Submitted:
23 January 2024
Posted:
25 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
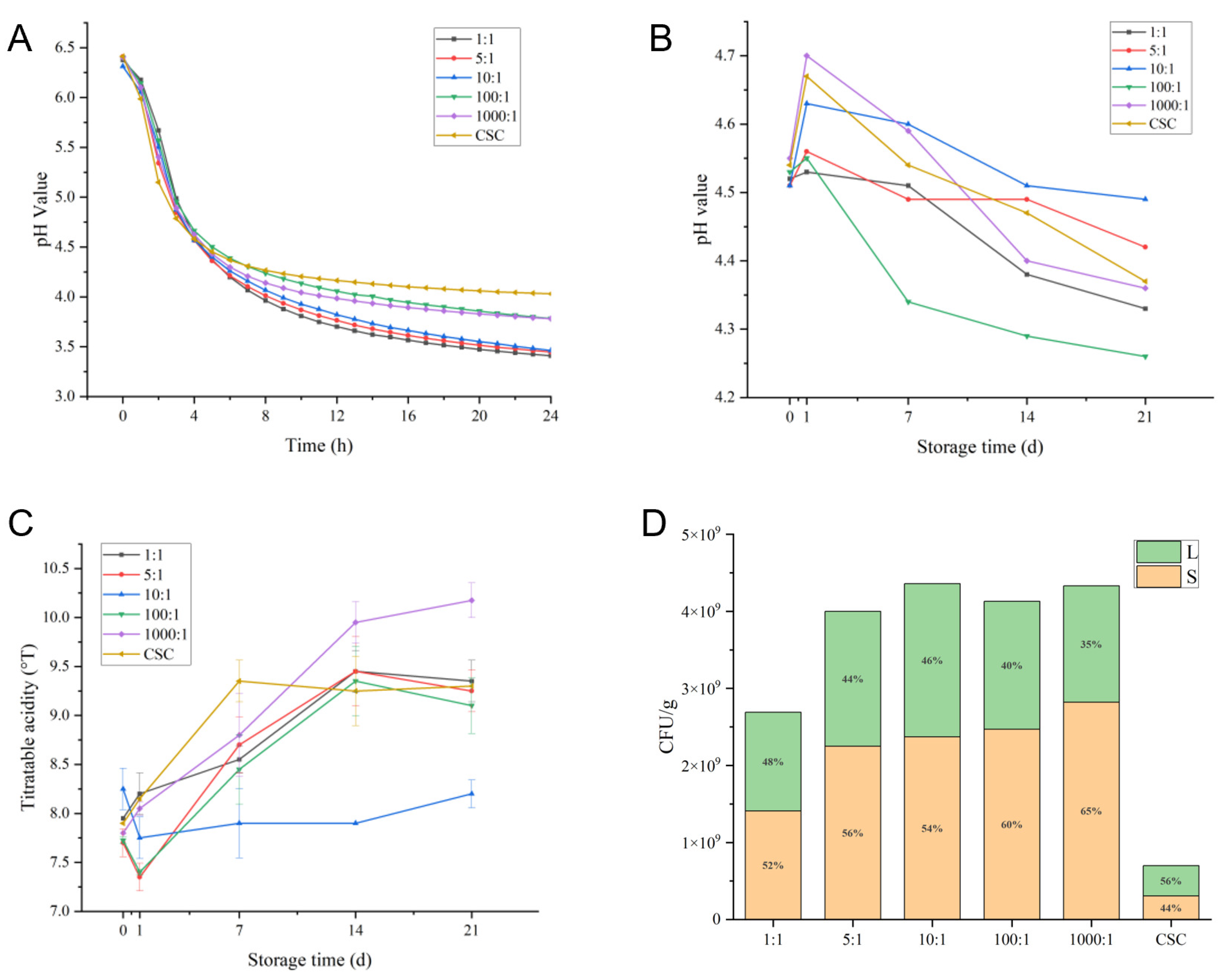
2.1. Physicochemical Characteristics of Fermented Milk in Different Inoculum Ratios
2.2. Rheological Properties of Fermented Milk in Different Inoculum Ratios
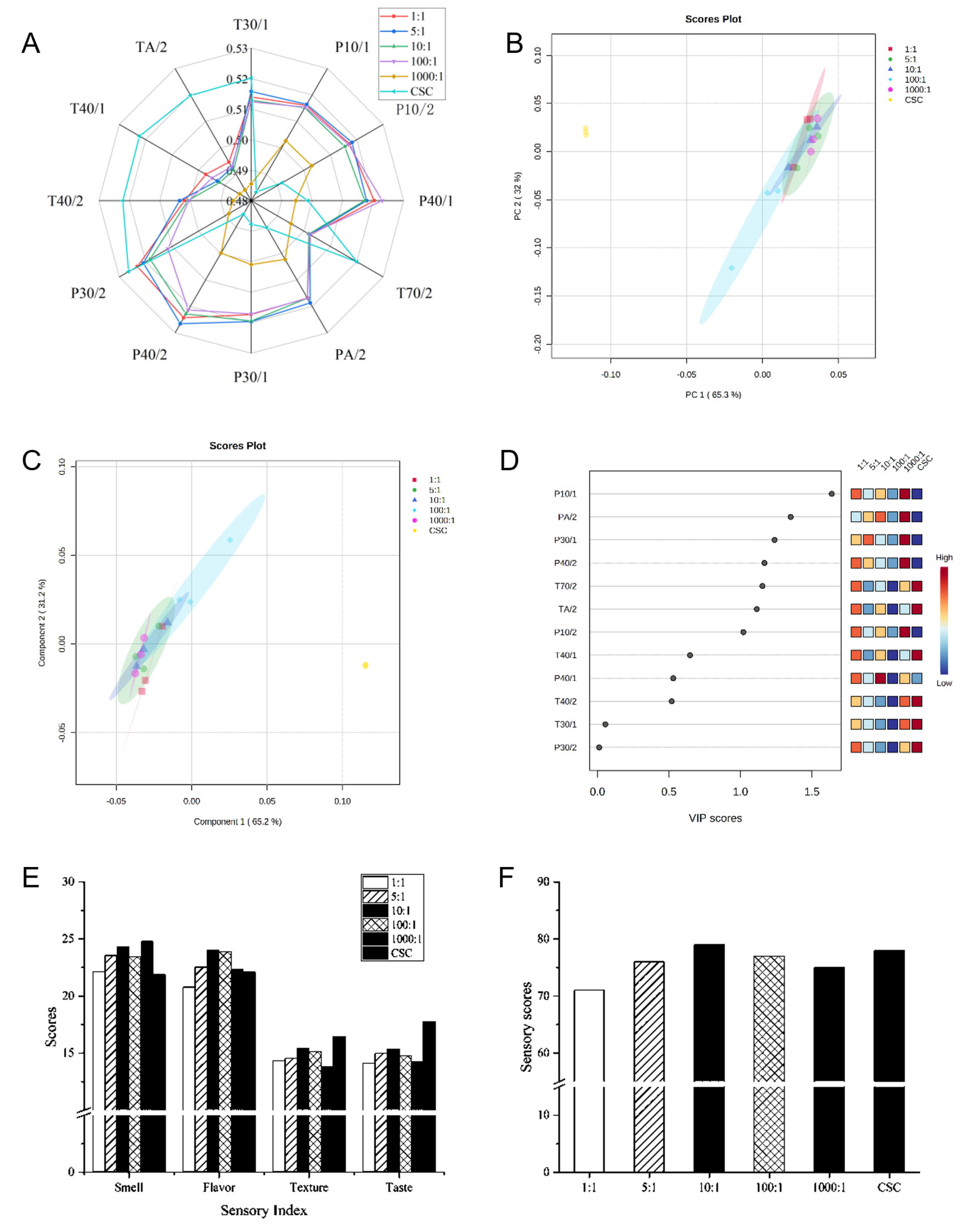
2.3. Sensory Characteristics of Fermented Milk in Different Inoculum Ratios
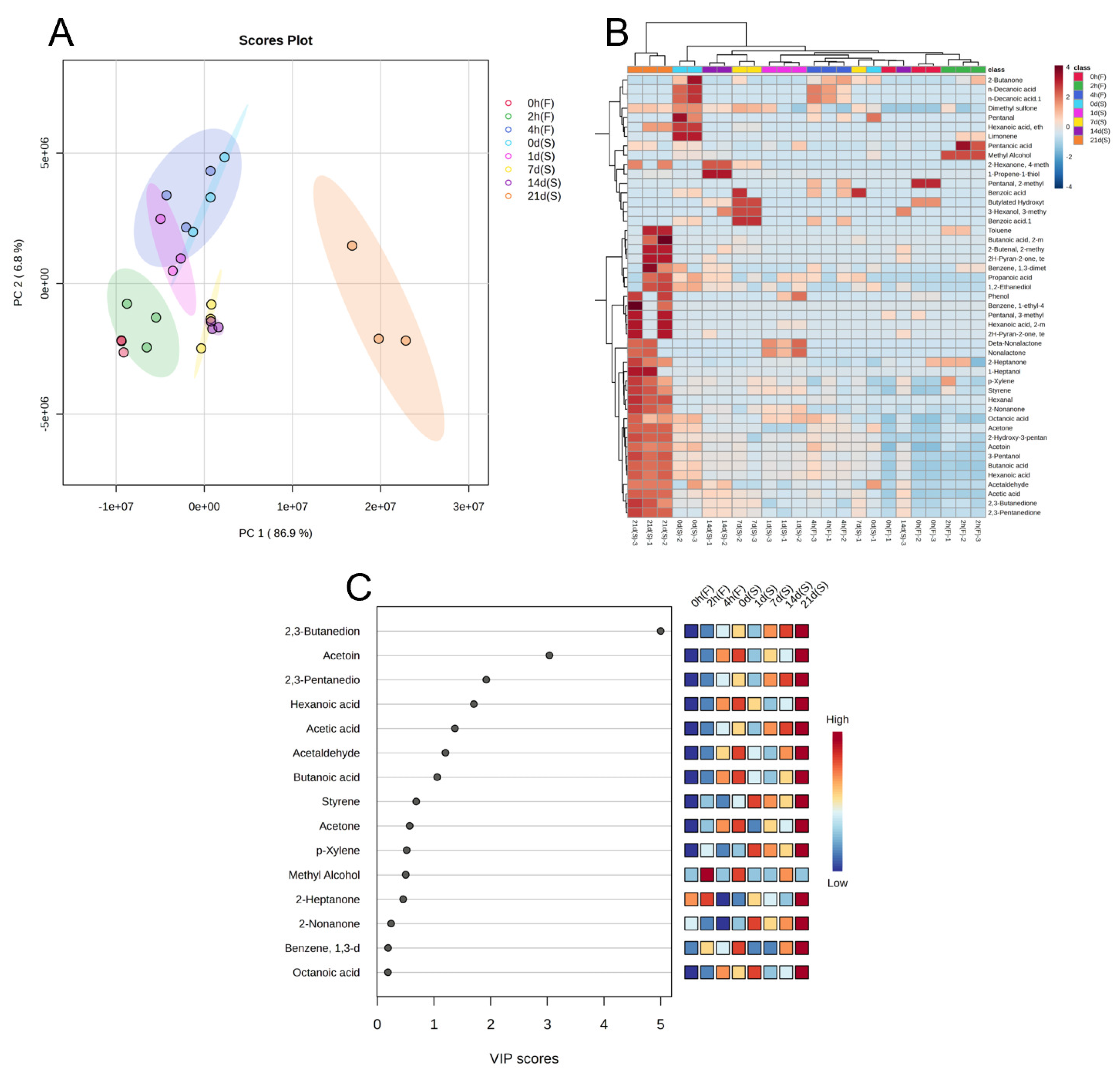
2.4. Volatile Compounds Profiles during Fermentation and Storage
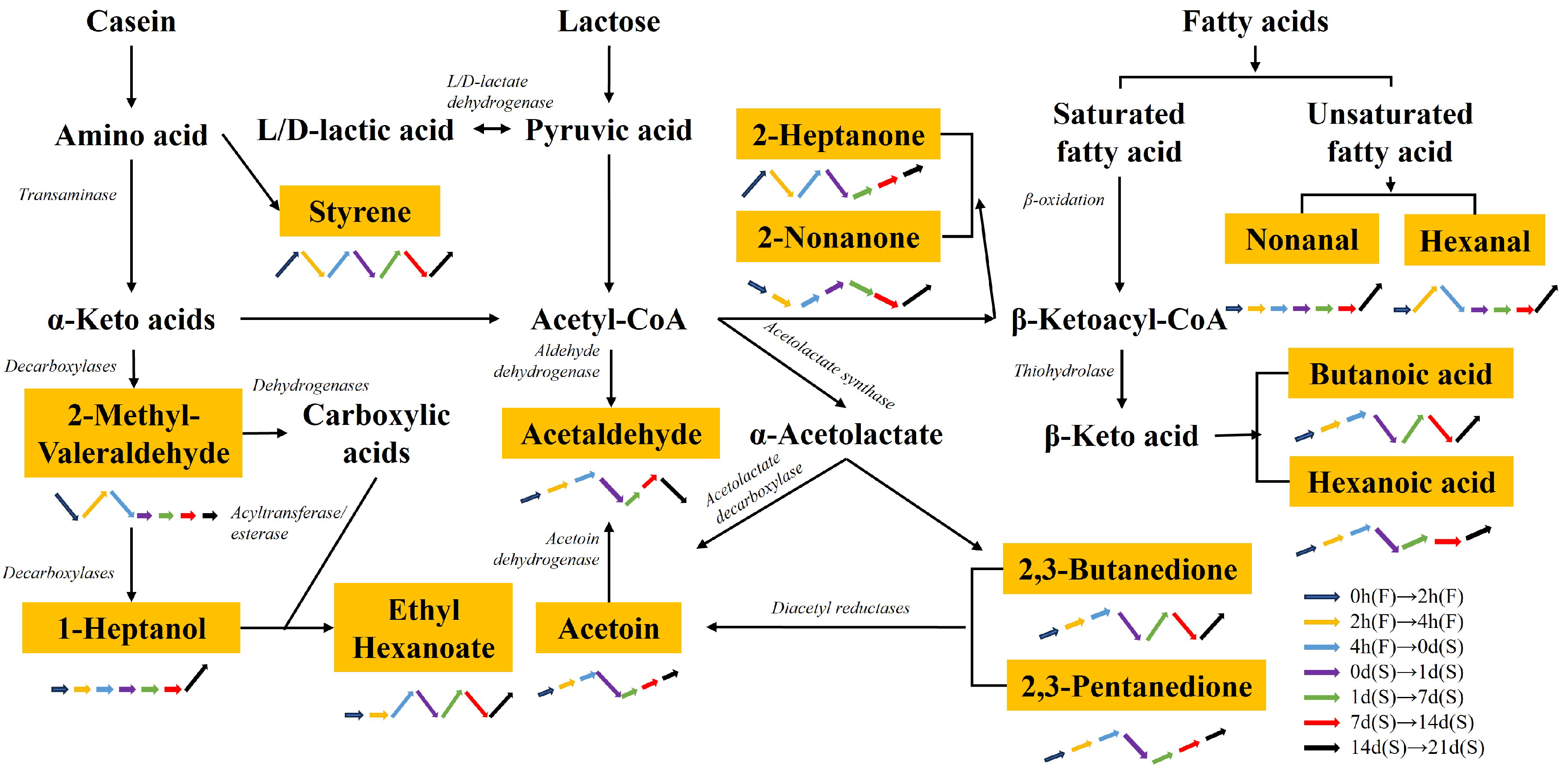
2.5. Analysis of Volatile Compounds during Fermentation and Storage
2.6. Evaluation of OAVs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of Fermented Milk
4.3. pH Value, Titratable Acidity Determination and Enumeration of Viable Cell
4.4. Rheological Property Analysis
4.5. Electronic Nose Analysis
4.6. Sensory Evaluation
4.7. Analysis of Volatile Flavor Compounds by SPME-GC-MS
4.8. Qualitative analysis
4.9. Odor Activity Values Calculation
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alimentarius, C. Milk and milk products; FAO/WHO: Rome, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Dysvik, A.; Liland, K.H.; Myhrer, K.S.; Westereng, B.; Rukke, E.O.; De Rouck, G.; Wicklund, T. Pre-fermentation with lactic acid bacteria in sour beer production. Journal of the Institute of Brewing 2019, 125, 342–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, Ó.J.; Barragán, P.J.; Serna, L. Review of Lactobacillus in the food industry and their culture