1. Introduction
Biofilm-associated infections can lead to major problems in human health care and food industries. Multidrug-resistant bacteria capable of forming biofilms were estimated to be associated with 4.95 million deaths worldwide in 2019 [
1] Biofilms are a cluster of microorganisms embedded in a common niche of extracellular polymeric substance (EPS), and their formation is closely associated with increased resistance to conventional antibiotics and high recalcitrance to immune responses [
2], [
3]. The intricate nature of biofilms formed by both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria necessitates a thorough investigation into the mechanisms of inherent and acquired resistance to antibiotic treatments and their role in infectious diseases in humans. The leading infective bacteria in burn trauma and other wounds include
Staphylococcus aureus and
Pseudomonas aeruginosa [
4], [
5]. Gram-negative
Escherichia coli is commonly associated with bacterial translocation and sepsis complications due to severe burn injury.
Maresin-like specialized proresolving lipid mediators (MarLs) are 14-hydroxyl-containing small molecules transformed enzymatically from essential ω3-docosahexaenoic acid (DHAs) by the cells and tissue of humans or animals [
6], [
7], [
8], [
9], [
10], [
11]. MarLs include 14
S,22-dihydroxy-docosa-4
Z,7
Z,10
Z,12
E,16
Z,19
Z-hexaenoic acid (MarL1), 14
R,22--dihydroxy-docosa-4
Z,7
Z,10
Z,12
E,16
Z,19
Z-hexaenoic acid (MarL2) [
9], and 14
S,21
R-dihydroxy-docosa-4
Z,7
Z,10
Z,12
E,16
Z, 19
Z-hexaenoic acid (MarL3) [
6], [
7], [
8]. Similar to maresins [
9], [
11,
12], [
13], MarLs can resolve inflammation and promote tissue regeneration and repair [
6], [
7], [
8], [
9].
Maresins and MarLs have been extensively studied for their efficacy in resolving inflammation in multiple organ systems, including the cardiovascular [
14], digestive [
15], immune [
16] endocrine [
17], nervous [
18], [
19], respiratory [
20], reproductive [
21], and musculoskeletal systems [
22]. Nevertheless, whether their combined use with traditional antibiotics enhances their anti-inflammatory effects remains unknown, especially for biofilm-forming bacteria. Carbenicillin is a semisynthetic broad-spectrum β-lactam antibiotic that is stable in the presence of gastric acids and potent against a wide range of bacterial strains [
23], [
24]. In treating infections, a nonlethal antibiotic concentration may trigger alternate cellular response pathways leading to increased antibiotic resistance/tolerance [
25]. Combining the biofilm-resolving properties of MarL with the bactericidal action of carbenicillin presents a novel innovative therapeutic strategy for addressing the challenges posed by persistent and drug-resistant biofilm-associated infections and improving patient outcomes.
In this study, we investigated the effects of the combination of MarLs and carbenicillin on clinically relevant biofilm-forming S. aureus, P. aeruginosa, and E. coli. In the face of persistent and drug resistant biofilm infections, it is critical to investigate the co-actions of maresin-like mediators and carbenicillin as a potential innovative therapeutic strategy for improving inhibition of bacteria in biofilm that is associated infections. Our results revealed that this combination can lower the antibiotic requirements to kill the bacteria in the preformed biofilm.
2. Results
2.1. Determination of concentration-dependent bactericidal actions of carbenicillin
P. aeruginosa,
S. aureus, and
E. coli biofilms were formed on 96-well plates. The wells were treated with serial dilutions of carbenicillin to determine a concentration range at which bactericidal effect is recorded. Carbenicillin has been shown to possess increased potency against most gram-negative bacteria and less so against gram-positive bacteria; therefore, it is less commonly used for treating gram-positive bacteria [
23], [
24].
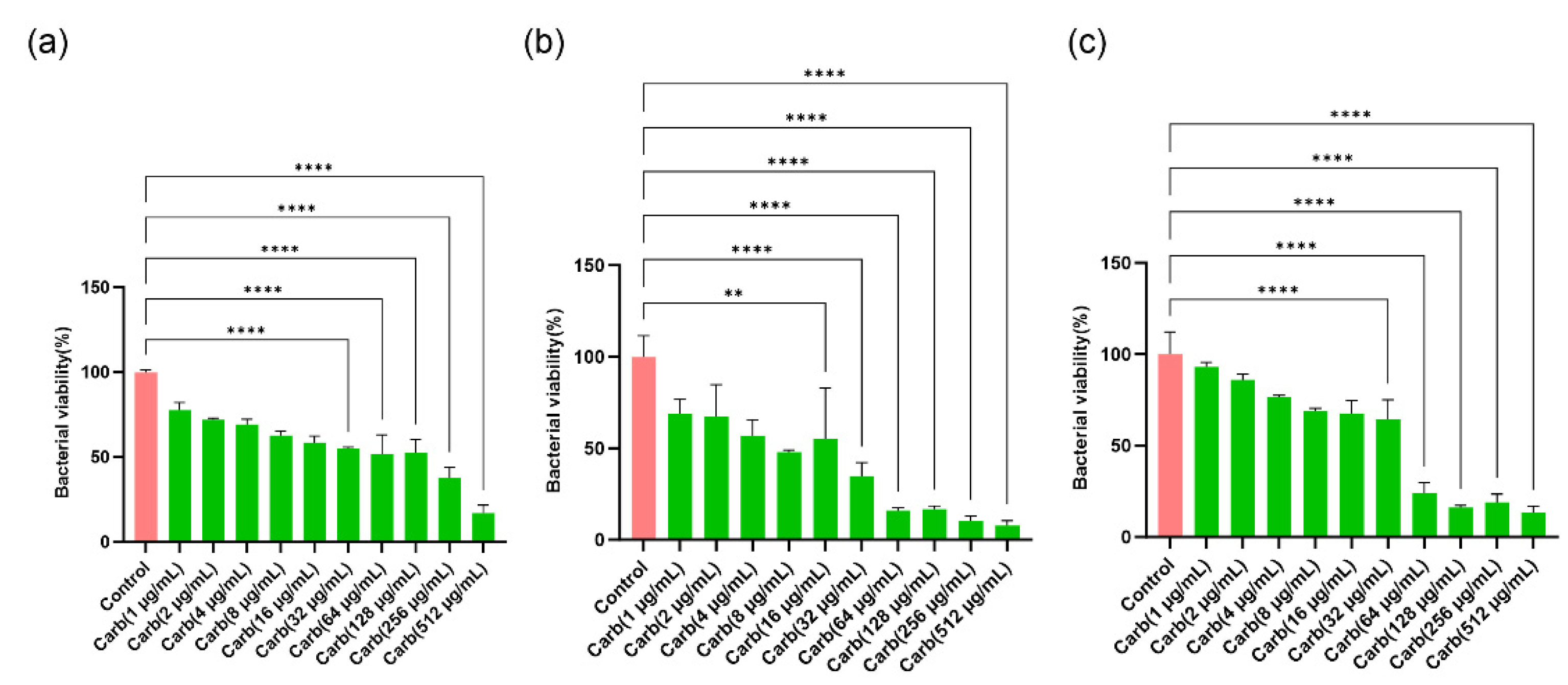
Figure 1 shows that with increasing carbenicillin concentration, the bactericidal activity on preformed bacterial biofilm biomass increased. An approximate
E. coli cell death of 50% or more was achieved at carbenicillin concentrations of 32 µg/mL or higher. Similarly, 16 µg/mL or higher of carbenicillin treatment resulted in decreased
P. aeruginosa viability by ≈ 50%. With respect to
S. aureus, the carbenicillin concentrations that resulted in approximately 50% bactericidal effect or lower was recorded between 32 µg/mL and 512 µg/mL. Subsequently, for assessing the synergistic properties of MarLs and carbenicillin against bacteria, carbenicillin (32 µg/mL) was chosen for
