1. Introduction
In both developed and developing countries, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most notable chronic liver disease, where it is associated with the risk factors of insulin resistance, hypertension, diabetes, overweight or obesity, and metabolic syndrome[
1,
2]. NAFLD is generally defined as the accumulation of more than equally 5% of triglycerides within hepatocytes from imaging or biopsy, without secondary causes such as viral hepatitis, autoimmune liver disease, haemochromatosis, Wilson’s disease, or drug-induced liver disease[
1,
3,
4]. The benign form of NAFLD including isolated steatosis which is nonalcoholic fatty liver (NAFL). This disease can extremely cause an end-stage caused by the complicated liver-cell injury and accumulation of inflammatory cells, which causes the changes of normal histology into aggressive from called nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which can progressively changed into fibrous scars with varying degrees of fibrosis. This will increase the risk of morbidity and mortality of patients with NAFLD from liver cancer by as much as 1-2% per year if there is no special and individual treatment for each patient [
1,
3].
Commonly, individuals with NAFLD will remain asymptomatic until evidence of raised liver enzymes and acculumulation of liver fat is found in liver imaging [
3]. Updated clinical practice from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD), the American College of Gastroenterology and the American Gastroenterological Association stated that NAFLD must be diagnosed by (1) the imaging evidence of increase hepatic fat, (2) no significant consumption of excessive alcohol (> 30 gram/day), and (3) no existing causes of other chronic liver disease[
5,
6].
Current treatment regarding NAFLD starts with defining and treating the comorbidities based on existing guidelines and lifestyle modifications such as diet, weight loss, and physical activity, which are the foundation of NAFLD treatment[
7,
8,
9]. Particularly, no medication has been approved as the first choice for the disease[
8]. However, clinicians have many problems with lack of disease information and compliance of patients due to the COVID-19, there were limitation for patients coming to health care facilities, limited outdoor movement and exercises causes sedentary lifestyle [
10]. Herewith, telemedicine can be a digital health forum for providing integrated health services through virtual communication technology that connects health workers and patients.
The development beneficiaries have greatly developed in this pandemic era, where telemedicine could be used to help monitor patients when social distancing is required, reducing the potential spread of the COVID-19 virus and saving health costs. The impact of monitoring patients through telemedicine has improved the overall quality of medical services, including those for communicable diseases (COVID-19) and non-communicable diseases (asthma, hypertension, diabetes, etc.). Therefore, the objective of this review was to evaluate the telemedicine could help for monitoring the outcome of treatment in NAFLD patients.
2. Materials and Methods
This article was conducted following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) statement.
2.1. Search Strategy
A comprehensive search stratery from literature databases of PubMed Central and ScienceDirect was performed from June 2020 to July 2023. We conducted manual searches in JMIR MHealth and UHealth to maximize the tracing search strategy. The search strategy keywords to retrieve articles were "telemedicine, telehealth, telemessaging, or digital health intervention" "non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, or NAFLD, or hepatic steatosis" and "weight loss, lifestyle modification, or lifestyle changes", “liver function test and biochemical markers”. The following results were exported to Zotero 6.0.26 for duplicate records.
2.2. Study Selection and Data Extraction
The inclusion criteria in this literature review were: (1) an original research from randomized controlled trial (RCT) or non RCT; (2) a human study subject; (3) publication within 2020–2023, and (4) English and online access only with free full text. There were no limitations on the criteria for the patients in this review. Two independent reviewers (Safira Rosiana Choirida and Ahmad Zaqi Zaenal Muttaqin) screened through the title and abstract of the relevant studies and read the full text of the selected studies. If there were any discrepancies, the third and fourth reviewers were available to discussion.(Femmy Nurul Akbar and Hari Hendarto). The collected journal articles were also extracted into Microsoft Excel, 2019 to pass data extraction into specific results figured into author, year of publication, study design, setting, sample size, methods of intervention, health co-worker-related, and findings.
2.3. Risk of Bias Assessment
Two independent reviewers (Safira Rosiana Choirida and Ahmad Zaqi Zaenal Muttaqin) were assessed the risk of bias using Cochrane risk-of-bias tool for RCTs and Newcastle-Ottawa scale (NOS) for non RCTs.[
11,
12] If there were any discrepancies, the third and fourth reviewers were available to do discussion (Femmy Nurul Akbar and Hari Hendarto).