media. Revista Colombiana de Biotecnología 2019, 21, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Rio, B.; Linares, D.M.; Ladero, V.; Redruello, B.; Fernández, M.; Martin, M.C.; Alvarez, M.A. Putrescine production via the agmatine deiminase pathway increases the growth of Lactococcus lactis and causes the alkalinization of the culture medium. Applied microbiology and biotechnology 2015, 99, 897–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, F.; De Vuyst, L. Lactic acid bacteria as functional starter cultures for the food fermentation industry. Trends in Food Science & Technology 2004, 15, 67–78. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cui, S.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Comparative Peptidomics Analysis of Milk Fermented by Lactobacillus helveticus. Foods 2022, 11, 3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taverniti, V.; Guglielmetti, S. Health-promoting properties of Lactobacillus helveticus. Frontiers in microbiology 2012, 3, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.U.; Nayab, H.; Shafique, F.; Williamson, M.P.; Almansouri, T.S.; Asim, N.; Shafi, N.; Attacha, S.; Khalid, M.; Ali, N.; others. Probiotic properties of Lactobacillus helveticus and Lactobacillus plantarum isolated from traditional Pakistani yoghurt. BioMed Research International 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narva, M.; Nevala, R.; Poussa, T.; Korpela, R. The effect of Lactobacillus helveticus fermented milk on acute changes in calcium metabolism in postmenopausal women. European Journal of Nutrition 2004, 43, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rul, F. Yogurt: Microbiology, organoleptic properties and probiotic potential, 2017.