E. coli and
S. aureus, and carbenicillin (16 µg/mL) for
P. aeruginosa.
2.2. Combined effect of a maresin-like mediator and carbenicillin on bacterial viabilities in their biofilms
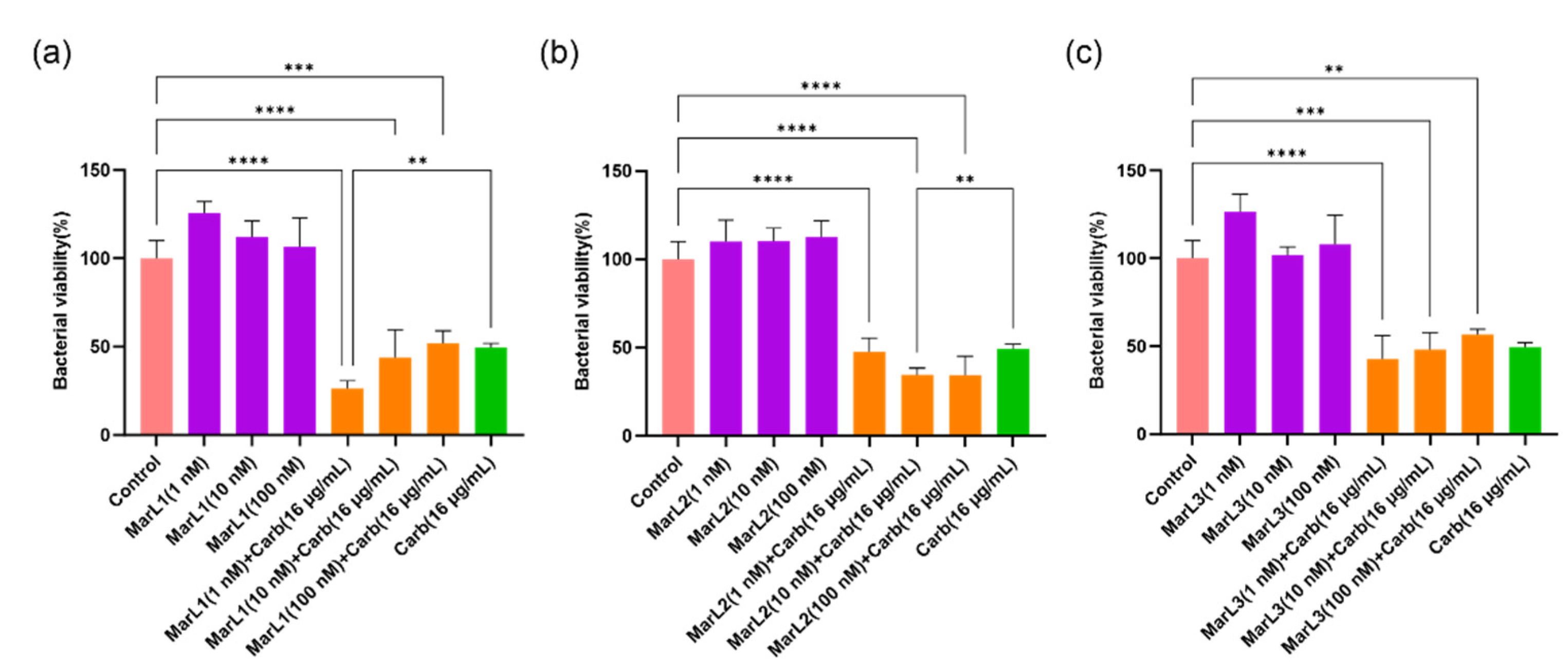
We used an in vitro preformed biofilm system to examine the potential synergistic effect of MarL1, MarL2, or MarL3 with and without carbenicillin to inhibit bacterial biofilm formation or enhance the carbenicillin’s bactericidal activity. MarL1 at concentrations of 1, 10, or 100 nM combined with 16 µg/mL carbenicillin significantly reduced the optical densities and, thus, the relative amounts of active
P. aeruginosa compared with control. However, no such effects were seen when compared to carbenicillin (16 µg/mL) treatment alone except for MarL1 in combination with carbenicillin (16 µg/mL), which resulted in a significant reduction in bacterial viability from approximately 50% in carbenicillin (16 µg/mL) group to 25% in the MarL1 (1 nM) + carb (16 µg/mL) group (**
p < 0.01) as seen in
Figure 2(a). All three concentrations of MarL2 (1 nM, 10 nM or 100 nM) similarly reduced the amount of viable
P. aeruginosa significantly compared to the control untreated group (
Figure 2b). However, only 10nM or 100 nM MarL2 + carbenicillin (16 µg/mL) significantly affected bacterial viability in comparison to carbenicillin (16 µg/mL) alone treatment (**
p < 0.01). With respect to the combination of MarL3 and carbenicillin (16 µg/mL), cell viability was significantly reduced relative to the untreated control group (***
p < 0.001, ****
p < 0.0001), with no such effect seen in comparison with the carbenicillin (16 µg/mL) alone treatment group. Interestingly, the treatment of
P. aeruginosa with a combined dose of MarL1(1 nM) + carbenicillin (16 µg/mL) as shown in
Figure 2(a) was as effective as treating the bacteria with a high concentration of carbenicillin (32 µg/mL) as seen in
Figure 1(b) with bacterial viabilities of approximately 26% and 34% respectively (
p = 0.16). Similarly, MarL2 (10 nM or 100 nM) and MarL3 (1 nM or 10 nM) in combination with carbenicillin (16 µg/mL) resulted in a bactericidal effect equivalent to treating
P. aeruginosa with a high carbenicillin concentration of 32 µg/mL with
p-values of 0.98 and 0.42 respectively.
