Submitted:
31 January 2024
Posted:
31 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
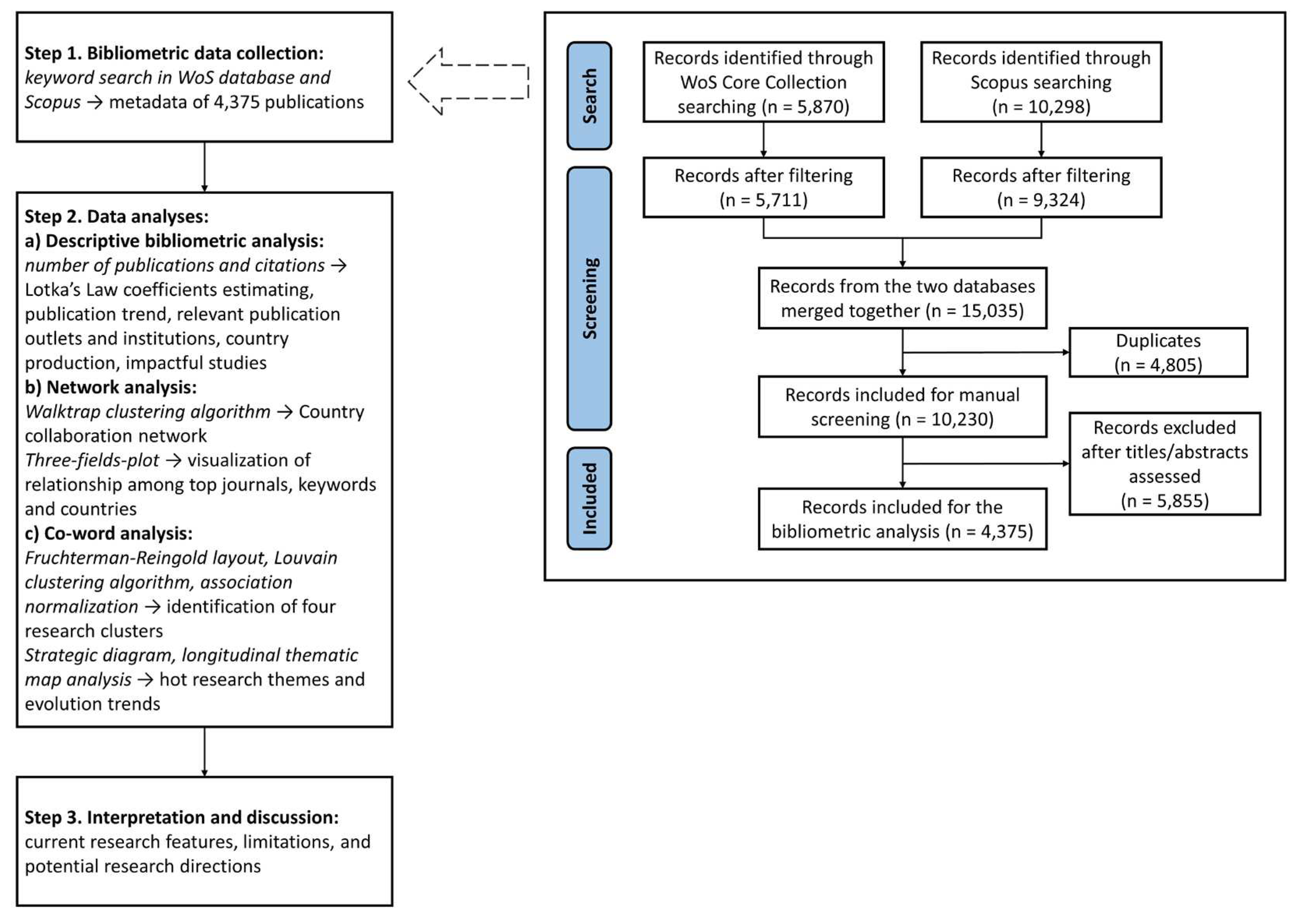
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Screening Strategy
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Standalone Research Domain
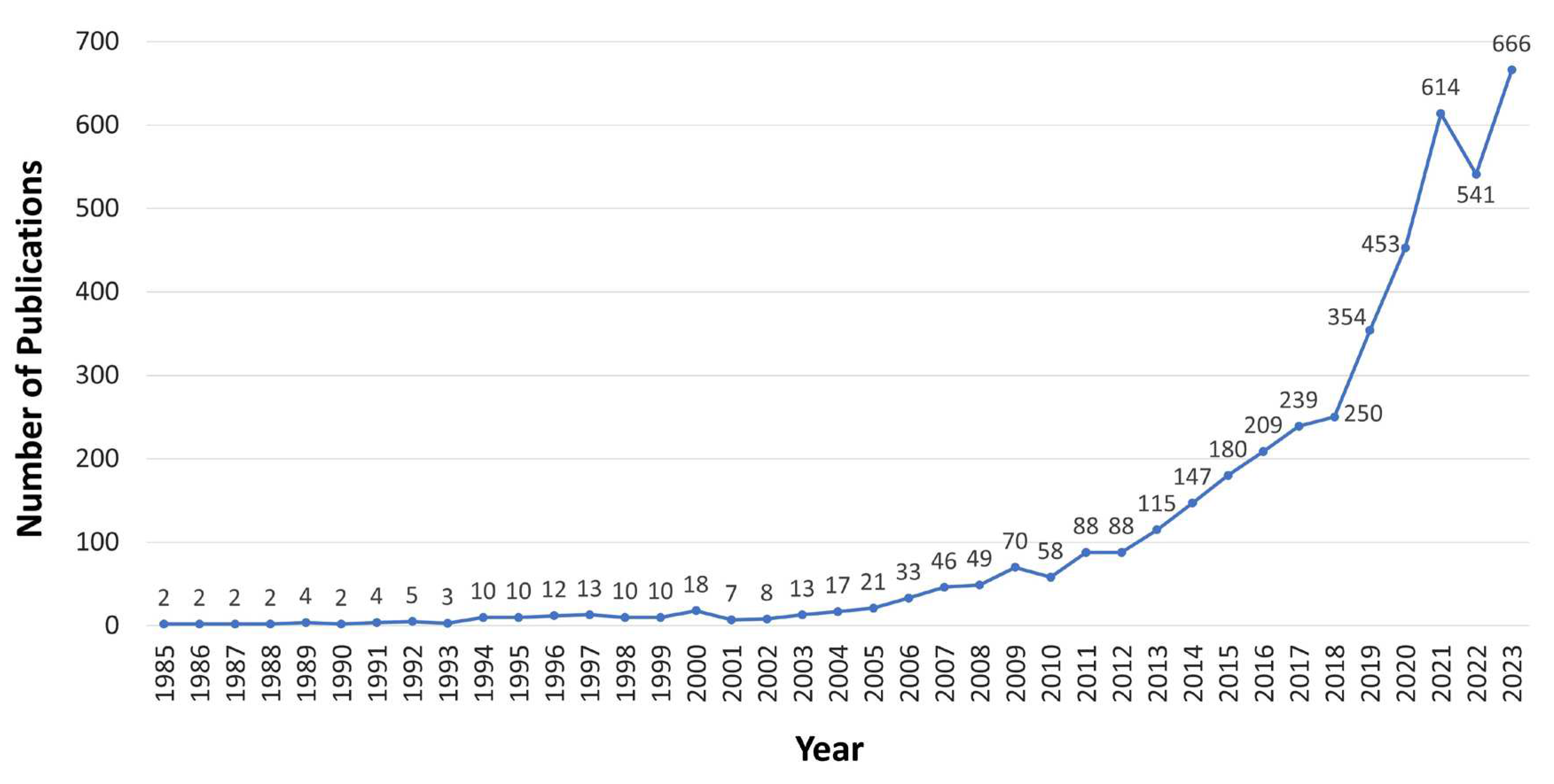
3.2. Publication Trend
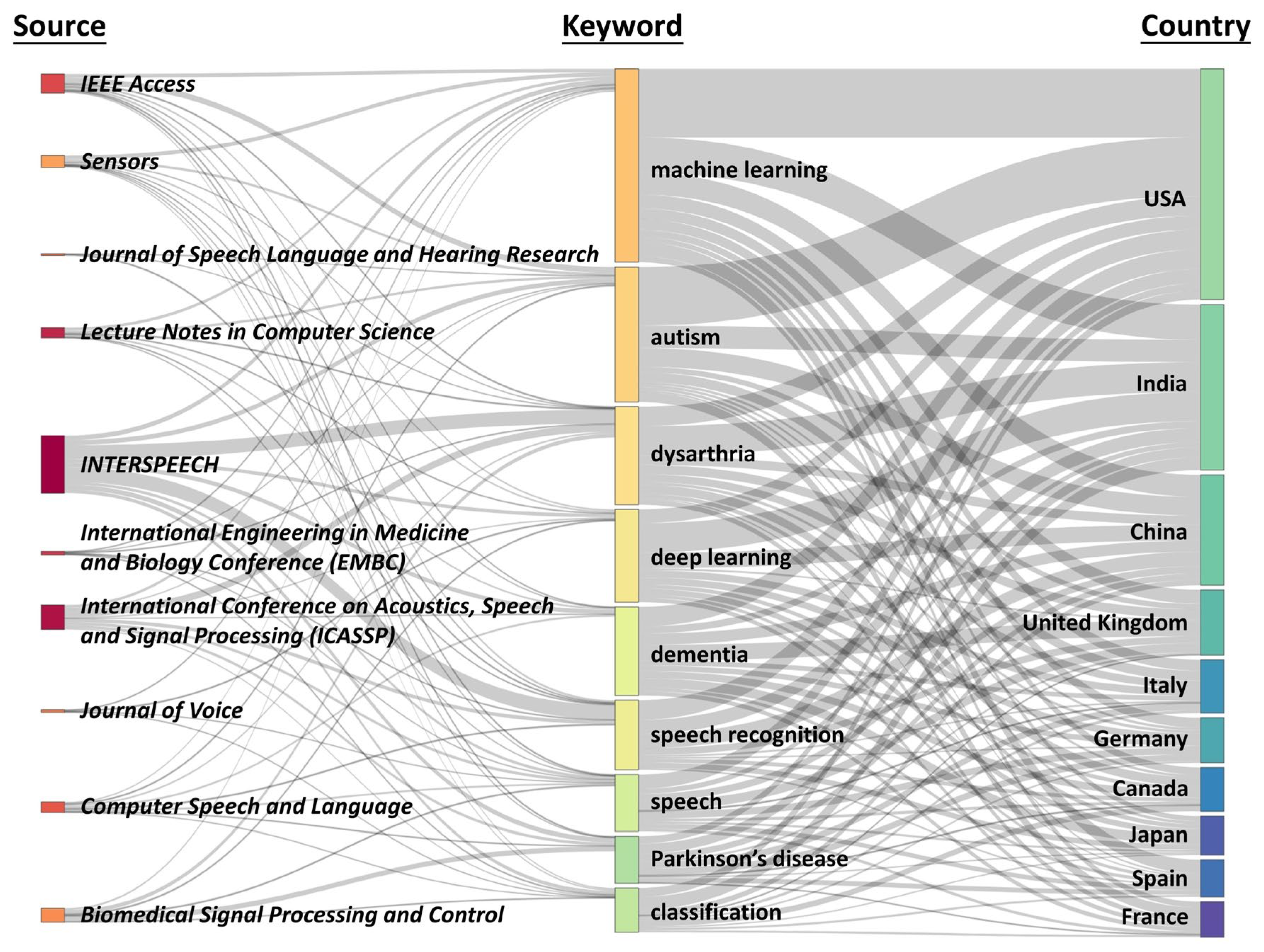
3.3. Publication Patterns
3.4. Characteristics of Research Activities
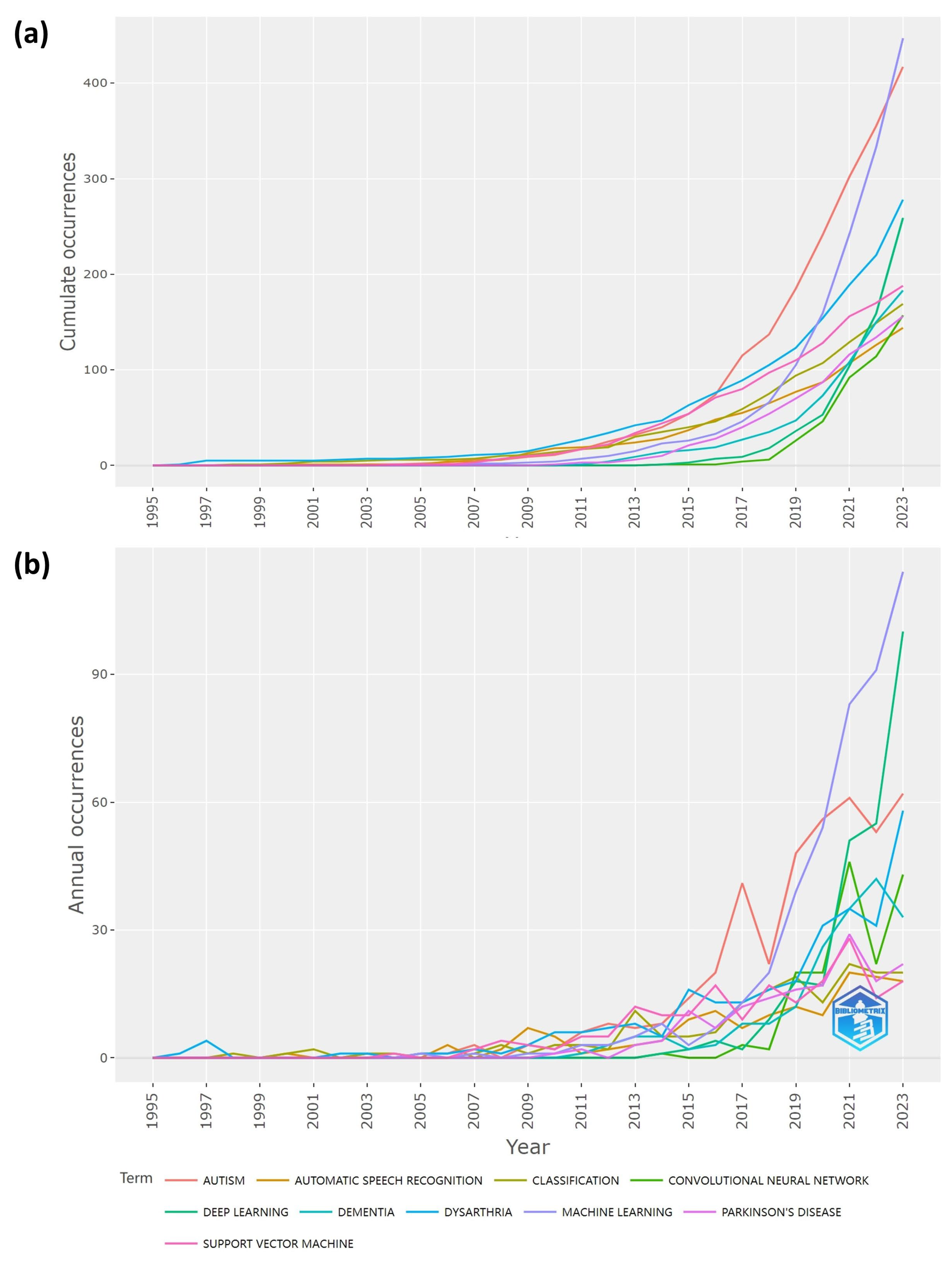
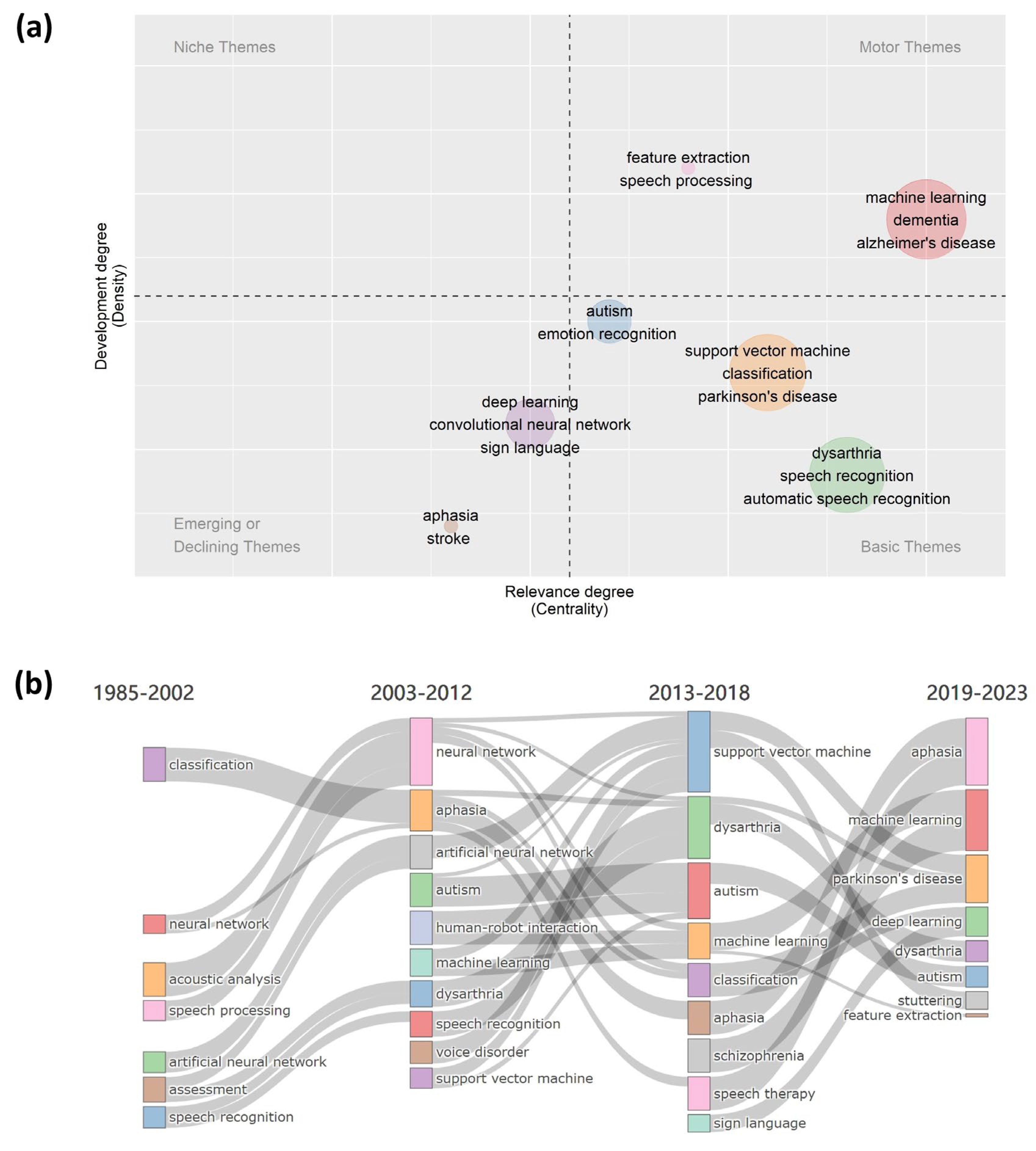
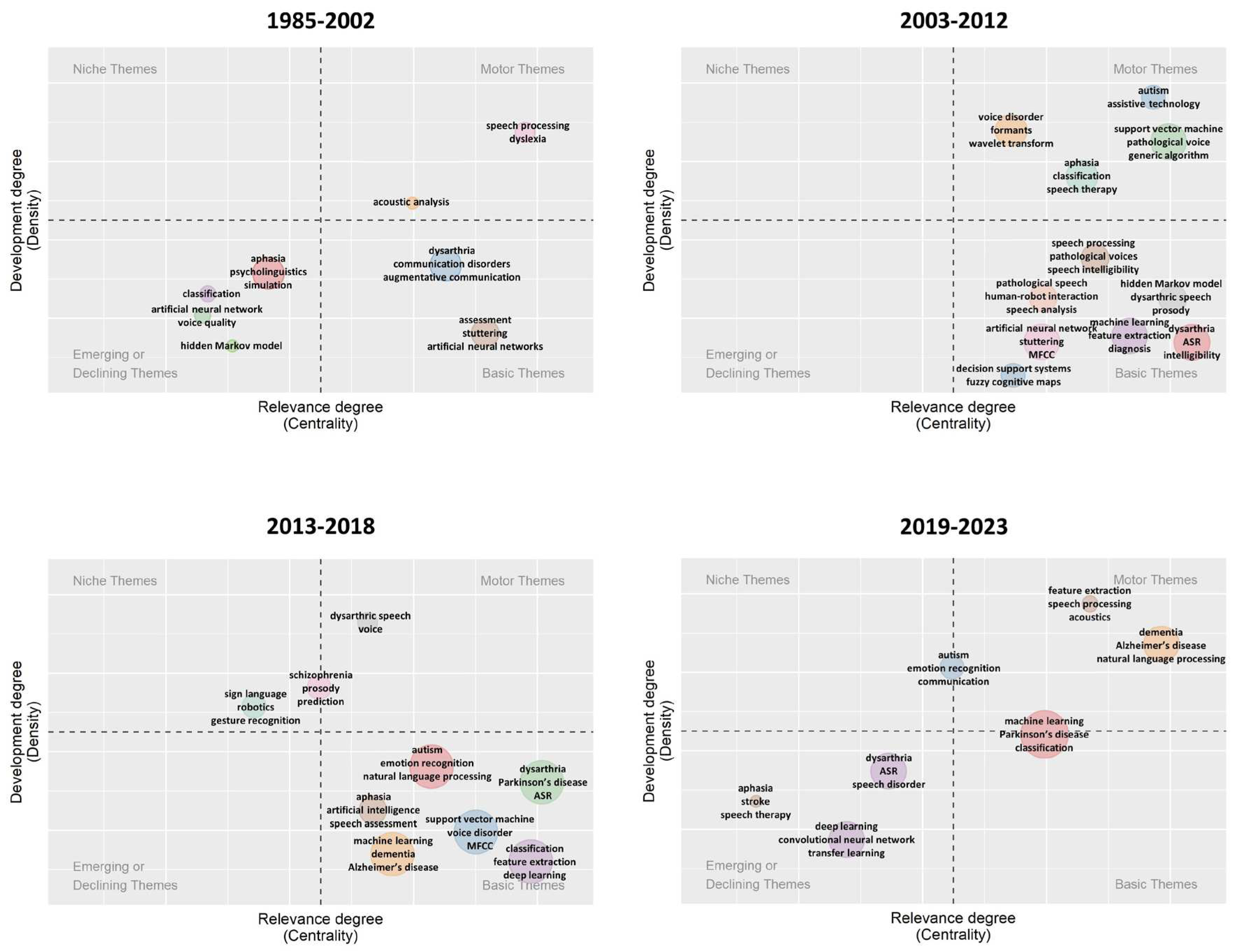
3.5. Research Hotspot Tendencies
4. Discussion
4.1. Main Findings of Bibliometric Analysis
4.2. Benefits of AI in the HCD Field
4.3. Challenges and Future Developments
4.4. Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, Y.; Hao, Z.; Zhao, S.; Gong, J.; Yang, F. Artificial Intelligence in Health Care: Bibliometric Analysis. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e18228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kermany, D.S.; Goldbaum, M.; Cai, W.; Valentim, C.C.; Liang, H.; Baxter, S.L.; McKeown, A.; Yang, G.; Wu, X.; Yan, F.; et al. Identifying Medical Diagnoses and Treatable Diseases by Image-Based Deep Learning. Cell 2018, 172, 1122–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, H.; Tan, G. Data Mining Applications in Healthcare. J. Healthc. Inf. Manag. 2005, 19, 64–72. [Google Scholar]
- Wimmer, H.; Yoon, V.Y.; Sugumaran, V. A Multi-Agent System to Support Evidence Based Medicine and Clinical Decision Making Via Data Sharing and Data Privacy. Decision Support Systems 2016, 88, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, A.; Kambhampati, C.; Monson, J.; Drew, P. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 2004, 86, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, L. Communication Disorders: A Complex Population in Healthcare. Language and Health 2023, 1, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeThorne, L.S.; Hengst, J.; Hamilton, M.B. Communication Disorders. In Encyclopedia of Mental Health; 2016; Volume 1, pp. 324–329. [Google Scholar]
- Cummings, L. The Cambridge Handbook of Communication Disorders; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Owens, R.E., Jr.; Farinella, K.A.; Metz, D.E. Introduction to Communication Disorders: A Lifespan Evidence-Based Perspective. Pearson Higher Ed, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cummings, L. Chapter One: The Study of Communication Disorders. In Communication Disorders; Palgrave Macmillan: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Robb, M.P. Intro: A Guide to Communication Sciences and Disorders; Plural publishing: San Diego, CA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Maier, A.; Haderlein, T.; Eysholdt, U.; Rosanowski, F.; Batliner, A.; Schuster, M.; Nöth, E. Peaks – a System for the Automatic Evaluation of Voice and Speech Disorders. Speech Commun. 