2.4. Data Analysis
The outcomes were reported as quantifiable measures for evaluating the effect of the intervention on lifestyle modification on body mass index (BMI), body weight (BW), liver function such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), Weight Circumference (WC), lipid profile, and hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c). We conducted qualitative analysis by extracting the data using Microsoft Excel into descriptive text and tables and analyzing the outcome of BW, BMI, WC, AST, ALT, lipid profile, HbA1c. For the meta-analysis, we excluded any studies that did not perform standard care for the comparison with the intervention group. The Review Manager software (version 5.4, Cochrane Collaboration, 2020) was used. The mean, standard deviation (SD), sample size of the intervention, and standard care group were inputted Mean difference (MD), 95% confidence interval (CI), and statistical heterogeneity using the I
2 statistic were used. The illustrated results of the metanalysis were conducted in a forest plot (
Figure 3).
3. Results
3.1. Study selection
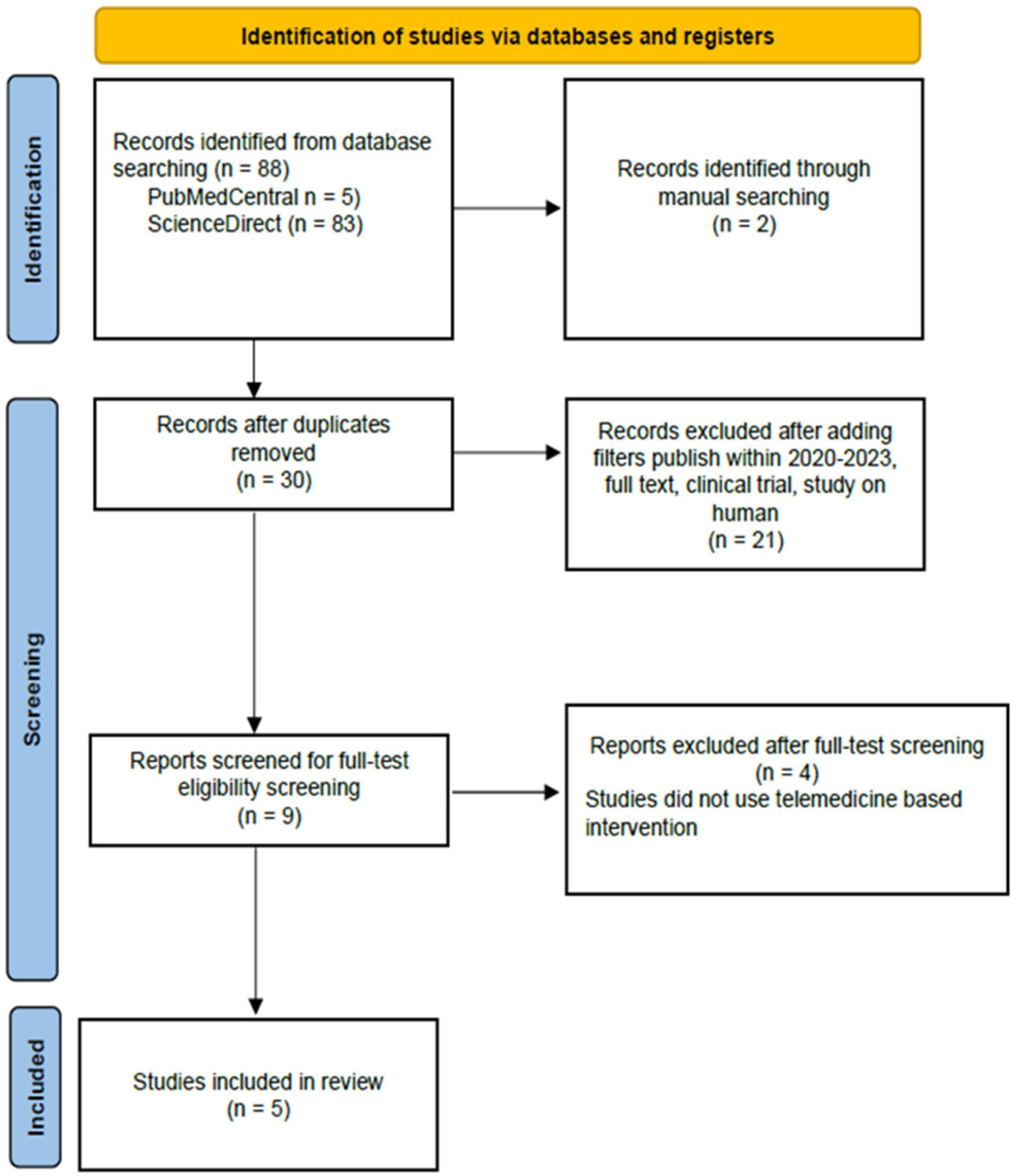
From our 90 initial studies from databases, 88 studies were from
PubMed Central and
ScienceDirect. We manually added two studies from JMIR, Mhealth, and Uhealth to maximize the tracing. After removing duplicates and adding filters, nine articles were ready for manual screening. In the end, we included five studies. A PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) Flow Chart is shown in
Figure 1. We found four studies mentioned about BW, BMI, ALT, and AST. Three studies mentioned about WC, three studies about lipid profile, and three studies about HbA1c.