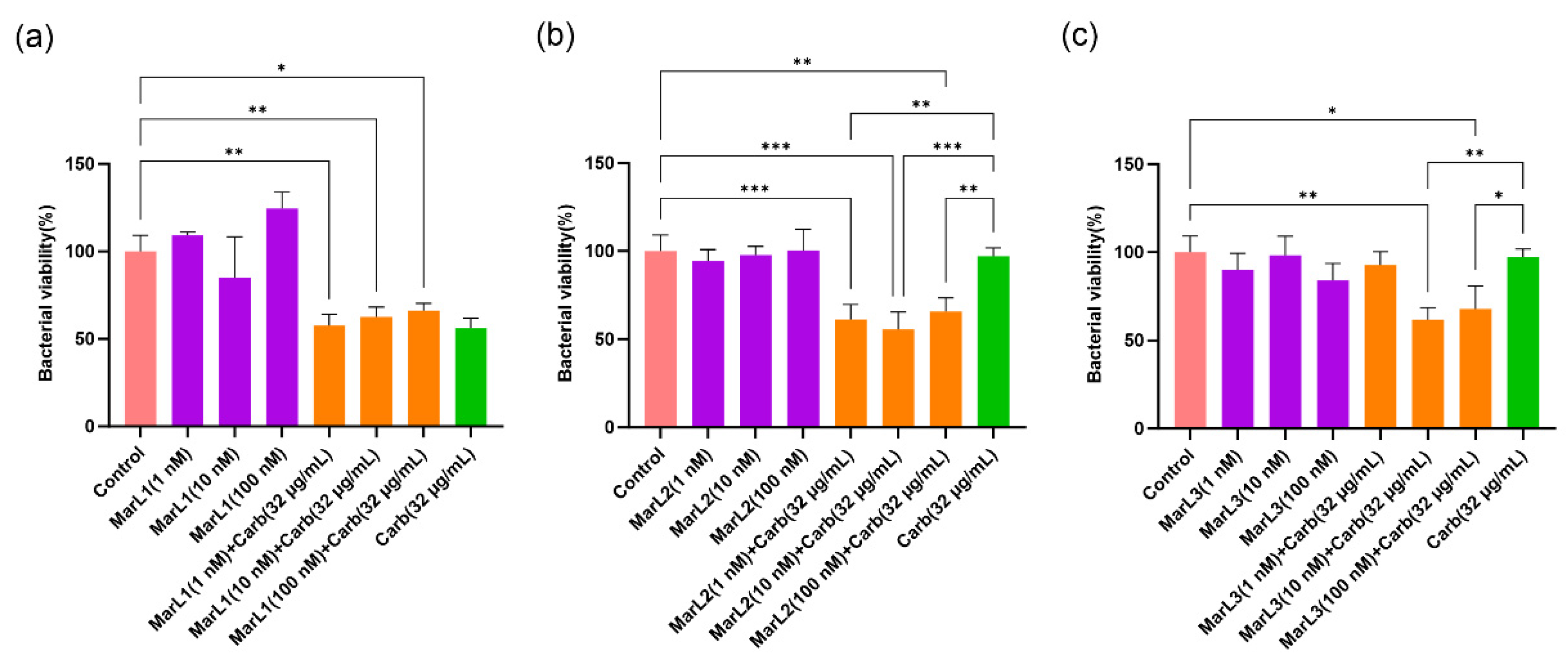
A similar trend was observed with gram-negative
E. coli, where 1, 10, and 100 nM of MarL1 in combination with carbenicillin (32 µg/mL) significantly lowered the relative amounts of metabolically active bacteria present in the biofilms compared to the control group. The viability of
E. coli reduced from approximately 110%, 105% and 115% in the MarL1 alone treatment group to 57%, 62%, and 66% in the MarL1 + carbenicillin (32 µg/mL) treatment group at concentrations of 1, 10, and 100 nM, respectively, as seen in
Figure 3(a). All three concentrations of MarL1 in combination with carbenicillin (32 µg/mL) showed similar efficacy against
E. coli compared to carbenicillin (32 µg/mL) alone treatment. A combination of MarL2 with carbenicillin (32 µg/mL) demonstrated a relatively improved effect with reductions in bacterial cell viabilities at all three concentrations compared with the untreated control and the carbenicillin (32 µg/mL) alone treatment group as seen in
Figure 3(b) (**
p < 0.01, ***
p < 0.001). From
Figure 3(c), an existing synergy was recorded only in MarL3 (10 nM or 100nM) combined with carbenicillin (32 µg/mL) as
E. coli viability reduced in these groups compared to the untreated control group and the carbenicillin (32 µg/mL) alone treatment group (*
p < 0.05, **
p < 0.01). Unlike
P. aeruginosa, the treatment of
E. coli with a combined dose of MarL1(1 nM) + carbenicillin (32 µg/mL) as shown in
Figure 3(a) was as effective as treating the bacteria with high concentrations of carbenicillin (64 µg/mL) and carbenicillin (128 µg/mL) as seen in
Figure 1(b)
p-values of 0.319 and 0.453 respectively. Additionally, the bactericidal activity of a combined dose of MarL1(10 nM) + carbenicillin (32 µg/mL) was equivalent to the bactericidal activity of high concentrations of carbenicillin (64 µg/mL) and carbenicillin (128 µg/mL) with
p-values of 0.216 and 0.150 respectively. MarL1 (100 nM) combined with carbenicillin (32 µg/mL) had a bactericidal efficacy equivalent to treating
E. coli with carbenicillin (64 µg/mL).
Similarly, MarL2 (1 nM) in combination with carbenicillin (32 µg/mL) was seen to have a bactericidal efficacy equivalent to treating
E. coli with carbenicillin concentrations as high as 64 µg/mL and 128 µg/mL, with
p-values of 0.319 and 0.274 respectively. With respect to treatment of
E. coli with MarL2 (10 nM) +carbenicillin (32 µg/mL), the bactericidal effect recorded corresponded to that of carbenicillin (64 µg/mL, 128 µg/mL, or 256 µg/mL) alone treatment as seen in
Figure 1(a). The
p-values recorded were 0.697, 0.724 and 0.059 respectively.
MarL3 (10 nM) in combination with carbenicillin (32 µg/mL) resulted in a bactericidal effect equivalent to treating E. coli with a high carbenicillin concentration of 64 µg/mL or 128 µg/mL with p-values of 0.261 and 0.202 respectively. MarL3 (100 nM) combined with carbenicillin (32 µg/mL) was recorded to have a potency against E. coli equivalent to carbenicillin (64 µg/mL) (p = 0.186) or carbenicillin (128 µg/mL) (p = 0.162).
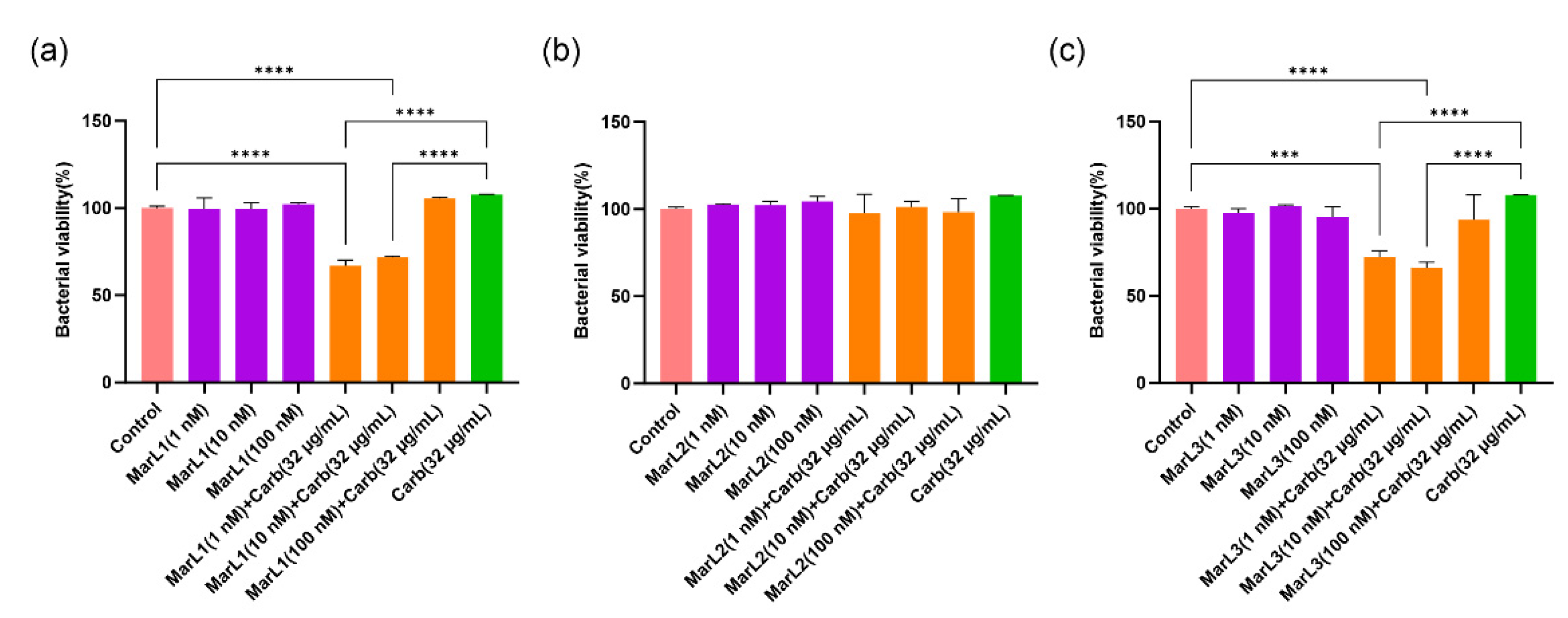
For
S. aureus, treatment of bacterial biofilm with 1 nM and 10 nM MarL1 combined with carbenicillin (32 µg/mL) significantly reduced bacterial cell viability compared with the untreated control group and with the carbenicillin (32 µg/mL) group with approximately 40% decreases in bacterial cell viability as seen in
Figure 4(a) (****
p < 0.0001). On the contrary, MarL2 alone at all three concentrations or in combination with carbenicillin (32 µg/mL) showed no impact on
S. aureus viability compared with both the control and the carbenicillin (32 µg/mL) alone treatment group as seen in
Figure 4(b). Again, 1 nM and 10 nM MarL3 combined with carbenicillin (32 µg/mL) significantly reduced the viability of the
S. aureus biofilm in comparison with the control and the carbenicillin (32 µg/mL) alone treatment group, whereas 100 nM MarL3 combined with carbenicillin (32 µg/mL) showed no such synergistic effect. The observed differences had
p-values of ***
p < 0.001, ****
p < 0.0001.