- Hati, S.; Patel, N.; Mandal, S. Comparative growth behaviour and biofunctionality of lactic acid bacteria during fermentation of soy milk and bovine milk. Probiotics and antimicrobial proteins 2018, 10, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, C.; Chen, X.; Zhao, R.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, X.; Su, J.; Ding, X.; Chen, X.; Huang, Y.; Gu, R. A weak post-acidification Lactobacillus helveticus UV mutant with improved textural properties. Food Science & Nutrition 2021, 9, 469–479. [Google Scholar]
- Ayad, E.H.; Verheul, A.; Engels, W.J.; Wouters, J.; Smit, G. Enhanced flavour formation by combination of selected lactococci from industrial and artisanal origin with focus on completion of a metabolic pathway. Journal of applied microbiology 2001, 90, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Guo, L.; Chen, H.; Ke, W.; Guo, W.; Guo, X.; Zhang, Y. Characteristics of volatile flavor components in traditional fermented yak milk produced in different ecoregions of the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau. Journal of dairy science 2020, 103, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krastanov, A.; Yeboah, P.J.; Wijemanna, N.D.; Eddin, A.S.; Ayivi, R.D.; Ibrahim, S.A. Volatile Aromatic Flavor Compounds in Yogurt: A Review. Current Issues and Advances in the