Submitted:
19 January 2024
Posted:
25 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. INTRODUCTION
1.1. Germ cell origin and prenatal development
1.2. Testicular Germ Cell Tumors
1.3. Genetics of testicular germ cell tumors
1.4. Epigenetics of Testicular germ cell tumors
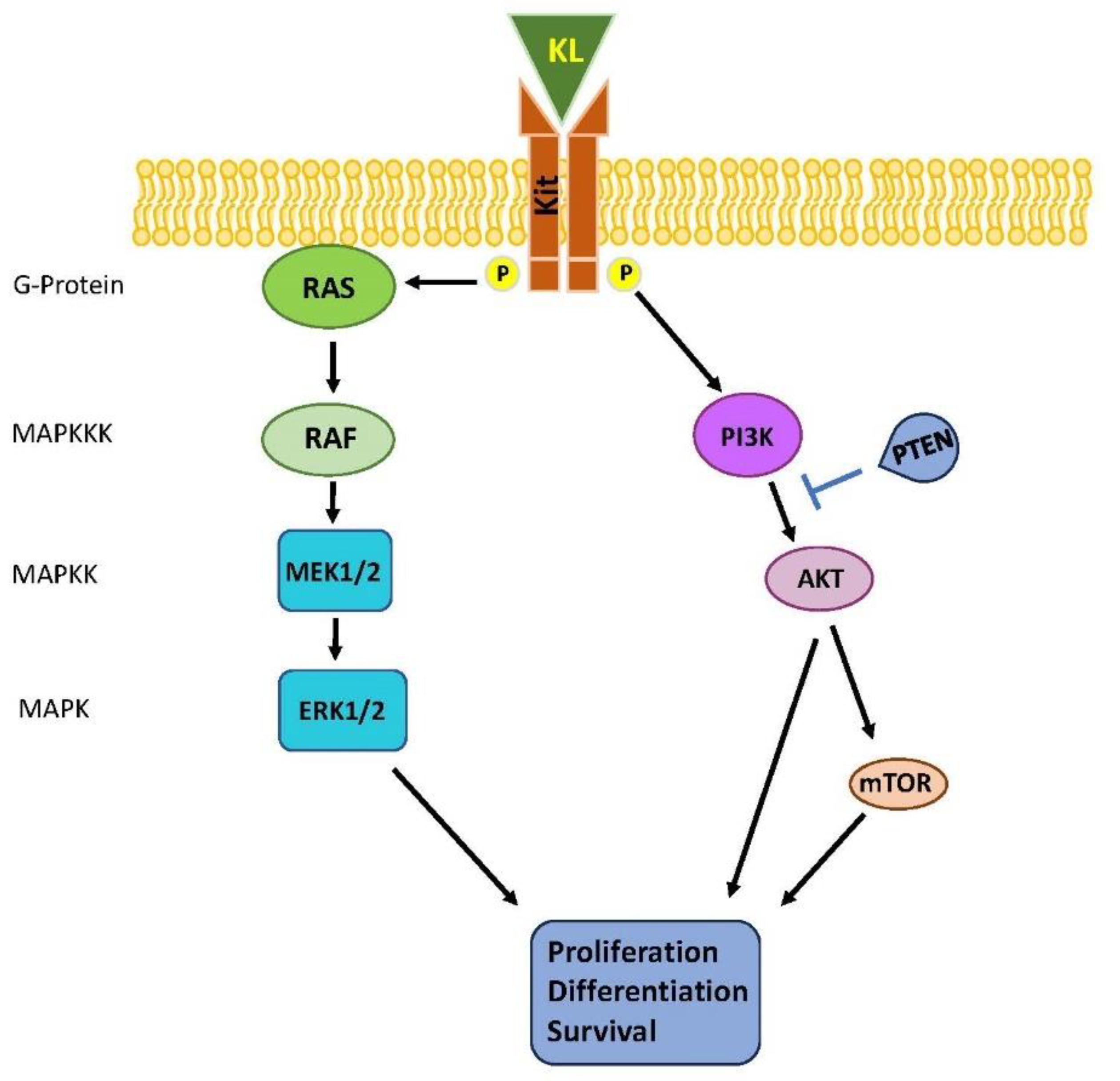
1.5. MAPK signaling pathway in cancer.
1.6. ERK/MAPK signaling in tumor invasion and metastasis.
1.7. Alterations of MAPK pathway in TGCTs
1.8. Prognosis and response to treatment
2. CONCLUSIONS
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Irie, N.; Weinberger, L.; Tang, W.W.; Kobayashi, T.; Viukov, S.; Manor, Y.S.; Dietmann, S.; Hanna, J.H.; Surani, M.A. SOX17 is a critical specifier of human primordial germ cell fate. Cell 2015, 160, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.W.; Kobayashi, T.; Irie, N.; Dietmann, S.; Surani, M.A. Specification and epigenetic programming of the human germ line. Nat Rev Genet 2016, 17, 585–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Liu, W.; Zimmerman, J.; Pastor, W.A.; Kim, R.; Hosohama, L.; Ho, J.; Aslanyan, M.; Gell, J.J.; Jacobsen, S.E.; et al. The TFAP2C-Regulated OCT4 Naive Enhancer Is Involved in Human Germline Formation. Cell Rep 2018, 25, 3591–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Sun, N.; Hou, L.; Kim, R.; Faith, J.; Aslanyan, M.; Tao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Fu, J.; Liu, W.; et al. Human Primordial Germ Cells Are Specified from Lineage-Primed Progenitors. Cell Rep 2019, 29, 4568–4582 e4565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, B. The active migration of germ cells in the embryos of mice and men is a myth. Reproduction 2003, 125, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Runyan, C.; Shoemaker, A.; Surani, A.; Wylie, C. Steel factor controls primordial germ cell survival and motility from the time of their specification in the allantois, and provides a continuous niche throughout their migration. Development 2009, 136, 1295–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oosterhuis, J.W.; Stoop, H.; Honecker, F.; Looijenga, L.H. Why human extragonadal germ cell tumours occur in the midline of the body: old concepts, new perspectives. Int J Androl 2007, 30, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamblott, M.J.; Axelman, J.; Wang, S.; Bugg, E.M.; Littlefield, J.W.; Donovan, P.J.; Blumenthal, P.D.; Huggins, G.R.; Gearhart, J.D. Derivation of pluripotent stem cells from cultured human primordial germ cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1998, 95, 13726–13731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolci, S.; Williams, D.E.; Ernst, M.K.; Resnick, J.L.; Brannan, C.I.; Lock, L.F.; Lyman, S.D.; Boswell, H.S.; Donovan, P.J. Requirement for mast cell growth factor for primordial germ cell survival in culture. Nature 1991, 352, 809–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, Y.; Zsebo, K.; Hogan, B.L. Derivation of pluripotential embryonic stem cells from murine primordial germ cells in culture. Cell 1992, 70, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resnick, J.L.; Bixler, L.S.; Cheng, L.; Donovan, P.J. Long-term proliferation of mouse primordial germ cells in culture. Nature 1992, 359, 550–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donovan, P.J.; de Miguel, M.P. Turning germ cells into stem cells. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2003, 13, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conway, A.E.; Lindgren, A.; Galic, Z.; Pyle, A.D.; Wu, H.; Zack, J.A.; Pelligrini, M.; Teitell, M.A.; Clark, A.T. A self-renewal program controls the expansion of genetically unstable cancer stem cells in pluripotent stem cell-derived tumors. