Submitted:
24 January 2024
Posted:
24 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- We propose a novel SA-LSTM model that integrates the self-attention mechanism and LSTM networks. SA-LSTM treats the localization problem as a sequence learning task. It processes the RSSI values of consecutive time instances and predicts the position at the final moment in the input sequence. The self-attention mechanism enables the LSTM to more effectively capture the interdependencies between the RSSI values at different time instances, thereby facilitating improved extraction of location information and reducing the localization error.
- We validate the performance of the proposed SA-LSTM model in two distinct experimental environments. The first experiment scenario involves collecting Bluetooth RSSI data while moving in 2D trajectories on a specific floor. In the second experiment, we used an open-source WiFi RSSI dataset containing 3D-moving trajectories across various floors within a building.
- We conduct a comparative analysis between our proposed model and several state-of-the-art methods. The experimental results reveal that our proposed SA-LSTM model achieves the highest localization accuracy in both experimental scenarios, demonstrating its robustness and precision.
2. Related Work
3. Methodology
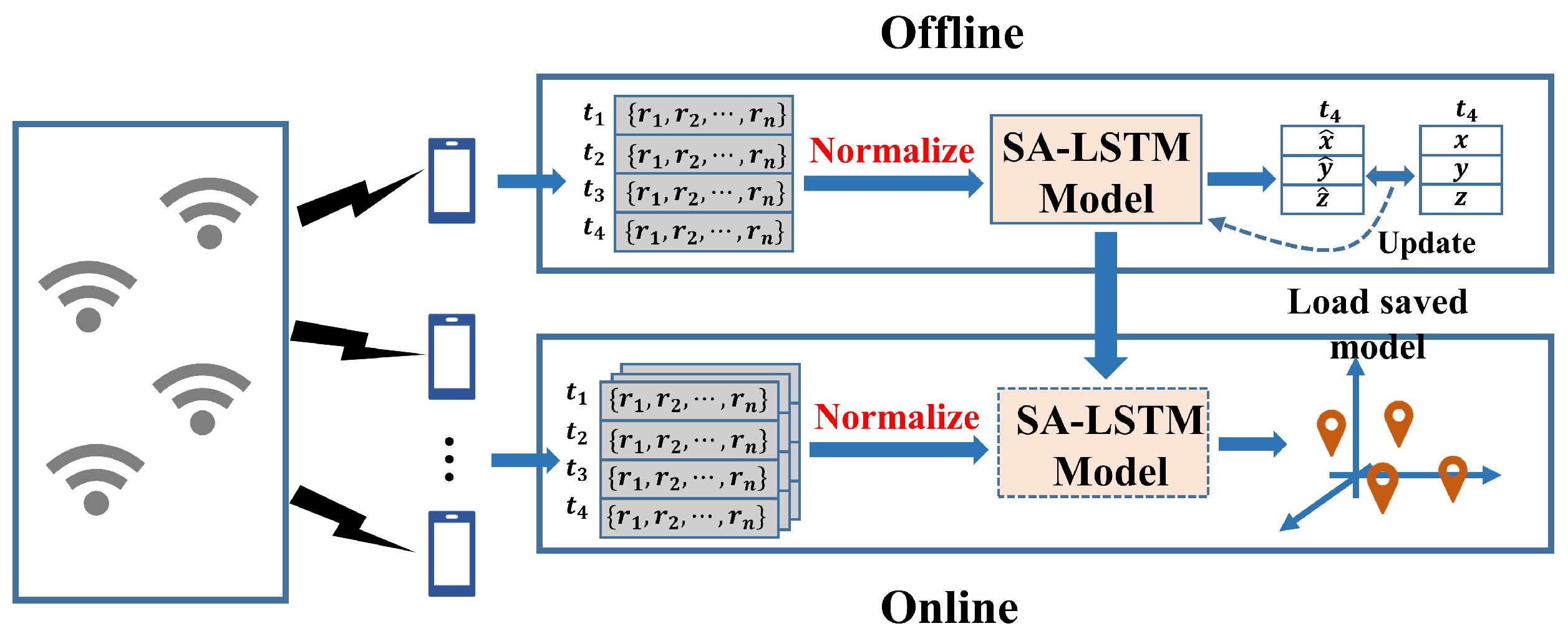
3.1. SA-LSTM based Localization Algorithm
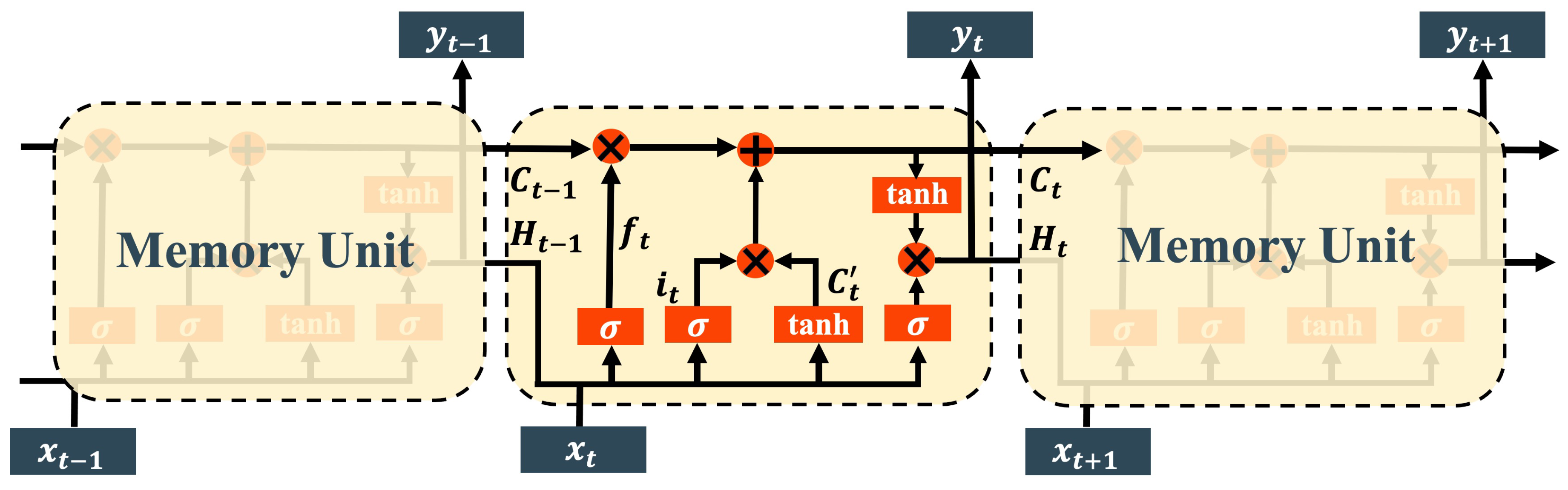
3.2. LSTM Network
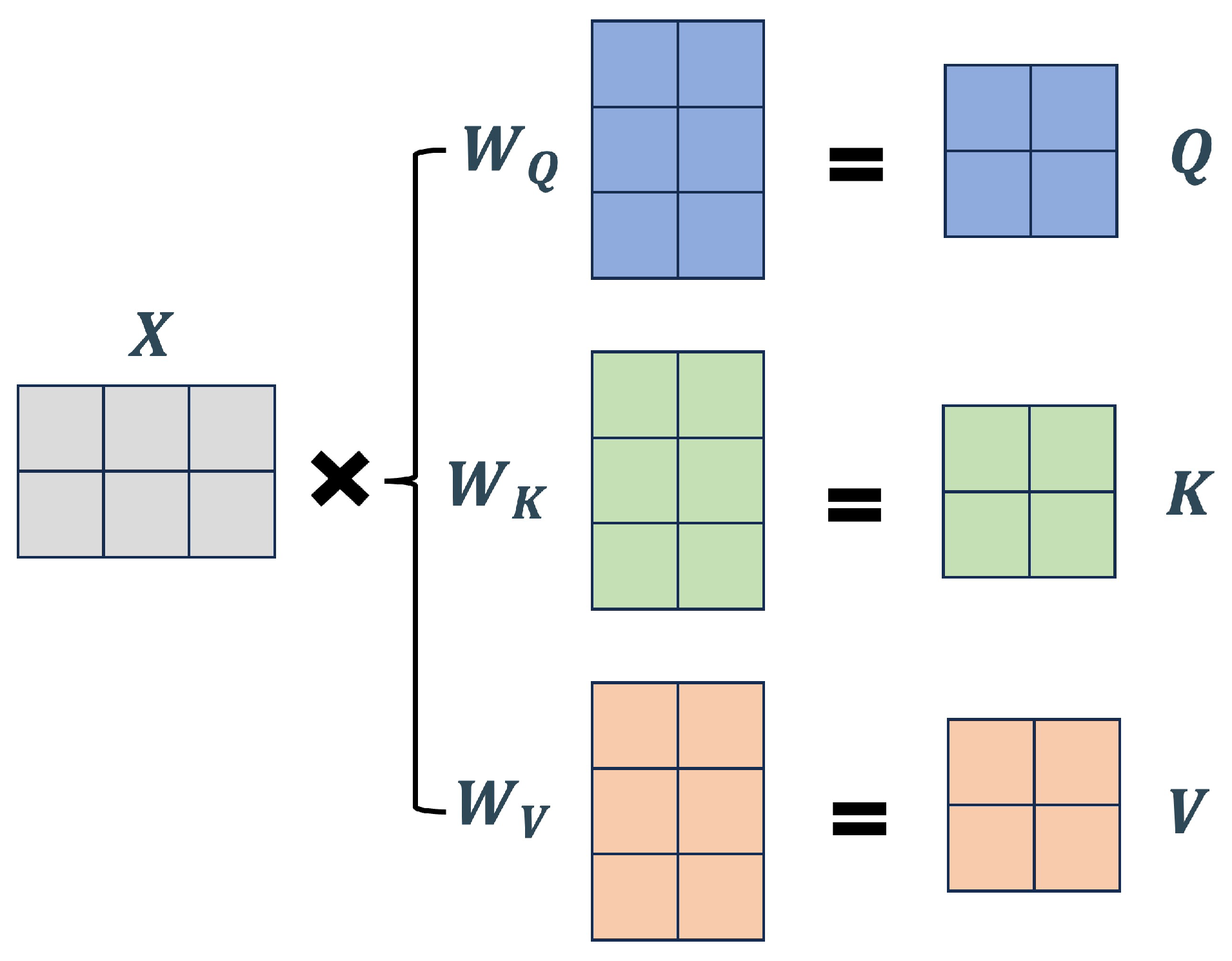
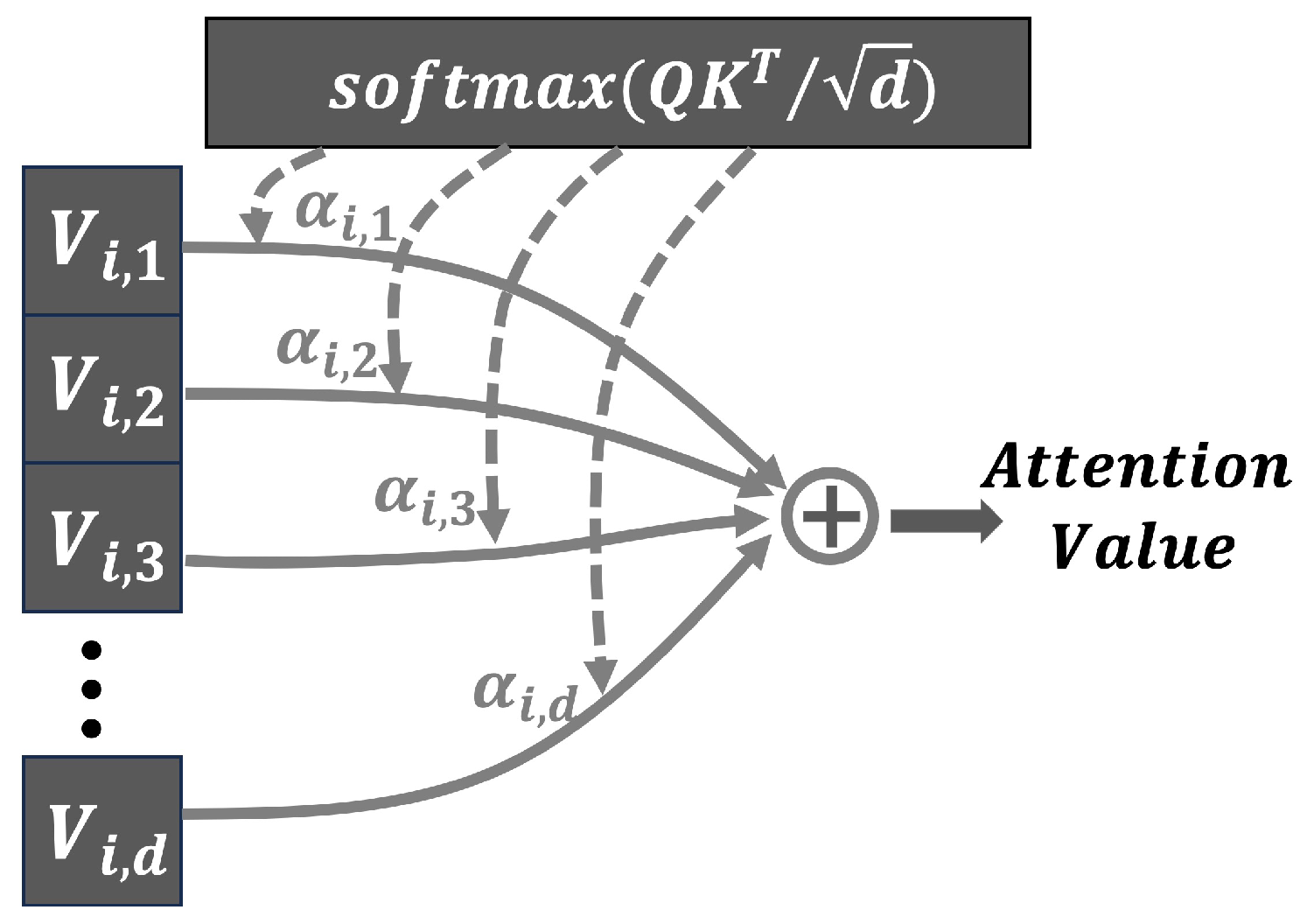
3.3. Self-attention Mechanism
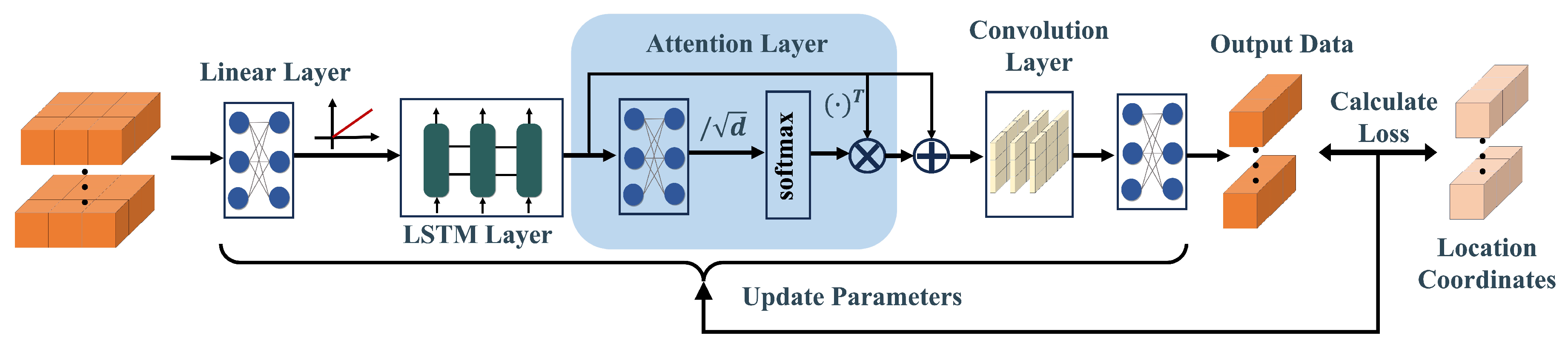
3.4. Proposed SA-LSTM Network
3.4.1. Input Sequence Data
3.4.2. The Layers of Network
4. Experimental Setup
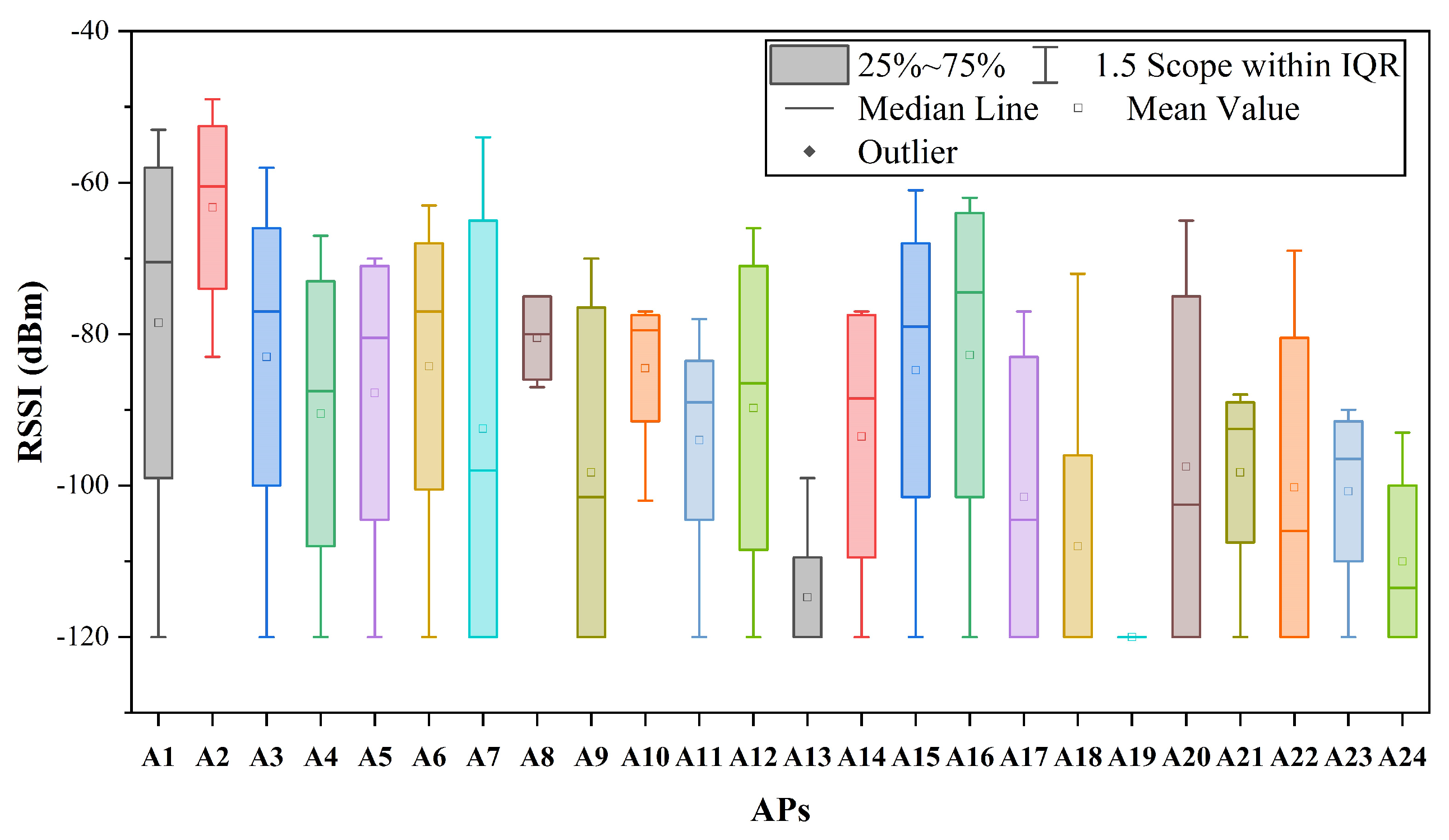
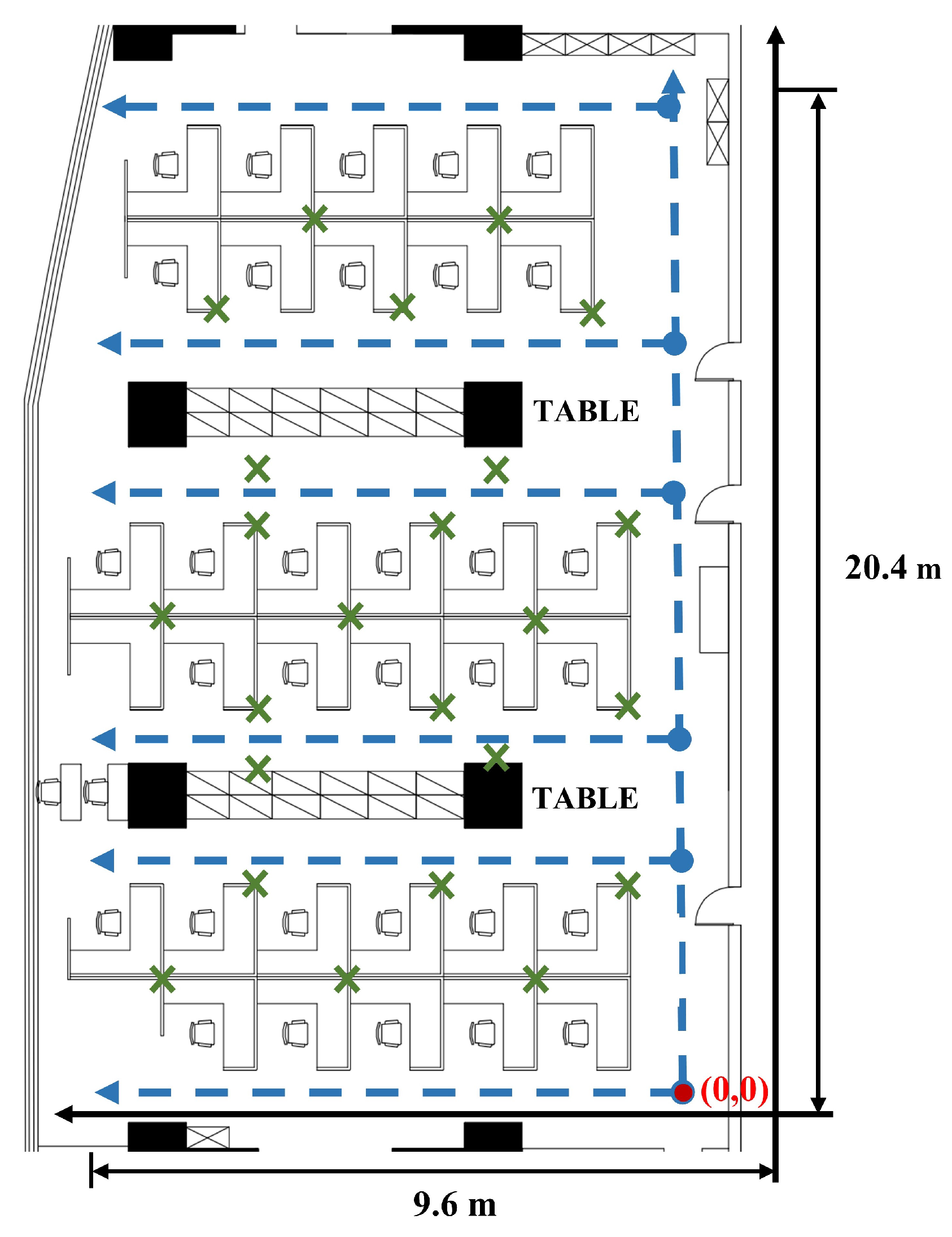
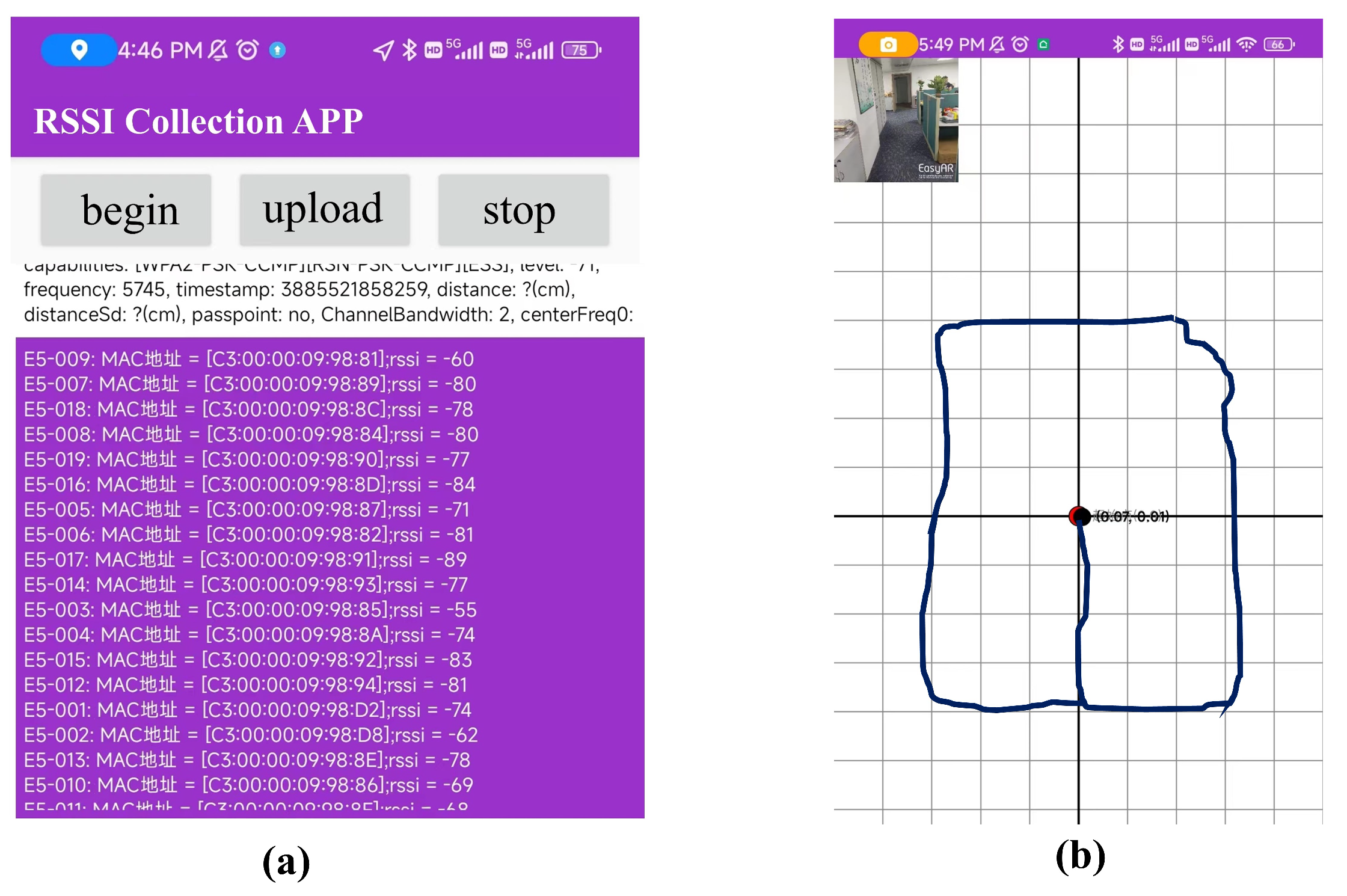
4.1. 2D-moving Experiment Setup
4.2. 3D-moving Experiment Setup
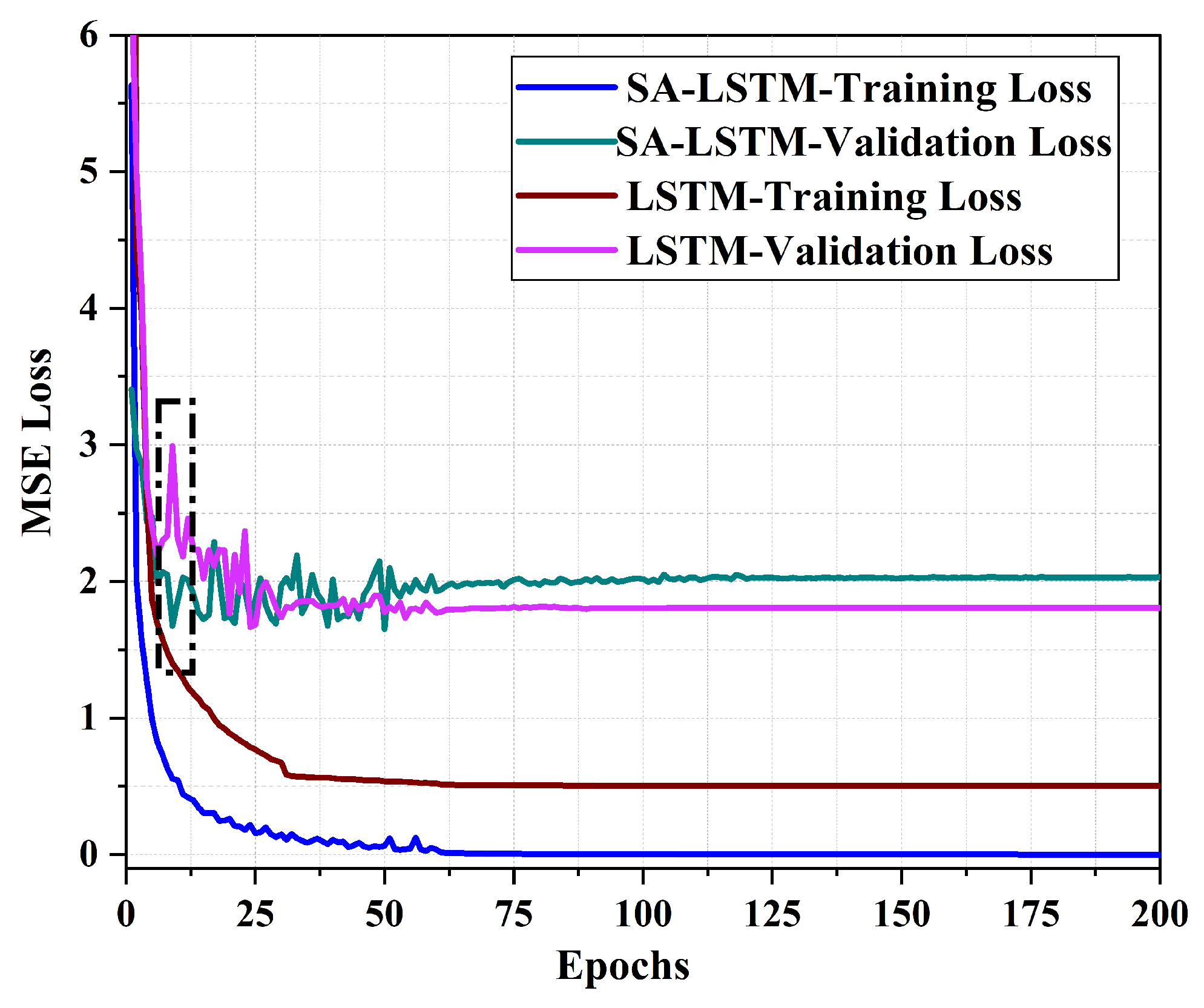
4.3. SA-LSTM Training Setup
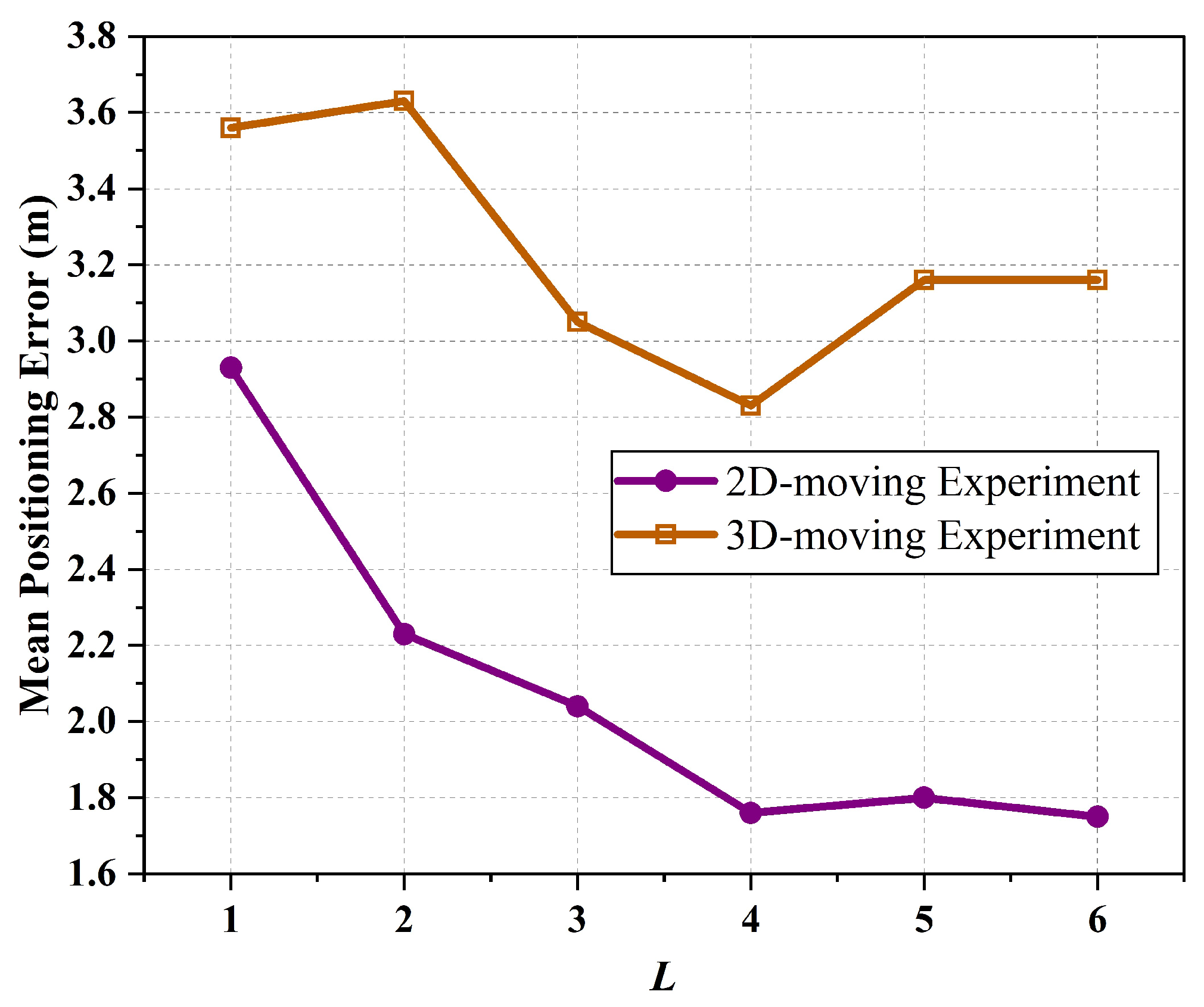
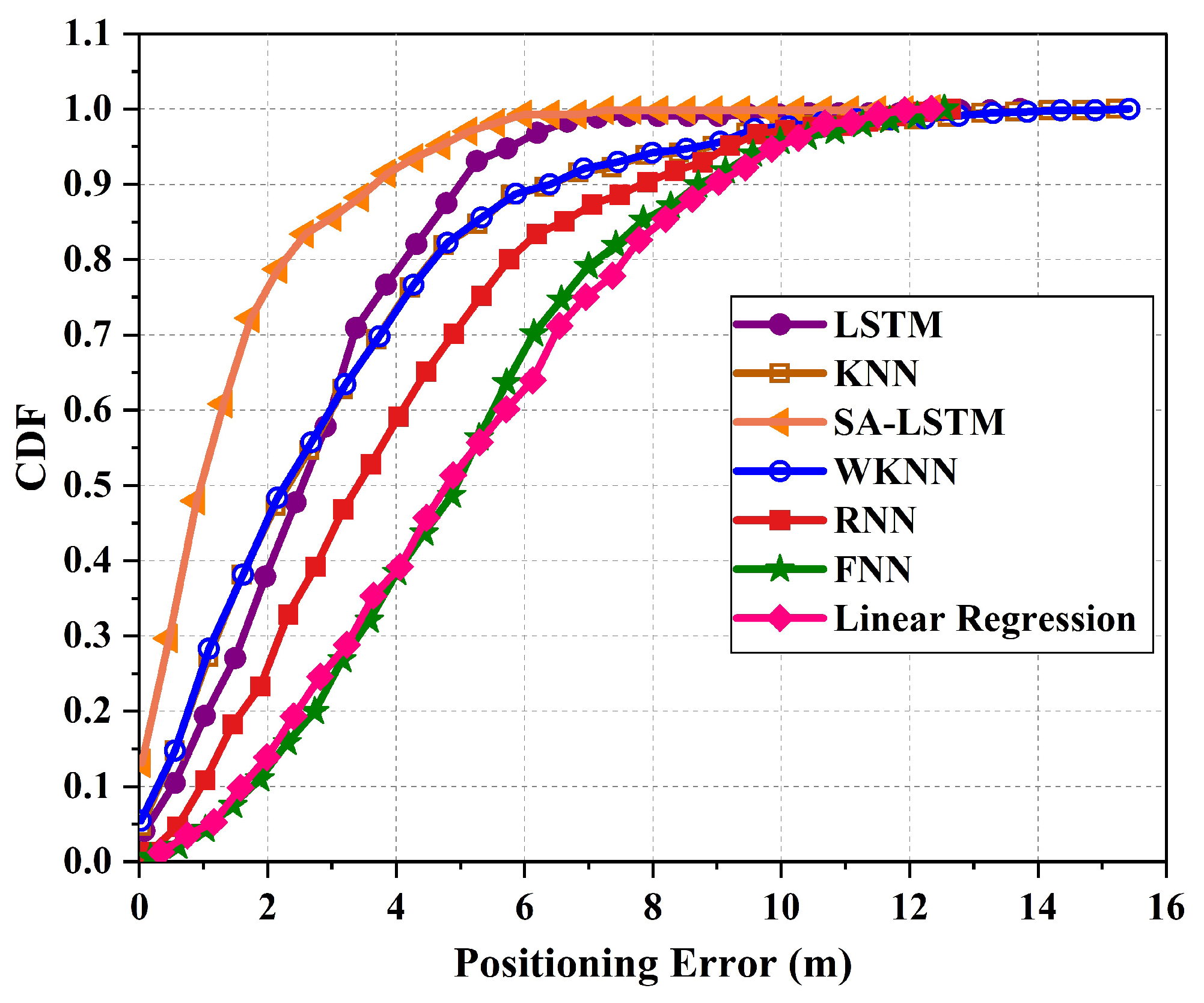
5. Results and Discussion
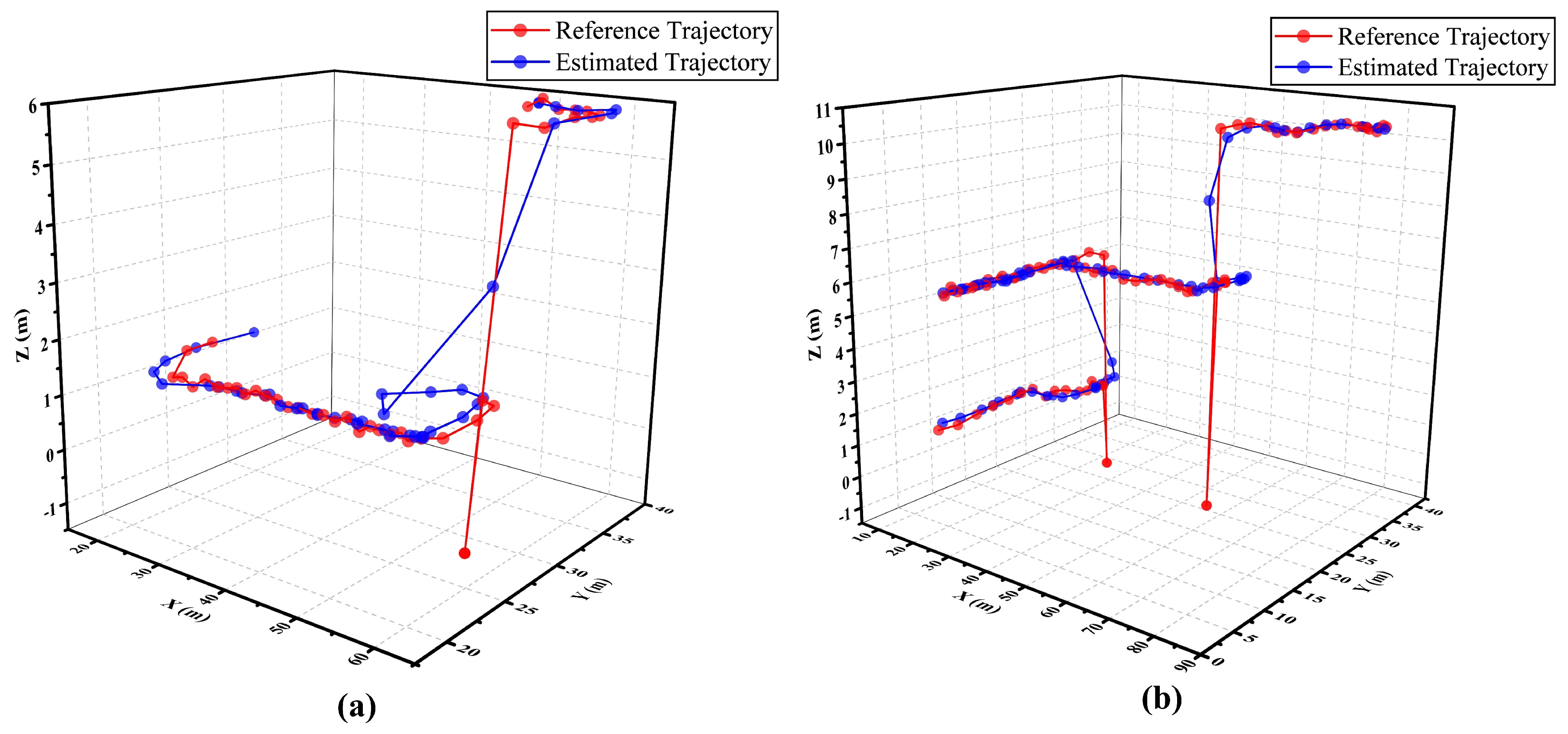
6. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LBS | Location-based services |
| GPS | Global Positioning System |
| BDS | BeiDou Satellite Navigation System |
| UWB | Ultra-Wide Bandwidth |
| RFID | Radio Frequency Identification |
| AOA | Angle of Arrival |
| TOA | Time of Arrival |
| APs | Access Points |