Dairy Industry 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zareba, D.; Ziarno, M.; Obiedzinski, M. Volatile profile of non-fermented milk and milk fermented by Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis. International Journal of Food Properties 2012, 15, 1010–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, F.J.; González-Crespo, J.; Cava, R.; García-Parra, J.; Ramírez, R. Characterisation by SPME–GC–MS of the volatile profile of a Spanish soft cheese PDO Torta del Casar during ripening. Food Chemistry 2010, 118, 182–189. [Google Scholar]
- Dan, T.; Jin, R.; Ren, W.; Li, T.; Chen, H.; Sun, T. Characteristics of milk fermented by Streptococcus thermophilus MGA45-4 and the profiles of associated volatile compounds during fermentation and storage. Molecules 2018, 23, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieuwerts, S.; Molenaar, D.; van Hijum, S.A.; Beerthuyzen, M.; Stevens, M.J.; Janssen, P.W.; Ingham, C.J.; de Bok, F.A.; de Vos, W.M.; van Hylckama Vlieg, J.E. Mixed-culture transcriptome analysis reveals the molecular basis of mixed-culture growth in Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactobacillus bulgaricus. Applied and environmental microbiology 2010, 76, 7775–7784. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Lan, F.; Wang, J. Screening of the Best Strain for Naked Oat Fermentation Beverage and its Production Process Study. Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Applied Biotechnology (ICAB 2012) Volume 1. Springer, 2014, pp. 181–191.
