1. Introduction
Employee well-being has gained increasing importance in recent years, as evidenced by the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of burnout as a medical condition resulting from chronic workplace stress in the 11th Revision of the International Classification of Diseases [
1]. This change in classification by a globally recognized health authority acknowledges the impact of chronic stress in the workplace and promotes awareness and research into preventative measures and supportive policies.
The majority of studies assessing and improving well-being rely on surveys, which impose a burden on employees due to the time required for completion. This limitation hinders the frequent assessment of well-being, which is crucial for improvement. A potential solution to this limitation is to assess well-being in real-time and provide individuals with feedback, a process referred to as virtual mirroring [
2].
To realize this vision, it is first necessary to develop a method to identify relevant communication features, e.g., speech patterns, relating to individual well-being during collaboration [
3]. These features can then be reflected back to employees, enabling them to become more aware of their well-being. This process can lead to behavioral changes that enhance happiness and the quality of relationships with others [
2]. The primary objective of this study is to determine the appropriate computational methods and measurements to facilitate the implementation of virtual mirroring in the context of employee well-being.
Our contribution is the creation of a noise-robust multi-modal speaker diarization tool applied on a curated dataset of 20 teams collaborating on a creative task for four days. Our tool accounts for background noise and determines speaker identities through speaker diarization for teams working in close proximity. This tool facilitates the multi-modal analysis of speech signals captured in noisy field settings. Privacy concerns are addressed by identifying and removing the data from individuals who want to opt out of data collection. To encourage further research, the algorithms are implemented in a modular design, and the output is standardized by a rich transcription time marked (RTTM) file. Further, an automatic feature extraction pipeline is developed. This pipeline computes a plethora of speech features per individual, time series as well as aggregates, throughout each teamwork session. Lastly, predictive models are developed to predict well-being based on speech features extracted from teamwork sessions, using the positive emotion, engagement, relationships, meaning, and accomplishment (PERMA) framework developed by Seligman [
4] as a theoretical foundation. By leveraging SHAP explainability, this contribution advances the understanding of the relationship between speech features and individual well-being, informing potential interventions and strategies to enhance well-being in teamwork settings.
All of our code, including speaker diarization, the automatic feature extraction pipeline, and best models, is publicly available
1. It is used by the authors of this work to answer the following research questions:
RQ1. What are the challenges of individual well-being prediction in team collaboration based on multi-modal speech data? How can they be addressed?
RQ2. Based on our own data, what are suitable algorithms and target labels for predicting well-being in teamwork contexts based on multi-modal speech data?
RQ3. Based on our own data, which speech features serve as predictors of individual well-being in team collaboration?
2. Related Work
We are drawing on related work in three areas: data collection, data preparation using speaker diarization, and data analysis to predict and understand individual well-being.
2.1. Onsite Team Collaboration Data
Numerous studies examined data collection techniques for team collaboration, with most focusing on recording at least two people using different sensing modalities [
5,
6,
7,
8,
9]. For example, Ringeval et al. [
5] used a webcam setup to record video and audio for dyadic discussions. Oxelmark et al. [
6] surveyed participants via interviews to analyze teamwork among students but did not include video and audio data. Koutsombogera and Vogel [
7] used surveys and multi-modal sensors, including video, and audio, to analyze teamwork, but the camera setup was complex and not easily replicable in a large-scale setting. Similarly, Sanchez-Cortes et al. [
8], Braley and Murray [
9] analyzed teamwork using a similar multi-modal approach, but in a controlled environment where participants did not have real-world projects to work on, but rather the usual survival task commonly used for teamwork experiments. All of these experiments were conducted in a controlled environment, and a new setup is needed to collect data in an in-the-wild environment where participant behavior is less predictable. While some experiments were conducted in-the-wild, such as in Christensen and Abildgaard [
10], in which one team was observed at their work site for several weeks using expensive cameras, these experiments are not scalable for many teams. Ivarsson and Åberg [
11] also used audio and video sensors to analyze teamwork in-the-wild, but in a different setting, i.e., hospital operating rooms.
2.2. Multi-Modal Speaker Diarization
The application scenario defines which signal can be used to determine "who spoke when". In our case of team collaboration, all team members are sitting at one table. Thus, the most reliable and least intruding way of data collection uses one 360° room camera and a room microphone. Recent studies often leveraged a multi-stage approach when incorporating video data, rather than using a single end-to-end model [
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17]. The method proposed by Yoshioka et al. [
12] uses face tracking and identification, sound source localization, and speaker identification, yet it requires multi-channel audio input. Another method, initially introduced by Nagrani et al. [
13], first performs face detection and tracking and then uses active speaker detection (ASD) to determine the synchronization between the mouth movement and speech in the video to identify the speaker. After that, the approach uses face verification to classify whether the recognized face belongs to a specific individual. However, this requires prior knowledge such as the number and images of the speakers, see also Chung et al. [
14,
17]. To solve this problem, this step was replaced by the clustering of face tracks in the latest version [
15]. This identifies all visible speakers in a video based on face embeddings and does not rely on any prior information. However, the integrated ASD step requires two models and does not use all available information, such as temporal context. Xu et al. [
16] used audiovisual information for the final clustering without comparing it with state-of-the-art face recognition systems, which could decrease the model complexity. Still, we do not yet see a publicly available speaker diarization system suitable for noisy field environments with low overall complexity.
2.3. Individual Well-Being Data Analysis
The most common method to measure well-being is the use of a survey [
18]. Prior research analyzed various predictors of subjective well-being utilizing this method, e.g., personality [
19], emotions [
20], neuroticism [
21,
22], or health [
23,
24]. None of these studies focused on teamwork context. Measuring individual well-being in the workplace is a topic that has been widely studied [
25,
26]. These studies relied on surveys, which can be time-consuming and introduce bias. Various sensors can be leveraged to collect data and automatically predict well-being, e.g., motion and temperature sensors in smart home environments [
27,
28] or smartphone application usage [
29,
30,
31]. Regarding speech features, to predict well-being in the context of depression, researchers [
32,
33,
34] used speech features obtained from audio and video, such as, interviews and reading tasks. Huang et al. [
35], Kim et al. [
36] focused specifically on speech features. Regarding work-related environments, Kuutila et al. [
37] used software repositories to predict well-being without collecting audio data. Izumi et al. [
38] took a multi-modal approach including audio and speech data. In summary, there is research on automated well-being prediction in work contexts leveraging speech features. However, we see a lack of research and related tooling focusing on speech features.
3. Study Design
This section presents the data collection, extraction of speech features, e.g., emotions or communication patterns, and data analysis, relating speech features to PERMA well-being scores.
3.1. Teamwork Setting
Study Context
Anonymous Institute (AIA) offers the Anonymous Study (AS) program [
39], combining engineering with management sciences, educating early and mid-career professionals to become technically skilled leaders in their organizations [
39]. As part of this course, students participate in a yearly workshop. This event spans five days and includes a workshop where selected companies present projects on the first day. Students form teams to work on these projects for the remaining four days, with daily milestones determining team performance.
Teams
Team sizes varied from two to five members. Out of 82 students, 56 joined the experiment. The teams were formed based on their project preferences and thus were allowed to work on their preferred projects rather than being assigned to a completely unfamiliar project. Participation in our analysis was voluntary and had no influence on their academic grades.
Each team had access to a table, a monitor, and a whiteboard. Participants used their own laptops as needed. They mostly worked together at the table, occasionally standing up to use the whiteboard. Although each team worked on a different project, the tasks were the same throughout the week (e.g., stakeholder analysis). Only teamwork sessions, which lasted between 10 and 90 minutes each, were considered for our analysis of well-being. These sessions accounted for about 25% of the daily schedule, the remaining time was allocated to workshops. The daily program consists of a mix of workshops and teamwork, with the duration of each component varying from day to day.