| UE | User Equipment |
| LSTM | Long Short-term Memory |
| RSSI | Received Signal Strength Indicator |
| TPs | Test Points |
| RPs | Reference Points |
| KNN | K-Nearest Neighbors |
| WKNN | Weighted K-Nearest Neighbors |
| SVM | Support Vector Machines |
| FNN | Feedforward Neural Networks |
| SA-LSTM | Self-Attention and LSTM |
| VSLAM | Simultaneous Localization and Mapping |
| RNN | Recurrent Neural Networks |
References
- Zhong, S.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.G.; Yang, Y.R. Privacy-preserving location-based services for mobile users in wireless networks. Department of Computer Science, Yale University, Technical Report ALEU/DCS/TR-1297 2004, 26.
- Spilker Jr, J.J.; Axelrad, P.; Parkinson, B.W.; Enge, P. Global positioning system: theory and applications, volume I; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 1996.
- Yang, Y.; Gao, W.; Guo, S.; Mao, Y.; Yang, Y. Introduction to BeiDou-3 navigation satellite system. Navigation 2019, 66, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khassanov, Y.; Nurpeiissov, M.; Sarkytbayev, A.; Kuzdeuov, A.; Varol, H.A. Finer-level sequential wifi-based indoor localization. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII). IEEE, 2021, pp. 163–169.
