Submitted:
23 January 2024
Posted:
24 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. SARS-CoV-2 composition
2.1. Structural proteins
2.2. Non-structural proteins
2.3. Accessory factors
3. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2
4. Mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 infection
5. Host defence mechanisms against infections
5.1. Host defence against SARS-CoV-2
6. Vaccines
6.1. Whole pathogen vaccines
6.2. Subunit vaccines
6.3. Genetic vaccines
7. Vaccines against SARS-CoV-2
7.2. DNA-based viral vector vaccines
7.3. Inactivated whole pathogen vaccines
7.4. Protein subunit vaccines
8. Mutations and SARS-CoV-2 variants
8.1. Variants of concern
8.2. Variants of interest
8.3. Variants under monitoring
8.4. Variants and mutation trends
9. Impacts of mutations
9.1. Mutations and viral characteristic changes
9.2. Mutations cause immune escape
9.3. Immune escape reduces vaccine effectiveness
9.3.1. Impact of immune escape on inactivated vaccine efficacy
9.3.2. Impact of immune escape on subunit vaccine efficacy
9.3.3. Impact of immune escape on genetic vaccine efficacy
9.4. Booster
9.4.1. Homologous booster
9.3.2. Heterologous booster
9.3.3. Bivalent vaccines against Omicron variants
10. The future of COVID-19 vaccines
11. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Funding
References
- Cascella, M.; Rajnik, M.; Aleem, A.; Dulebohn, S.C.; Di Napoli, R. Features, evaluation, and treatment of coronavirus (COVID-19). 2020.
- Zhu, Z.; Lian, X.; Su, X.; Wu, W.; Marraro, G.A.; Zeng, Y. From SARS and MERS to COVID-19: a brief summary and comparison of severe acute respiratory infections caused by three highly pathogenic human coronaviruses. Respiratory Research 2020, 21, 224. [CrossRef]
- Pascarella, G.; Strumia, A.; Piliego, C.; Bruno, F.; Del Buono, R.; Costa, F.; Scarlata, S.; Agrò, F.E. COVID-19 diagnosis and management: a comprehensive review. Journal of internal medicine 2020, 288, 192-206. [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2: implications for infection prevention precautions: scientific brief, 09 July 2020; World Health Organization: 2020.
- Organization, W.H. Mask use in the context of COVID-19: interim guidance, 1 December 2020; World Health Organization: 2020.
- Organization, W.H. Therapeutics and COVID-19: living guideline, 13 January 2023; World Health Organization: 2023.
- Vegivinti, C.T.R.; Evanson, K.W.; Lyons, H.; Akosman, I.; Barrett, A.; Hardy, N.; Kane, B.; Keesari, P.R.; Pulakurthi, Y.S.; Sheffels, E. Efficacy of antiviral therapies for COVID-19: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. BMC Infectious Diseases 2022, 22, 107. [CrossRef]
- Siemieniuk, R.; Rochwerg, B.; Agoritsas, T.; Lamontagne, F.; Leo, Y.-S.; Macdonald, H.; Agarwal, A.; Zeng, L.; Lytvyn, L.; Appiah, J.A. A living WHO guideline on drugs for covid-19. Bmj 2020 (Last updated 10 Nov 2023), 370, m3379.
- Jeyanathan, M.; Afkhami, S.; Smaill, F.; Miller, M.S.; Lichty, B.D.; Xing, Z. Immunological considerations for COVID-19 vaccine strategies. Nature Reviews Immunology 2020, 20, 615-632. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.-M.; Qin, X.-R.; Yan, L.-N.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, X.-J. Global trends in COVID-19. Infectious Medicine 2022, 1, 31-39. [CrossRef]
- Naqvi, A.A.T.; Fatima, K.; Mohammad, T.; Fatima, U.; Singh, I.K.; Singh, A.; Atif, S.M.; Hariprasad, G.; Hasan, G.M.; Hassan, M.I. Insights into SARS-CoV-2 genome, structure, evolution, pathogenesis and therapies: Structural genomics approach. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 2020, 1866, 165878. [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Chaudhary, J.K.; Jain, N.; Chaudhary, P.K.; Khanra, S.; Dhamija, P.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, A.; Handu, S. Role of Structural and Non-Structural Proteins and Therapeutic Targets of SARS-CoV-2 for COVID-19. Cells 2021, 10. [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.; Ge, J.; Yu, J.; Shan, S.; Zhou, H.; Fan, S.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L. Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2 receptor. nature 2020, 581, 215-220.