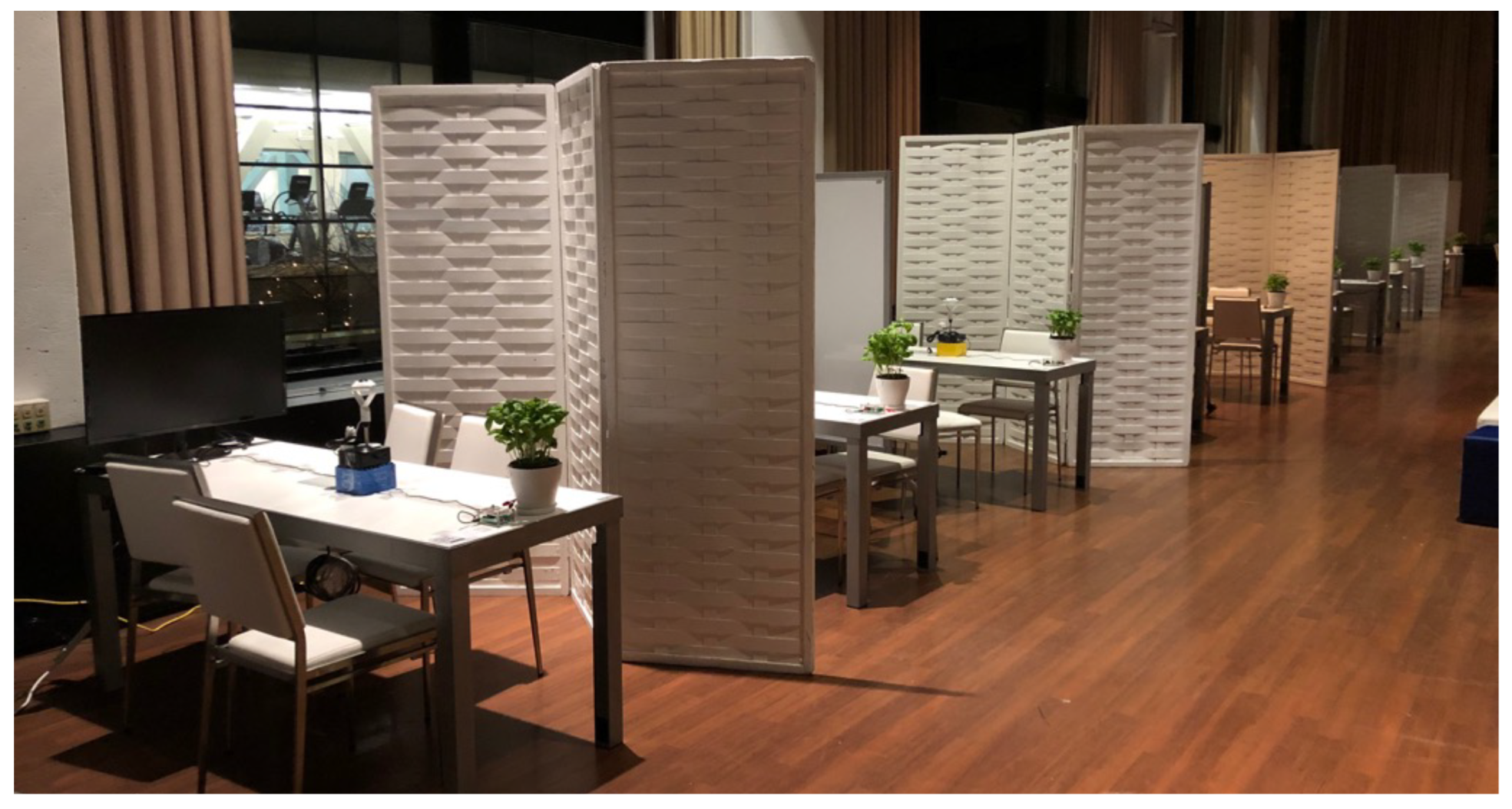
The teams were physically co-located in a single room but visually separated by whiteboards, as shown in
Figure 1.
3.2. Data Collection
Recording
For this study we collected multi-modal video and audio speech data. Video was necessary to support speaker identification in noisy environments.
To minimize the intrusiveness for the participants and to capture the faces as best as possible, one 360° camera was used for each team placed in the center of each table, see
Figure 1. We used the 360° camera JVCU360 from j5create to record at a frame rate of 30 fps in HD [
40] resulting in one video per team. To achieve a balance between audio quality, intrusiveness, and affordability, one omni-directional conference microphone from TKGOU was placed in the center of each team’s table, see
Figure 1. Audio quality was degraded by the high level of background noise which presented challenges for subsequent data cleansing. To record the captured audio and video, we opted for Zoom, a video conferencing software that is widely used in research [
41]. Zoom’s intuitive interface and two important features, noise reduction and access to unlimited cloud storage via the Enterprise license, were particularly advantageous for our experiment. Recordings were streamed directly to the cloud, stored in MP4 format, and could be accessed later, since the mapping between the meeting link and the corresponding team was stored locally. Zoom itself was running on Intel NUC mini-computers placed on the tables.
Surveys
To answer the research questions, it was necessary to collect data on the subjective well-being of the participants using the PERMA framework. We rely on the PERMA questionnaire from Donaldson et al. [
42] (29 questions), since it is validated, work-related, short, and minimizes intrusiveness for participants. It is based on the PERMA+4 model, accounting for additional variance in work-related well-being and performance through the use of four additional components: Physical health, mindset, environment, and economic security. To further minimize intrusiveness, we included only the five common PERMA pillars (P Positivity, E Engagement, R Relationships, M Meaning, A Accomplishment) in our questionnaire consisting of 16 questions. Each question was rated on a Likert scale from 1 to 7. It took between 3–5 minutes to complete the online survey.
In total, data were collected from 56 students over four days, and the PERMA survey was answered by an average of 52 students per day. At the team level, no data was collected from two teams, resulting in data from 20 teams, each of which had at least one participant with informed consent.
3.3. Data Preparation
3.3.1. Data Preprocessing
The first step of data analysis involves data reduction, which is done specifically for the video and audio data types. Based on our notes taken during the Workshop Week, the start and end times in seconds of the sessions are captured for each team in a spreadsheet, which enables the automatic extraction of the sessions using a Python script and the MoviePy library
2. No data was extracted on Wednesday of the Workshop Week, as no teamwork took place that day. After reducing the MP4 data for 20 teams, a total of 93:06 hours of data remained, representing 4:39 hours of collaboration per team and approximately 1:33 hours of collaboration per team per day.
3.3.2. Speaker Diarization
The speaker diarization model takes an MP4 file as input and outputs an RTTM file for a given video. The implementation of each algorithm in the pipeline is explained below.
Face Detection
The model weights and code for the face detection model single shot scale-invariant face detector (S3FD) are taken from a publicly available GitHub repository
3. It is trained on the WIDER FACE dataset [
43]. To reduce runtime by a factor of 2, we updated the code to track every second instead of every frame, which was implemented throughout the pipeline. Although no quantitative measures are taken to evaluate the exact impact of this change, a qualitative evaluation is performed, which is described in subsubsection 3.3.4.
Face Tracking
The face tracking algorithm used in our study is based on the code from Chung and Zisserman [
44], which is given in a publicly available GitHub repository
4. We determine the parameters of this rule-based face tracking algorithm based on the qualitative audiovisual speaker diarization evaluation in subsubsection 3.3.4 as follows. To assign a bounding box to a track, we set the threshold for intersection over union (IOU) to 0.3. We reduced this threshold in comparison to the one used for ASD
5, which is 0.5, to maintain high tracking accuracy while reducing the number of tracks. The threshold for terminating a track after a face is no longer detected was set to 100 frames (i.e., 4 seconds in a 25 frames per second (fps) video). The minimum number of faces per track was set to 25, as opposed to 10 used for ASD
5, to exclude short video tracks. Consistent with the original code, the minimum size of each detected face is one pixel.
Face Cropping
The original code5 implemented a loop for each track of the input video to crop the faces, which results in a significant increase in runtime with the number of tracks. To mitigate this problem and optimize the algorithm, a new approach was developed looping over the input video only once and directly crop the faces for all tracks.
Before saving the files, several image transformations are performed, including resizing and grayscale conversion. The order of these transformations is based on the original code5.
Active Speaker Detection
For the active speaker detection, the code from Tao et al. [
45]
5 is used as the base. However, as mentioned earlier, a downsampled version of the video data is used in our study, with every second frame processed. To ensure that the output vector of the ASD model represents the original timeline, the lengths of both the video and audio data are doubled before feeding them into TalkNet. This is achieved by replacing the skipped frames in both the video and audio data with the data from each preceding frame.
Face-Track Clustering
For each track
i containing the face of one person over time, ten face embeddings for randomly selected images
j were stored, denoted by
. To improve robustness, an average face embedding with a size of 512, denoted by
, is calculated for track
i as follows:
where
is the number of embeddings with a detection probability greater than 0.65 for track
i, and
is an indicator function that evaluates to 1 if the detection probability
, and 0 otherwise. If the indicator function evaluates to 0 for all ten images, the track is discarded as a high-quality face embedding cannot be guaranteed. The detection probability is provided by the face embedding model and is a score between 0 and 1, where 1 means the highest confidence in the face detection decision. With the threshold set to 0.65, only high-confidence face embeddings are used to calculate the average embedding, resulting in a more robust average embedding. The threshold is manually set to
based on the qualitative audiovisual speaker diarization evaluation, which is described in subsubsection 3.3.4.
To cluster the face tracks with density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise (DBSCAN), cosine similarity is used as a distance measure. The choice of a threshold is critical for determining clusters of embeddings. After running several tests, a threshold of 0.3 was found to be optimal.
