Introduction
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most frequently diagnosed cancer and the second cause of cancer-related deaths, globally [
1]. According to WHO reports CRC is the second most diagnosed cancer in women and the third in men. Familial, environmental, and dietary factors play pivotal roles in the etiology of CRC [
2]. Animal models of CRC provide a wide area of investigation for a better understanding of the possible pathways triggering CRC induction and studying the effects of dietary and environmental agents on disease prevention and treatment [
3]. DMH, a strong DNA alkylating agent, is broadly utilized to induce CRC in animal models. Azoxymethane and methylazoxymethanol are the products of DMH metabolism in the liver. They are further metabolized in the colon to generate the ultimate metabolite, diazonium ions, after being transported through bile or blood [
4,
5]. Diazonium ions cause colon carcinogenesis by forming reactive oxygen species (ROS) which results in lipid peroxidation and oxidative stress [
6]. Furthermore, many reports addressed the impact of high levels of ROS on proliferation, invasion, drug resistance, and metastasis [
7,
8]. Antioxidant enzymes including superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and catalase
play a crucial role in maintaining redox balance via preventing ROS activity and accumulation in the cells [9]; nonetheless, higher lipid peroxidation end products such as malondialdehyde (MDA) relative to the antioxidant levels may result in CRC initiation and progression [
10]. In addition, the pro-inflammatory cytokine, tumor necrotizing factor (TNF-α), as one of the targets of NF-κB was indicated to have an important role in the CRC initiation and progression stages [
11].
Combination chemotherapy regimens like FOLFOX, FOLFOXIRI, CAPIRI, and CAPOX along with monoclonal antibodies are the cornerstone of CRC treatment. They aim at improving anticancer effects such as reduced metastatic potential and cancer stem cell populations, and induction of apoptosis as well as suppressing the possible drug resistance of cancer cells to single drugs [
12]. IRI is an inhibitor of topoisomerase I that prevents DNA replication and induces apoptosis by inhibiting DNA supercoil relaxation. IRI monotherapy was first introduced as a potential agent for the treatment of CRC refractory to 5-FU [
13]. IRI in combination with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) is usually used in the clinical treatment of CRC [
14]. CAP, an orally administered fluoropyrimidine, is a prodrug of 5-FU that converts to 5-FU in tumor tissues by thymidine phosphorylase and is shown to be less toxic and as effective and well-tolerated as 5-FU/LV for stage III CRC [
15]. Several investigations have reported the effectiveness of IRI in combination with CAP (CAPIRI or XELIRI) in patients suffering from CRC as the first or second line of chemotherapy. For instance, Laudani
et al. indicated the effectiveness and tolerability of CAPIRI as the first-line therapy for metastatic colon cancer suggesting the replacement of 5-FU with CAP in 5-FU-based regimens [
16]; however, various side effects were observed despite the therapeutic effects of these agents. Bone marrow suppression, and gastrointestinal, and dermatologic toxicity were reported prevalently in patients undergoing treatment with CAP [
17]. In addition, gastrointestinal toxicity symptoms like diarrhea as one of the main toxic side effects in IRI monotherapy or combination therapy with fluoropyrimidines were documented [
18]. Unfortunately, these adverse effects can affect the patient’s quality of life and drug dose adjustment.
Flavonoids have gained great interest in cancer prevention and treatment due to their safety and effectiveness. Regardingly, SMN, a flavonoid extracted from
Silybum marianum, has been used for treating hepatic problems such as cirrhosis and hepatitis for many years [
19]. Functionally, SMN acts as a potent antioxidant through free radical scavenging, increasing the amounts of glutathione, and inhibiting lipid peroxidation [
20]. SMN exerts its anti-inflammatory effects by modulating the genes involved in the NF-κB pathway including interleukin-1, cyclooxygenase-2, inducible nitric oxide synthase, and TNF-α [
21]. Numerous preclinical and clinical studies have confirmed the anticancer effects of SMN including induction of apoptosis and suppression of cell proliferation, angiogenesis, and metastasis [
22]. Due to the lack of investigative studies about SMN-supplemented chemotherapy regimens, we conducted a study to evaluate the effect of SMN supplementation on the mono- and combination therapy of CAP and IRI in the mouse model of DMH-induced colon carcinogenesis.
Materials and Methods
Chemicals
DMH and SMN were obtained from Sigma St. Louis, MO, USA. Capecitabine was purchased from Actero Pharmaceuticals, Iran. Irinotecan was purchased from Mylan, France.
Animals, Housing, and Diet
Fifty-six male BALB/c mice weighing between 25-30 g were obtained from the Central Animal House of Urmia University of Medical Sciences, Urmia, Iran. The animals were housed in plastic cages at the temperature of 25 ˚C with 12 h: 12 h light: dark cycles until the end of the study period. A modified pellet diet containing 2500 ppm SMN was prepared daily for the SMN-supplemented treatment groups. Animals had access to the diet and water ad libitum.
Cancer Induction
DMH was dissolved in a 0.9% saline solution containing 1 mM EDTA and 10 mM sodium citrate, pH 8. CRC in mice was induced by weekly intraperitoneally (i.p.) injection of 20 mg/kg (b.w.) DMH for ten consecutive weeks.
Experimental Design
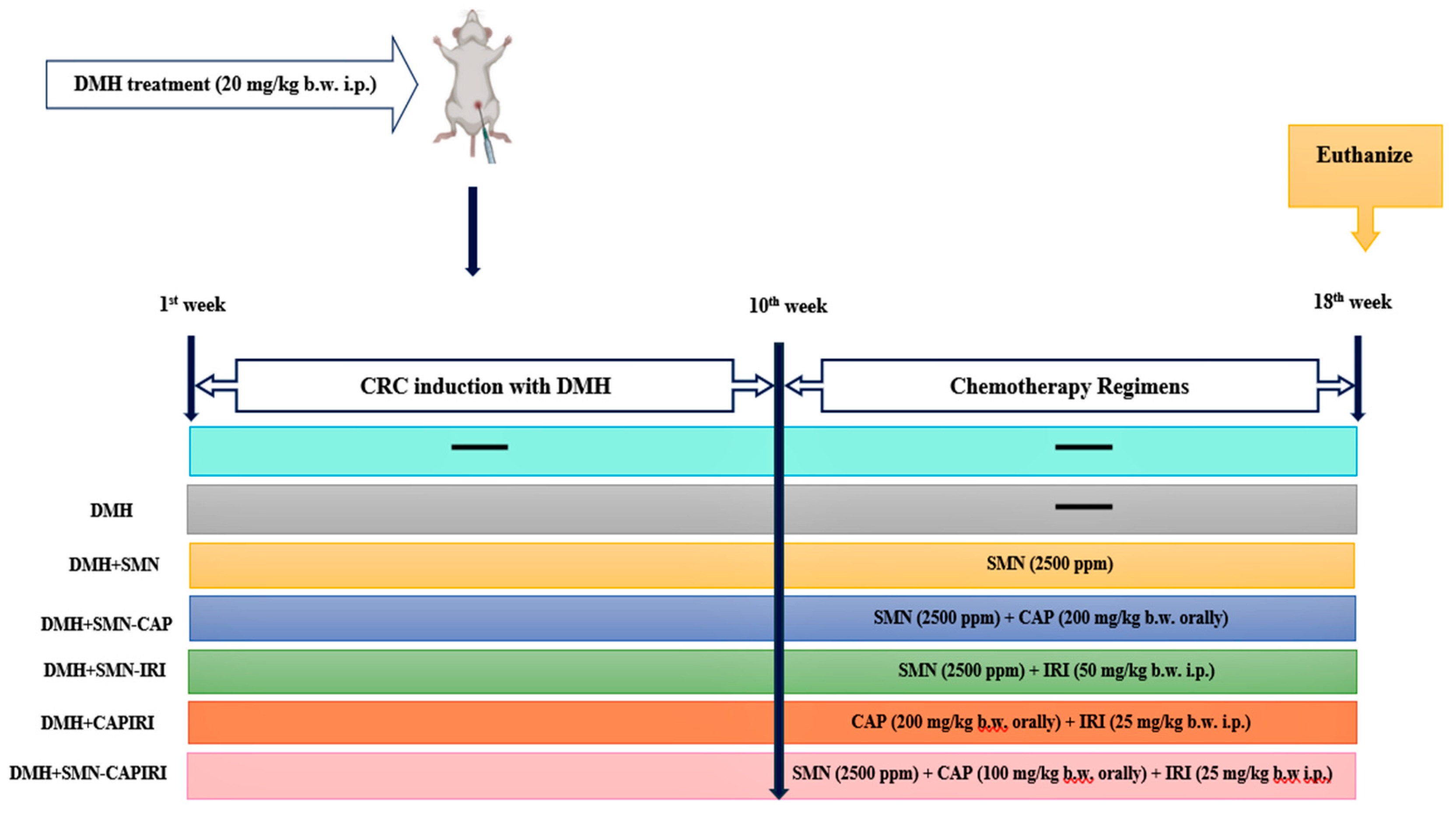
Following one week of acclimatization, mice were randomly allocated into seven groups with eight mice per group. The treatment schedule was as follows:
Control group (group 1): Animals were administered i.p. the vehicle (0.9% saline solution containing 1 mM EDTA and 10 mM sodium citrate) weekly for 10 weeks and received a normal commercial diet.