3.2. Study Characteristics
The study characteristics of the included studies were provided in
Table 1, along with additional information. Mostly, studies were performed in the USA[
13,
14,
15], followed by Portugal[
16] and Singapore[
17]. Three of the five studies
Lim, et al, Policarpo et aland Stine et al were RCTs from a single center in the setting of an outpatient hospital and clinic. The remaining non-RCT study was from Motz
et al. and Tincopa
et al. The total sample size from 239 patients divided into the intervention group and the standard care group, except Motz et al. and Tincopa
et al. did not present the standard care. In total, 136 (56.9 %) males and 103 (43,1%) females were recruited; Motz
et al. only recruited female participants due to COVID-19 restrictions. Most of the participants were obese patients and Caucasians, followed by Chinese. The mean age was 51.3 years. Median intervention lasted 5.5 months Most of the studies have stated their inclusion of patients with the same standard as recent guidelines. All studies also had the same proposal to evaluate whether telemedicine is beneficial for lifestyle changes in patients with NAFLD.
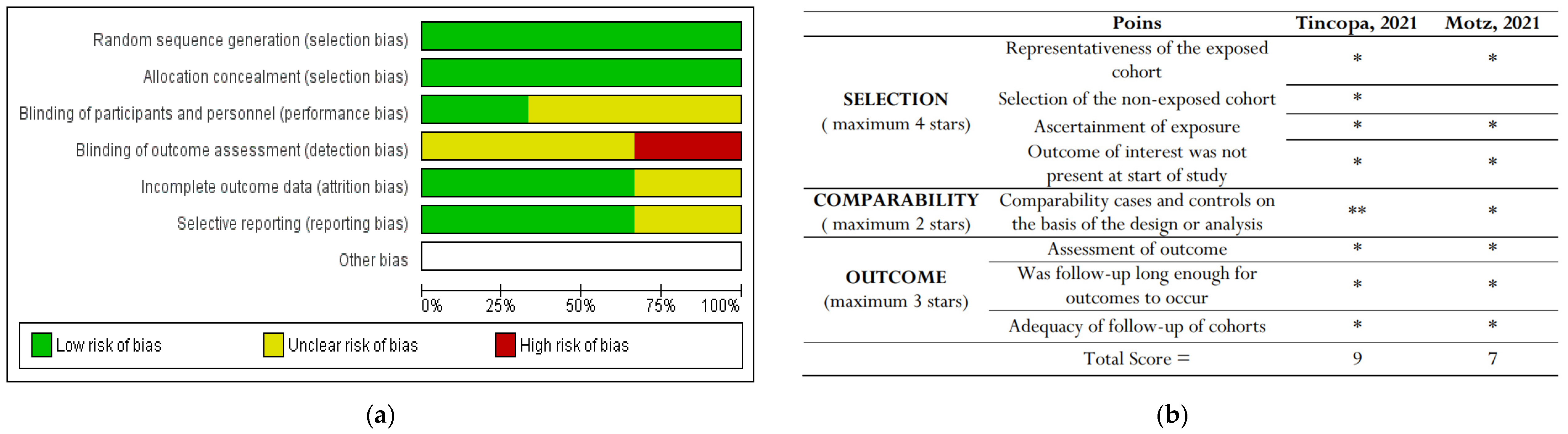
3.3. Assessment of bias
Only RCT studies were included in the Cochrane Risk of Bias (RoB) tool for randomized clinical trials [
12]
.. Of all these three studies, Lim
et al. achieved the highest risk of detection bias, where they stated that the assessors were not blinded to the groups allocated to the study. Policarpo
et al. and Stine
et al. did not clearly stated their blinding participants and personnel (performance bias) and the detection bias.