- Salamah, A.H.; Tamazin, M.; Sharkas, M.A.; Khedr, M. An enhanced WiFi indoor localization system based on machine learning. In Proceedings of the 2016 International conference on indoor positioning and indoor navigation (IPIN). IEEE, 2016, pp. 1–8.
- Abbas, M.; Elhamshary, M.; Rizk, H.; Torki, M.; Youssef, M. WiDeep: WiFi-based accurate and robust indoor localization system using deep learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications (PerCom. IEEE, 2019, pp. 1–10.
- Chen, C.; Chen, Y.; Lai, H.Q.; Han, Y.; Liu, K.R. High accuracy indoor localization: A WiFi-based approach. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP). IEEE, 2016, pp. 6245–6249.
- Altini, M.; Brunelli, D.; Farella, E.; Benini, L. Bluetooth indoor localization with multiple neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE 5th International Symposium on Wireless Pervasive Computing 2010. IEEE, 2010, pp. 295–300.
- Wang, Y.; Ye, Q.; Cheng, J.; Wang, L. Wang, L. RSSI-based bluetooth indoor localization. In Proceedings of the 2015 11th international conference on mobile ad-hoc and sensor networks (MSN). IEEE, 2015, pp. 165–171.
- Zhang, C.; Kuhn, M.; Merkl, B.; Fathy, A.E.; Mahfouz, M. Accurate UWB indoor localization system utilizing time difference of arrival approach. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE radio and wireless symposium. IEEE, 2006, pp. 515–518.
- Poulose, A.; Han, D.S. UWB indoor localization using deep learning LSTM networks. Applied Sciences 2020, 10, 6290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaser, A.; Moselhi, O. RFID indoor location identification for construction projects. Automation in Construction 2014, 39, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lymberopoulos, D.; Liu, J.; Priyantha, B. Indoor localization using FM signals. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing 2013, 12, 1502–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.; Wang, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, S. Fingerprint augment based on super-resolution for WiFi fingerprint based indoor localization. IEEE Sensors Journal 2022, 22, 12152–12162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Sospedra, J.; Montoliu, R.; Martínez-Usó, A.; Avariento, J.P.; Arnau, T.J.; Benedito-Bordonau, M.; Huerta, J. UJIIndoorLoc: A new multi-building and multi-floor database for WLAN fingerprint-based indoor localization problems. In Proceedings of the 2014 international conference on indoor positioning and indoor navigation (IPIN). IEEE, 2014, pp. 261–270.
- Roy, P.; Chowdhury, C. A survey of machine learning techniques for indoor localization and navigation systems. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems 2021, 101, 63. [Google Scholar]
- Brunato, M.; Battiti, R. Statistical learning theory for location fingerprinting in wireless LANs. Computer Networks 2005, 47, 825–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, M.T.; Zhu, Y.; Yuen, B.; Reese, T.; Dong, X.; Lu, T.; Westendorp, R.; Xie, M. A soft range limited K-nearest neighbors algorithm for indoor localization enhancement. IEEE Sensors Journal 2018, 18, 10208–10216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.H.; Lin, T.N. Indoor location system based on discriminant-adaptive neural network in IEEE 802.11 environments. IEEE Transactions on Neural networks 2008, 19, 1973–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurpeiissov, M.; Kuzdeuov, A.; Assylkhanov, A.; Khassanov, Y.; Varol, H.A. End-to-end sequential indoor localization using smartphone inertial sensors and WiFi. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII). IEEE, 2022, pp. 566–571.