DMH group (Group 2): Weekly i.p. injection of 20 mg/kg (b.w.) DMH was done on the mice for ten weeks. Animals were fed with a normal commercial pellet diet.
DMH+SMN (Group 3): Animals were fed with the modified diet containing SMN (2500 ppm) prepared daily for eight consecutive weeks post CRC initiation (11th -18th w).
DMH+SMN-CAP (Group 4): Animals received CAP orally at the dose of 200 mg/kg (b.w.) dissolved in sterile normal saline daily for eight weeks.
DMH+SMN-IRI (Group 5): IRI was injected i.p. to the mice at the dose of 50 mg/kg (b.w.) once a week for eight weeks.
DMH+CAPIRI (group 6): Mice received daily oral administration of CAP at the dose of 100 mg/kg (b.w.) and weekly injections of IRI at the dose of 25 mg/kg (b.w.) i.p. for eight weeks.
DMH+SMN-CAPIRI (group 7): Mice received CAP orally at the dose of 100 mg/kg (b.w.) daily and were given weekly injections of IRI at the dose of 25 mg/kg (b.w.) i.p. for eight weeks
Tumor induction in groups 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7 was done similarly to group 2. Additionally, groups 3, 4, 5, and 7 daily received the SMN-supplemented diet during the chemotherapy period.
Figure 1 shows the time course of the experiment.
Animal Euthanasia, Blood Sample Collection, and Tissue Preparation
At the end of the 18th week, blood samples of all animals were collected through cardiac puncture while they were under anesthesia with a ketamine-xylazine cocktail (ketamine: 90 mg/kg and xylazine: 9 mg/kg, i.p.). The blood samples were left to coagulate at room temperature for 15 minutes and then were centrifuged at 3000 × g for 10 min to obtain the sera. After the blood collection, the animals were euthanized using an overdose injection of sodium pentobarbital (200 mg/kg, (b.w.), i.p.), and immediately the colon and liver tissues were dissected. Following the dissection, colons were opened longitudinally and flushed with physiological saline for further macroscopic evaluation of the polyps. Later, the colon tissues were divided into two parts. One part was washed with chilled saline and was kept at -70 ˚C for biochemical and enzymatic examinations. The second part was preserved in 10% buffered formaldehyde for further histopathological analysis. The same procedure was done to the liver tissues.
Measurement of Polyp Incidence
To measure the polyp incidence in the colon, following the cleansing and flushing of the colons, the number of the present polyps in every mouse was counted precisely to determine the average number of the polyps per group as well as the percentage of the polyp incidence. An average number of polyp-bearing mice was calculated as the ratio of the total number of polyps to the number of polyp-bearing mice in each experimental group. Moreover, the polyp incidence percentage was calculated as the percentage of the ratio of the total number of polyps in every treatment group to the same value of the DMH group.
Biochemical Estimations
The serum levels of total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL), high-density lipoprotein (HDL), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) were measured with a Biochemistry Autoanalyzer System (BT 3000, Biotecnica instruments, Italy).
Determination of Antioxidant Enzymes
The enzymatic activities of SOD and GPx in the serum, colon, and liver specimens were measured using commercially available kits (Zellbio GmbH, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Malondialdehyde Measurement
To evaluate the lipid peroxidation rate, the MDA content of colon and liver samples was examined via thiobarbituric acid reaction as described previously [
23]. The MDA levels were measured at 540 nm and were expressed as nmol/mg protein of the samples.
Nitric oxide Determination
To assess the nitrosative stress, the nitric oxide (NO) content of the colonic and hepatic homogenates was measured using the Griess reaction [
24] in which, nitric oxide is transformed to nitrite as a more stable metabolite that is then, converted to HNO2 in an acidic environment. HNO2 forms a diazonium salt in reaction with sulphanilamide, which reacts with N-(1-naphthyl) ethylenediamine.2HCl to generate an azo dye detectable at 540 nm. The NO content of the examined specimens was expressed as nmol per mg of protein in the sample.
Myeloperoxidase Activity Assessment
Myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity was measured in the colonic and hepatic homogenates as previously described [
25]. The color change was measured at 650 nm spectrophotometrically and the MPO activity was expressed as units per milligram of tissue sample.
Inflammatory Cytokines Assessment
The serum levels of C-reactive protein (CRP) and TNF-α were determined using mice-specific ELISA kits (R&D systems, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instruction and were expressed as pmol/ml.
Protein Content Estimation
Lowry method was utilized to measure the total protein content of the samples [
26].
Histopathological Examinations
Fixed colon tissues of all groups were embedded in paraffin. Then, vertical sections of the tissues were cut and stained with hematoxylin and eosin and later evaluated with a light microscope for any histoarchitecture changes in the colonic mucosa.
Western Blotting Analysis
To evaluate the effect of SMN treatment strategies on crucial anti-apoptotic and pro-apoptotic genes involved in CRC, the protein levels of BAX and Bcl-2 in colon samples of all test groups were estimated via western blotting. First, RIPA buffer (Sigma-Aldrich, USA) was utilized to prepare colon tissue protein samples for the test. Bradford method was used for determining the protein concentration of the colon samples. Later, protein separation was carried out via 10% SDS-poly acrylamide gel electrophoresis, followed by transferring the separated proteins onto the PVDF membrane (Sigma-St. Louis, MO, USA). Thereafter, the PVDF membrane was placed in a buffer containing 5% bovine serum albumin at room temperature for 2 h, followed by adding polyclonal primary antibodies (Santa Cruz, UK) of BAX and Bcl-2 and incubating at 4 ºC overnight. This step was followed by adding secondary antibodies (Santa Cruz, UK), and incubating at room temperature for 2h. Eventually, enhanced chemiluminescence (BIO rad, USA) was applied for antigen-antibody visualization, and Image J software (National Institute of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, USA) was utilized for densitometry analysis.
Results
General Observations
All mice except for the CAPIRI and DMH groups could survive until the end of the study period. Three mice in the CAPIRI group and one mouse in the DMH group died during the experimental period. The data regarding the body weight changes and the growth ratio are presented in
Table 1. DMH-exposed mice displayed a significant weight loss at the end of the study compared to the control group (P<0.05). Except for SMN alone and SMN-IRI, other treatment strategies did not significantly affect the weight changes compared to the DMH group. A significant difference in weight gain was seen between the CAPIRI and SMN-CAPIRI groups (P<0.05). Additionally, the growth rate was calculated as the difference between the final and initial weight gain divided by the total days (126) of the study. The results indicated that DMH led to a remarkable reduction in the weight gain and growth rate parameters; while SMN alone, SMN-IRI, and SMN-CAPIRI experimental groups showed significant changes in the weight gain and growth rate compared to the DMH group. SMN-CAPIRI could significantly improve the growth rate in comparison with CAPIRI, as well (P<0.05).
Effects of SMN-added Chemotherapy Regimens on Colonic Polyp Incidence
The results showed that the highest percentage of tumor incidence belonged to the DMH group (100%) and the polyps were usually observed at the distal segment of the colons. SMN alone could significantly reduce tumor incidence to half of the DMH group. Further, the tumor incidence in SMN-CAP was lower than SMN lone and SMN-IRI. The highest reducing effect was observed in SMN-CAPIRI (4%) followed by CAPIRI (8%) suggesting their ability for optimum prevention of DMH-induced CRC (
Table 2,
Figure 2).