RTTM File
Each person identified in the input video is assigned a unique ID in the RTTM file, and an image containing the ID as a filename is stored in a folder for identification purposes. At the end of the pipeline, a single file is created for each input video, allowing the calculation of individual audio features. Since it is a standardized format, this part is modular and can be easily replaced by other speaker diarization methods that output an RTTM file, while the subsequent parts can remain unchanged. This file standard is commonly used for speaker diarization tasks and described by Ryant et al. [
46]. Nevertheless, the generated file lacks information about the presence or absence of people in the meeting. In cases where a person does not speak in part of the meeting because they are not present, they are still counted as if they are present but not speaking. Thus, once a person is mentioned in the output file, he or she is assumed to be present for the entire duration of the meeting.
3.3.3. Audio Feature Calculation
We use standard Python to calculate speaking duration, number of utterances, and number of interruptions. These three values are calculated in an absolute and relative manner, resulting in overall six speech features. We approximate interruptions as defined by Fu et al. [
47] by checking two conditions: a) the interrupter starts speaking before the interrupted has finished and b) the interrupter speaks longer than the interrupted. In addition, three emotional features, i.e., valence, arousal, and dominance, are derived from our speech audio signals using the wav2vec 2.0 model provided by Wagner et al. [
48] on their GitHub repository
6. This approach allows the model to base its predictions solely on the content of what is said, rather than how it is said. The output layer is a three-dimensional vector, where each dimension corresponds to one of the three dimensions of emotions (arousal, dominance, and valence) and has a value between 0 and 1. We choose a time window of five minutes for our study, for each of which nine time series are computed, i.e., one for each feature. Each single time series is aggregated as explained later on.
3.3.4. Qualitative Assessment of the Software
In order to find the right parameters for the audiovisual speaker diarization and the subsequent time series feature calculation, a manual qualitative evaluation was conducted, since a complete annotation of the whole dataset for tuning each parameter is practically not feasible. Therefore, a random 30-minute video representative of the data set was selected. The video included a team of four individuals of different ethnic backgrounds and genders, including one female and three males. It should be noted that the disadvantage of using a video from the database for the evaluation is that the content cannot be controlled, while the advantage is that it represents the original environment, including factors such as background noise, video quality, and lighting conditions.
Audiovisual Speaker Diarization Evaluation
The accuracy of the audiovisual speaker diarization is evaluated by examining the output of the RTTM file. The evaluation criteria chosen are whether the speech segments are assigned to the correct person and whether they match the actual speaking segments of that person. To this end, software is written to graphically highlight the speech segments for each team member using a bounding box calculated by face recognition. The software colors the bounding box red when the corresponding person is not speaking and green when they are speaking. The track ID of each speech segment is also displayed so that it can be analyzed to which cluster or person it is associated.
The first step in the evaluation process involves the assessment of two criteria for the speaker diarization algorithm
without skipping frames, i.e., the vanilla version. Qualitative analysis indicates that accuracy in detecting speech segments of a person is comparable to that reported in the original study of the ASD model by Tao et al. [
45]. In most cases, the software is able to detect when a person is speaking, with speaking segments interrupted by short pauses in sentences. However, the accuracy of the algorithm decreases in poor lighting conditions or when only part of a person’s face is visible. In addition, if a person’s face is not visible because they are writing on a whiteboard or turning their back, no data can be computed because the ASD model relies on the person’s frontal face. The accuracy of the face verification and clustering algorithms used to match speech segments to specific individuals is high, even for individuals wearing face masks. However, accuracy decreases in low light conditions or when only part of a person’s face is visible. In addition, it also declines as more tracks are created because of the increased chance that some outlier tracks are merged with the wrong cluster (i.e., the wrong person). Many tracks occur when a person’s face reappears frequently during the session, e.g., when they frequently leave the camera’s field of view and then return.
Next, the evaluation criteria are examined,
with frames skipped to shorten the runtime. The accuracy of the algorithm decreases when tracking every third frame, especially for short speech segments. This is likely due to the dynamic nature of the speech, which requires finer granularity in time prediction [
45]. However, when skipping every second frame, no noticeable drop in accuracy can be observed in the visual evaluation. This is especially true for the face verification algorithm, which does not depend on frame-level granularity. A decrease in accuracy is observed for very short speaking segments below 0.1 seconds, which are not detected by the software. This observation is made by comparing the two output RTTM files. However, since such segments are rare and the observed difference is small, this method is chosen for its shorter runtime. Hence, the runtime is approximately halved, which is a crucial step towards the research team’s goal of achieving real-time performance.
Audio Feature Calculation Evaluation
The evaluation criteria for accuracy of audio analysis are based on a binary classification of whether the computed features matched the ground truth or not. To assess the accuracy of the computed features, a sample RTTM file is created, which is used to test the algorithms. Since the ground truth of the speaking duration, the number of utterances, and the number of interruptions for this file are known, the accuracy of the algorithms can be determined.
Finally, the emotional content of the video is assessed using a qualitative evaluation approach. The criteria for the evaluation are based on the identification of scenes in which the model is expected to produce high or low arousal, valence, and dominance values based on linguistic information. The output of the voice emotion recognition (VER) model is then compared to the expected values and evaluated accordingly. The evaluation is performed for the entire 30-minute video. Our qualitative judgment indicates that the model performs best for arousal, consistent with the results by Wagner et al. [
49]. However, not all identified scenes show a significant increase or decrease in emotion. This can be due to the limitations of the performance measured for each of the three emotion categories described in subsubsection 3.3.3 and the fact that the current pipeline does not filter out overlaps. Consequently, the audio clip of a speech segment may also contain the voice of another person speaking at the same time.
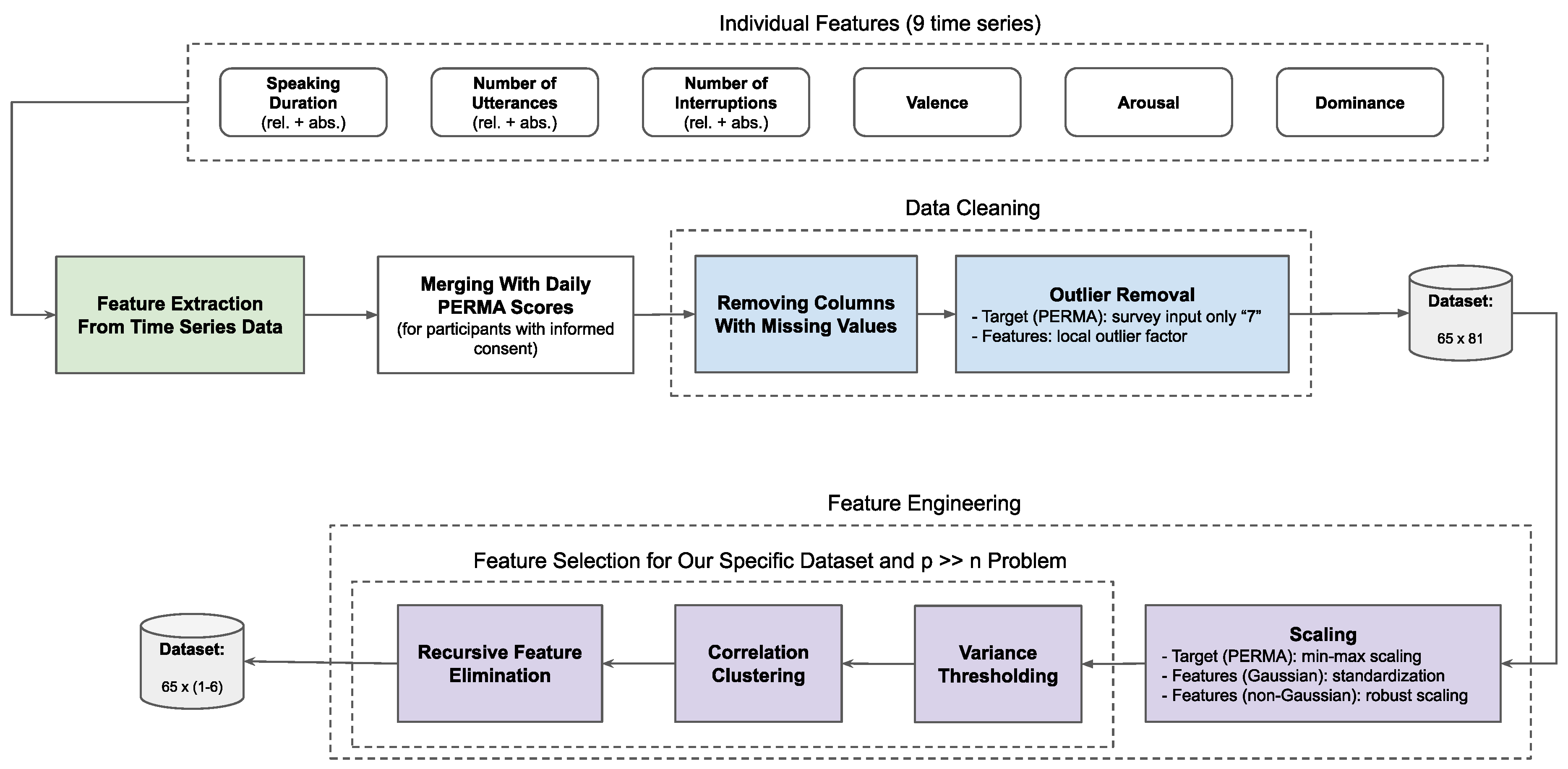
3.3.5. Feature Extraction, Data Cleaning, and Feature Engineering
The following section first describes the full pipeline, consisting of feature extraction, data cleaning, and feature engineering. It is presented in
Figure 2. To curate the dataset that serves as input to this pipeline, we extract the nine time-series features from the MP4 files of the 17 teams that are included in the final dataset. The students who did not sign an informed consent form were excluded from the feature extraction and analysis by using our visual speaker identification pipeline. Subsequently, all teamwork sessions in a day were concatenated and assigned to the corresponding daily PERMA scores, as scores are collected at the individual level and on a daily basis. In this way, this study assumes that only the teamwork sessions (and not the other workshop sessions) are reflected in the well-being scores. In addition, each day is considered independent of the others for each speaker, resulting in up to three data points per speaker, as the teamwork sessions occurred on three out of four workshop days. This leaves a total of 87 data points.
