microparticles on the environment and human health.
Author Contributions
All authors have contributed to this review equally. Conceptualization, C.M., M.V. and Z.S.; methodology, C.M., M.V. and Z.S.; software, C.M., M.V. and Z.S..; validation, C.M., M.V. and Z.S..; formal analysis, C.M., M.V. and Z.S.; investigation, C.M., M.V. and Z.S..; resources, C.M., M.V. and Z.S..; data curation, C.M., M.V. and Z.S..; writing—original draft preparation, C.M., M.V. and Z.S..; writing—review and editing, C.M., M.V. and Z.S.; visualization, C.M., M.V. and Z.S..; supervision, C.M., M.V. and Z.S.; project administration, C.M., M.V. and Z.S..; funding acquisition, C.M., M.V. and Z.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by projects of Slovak internal grant (SVG) number 06/2021; 07/2021 and 08/2021 of the Slovak Medical University in Bratislava.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Calatayud Arroyo, M.; García Barrera, T.; Callejon Leblic, B.; Arias Borrego, A.; Collado, M.C. A review of the impact of xenobiotics from dietary sources on infanthealth: Early life exposures and the role of the microbiota. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 269, 115994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, P.K.; Jain, M.; Kataria, N.; Sahoo, P.K.; Garg, V.K.; Yadav, A. Microplastics in multimedia environment: A systematic review on its fate, transport, quantification, health risk, and remedial measures. Groundwater Sustainable Development 2023, 20, 100889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, K.D.; Covernton, G.A.; Davies, H.L.; Dower, J.F.; Juanes, F.; Dudas, S.E. Human Consumption of Microplastics. Environ Sci Technol 2019, 53, 7068–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, L.; Xiong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Ch.; Xu, X.; Sun, Ch.; Shi, H. Global transportation of plastics and microplastics: A critical review of pathways and influences. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wo´zniak-Budych, M.; Staszak, K.; Wieszczycka, K.; Bajek, A.; Staszak, M.; Roszkowski, S.; Giamberini, M.; Tylkowski, B. Microplastic label in microencapsulation field – Consequence of shell material selection. J. Hazard. Materials 2024, 465, 133000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Chen, H.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, B. Microplastic pollution in soils and groundwater: Characteristics, analytical methods and impacts. Chem. Engin. J. 2021, 425, 131870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, E.B.; Sankhla, M.S.; Bhat, R.A.; Bhagat, D.S. Microplastics from food packaging: An overview of human consumption, health threats, and alternative solutions. Environ. Nanotech. Monit. Manag. 2021, 16, 100608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, P.K.; Jain, M.; Kataria, N.; Sahoo, P.K.; Garg, V.K.; Yadav, A. Microplastics in multimedia environment: A systematic review on its fate, transport, quantification, health risk, and remedial measures. Groundwater Sustainable Development 2023, 20, 100889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cverenkárová, K.; Valachovičová, M.; Mackul’ak, T.; Žemlička, L.; Bírošová, L. Microplastics in the Food Chain. Life 2021, 11, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, K.; Vimalkumar, K. A Review of Human Exposure to Microplastics and Insights Into Microplastics as Obesogens. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 724989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Tran, T.; Jalil, A.A.; Nguyen, T.M.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; Duyen, W.D.; Nguyen, T.C. A review on the occurrence, analytical methods, and impact of microplastics in the environment. Environm. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 102, 104248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Jeong, S. Approach to an answer to “How dangerous microplastics are to the human body”: A systematic review of the quantification of MPs and simultaneously exposed chemicals. J. Hazard. Materials 2023, 460, 132404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridhar, A.; Kannan, D.; Kapoor, A.; Prabhakar, S. Extraction and detection methods of microplastics in food and marine systems: A critical review. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadac-Czapska, K.; Knez, E.; Grembecka, M. Food and human safety: The impact of Microplastics. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutrition 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sewwandi, M.; Wijesekara, H.; Rajapaksha, A.U.; Soysa, S.; Vithanage, M. Microplastics and plastics-associated contaminants in food and beverages; Global trends, concentrations, and human exposure. Environ Pollution 2023, 317, 120747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.; Choi, D.; Han, S.; Yong Jung, S.; Choi, J.; Hong, J. Potential toxicity of polystyrene microplastic particles. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olewnik-Kruszkowska, E.; Nowaczyk, J.; Kadac, K. Effect of ozone exposure on thermal and structural properties of polylactide based composites. Polymer Testing 2016, 56, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periyasamy, A.P.; Tehrani-Bagha, A. A review on microplastic emission from textile materials and its reduction techniques. Polymer Degr. Stab. 2022, 199, 109901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ma, J.B.; Wong, M.H.; Owen, R.B.; Chow, K.L. Environmental health impacts of microplastics exposure on structural organization levels in the human body. Sc.i Total Environ. 2022, 825, 154025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadac-Czapska, K.; Knez, E.; Gierszewska, M.; Olewnik-Kruszkowska, E.; Grembecka, M. Microplastics Derived from Food Packaging Waste—Their Origin and Health Risks. Materials 2023, 16, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vethaak, A.D.; Legler, J. Microplastics and human health. Science 2021, 371, 672–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wua, P.; Huang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; He, F.; Chen, H.; Quan, G.; Yan, J.; Li, T.; Gao, B. Environmental occurrences, fate, and impacts of microplastics. Ecotoxicol.Environ. Safety 2019, 184, 109612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grafmueller, S.; Manser, P.; Diener, L.; Diener, P.-A.; Maeder-Althaus, X.; Maurizi, L.; Jochum, W.; Krug, H.F.; Buerki-Thurnherr, T.; von Mandach, U.; Wick, P. Bidirectional transfer study of polystyrene nanoparticles across the placental barrier in an ex vivo human placental perfusion model. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 1280–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhib, I.; Uddin, K.; Rahman, M.; Malafaia, G. Occurrence of microplastics in tap and bottled water, and food packaging: A narrative review on current knowledge. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 865, 161274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union. Directive (EU) 2019/904 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 5 June 2019 on the Reduction of theImpact of Certain Plastic Products on the Environment. Off. J. Eur. Union 2019, 155, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, A.; Upadhyay, V.; Kumar, S. A critical insight into occurrence and fate of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and their green remediation approaches. Chemosphere 2023, 329, 138579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Trasande, L.; Kannan, K. Occurrence of Polyethylene Terephthalate and Polycarbonate Microplastics in Infant and Adult Feces. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2021, 8, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurier, H.S.; Goddard, J.M. Biodegradation of microplastics in food and agriculture. Curr. Opin+ion Food Sci. 2021, 37, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- YuYusuf, A.; Sodiq, A.; Giwa, A.; Eke, J.; Pikuda, O.; Eniola, J.O.; Ajiwokewu, B; Sambudi, N.S.; Bilad, M.R. Updated review on microplastics in water, their occurrence, detection, measurement, environmental pollution, and the need for regulatory standards. Environ. Pollution 2022, 292, 118421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schymanski, D.; Goldbeck, Ch.; Humpf, H.-U.; Fürst, P. Analysis of microplastics in water by micro-Raman spectroscopy: Release of plastic particles from different packaging into mineral water. Water Res. 2018, 129, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sripada, K.; Wierzbicka, A.; Abass, K.; Grimalt, J.O.; Erbe, A.; Röllin, H.B.; Weihe, P.; Jiménez Díaz, G.; Singh, R.R.; Visnes, T.; Rautio, A.; Odland, J.Q.; Wagner, M. A. Children’s Health Perspective on Nano- and Microplastics. Environ. Health Persp. 