2009, 51, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beccaluva, E.A.; Catania, F.; Arosio, F.; Garzotto, F. Predicting Developmental Language Disorders Using Artificial Intelligence and a Speech Data Analysis Tool. Human–Computer Interaction 2024, 39, 8–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevitz, J.S.; Kiefer, B.R.; Huber, J.E.; Troche, M.S. Obtaining Objective Clinical Measures During Telehealth Evaluations of Dysarthria. Am. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 2021, 30, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togher, L. Challenges Inherent in Optimizing Speech-Language Pathology Outcomes: It's Not Just About Counting the Hours. International Journal of Speech-Language Pathology 2012, 14, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, S.S.; Fang, Q.; Alsulami, M.; Kumar, A. Application of Machine Learning Algorithms to Disordered Speech. In Blockchain and Deep Learning: Future Trends and Enabling Technologies; Ahmed, K.R., Hexmoor, H., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 159–178. [Google Scholar]
- Squires, K. Addressing the Shortage of Speech-Language Pathologists in School Settings. Journal of the American Academy of Special Education Professionals 2013, 131, 137. [Google Scholar]
- O’Brien, R.; Byrne, N.; Mitchell, R.; Ferguson, A. Rural Speech-Language Pathologists’ Perceptions of Working with Allied Health Assistants. International Journal of Speech-Language Pathology 2013, 15, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairweather, G.C.; Lincoln, M.A.; Ramsden, R. Speech-Language Pathology Teletherapy in Rural and Remote Educational Settings: Decreasing Service Inequities. International Journal of Speech-Language Pathology 2016, 18, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, S.S.; Kumar, A.; Tang, Y.; Li, Y.; Gu, X.; Fu, J.; Fang, Q. An Efficient Deep Learning Based Method for Speech Assessment of Mandarin-Speaking Aphasic Patients. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics 2020, 24, 3191–3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakin, B.; Bal, E. Language Disorders and Artificial Intelligence. In Theory and Research in Health Sciences; 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Girardi, A.M.; Cardell, E.A.; Bird, S.P. Artificial Intelligence in the Interpretation of Videofluoroscopic Swallow Studies: Implications and Advances for Speech and Language Pathologists. Big Data and Cognitive Computing 2023, 7, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, N.; Kehayia, E.; Jarema, G.; Le Dorze, G.; Beaujard, C.; Yvon, M. How