- Monge, M.E.; Negri, R.M.; Giacomazza, D.; Bulone, D. Correlation between rheological properties and limonene release in pectin gels using an electronic nose. Food hydrocolloids 2008, 22, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rault, A.; Bouix, M.; Béal, C. Fermentation pH influences the physiological-state dynamics of Lactobacillus bulgaricus CFL1 during pH-controlled culture. Applied and environmental microbiology 2009, 75, 4374–4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Shen, Y.; Yu, H.; He, Y.; Chen, C. Effects of 4 probiotic strains in coculture with traditional starters on the flavor profile of yogurt. Journal of Food Science 2017, 82, 1693–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.; Prajapati, J. Effect of carbon dioxide on sensory attributes, physico-chemical parameters and viability of Probiotic L. helveticus MTCC 5463 in fermented milk. Journal of food Science and Technology 2014, 51, 3886–3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaridou, A.; Serafeimidou, A.; Biliaderis, C.G.; Moschakis, T.; Tzanetakis, N. Structure development and acidification kinetics in fermented milk containing oat β-glucan, a yogurt culture and a probiotic strain. Food Hydrocolloids 2014, 39, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, W.; Bai, M.; Wang, J.; Sun, Z. Analysis of cofermentation characteristics of Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus based on microrheology. Food Bioengineering 2022, 1, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Tian, Y.; Liang, Q.; Ren, F. Rennet-induced coagulation properties of yak casein micelles: A comparison with cow casein micelles. Food Research International 2017, 102, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Hu, R.; Zhao, J.; Liu, W.; Kwok, L.Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y. Acetate kinase and peptidases are associated with the proteolytic activity of Lactobacillus helveticus isolated from fermented food. Food Microbiology 2021, 94, 103651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titapiccolo, G.I.; Corredig, M.; Alexander, M. Acid coagulation behavior of homogenized milk: effect of interacting and non-interacting droplets observed by rheology and diffusing wave spectroscopy. Dairy science & technology 2011, 91, 185–201. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H. Volatile flavor compounds in yogurt: A review. Critical reviews in food science and nutrition 2010, 50, 938–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Mi, S.; Liu, R.; Sang, Y.; Wang, X. Evaluation of volatile compounds in milks fermented using traditional starter cultures and probiotics based on odor activity value and chemometric techniques. Molecules 2020, 25, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Xu, S. Effects of different commercial lipases on the volatile profile of lipolysed milk fat. Flavour and fragrance journal 2009, 24, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadwallader, K.R.; Singh, T.K.; Jerrell, J.P. Streamlined analysis of short-, medium-, and long-chain free fatty acids in dairy products; ACS Publications, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Xu, X.; Shi, Y.; Wang, C. Nutritional value and current research status of goat milk. J. Dairy Sci. Technol 2013, 36, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Brányik, T.; Silva, D.P.; Baszczyňski, M.; Lehnert, R.; e Silva, J.B.A. A review of methods of low alcohol and alcohol-free beer production. Journal of Food Engineering 2012, 108, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranowska, M.; others. Intensification of the synthesis of flavour compounds in yogurt by milk enrichment with their precursors. Polish journal of food and nutrition sciences 2006, 15, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Bongers, R.S.; Hoefnagel, M.H.; Kleerebezem, M. High-level acetaldehyde production in Lactococcus lactis by metabolic engineering. Applied and environmental microbiology 2005, 71, 1109–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villavicencio, J.D.; Zoffoli, J.P.; Plotto, A.; Contreras, C. Aroma compounds are responsible for an herbaceous off-flavor in the sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) Cv. regina during fruit development. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, T.; Ren, W.; Liu, Y.; Tian, J.; Chen, H.; Li, T.; Liu, W. Volatile flavor compounds profile and fermentation characteristics of milk fermented by Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus. Frontiers in Microbiology 2019, 10, 2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincon-Delgadillo, M.; Lopez-Hernandez, A.; Wijaya, I.; Rankin, S. Diacetyl levels and volatile profiles of commercial starter distillates and selected dairy foods. Journal of dairy science 2012, 95, 1128–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedamuthu, E.R. Starter cultures for yogurt and fermented milks. Manufacturing yogurt and fermented milks 2013, pp. 115–148.