Effects of SMN-added Chemotherapy Regimens on the Lipid Profile
Any alterations in lipid profile indices are presented in
Table 3. Our results indicated that DMH significantly increased serum TC levels compared to the control group (P<0.05). All treatment regimens could markedly reduce TC levels especially CAPIRI and SMN-CAPIRI regimens could restore TC alteration to normal levels (P<0.05); nonetheless, no significant changes were found among groups 3, 4, and 5 in TC levels (P>0.05).
DMH also elevated TG levels significantly relative to the control group (P<0.05). In all groups, there was a significant decrease in serum TG levels compared with the DMH group (P<0.05). There were not any significant changes among groups 3, 4, and 5 in TG levels. Despite a decrease in TG levels due to SMN-CAPIRI treatment relative to CAPIRI, the changes were not statistically significant (P>0.05). HDL levels declined significantly in the sera of DMH-treated mice in comparison with the control mice; while insignificant and significant increases in HDL levels were seen in SMN-IRI and other all treatment groups, respectively (P<0.05). In addition, DMH elevated LDL levels significantly as compared with the control group; however, they were reduced significantly by all chemotherapy regimens (P<0.05). SMN alone reduced LDL levels more than SMN-added monotherapy regimens (P<0.05). No significant differences between SMN-CAP and SMN-IRI as well as CAPIRI and SMN-CAPIRI were observed (P>0.05). Notably, CAPIRI and especially SMN-CAPIRI treatment groups could normalize the alterations of lipid profile.
Effects of SMN-added Chemotherapy Regimens on the Circulatory Inflammatory Cytokines and LDH Levels
Data regarding the serum levels of TNF-α, CRP, and LDH are presented in
Table 4. The results indicated that the serum TNF-α and CRP levels elevated significantly in the DMH group in comparison with the control group; whereas all chemotherapy regimens significantly decreased TNF-α levels compared with the DMH group (P<0.05). SMN alone and SMN-IRI were able to produce a greater reduction than SMN-CAP in TNF-α levels; while this effect was reversed in CRP levels (P<0.05). Additionally, SMN-CAPIRI caused a significant decrease in TNF-α levels and an insignificant decrease in CRP levels compared to CAPIRI (P<0.05).
Furthermore, serum LDH levels increased significantly in the DMH-injected mice in comparison with the control mice. The treatment regimens could reduce LDH levels significantly (P<0.05); however, the least decreasing effect was seen in the CAPIRI group. SMN alone followed by SMN-IRI could decrease LDH levels compared to SMN-CAP. There was a significant difference between SMN-CAP and SMN-IRI as well as CAPIRI and SMN-CAPIRI (P<0.05).
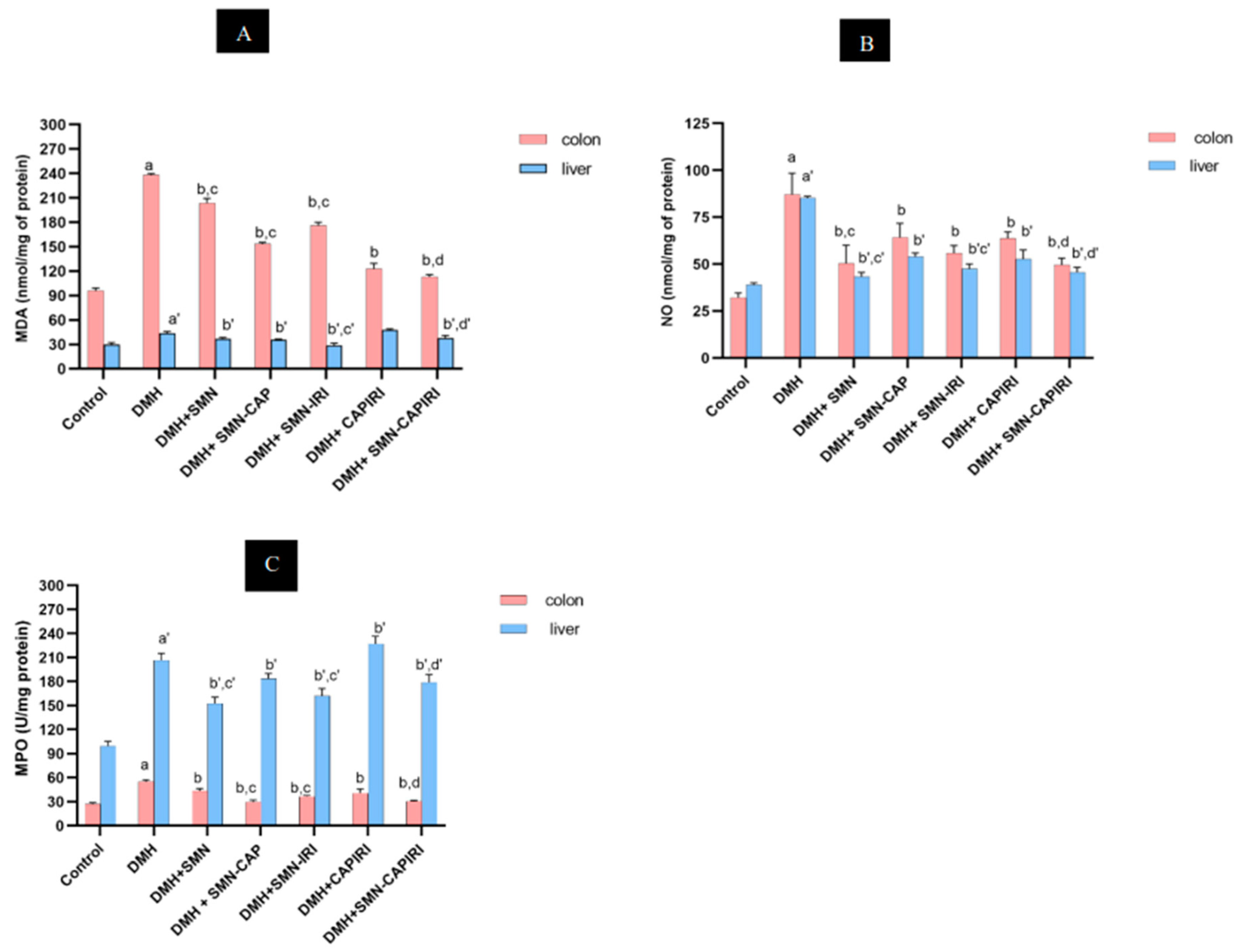
Effects of SMN-added Chemotherapy Regimens on the Colonic MDA and NO Content and MPO Activity Levels
The changes in the levels of MDA and NO as well as MPO activity are indicated in
Figure 3A,
Figure 3B, and
Figure 3C, respectively. The results displayed that DMH treatment led to a considerable rise in the MDA levels of colon tissue in comparison with the control group; whilst, they reduced significantly in all treatment groups (P<0.05). SMN-CAP had the highest-reducing capacity as compared with SMN alone and SMN-IRI. Also, the levels of MDA decreased more in the SMN-CAPIRI group than in the CAPIRI-treated mice. SMN-CAPIRI reduced MDA levels significantly as compared to CAPIRI (P<0.05).
DMH caused a considerable increase in the colonic NO levels, which were reversed significantly by all chemotherapy regimens (P<0.05). SMN alone had the best-decreasing effect in comparison with SMN-CAP and SMN-IRI; while no significant changes were observed between SMN-CAP and SMN-IRI. Furthermore, SMN-CAPIRI had a significantly greater effect on reducing the NO levels in comparison with CAPIRI.
The levels of colonic MPO activity were assessed, as well. Our findings demonstrated that DMH led to a significant elevation in the MPO activity in the colonic homogenates compared to the control group (P<0.05); whereas, it decreased significantly in all chemotherapy groups. The evaluation of the effects of SMN alone and in combination with CAP and IRI revealed that SMN-CAP had the strongest attenuating effect on the colonic MPO activity (P<0.05). Besides, adding SMN to the CAPIRI combination therapy resulted in a significant decrease in the colonic MPO activity levels (P<0.05).