Artificial Intelligence (AI) Is Used in Aphasia Rehabilitation: A Scoping Review. Aphasiology 2024, 38, 305–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deka, C.; Shrivastava, A.; Nautiyal, S.; Chauhan, P. Human-Centered AI Goals For speech Therapy Tools; da Silva, H.P., Cipresso, P., Eds.; Computer-Human Interaction Research and Applications; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 121–136. [Google Scholar]
- Pierce, J.E. AI-Generated Images for Speech Pathology—an Exploratory Application to Aphasia Assessment and Intervention Materials. Am. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 2024, 33, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Zhang, M.; Li, J. Research on the Application of Artificial Intelligence in the Rehabilitation Training of Children with Speech Disorders. Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Computer Engineering and Networks; Liu, Q., Liu, X., Cheng, J., Shen, T., Tian, Y., Eds.; Springer Nature Singapore: Singapore, 2022; pp. 1463–1469. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Xie, H.; Wang, F.L.; Yan, J.; Hao, T. Trends and Features of Human Brain Research Using Artificial Intelligence Techniques: A Bibliometric Approach; Zeng, A., Pan, D., Hao, T., Zhang, D., Shi, Y., Song, X., Eds.; Human Brain and Artificial Intelligence; Springer Singapore: Singapore, 2019; pp. 69–83. [Google Scholar]
- Vitevitch, M.S. Speech, Language, and Hearing in the 21st Century: A Bibliometric Review of JSLHR from 2001 to 2021. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2023, 66, 3428–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreps, G.L.; Neuhauser, L. Artificial Intelligence and Immediacy: Designing Health Communication to Personally Engage Consumers and Providers. Patient. Educ. Couns. 2013, 92, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, B.; Hong, S.; Yuan, J.; Peng, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X. Global Trends in Sediment-Related Research in Earth Science During 1992–2011: A Bibliometric Analysis. Scientometrics 2013, 98, 511–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aria, M.; Cuccurullo, C. Bibliometrix: An R-Tool for Comprehensive Science Mapping Analysis. Journal of Informetrics 2017, 11, 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munim, Z.H.; Dushenko, M.; Jimenez, V.J.; Shakil, M.H.; Imset, M. Big Data and Artificial Intelligence in the Maritime Industry: A Bibliometric Review and Future Research Directions. Maritime Policy & Management 2020, 47, 577–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, A.; Kargina, M. A User-Friendly Method to Merge Scopus and Web of Science Data During Bibliometric Analysis. Journal of Marketing Analytics 2022, 10, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrt, T.; Bishop, J.; Carlin, J.B. Bias, Prevalence and Kappa. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 1993, 46, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The Measurement of Observer Agreement for Categorical Data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotka, A.J. The Frequency Distribution of Scientific Productivity. Journal of the Washington Academy of Sciences 1926, 16, 317–323. [Google Scholar]
- Pons, P.; Latapy, M. Computing Communities in Large Networks Using Random Walks. In Computer and Information Sciences - ISCIS 2005; Yolum, p., Güngör, T., Gürgen, F., Özturan, C., Eds.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2005; pp. 284–293. [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker, J. Creativity and Conformity in Science: Titles, Keywords and Co-Word Analysis. Social Studies of Science 1989, 19, 473–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruchterman, M.J.; Reingold, M. Graph Drawing by Force-Directed Placement. Software - Practice and Experience 1991, 21, 1129–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondel, V.D.; Guillaume, J.-L.; Lambiotte, R.; Lefebvre, E. Fast Unfolding of Communities in Large Networks. Journal of Statistical Mechanics: Theory and Experiment 2008, 2008, P10008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. How to Normalize Cooccurrence Data? An Analysis of Some Well-Known Similarity Measures. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology 2009, 60, 1635–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobo, M.J.; López-Herrera, A.G.; Herrera-Viedma, E.; Herrera, F. An Approach for Detecting, Quantifying, and Visualizing the Evolution of a Research Field: A Practical Application to the Fuzzy Sets Theory Field. Journal of Informetrics 2011, 5, 146–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, A.E.; Thomsen, C. Sustainable Development: The Role of Network Communication. Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management 2011, 18, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q. Knowledge Discovery through Co-Word Analysis. Library Trends 1999, 48, 133–159. [Google Scholar]
- Callon, M.; Courtial, J.P.; Laville, F. Co-Word Analysis as a Tool for Describing the Network of Interactions between Basic and Technological Research: The Case of Polymer Chemistry. Scientometrics 1991, 22, 155–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viedma-del-jesús, F.M.M.I.; López-herrera, J.S.A.G. An Application of Co-Word Analysis and Bibliometric Maps for Detecting the Most Highlighting Themes in the Consumer Behaviour Research from a Longitudinal Perspective. Quality & Quantity 2012, 46, 1077–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Goncalves, J.; Kostakos, V.; Xiao, B. Fragmentation or Cohesion? Visualizing the Process and Consequences of Information System Diversity, 1993–2012. European Journal of Information Systems 2016, 25, 509–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pao, M.L. An Empirical Examination of Lotka’s Law. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology 1986, 37, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, K.C.; Meltzer, J.A.; Rudzicz, F. Linguistic Features Identify Alzheimer's Disease in Narrative Speech. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease 2016, 49, 407–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.-Q.; Tian, H.; Liu, Y.; Ju, Z.-Y.; Pang, Y.; Chen, Y.-Q.; Wang, D.-Y.; Tian, X.-G.; Yan, J.-C.; Deng, N.-Q.; et al. An Intelligent Artificial Throat with Sound-Sensing Ability Based on Laser Induced Graphene. Nature Communications 2017, 8, 14579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luz, S.; Haider, F.; Fuente, S.d.l.; Fromm, D.; MacWhinney, B. Alzheimer’s Dementia Recognition through Spontaneous Speech: The ADReSS Challenge; 2020; pp. 2172–2176. [Google Scholar]
- Vieira, S.; Pinaya, W.H.L.; Mechelli, A. Using Deep Learning to Investigate the Neuroimaging Correlates of Psychiatric and Neurological Disorders: Methods and Applications. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 74, 58–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsanas, A.; Little, M.A.; McSharry, P.E.; Spielman, J.; Ramig, L.O. Novel Speech Signal Processing Algorithms for High-Accuracy Classification of Parkinson's Disease. IEEE Transactions on Bio-medical Engineering 2012, 59, 1264–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardo, M.V.; Lai, M.C.; Baron-Cohen, S. Big Data Approaches to Decomposing Heterogeneity across the Autism Spectrum. Molecular Psychiatry 2019, 24, 1435–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosztolya, G.; Vincze, V.; Tóth, L.; Pákáski, M.; Kálmán, J.; Hoffmann, I. Identifying Mild Cognitive Impairment and Mild Alzheimer's Disease Based on Spontaneous Speech Using ASR and Linguistic Features. Computer Speech & Language 2019, 53, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedi, G.; Carrillo, F.; Cecchi, G.A.; Slezak, D.F.; Sigman, M.; Mota, N.B.; Ribeiro, S.; Javitt, D.C.; Copelli, M.; Corcoran, C.M. Automated Analysis of Free Speech Predicts Psychosis Onset in High-Risk Youths. NPJ Schizophrenia 2015, 1, 15030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, F.; Barker, J.; Yue, Z.; Christensen, H. Source Domain Data Selection for Improved Transfer Learning Targeting Dysarthric Speech Recognition. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020 - 2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP); pp. 7424–7428.