- Zhao, M.; Li, H.; Zhang, D.; Li, J.; Wen, R.; Ma, H.; Zou, T.; Hou, Y.; Song, H. Variation of Aroma Components of Pasteurized Yogurt with Different Process Combination before and after Aging by DHS/GC-O-MS. Molecules 2023, 28, 1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comasio, A.; Harth, H.; Weckx, S.; De Vuyst, L. The addition of citrate stimulates the production of acetoin and diacetyl by a citrate-positive Lactobacillus crustorum strain during wheat sourdough fermentation. International journal of food microbiology 2019, 289, 88–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molimard, P.; Spinnler, H.E. Compounds involved in the flavor of surface mold-ripened cheeses: Origins and properties. Journal of dairy science 1996, 79, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, T.; Wang, D.; Jin, R.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, T.; Sun, T. Characterization of volatile compounds in fermented milk using solid-phase microextraction methods coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Journal of dairy science 2017, 100, 2488–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wen, R.; Chen, Q.; Kong, B. Role of lactic acid bacteria in flavor development in traditional Chinese fermented foods: A review. Critical reviews in food science and nutrition 2022, 62, 2741–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curioni, P.; Bosset, J. Key odorants in various cheese types as determined by gas chromatography-olfactometry. International Dairy Journal 2002, 12, 959–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, O.; FitzGerald, R.; O’Cuinn, G.; Beresford, T.; Jordan, K. Autolysis of selected Lactobacillus helveticus adjunct strains during Cheddar cheese ripening. International Dairy Journal 2006, 16, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lortal, S.; Chapot-Chartier, M.P. Role, mechanisms and control of lactic acid bacteria lysis in cheese. International Dairy Journal 2005, 15, 857–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Routray, W.; Mishra, H.N. Scientific and technical aspects of yogurt aroma and taste: a review. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety 2011, 10, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Ye, L.; Wang, J.; Wei, Z.; Cheng, S. Quality tracing of peanuts using an array of metal-oxide based gas sensors combined with chemometrics methods. Postharvest Biology and Technology 2017, 128, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Guo, S.; Wu, T.; Yang, Y.; Yu, X.; Yao, S. Inoculum size of co-fermentative culture affects the sensory quality and volatile metabolome of fermented milk over storage. Journal of Dairy Science 2022, 105, 5654–5668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, T.; Chen, H.; Li, T.; Tian, J.; Ren, W.; Zhang, H.; Sun, T. Influence of Lactobacillus plantarum P-8 on fermented milk flavor and storage stability. Frontiers in microbiology 2019, 9, 3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, T.; Hu, H.; Li, T.; Dai, A.; He, B.; Wang, Y. Screening of mixed-species starter cultures for increasing flavour during fermentation of milk. International Dairy Journal 2022, 135, 105473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Volatile Compound | µg/L | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2h (F) | 4h (F) | 1d (S) | 7d (S) | 14d (S) | 21 d(S) | |||||||
| Carboxylic acid compounds | ||||||||||||
| Acetic acid | 23.51 | 1408 | 1461 | MS, RI | 0.39±0.03 | 4.25±2.92 | 27.68±7.06 | 39.44±12.65 | 12.71±1.22 | 34.53±2.51 | 42.38±0.91 | 35.62±0.93 |
| Propanoic acid | 27.111 | 1516 | 1540 | MS, RI | - | - | 0.18±0 | 0.32±0.1 | 0.11±0 | 0.17±0.05 | 0.17±0 | 0.16±0.01 |
| Butanoic acid | 30.655 | 1605 | 1647 | MS, RI | - | 4.19±4.17 | 34.75±6.65 | 50.45±14.54 | 15.42±1.17 | 25.69±4.15 | 26.67±1.1 | 31.56±0.82 |
| 2-Methyl-hexanoic acid | 32.183 | 1645 | nf | MS | - | - | - | - | 0.09±0 | - | - | 0.34±0 |