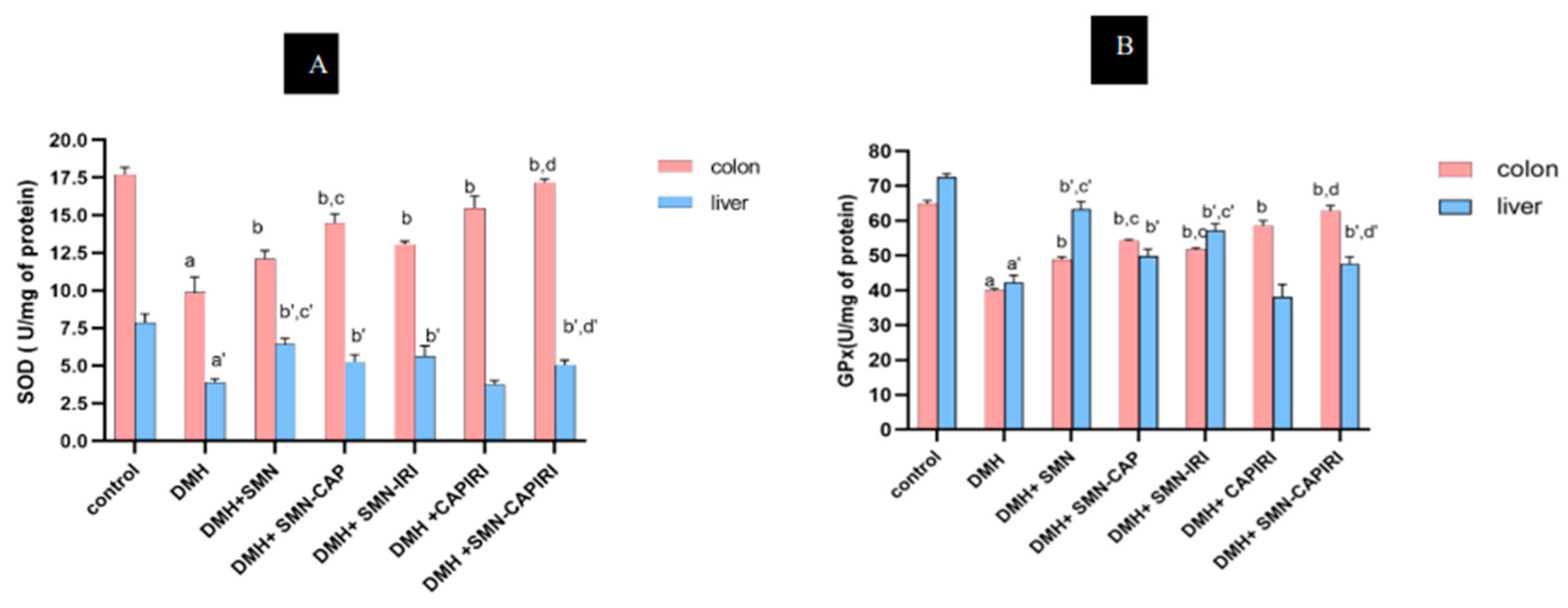
Effects of SMN-added Chemotherapy Regimens on the Circulatory and Colonic Antioxidant Enzymes
The antioxidant changes are presented in
Table 4 and
Figure 4A,B. SOD activity in the colon and serum was significantly lowered in the DMH-treated mice compared to the control mice; however, the circulatory and colonic SOD levels elevated significantly in all chemotherapy groups relative to the DMH-administered group (P<0.05). SMN-CAP caused a significant rise in the colonic SOD levels in comparison with SMN-IRI and SMN-alone; while the changes in the circulatory SOD levels between SMN-CAP and SMN-IRI showed no significant differences (P<0.05). In addition, circulatory and colonic SOD levels were significantly (P<0.05) increased by the SMN-CAPIRI regimen compared with CAPIRI.
Similarly, DMH led to a remarkable reduction in the circulatory and colonic GPx activity which was reversed by all treatment regimens (P<0.05). The circulatory and colonic GPx activity in the SMN-CAP group showed a significant increase compared to SMN-IRI and SMN alone. Moreover, there were significant differences (P<0.05) in the circulatory and colonic GPx activity between SMN-CAPIRI and CAPIRI regimens.
Effects of SMN-added Chemotherapy Regimens on Liver
We examined the liver function enzymes together with inflammation and oxidative stress markers of the liver to assess the liver changes during carcinogenesis and chemotherapy. The alterations regarding the liver examinations are shown in
Table 3 and
Table 4, and
Figure 3 and
Figure 4.
Our results indicated that DMH exposure led to a significant increase in serum transaminases compared to the control group (P<0.05). All treatment regimens could restore the alterations significantly (P<0.05). SMN alone had the highest reducing effect on ALT levels; whereas, the least decreasing effect was observed in the CAPIRI regimen. SMN-CAPIRI compared to CAPIRI could significantly decline the transaminase levels (P<0.05).
Furthermore, DMH led to a noticeable increase in the hepatic MDA levels and MPO activity to those of the control group (P<0.05). The treatment regimens could significantly reduce them as compared with the DMH group except for CAPIRI which caused elevated amounts of MDA and MPO (P<0.05). Contrary to the colonic MDA values, SMN-IRI reduced the liver MDA levels better in comparison to the SMN-CAP and SMN alone; while, concerning MPO activity, the most improving effect was seen in SMN alone group compared to SMN-supplemented monotherapies (P<0.05). Moreover, there was a significant difference between SMN-CAP and SMN-IRI in MDA and MPO levels (P<0.05). SMN addition to CAPIRI chemotherapy could reduce MDA and MPO levels markedly as compared to CAPIRI (P<0.05).
Hepatic NO levels in the DMH group showed a dramatic increase compared with the control group (P<0.05). Surprisingly, all treatment strategies declined NO levels significantly when compared with the DMH group (P<0.05). SMN alone had the most pronounced decreasing effect relative to the SMN-added monotherapy agents. Furthermore, SMN-IRI compared to SMN-CAP as well as SMN-CAPIRI compared to CAPIRI led to a significantly greater decrease in the hepatic NO levels (P<0.05).
A significant decrease in SOD and GPx activity levels in DMH –exposed mice was evident in the liver homogenates (P<0.05); whilst, all treatment groups except for CAPIRI could enhance the antioxidant activities (P<0.05). In both enzymes, SMN alone exhibited the most pronounced effect on increasing the enzyme activities (P<0.05). SMN-IRI caused a significant and insignificant increase in the SOD and GPx levels relative to SMN-CAP, respectively (P<0.05). Moreover, a significant elevation in the antioxidant activity of liver specimens was shown in SMN-CAPIRI as compared with CAPIRI (P<0.05).