- Zhang, Y.; Qu, C.; Wang, Y. An indoor positioning method based on CSI by using features optimization mechanism with LSTM. IEEE Sensors Journal 2020, 20, 4868–4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, F.X. Self-attention and behavior: A review and theoretical update. Advances in experimental social psychology 1990, 23, 249–303. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Jia, J.; Koltun, V. Exploring self-attention for image recognition. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2020, pp. 10076–10085.
- Humphreys, G.W.; Sui, J. Attentional control and the self: The self-attention network (SAN). Cognitive neuroscience 2016, 7, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Advances in neural information processing systems 2017, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Bahl, P.; Padmanabhan, V.N. RADAR: An in-building RF-based user location and tracking system. In Proceedings of the Proceedings IEEE INFOCOM 2000. Conference on computer communications. Nineteenth annual joint conference of the IEEE computer and communications societies (Cat. No. 00CH37064). Ieee, 2000, Vol. 2, pp. 775–784.
- Brunato, M.; Battiti, R. Statistical learning theory for location fingerprinting in wireless LANs. Computer Networks 2005, 47, 825–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zou, H.; Yang, J.; Jiang, H.; Xie, L. WiFi fingerprinting indoor localization using local feature-based deep LSTM. IEEE Systems Journal 2019, 14, 3001–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorowski, J.K.; Bahdanau, D.; Serdyuk, D.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y. Attention-based models for speech recognition. Advances in neural information processing systems 2015, 28. [Google Scholar]
- Zang, H.; Xu, R.; Cheng, L.; Ding, T.; Liu, L.; Wei, Z.; Sun, G. Residential load forecasting based on LSTM fusing self-attention mechanism with pooling. Energy 2021, 229, 120682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finney, D.J. Probit analysis; a statistical treatment of the sigmoid response curve. 1947.