| 2-Methyl-butanoic acid | 32.242 | 1647 | 1652 | MS, RI | - | - | - | - | - | 0.15±0 | - | 0.4±0.15 |
| Hexanoic acid | 38.709 | 1822 | 1861 | MS, RI | - | 13.85±0 | 60.05±11.77 | 90.84±35.89 | 28.92±3.44 | 37±3.63 | 37.12±3.47 | 55.67±3.65 |
| Pentanoic acid | 38.735 | 1822 | 1762 | MS, RI | - | 2.84±0.62 | - | 0.54±0.22 | 0.28±0.2 | - | 0.12±0.05 | 0.21±0.01 |
| Octanoic acid | 45.911 | 2036 | 2072 | MS, RI | - | 3.06±2.6 | 10.81±3.11 | 14.34±6.93 | 6.8±0.85 | 4.97±0.83 | 5.71±0.68 | 6.34±1.45 |
| n-Decanoic acid | 52.46 | 2248 | 2314 | MS, RI | - | - | 1.15±0.41 | 2.47±0.35 | - | - | - | - |
| Benzoic acid | 57.177 | 2413 | 2457 | MS, RI | - | - | 3.63±0 | 3.3±0.48 | - | 7.41±0 | - | - |
| Aldehydes | ||||||||||||
| Acetaldehyde | 3.497 | STD | 714 | MS | - | 5.59±0 | 20.26±5.27 | 74.39±56.32 | 8.35±5.89 | 5.93±0.58 | 41.32±10.56 | 35.62±0 |
| Pentanal | 8.955 | 1056 | 1100 | MS, RI | - | - | 0.31±0 | 1.11±0.33 | - | - | - | - |
| Hexanal | 9.087 | 1061 | 1079 | MS, RI | - | - | 0.78±0.27 | - | - | - | - | 2.4±0.23 |
| 3-Methyl-pentanal | 9.207 | 1065 | nf | MS | 1.1±0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.23±0 |
| 2-Methyl-2-butenal | 13.622 | 1195 | 1104 | MS, RI | 0.15±0 | - | - | - | - | 0.31±0 | 0.72±0 | 1.11±0 |
| 2-Methyl-pentanal | 21.114 | 1370 | nf | MS | 6.26±0 | - | 2.32±0 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 2-Methyl-hexanal | 21.306 | 1375 | nf | MS | - | - | - | - | - | - | 4.77±0 | - |
| Nonanal | 23.814 | 1410 | 1390 | MS, RI | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.76±0 |
| Furfural | 23.865 | 1410 | 1468 | MS, RI | - | - | 0.22±0 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Benzaldehyde | 26.316 | 1428 | 1520 | MS, RI | - | - | - | 1.94±0 | - | - | - | - |
| Ketones | ||||||||||||
| Acetone | 4.237 | STD | 814 | MS | - | 18.81±0 | 23.45±0 | 42.99±0 | 2.51±0 | 14.85±0 | 13.63±0 | 22.63±0 |
| 2-Butanone | 4.994 | STD | 881 | MS | - | 2.06±1.36 | 2.04±0.86 | 4.02±2.56 | - | 1.42±0 | - | - |
| 2,3-Butanedione | 6.418 | STD | 971 | MS | - | 52.39±0 | 49.75±36.67 | 111.51±9.48 | 32.44±0 | 129±1.94 | 122.87±6.89 | 135.28±24.24 |
| 2,3-Pentanedione | 8.311 | 1033 | 1062 | MS, RI | - | 6.08±1.85 | 12.93±2.91 | 21.8±2.99 | 9.18±0.35 | 37.25±5.72 | 45.01±0.47 | 51.36±3.78 |
| 2-Heptanone | 12.604 | 1167 | 1184 | MS, RI | 64.9±26.76 | 108.5±0 | 28.79±2.37 | 41.34±13.74 | 22.85±0.23 | 31.77±2.88 | 28.91±2.84 | 39.17±5.93 |
| Acetoin | 16.66 | 1267 | 1280 | MS, RI | - | 76.26±28.11 | 153.22±38.03 | 231.14±45.89 | 58.65±3.37 | 109.48±19.04 | 97.74±1.95 | 104.88±6.01 |
| Cyclohexanone | 16.945 | 1274 | 1282 | MS, RI | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.73±0 |
| 2-Hydroxy-3-pentanone | 19.702 | 1338 | 1380 | MS, RI | - | 3.21±0 | 4.95±0.79 | 6.57±1.61 | 2.42±0.25 | 4.19±0.03 | 4.18±0 | 5.69±0.26 |
| 4-Methyl-2-hexanone | 21.205 | 1372 | nf | MS | - | - | - | - | - | 1.39±0 | 3.03±0 | 1.02±0 |
| 2-Nonanone | 21.441 | 1378 | 1386 | MS, RI | 2.91±0 | 1.46±0 | - | 2.99±0 | 4.57±0.92 | 3.99±1.55 | 3.95±0 | 7.79±0.92 |
| 2h (F) | 4h (F) | 1d (S) | 7d (S) | 14d (S) | 21 d(S) | |||||||
| Alcohols | ||||||||||||
| Methyl alcohol | 3.669 | STD | 888 | MS | - | 97.33±0 | - | 20.41±0 | - | - | 8.35±2.54 | - |
| 2-Methyl-1-pentanol | 17.213 | 1281 | nf | MS | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.19±0 |
| 3-Penten-2-ol | 18.304 | 1306 | 1170 | MS, RI | - | - | 0.82±0 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 3-Pentanol | 19.017 | 1323 | 1108 | MS, RI | - | - | 4.17±1.34 | 6.29±1.7 | 2.39±0.18 | 3.86±0.78 | 4.09±0.1 | 5.48±0.4 |
| 2-Hexanol | 19.721 | 1339 | 1226 | MS, RI | - | - | - | - | - | 3.47±0 | - | - |
| 1,2-Ethanediol | 20.355 | 1353 | 1621 | MS, RI | - | - | - | 1.61±0.32 | 0.43±0.05 | 0.58±0 | 0.64±0.08 | 0.83±0.03 |
| Benzaldehyde | 26.316 | 1428 | 1520 | MS, RI | - | - | - | 1.94 | - | - | - | - |
| Linalool | 27.563 | 1527 | 1549 | MS, RI | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.18±0 |