2.3. Live/Dead assay imaging revealed combined effects of a maresin-like mediator and carbenicillin on bacterial survival in their biofilms
A live/dead assay was conducted to validate the antibiofilm activity of the MarLs with or without carbenicillin. Drug penetration and bactericidal activity in the biofilm were assessed through staining with a green SYTO 9 dye, a membrane penetrable dye for both live and dead bacteria with high affinity for DNA, and red propidium iodide dye, which stains nuclear chromatin upon cell membrane disruption, resulting in fluorescence enhancement.
Treatment with MarL1, MarL2, or MarL3 monotherapy at all three concentrations (1 nM, 10 nM or 100 nM) exhibited no activity against
S. aureus,
P. aeruginosa, and
E. coli compared with the control group as seen in
Figure 5(a, b,c) (upper)
Figure 6 (a, b, c) (upper) and
Figure 7(a, b, c) (upper). However, in conjunction with carbenicillin (32 µg/mL), MarL1(1 nM or 10 nM) positively affected the disruption of S. aureus biofilm, with the most effect recorded by MarL1 (1 nM) as seen in
Figure 5 (a) (lower). MarL2 in combination with carbenicillin (32 µg/mL) was recorded to disrupt biofilm structure formed by microbially active
S. aureus at concentrations of 10 nM and 200 nM. MarL3 at all three concentrations of 1, 10, and 100 nM effectively lowered the relative amounts of microbially active bacteria in the biofilms and disrupted the
S. aureus biofilm most effectively as seen in
Figure 1c.
A similar trend was seen with respect to P. aeruginosa and E. coli, except that all three MarLs at all three concentrations (1 nM, 10 nM or 100 nM) were significantly effective at disrupting the formed biofilms with more dead cells visible in
Figure 6 and
Figure 7 (lower) compared to treatments with MarLs only (upper).
In summary, biofilms treated with MarLs alone maintained their integrity and bioactivity, as seen by the uniform green fluorescence with respect to all three bacteria. Concomitantly, an increased number of red-stained dead cells were recorded when bacterial biofilms were treated with corresponding MarLs in conjunction with appropriate concentrations of carbenicillin. This disruption in the biofilm architecture after the combination treatment suggests that MarLs may interfere with the adhesion mechanisms, increasing bacterial susceptibility to carbenicillin. These results were consistent with those of the thiazolyl blue tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay.
3. Discussion
Our study suggests a promising approach for treating biofilm-associated infections via the synergistic actions of MarLs and carbenicillin. Microorganisms, specifically planktonic bacteria, attach to surfaces and multiply based on the characteristics of the substrata and secrete EPS that form biofilms [
26]. Biofilm formation is succeeded by the formation of a multilayered defense system comprised persister cells that emerge from dissolved focus areas in the biofilm. This stage is characterized by maximum antibiotic resistance, limited nutrition, subdued antibiotic penetration, and limited proliferation [
26], [
27], [
28]. Secreted toxins such as lyases and hydrolases also influence the development of antibiotic resistance, as they modify antibiotics into less toxic forms [
29], [
30]. Treatment with antibiotics is effective against planktonic bacteria but not that efficacious against persister cells present in bacterial biofilms. This study provides evidence that Marls have beneficial effects on disrupting biofilms formed by
E. coli,
P. aeruginosa, and
S. aureus. In concert with carbenicillin, MarL1 (1 nM) increased the efficacy of carbenicillin (32 µg/mL) by disrupting biofilm formation and killing
P. aeruginosa in the preformed biofilm. Higher concentrations of MarL1 (10 nM or 100 nM) in conjunction with carbenicillin (32 µg/mL), though less effective, also disrupted
P. aeruginosa biofilm formation. MarL2 and MarL3 at all 3 concentrations were effective at suppressing
P. aeruginosa biofilm formation with bactericidal activity of at least 50%. Endogenous SPMs have been documented to possess proresolving properties against bacterial infections [
31], [
32] but the direct mechanism of action of SPMs on microbes is yet to be fully established. Donghoon Kang et al established the relevance of PqSA, a virulence gene and one of multiple genes [
33] implicated in biofilm formation, in the production of cell-cell communication molecules such as 2,4-dihydroxyquinoline [
34]. The researchers established that disruption of the PQS biosynthetic protein PqsA affects biofilm formation. Further studies conducted showed that down-regulation of PqSA and subsequent disruption of bacterial biofilms was feasible using specialized proresolving mediators, and that solitary treatment with these molecules had no dose-dependent biofilm inhibitory effect [
35]. This is consistent with our findings which suggest that the pro-resolving properties of MarLs disrupted the protective biofilm matrix, increasing antibiotic penetration and rendering the bacteria more susceptible to the bactericidal effects of carbenicillin at low doses. This was evident due to the significant reduction in bacterial cell viability demonstrated by the MTT assays carried out in this study, and further supported by the visual data obtained from the live/dead fluorescence assay. However, further research is warranted to explore the underlying mechanisms. The observed synergy, however, suggests a promising approach for overcoming microbial resistance to antibiotics and for improving the treatment outcomes of biofilm-related infections.
4. Materials and Methods
Materials
S. aureus (Xen 29), P. aeruginosa (Xen 41), and E. coli (Xen 14) strains were generously gifted by PerkinElmer (Waltham, MA, USA). Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), tryptic soy agar (TSA), and carbenicillin sodium salt (CAS No. 4800-94-6) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). MTT was purchased from Invitrogen (Catalog number: M6494). Luria-Bertani (LB) broth was purchased from Daily Bio (product: SD7002). MarL1, MarL2, and MarL3 were prepared through total organic synthesis, as described in our previous publications217. Prior to use, MarLs were diluted in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) to the desired concentrations (1, 10, and 100 nM) for the experiments. Carbenicillin sodium salt was prepared as a stock solution from which the following concentrations were made: 512 µg/mL, 256 µg/mL, 128 µg/mL, 64 µg/mL, 32 µg/mL, 16 µg/mL, 8 µg/mL, 4 µg/mL, 2 µg/mL, and 1 µg/mL. LIVE/DEAD BacLight Bacterial Viability Kit was purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific (Cat. No. L7012).
Biofilm formation
Biofilm was grown on the surface of 96 well microtiter plates according to the following protocols but with revisions [
36]. LB broth and TSA were autoclaved for 15 min at 121 °C and brought to room temperature. TSA plates were made by casting 30 mL of the solution into 100-mm petri dishes. From frozen glycerol stocks, bacterial inoculums were made by dipping the loop into the stock solution to scrape bacteria streaking onto corresponding labeled TSA plates. The plates were then incubated overnight at 37 °C. Three individual bacterial colonies were then scooped from each bacterial streaked agar plate into 10 mL liquid LB broth and cultured at 37 °C with mild shaking at 50 x g overnight. Subsequently, 120 µL of each culture sample were diluted in 6 mL of liquid LB and incubated at 37 °C for 2 h. The optical densities of the microbial suspensions were adjusted to 0.5 McFarland units with turbidity between 0.08 - 0.1 at 540 nm by adding ice-cold PBS (~1 × 10
9 colony-forming units [CFU]/mL). This was followed by centrifugation at 3000xg for 10 min at 4 °C, carefully decanting the supernatant, and resuspending the pellets in PBS. After a second centrifugation step at 3000xg for 10 min at 4 °C, bacterial pellets were resuspended in 1.5 mL of PBS on ice. The bacterial concentration was further verified by serially diluting 500 µL of the bacterial suspensions in cold PBS at concentrations of 1:10, 1:100, 1:1000, 1:10,000, 1:100,000, and 1:1,000,000, and plating 20 µL on an LB agar plate followed by an overnight incubation of the plates at 37 °C in a humidified incubator. CFU were counted by gross examination to calculate the bacterial concentration. Next, 150 µL of bacterial suspensions were added to each well of a 96-well plate and incubated at 37 °C for 24 h without shaking to form biofilms. Fluorescence microscopy on an OLYMPUS scanning microscope with an OLYMPUS OLyVIA software version 3.4.1 was used to assess the formed biofilms.