The bias results for non-RCTs showed that
Tincopa, et al. showed the best results for risk of bias assessement. The risk-of-bias assessment are shown in
Figure 2.
3.4. Meta-Analysis: The Pooled Effects of Telemedicine
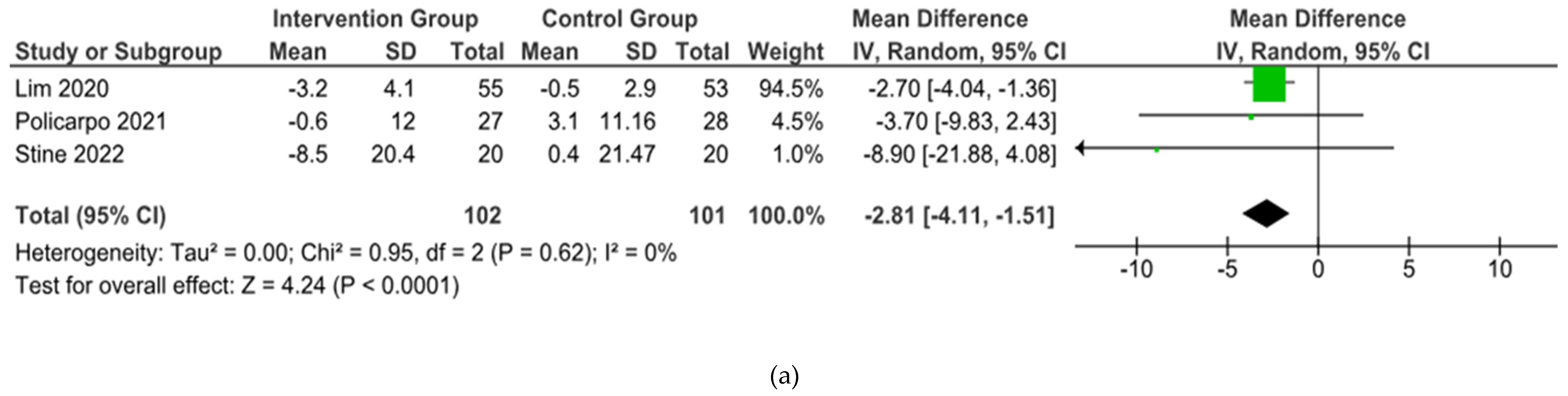
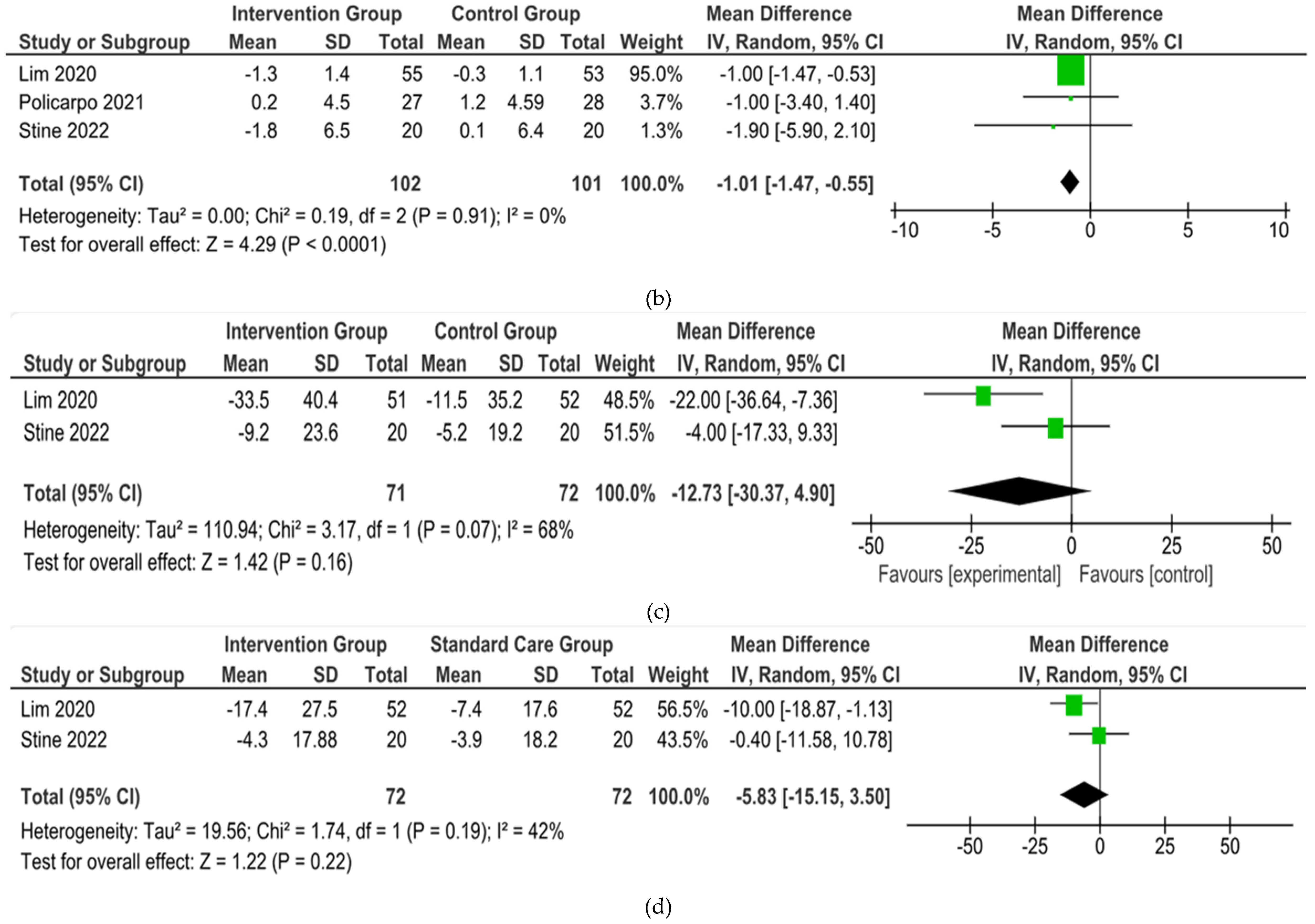
From 5 studies included, 3 were included in the meta-analysis but 2 studies conducted with single arm and. Three studies (
Lim, et al., Policarpo, et al., Stine, et al.) showed their outcomes about BW and BMI [
15,
17]. However, 1 studies (
Policarpo, et al.) did not reported the SD result of ALT and AST [
16].
In the end, the brief summary of those included studies was pooled into a forest plot of body weight, BMI, ALT, and AST. Results from meta-analyses (
Figure 3) indicated no heterogeneity in body weight and BMI (I
2 = 0%). The pooled MD for the effects of digital health intervention and body weight (MD -2.81: 95% CI, -4.11 to -1.51,
p = 0.0001) and BMI (MD -1.01: 95% CI, -1.47 to -0.55,
p = 0.0001) were statistically significant. No statistically significant relation exists between ALT (MD -12.73: 95% CI, -30.37 to -4.90,
p = 0,16) and AST (MD -5.83: 95% CI, -15.15 to -3.50,
p = 0.22), with a moderate level of heterogeneity (I
2 = 68% for ALT and I
2 = 42% for AST).
3.5. Result of individual studies
All the included studies focus on modification of lifestyle including weight loss, physical activities and stress management. We found four studies about BW, BMI, AST, and ALT. Three studies about WC and HbA1c, and two studies about lipid profile.