Outlier Removal
Due to the small sample size, the machine learning model is sensitive to outliers. To address this issue, we remove outliers from both the target variable and the feature set. First, we plot individuals’ PERMA scores to identify and remove three participants who completed all 16 questions with the highest possible score. To detect outliers in the feature set, we use the local outlier factor (LOF) algorithm, which is appropriate for high-dimensional data [
51]. The algorithm computes a density measure, called the glslof value, by comparing the local density of a sample to that of its neighbors, and identifies potential outliers based on this measure [
52]. We use the default number of neighbors for the corresponding scikit-learn function
7 (i.e., 20) and set the contamination value to 0.03 assuming a similar amount of outliers as for the target variable. This results in the identification and removal of two outliers. Given the training-test split as described above, 65 samples remain after the removal of all identified outliers.
Scaling
Linear regression models are sensitive to the scaling of input features, while tree-based models are not [
53]. Since both types of models are used later, feature scaling is required. Scaling is usually performed separately for each feature type [
53]. Therefore, different scaling methods are used for the target variable (PERMA scores), features with a Gaussian distribution, and features with a non-Gaussian distribution. For the target variable, two of the PERMA columns have values in the range of 3 to 7, while the range for the remaining three columns is even shorter. Assuming that this distribution is representative of future inference, and with prior knowledge of the lower and upper limits of PERMA scores based on the survey design, we apply min-max scaling from the scikit-learn library
8. This scales the resulting scores to a range between 0 and 1. This involves removing the mean and scaling the data to unit variance. Since the original features follow a Gaussian distribution, the scaled features also follow a Gaussian distribution [
53]. Because min-max scaling and standardization are sensitive to outliers [
54], robust scaling is applied to features with a non-Gaussian distribution. This involves removing the median and scaling the data according to the interquartile range and is implemented in the scikit-learn library
9 [
55].
Feature Selection
The first algorithm applied in the feature selection process is variance thresholding. In the second step, correlation clustering is applied to remove redundant features in terms of the Pearson correlation coefficient. The final step in the feature selection process utilizes recursive feature elimination (RFE) based on the scikit-learn library
10. Consequently, our approach, with rigorous validation procedures, provides a solid foundation for the robustness of our models.
3.4. Data Analysis
The computed audio features are correlated with and used to predict well-being, i.e., the PERMA pillars. Further, feature importance is explored. These three experiments are explained below.
3.4.1. Correlation of Features With PERMA Pillars
The RFE algorithm is performed separately for each target variable. Subsequently, the correlation between the selected characteristics and the corresponding target variable is determined for each pillar using the Pearson correlation coefficient. The results are then sorted in descending order from high positive to high negative correlation.
3.4.2. Evaluation of Classification Models
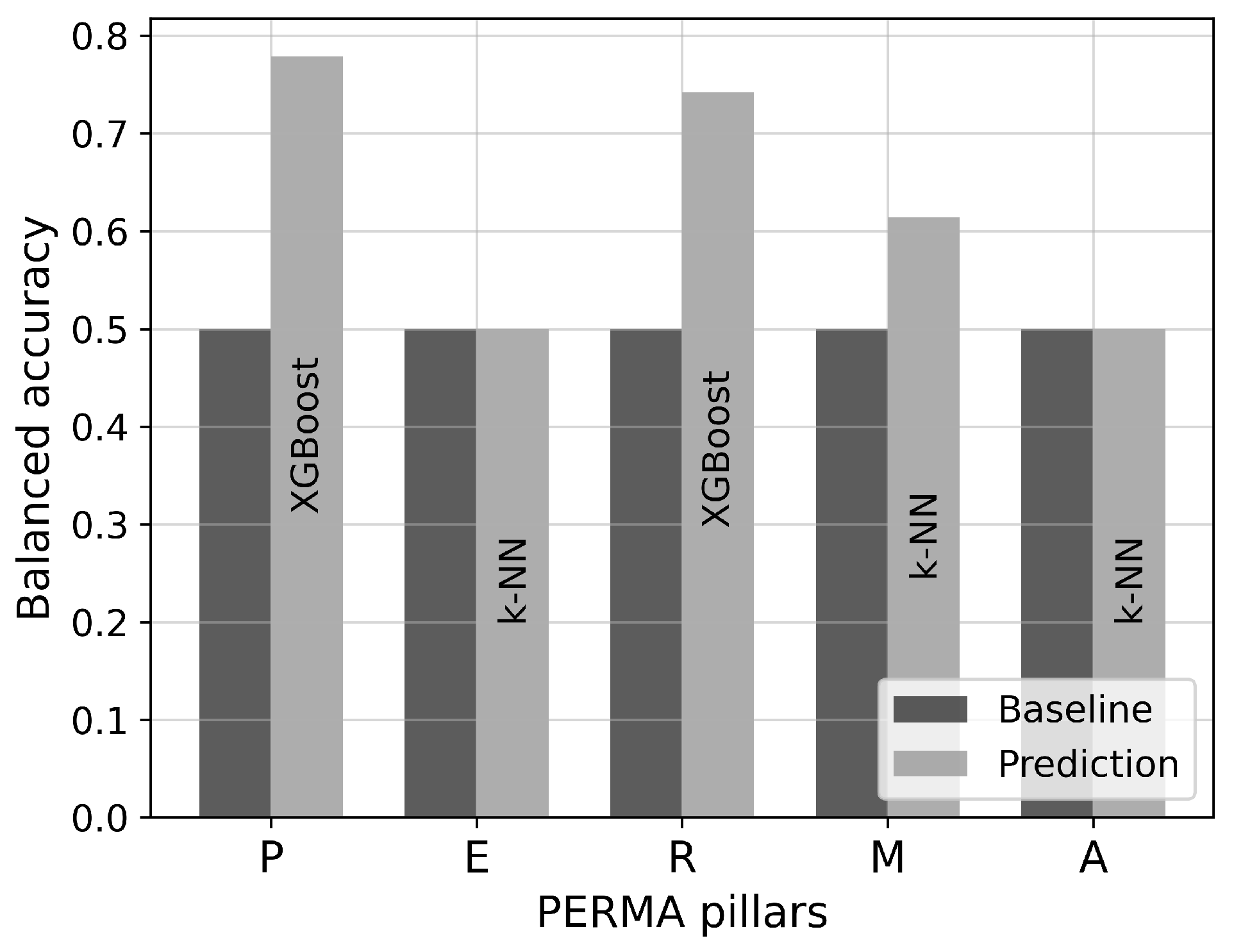
Experimenting with different prediction methods, we found that classification is well suited as a method for predicting the target variables. To this end, the target variables are categorized using percentile-based binning because the distribution of the target variables is found to be non-uniform. Here, each class represents a percentile range. However, it is important to note that this approach does not guarantee optimal class balance. For this reason, balanced accuracy is used as an evaluation measure, as it is appropriate for unbalanced datasets [
56]. The same procedure as for the regression models is used to train the classification models, including finding the best model per pillar by grid search and leave-one-out cross-validation (LOOCV). The hyperparameters used to train the four selected models are listed in
Table 1. For the k-nearest neighbor (k-NN) classifier, the hyperparameters used are the number of neighbors, distance weighting, and distance metric. For the random forest model, class_weight is set to balanced to account for imbalanced datasets, and the number of estimators in the ensemble and the maximum depth are chosen as hyperparameters to prevent overfitting. Similarly, hyperparameters such as learning rate and maximum depth are set for the extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) model. Since there is no hyperparameter for the maximum depth for the categorical boosting (CatBoost) classifier, the depth is set as a parameter in combination with the learning rate.