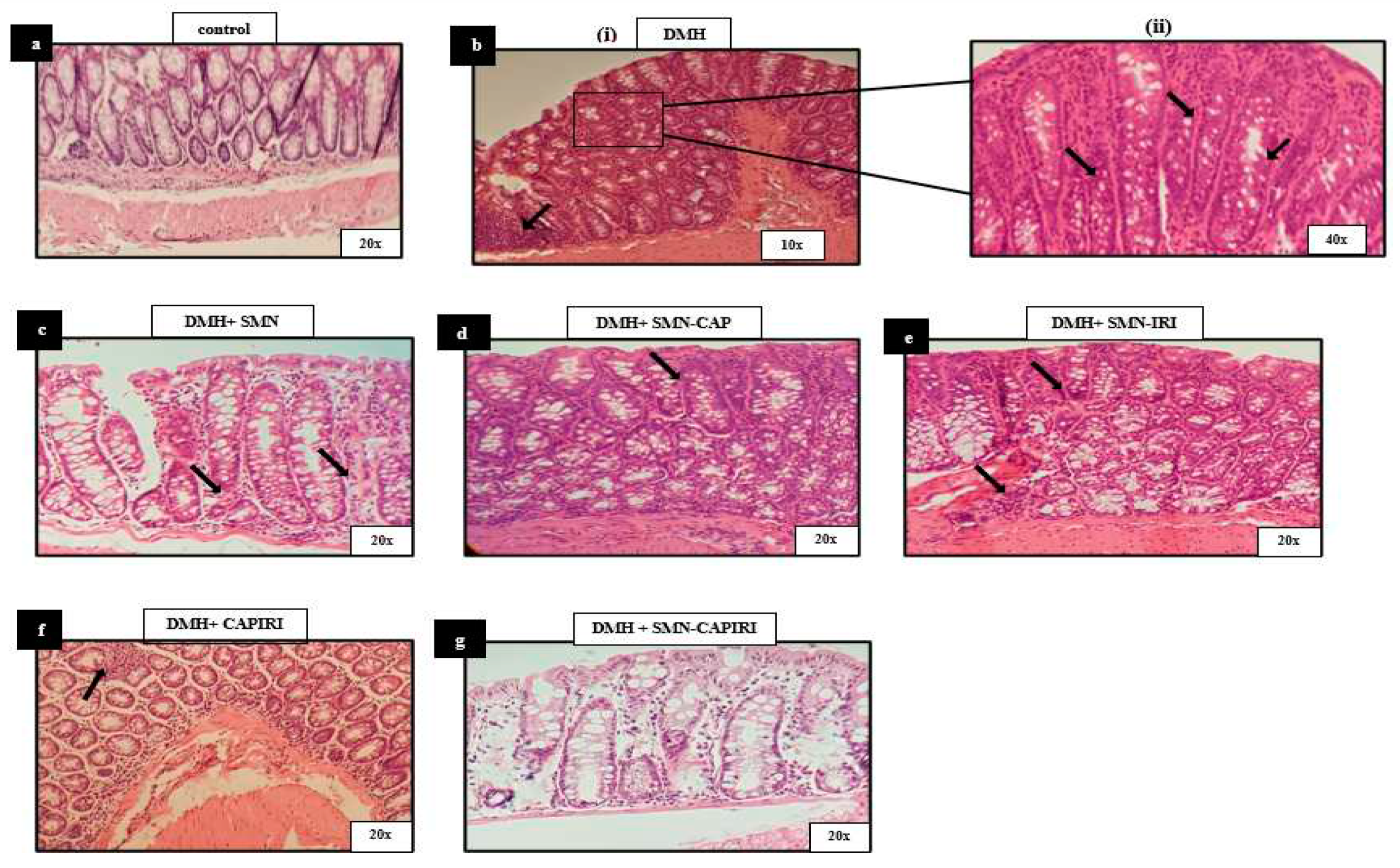
Effects of DMH and SMN-added Chemotherapy Regimens on the Colon Histopathology
The histopathological assessment of the control group exhibited the normal structure of the colon mucosa. Exposure to DMH caused high-grade dysplastic changes including goblet cell depletion, nuclear pleomorphism, and stratification. In addition, lymphocytic aggregation and infiltration were observed. Nevertheless, treatment with SMN alone and in combination with CAP and IRI resulted in a remarkable elevation in the number of goblet cells as well as a reduction in the stratified and inflamed areas, thus, an amelioration of the dysplastic changes was apparent. Notably, the changes in SMN-added chemotherapy agents were obvious in the lower parts of the mucosa adjacent to the muscular layer. Moreover, CAPIRI and SMN-CAPIRI regimens resulted in almost complete resolution of the dysplastic changes. The minor traces of inflammation in the CAPIRI group were eliminated in the colon sections of the SMN-CAPIRI group (
Figure 5).
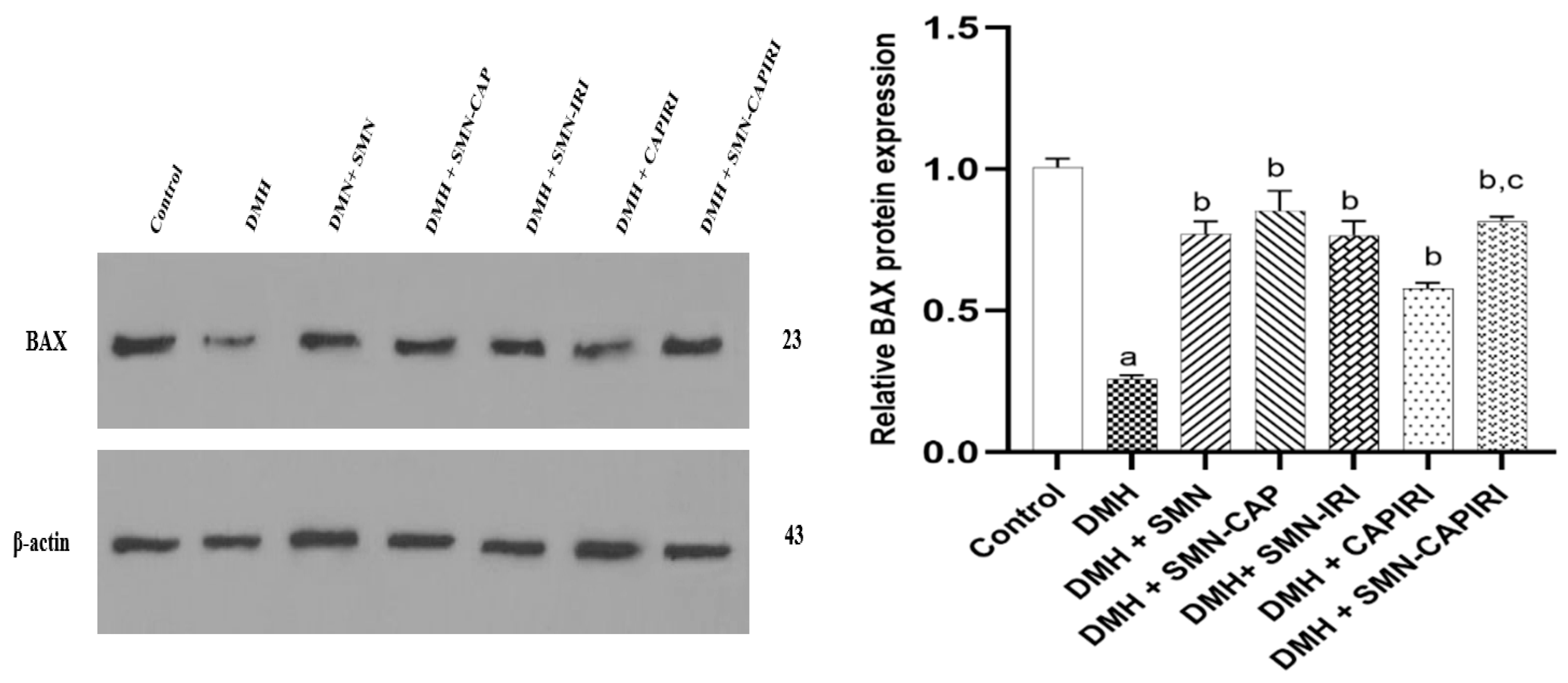
Effects of DMH and SMN-added Chemotherapy Regimens on the Protein Expression of BAX and Bcl-2
BAX levels were found to reduce dramatically in DMH-administered mice in comparison to the control group mice. The treatment regimens could significantly increase the BAX levels (P<0.05). SMN addition to CAPIRI could upregulate BAX expression levels significantly when compared to CAPIRI (P<0.05); nonetheless, no significant changes were observed among SMN alone and SMN-added monotherapy agents (
Figure 6).