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Felici, M.; Dolci, S. From testis to teratomas: a brief history of male germ cells in mammals. Int J Dev Biol 2013, 57, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolci, S.; Campolo, F.; De Felici, M. Gonadal development and germ cell tumors in mouse and humans. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2015, 45, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oosterhuis, J.W.; Looijenga, L.H. Testicular germ-cell tumours in a broader perspective. Nat Rev Cancer 2005, 5, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moch, H.; Cubilla, A.L.; Humphrey, P.A.; Reuter, V.E.; Ulbright, T.M. The 2016 WHO Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs-Part A: Renal, Penile, and Testicular Tumours. Eur Urol 2016, 70, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, V.E. Origins and molecular biology of testicular germ cell tumors. Mod Pathol 2005, 18 Suppl 2, S51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skakkebaek, N.E.; Berthelsen, J.G.; Giwercman, A.; Muller, J. Carcinoma-in-situ of the testis: possible origin from gonocytes and precursor of all types of germ cell tumours except spermatocytoma. Int J Androl 1987, 10, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almstrup, K.; Sonne, S.B.; Hoei-Hansen, C.E.; Ottesen, A.M.; Nielsen, J.E.; Skakkebaek, N.E.; Leffers, H.; Rajpert-De Meyts, E. From embryonic stem cells to testicular germ cell cancer-- should we be concerned? Int J Androl 2006, 29, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guida, E.; Tassinari, V.; Colopi, A.; Todaro, F.; Cesarini, V.; Jannini, B.; Pellegrini, M.; Botti, F.; Rossi, G.; Rossi, P.; et al. MAPK activation drives male and female mouse teratocarcinomas from late primordial germ cells. J Cell Sci 2022, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barchi, M.; Guida, E.; Dolci, S.; Rossi, P.; Grimaldi, P. Endocannabinoid system and epigenetics in spermatogenesis and testicular cancer. Vitam Horm 2023, 122, 75–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tassinari, V.; Campolo, F.; Cesarini, V.; Todaro, F.; Dolci, S.; Rossi, P. Fgf9 inhibition of meiotic differentiation in spermatogonia is mediated by Erk-dependent activation of Nodal-Smad2/3 signaling and is antagonized by Kit Ligand. Cell Death Dis 2015, 6, e1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolci, S.; Pellegrini, M.; Di Agostino, S.; Geremia, R.; Rossi, P. Signaling through extracellular signal-regulated kinase is required for spermatogonial proliferative response to stem cell factor. J Biol Chem 2001, 276, 40225–40233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Siena, S.; Campolo, F.; Rossi, P.; Jannini, E.A.; Dolci, S.; Pellegrini, M. UV and genotoxic stress induce ATR relocalization in mouse spermatocytes. Int J Dev Biol 2013, 57, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litchfield, K.; Summersgill, B.; Yost, S.; Sultana, R.; Labreche, K.; Dudakia, D.; Renwick, A.; Seal, S.; Al-Saadi, R.; Broderick, P.; et al. Whole-exome sequencing reveals the mutational spectrum of testicular germ cell tumours. Nat Commun 2015, 6, 5973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor-Weiner, A.; Zack, T.; O'Donnell, E.; Guerriero, J.L.; Bernard, B.; Reddy, A.; Han, G.C.; AlDubayan, S.; Amin-Mansour, A.; Schumacher, S.E.; et al. Genomic evolution and chemoresistance