After training the four models for each pillar, the model with the highest balanced accuracy on the validation set is selected as the optimal model per pillar. The final performance of the selected models is evaluated by calculating the balanced accuracy on the test set. The baseline is defined as chance level, i.e.,
for four classes – see
Figure 3. In this context, the performance of a model is expected to outperform this baseline, indicating higher accuracy than random guessing. In that case, it is expected that SHAP values indicate relevant features for classification, too.
A ratio greater than 1 is expected, indicating better performance than the baseline. The version with the highest average ratio across all pillars is selected as the best performing version.
The scikit-learn library is used to implement the k-NN
11 and random forest classifiers
12. The XGBoost
13 and CatBoost
14 models are implemented leveraging the respective Python libraries.
3.4.3. Feature Importance of Classification Models
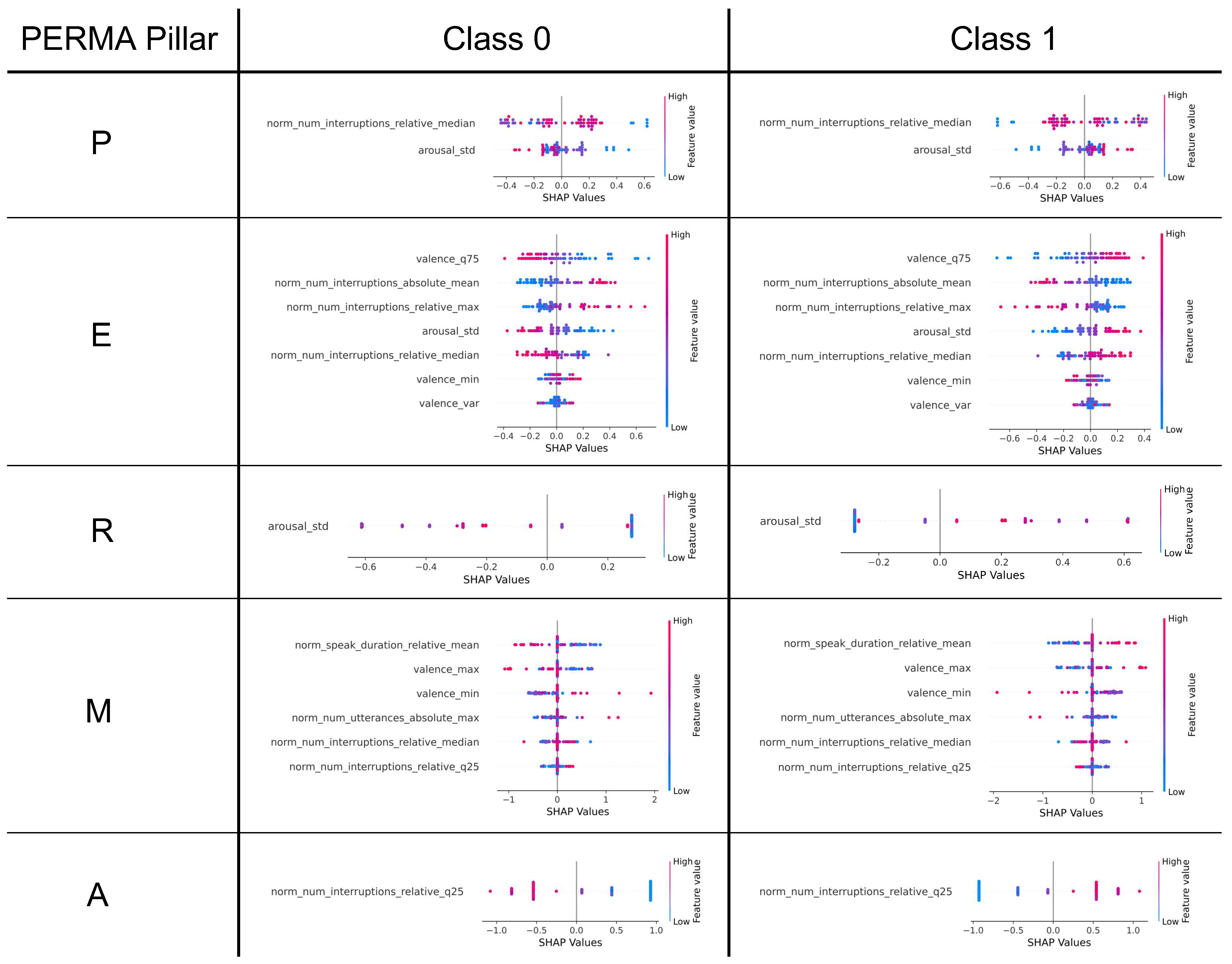
The feature importance values are calculated for each pillar. However, because feature importance for k-NN cannot be calculated directly, Shapley additive explanations (SHAP) values are used to examine the influence of each feature on the model for each class. The SHAP values are calculated for each class to better interpret which features have which influence on the class assignment. For this, the same library is used as for the regression task.
4. Results
The results of the experiments explained previously in subsection 3.4 are presented below. The interpretation of these results is done in section 5.
4.1. Selected Features for Classification Models
In
Table 2, the number of the selected features as well as the feature names are presented for each PERMA pillar in the dataset. The RFE algorithm identified the most features for pillar E and the fewest for pillars R and A. Some features are selected for multiple pillars, such as norm_num_interruptions_relative_median and arousal_std. Six of the nine original time series features are represented, while the extracted features from the relative number of utterances, absolute speaking duration, and dominance are not selected.
4.2. Evaluation of Classification Models
The final performance evaluation of the selected models is performed for each PERMA pillar on the test set after selecting the best models based on their performance on the validation set.
Figure 3 shows the comparison between the baseline and the prediction of the best models with their corresponding balanced accuracy on the test set for the two-class version. The XGBoost is the best performing model for pillars P and R, while the k-NN classifier is the best performing model for the other pillars. For pillars E and A, the prediction accuracy is equal to the baseline. The accuracy of the model for pillar P is 78%, for R 74%, and for M 61%.
4.3. SHAP Values of Classification Models
The SHAP values for each PERMA pillar are presented in
Figure 4. The interpretation of some features is obvious, such as the 75% quantile of valence for class 1 and Pillar E (Engagement), where higher values indicated by red colored points lead to higher SHAP values and thus to a higher probability of belonging to class 1. However, the interpretation of other features, such as the variance of valence for the same pillar and class, is not clear.
5. Findings
5.1. Answers to Research Questions
Three research questions are formulated and addressed in this study. Based on the results presented in the previous chapter, these are answered below.
We focused on onsite team collaboration in a real-world working scenario, i.e., up to five academic team members mostly sitting at a table while being engaged in conversations for conceptual work. Some problems encountered and proposed solutions are listed as follows. To account for many individuals whose movements cannot be controlled, it is helpful to use unobtrusive 360° cameras and room microphones for recording. Only signals from individuals should be considered who give a privacy consent, which is solved using noise-robust multi-modal speaker identification and diarization to filter data from relevant individuals. To achieve large-scale well-being data collection without incentives, the reduced and unobtrusive PERMA questionnaire from Donaldson et al. [
42] is suitable. To extract affective speech features relevant for well-being, the state-of-the-art wav2vec 2.0 model provided by Wagner et al. [
48] extracts dominance, valence, and arousal. To tackle the small number of annotated samples vs. high number of speech features, feature selection can be based on variance thresholding, correlation clustering, and recursive feature elimination. We provide the whole data pipeline as open source repository along with this publication.
One goal of this study is to identify the most appropriate method for predicting well-being based on audio data in a team collaboration context. For this purpose, the performance of classification methods is compared. Classification predicts a category such as "low" or "high" engagement, which is a common practice in sentiment analysis and is shown to be beneficial in the comparison in section A. A single classifier that performed best for all pillars cannot be identified. Instead, the XGBoost classifier proves to be optimal for pillars P and R, which also achieves the highest accuracies among all pillars. The maximum depth of the ensembled trees in both XGBoost classifiers is 5, which corresponds to the middle of the specified range. For pillars E, M, and A, the k-NN model performs better. Here, the euclidean metric rather than the manhattan metric proves optimal for all three pillars, and uniform weights perform better than distance weights.
