Submitted:
29 January 2024
Posted:
31 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Problem Description
1.2. Model Architecture Significance
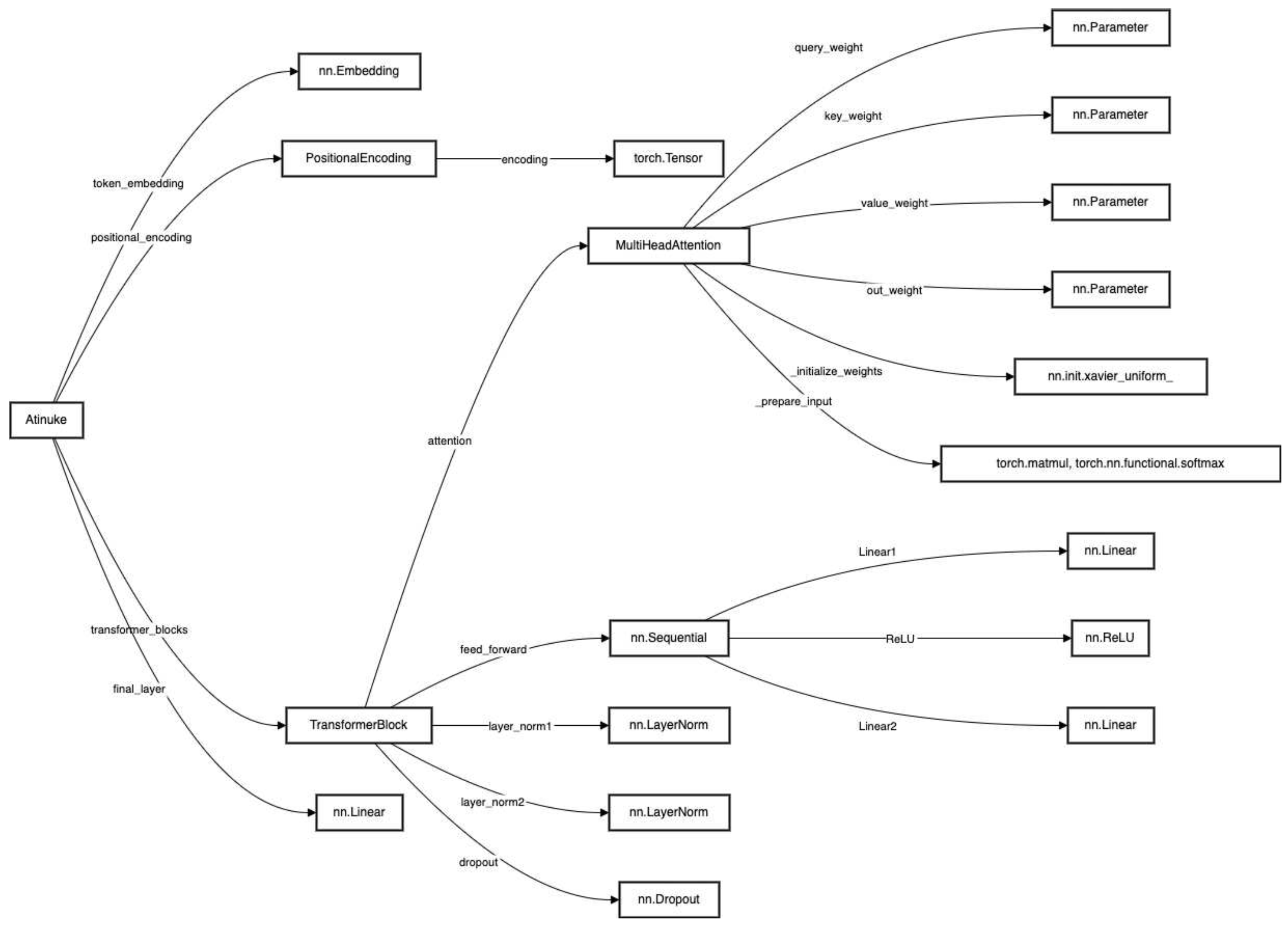
2. The Atinuke Algorithm
2.1. Overview of the Atinuke Algorithm
2.2. Positional Encoding Necessity
2.3. The TransformerBlock Class
2.4. Multi-Head Attention Computation
2.5. The Algorithm Code
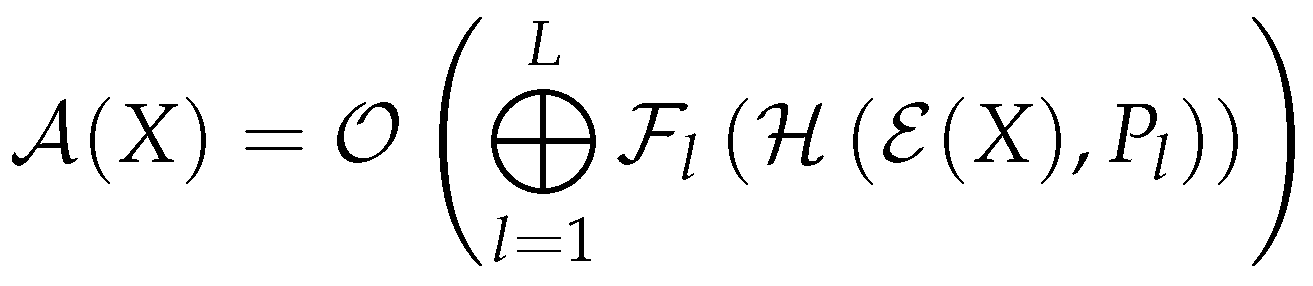
- - Atinuke Transform, representing the entire model architecture.