Determination of concentration-dependent bactericidal actions of carbenicillin
An experiment was conducted to identify the range of carbenicillin concentrations within which a bactericidal effect is achieved. Varying concentrations of carbenicillin (512, 256, 128, 64, 32, 16, 8, 4, 2, and 1 µg/mL) were added to the wells of a 96-well plate containing bacterial biofilms as previously described and incubated for 24 h at 37 °C. After washing the wells three times with 1× PBS to remove planktonic bacteria, 10 μL of the 12-mM MTT solution was added to each well. A negative control well was created by adding 10 µL of the MTT stock solution to 100 µL of LB medium alone. The plates were incubated for 3 h, followed by adding 150 µL of DMSO, incubating for 10 min at 37 °C, and measuring absorbance values at 540 nm using a SpectraMax M5e spectrophotometer (Molecular Devices, China).
Determination of bacterial viability with the MTT assay
Bacterial cell viability was determined via MTT assay according to Mohamed et al and Grela et al with modifications [
37], [
38]. The old medium was removed from the wells containing the biofilms and replaced with MarLs alone or in combination with carbenicillin at concentrations of 1, 10, and 100 nM. Wells containing untreated biofilms served as negative controls, and positive control wells were those treated with carbenicillin (32 µg/mL) only. The plates were incubated at 37 °C for 24 h without shaking. The medium was discarded, and the wells were washed with PBS to remove planktonic bacteria. Next, 10 µL of 12 mM (MTT) were added to each well, with a negative control well included by adding 10 μL of MTT to 100 µL of LB medium. After 3 h of incubation, the solutions in the well were replaced with 150 µL of DMSO, incubated for another 10 min at 37 °C, and the absorbance read at 540 nm to quantify formazan – a soluble compound that reflects the relative amount of metabolically active bacterial cells in the biofilm.
Live/dead assay
To assess the integrity of microbial biofilms, microbes were grown on microscope slides by adding 100 µL of bacterial suspensions to each well of an 8-well plate and cultured at 37 °C for 24 h as follows: P. aeruginosa - concentration 5.50 × 106 CFU·mL-1; E. coli- concentration 1.58 × 107 CFU·mL-1; and S. aureus - concentration 4.8 × 106 CFU·mL-1. The wells containing the microbial biofilms were grouped according to the following treatment groups: carbenicillin (32 µg/mL), MarL1, MarL2 and MarL3 at concentrations of 1, 10, and 100 nM, carbenicillin + MarL1 (1nM, 10 nM, and 100 nM), carbenicillin + MarL2 (1nM, 10 nM, and 100 nM), and carbenicillin + MarL3 (1nM, 10 nM, and 100 nM). Untreated wells served as control. After treatment, the plates were incubated at 37 °C for 24 h, followed by washing with 1X PBS and staining using LIVE/DEAD BacLight Bacterial Viability Kit for 15 min at room temperature according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Fluorescence images were obtained on an Olympus microscope with Z-stack images used to assess the depth of cell lysis within the bacterial film.
Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA using Graphpad Prism software (version 10.1.2(324) and R (version 4.3.2) to assess significant differences between groups. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Data were mean ± standard error of mean (SEM) of three independent experiments. A p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
5. Conclusions
We investigated the therapeutic activity of MarLs on bacterial biofilms formed by clinically relevant gram-positive S aureus and gram-negative P. aeruginosa and E. coli. The metabolic activities in these bacteria inhabiting the biofilms were assessed using the MTT colorimetric method and fluorescence microscopy before and after treatment with MarLs alone and combined with carbenicillin. We identified 16 µg/mL and 32 µg/mL to be the carbenicillin concentration that causes a decrease in the relative amounts of standard P. aeruginosa, S. aureus, or E. coli inoculums, respectively. In other words, the combination helped disrupt biofilm integrity and reduce the relative amounts of microbially active pathogens. This is especially critical in combating antibiotic resistance since low/nonlethal antibiotic doses are rendered effective by the existing synergy with MarLs.
Our ongoing research delves into the molecular mechanisms underlying this synergy—specifically, the molecular/genetic make-up of bacterial colonies in a biofilm following treatment with MarLs with and without carbenicillin. Future studies should target the broader applicability of combination therapies involving MarLs and antibiotics across varying strains of bacteria, as well as different compositions of bacterial biofilms. Additionally, we plan to explore the role of host-directed MarLs-enhanced carbenicillin effect on immune cell infiltration, anti-inflammation, bacterial clearance, tissue re-epithelization, and healing outcomes in a burn wound infection in animal models.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.H., Y.L.; methodology, S.H., Y.K., A.M.T., Y.L. (MarL preparation and LC-MS/MS verification), A.-R.M., S.C., H.P., Y.W., N.A.; formal analysis, A.M.T., A.-R.M., S.C., Y.L., S.H., H.P.; investigation, Y.K., A.M.T., A.-R.M., S.C., Y.L., H.P., S.H.; writing—original draft preparation, A.-R.M., A.M.T., Y.L., S.C., H.P., S.H., Y.W., N.A.; writing—review, A.-R.M., Y.L., S.C., H.P., S.H., Y.W., N.A., A.M.T.; editing, A.-R.M., Y.L., S.C., H.P., S.H., Y.W., N.A., A.M.T.; supervision, S.H.; funding acquisition, S.H.. All authors have read and agreed to the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by LSU Health-New Orleans research enhancement fund (to S.H.) and USA National Institute of Health grant 1R01GM136874, 1R21AG068756, and 1R21AG066119 (to S.H.), as well as by KAKENHI Grant Number JP15H05904, JP15H05898, JP15H05897, JP15H04648 and the Kobayashi International Scholarship (to K. Y.).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The bacteria use protocol has been authorized and approved by the Institutional Biosafety Committee of Louisiana State University, Health, New Orleans, USA.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
We are very grateful to Professor Nicholas G Bazan, the director of Neuroscience Center of LSU Health and School of Medicine, LSU, Health-New Orleans, USA for the strong support to make this research possible.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors do not have any conflict of interest.