This study suggests that the standard deviation of arousal is the most important factor for overall well-being, as it is found to be an important feature in three of the five pillars (P, E, and R). In all three pillars, a higher standard deviation leads to a higher score on the target variable. However, causality cannot be established on the basis of SHAP values alone, and further research is needed to investigate this relationship. Nevertheless, it is possible to hypothesize that high average levels of positive emotions do not necessarily lead to higher well-being. Instead, a high "emotional roller coaster", as reflected by greater fluctuations in the intensity levels associated with an emotion, might be more likely to promote overall well-being. This hypothesis is further supported by the fact that two of the three pillars where this feature is present have the highest accuracies and thus reliabilities among all pillars, with 78% and 74% for pillars P and R, respectively.
5.2. Limitations
Our study shows limitations both on the technical and the organizational side.
On the organizational side, positive psychology frameworks, such as PERMA, are known to be sensitive to cultural, gender, and social class differences [
57,
58,
59]. Therefore, people from different cultures may rate their well-being differently in surveys. This potential source of bias is not considered in this study. Also, the results cannot be generalized due to the limited sample size and the specific group of participants.
Besides that, both the ASD and face detection algorithms depend on visible and frontal faces, which makes it difficult to capture speech segments when the subjects’ faces are not visible or frontal. In addition, the performance of the ASD algorithm decreases with more visible faces in the video and fewer pixels per face, as explained by Tao et al. [
45]. Another limitation comes from creating a single RTTM file per teamwork session, which assumes that a person who speaks once in the session is present for the entire duration. The current system cannot distinguish between a person’s absence and their silence during the session.
While a qualitative assessment of the built speaker diarization and audio feature calculation system is conducted, there is a lack of quantitative measures to support the reliability of the system.
When computing emotions such as valence, arousal, and dominance, overlapping speech is not filtered out because single-channel speech separation techniques are not effective in real-world multispeaker scenarios [
60]. Moreover, the study of VER is an ongoing research topic with challenges such as improving valence performance and addressing generalization and robustness issues [
49].
The calculation of the number of interruptions has to be approximated because more information is needed to follow the exact definition, e.g., through speech recognition.
Moreover, features such as interruptions, speaking duration, and the number of utterances are culture-dependent. It has been observed that people from Western countries, such as the U.S. and Germany, tend to avoid silence during a conversation, while people from Eastern countries, such as India and Japan, appreciate it [
61].
Finally, this study used only a limited number of audio features to predict well-being, which does not comprehensively capture the full spectrum of communication processes in a teamwork session. Furthermore, individual well-being in a team is influenced not only by team processes such as communication but also by input variables such as team composition and other team processes such as cohesion.
Although all best practices are followed to avoid overfitting, too few data samples are available to train reliable and robust machine learning models. Consequently, the accuracy of the models on the validation set fluctuates depending on the training split used. It should be noted that although the final accuracies of the two-class version have an average accuracy of 62.71% per pillar, which is better than the baseline accuracy of 50%, the performance is still not sufficient to reliably predict well-being.
In addition, the SHAP values do not provide causal information about the relationship between features and target variables. Instead, they serve to identify features that strongly influence the predictions of the model. Although this information may suggest causality in some cases, it should be used with caution because it does not necessarily prove it.
6. Future Work
To enhance the overall robustness of speaker diarization, multiple state-of-the-art systems can be fused by applying the diarization output voting error reduction (DOVER) method [
62], which combines multiple diarization results based on a voting scheme. To obtain a quantitative measure of the built speaker diarization system, it can be evaluated based on the diarization error rate (DER) by using standard datasets, such as VoxCeleb [
13], VoxCeleb2 [
14], or AVA-AVD [
16]. These datasets provide a benchmark for speaker diarization systems and allow for a comparison of the performance of the developed system to state-of-the-art approaches.
Moreover, VER can be improved by adding visual information, as suggested by Rajasekar et al. [
63].
Since well-being cannot be predicted from audio data alone, additional team processes and inputs based on the input-process-output (IPO) model can be included to improve prediction quality. This requires deriving new features that can be extracted from the same dataset, e.g., video features as used by Müller [
64]. New features can also be calculated by using state-of-the-art speech recognition methods such as Whisper [
65] to extract linguistic features. The inclusion of these additional features can potentially improve the performance of the model and deepen our understanding of the factors that contribute to well-being.
To reduce variability and increase model accuracy, it is necessary to obtain a larger number of data samples. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct additional experiments that are similar in nature and combine the resulting datasets with those collected in this study.
7. Conclusion
In conclusion, this study aims to predict individual well-being based on audio data from teamwork sessions, focusing on identifying the best method and understanding which speech features are the most important predictors. This research suggests that classification methods, particularly two-class classification, are best for predicting well-being based on the PERMA framework. Different machine learning models, such as XGBoost and k-NN, are shown to be optimal for different PERMA pillars.
The study identifies important features for the prediction of each PERMA pillar, with the standard deviation of arousal being the most important factor for well-being. A higher variation in the arousal of a person’s voice is related to higher perceived well-being. Further research could investigate causality between these feature relationships. However, this research shows the potential to use speech features as proxies for automatically predicting well-being without the need for surveys. This is an important step toward virtual mirroring, allowing individuals to improve their happiness.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.G.; methodology P.G. and J.H.; software, T.Z.; formal analysis, T.Z. and M.M.; investigation, T.Z. and M.M.; resources, I.V. and P.G.; data curation, T.Z. and M.M.; writing—original draft preparation, T.Z.; writing—review and editing, T.Z. J.H. P.G., and I.V.; visualization, supervision P.G., I.V. and J.H .; project administration, I.V. and P.G.; funding acquisition, I.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by MIT COUHES under IRB 1701817083 dated 1/19/2023
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data is unavailable due to privacy restrictions.
Acknowledgments
We thank Bryan Moser for generously supporting our experiments, and Luis De la Cal for his assistance in running the experiments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
| AIA |
Anonymous Institute. |
| AS |
Anonymous Study. |
| ASD |
active speaker detection. |
| CatBoost |
categorical boosting. |
| DBSCAN |
density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise. |
| fps |
frames per second. |
| IOU |
intersection over union. |
| IPO |
input-process-output. |
| k-NN |
k-nearest neighbor. |
| LOF |
local outlier factor. |
| LOOCV |
leave-one-out cross-validation. |
| PERMA |
positive emotion, engagement, relationships, meaning, and accomplishment. |
| RFE |
recursive feature elimination. |
| RTTM |
rich transcription time marked. |
| S3FD |
single shot scale-invariant face detector. |
| SHAP |
Shapley additive explanations. |
| VER |
voice emotion recognition. |
| XGBoost |
extreme gradient boosting. |
Appendix A
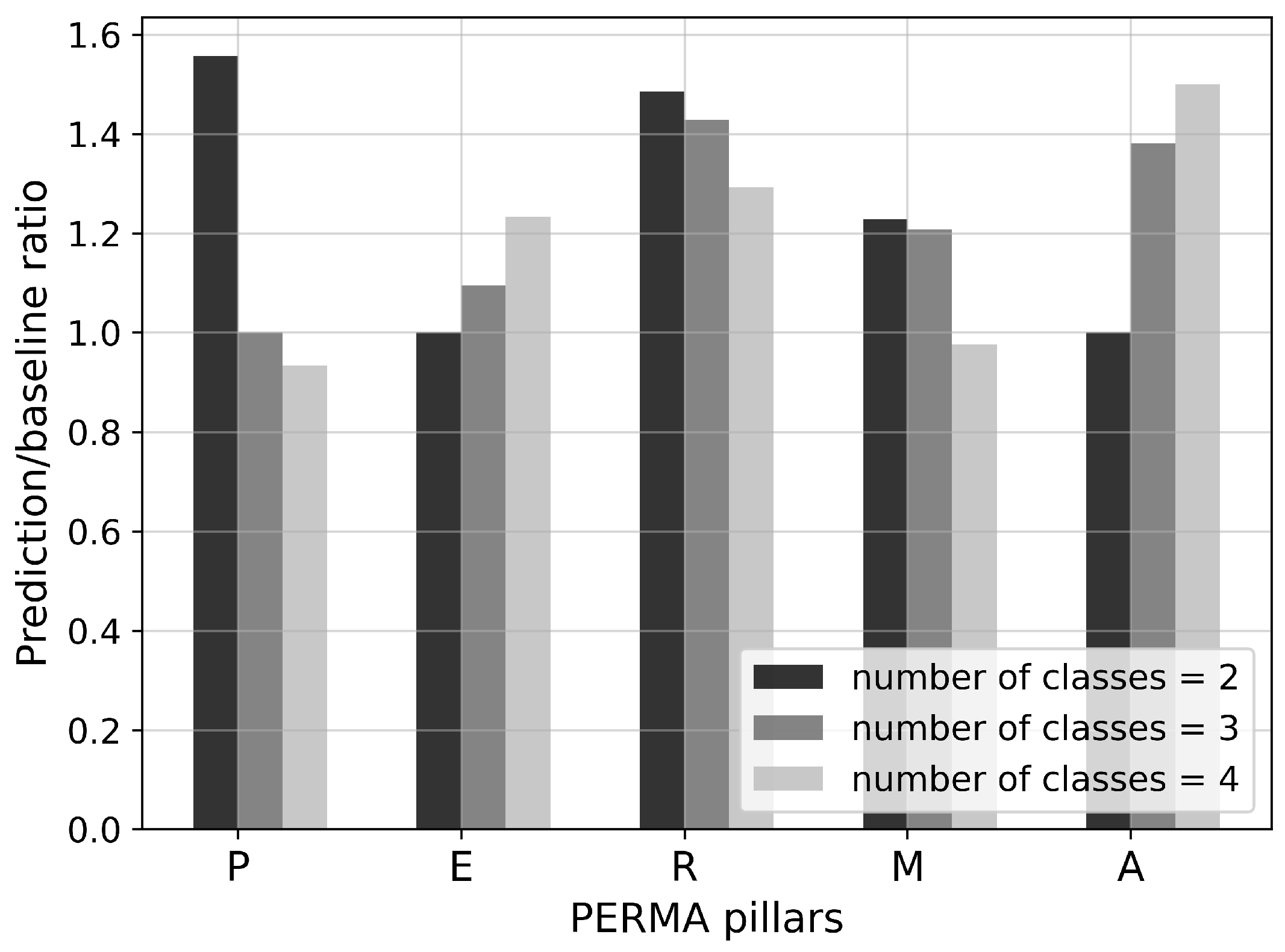
This section answers the question, how the satisfaction scores should be classified, i.e., if it should be a two-class classification problem (satisfactory vs. non-satisfactory), a three-class classification problem (satisfactory vs. neutral vs. non-satisfactory), or a four class classification problem. To determine the optimal number of classes, the ratio between prediction and baseline scores for the different versions is calculated for each pillar (see
Figure A1). Each version performs differently for different pillars.