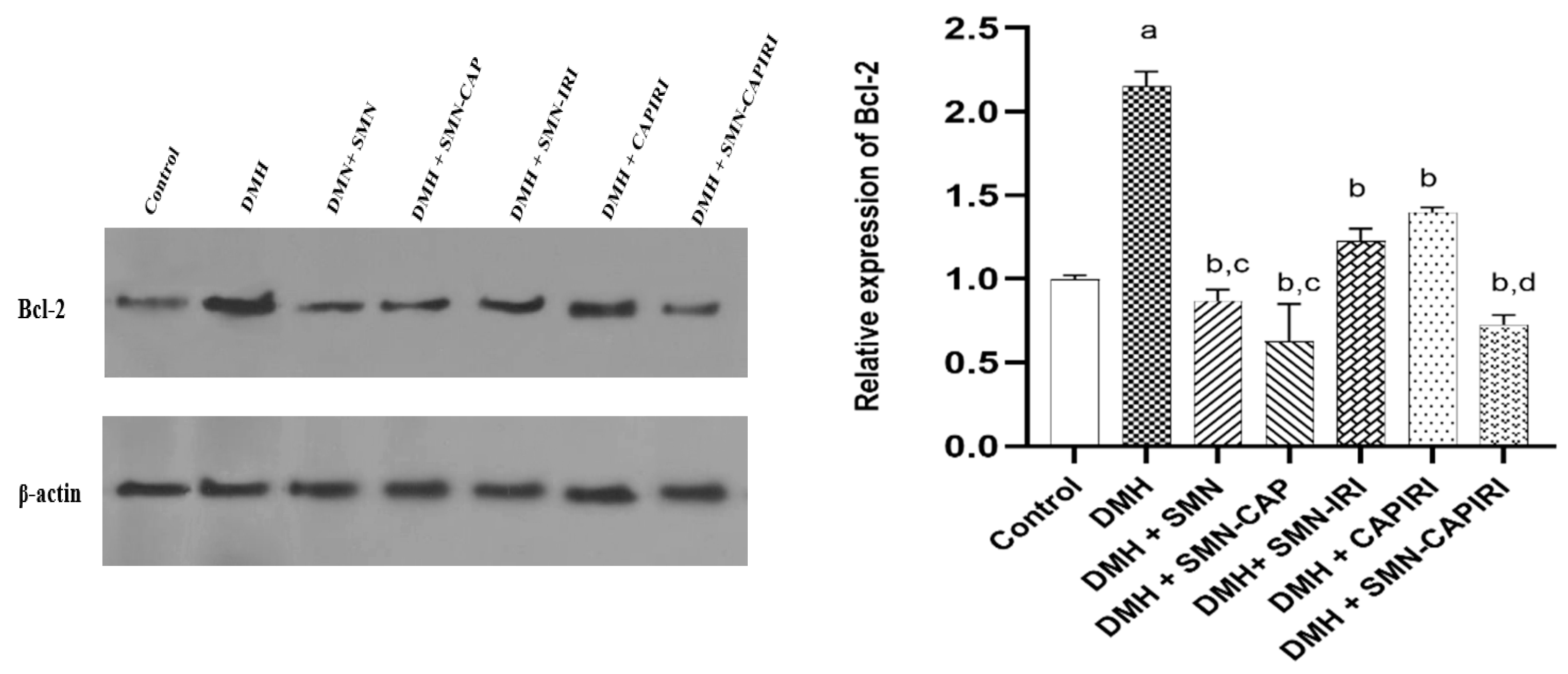
On the other hand, DMH administration caused a remarkable elevation in Bcl-2 expression levels which was reversed significantly in all treated groups (P<0.05). SMN-CAP had a better effect compared with SMN-IRI while no significant changes were seen between SMN lone and SMN-CAP (P<0.05). SMN-CAPIRI was able to downregulate the expression of Bcl-2 noticeably relative to CAPIRI and almost near to the control group (
Figure 7).
Discussion
Previous reports have documented the close association between inflammation and CRC development. Thus, patients enduring ulcerative colitis are at high risk of CRC progression [
27]. A combination of chemotherapy agents is extensively utilized for various types of cancer, which in the case of CRC adjuvant fluoropyrimidine-based (5-FU or CAP) chemotherapy combined with oxaliplatin and/or IRI is frequently used [
28]; however, organ toxicities mainly the hepatotoxicity caused by every single drug may accumulate, and therefore, affect the treatment process negatively. Studies postulated that the addition of dietary supplements, especially flavonoids to traditional chemotherapy medicines could contain protective effects with lower toxicity [
29]. Given the reported anti-tumor and anti-inflammatory properties of SMN, it has been used widely in cancer prevention and treatment investigations. In the current study, we evaluated the possible potentiating effects of SMN supplementation on monotherapies and combination therapy with CAP and IRI in the mouse CRC model.
We observed that the body weight and the growth ratio of the DMH-exposed mice reduced significantly throughout the experiment period compared to the control mice, which is also reported by Thangaraj
et al. [
30]. Declined body weight and food intake are associated with altered metabolism, polyp development, and inflammation of the colon which indicates the importance of body weight changes in cancer research [
31]. SMN-supplemented IRI and CAPIRI regimens could significantly improve weight gain in mice.
Previous investigations indicated the link between dyslipidemia and increased risk of CRC [
32]. Besides, colorectal polyp formation was reported to increase in case of elevated serum levels of TG and TC [
33]. In agreement with the previous studies, we found dyslipidemia signs including remarkably increased serum levels of TG, TC, LDL, and decreased levels of HDL in mice treated with DMH [
34]. Lipid profile imbalance improved noticeably by the SMN-containing diet along with the CAPIRI combination therapy signifying the protective effect of SMN while added to the monotherapy and combination chemotherapy regimens of CAP and IRI which may be related to the decreased number of colorectal polyps in SMN-CAPIRI group that was comparable with the control group. In line with our results, supplementation with silibinin, the major active component of SMN, in DMH-induced rat colon cancer could resolve the hyperlipidemia of the carcinogen group remarkably confirming the anti-hyperlipidemic properties of silibinin [
35].
Oxidative stress is characterized by an elevation in ROS and RNS production along with a decrease in antioxidant levels that is involved in the onset and progression of CRC [
36]. Previous studies indicated that MDA as one of the main products of lipid peroxidation and a potential mutant was attributed to the occurrence of CRC [
5]. Meanwhile, colon cells exposed to DMH were indicated to possess the characteristics of cancerous cells due to the increased levels of lipid peroxidation [
37]. Further, NO is one of the mediators of the major CRC pathways e.g., Wnt/ β-catenin and higher levels of NO were seen in the inflamed and cancerous areas due to the over-expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in inflammation-induced CRC [
38]. SOD and GPx are the major enzymatic antioxidants that are directly involved in ROS elimination reactions. SOD exerts its antioxidant activity through scavenging superoxide onions [
39]. GPx as one of the members of the glutathione system is responsible for the elimination of hydrogen peroxides [
40]. Various reports suggested that DMH can decrease the levels of antioxidant enzymes like SOD, CAT, GR, and GPx [
5,
41]. Similarly, our results demonstrated the signs of impaired redox balance in favor of oxidants, since DMH increased the colonic levels of MDA and NO and concomitantly decreased the circulatory and colonic SOD and GPx activities; while all treatment strategies could alleviate the oxidative stress conditions. SMN-CAP could improve serum and colonic oxidative stress markers (MDA, SOD, and GPx) the most pronouncedly among SMN alone and SMN-containing monotherapies; whereas SMN alone had the greatest alleviating effect on colonic NO levels. Also, SMN supplementation in the diet could improve the effects of the CAPIRI regimen. SMN has been shown to exert its antioxidant activity through scavenging free radicals and affecting antioxidant systems linked to SOD and glutathione. These effects are due to the phenolic nature of SMN which makes it capable of stabilizing free radicals and ROS via donating electrons [
42]. Moreover, Sangeetha
et al. showed that silibinin could act as a chemopreventive substance through modulating lipid peroxidation and the antioxidant defense in DMH-induced CRC [
43].
Inflammation is the physiologic reaction of the body to tissue damage; however, chronic inflammation may predispose cell mutation and proliferation, which may result in cancer initiation. Likewise, inflammatory cytokines like IL-6, TNF-α, CRP, and IL-1 have been associated with chronic inflammation [
11]. TNF-α is frequently used to describe colitis-associated CRC in animal models and high serum levels of TNF-α are attributed to an increased risk of colorectal adenomas. It also plays a key role in tumor initiation via involvement in leukocyte recruitment, angiogenesis, and invasion along with contributing to epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition [
44]. CRP is another inflammatory cytokine that plays a crucial role in the acute phase of inflammation. Moreover, it was reported that higher serum levels of CRP were linked to an increased risk of colon cancer [
45,
46]. MPO, on the other hand, as an enzyme that is mostly found in neutrophils, serves as a quantitative index of inflammation in a variety of tissues like the intestines [
47]. Zhao
et al. indicated that the oral administration of SMN could inhibit inflammatory reactions by enhancing antioxidant enzyme levels as well as reducing cytokine levels [
48]. Also, in azoxymethane-induced CRC, dietary administration of silibinin could downregulate nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 [
49].
To further investigate the anti-inflammatory effects of SMN supplementation, we evaluated TNF-α, CRP, and MPO levels as the markers of inflammation. The results revealed that DMH-exposed mice had remarkably higher serum levels of CRP and TNF-α along with colonic MPO activity as compared to the mice in the control group. SMN alone could drastically decline the amounts of these factors, which was reported previously [
50]. SMN-supplementation to CAPIRI resulted in a significant reduction in TNF-α as well as an insignificant reduction in CRP and MPO levels, reflecting the potential anti-inflammatory effects of SMN; however, we obtained different results from SMN-added monotherapies which could be attributed to the different mechanisms of action of drugs and various responses to the treatment strategies. All these observations elucidated the ability of SMN to potentiate the effects of chemotherapy agents via ameliorating oxidative stress and inflammation along with possibly augmenting mechanisms of tissue repair in colonic mucosa.