However, every each studies had their main topic including lifestyle change program for nutrition, physical activity, and sustainable behavioral changes through mobile based health application called NoomWeight (NW) from Stine,
et al. Special care consisting of dietary and lifestyle advice through mobile health application called nBuddy from Lim
et al., and FitBit, mobile digital health technology, used by Tincopa et al. which used to track daily step and nutritional assessment[
14,
15,
17].This mobile application provided access that focusing on body weight loss and behavioral changes, which technically including monitoring and giving feedback to patients personally. Patients can easily log their daily meals, daily step counts, body weight, and accsess many health information and stress management. Conversely, studies from Motz,
et al and Policarpo, et al using video and/or phone as their main digital health intervention for monitoring the intervention group (IG)[
13,
16]. Most of the included studies, participants were taught to do physical activities at least in with moderate-intensity aerobic training. For the dietary intervention, three studies considered giving recommendation of Mediterranian diet [
14,
15,
16], one study represent nutritional counseling according to the original study protocol [
13], and one study represented dietary intervention via general advice from dietitian.[
17]
Stine
et al., added 40 participants to their research divided equally into a intervention group and a standard care group. This
trial was 4 months in duration, where both of the groups received education from an academic hepatologist regarding the current guidelines of NASH in clinical practice regarding the Mediterranean diet and 150 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity per week. The IG received the Noom Weight application and coach. At the end of the trials, the IG significantly decreased body weight (
p =
0.0008) and BMI (
p = 0.037) compared to standard care (SC). Moreover, 45% of the patients successfully reduced 5% of their body weight. Regarding liver function test, albumin level, blood sugar level, fibrosis-4 index (FIB-4), and NAFLD fibrosis score (NFS) were not statistically significant, respectively (
p > 0.05). Morover, the IG received significant reduction in platelet count compared to SC (-28 vs. -5.7 ×109,
p = 0.038). For feasibility and acceptability, 70% and 75% of the IG met the criteria for feasibility and acceptability regarding the use of Noom Weight[
15].
Study from Lim
et al., a 6-month period of RCT where IG received advice on dietary and physical activity from a dietitian via offline in clinic and the nBuddy mobile app to log their diet, physical activity, and behavioral changes. The SC received advice from a trained nurse based on American Heart Association guidelines via an offline clinic. At the end of sx month of the trial, the IG presented significant reductions in body weight (mean 3.2, SD 4.1 kg vs mean 0.5, SD 2.9 kg;
p < 0.001), waist circumference (mean 2.9, SD 5.0 cm vs mean –0.7, SD 4.4 cm;
p < 0.001), systolic blood pressure (mean 12.4, SD 14.8 mmHg vs mean 2.4, SD 12.4 mmHg;
p = 0.003), diastolic blood pressure (mean 6.8, SD 8.9 mmHg vs mean –0.9, SD 10.0 mmHg;
p = 0.001), ALT (mean 33.5, SD 40.4 IU/L vs mean 11.5, SD 35.2 IU/L;
p = 0.004), and AST (mean 17.4, SD 27.5 U/L vs mean 7.4, SD 17.6 IU/L,
p = 0.03) compared to SC [
17]
.
In the Policarpo
et al. trial, an outpatient infectious disease clinic was used, which NAFLD-HIV patients were allocated to IG and SC. Both groups received the same advice about structured dietary intervention about caloric restriction and weight loss based on the Mediterranean diet. At months 3 and 4, patients got a call via video and/or phone to do a review of diet advice, eating habits, and lifestyle changes during the pandemic, including four stress questionnaires in Portuguese. Before lockdown was applied, the IG showed a reduction in body weight, with a median loss of 1.5 kg vs. a median loss of 0.65 kg in the SC (
p < 0.001). After 3 months of lockdown, both groups presented weight gain where the SC (around 3 kg) showed higher weight gain compared to the IG (less than 1 kg) (
p < 0.001).[
16]
Motz
et al. presented 20 weeks of moderate-intensity aerobic training with telehealth that was given to NAFLD patients under direct supervision through an audio-visual telehealth platform. At the end of the trials, there were improvements in body weight, body fat, waist circumference, and reduction in hemoglobin A1c, respectively (–0.5% [SD 0.2%]). Then, all the participants met the a priori definition of feasibility.[
13]
Additionally, Tincopa
et al. also demonstrated physical activity based on the FitBit mobile app and nutritional assessment to assess the feasibility and acceptability of lifestyle changes in NAFLD patients through mobile technology. They also interfere the participants with secondary outcomes, including body weight, physical fitness, hepatic transient elastrography, laboratory testing, and quality of life. Approximately 50% of participants showed statistically significance reduction in weight circumference, lipid profile including HDL, LDL, and triglyceride, hemoglobin A1c with
p-value < 0.05. Their participants around 59% also reported that their mobile application was easy to use and 66% of the patients were motivated to improve their physical activity when using daily step count tracker. This would be beneficial and promising tools that feasible and acceptable. [
14]
Figure 3.