2022, 130, 015001–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadac-Czapska, K.; Jutrzenka Trzebiatowska, P.; Mazurkiewicz, M.; Kowalczyk, P.; Knez, E.; Behrendt, M.; Mahlik, S.; Zaleska-Medynska, A.; Grembecka, M. Isolation and identification of microplastics in infant formulas – A potential health risk for children. Food Chem. 2024, 138246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; Wang, X.; Niu, X.; Zeng, J.; Zhou, Y.; Suona, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, X. Overview of analytical methods for the determination of microplastics: Current status and trends. Trends Anal.Chem. 2023, 167, 117261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shruti, V.C.; Perez-Guevara, F.; Elizalde-Martínez, I.; Kutralam-Muniasamy, G. Toward a unified framework for investigating micro(nano)plastics in packaged beverages intended for human consumption. Environ. Poll. 2021, 268, 115811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Gómez, B.; Elmore, J.S.; Valverde, S.; . Ares, A.M.; Bernal, J. Recent applications of chromatography for determining microplastics and related compounds (bisphenols and phthalate esters) in food. Microchem J. 2024, 197, 109903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Min, J.; Jiang, W.; Li, W.; Zhang, W. Separation, characterization and identification of microplastics and nanoplastics in the environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 721, 137561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellasamy, G.; Ramasundaram, S.; Veerapandian, M.; Chandran, M.; Dhanasekaran, B.; Oh, T.H.; Govindaraju, S.; Yun, K. Systematic review on fate and behavior of microplastics towards the environment. Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 169, 117390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa, J.P.; Avellan, A.; Mouneyrac, C.; Duarte, A.; Rocha-Santos, T. Plastic additives and microplastics as emerging contaminants:Mechanisms and analytical assessment. Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 258, 116898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Skrzypek, G.; Ortega-Zamora, O.; González-Sálamoa, J.; Hernández-Sánchez, C.; Hernández-Borges, J. The current role of chromatography in microplastic research: Plastics chemical characterization and sorption of contaminants. J. Chromatogr. Open 2021, 1, 100001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization: Healthy Diet. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/healthy-diet.
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition, and Allergies. Scientific opinion on dietary reference values for water. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1459. [Google Scholar]
- Ragusa, A.; Svelato, A.; Santacroce, C.; Catalano, P.; Notarstefano, V.; Carnevali, O.; Papa, F.; Rongioletti, M.C.A.; Baiocco, F.; Draghi, S.; D’Amore, E.; Rinaldo, D.; Matta, M.; Giorgini, E. Plasticenta: First evidence of microplastics in human placenta. Environ. Inter. 2021, 146, 106274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Guo, J.; Liu, X.; Yang, R.; Wang, H.; Sun, Y.; Chen, Bo.; Dong, R. Detection of various microplastics in placentas, meconium, infant feces, breastmilk and infant formula: A pilot prospective study. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 854, 158699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghaei, Z.; Sled, J.G.; Kingdom, J.C.; Baschat, A.A.; Helm, P.A.; Jobst, K.J.; Cahill, L.S. Maternal exposure to polystyrene micro- and nanoplastics causes fetal growth restriction in mice. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2022, 9, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Qin, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zeng, W.; Lin, Y.; Liu, X. Polystyrene microplastics disturb maternal-fetal immune balance and cause reproductive toxicity in pregnant mice. Reprod. Toxicol. 2021, 106, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, P.; Malek, A.; Manser, P.; Meili, D.; Maeder-Althaus, X.; Diener, L.; Diener, P.-A.; Zisch, A.; Krug, H.F.; von Mandach, U. Barrier capacity of human placenta for nanosized materials. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, S.B.; D’Errico, J.N.; Adler, D.S.; Kollontzi, S.; Goedken, M.J.; Fabris, L.; Yurkow, E.J.; Stapleton, P.A. Nanopolystyrene translocation and fetal deposition after acute lung exposure during late-stage pregnancy. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, B.; Baek, J.Y.; Koo, J.; park, S.; Ryu, Y.-K.; Kim, K.-S.; Zhang, S.; Chung, Ch.; Dogan, R.; Choi, H.-S.; Um, D.; Kim, T.-K.; Lee, W.S.; Jeong, J.; Shin, W.-H.; Lee, J.-. Ran, kim, N.-S.; Lee, D.Y. Maternal exposure to polystyrene nanoplastics causes brain abnormalities in progeny. J. Hazard Mater. 