It is well evidenced that dysplastic aberrant crypt foci (ACF) were the earliest detectable lesions indicating CRC development [
51]. In this regard, the microscopic observation of DMH-influenced colon tissues exhibited dysplastic ACFs and adenomas as well as the infiltration and accumulation of inflammatory cells which is supported by previous studies [
52]. SMN treatment alone and in combination with CAP and IRI could ameliorate the dysplastic changes in comparison to the DMH group. SMN-supplementation of CAPIRI also could maintain the normal appearance of colon tissue. These findings could be correlated with the antiproliferative effects of SMN, which elevated the antitumor effects of the chemotherapy agents. The antiproliferative property of SMN could be associated with its ability to improve the resistance of colon cells to lipid peroxidation, restore the activities of colonic antioxidant enzymes, and inhibit the activity of cell growth-contributing inflammatory cytokines e.g. TNF-α [
53], which may strengthen the effects of chemotherapy drugs.
Apoptosis is a crucial process in intestinal turnover, especially colons. Thus, inhibition of apoptosis is associated with the transformation of colon epithelium to carcinoma [
54]. Bcl-2 family proteins are the key regulators of apoptosis. Bcl-2 plays a key role in the early stages of CRC due to the overexpression of Bcl-2 in adenomas rather than carcinomas and inhibits apoptosis in cancer cells via suppression of BAX [
55]. The expression of the pro-apoptotic protein, BAX, was proved to reduce during the CRC initiation and progression phases. Thus, the crosstalk between these proteins and apoptosis can determine the response to therapy. DMH resulted in the upregulation of Bcl-2 and downregulation of BAX and, hence an increase in the Bcl-2 to BAX ratio in comparison with the control group which was also reported by Wang
et al. [
56]. Besides,
in vitro and
in vivo studies supported that the chemoprotective effects of SMN could be relevant to modulating the expression of BAX and Bcl-2 proteins [
57,
58]. Silibinin was also reported to elevate the mRNA and protein levels of BAX and decrease Bcl-2 levels in the azoxymethane-induced CRC model in rats [
59]. All treatment groups significantly reversed the alterations caused by DMH in apoptosis-related proteins. SMN-CAPIRI in comparison to CAPIRI resulted in a significant decrease and increase in Bcl-2 and BAX expression levels, respectively. Despite we didn’t observe any significant changes among SMN and SMN-added monotherapy regimens in BAX levels, SMN-CAP could downregulate Bcl-2 levels considerably in comparison to SMN alone and SMN-IRI. These observations supported that the apoptotic properties of SMN could reinforce the effects of chemotherapy agents on BAX and Bcl-2 which further ameliorated the histopathological changes.
The liver is the major organ where most toxic agents such as drugs, pollutants, carcinogens, and mutagens go under metabolism. It was well-documented that the free radicals generated from the hepatic metabolism of DMH induce liver necrosis, fatty infiltration, and the secretion of transaminases into the circulation [
60]. Besides, most patients under chemotherapy were reported to develop liver steatosis, which can turn into inflammatory liver damage [
61]. Increased levels of transaminases and LDH are the indicators of hepatocellular damage and the possibility of liver metastases [
62]. In the current study, DMH treatment elevated ALT, AST, and LDH enzyme levels. In addition, a considerable increase in the levels of inflammation and oxidative stress indices (MDA, NO, and MPO) along with a significant reduction of enzymatic antioxidant levels was observed which were also indicated by Goyal
et al [
63]. These changes were markedly resolved by SMN alone and SMN-containing regimens implying the hepatoprotective and antioxidant effect of SMN alone and combined with chemotherapy agents. These findings could be linked to the modulatory ability of SMN on the free radicals formed during the liver metabolism of the toxic substances [
42]. The hepatoprotective and cardioprotective effect of silibinin was evidenced against doxorubicin toxicity [
64]. Moreover, SMN could decrease the elevated levels of liver enzymes and improve the histopathological changes in the liver induced by epirubicin in mice [
65]. Despite the significantly improving effects of CAPIRI on the colon examinations, we did not observe the same results in the liver examinations which could be associated with hepatotoxicity caused by this regimen exacerbated by DMH metabolism, since the hepatotoxicity of CAP and IRI was previously recorded [
61].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.H., F.K, and H.M.; Methodology, S.H., H.M.; Validation, S.H., H.M., A.A., and M.K.; Formal Analysis, S.H., H.M.; Investigation, S.H.; Resources, F.K.; Data Curation, F.K. and H.M.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, S.H; Writing—Review and Editing, F.K., H.M., A.A., and M.K.; Visualization, S.H.; Supervision, F.K.; Project Administration, F.K.; Funding Acquisition, F.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Figure 1.
The time course and treatment design.
Figure 1.
The time course and treatment design.
Figure 2.
Macroscopic evaluation of the polyps.
Figure 2.
Macroscopic evaluation of the polyps.
Figure 3.
Effect of SMN-supplementation in chemotherapy regimens on the colonic and hepatic MDA, NO, and MPO levels. Data were represented as Mean ± SD. Values are statistically significant at P< 0.05. a, a’: significant differences between DMH and control; b, b’: significant differences between DMH and treatment groups; c, c’: significant differences among DMH+SMN, DMH+SMN-CAP, and DMH+SMN-IRI; d, d’: significant differences between DMH+CAPIRI and DMH+SMN-CAPIRI. (a-d: colon, a’- d’: liver). MDA; malondialdehyde, NO; nitric oxide, MPO; myeloperoxidase.
Figure 3.
Effect of SMN-supplementation in chemotherapy regimens on the colonic and hepatic MDA, NO, and MPO levels. Data were represented as Mean ± SD. Values are statistically significant at P< 0.05. a, a’: significant differences between DMH and control; b, b’: significant differences between DMH and treatment groups; c, c’: significant differences among DMH+SMN, DMH+SMN-CAP, and DMH+SMN-IRI; d, d’: significant differences between DMH+CAPIRI and DMH+SMN-CAPIRI. (a-d: colon, a’- d’: liver). MDA; malondialdehyde, NO; nitric oxide, MPO; myeloperoxidase.
Figure 4.
Effect of SMN-supplementation in chemotherapy regimens on the colonic and hepatic SOD and GPx levels. Data were represented as Mean ± SD. Values are statistically significant at P < 0.05. a, a’: significant differences between DMH and control; b, b’: significant differences between DMH and treatment groups; c, c’: significant differences among DMH+SMN, DMH+SMN-CAP, and DMH+SMN-IRI; d, d’: a significant difference between DMH+CAPIRI and DMH+SMN-CAPIRI (a-d: colon, a’- d’: liver).
Figure 4.
Effect of SMN-supplementation in chemotherapy regimens on the colonic and hepatic SOD and GPx levels. Data were represented as Mean ± SD. Values are statistically significant at P < 0.05. a, a’: significant differences between DMH and control; b, b’: significant differences between DMH and treatment groups; c, c’: significant differences among DMH+SMN, DMH+SMN-CAP, and DMH+SMN-IRI; d, d’: a significant difference between DMH+CAPIRI and DMH+SMN-CAPIRI (a-d: colon, a’- d’: liver).
Figure 5.
Photomicrographs of histologic (H&E) cross sections of the colon samples from the control, DMH, DMH+SMN, DMH+SMN-CAP, DMH+SMN-IRI, DMH+CAPIRI, and DMH+SMN-CAPIRI groups examined after 18 weeks of treatment schedule. (a) Control sections show the normal mucosal and submucosal architecture (×20). (b) (i) high-grade dysplasia and lymphocytic aggregation (10x). (ii) stratification, goblet cell depletion, lymphocytic infiltration, and atypia (40x). (c). Mild dysplasia and attenuation of inflammation (20x). (d, e) mild dysplasia (20x). (f). Almost normal histology of the mucosal and submucosal layers, mild inflammation (20x). (g). Normal histology of the mucosal and submucosal layers (20x). DMH: 1,2-dimethylhydrazine, SMN: silymarin, CAP: capecitabine, IRI: irinotecan.
Figure 5.