Forest plot of the effects of digital health intervention compared with standard care on the (a) Body weight, (b) BMI, (c) ALT, (d) AST of NAFLD patients.
Figure 3.
Forest plot of the effects of digital health intervention compared with standard care on the (a) Body weight, (b) BMI, (c) ALT, (d) AST of NAFLD patients.
4. Discussion
This systematic review summarized the use of telemedicine for monitoring lifestyle modification intervention in NAFLD patients among adults. All the studies included were published from 2020 until 2023. Regarding current studies, lowering body weight will be followed by reducing AST and ALT biochemical markers. From our included studies, telemedicine is beneficial in reducing body weight and BMI in NAFLD patients. However, our meta-analysis showed that telemedicine did not significantly lower the AST and ALT levels in NAFLD patients. Waist circumference was also reported in three studies, which indicated improvement in the intervention groups. Weight loss also improved the other marker of NAFLD risk factors, a panel of lipids, liver stiffness, and HbA1c.
Moreover, the pandemic is causing limitations for patients entering healthcare facilities, causing reduction in treatment sustainability. One of the breakthroughs is using telemedicine to improve the connectivity between patients and healthcare professionals. The cornerstone of treatment for NAFLD is lifestyle modification because there is no adequate evidence for pharmacological treatment[
1,
8]
.
In that case, it is recommended that lifestyle changes be made. Several guidelines have stated that reducing body weight by 3-5% will improve hepatic steatosis, and reducing body weight by 7% will change the histological features of NASH.[
8] For NAFLD, dietary recommendations allow reducing daily calorie intake by 500–1.000 kcal per day (hypocaloric diet), Mediterranean diet, low-carbohydrate diet, and low-fructose diet. Then, moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity with a minimum duration of 150–200 minutes per week or 30 minutes per day and a frequency of more than twice per week (3-5 days a week) should be applied[
8].
According to our findings, interventions using telemedicine for NAFLD were significantly better at achieving reductions in body weight and BMI compared to standard care. Reducing body weight by 5% was more effective when conducted for more than 4-6 months rather than three months[
14,
15,
17]. The changes in biochemical markers were also remarkably reduced for over 5–6 months of duration[
13,
17].
. The duration and frequency of digital interventions varied widely, ranging from 1 to 6 months, but most of the articles carried out interventions with a duration of 5-6 months. Until now, no standards have regulated how long the application of digital intervention in NAFLD patients may enhance the clinical and chemical outcomes of NAFLD. These days, the duration and frequency of digital health interventions are only based on what researcher target. Moreover, the proof that digital health interventions could improve BW and BMI in NAFLD patients is shown in this review.
Telemedicine could be a bridge that makes it easier for health workers to monitor patients directly and virtually, including their body weight and daily physical activity. There are also advantages where patients could save money, rather than coming to the health care facilities with transportation[
18]. This shows that telemedicine is feasible and acceptable for monitoring patients with NAFLD, primarily through mobile applications. Telemedicine allows patients to stay connected with healthcare professionals while avoiding the risks of disease exposure, including the spread of COVID-19 infection in offline healthcare.