Figure A1.
Comparison between the prediction baseline ratios for the versions with the different number of classes (higher is better).
Figure A1.
Comparison between the prediction baseline ratios for the versions with the different number of classes (higher is better).
For example, the two-class version performed best for pillars P and R, whereas the three-class version performed best for pillars R and A. Almost all ratios are above 1, indicating better performance than the baseline. The average ratio across all pillars is then calculated to determine the best performing version. The results showed that the two-class version performed best with an average ratio of 1.25. In contrast, the three-class version has an average ratio of 1.22, and the four-class version of 1.19.
The comparison is based on percentage improvement compared to the baseline, which is a metric-independent measure of performance. For classification, the two-class version outperforms the three-class and four-class versions with an overall improvement of 25.41%. Thus, two-class classification is found to be the best method.
Notes
| 1 |
An URL will be inserted at this position after acceptance due to double-blind peer review. |
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
|
References
- World Health Organization. International Classification of Diseases (ICD).
- Gloor, P.A. Happimetrics: Leveraging AI to Untangle the Surprising Link Between Ethics, Happiness and Business Success; Edward Elgar Publishing, 2022.
- Landy, F.J.; Conte, J.M. Work in the 21st Century: An Introduction to Industrial and Organizational Psychology; John Wiley & Sons, 2010. Google-Books-ID: 1K1rnp9uAscC.
- Seligman, M.E.P. Flourish: A Visionary New Understanding of Happiness and Well-being; Simon and Schuster, 2012. Google-Books-ID: YVAQVa0dAE8C.
- Ringeval, F.; Sonderegger, A.; Sauer, J.; Lalanne, D. Introducing the RECOLA multimodal corpus of remote collaborative and affective interactions. In Proceedings of the 2013 10th IEEE International Conference and Workshops on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG); 2013; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oxelmark, L.; Nordahl Amorøe, T.; Carlzon, L.; Rystedt, H. Students’ understanding of teamwork and professional roles after interprofessional simulation—a qualitative analysis. Advances in Simulation, 2, 8. [CrossRef]
- Koutsombogera, M.; Vogel, C. Modeling Collaborative Multimodal Behavior in Group Dialogues: The MULTISIMO Corpus. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC 2018). European Language Resources Association (ELRA), 2018.
- Sanchez-Cortes, D.; Aran, O.; Jayagopi, D.B.; Schmid Mast, M.; Gatica-Perez, D. Emergent leaders through looking and speaking: from audio-visual data to multimodal recognition. Journal on Multimodal User Interfaces 2013, 7, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braley, M.; Murray, G. The Group Affect and Performance (GAP) Corpus. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the Group Interaction Frontiers in Technology. Association for Computing Machinery, 2018, GIFT’18, pp.
1–9. [CrossRef]
- Christensen, B.T.; Abildgaard, S.J.J. Inside the DTRS11 dataset: Background, content, and methodological choices. In Analysing design thinking: Studies of cross-cultural co-creation; CRC Press, 2017; pp. 19–37.
- Ivarsson, J.; Åberg, M. Role of requests and communication breakdowns in the coordination of teamwork: a video-based observational study of hybrid operating rooms. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e035194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshioka, T.; Abramovski, I.; Aksoylar, C.; Chen, Z.; David, M.; Dimitriadis, D.; Gong, Y.; Gurvich, I.; Huang, X.; Huang, Y.; et al. Advances in Online Audio-Visual Meeting Transcription, [1912.04979 [cs, eess]]. [CrossRef]
- Nagrani, A.; Chung, J.S.; Zisserman, A. VoxCeleb: a large-scale speaker identification dataset. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2017, 2017, pp. 2616–2620, [1706.08612 [cs]]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.S.; Nagrani, A.; Zisserman, A. VoxCeleb2: Deep Speaker Recognition. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2018, 2018, pp. 1086–1090, [1806.05622 [cs, eess]]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.S.; Huh, J.; Nagrani, A.; Afouras, T.; Zisserman, A. Spot the conversation: speaker diarisation in the wild. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2020, 2020, pp. 299–303, [2007.01216 [cs, eess]]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, E.Z.; Song, Z.; Tsutsui, S.; Feng, C.; Ye, M.; Shou, M.Z. AVA-AVD: Audio-visual Speaker Diarization in the Wild. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. Association for Computing Machinery, 2022, MM ’22, pp. 3838–3847. [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.S.; Lee, B.J.; Han, I. Who said that?: Audio-visual speaker diarisation of real-world meetings, [1906.10042 [cs, eess]]. [CrossRef]
- Sonnentag, S. Dynamics of Well-Being. Annual Review of Organizational Psychology and Organizational Behavior, 2, 261–293. [CrossRef]
- Anglim, J.; Horwood, S.; Smillie, L.D.; Marrero, R.J.; Wood, J.K. Predicting psychological and subjective well-being from personality: A meta-analysis. Psychological Bulletin, 146, 279–323. Place: US Publisher: American Psychological Association. [CrossRef]
- Dejonckheere, E.; Mestdagh, M.; Houben, M.; Rutten, I.; Sels, L.; Kuppens, P.; Tuerlinckx, F. Complex affect dynamics add limited information to the prediction of psychological well-being. Nature Human Behaviour, 3, 478–491. Number: 5 Publisher: Nature Publishing Group. [CrossRef]
- Smits, C.H.M.; Deeg, D.J.H.; Bosscher, R.J. Well-Being and Control in Older Persons: The Prediction of Well-Being from Control Measures. The International Journal of Aging and Human Development, 40, 237–251. Publisher: SAGE Publications Inc. [CrossRef]
- Karademas, E.C. Positive and negative aspects of well-being: Common and specific predictors. Personality and Individual Differences 2007, 43, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharadwaj, L.; Wilkening, E.A. The prediction of perceived well-being. Social Indicators Research 1977, 4, 421–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridner, S.L.; Newton, K.S.; Staten, R.R.; Crawford, T.N.; Hall, L.A. Predictors of well-being among college students. Journal of American College Health 2016, 64, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Mierlo, H.; Rutte, C.G.; Kompier, M.A.J.; Doorewaard, H.A.C.M. Self-Managing Teamwork and Psychological Well-Being: Review of a Multilevel Research Domain, Group & Organization Management, 30, 211–235. Publisher: SAGE Publications Inc. [CrossRef]
- Markova, G.; T. Perry, J. Cohesion and individual well-being of members in self-managed teams. Leadership & Organization Development Journal 2014, 35, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawadi, P.N.; Cook, D.J.; Schmitter-Edgecombe, M. Automated Cognitive Health Assessment From Smart Home-Based Behavior Data. IEEE journal of biomedical and health informatics 2016, 20, 1188–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casaccia, S.; Romeo, L.; Calvaresi, A.; Morresi, N.; Monteriù, A.; Frontoni, E.; Scalise, L.; Revel, G.M. Measurement of Users’ Well-Being Through Domotic Sensors and Machine Learning Algorithms. IEEE Sensors Journal 2020, 20, 8029–8038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickard, N.; Arjmand, H.A.; Bakker, D.; Seabrook, E. Development of a Mobile Phone App to Support Self-Monitoring of Emotional Well-Being: A Mental Health Digital Innovation. JMIR Mental Health, 3, e6202. Company: JMIR Mental Health Distributor: JMIR Mental Health Institution: JMIR Mental Health Label: JMIRMental Health Publisher: JMIR Publications Inc., Toronto, Canada. [CrossRef]