- Sakar, B.E.; Isenkul, M.E.; Sakar, C.O.; Sertbas, A.; Gurgen, F.; Delil, S.; Apaydin, H.; Kursun, O. Collection and Analysis of a Parkinson Speech Dataset with Multiple Types of Sound Recordings. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics 2013, 17, 828–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dautenhahn, K. Socially Intelligent Robots: Dimensions of Human-Robot Interaction. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2007, 362, 679–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.H.; Tsao, Y.; Hsiao, M.J.; Chen, J.Y.; Lai, Y.H.; Lin, F.C.; Wang, C.T. Detection of Pathological Voice Using Cepstrum Vectors: A Deep Learning Approach. J. Voice 2019, 33, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, S.; Shetty, S.; Rai, S.; Dodderi, T. A Survey on Machine Learning Approaches for Automatic Detection of Voice Disorders. J. Voice 2019, 33, 947.e911–947.e933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, M.A.; McSharry, P.E.; Roberts, S.J.; Costello, D.A.E.; Moroz, I.M. Exploiting Nonlinear Recurrence and Fractal Scaling Properties for Voice Disorder Detection. BioMedical Engineering OnLine 2007, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, M.S.S.; Syed, Z.S.; Lech, M.; Pirogova, E. Automated Screening for Alzheimer’s Dementia through Spontaneous Speech; 2020; pp. 2222–2226. [Google Scholar]
- Didehbani, N.; Allen, T.; Kandalaft, M.; Krawczyk, D.; Chapman, S. Virtual Reality Social Cognition Training for Children with High Functioning Autism. Computers in Human Behavior 2016, 62, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, D.M.; Bentley, K.H.; Ghosh, S.S. Automated Assessment of Psychiatric Disorders Using Speech: A Systematic Review. Laryngoscope Investigative Otolaryngology 2020, 5, 96–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lascialfari, M.; Magrini, M.B.; Cabanac, G. Unpacking Research Lock-in through a Diachronic Analysis of Topic Cluster Trajectories in Scholarly Publications. Scientometrics 2022, 127, 6165–6189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topol, E.J. High-Performance Medicine: The Convergence of Human and Artificial Intelligence. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohr, A.; Memarzadeh, K. The Rise of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare Applications. Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare 2020, 25–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaky, E. Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD); the Past, the Present, and the Future. J. Child. Adolesc. Behav. 2017, 5, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Zhang, Y. Speech Prosody in Mental Disorders. Annu. Rev. Linguist. 2023, 9, 335–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porayska-Pomsta, K.; Alcorn, A.M.; Avramides, K.; Beale, S.; Bernardini, S.; Foster, M.E.; Frauenberger, C.; Good, J.; Guldberg, K.; Keay-Bright, W.; et al. Blending Human and Artificial Intelligence to Support Autistic Children’s Social Communication Skills. ACM Trans. Comput.-Hum. Interact. 2018, 25, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari, M.; Chen, L.; Fombonne, E. Quantifying Voice Characteristics for Detecting Autism. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sennott, S.C.; Akagi, L.; Lee, M.; Rhodes, A. AAC and Artificial Intelligence (AI). Top. Lang. Disord. 2019, 39, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barua, P.D.; Vicnesh, J.; Gururajan, R.; Oh, S.L.; Palmer, E.; Azizan, M.M.; Kadri, N.A.; Acharya, U.R. Artificial Intelligence Enabled Personalised Assistive Tools to Enhance Education of Children with Neurodevelopmental Disorders: A Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2022, 19, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leinweber, J.; Alber, B.; Barthel, M.; Whillier, A.S.; Wittmar, S.; Borgetto, B.; Starke, A. Technology Use in Speech and Language Therapy: Digital Participation Succeeds through Acceptance and Use of Technology. Frontiers in Communication 2023, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucirkova, N.I.; Zuckerman, B. Generative AI for Children's Digital Health: Clinician Advice. Journal of Developmental & Behavioral Pediatrics 2022, 45, e86–e87. [Google Scholar]
- Fazana, F.; Alsadoon, A.; Prasad, P.W.C.; Costadopoulos, N.; Elchouemi, A.; Sreedharan, S. Integration of Assistive and Wearable Technology to Improve Communication, Social Interaction and Health Monitoring for Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Region 10 Symposium (TENSYMP); pp. 1–5.
- Ramkumar, N.; Renuka, D.K. An Analysis on Augmentative and Assistive Technology for the Speech Disorder People. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Intelligent Systems for Communication; IoT and Security (ICISCoIS). pp. 601–607.