The main limitation of our study is that the number of included studies and participants needs to be bigger, reducing the generalizability of the findings and making them difficult to apply in a real-world setting. Another limitation of the included studies was that the workers related to the recommendations or interventions had different competencies, and there was no recommendation for an adequate length of intervention for digital interventions. Our study strengths are that this review only included current studies during the pandemic, which is up-to-date.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, this mobile based application regarding telemedicine interventions could be an option for monitoring body weight and BMI in NAFLD patients to facing the pandemic. Future studies must be applied in larger population to evaluate the generalizability of using telemedicine in the clinical settings.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.N.A., S.R.C., A.Z.Z.M.; validation, F.N.A., S.R.C., A.Z.Z.M.; visualization, F.N.A., S.R.C., A.Z.Z.M.; screened abstracts, S.R.C., A.Z.Z.M.; resolved discrepancies, F.N.A. and H.H, F.E. ; writing—original draft preparation F.N.A., S.R.C., A.Z.Z.M. ,F.E.; writing – reviwing and editing, F.N.A., S.R.C., A.Z.Z.M., H.H; analysis, F.N.A., S.R.C., A.Z.Z.M., H.H; supervision, H.H. All authors have read and agreed to the final version of manuscript.
Funding
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare there is no conflict of interest., or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results”.
References
- Shen, K.; Singh, A.D; Modaresi, E. J.; Wakim, F.J. Therapies for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A 2022 update. World J Hepatol 2022, 14, 1718–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, X.; Zheng, L.; Wang, M.; Du, Y.; Jiang, J. Prevalence trends in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease at the global, regional and national levels, 1990–2017: a population-based observational study. BMJ Open 2020, 10, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manal F.; Abdelmalek.; Anna MD. Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. In Harrison Principles Internal Medicine, 21st ed.; Loscalzo, J.; Kasper, D.L.; Longo, D.L.; et al. Mc Graw Hill, New York, 2022, Volume 1, pp. 2619-2624.
- Torres, D.M.; Williams, C.D; Harrison, S.A. Features, diagnosis, and treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012, 10, 837–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cusi, K.; Isaacs, S.; Barb, D.; Basu, R.; Caprio, S.; Garvey, W.T. American Association of Clinical Endocrinology Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Primary Care and Endocrinology Clinical Settings. Endocrine Practice 2022, 28, 528–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallacher, J.; McPherson, S. Practical Diagnosis and Staging of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Narrative Review. EMJ 2018, 6, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, A.; Wong, R.J.; Harrison, S.A. ; Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease review: diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2015, 13, 2062–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paternostro, R.; Trauner, M. Current treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Journal of Internal Medicine 2022, 2, 190–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufour, J.F.; Anstree, Q.M.; Bugianesi, E.; et al. Curent therapies anf new developments in NASH. Gut 2022, 71, 2123–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteban, J. R.; Nuñez, R. M.; Broquetas, T.; et al. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the care and outcome of people with NAFLD-related cirrhosis. JHEP Reports 2022, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, C.K.L.; Mertz, D.; Loeb, M. Newcastle-Ottawa Scale: comparing reviewers’ to authors’ assessments. BMC Med Res Methodol 2014, 14, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Altman, D.G.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Juni, P.; Moher, D.; Oxman, A.D.; et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011, 18, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motz, V.; Faust, A.; Dahmus, J.; Stern, B.; Soriano, C.; Stine, J.G. Utilization of a Directly Supervised Telehealth-Based Exercise Training Program in Patients With Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: Feasibility Study. JMIR Form Res 2021, 5, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tincopa, M.A.; Lyden, A.; Wong, J.; Jackson, EA.; Richardson, C.; Lok, A.S. Impact of a Pilot Structured Mobile Technology Based Lifestyle Intervention for Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Dig Dis Sci 2022, 67, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stine, J.G.; Rivas, G.; Hummer, B.; Duarte, R.A.; May, C.N.; Geyer, N.; et al. Mobile health lifestyle intervention program leads to clinically significant loss of body weight in patients with NASH. Hepatol Commun 2023, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Policarpo, S.; Machado, M.V.; Cortez, P.H. Telemedicine as a tool for dietary intervention in NAFLD-HIV patients during the COVID-19 lockdown: A randomized controlled trial. Clin Nutr ESPEN 2021, 43, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.L.; Johal, J.; Ong, K.W.; Han, C.Y.; Chan, Y.H.; Lee, Y.M.; et al. Lifestyle Intervention Enabled by Mobile Technology on Weight Loss in Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Randomized Controlled Trial. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2020, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snoswell, C.L.; Taylor, M.L.;, Comans, T.A.; et al. Determining if Telehealth Can Reduce Health System Costs: Scoping Review. J Med Internet Res 2020, 10, 1-6. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).