References
- C. J. Murray et al., “Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: a systematic analysis,” The Lancet, vol. 399, no. 10325, pp. 629–655, Feb. 2022. [CrossRef]
- G. Shineh, M. Mobaraki, M. J. Perves Bappy, and D. K. Mills, “Biofilm Formation, and Related Impacts on Healthcare, Food Processing and Packaging, Industrial Manufacturing, Marine Industries, and Sanitation–A Review,” Appl Microbiol, vol. 3, no. 3, pp. 629–665, Jun. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Y. A. Costa, J. M. Raaijmakers, and E. E. Kuramae, “Microbial extracellular polymeric substances: Ecological function and impact on soil aggregation,” Frontiers in Microbiology, vol. 9, no. JUL. Frontiers Media S.A., Jul. 23, 2018. [CrossRef]
- D. N. Frank et al., “Microbial diversity in chronic open wounds,” Wound Repair and Regeneration, vol. 17, no. 2, pp. 163–172, Mar. 2009. [CrossRef]
- M. Tomic-Canic, J. L. Burgess, K. E. O’Neill, N. Strbo, and I. Pastar, “Skin Microbiota and its Interplay with Wound Healing,” American Journal of Clinical Dermatology, vol. 21. Adis, pp. 36–43, Sep. 01, 2020. [CrossRef]
- H. Tian, Y. Lu, S. P. Shah, and S. Hong, “14S,21R-dihydroxydocosahexaenoic acid remedies impaired healing and mesenchymal stem cell functions in diabetic wounds,” Journal of Biological Chemistry, vol. 286, no. 6, pp. 4443–4453, Feb. 2011. [CrossRef]
- Y. Lu, H. Tian, and S. Hong, “Novel 14,21-dihydroxy-docosahexaenoic acids: Structures, formation pathways, and enhancement of wound healing,” J Lipid Res, vol. 51, no. 5, pp. 923–932, May 2010. [CrossRef]
- H. Tian, Y. Lu, S. P. Shah, Q. Wang, and S. Hong, “14S,21R-dihydroxy-docosahexaenoic acid treatment enhances mesenchymal stem cell amelioration of renal ischemia/reperfusion injury,” Stem Cells Dev, vol. 21, no. 7, pp. 1187–1199, May 2012. [CrossRef]
- S. Hong et al., “Maresin-like lipid mediators are produced by leukocytes and platelets and rescue reparative function of diabetes-impaired macrophages,” Chem Biol, vol. 21, no. 10, pp. 1318–1329, Oct. 2014. [CrossRef]
- S. Hong et al., “Stereoselective Synthesis of Maresin-Like Lipid Mediators,” Synlett, vol. 30, no. 3, pp. 343–347, 2019. [CrossRef]
- K. Nishimura et al., “Stereoselective Total Synthesis of Macrophage-Produced Prohealing 14,21-Dihydroxy Docosahexaenoic Acids,” Journal of Organic Chemistry, vol. 83, no. 1, pp. 154–166, Jan. 2018. [CrossRef]
- N. Ogawa, T. Tojo, and Y. Kobayashi, “Synthesis of maresin 1 and (7S)-isomer,” Tetrahedron Lett, vol. 55, no. 16, pp. 2738–2741, Apr. 2014. [CrossRef]
- N. Ogawa, T. Amano, and Y. Kobayashi, “Synthesis of Optically Active Maresin 2 and Maresin 2 n-3 DPA,” Synlett, vol. 32, no. 3, pp. 295–298, Feb. 2021. [CrossRef]
- H. Li et al., “Maresin 1 intervention reverses experimental pulmonary arterial hypertension in mice,” Br J Pharmacol, vol. 179, no. 22, pp. 5132–5147, Nov. 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. J. Rodríguez et al., “Maresin-1 prevents liver fibrosis by targeting Nrf2 and NF-κB, reducing oxidative stress and inflammation,” Cells, vol. 10, no. 12, Dec. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, C. Sarabia, M. Torres, and E. Juárez, “Resolvin D1 (RvD1) and maresin 1 (Mar1) contribute to human macrophage control of M. tuberculosis infection while resolving inflammation,” Int Immunopharmacol, vol. 74, p. 105694, 2019. [CrossRef]
- S. Sugimoto et al., “Brown adipose tissue-derived MaR2 contributes to cold-induced resolution of inflammation,” Nat Metab, vol. 4, no. 6, pp. 775–790, 2022. [CrossRef]
- C. Emre et al., “Intranasal delivery of pro-resolving lipid mediators rescues memory and gamma oscillation impairment in AppNL-G-F/NL-G-F mice,” Commun Biol, vol. 5, no. 1, p. 245, 2022. [CrossRef]
- A. Sánchez-Fernández et al., “Administration of Maresin-1 ameliorates the physiopathology of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis,” J Neuroinflammation, vol. 19, no. 1, p. 27, 2022. [CrossRef]
- J. Pan et al., “MCTR1 intervention reverses experimental lung fibrosis in mice,” J Inflamm Res, vol. 14, pp. 1873–1881, 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. L. Falsetta et al., “Specialized Pro-resolving Mediators Reduce Pro-nociceptive Inflammatory Mediator Production in Models of Localized Provoked Vulvodynia,” J Pain, vol. 22, no. 10, pp. 1195–1209, 2021. [CrossRef]
- R. Huang, L. Vi, X. Zong, and G. S. Baht, “Maresin 1 resolves aged-associated macrophage inflammation to improve bone regeneration,” FASEB Journal, vol. 34, no. 10, pp. 13521–13532, Oct. 2020. [CrossRef]
- K. Butler, A. R. English, V. A. Ray, and A. E. Timreck, “Carbenicillin: Chemistry and Mode of Action,” 1970. [Online]. Available: https://about.jstor.org/terms.
- S. S. Castle, “Carbenicillin,” xPharm: The Comprehensive Pharmacology Reference, pp. 1–5, Jan. 2007. [CrossRef]
- S. P. Bernier and M. G. Surette, “Concentration-dependent activity of antibiotics in natural environments,” Frontiers in Microbiology, vol. 4, no. FEB. Frontiers Research Foundation, 2013. [CrossRef]
- R. M. Donlan, “Biofilm Formation: A Clinically Relevant Microbiological Process,” 2001.
- M. A. Rather, K. Gupta, and M. Mandal, “Microbial biofilm: formation, architecture, antibiotic resistance, and control strategies,” Brazilian Journal of Microbiology, vol. 52, no. 4. Springer Science and Business Media Deutschland GmbH, pp. 1701–1718, Dec. 01, 2021. [CrossRef]
- N. Høiby, T. Bjarnsholt, M. Givskov, S. Molin, and O. Ciofu, “Antibiotic resistance of bacterial biofilms,” International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, vol. 35, no. 4. pp. 322–332, Apr. 2010. [CrossRef]
- G. D. Wright, “Bacterial resistance to antibiotics: Enzymatic degradation and modification,” Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, vol. 57, no. 10. pp. 1451–1470, Jul. 29, 2005. [CrossRef]
- M. Schroeder, B. D. Brooks, and A. E. Brooks, “The complex relationship between virulence and antibiotic resistance,” Genes, vol. 8, no. 1. MDPI AG, Jan. 18, 2017. [CrossRef]
- N. Chiang, J. Dalli, R. A. Colas, and C. N. Serhan, “Identification of resolvin D2 receptor mediating resolution of infections and organ protection,” Journal of Experimental Medicine, vol. 212, no. 8, pp. 1203–1217, Jul. 2015. [CrossRef]
- J. Walker et al., “Lipoxin A4 increases survival by decreasing systemic inflammation and bacterial load in sepsis,” Shock, vol. 36, no. 4, pp. 410–416, Oct. 2011. [CrossRef]
- M. Müsken, S. Di Fiore, A. Dötsch, R. Fischer, and S. Häussler, “Genetic determinants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm establishment,” Microbiology (N Y), vol. 156, no. 2, pp. 431–441, 2010. [CrossRef]
- D. Kang, K. E. Turner, and N. V. Kirienko, “PqsA promotes pyoverdine production via biofilm formation,” Pathogens, vol. 7, no. 1, Mar. 2018. [CrossRef]
- J. M. Thornton, J. M. Walker, P. Y. K. Sundarasivarao, B. W. Spur, A. Rodriguez, and K. Yin, “Lipoxin A4 promotes reduction and antibiotic efficacy against Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm,” Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat, vol. 152, Feb. 2021. [CrossRef]
- R. Thibeaux, M. Kainiu, and C. Goarant, “Biofilm Formation and Quantification Using the 96-Microtiter Plate,” in Methods in Molecular Biology, vol. 2134, Humana Press Inc., 2020, pp. 207–214. [CrossRef]
- M. A. Mohamed, M. Nasr, W. F. Elkhatib, and W. N. Eltayeb, “In Vitro Evaluation of Antimicrobial Activity and Cytotoxicity of Different Nanobiotics Targeting Multidrug Resistant and Biofilm Forming Staphylococci,” Biomed Res Int, vol. 2018, 2018. [CrossRef]
- E. Grela, J. Kozłowska, and A. Grabowiecka, “Current methodology of MTT assay in bacteria – A review,” Acta Histochemica, vol. 120, no. 4. Elsevier GmbH, pp. 303–311, May 01, 2018. 01 May. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Dose–response graph of carbenicillin inhibition of three key biofilm-forming burn-trauma infection-related bacteria: (a) E. coli, (b) P. aeruginosa, and (c) S. aureus. These bacteria were treated in their preformed biofilms. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, n = 3. **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001 vs. control.