in germ-cell tumours. Nature 2016, 540, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.B.; Lin, X.P.; Xu, Y.; Shen, Z.F.; Pan, W.W. DAXX promotes ovarian cancer ascites cell proliferation and migration by activating the ERK signaling pathway. J Ovarian Res 2018, 11, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, F.C.; Conduit, C.; Loveland, K.L.; Thomas, B.; Lewin, J.; Tran, B. Genetics of testicular cancer: a review. Curr Opin Urol 2022, 32, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluta, J.; Pyle, L.C.; Nead, K.T.; Wilf, R.; Li, M.; Mitra, N.; Weathers, B.; D'Andrea, K.; Almstrup, K.; Anson-Cartwright, L.; et al. Identification of 22 susceptibility loci associated with testicular germ cell tumors. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 4487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krentz, A.D.; Murphy, M.W.; Zhang, T.; Sarver, A.L.; Jain, S.; Griswold, M.D.; Bardwell, V.J.; Zarkower, D. Interaction between DMRT1 function and genetic background modulates signaling and pluripotency to control tumor susceptibility in the fetal germ line. Dev Biol 2013, 377, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krentz, A.D.; Murphy, M.W.; Kim, S.; Cook, M.S.; Capel, B.; Zhu, R.; Matin, A.; Sarver, A.L.; Parker, K.L.; Griswold, M.D.; et al. The DM domain protein DMRT1 is a dose-sensitive regulator of fetal germ cell proliferation and pluripotency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009, 106, 22323–22328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meissner, A.; Mikkelsen, T.S.; Gu, H.; Wernig, M.; Hanna, J.; Sivachenko, A.; Zhang, X.; Bernstein, B.E.; Nusbaum, C.; Jaffe, D.B.; et al. Genome-scale DNA methylation maps of pluripotent and differentiated cells. Nature 2008, 454, 766–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popp, C.; Dean, W.; Feng, S.; Cokus, S.J.; Andrews, S.; Pellegrini, M.; Jacobsen, S.E.; Reik, W. Genome-wide erasure of DNA methylation in mouse primordial germ cells is affected by AID deficiency. Nature 2010, 463, 1101–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, F.; Yan, L.; Guo, H.; Li, L.; Hu, B.; Zhao, Y.; Yong, J.; Hu, Y.; Wang, X.; Wei, Y.; et al. The Transcriptome and DNA Methylome Landscapes of Human Primordial Germ Cells. Cell 2015, 161, 1437–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, H.; Matsui, Y. Epigenetic events in mammalian germ-cell development: reprogramming and beyond. Nat Rev Genet 2008, 9, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hata, K.; Okano, M.; Lei, H.; Li, E. Dnmt3L cooperates with the Dnmt3 family of de novo DNA methyltransferases to establish maternal imprints in mice. Development 2002, 129, 1983–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kota, S.K.; Feil, R. Epigenetic transitions in germ cell development and meiosis. Dev Cell 2010, 19, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmins, S.; Sassone-Corsi, P. Chromatin remodelling and epigenetic features of germ cells. Nature 2005, 434, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messerschmidt, D.M.; Knowles, B.B.; Solter, D. DNA methylation dynamics during epigenetic reprogramming in the germline and preimplantation embryos. Genes Dev 2014, 28, 812–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fendler, A.; Stephan, C.; Yousef, G.M.; Kristiansen, G.; Jung, K. The translational potential of microRNAs as biofluid markers of urological tumours. Nat Rev Urol 2016, 13, 