- Cappadona, I.; Ielo, A.; La Fauci, M.; Tresoldi, M.; Settimo, C.; De Cola, M.C.; Muratore, R.; De Domenico, C.; Di Cara, M.; Corallo, F.; et al. Feasibility and Effectiveness of Speech Intervention Implemented with a Virtual Reality System in Children with Developmental Language Disorders: A Pilot Randomized Control Trial. Children 2023, 10, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherson, S.; Tripp, R.; Goudelias, D.; Johnson, A.M. Rapid Implementation of Teletherapy for Voice Disorders: Challenges and Opportunities for Speech-Language Pathologists. J. Voice 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utepbayeva, A.; Zhiyenbayeva, N.; Assylbekova, L.; Tapalova, O. Artificial Intelligence in the Diagnosis of Speech Disorders in Preschool and Primary School Children. World Journal on Educational Technology: Current Issues 2022, 14, 1698–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egaji, O.A.; Asghar, I.; Griffiths, M.; Warren, W. Digital Speech Therapy for the Aphasia Patients: Challenges, Opportunities and Solutions. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Information Communication and Management; 2019; pp. 85–88. [Google Scholar]
- Juhn, Y.; Liu, H. Artificial Intelligence Approaches Using Natural Language Processing to Advance Ehr-Based Clinical Research. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2020, 145, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, S.D.; Zeng, F.-G.; Clark, J. Adopting Change and Incorporating Technological Advancements in Audiology Education, Research, and Clinical Practice. American Journal of Audiology 2022, 31, 1052–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhud, D.D.; Zokaei, S. Ethical Issues of Artificial Intelligence in Medicine and Healthcare. Iran J Public Health 2021, 50, i. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.P.; Hom, G.L.; Abramoff, M.D.; Campbell, J.P.; Chiang, M.F.; Intelligence, o.b.o.t.A.T.F.o.A. Current Challenges and Barriers to Real-World Artificial Intelligence Adoption for the Healthcare System, Provider, and the Patient. Translational Vision Science & Technology 2020, 9, 45–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogel, A.L.; Kvedar, J.C. Artificial Intelligence Powers Digital Medicine. npj Digital Medicine 2018, 1, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Fuente Garcia, S.; Ritchie, C.W.; Luz, S. Artificial Intelligence, Speech, and Language Processing Approaches to Monitoring Alzheimer's Disease: A Systematic Review. J Alzheimers Dis 2020, 78, 1547–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tornero-Costa, R.; Martinez-Millana, A.; Azzopardi-Muscat, N.; Lazeri, L.; Traver, V.; Novillo-Ortiz, D. Methodological and Quality Flaws in the Use of Artificial Intelligence in Mental Health Research: Systematic Review. JMIR Ment Health 2023, 10, e42045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, W.J.; Ruan, Q.N.; Jiang, K. Challenges for Artificial Intelligence in Recognizing Mental Disorders. Diagnostics (Basel) 2022, 13, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Research area | Query text |
|---|---|
| (1) AI technologies | “artificial intelligen*” OR “machine intelligen*” OR “machine learning” OR “data learning” OR “neural network” OR “support vector*” OR “k-nearest neighbor*” OR “markov decision” OR “markov chain” OR “markov random field” OR “natural language process” OR “deep learn*” OR “big data” OR “fuzzy” OR “cluster*” OR “classifier” OR “classification algorithm” OR “automatic” OR “autonomous” OR “automated” OR “computational intelligence” OR “computer vision” OR “intelligent comput*” OR “robot*” OR “intelligent tutor*” OR “intelligent agent*” OR “intelligent system*” OR “expert system*” OR “voice recognition” OR “speech recognition” |
| (2) HCD | “speech* patholog*” OR “communication disorder*” OR “speech* disorder*” OR “language disorder*” OR “speech* impair*” OR “speech* therap*” OR “speech* assess*” OR “pathological speech” OR “pathological language” OR “stutter*” OR “dysarthria” OR “swallow* disorder*” OR “voic* disorder*” OR “aphasia” OR “speech apraxia” OR (“autis*” AND (“speech” OR “language”)) OR (“schizophreni*” AND (“speech” OR “language”)) OR (“brain injur*” AND (“speech” OR “language”)) OR (“dement*” AND (“speech” OR “language”)) |
| Rank | Country (Ranking by output) |
Output* n (%) |
Country (Ranking by citations) |
Citations** n (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
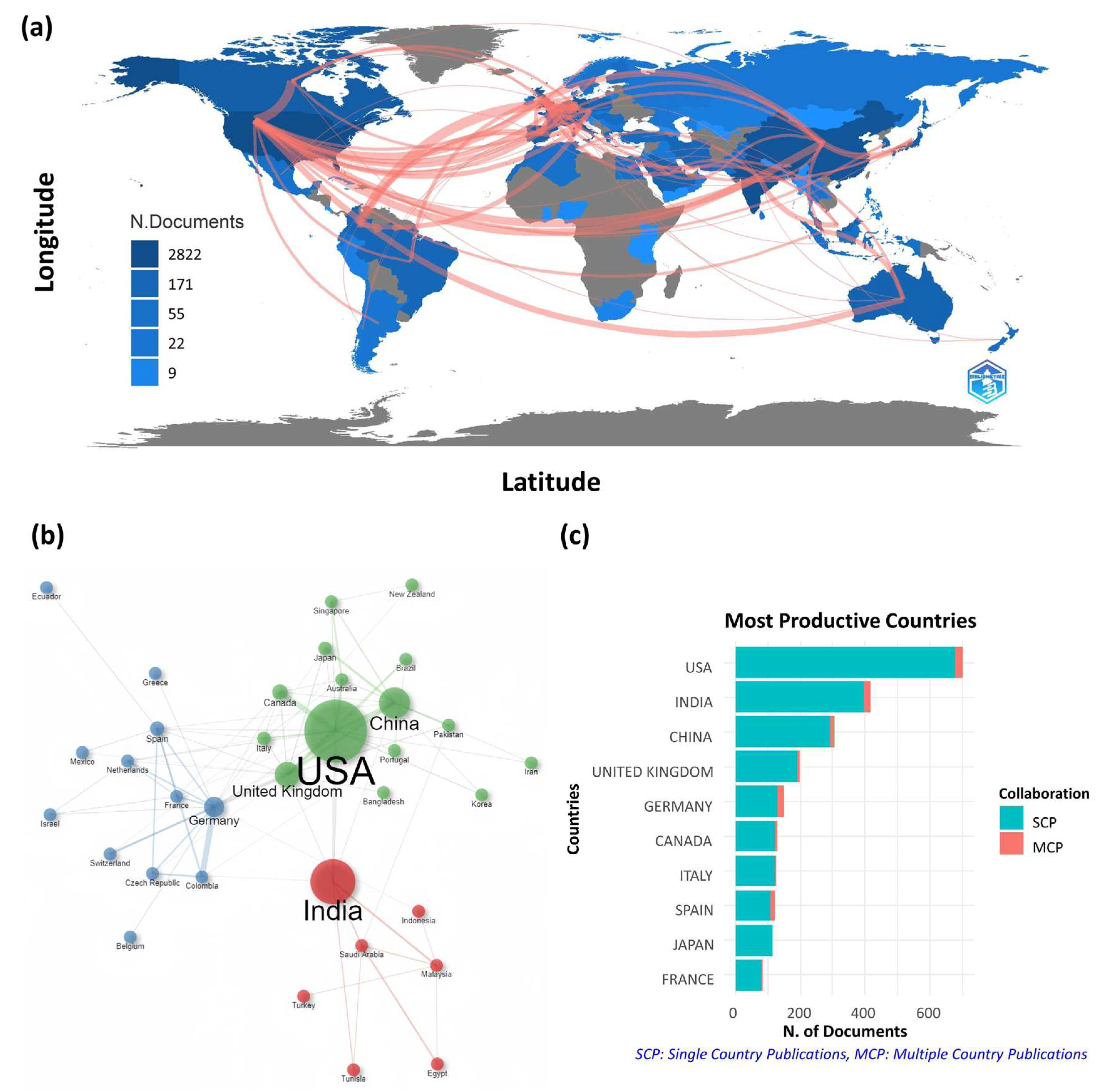
| 1 | USA | 1395 (32.05) | USA | 8877 (24.84) |
| 2 | India | 787 (18.08) | United Kingdom | 4051 (11.33) |
| 3 | China | 559 (12.84) | Canada | 1815 (5.08) |
| 4 | United Kingdom | 382 (8.78) | Spain | 1576 (4.41) |