Figure 1.
Dose–response graph of carbenicillin inhibition of three key biofilm-forming burn-trauma infection-related bacteria: (a) E. coli, (b) P. aeruginosa, and (c) S. aureus. These bacteria were treated in their preformed biofilms. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, n = 3. **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001 vs. control.
Figure 2.
Effects of MarL1, MarL2, or MarL3 at different concentrations on the carbenicillin inhibition of P. aeruginosa in preformed biofilms. (a) MarL1, MaL2 + Carb 16 µg/mL (b) MarL2, MarL2 + Carb 16 µg/mL and (c) MarL3, MarL3 + Carb 16 µg/mL. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, n = 3. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.
Figure 2.
Effects of MarL1, MarL2, or MarL3 at different concentrations on the carbenicillin inhibition of P. aeruginosa in preformed biofilms. (a) MarL1, MaL2 + Carb 16 µg/mL (b) MarL2, MarL2 + Carb 16 µg/mL and (c) MarL3, MarL3 + Carb 16 µg/mL. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, n = 3. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.
Figure 3.
Effects of MarL1, MarL2, or MarL3 at different concentrations on the carbenicillin inhibition of E. coli in preformed biofilms. (a) MarL1, MarL1+Carb 32 µg/mL and (b) MarL2, MarL2+Carb 32 µg/mL and (c) MarL3, MarL3+Carb 32 µg/mL. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, n = 3. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
Figure 3.
Effects of MarL1, MarL2, or MarL3 at different concentrations on the carbenicillin inhibition of E. coli in preformed biofilms. (a) MarL1, MarL1+Carb 32 µg/mL and (b) MarL2, MarL2+Carb 32 µg/mL and (c) MarL3, MarL3+Carb 32 µg/mL. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, n = 3. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
Figure 4.
Effects of MarL1, MarL2, or MarL3 at different concentrations on the carbenicillin inhibition of S. aureus in preformed biofilms. (a) MarL1, MarL1 + Carb 32 µg/mL; (b) MarL2, MarL2 + Carb 32 µg/mL; and (c) MarL3, MarL3 + Carb 32 µg/mL. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, n = 3. ***p < 0.001, ***p < 0.0001.
Figure 4.
Effects of MarL1, MarL2, or MarL3 at different concentrations on the carbenicillin inhibition of S. aureus in preformed biofilms. (a) MarL1, MarL1 + Carb 32 µg/mL; (b) MarL2, MarL2 + Carb 32 µg/mL; and (c) MarL3, MarL3 + Carb 32 µg/mL. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, n = 3. ***p < 0.001, ***p < 0.0001.
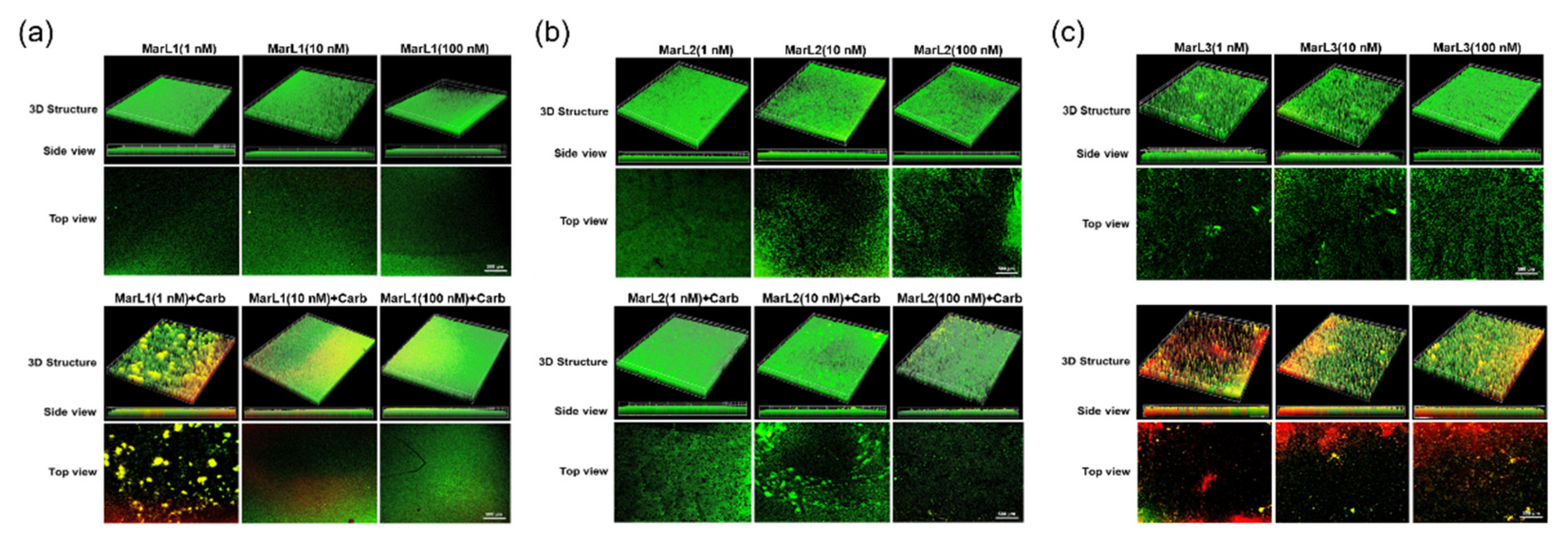
Figure 5.
Fluorescence microscopic images showed the effects of MarL1, MarL2, or MarL3 at different concentrations on the carbenicillin inhibition of S. aureus in preformed biofilms. (a) MarL1 (1, 10, or 100 nM) (upper), and MarL1 (1, 10, or 100 nM) + Carb 32 µg/mL (lower). (b) MarL2 (1, 10, or 100 nM) (upper), and MarL2 (1, 10, or 100 nM) + Carb 32 µg/mL (lower) (c) MarL3 (1, 10, or 100 nM) (upper) and MarL3 (1, 10, or 100 nM) + Carb 32 µg/mL (lower). Green indicates live + dead cells, and red indicates dead cells. Images were taken at 4× magnification.
Figure 5.
Fluorescence microscopic images showed the effects of MarL1, MarL2, or MarL3 at different concentrations on the carbenicillin inhibition of S. aureus in preformed biofilms. (a) MarL1 (1, 10, or 100 nM) (upper), and MarL1 (1, 10, or 100 nM) + Carb 32 µg/mL (lower). (b) MarL2 (1, 10, or 100 nM) (upper), and MarL2 (1, 10, or 100 nM) + Carb 32 µg/mL (lower) (c) MarL3 (1, 10, or 100 nM) (upper) and MarL3 (1, 10, or 100 nM) + Carb 32 µg/mL (lower). Green indicates live + dead cells, and red indicates dead cells. Images were taken at 4× magnification.