2022, 426, 127815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D'Errico, J.N.; Fournier, S.B.; Stapleton, P.A. Ex vivo perfusion of the rodent placenta. J. Vis. Exp. 2019, 147. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez, L.M.; Xu, E.G.; Larsson, H.C.E.; Tahara, R.; Maisuria, V.B.; Tufenkji, N. Plastic Teabags Release Billions of Microparticles and Nanoparticles into Tea. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 12300–12310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- P´erez-Guevara, F.; Kutralam-Muniasamy, G.; Shruti, V. Critical review on microplastics in fecal matter: Research progress, analytical methods and future outlook. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halfar, J.; Čabanová, K.; Vávra, K.; Delongová, P.; Motyka, O.; Špaček, R.; Kukutschová, J.; Šimetka, O.; Hevianková, S. Microplastics and additives in patients with preterm birth: The first evidence of their presence in both human amniotic fluid and placenta. Chemosphere 2023, 343, 140301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Yang, L.; Kavanagh, R.; Xiao, L.; Shi, Y.; Kehoe, D.K.; Gun’ko, Y.K.; Boland, J.J.; Wang, J.J. Sampling, Identification and Characterization of Microplastics Release from Polypropylene Baby Feeding Bottle during Daily Use. J. Vis. Exp. 2021, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Shi, Y.; Yang, L.; Xiao, L.; Kehoe, D.K.; Gun’ko, Y.K.; Boland, J.J.; Wang, J.J. Microplastic release from the degradation of polypropylene feeding bottles during infant formula preparation. Nature Food 2020, 1, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Shen, J.; Lin, L.; Chen, J.; Wang, L.; Deng, X.; Wu, X.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, R.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Ch. Exposure to irregular microplastic shed from baby bottles activates the ROS/NLRP3/Caspase-1 signaling pathway, causing intestinal inflammation. Environ. Intern. 2023, 181, 108296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, K.; Ding, R.; Sun, C.; Yao, L.; Zhang, W. Microparticles and microplastics released from daily use of plastic feeding and water bottles and plastic injectors: Potential risks to infants and children in China. Environ. Sci. Pollution Res. 2021, 28, 59813–59820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwabl, P.; Köppel, S.; Königshofer, P.; Bucsics, T.; Trauner, M.; Reiberger, T.; Liebmann, B. Detection of Various Microplastics in Human Stool: A Prospective Case Series. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 171, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, R.; Bonilla, M. M.; Yang, X.; Ren, H.; Lemos, B. Evidence that microplastics aggravate the toxicity of organophosphorus flame retardants in mice (Mus musculus). J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 357, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y. F.; Chen, C. Y.; Lu, T. H.; Liao, C. M. Toxicity-based toxicokinetic/toxicodynamic assessment for bioaccumulation of polystyrene microplastics in mice. 2019, 366, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, D.; Li, X.; Xu, J.; Ma, J.; Xiao, Q.; Fu, J.; Guo, Z.; Zhu, J.; Ji, J.; Lu, S. Bisphenol analogues in infant foods in south China and implications for infant exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 910, 168509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Guo, L.; Liu, X.; Yang, R.; Wang, H.; Sun, Y.; Chen, B.; Dong, R. Detection of various microplastics in placentas, meconium, infant feces, breastmilk and infant formula: A pilot prospective study. Sci.Total Environ. 2023, 854, 158699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Jia, P.; He, S.; Dai, H.; Deng, S.; Han, J. Release of microplastics from breastmilk storage bags and assessment of intake by infants: A preliminary study. Environ Pollution 2023, 323, 121197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Trasande, L.; Kannan, K. Occurrence of Polyethylene Terephthalate and Polycarbonate Microplastics in Infant and Adult Feces. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2021, 8, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutralam-Muniasamy, G.; Pérez-Guevara, F.; Elizalde-Martínez, I.; Shruti, C. Branded milks – Are they immune from microplastics contamination? Sci.Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marie, C.; Vendittelli, F.; Sauvant-Rochat, M.-P. Obstetrical outcomes and biomarkers to assess exposure to phthalates: A review. Environ. Int. 2015, 83, 116–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).