734–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netto, G.J.; Nakai, Y.; Nakayama, M.; Jadallah, S.; Toubaji, A.; Nonomura, N.; Albadine, R.; Hicks, J.L.; Epstein, J.I.; Yegnasubramanian, S.; et al. Global DNA hypomethylation in intratubular germ cell neoplasia and seminoma, but not in nonseminomatous male germ cell tumors. Mod Pathol 2008, 21, 1337–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, D.G.; Nielsen, J.E.; Jorgensen, A.; Skakkebaek, N.E.; Rajpert-De Meyts, E.; Almstrup, K. Evidence that active demethylation mechanisms maintain the genome of carcinoma in situ cells hypomethylated in the adult testis. Br J Cancer 2014, 110, 668–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landero-Huerta, D.A.; Vigueras-Villasenor, R.M.; Yokoyama-Rebollar, E.; Arechaga-Ocampo, E.; Rojas-Castaneda, J.C.; Jimenez-Trejo, F.; Chavez-Saldana, M. Epigenetic and risk factors of testicular germ cell tumors: a brief review. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 2017, 22, 1073–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lister, R.; Pelizzola, M.; Dowen, R.H.; Hawkins, R.D.; Hon, G.; Tonti-Filippini, J.; Nery, J.R.; Lee, L.; Ye, Z.; Ngo, Q.M.; et al. Human DNA methylomes at base resolution show widespread epigenomic differences. Nature 2009, 462, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, Z.; Duan, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, B.; Guo, Y.L.; Tian, Z. DNA methylation footprints during soybean domestication and improvement. Genome Biol 2018, 19, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smiraglia, D.J.; Szymanska, J.; Kraggerud, S.M.; Lothe, R.A.; Peltomaki, P.; Plass, C. Distinct epigenetic phenotypes in seminomatous and nonseminomatous testicular germ cell tumors. Oncogene 2002, 21, 3909–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burbee, D.G.; Forgacs, E.; Zochbauer-Muller, S.; Shivakumar, L.; Fong, K.; Gao, B.; Randle, D.; Kondo, M.; Virmani, A.; Bader, S.; et al. Epigenetic inactivation of RASSF1A in lung and breast cancers and malignant phenotype suppression. J Natl Cancer Inst 2001, 93, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dammann, R.; Yang, G.; Pfeifer, G.P. Hypermethylation of the cpG island of Ras association domain family 1A (RASSF1A), a putative tumor suppressor gene from the 3p21.3 locus, occurs in a large percentage of human breast cancers. Cancer Res 2001, 61, 3105–3109. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, F.; Surve, P.; Natarajan, S.; Patil, A.; Pol, S.; Patole, K.; Das, B.R. Aberrant epigenetic inactivation of RASSF1A and MGMT gene and genetic mutations of KRAS, cKIT and BRAF in Indian testicular germ cell tumours. Cancer Genet 2020, 241, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, M.; Samaei, N.M.; Mowla, S.J.; Shafiee, M.; Vasei, M.; Ghasemian, N. Upregulation of miR-371-373 cluster, a human embryonic stem cell specific microRNA cluster, in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Cancer Res Ther 2018, 14, S132–S137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.K.; Evensen, H.S.F.; Furu, K.; Haugen, T.B. miRNA-302s may act as oncogenes in human testicular germ cell tumours. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 9189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.J.; Pan, W.W.; Liu, S.B.; Shen, Z.F.; Xu, Y.; Hu, L.L. ERK/MAPK signalling pathway and tumorigenesis. Exp Ther Med 2020, 19, 1997–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Tournier, C. Regulation of cellular functions by the ERK5 signalling pathway. Cell Signal 2006, 18, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolch, W.; Calder, M.; Gilbert, D. When kinases meet mathematics: the systems biology of MAPK signalling. FEBS Lett 2005, 579, 1891–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolch, W. Coordinating ERK/MAPK signalling through scaffolds and inhibitors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2005, 6, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyriakis, J.M.; Avruch, J. Mammalian mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathways activated by stress and inflammation. Physiol Rev 2001, 81, 807–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Karin, M. Mammalian MAP kinase signalling cascades. Nature 2001, 410, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Songyang, Z.; Lu, K.P.; Kwon, Y.T.; Tsai, L.H.; Filhol, O.; Cochet, C.; Brickey, D.A.; Soderling, T.R.; Bartleson, C.; Graves, D.J.; et al. A structural basis for substrate specificities of protein Ser/Thr kinases: primary sequence preference of casein kinases I and II, NIMA, phosphorylase kinase, calmodulin-dependent kinase II, CDK5, and Erk1. Mol Cell Biol 1996, 16, 6486–6493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Gibson, T.B.; Robinson, F.; Silvestro, L.; Pearson, G.; Xu, B.; Wright, A.; Vanderbilt, C.; Cobb, M.H. MAP kinases. Chem Rev 2001, 101, 2449–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, A.C.; Vaillancourt, R.R. Tyrosine kinase receptor-activated signal transduction pathways which lead to oncogenesis. Oncogene 1998, 17, 1343–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blume-Jensen, P.; Hunter, T. Oncogenic kinase signalling. Nature 2001, 411, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarden, Y. The EGFR family and its ligands in human cancer. signalling mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Eur J Cancer 2001, 37 Suppl 4, S3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bache, K.G.; Slagsvold, T.; Stenmark, H. Defective downregulation of receptor tyrosine kinases in cancer. EMBO J 2004, 23, 2707–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zandi, R.; Larsen, A.B.; Andersen, P.; Stockhausen, M.T.; Poulsen, H.S. Mechanisms for oncogenic activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Cell Signal 2007, 19, 2013–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, S.; Levitzki, A. Targeting the EGFR and the PKB pathway in cancer. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2009, 21, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karnoub, A.E.; Weinberg, R.A. Ras oncogenes: split personalities. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2008, 9, 517–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollag, G.; Tsai, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Ibrahim, P.; Nolop, K.; Hirth, P. Vemurafenib: the first drug approved for BRAF-mutant cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2012, 11, 873–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Gomez, R.; Bustelo, X.R.; Crespo, P. Protein-Protein Interactions: Emerging Oncotargets in the RAS-ERK Pathway. Trends Cancer 2018, 4, 616–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khotskaya, Y.B.; Holla, V.R.; Farago, A.F.; Mills Shaw, K.R.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Hong, D.S. Targeting TRK family proteins in cancer. Pharmacol Ther 2017, 173, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maik-Rachline, G.; Hacohen-Lev-Ran, A.; Seger, R. Nuclear ERK: Mechanism of Translocation, Substrates, and Role in Cancer. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Vega, F.; Mina, M.; Armenia, J.; Chatila, W.K.; Luna, A.; La, K.C.; Dimitriadoy, S.; Liu, D.L.; Kantheti, H.S.; Saghafinia, S.; et al. Oncogenic Signaling Pathways in The Cancer Genome Atlas. Cell 2018, 173, 321–337 e310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holderfield, M.; Deuker, M.M.; McCormick, F.; McMahon, M. Targeting RAF kinases for cancer therapy: BRAF-mutated melanoma and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer 2014, 14, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohno, M.; Pouyssegur, J. Targeting the ERK signaling pathway in cancer therapy. Ann Med 2006, 38, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, H.; Bignell, G.R.; Cox, C.; Stephens, P.; Edkins, S.; Clegg, S.; Teague, J.; Woffendin, H.; Garnett, M.J.; Bottomley, W.; et al. Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature 2002, 417, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terrell, E.M.; Morrison, D.K. Ras-Mediated Activation of the Raf Family Kinases. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burotto, M.; Chiou, V.L.; Lee, J.M.; Kohn, E.C. The MAPK pathway across different malignancies: a new perspective. Cancer 2014, 120, 3446–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Ye, W.; Wu, J.; Liu, L.; Yang, L.; Gao, L.; Chen, B.; Zhang, F.; Yang, H.; Li, Y. Sp1-CD147 positive feedback loop promotes the invasion ability of ovarian cancer. Oncol Rep 2015, 34, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulzmaier, F.J.; Ramos, J.W. RSK isoforms in cancer cell invasion and metastasis. Cancer Res 2013, 73, 6099–6105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gialeli, C.; Theocharis, A.D.; Karamanos, N.K. Roles of matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression and their pharmacological targeting. FEBS J 2011, 278, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda-Yamamoto, M.; Suzuki, N.; Sawai, Y.; Miyase, T.; Sano, M.; Hashimoto-Ohta, A.; Isemura, M. Association of suppression of extracellular signal-regulated kinase phosphorylation by epigallocatechin gallate with the reduction of matrix metalloproteinase activities in human fibrosarcoma HT1080 cells. J Agric Food Chem 2003, 51, 1858–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braicu, C.; Buse, M.; Busuioc, C.; Drula, R.; Gulei, D.; Raduly, L.; Rusu, A.; Irimie, A.; Atanasov, A.G.; Slaby, O.; et al. A Comprehensive Review on MAPK: A Promising Therapeutic Target in Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, W.; Meng, K.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y.; He, Q.Y. RNF128 Promotes Invasion and Metastasis Via the EGFR/MAPK/MMP-2 Pathway in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers (Basel) 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horiuchi, H.; Kawamata, H.; Furihata, T.; Omotehara, F.; Hori, H.; Shinagawa, Y.; Ohkura, Y.; Tachibana, M.; Yamazaki, T.; Ajiki, T.; et al. A MEK inhibitor (U0126) markedly inhibits direct liver invasion of orthotopically inoculated human gallbladder cancer cells in nude mice. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2004, 23, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Basu, M.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Chatterjee, U.; Roy, S.S. FGF16 promotes invasive behavior of SKOV-3 ovarian cancer cells through activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway. J Biol Chem 2014, 289, 1415–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todaro, F.; Campolo, F.; Barrios, F.; Pellegrini, M.; Di Cesare, S.; Tessarollo, L.; Rossi, P.; Jannini, E.A.; Dolci, S. Regulation of Kit Expression in Early Mouse Embryos and ES Cells. Stem Cells 2019, 37, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loveday, C.; Litchfield, K.; Proszek, P.Z.; Cornish, A.J.; Santo, F.; Levy, M.; Macintyre, G.; Holryod, A.; Broderick, P.; Dudakia, D.; et al. Genomic landscape of platinum resistant and sensitive testicular cancers. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, A.; Summersgill, B.; Grygalewicz, B.; Gillis, A.J.; Stoop, J.; van Gurp, R.J.; Dennis, N.; Fisher, C.; Huddart, R.; Cooper, C.; et al. Amplification and overexpression of the KIT gene is associated with progression in the seminoma subtype of testicular germ cell tumors of adolescents and adults. Cancer Res 2005, 65, 8085–8089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Shih, J.; Hollern, D.P.; Wang, L.; Bowlby, R.; Tickoo, S.K.; Thorsson, V.; Mungall, A.J.; Newton, Y.; Hegde, A.M.; et al. Integrated Molecular Characterization of Testicular Germ Cell Tumors. Cell Rep 2018, 23, 3392–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
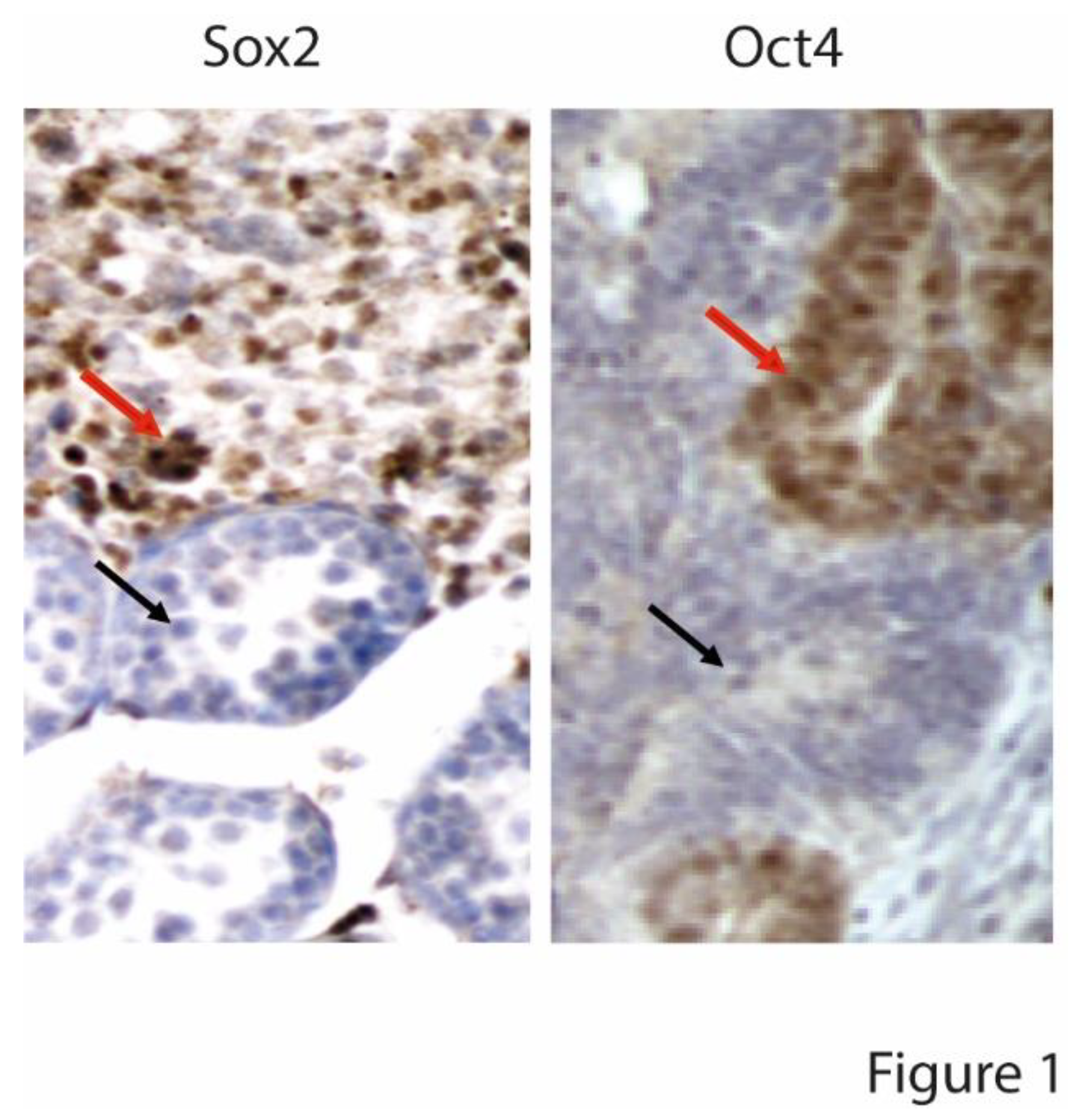
- Pierpont, T.M.; Lyndaker, A.M.; Anderson, C.M.; Jin, Q.; Moore, E.S.; Roden, J.L.; Braxton, A.; Bagepalli, L.; Kataria, N.; Hu, H.Z.; et al. Chemotherapy-Induced Depletion of OCT4-Positive Cancer Stem Cells in a Mouse Model of Malignant Testicular Cancer. Cell Rep 2017, 21, 1896–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poynter, J.N.; Hooten, A.J.; Frazier, A.L.; Ross, J.A. Associations between variants in KITLG, SPRY4, BAK1, and DMRT1 and pediatric germ cell tumors. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2012, 51, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Aksoy, B.A.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E.; et al. The cBio cancer genomics portal: an open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov 2012, 2, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roelofs, H.; Mostert, M.C.; Pompe, K.; Zafarana, G.; van Oorschot, M.; van Gurp, R.J.; Gillis, A.J.; Stoop, H.; Beverloo, B.; Oosterhuis, J.W.; et al. Restricted 12p amplification and RAS mutation in human germ cell tumors of the adult testis. Am J Pathol 2000, 157, 1155–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boublikova, L.; Bakardjieva-Mihaylova, V.; Skvarova Kramarzova, K.; Kuzilkova, D.; Dobiasova, A.; Fiser, K.; Stuchly, J.; Kotrova, M.; Buchler, T.; Dusek, P.; et al. Wilms tumor gene 1 (WT1), TP53, RAS/BRAF and KIT aberrations in testicular germ cell tumors. Cancer Lett 2016, 376, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommerer, F.; Hengge, U.R.; Markwarth, A.; Vomschloss, S.; Stolzenburg, J.U.; Wittekind, C.; Tannapfel, A. Mutations of BRAF and RAS are rare events in germ cell tumours. Int J Cancer 2005, 113, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hacioglu, B.M.; Kodaz, H.; Erdogan, B.; Cinkaya, A.; Tastekin, E.; Hacibekiroglu, I.; Turkmen, E.; Kostek, O.; Genc, E.; Uzunoglu, S.; et al. K-RAS and N-RAS mutations in testicular germ cell tumors. Bosn J Basic Med Sci 2017, 17, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntyre, A.; Summersgill, B.; Spendlove, H.E.; Huddart, R.; Houlston, R.; Shipley, J. Activating mutations and/or expression levels of tyrosine kinase receptors GRB7, RAS, and BRAF in testicular germ cell tumors. Neoplasia 2005, 7, 1047–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carcano, F.M.; Lengert, A.H.; Vidal, D.O.; Scapulatempo Neto, C.; Queiroz, L.; Marques, H.; Baltazar, F.; Berardinelli, G.N.; Martinelli, C.M.; da Silva, E.C.; et al. Absence of microsatellite