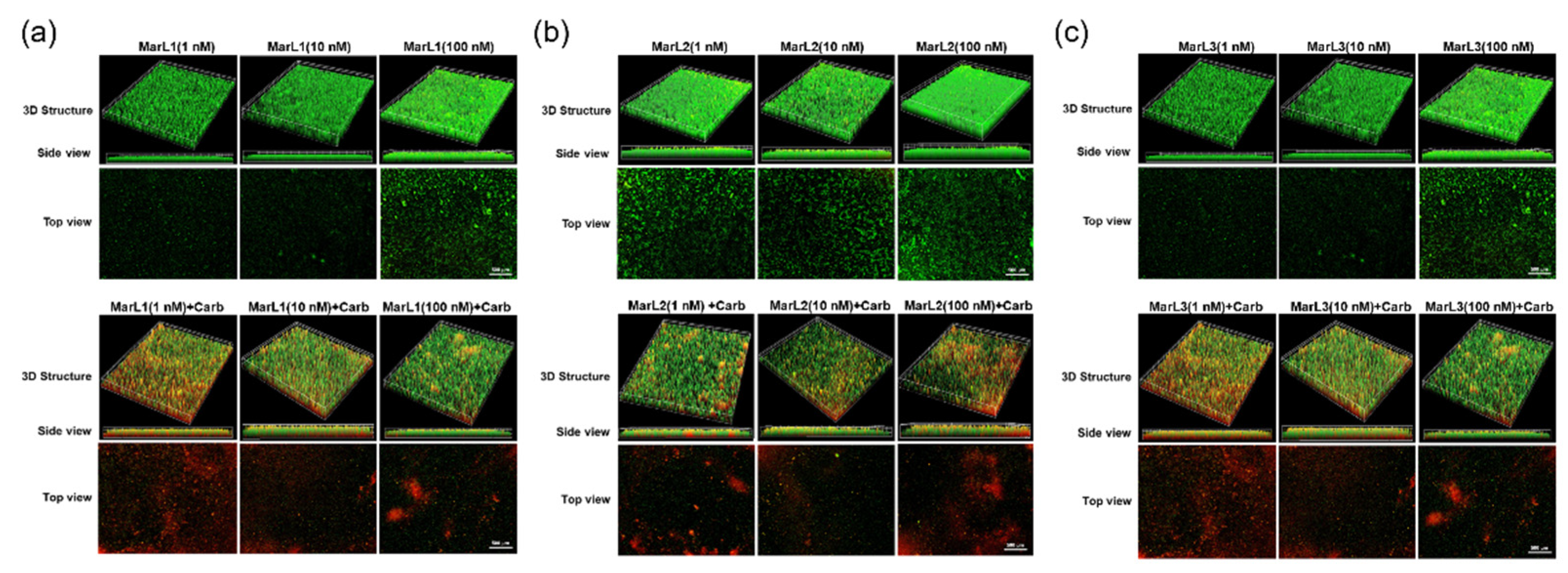
Figure 6.
Fluorescence microscopic images showed the effects of MarL1, MarL2, or MarL3 at different concentrations on the carbenicillin inhibition of P. aeruginosa in preformed biofilms (a) MarL1 (1, 10, or 100 nM) (upper), and MarL1 (1, 10, or 100 nM) + Carb 32 µg/mL (lower) (b) MarL2 (1, 10, or 100 nM) (upper) and MarL2 (1, 10, or 100 nM) (lower) + Carb 32 µg/mL (c) MarL3 (1, 10, or 100 nM) (upper) and MarL3 (1, 10, or 100 nM) + Carb 32 µg/mL (lower). Green indicates live + dead cells, and red indicates dead cells. Images were taken at 4× magnification.
Figure 6.
Fluorescence microscopic images showed the effects of MarL1, MarL2, or MarL3 at different concentrations on the carbenicillin inhibition of P. aeruginosa in preformed biofilms (a) MarL1 (1, 10, or 100 nM) (upper), and MarL1 (1, 10, or 100 nM) + Carb 32 µg/mL (lower) (b) MarL2 (1, 10, or 100 nM) (upper) and MarL2 (1, 10, or 100 nM) (lower) + Carb 32 µg/mL (c) MarL3 (1, 10, or 100 nM) (upper) and MarL3 (1, 10, or 100 nM) + Carb 32 µg/mL (lower). Green indicates live + dead cells, and red indicates dead cells. Images were taken at 4× magnification.
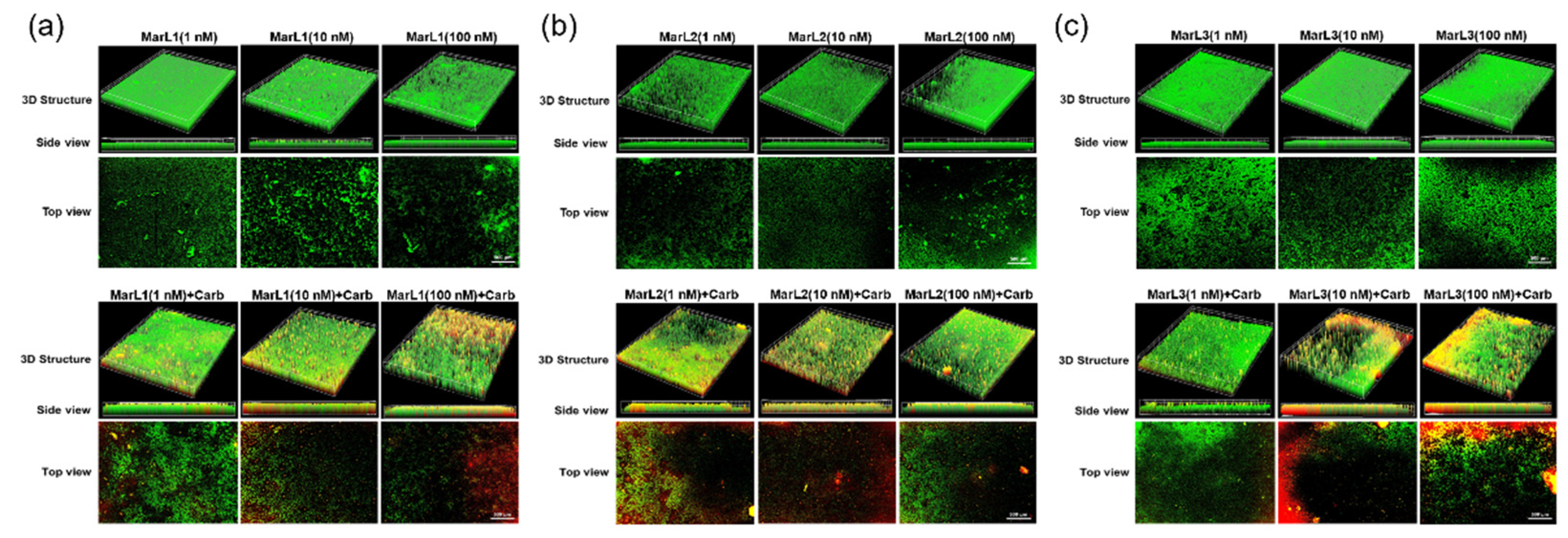
Figure 7.
Fluorescence microscopic images showed the effects of MarL1, MarL2, or MarL3 at different concentrations on the carbenicillin inhibition of E. coli in preformed biofilms (a) MarL1 (1, 10, or 100 nM)(upper), and MarL1 (1, 10, or 100 nM) (lower) + Carb 32 µg/mL (b) MarL2 (1, 10, or 100 nM) (upper) and MarL2 (1, 10, or 100 nM) + Carb 32 µg/mL (lower) (c) MarL3 (1, 10, or 100 nM) (upper) and MarL3 (1, 10, or 100 nM) + Carb 32 µg/mL (lower). Green indicates live + dead cells, and red indicates dead cells. Images were taken at 4× magnification.
Figure 7.
Fluorescence microscopic images showed the effects of MarL1, MarL2, or MarL3 at different concentrations on the carbenicillin inhibition of E. coli in preformed biofilms (a) MarL1 (1, 10, or 100 nM)(upper), and MarL1 (1, 10, or 100 nM) (lower) + Carb 32 µg/mL (b) MarL2 (1, 10, or 100 nM) (upper) and MarL2 (1, 10, or 100 nM) + Carb 32 µg/mL (lower) (c) MarL3 (1, 10, or 100 nM) (upper) and MarL3 (1, 10, or 100 nM) + Carb 32 µg/mL (lower). Green indicates live + dead cells, and red indicates dead cells. Images were taken at 4× magnification.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).