- Torres-Sospedra, J.; Montoliu, R.; Trilles, S.; Belmonte, Ó.; Huerta, J. Comprehensive analysis of distance and similarity measures for Wi-Fi fingerprinting indoor positioning systems. Expert Systems with Applications 2015, 42, 9263–9278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Fan, X.; Xiang, C.; Ye, Q.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; He, X.; Yang, N.; Fang, G. A novel convolutional neural network based indoor localization framework with WiFi fingerprinting. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 110698–110709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2016, pp. 770–778.
- Morselli, F.; Razavi, S.M.; Win, M.Z.; Conti, A. Soft information based localization for 5G networks and beyond. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
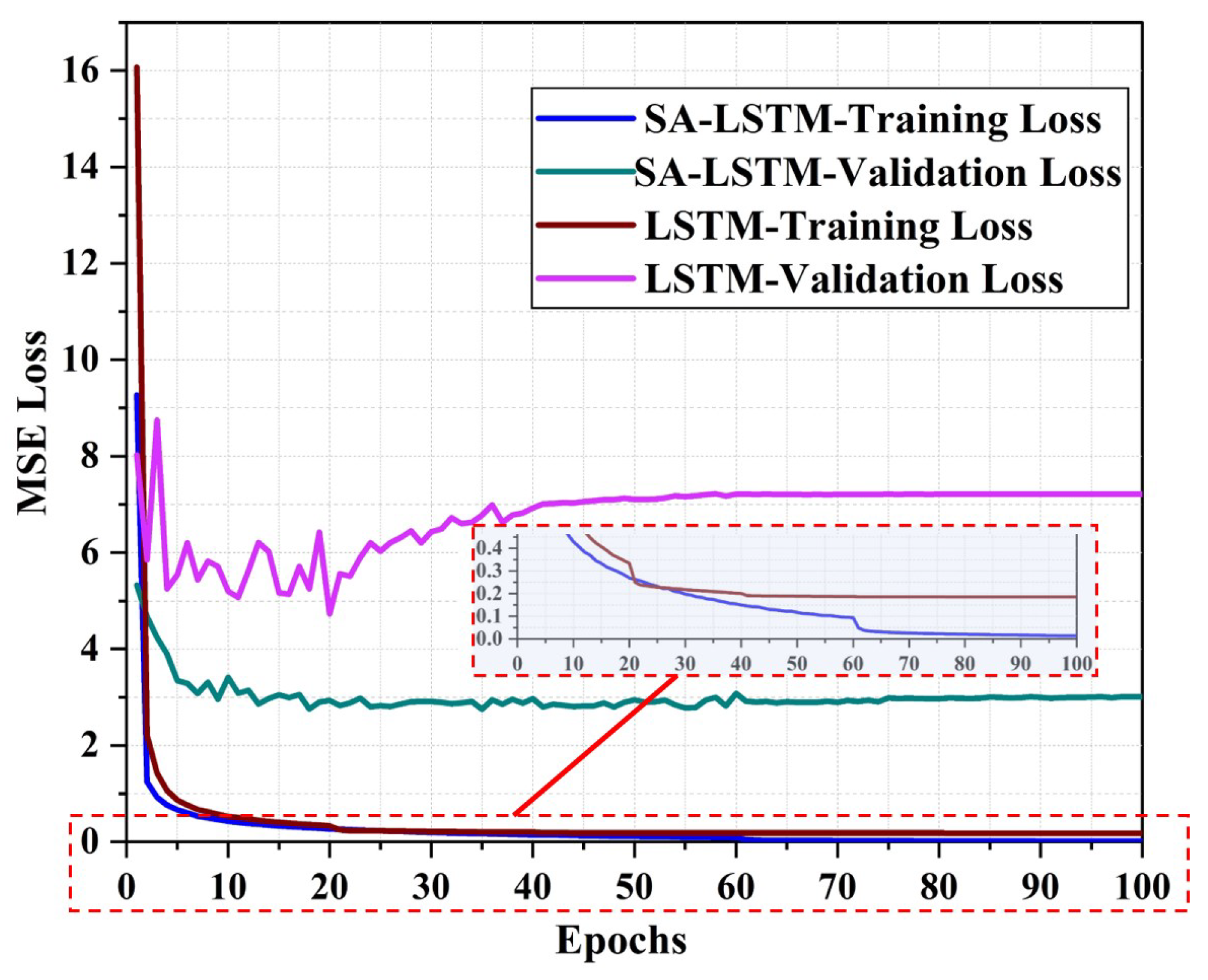
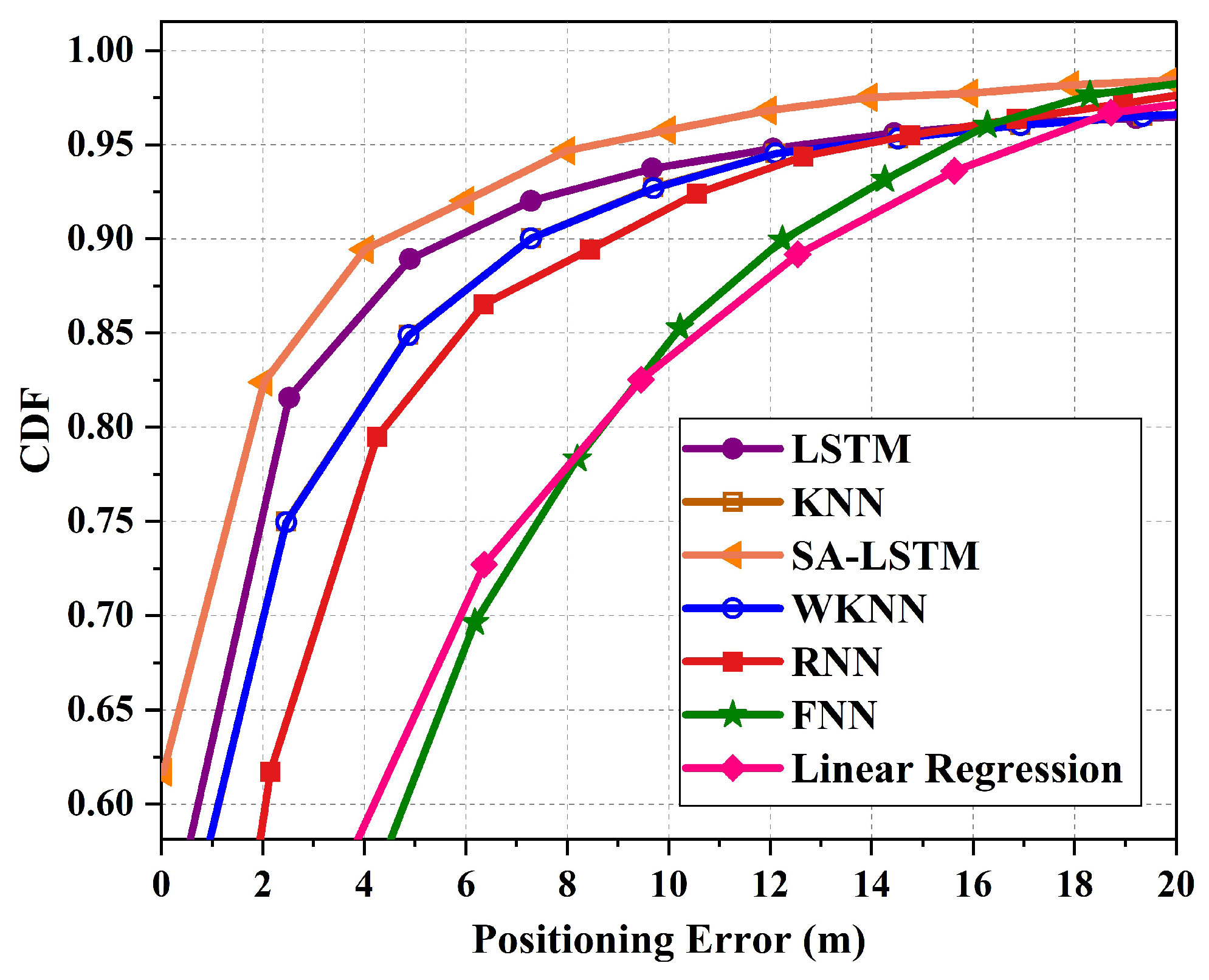
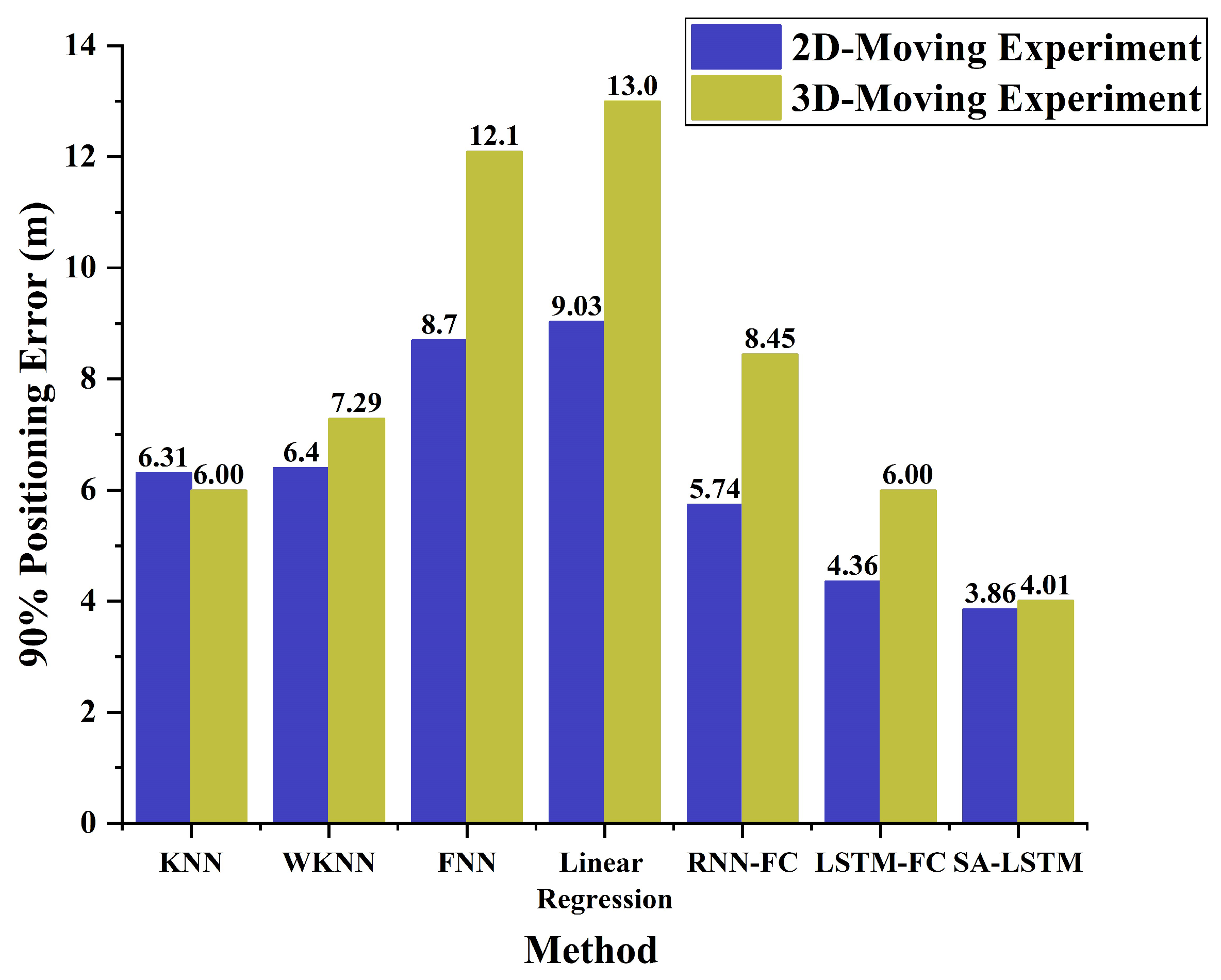
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Bluetooth Version | BLE 5.0 |
| Bluetooth Protocol | iBeacon |
| Working Temperature | -30 ∼ |
| Maximum Transmission Distance | 120 m |
| Transmitted Power | -30 ∼ +4 dBm (default: 0 dBm) |
| Broadcast Interval | 100 ms ∼ 10 s (default: 500 ms) |
| Layer | 2D Experiment | 3D Experiment |
|---|---|---|
| Linear Layer 1 | (24×64) | (436×128) |
| LSTM Layer | (64×64) | (128×128) |
| Linear Layer 2 | (64×4) | (128×4) |
| Convolution Layer | 3 × 3 kernels, 1 filter |
3 × 3 kernels, 1 filter |
| Linear Layer 3 | (62×2) | (126×3) |
| Batch Size | 2 | 2 |
| Initial Learning Rate | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| Optimizer | Adam | Adam |
| Loss Function | MSE | MSE |
| Training Epochs | 200 | 100 |
| Method | Average Error (m) | Maximum Error (m) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Validation Set | Test Set | Validation Set | Test Set | |
| KNN | 2.53 | 3.36 | 18.39 | 15.22 |
| WKNN | 2.53 | 3.33 | 18.41 | 15.42 |
| FNN | 3.49 | 5.28 | 12.44 | 12.54 |
| Linear Regression | 3.64 | 5.31 | 13.06 | 12.34 |
| RNN | 3.37 | 4.16 | 12.67 | 12.64 |
| LSTM | 2.57 | 3.07 | 13.73 | 13.73 |
| SA-LSTM | 1.67 | 1.76 | 12.35 | 12.35 |
| Method | Average Error (m) | Maximum Error (m) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Validation Set | Test Set | Validation Set | Test Set | |
| KNN | 3.42 | 3.45 | 68.95 | 69.99 |
| WKNN | 3.41 | 3.44 | 68.95 | 69.99 |
| FNN | 6.41 | 6.81 | 68.79 | 58.70 |
| Linear Regression | 7.06 | 7.56 | 100.44 | 89.74 |
| RNN | 3.73 | 4.93 | 40.71 | 60.96 |
| LSTM | 3.91 | 4.14 | 66.91 | 69.29 |
| SA-LSTM | 2.56 | 2.83 | 28.46 | 57.64 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