| 1-Propene-1-thiol | 41.706 | 1908 | nf | MS | - | - | - | - | 0.05±0 | 0.03±0 | 2.58±0 | 0.06±0 |
| 1,4-Butanediol | 41.75 | 1909 | nf | MS | - | - | - | 0.77±0 | - | - | - | - |
| 3-Methyl-3-hexanol | 43.237 | 1954 | nf | MS | - | - | - | - | - | 0.02±0 | 0.02±0 | - |
| Esters | ||||||||||||
| Ethyl acetate | 8.77 | 1049 | nf | MS | - | 0.16±0 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Ethyl hexanoate | 14.494 | 1216 | 1246 | MS, RI | - | - | - | 2.12±0 | - | 0.19±0 | - | 0.36±0 |
| Ethyl orthoformate | 29.256 | 1570 | nf | MS | - | - | - | - | - | 0.04±0 | - | - |
| -Nonalactone | 50.4 | 2179 | nf | MS | - | - | - | - | 0.42±0.1 | - | - | 0.35±0.01 |
| 2H-Pyran-2-one, tetrahydro-6-pentyl- | 50.435 | 2180 | 1999 | MS, RI | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.21±0.01 | 0.37±0 |
| Others | ||||||||||||
| Toluene | 7.28 | STD | 1037 | MS | - | 2.09±0 | - | - | - | - | - | 1.32±0 |
| p-Xylene | 10.532 | 1110 | 1164 | MS, RI | - | 29.83±30.25 | 12.41±5.51 | 18.13±3.89 | 8.74±1.93 | 14.87±3.51 | 13.86±3.21 | 17.04±4.02 |
| 1,3-Dimethyl-benzene | 10.919 | 1121 | 1141 | MS, RI | - | 12.01±0 | 8.28±4.67 | 16.18±9.71 | - | - | 8.67±0 | 11.84±4.84 |
| Limonene | 13.047 | 1179 | 1198 | MS, RI | - | 2.91±0 | - | 8.86±0 | - | - | - | - |
| 1-Ethyl-4-methyl-benzene | 14.106 | 1207 | 1216 | MS, RI | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.39±0.5 |
| Styrene | 15.405 | 1238 | 1259 | MS, RI | 1.8±1.29 | 20.24±11.45 | 14.34±4.11 | 21.29±7.97 | 14.99±0.97 | 18.22±4.9 | 16.79±2.2 | 22.01±3.41 |
| Mesitylene | 16.363 | 1261 | 1237 | MS, RI | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.14 |
| Dimethyl sulfone | 40.667 | 1878 | 1912 | MS, RI | - | 0.42±0.26 | 0.35±0.28 | 0.91±0.36 | 0.22±0.15 | 0.59±0.11 | 0.41±0.03 | 0.21±0.02 |
| Butylated Hydroxytoluene | 40.851 | 1883 | 1920 | MS, RI | 0.31±0 | - | - | - | - | 0.32±0 | 0.1±0 | - |
| Phenol | 43.943 | 1975 | 1987 | MS, RI | 0.06±0 | - | - | - | 0.1±0.04 | - | - | 0.1±0 |
| Internal standard | ||||||||||||
| 3-Heptanone, 2-methyl- | 11.987 | 1150 | nf | MS | 81.60 | 81.60 | 81.60 | 81.60 | 81.60 | 81.60 | 81.60 | 81.60 |
| Volatile Compound | Odor threshold ( µg/L)1 | Description1 | OAV | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h (F)2 | 2 h (F) | 4 h (F) | 0 d (S)3 | 1 d (S) | 7 d(S) | 14 d(S) | 21 d (S) | |||
| Acetaldehyde | 0.7 | as a flavor ingredient /enhancer | - | 7.99 | 28.94 | 106.26 | 17.90 | 27.96 | 59.02 | 50.88 |
| 2, 3-Butanedione | 0.3 | buttery odor | - | 174.62 | 204.29 | 371.71 | 108.12 | 429.99 | 409.57 | 450.95 |
| 2, 3-Pentanedione | 20 | a penetrating, buttery taste | - | 0.30 | 0.65 | 1.09 | 0.46 | 1.86 | 2.25 | 2.57 |
| Hexanal | 4.1 | fatty, green, grassy, fruity odor | - | - | 0.19 | - | - | - | - | 0.59 |
| 2-Heptanone | 1 | fruity, spicy, cinnamon, banana | 49.47 | 108.50 | 28.79 | 41.34 | 22.85 | 29.09 | 30.96 | 39.17 |
| Ethyl Hexanoate | 0.3 | a powerful, fruity odor | - | - | - | 7.08 | - | 0.64 | - | 1.20 |
| Styrene | 3.6 | a characteristic, sweet, balsamic, almost floral odor | 0.50 | 5.62 | 3.98 | 5.91 | 4.16 | 5.06 | 4.66 | 6.11 |
| Acetoin | 5 | a bland, woody, yogurt odor | - | 15.25 | 26.31 | 46.23 | 11.73 | 17.59 | 19.55 | 20.98 |
| 2-Methyl-Valeraldehyde | 1.6 | ethereal, fruity odor | 3.92 | - | 1.45 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 2-Nononone | 5 | a rose and tea-like flavor | 0.58 | 0.29 | - | 0.60 | 0.91 | 0.80 | 0.79 | 1.56 |
| Nonanal | 1 | a fatty, citrus-like flavor | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.76 |
| 1-Heptanol | 3 | fragrant, woody, heavy, oily, faint, aromatic, fatty odor | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.12 |
| Butanoic acid | 240 | persistent, butter-like odor | - | 0.02 | 0.14 | 0.21 | 0.06 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.13 |
| Hexanoic acid | 93 | sour, pungent, cheesy, fatty | 0.01 | 0.15 | 0.57 | 0.98 | 0.31 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