- Nosakhare, E.; Picard, R. Toward Assessing and Recommending Combinations of Behaviors for Improving Health and Well-Being. ACM Transactions on Computing for Healthcare, 1, 4:1–4:29. [CrossRef]
- Robles-Granda, P.; Lin, S.; Wu, X.; D’Mello, S.; Martinez, G.J.; Saha, K.; Nies, K.; Mark, G.; Campbell, A.T.; De Choudhury, M.; et al. Jointly Predicting Job Performance, Personality, Cognitive Ability, Affect, and Well-Being, [2006.08364 [cs]]. [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Poellabauer, C. Topic Modeling Based Multi-modal Depression Detection. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 7th Annual Workshop on Audio/Visual Emotion Challenge. Association for Computing Machinery, 2017, AVEC ’17, pp. 69–76. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Malandrakis, N.; Xiao, B.; Guha, T.; Van Segbroeck, M.; Black, M.; Potamianos, A.; Narayanan, S. Multimodal Prediction of Affective Dimensions and Depression in Human-Computer Interactions. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 4th International Workshop on Audio/Visual Emotion Challenge. Association for Computing Machinery, 2014, AVEC ’14, pp. 69–76. [CrossRef]
- Williamson, J.R.; Young, D.; Nierenberg, A.A.; Niemi, J.; Helfer, B.S.; Quatieri, T.F. Tracking depression severity from audio and video based on speech articulatory coordination. Computer Speech & Language, 55, 40–56. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.N.; Zhao, S.; Rivera, M.L.; Hong, J.I.; Kraut, R.E. Predicting Well-being Using Short Ecological Momentary Audio Recordings. In Proceedings of the Extended Abstracts of the 2021 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. Association for Computing Machinery, 2021, CHI EA ’21; pp. 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kwon, N.; O’Connell, H. Toward estimating personal well-being using voice, [1910.10082 [cs, eess]]. [CrossRef]
- Kuutila, M.; Mäntylä, M.; Claes, M.; Elovainio, M.; Adams, B. Individual differences limit predicting well-being and productivity using software repositories: a longitudinal industrial study. Empirical Software Engineering, 26, 88. [CrossRef]
- Izumi, K.; Minato, K.; Shiga, K.; Sugio, T.; Hanashiro, S.; Cortright, K.; Kudo, S.; Fujita, T.; Sado, M.; Maeno, T.; et al. Unobtrusive Sensing Technology for Quantifying Stress and Well-Being Using Pulse, Speech, Body Motion, and Electrodermal Data in a Workplace Setting: Study Concept and Design. Frontiers in Psychiatry.
- MIT. MIT SDM - System Design and Management.
- j5create. 360° All Around Webcam.
- Lobe, B.; Morgan, D.; Hoffman, K.A. Qualitative Data Collection in an Era of Social Distancing. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 19, 1609406920937875. Publisher: SAGE Publications Inc. [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, S.I.; van Zyl, L.E.; Donaldson, S.I. PERMA+4: A Framework for Work-Related Wellbeing, Performance and Positive Organizational Psychology 2.0. Frontiers in Psychology, 12, 817244. [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Luo, P.; Loy, C.C.; Tang, X. WIDER FACE: A Face Detection Benchmark, [1511.06523 [cs]].
- Chung, J.S.; Zisserman, A. Out of time: automated lip sync in the wild. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Multi-view Lip-reading, ACCV; 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, R.; Pan, Z.; Das, R.K.; Qian, X.; Shou, M.Z.; Li, H. Is Someone Speaking? Exploring Long-term Temporal Features for Audio-visual Active Speaker Detection. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, 2021, pp. 3927–3935, [2107.06592 [cs, eess]]. [CrossRef]
- Ryant, N.; Church, K.; Cieri, C.; Cristia, A.; Du, J.; Ganapathy, S.; Liberman, M. First DIHARD Challenge Evaluation Plan. tech. Rep. Publisher: Zenodo. [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.W.; Fan, Y.; Hosseinkashi, Y.; Gupchup, J.; Cutler, R. Improving Meeting Inclusiveness using Speech Interruption Analysis, 2023, [arXiv:eess.AS/2304.00658]; arXiv:eess.AS/2304.00658].
- Wagner, J.; Triantafyllopoulos, A.; Wierstorf, H.; Schmitt, M.; Burkhardt, F.; Eyben, F.; Schuller, B.W. Dawn of the Transformer Era in Speech Emotion Recognition: Closing the Valence Gap. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2023, pp. 1–13.
- Wagner, J.; Triantafyllopoulos, A.; Wierstorf, H.; Schmitt, M.; Burkhardt, F.; Eyben, F.; Schuller, B.W. Dawn of the transformer era in speech emotion recognition: closing the valence gap, [2203.07378 [cs, eess]]. [CrossRef]
- Christ, M.; Braun, N.; Neuffer, J.; Kempa-Liehr, A.W. Time Series FeatuRe Extraction on basis of Scalable Hypothesis tests (tsfresh – A Python package). Neurocomputing, 307, 72–77. [CrossRef]
- Breunig, M.M.; Kriegel, H.P.; Ng, R.T.; Sander, J. LOF: identifying density-based local outliers. ACM SIGMOD Record, 29, 93–104. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Zou, C.; Dong, J. Outlier detection using isolation forest and local outlier factor. In Proceedings of the Conference on Research in Adaptive and Convergent Systems. Association for Computing Machinery, 2019, RACS ’19, pp. 161–168. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, A.; Casari, A. Feature Engineering for Machine Learning: Principles and Techniques for Data Scientists; "O’Reilly Media, Inc.", 2018. Google-Books-ID: sthSDwAAQBAJ.
- Jain, A.; Nandakumar, K.; Ross, A. Score normalization in multimodal biometric systems. Pattern Recognition, 38, 2270–2285. [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 12, 2825–2830.
- Kelleher, J.D.; Mac Namee, B.; D’Arcy, A. Fundamentals of machine learning for predictive data analytics: algorithms, worked examples, and case studies; The MIT Press, 2015.
- Disabato, D.J.; Goodman, F.R.; Kashdan, T.B.; Short, J.L.; Jarden, A. Different types of well-being? A cross-cultural examination of hedonic and eudaimonic well-being. Psychological Assessment, 28, 471–482. [CrossRef]
- Mirehie, M.; Gibson, H. Empirical testing of destination attribute preferences of women snow-sport tourists along a trajectory of participation. Author. Accepted: 2020-10-13T18:50:52Z Publisher: Taylor & Francis.
- Mirehie, M.; Gibson, H. Women’s participation in snow-sports and sense of well-being: a positive psychology approach. Journal of Leisure Research, 51, 397–415. [CrossRef]
- Park, T.J.; Kanda, N.; Dimitriadis, D.; Han, K.J.; Watanabe, S.; Narayanan, S. A Review of Speaker Diarization: Recent Advances with Deep Learning, [2101.09624 [cs, eess]].
- Giri, V.N. Culture and Communication Style. Review of Communication, 6, 124–130. [CrossRef]
- Stolcke, A.; Yoshioka, T. DOVER: A Method for Combining Diarization Outputs, [1909.08090 [cs]]. [CrossRef]
- Rajasekar, G.P.; de Melo, W.C.; Ullah, N.; Aslam, H.; Zeeshan, O.; Denorme, T.; Pedersoli, M.; Koerich, A.; Bacon, S.; Cardinal, P.; et al. A Joint Cross-Attention Model for Audio-Visual Fusion in Dimensional Emotion Recognition, [2203.14779 [cs, eess]]. [CrossRef]
- Müller, M. Predicting Well-Being in Team Collaboration from Video Data Using Machine and Deep Learning; Technical University of Munich, 2023. in press.
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Xu, T.; Brockman, G.; McLeavey, C.; Sutskever, I. Robust Speech Recognition via Large-Scale Weak Supervision, [2212.04356 [cs, eess]]. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).