Photomicrographs of histologic (H&E) cross sections of the colon samples from the control, DMH, DMH+SMN, DMH+SMN-CAP, DMH+SMN-IRI, DMH+CAPIRI, and DMH+SMN-CAPIRI groups examined after 18 weeks of treatment schedule. (a) Control sections show the normal mucosal and submucosal architecture (×20). (b) (i) high-grade dysplasia and lymphocytic aggregation (10x). (ii) stratification, goblet cell depletion, lymphocytic infiltration, and atypia (40x). (c). Mild dysplasia and attenuation of inflammation (20x). (d, e) mild dysplasia (20x). (f). Almost normal histology of the mucosal and submucosal layers, mild inflammation (20x). (g). Normal histology of the mucosal and submucosal layers (20x). DMH: 1,2-dimethylhydrazine, SMN: silymarin, CAP: capecitabine, IRI: irinotecan.
Figure 6.
Effect of SMN-supplementation in chemotherapy regimens on the relative expression of BAX. Data were represented as Mean ± SD. Values are statistically significant at P< 0.05. a: significant differences between DMH and control; b: significant differences between DMH and treatment groups; c: significant differences between DMH+CAPIRI and DMH+SMN-CAPIRI.
Figure 6.
Effect of SMN-supplementation in chemotherapy regimens on the relative expression of BAX. Data were represented as Mean ± SD. Values are statistically significant at P< 0.05. a: significant differences between DMH and control; b: significant differences between DMH and treatment groups; c: significant differences between DMH+CAPIRI and DMH+SMN-CAPIRI.
Figure 7.
Effect of SMN-supplementation in chemotherapy regimens on the relative expression of Bcl-2. Data were represented as Mean ± SD. Values are statistically significant at P< 0.05. a: significant differences between DMH and control; b: significant differences between DMH and treatment groups; c: significant differences among DMH+SMN, DMH+SMN-CAP, and DMH+SMN-IRI; d: significant differences between DMH+CAPIRI and DMH+SMN-CAPIRI.
Figure 7.
Effect of SMN-supplementation in chemotherapy regimens on the relative expression of Bcl-2. Data were represented as Mean ± SD. Values are statistically significant at P< 0.05. a: significant differences between DMH and control; b: significant differences between DMH and treatment groups; c: significant differences among DMH+SMN, DMH+SMN-CAP, and DMH+SMN-IRI; d: significant differences between DMH+CAPIRI and DMH+SMN-CAPIRI.
Table 1.
Changes in body weight and growth ratio.
Table 1.
Changes in body weight and growth ratio.
Groups |
Initial body
weight (g) (1stweek) |
Final body
weight(g) (18th week) |
Weight Gain(g) |
Growth Rate |
| Control |
27.62±1.68 |
44.42±2.36 |
16.80 ± 2.30 |
0.133± 0.018 |
| DMH |
29.12±1.12 |
38.13±1.19 a
|
9.26 ± 1.46 a
|
0.073± 0.011a
|
| DMH+SMN |
27.75 ±1.28 |
41.92 ±1.18 b
|
13.55 ± 1.62 |
0.107 ± 0.010 b
|
| DMH+SMN-CAP |
28.62±1.31 |
40.75±2.48 |
12.12 ± 2.79 |
0.096 ± 0.022 |
| DMH+SMN-IRI |
28.87±1.45 |
43.01±2.95 b
|
14.14 ± 3.28 b
|
0.112 ± 0.026b
|
| DMH+CAPIRI |
28.61±1.34 |
37.45±1.13 |
8.85 ± 2.17 |
0.070 ± 0.017 |
| DMH+SMN-CAPIRI |
28.25±1.58 |
41.29±1.36 c
|
14.42 ± 2.53 b, c
|
0.110 ± 0.017 b, c
|
Table 2.
Effects of treatment strategies on colon polyps.
Table 2.
Effects of treatment strategies on colon polyps.
| Groups |
Total number of mice |
Total number
of polyps
|
Average number of
polyp-bearing mice
|
Percentage of polyp
incidence
|
| Control |
8/8 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| DMH |
7/8 |
23 |
3.21 |
100 |
| DMH+SMN |
8/8 |
12 |
1.75 |
52 |
| DMH+SMN-CAP |
8/8 |
9 |
1.125 |
39 |
| DMH+SMN-IRI |
8/8 |
11 |
1.375 |
47 |
| DMH+CAPIRI |
5/8 |
2 |
0.4 |
8 |
| DMH+SMN-CAPIRI |
8/8 |
1 |
0.125 |
4 |
Table 3.
Effect of SMN-supplementation in chemotherapy regimens on the lipid profile and hepatic enzymes changes.
Table 3.
Effect of SMN-supplementation in chemotherapy regimens on the lipid profile and hepatic enzymes changes.
Groups
|
TC (mg/dL) |
TG (mg/dL) |
HDL (mg/dL) |
LDL (mg/dL) |
ALT(U/L) |
AST(U/L) |
| Control |
83.33 ± 6.13
|
59.45 ± 2.97
|
77 ± 10.5
|
17.16 ± 2.19
|
11.25 ± 1.70 |
64. 20 ± 3.83 |
DMH
|
116.40 ± 3.04 a
|
115.2±10.48 a
|
49 ± 3.16 a
|
27.40 ± 3.50 a
|
57.00 ± 11.22 a
|
231.8 ± 29.36 a
|
DMH+SMN
|
97.30 ± 6.77 b
|
81.33 ± 11.13 b
|
65.6 ± 4.87 b
|
15.72 ± 1.86 b, c
|
16.10 ± 3.39 b
|
88 ± 3.16 b, c
|
DMH+SMN-CAP
|
99.66 ± 11.5 b
|
96.76 ± 6.1 b |
69.80 ± 3.49 b
|
24.58 ± 3.82 b
|
39.40 ± 8.41 b
|
221.4 ± 5.41 |
DMH+SMN-IRI
|
100.80 ± 5.63 b
|
91.56 ± 14.86 b
|
63.80 ± 5.26 |
23.00 ± 4.19 b
|
25.00 ± 2.84 b
|
215.20 ± 9.28 |
DMH+CAPIRI
|
96 ± 8.03 b
|
68.31±6.09 b |
70.60 ± 8.82 b
|
19.14 ± 2.00 b
|
53.5 ± 7.39 b
|
169.2 ± 26.75 b
|
| DMH+SMN-CAPIRI |
88 ± 7.35 b
|
62.42 ± 6.16 b, d
|
73.20 ± 5.80 b
|
16.38 ± 2.02 b
|
20.7 ± 3.43 b, d
|
101.50 ± 14.06 b, d
|
Table 4.
Effect of SMN-supplementation in chemotherapy regimens on the circulatory inflammatory cytokines, antioxidant enzymes, and LDH.
Table 4.
Effect of SMN-supplementation in chemotherapy regimens on the circulatory inflammatory cytokines, antioxidant enzymes, and LDH.
| Groups |
TNF-α (pmol/mL) |
CRP (pmol/mL) |
SOD(U/mL) |
GPx(U/mL) |
LDH (U/L) |
| Control |
422.1 ± 2.38 |
1553.16 ± 67.28 |
34.57 ± 0.65 |
127.9 ± 1.23 |
285.2 ± 47.65
|
| DMH |
673.6 ± 2.84a
|
2133.09 ± 49.16 a
|
19.80 ± 1.34 a
|
87.04 ± 1.73 a
|
1908 ± 203.5 a
|
| DMH+SMN |
561.3 ± 2.02b
|
1914.81 ± 36.46 b
|
24.28 ± 0.74 b
|
104.8 ± 1.79 b
|
797.1 ± 98.46 b,c
|
| DMH+SMN-CAP |
598.6 ± 4.43 b,c
|
1690.23 ± 29.95 b,c
|
28.57 ± 0.77 b,c
|
118.1 ± 1.36 b,c
|
1531 ± 115.9 b
|
| DMH+SMN-IRI |
564.2 ± 4.48b
|
1878.13 ± 22.68 b
|
26.65 ± 0.54 b,c
|
112.8 ± 0.99 b,c
|
1263 ± 181.5 b
|
| DMH+CAPIRI |
580.2 ± 6.33b
|
1884.11 ± 14.17 b
|
30.48 ± 1.12 b
|
117.3 ± 0.43 b
|
1802 ± 141.9 |
| DMH+SMN-CAPIRI |
496.4 ± 7.37 b,d
|
1828.95 ± 15.5 b
|
32.64 ± 1.21 b,d
|
123.5 ± 1.33 b,d
|
1396 ± 90.81 b,d
|