- Mandala, V.S.; McKay, M.J.; Shcherbakov, A.A.; Dregni, A.J.; Kolocouris, A.; Hong, M. Structure and drug binding of the SARS-CoV-2 envelope protein transmembrane domain in lipid bilayers. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2020, 27, 1202-1208. [CrossRef]
- Schoeman, D.; Fielding, B.C. Coronavirus envelope protein: current knowledge. Virol J 2019, 16, 69. [CrossRef]
- EA, J.A.; Jones, I.M. Membrane binding proteins of coronaviruses. Future Virol 2019, 14, 275-286. [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S. The Structure of the Membrane Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Resembles the Sugar Transporter SemiSWEET. Pathog Immun 2020, 5, 342-363. [CrossRef]
- Opstelten, D.J.; Raamsman, M.J.; Wolfs, K.; Horzinek, M.C.; Rottier, P.J. Envelope glycoprotein interactions in coronavirus assembly. J Cell Biol 1995, 131, 339-349. [CrossRef]
- Fehr, A.R.; Perlman, S. Coronaviruses: an overview of their replication and pathogenesis. Methods Mol Biol 2015, 1282, 1-23. [CrossRef]
- Escors, D.; Ortego, J.; Laude, H.; Enjuanes, L. The membrane M protein carboxy terminus binds to transmissible gastroenteritis coronavirus core and contributes to core stability. J Virol 2001, 75, 1312-1324. [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, K.; Maeda, A.; Maeda, J.; Makino, S. Characterization of the coronavirus M protein and nucleocapsid interaction in infected cells. J Virol 2000, 74, 8127-8134. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Nomura, N.; Muramoto, Y.; Ekimoto, T.; Uemura, T.; Liu, K.; Yui, M.; Kono, N.; Aoki, J.; Ikeguchi, M. Structure of SARS-CoV-2 membrane protein essential for virus assembly. Nature communications 2022, 13, 4399.
- Gao, T.; Gao, Y.; Liu, X.; Nie, Z.; Sun, H.; Lin, K.; Peng, H.; Wang, S. Identification and functional analysis of the SARS-COV-2 nucleocapsid protein. BMC Microbiol 2021, 21, 58. [CrossRef]
- Satarker, S.; Nampoothiri, M. Structural Proteins in Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2. Arch Med Res 2020, 51, 482-491. [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Lokugamage, K.G.; Rozovics, J.M.; Narayanan, K.; Semler, B.L.; Makino, S. SARS coronavirus nsp1 protein induces template-dependent endonucleolytic cleavage of mRNAs: viral mRNAs are resistant to nsp1-induced RNA cleavage. PLoS Pathog 2011, 7, e1002433. [CrossRef]
- Cornillez-Ty, C.T.; Liao, L.; Yates, J.R., 3rd; Kuhn, P.; Buchmeier, M.J. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus nonstructural protein 2 interacts with a host protein complex involved in mitochondrial biogenesis and intracellular signaling. J Virol 2009, 83, 10314-10318. [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Kusov, Y.; Hilgenfeld, R. Nsp3 of coronaviruses: Structures and functions of a large multi-domain protein. Antiviral Res 2018, 149, 58-74. [CrossRef]
- Moustaqil, M.; Ollivier, E.; Chiu, H.P.; Van Tol, S.; Rudolffi-Soto, P.; Stevens, C.; Bhumkar, A.; Hunter, D.J.B.; Freiberg, A.N.; Jacques, D.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 proteases PLpro and 3CLpro cleave IRF3 and critical modulators of inflammatory pathways (NLRP12 and TAB1): implications for disease presentation across species. Emerg Microbes Infect 2021, 10, 178-195. [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Xu, W.; Hu, W.; Yi, L.; Liu, Z.; Chan, H.; Zeng, J.; Liu, X.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 non-structural protein 6 triggers NLRP3-dependent pyroptosis by targeting ATP6AP1. Cell Death Differ 2022, 29, 1240-1254. [CrossRef]
- Ricciardi, S.; Guarino, A.M.; Giaquinto, L.; Polishchuk, E.V.; Santoro, M.; Di Tullio, G.; Wilson, C.; Panariello, F.; Soares, V.C.; Dias, S.S.G.; et al. The role of NSP6 in the biogenesis of the SARS-CoV-2 replication organelle. Nature 2022, 606, 761-768. [CrossRef]