instability and BRAF (V600E) mutation in testicular germ cell tumors. Andrology 2016, 4, 866–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honecker, F.; Wermann, H.; Mayer, F.; Gillis, A.J.; Stoop, H.; van Gurp, R.J.; Oechsle, K.; Steyerberg, E.; Hartmann, J.T.; Dinjens, W.N.; et al. Microsatellite instability, mismatch repair deficiency, and BRAF mutation in treatment-resistant germ cell tumors. J Clin Oncol 2009, 27, 2129–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, H.; Madar, S.; Rotter, V. Mutant p53 gain of function is interwoven into the hallmarks of cancer. J Pathol 2011, 225, 475–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Einhorn, L.H.; Donohue, J. Cis-diamminedichloroplatinum, vinblastine, and bleomycin combination chemotherapy in disseminated testicular cancer. Ann Intern Med 1977, 87, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achkar, I.W.; Abdulrahman, N.; Al-Sulaiti, H.; Joseph, J.M.; Uddin, S.; Mraiche, F. Cisplatin based therapy: the role of the mitogen activated protein kinase signaling pathway. J Transl Med 2018, 16, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schweyer, S.; Soruri, A.; Meschter, O.; Heintze, A.; Zschunke, F.; Miosge, N.; Thelen, P.; Schlott, T.; Radzun, H.J.; Fayyazi, A. Cisplatin-induced apoptosis in human malignant testicular germ cell lines depends on MEK/ERK activation. Br J Cancer 2004, 91, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.H.; Chang, J.Y. New Insights into Mechanisms of Cisplatin Resistance: From Tumor Cell to Microenvironment. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caggiano, C.; Cavallo, F.; Giannattasio, T.; Cappelletti, G.; Rossi, P.; Grimaldi, P.; Feldman, D.R.; Jasin, M.; Barchi, M. Testicular Germ Cell Tumors Acquire Cisplatin Resistance by Rebalancing the Usage of DNA Repair Pathways. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bokemeyer, C.; Nichols, C.R.; Droz, J.P.; Schmoll, H.J.; Horwich, A.; Gerl, A.; Fossa, S.D.; Beyer, J.; Pont, J.; Kanz, L.; et al. Extragonadal germ cell tumors of the mediastinum and retroperitoneum: results from an international analysis. J Clin Oncol 2002, 20, 1864–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Chun, J.; Pan, C.; Li, D.; Lin, R.; Alesi, G.N.; Wang, X.; Kang, H.B.; Song, L.; Wang, D.; et al. MAST1 Drives Cisplatin Resistance in Human Cancers by Rewiring cRaf-Independent MEK Activation. Cancer Cell 2018, 34, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.R.; Chua, K.N.; Sim, W.J.; Ng, H.C.; Bi, C.; Ho, J.; Nga, M.E.; Pang, Y.H.; Ong, W.R.; Soo, R.A.; et al. MEK Inhibition Overcomes Cisplatin Resistance Conferred by SOS/MAPK Pathway Activation in Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther 2015, 14, 1750–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, F.; Wermann, H.; Albers, P.; Stoop, H.; Gillis, A.J.; Hartmann, J.T.; Bokemeyer, C.C.; Oosterhuis, J.W.; Looijenga, L.H.; Honecker, F. Histopathological and molecular features of late relapses in non-seminomas. BJU Int 2011, 107, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| KIT | RAS | RAF | MEK/ERK | ||
| Sommerer et al., 2005 [96] |
SE | 7% 9% |
0% 9% |
Activated in all (but not mutated) | |
|
NSE | |||||
| Solomon et al., 2011 [101] | SE | 19% 2% |
5-7% 0% |
1% 2% |
|
|
NSE | |||||
| Hacioglu et al., 2017 [97] |
SE | 29% 26% |
|||
|
NSE | |||||
| Shen et al., 2018 [90] |
SE | 18-25% 2% |
KRAS:14% NRAS: 4% |
||
| NSE | low | ||||
| Ahmad et al., 2019 [50] |
SE | 0% | 4% 31% |
0% | |
|
NSE | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