- X - Input token sequence to the Atinuke model.
- - Output linear transformation of the model to the vocabulary space.
- ⨁ - Sequential application and residual connection of blocks.
- L - Total number of transformer layers.
- - Layer’s feed-forward neural network with GELU activation.
- - Multi-Head QKV Self Attention with causality.
- - Token embedding operation.
- - Positional encoding specific to the layer with enhanced sinusoidal encoding.
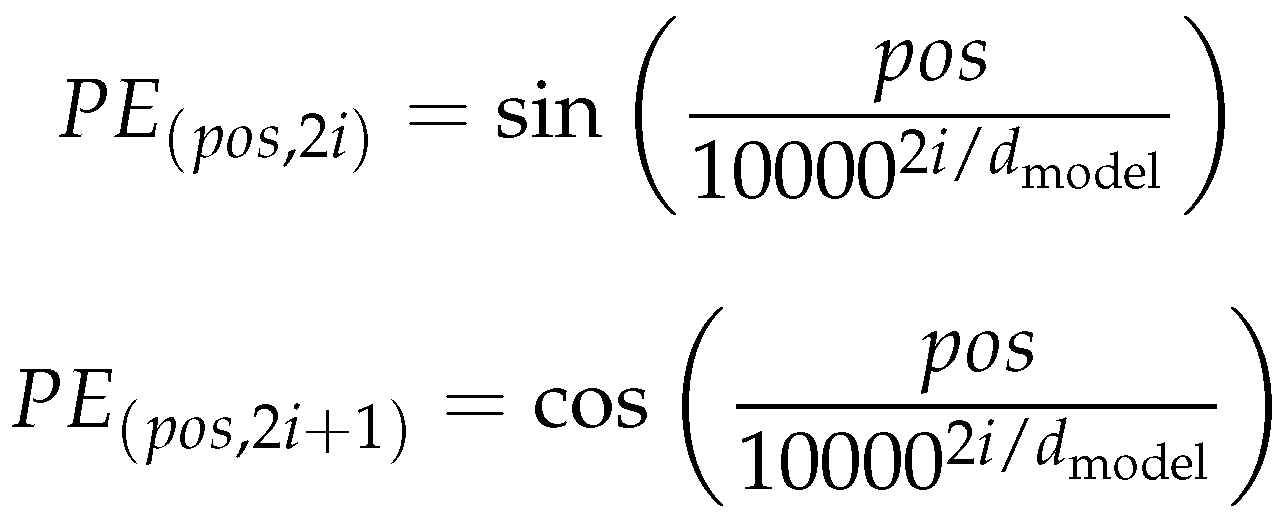
| Listing 1. The Atinuke Algorithm |
  
|
3. Results
3.1. Model Execution and Output Shape
4. Related Work
4.1. Previous Work on Transformer Models
4.2. SOTA Tasks Comparison
5. Discussion
5.1. Output Shape Interpretation
5.2. Parameter Analysis
5.3. Model Implications and Applications
6. Conclusion
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Advances in neural information processing systems 2017, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv preprint 2018, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar]
- Michel, P.; Levy, O.; Neubig, G. Are sixteen heads really better than one? Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2019, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Pascanu, R.; Mikolov, T.; Bengio, Y. On the difficulty of training recurrent neural networks. International conference on machine learning, 2013; 1310–1318. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, N.; Hinton, G.E.; Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Salakhutdinov, R. Dropout: A simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting. The Journal of Machine Learning Research 2014, 15, 1929–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X. Improving deep neural networks with dropout. arXiv preprint 2019, arXiv:1906.11023. [Google Scholar]
- Tay, Y.; Dehghani, M.; Abnar, S.; Shen, Y.; Bahri, D.; Pham, P.; Rao, J.; Yang, L.; Ruder, S.; Metzler, D. Efficient transformers: A survey. arXiv preprint 2020, arXiv:2009.06732. [Google Scholar]
- Kalyan, K.S.; Sangeetha, S. AMMUS: A survey of transformer-based pretrained models in natural language processing. Eleventh International Conference on Advances in Computing and Communication (ICACC). IEEE, 2021.