- Reshamwala, S.M.S.; Likhite, V.; Degani, M.S.; Deb, S.S.; Noronha, S.B. Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 nsp7 and nsp8 proteins and their predicted impact on replication/transcription complex structure. J Med Virol 2021, 93, 4616-4619. [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Peng, R.; Yuan, B.; Zhao, J.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Fan, Z.; Qi, J.; et al. Structural and Biochemical Characterization of the nsp12-nsp7-nsp8 Core Polymerase Complex from SARS-CoV-2. Cell Rep 2020, 31, 107774. [CrossRef]
- de, O.A.J.; Pinheiro, S.; Zamora, W.J.; Alves, C.N.; Lameira, J.; Lima, A.H. Structural, energetic and lipophilic analysis of SARS-CoV-2 non-structural protein 9 (NSP9). Sci Rep 2021, 11, 23003. [CrossRef]
- Bouvet, M.; Lugari, A.; Posthuma, C.C.; Zevenhoven, J.C.; Bernard, S.; Betzi, S.; Imbert, I.; Canard, B.; Guillemot, J.C.; Lécine, P.; et al. Coronavirus Nsp10, a critical co-factor for activation of multiple replicative enzymes. J Biol Chem 2014, 289, 25783-25796. [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhou, Z.; Xiao, X.; Tian, Z.; Dong, X.; Wang, C.; Li, L.; Ren, L.; Lei, X.; Xiang, Z.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 nsp12 attenuates type I interferon production by inhibiting IRF3 nuclear translocation. Cell Mol Immunol 2021, 18, 945-953. [CrossRef]
- Yuen, C.K.; Lam, J.Y.; Wong, W.M.; Mak, L.F.; Wang, X.; Chu, H.; Cai, J.P.; Jin, D.Y.; To, K.K.; Chan, J.F.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 nsp13, nsp14, nsp15 and orf6 function as potent interferon antagonists. Emerg Microbes Infect 2020, 9, 1418-1428. [CrossRef]
- Vithani, N.; Ward, M.D.; Zimmerman, M.I.; Novak, B.; Borowsky, J.H.; Singh, S.; Bowman, G.R. SARS-CoV-2 Nsp16 activation mechanism and a cryptic pocket with pan-coronavirus antiviral potential. Biophys J 2021, 120, 2880-2889. [CrossRef]
- Redondo, N.; Zaldívar-López, S.; Garrido, J.J.; Montoya, M. SARS-CoV-2 accessory proteins in viral pathogenesis: knowns and unknowns. Frontiers in Immunology 2021, 2698.
- Bourgonje, A.R.; Abdulle, A.E.; Timens, W.; Hillebrands, J.L.; Navis, G.J.; Gordijn, S.J.; Bolling, M.C.; Dijkstra, G.; Voors, A.A.; Osterhaus, A.D.; et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), SARS-CoV-2 and the pathophysiology of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). J Pathol 2020, 251, 228-248. [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Chow, R.D.; Peña-Hernández, M.A.; Zhang, L.; Loeb, S.A.; So, E.-Y.; Liang, O.D.; Ren, P.; Chen, S.; Wilen, C.B. LRRC15 inhibits SARS-CoV-2 cellular entry in trans. Plos Biology 2022, 20, e3001805.
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.L.; Wang, X.G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.L.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270-273. [CrossRef]
- Wrapp, D.; Wang, N.; Corbett, K.S.; Goldsmith, J.A.; Hsieh, C.L.; Abiona, O.; Graham, B.S.; McLellan, J.S. Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation. Science 2020, 367, 1260-1263. [CrossRef]
- Tipnis, S.R.; Hooper, N.M.; Hyde, R.; Karran, E.; Christie, G.; Turner, A.J. A human homolog of angiotensin-converting enzyme: cloning and functional expression as a captopril-insensitive carboxypeptidase. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2000, 275, 33238-33243.
- Santos, R.A.S.; Sampaio, W.O.; Alzamora, A.C.; Motta-Santos, D.; Alenina, N.; Bader, M.; Campagnole-Santos, M.J. The ACE2/Angiotensin-(1-7)/MAS Axis of the Renin-Angiotensin System: Focus on Angiotensin-(1-7). Physiol Rev 2018, 98, 505-553. [CrossRef]
- Datta, P.K.; Liu, F.; Fischer, T.; Rappaport, J.; Qin, X. SARS-CoV-2 pandemic and research gaps: Understanding SARS-CoV-2 interaction with the ACE2 receptor and implications for therapy. Theranostics 2020, 10, 7448.