| 5 | Germany | 318 (7.31) | Germany | 1475 (4.13) |
| 6 | Italy | 226 (5.19) | China | 1456 (4.07) |
| 7 | Canada | 224 (5.15) | Japan | 924 (2.59) |
| 8 | Spain | 224 (5.15) | India | 914 (2.56) |
| 9 | Japan | 222 (5.10) | France | 865 (2.42) |
| 10 | France | 159 (3.65) | Malaysia | 715 (2.00) |
| Rank | Journal/conference (Ranking by output) |
Output* n (%) |
Journal/conference (Ranking by citations) |
Citations** n (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | INTERSPEECH | 297 (6.80) | INTERSPEECH | 1722 (4.82) |
| 2 | IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) | 114 (2.61) | IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering | 1317 (3.68) |
| 3 | Lecture Notes in Computer Science | 77 (1.76) | Speech Communication | 793 (2.22) |
| 4 | Annual International Conference of The IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC) | 63 (1.44) | Philosophical Transactions of The Royal Society B: Biological Sciences | 736 (2.06) |
| 5 | IEEE Access | 52 (1.19) | Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders | 687 (1.92) |
| 6 | Computer Speech and Language | 50 (1.14) | Journal of Voice | 684 (1.91) |
| 7 | Journal of Speech Language and Hearing Research | 50 (1.14) | IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) | 632 (1.77) |
| 8 | Journal of Voice | 50 (1.14) | Biomedical Engineering Online | 556 (1.55) |
| 9 | Biomedical Signal Processing and Control | 48 (1.10) | IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics | 519 (1.45) |
| 10 | Sensors | 44 (1.01) | Biomedical Signal Processing and Control | 511 (1.43) |
| Rank | Research domain (Ranking by output) |
Output* n (%) |
Research domain (Ranking by citations) |
Citations** n (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Computer science | 1607 (60.62) | Computer science | 9504 (38.52) |
| 2 | Engineering | 1058 (39.91) | Engineering | 8104 (32.84) |
| 3 | Neurosciences | 236 (8.90) | Neurosciences | 3715 (15.06) |
| 4 | Acoustics | 233 (8.79) | Psychology | 2469 (10.01) |
| 5 | Language & linguistics | 201 (7.58) | Acoustics | 2052 (8.32) |
| 6 | Rehabilitation | 190 (7.17) | Audiology & speech-language pathology | 1825 (7.40) |
| 7 | Audiology & speech-language pathology | 190 (6.04) | Rehabilitation | 1674 (6.78) |
| 8 | Psychology | 160 (5.81) | Language & linguistics | 1564 (6.34) |
| 9 | Telecommunications | 154 (7.17) | Clinical neurology | 1442 (5.84) |
| 10 | Clinical neurology | 138 (5.21) | Medical informatics | 1325 (5.37) |
| Rank | Article (Ranking by TGC/y) |
TGC | TGC/y | Article (Ranking by TLC/y) |
TLC | TLC/y |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tao et al. (2017) [50] | 413 | 51.63 | Fraser et al. (2016) [49] | 44 | 4.89 |
| 2 | Fraser et al. (2016) [49] | 400 | 44.44 | Luz et al. (2020) [51] | 23 | 4.60 |
| 3 | Vieira et al. (2017) [52] | 331 | 41.38 | Tsanas et al. (2012) [53] | 42 | 3.23 |
| 4 | Lombardo et al. (2019) [54] | 229 | 38.17 | Gosztolya et al. (2019) [55] | 18 | 3.00 |
| 5 | Bedi et al. (2015) [56] | 343 | 34.30 | Xiong et al. (2020) [57] | 15 | 3.00 |
| 6 | Tsanas et al. (2012) [53] | 445 | 34.23 | Sakar et al. (2013) [58] | 34 | 2.83 |
| 7 | Dautenhahn (2007) [59] | 608 | 33.78 | Fang et al. (2019) [60] | 17 | 2.83 |
| 8 | Sakar et al. (2013) [58] | 356 | 29.67 | Hedge et al. (2019) [61] | 17 | 2.83 |
| 9 | Little et al. (2007) [62] | 499 | 27.72 | Syed et al. (2020) [63] | 14 | 2.80 |
| 10 | Didehbani et al. (2016) [64] | 204 | 22.67 | Low et al. (2020) [65] | 14 | 2.80 |
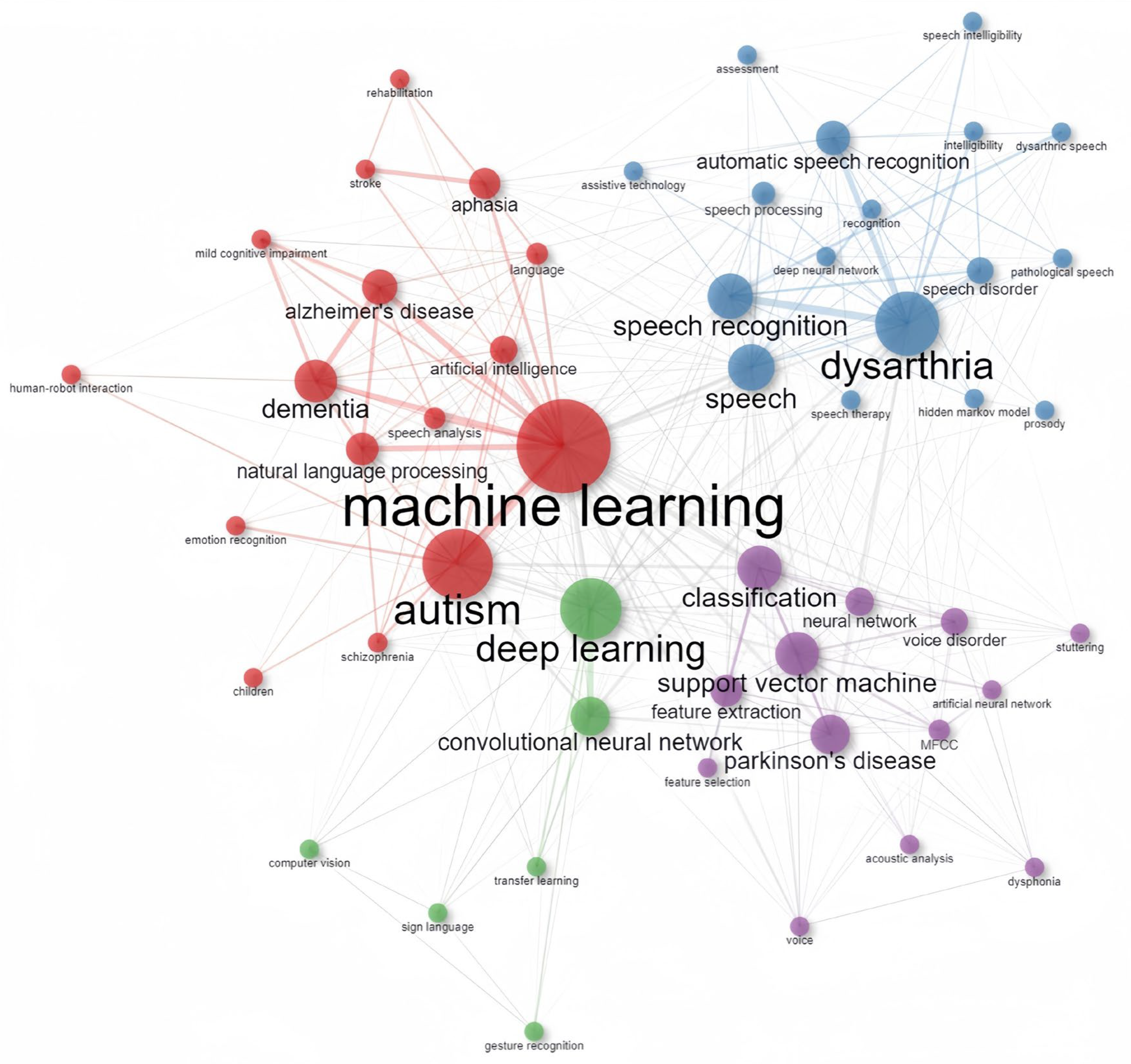
| Category | Frequency* | Category | Frequency* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Health condition | Technology | ||
| autism | 417 | machine learning | 448 |
| dysarthria | 278 | support vector machine | 188 |
| dementia | 184 | deep learning | 259 |
| Parkinson’s disease | 156 | convolutional neural network | 158 |
| aphasia | 132 | natural language processing | 119 |
| Alzheimer’s disease | 131 | artificial neural network | 68 |
| schizophrenia | 83 | hidden Markov model | 43 |
| voice disorders | 118 | transfer learning | 50 |
| speech disorders | 104 | deep neural network | 43 |
| stuttering | 66 | computer vision | 38 |
| Element | Function | ||
| speech | 128 | speech recognition (ASR) | 193 (144) |
| language (sign language) | 82 (52) | classification | 169 |
| MFCC | 81 | feature extraction/selection | 166 |
| intelligibility | 47 | speech/acoustic analysis | 133 |
| voice | 53 | speech therapy | 61 |
| robots | 44 | emotion recognition | 55 |
| prosody | 35 | assessment | 38 |
| children | 34 | rehabilitation | 38 |
| acoustic features | 25 | diagnosis | 32 |
| healthcare | 17 | screening | 21 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