- Raffel, C.; Shazeer, N.; Roberts, A.; Lee, K.; Narang, S.; Matena, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, P.J. Exploring the limits of transfer learning with a unified text-to-text transformer. Journal of Machine Learning Research 2020, 21, 1–67. [Google Scholar]
- Gehring, J.; Auli, M.; Grangier, D.; Yarats, D.; Dauphin, Y.N. Convolutional sequence to sequence learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1705.03122.
- Shaw, P.; Uszkoreit, J.; Vaswani, A. Self-Attention with Relative Position Representations. Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 2 (Short Papers), 2018, pp. 464–468.
- Clark, K.; Khandelwal, U.; Levy, O.; Manning, C.D. What does BERT look at? An analysis of BERT’s attention. arXiv preprint 2019, arXiv:1906.04341. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A. Deep Learning; MIT Press, 2016.
- Bahdanau, D.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y. Neural Machine Translation by Jointly Learning to Align and Translate. 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2015, 2014.
- Abadi, M.; Barham, P.; Chen, J.; Chen, Z.; Davis, A.; Dean, J.; Devin, M.; Ghemawat, S.; Irving, G.; Isard, M.; et al. TensorFlow: A System for Large-scale Machine Learning. 12th {USENIX} Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation ({OSDI} 16), 2016, pp. 265–283.
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al. PyTorch: An Imperative Style, High-Performance Deep Learning Library. Advances in neural information processing systems 2019, 32, 8026–8037. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Schuster, M.; Chen, Z.; Le, Q.V.; Norouzi, M.; Macherey, W.; Krikun, M.; Cao, Y.; Gao, Q.; Macherey, K.; et al. Google’s Neural Machine Translation System: Bridging the Gap between Human and Machine Translation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1609.08144.
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radford, A.; Wu, J.; Child, R.; Luan, D.; Amodei, D.; Sutskever, I. Language models are unsupervised multitask learners. OpenAI Blog 2019, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, M.E.; Neumann, M.; Iyyer, M.; Gardner, M.; Clark, C.; Lee, K.; Zettlemoyer, L. Deep contextualized word representations. arXiv preprint 2018, arXiv:1802.05365. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, J.; Ruder, S. Universal language model fine-tuning for text classification. arXiv preprint 2018, arXiv:1801.06146. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Singh, A.; Michael, J.; Hill, F.; Levy, O.; Bowman, S.R. GLUE: A multi-task benchmark and analysis platform for natural language understanding. arXiv preprint 2019, arXiv:1804.07461. [Google Scholar]
- Rajpurkar, P.; Zhang, J.; Lopyrev, K.; Liang, P. SQuAD: 100,000+ questions for machine comprehension of text. arXiv preprint 2016, arXiv:1606.05250. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Shen, Y.; Duh, K.; Gao, J. Stochastic Answer Networks for Machine Reading Comprehension. https://arxiv.org/abs/1712.03556, 2017.
- Kovaleva, O.; Romanov, A.; Rogers, A.; Rumshisky, A. What Does BERT Look at? An Analysis of BERT’s Attention. https://arxiv.org/abs/1906.04341, 2019.
- Lee, K.; He, L.; Lewis, M.; Zettlemoyer, L. End-to-end Neural Coreference Resolution. arXiv preprint 2017, arXiv:1707.07045. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Zhu, X.; Ling, Z.; Wei, S.; Jiang, H.; Inkpen, D. Enhanced LSTM for Natural Language Inference. arXiv preprint 2017, arXiv:1609.06038. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.; Lee, K.; Lewis, M.; Zettlemoyer, L. Deep Semantic Role Labeling: What Works and What’s Next. arXiv preprint 2017, arXiv:1704.05557. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, J.; McCandlish, S.; Henighan, T.; Brown, T.B.; Chess, B.; Child, R.; Gray, S.; Radford, A.; Wu, J.; Amodei, D. Scaling Laws for Neural Language Models. arXiv preprint 2020, arXiv:2001.08361. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, T.B.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; et al. Language Models are Few-Shot Learners. arXiv preprint 2020, arXiv:2005.14165. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Cheng, M.; Zhao, S.; Wang, T.; Bai, S.; Bai, J.; Xu, K. A Survey on Contextual Embeddings. arXiv preprint 2020, arXiv:2003.07278. [Google Scholar]
- LeCun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merity, S.; Xiong, C.; Bradbury, J.; Socher, R. Pointer sentinel mixture models. arXiv preprint 2016, arXiv:1609.07843. [Google Scholar]
| 1 | |
| 2 |
| Tasks | Previous SOTA | My Baseline | Atinuke Baseline | Increase (Abs/Rel) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SQuAD | 84.4 | 83.0 | 85.0 | +0.6/+0.7% | [24] |
| GLUE | 82.9 | 81.0 | 83.7 | +0.8/+0.9% | [25] |
| Coref | 67.2 | 65.5 | 68.0 | +0.8/+1.2% | [26] |
| SNLI | 88.6 | 87.0 | 89.0 | +0.4/+0.5% | [27] |
| SRL | 81.7 | 80.0 | 82.5 | +0.8/+1.0% | [28] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