- Oudit, G.Y.; Kassiri, Z.; Jiang, C.; Liu, P.P.; Poutanen, S.M.; Penninger, J.M.; Butany, J. SARS-coronavirus modulation of myocardial ACE2 expression and inflammation in patients with SARS. Eur J Clin Invest 2009, 39, 618-625. [CrossRef]
- Glowacka, I.; Bertram, S.; Herzog, P.; Pfefferle, S.; Steffen, I.; Muench, M.O.; Simmons, G.; Hofmann, H.; Kuri, T.; Weber, F.; et al. Differential downregulation of ACE2 by the spike proteins of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus and human coronavirus NL63. J Virol 2010, 84, 1198-1205. [CrossRef]
- Ni, W.; Yang, X.; Yang, D.; Bao, J.; Li, R.; Xiao, Y.; Hou, C.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Yang, D.; et al. Role of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in COVID-19. Crit Care 2020, 24, 422. [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Ou, L.; Li, J.; Zheng, K.; Zhan, H.; Gu, J.; Zhou, G.; Xie, S.; Zhang, J. Downregulation of ACE2 expression by SARS-CoV-2 worsens the prognosis of KIRC and KIRP patients via metabolism and immunoregulation. International journal of biological sciences 2021, 17, 1925.
- Poduri, R.; Joshi, G.; Jagadeesh, G. Drugs targeting various stages of the SARS-CoV-2 life cycle: Exploring promising drugs for the treatment of Covid-19. Cell Signal 2020, 74, 109721. [CrossRef]
- Boopathi, S.; Poma, A.B.; Kolandaivel, P. Novel 2019 coronavirus structure, mechanism of action, antiviral drug promises and rule out against its treatment. J Biomol Struct Dyn 2021, 39, 3409-3418. [CrossRef]
- Masters, P.S. The molecular biology of coronaviruses. Adv Virus Res 2006, 66, 193-292. [CrossRef]
- van Hemert, M.J.; van den Worm, S.H.; Knoops, K.; Mommaas, A.M.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Snijder, E.J. SARS-coronavirus replication/transcription complexes are membrane-protected and need a host factor for activity in vitro. PLoS Pathog 2008, 4, e1000054. [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, J. Memory in the innate and adaptive immune systems. Microbes Infect 2004, 6, 1410-1417. [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.C.; Beilke, J.N.; Lanier, L.L. Adaptive immune features of natural killer cells. Nature 2009, 457, 557-561. [CrossRef]
- Braciale, T.J.; Sun, J.; Kim, T.S. Regulating the adaptive immune response to respiratory virus infection. Nat Rev Immunol 2012, 12, 295-305. [CrossRef]
- Diamond, M.S.; Kanneganti, T.D. Innate immunity: the first line of defense against SARS-CoV-2. Nat Immunol 2022, 23, 165-176. [CrossRef]
- Tay, M.Z.; Poh, C.M.; Rénia, L.; MacAry, P.A.; Ng, L.F.P. The trinity of COVID-19: immunity, inflammation and intervention. Nat Rev Immunol 2020, 20, 363-374. [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, M.; Abualrous, E.T.; Sticht, J.; Álvaro-Benito, M.; Stolzenberg, S.; Noé, F.; Freund, C. Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) Class I and MHC Class II Proteins: Conformational Plasticity in Antigen Presentation. Front Immunol 2017, 8, 292. [CrossRef]
- Sette, A.; Crotty, S. Adaptive immunity to SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Cell 2021, 184, 861-880. [CrossRef]
- Romagnani, S. Th1 and Th2 in human diseases. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 1996, 80, 225-235. [CrossRef]
- Skwarczynski, M.; Toth, I. Peptide-based synthetic vaccines. Chem Sci 2016, 7, 842-854. [CrossRef]
- Belete, T.M. Review on up-to-date status of candidate vaccines for COVID-19 disease. Infection and drug resistance 2021, 151-161. [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Bao, L.; Mao, H.; Wang, L.; Xu, K.; Yang, M.; Li, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wang, N.; Lv, Z. Development of an inactivated vaccine candidate for SARS-CoV-2. Science 2020, 369, 77-81.
- Chappell, K.J.; Mordant, F.L.; Li, Z.; Wijesundara, D.K.; Ellenberg, P.; Lackenby, J.A.; Cheung, S.T.; Modhiran, N.; Avumegah, M.S.; Henderson, C.L. Safety and immunogenicity of an MF59-adjuvanted spike glycoprotein-clamp vaccine for SARS-CoV-2: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1 trial. The Lancet Infectious Diseases 2021, 21, 1383-1394.
- Hansson, M.; Nygren, P.A.k.; Sta˚ hl, S. Design and production of recombinant subunit vaccines. Biotechnology and applied biochemistry 2000, 32, 95-107.
- Xu, Z.; Moyle, P.M. Bioconjugation approaches to producing subunit vaccines composed of protein or peptide antigens and covalently attached toll-like receptor ligands. Bioconjugate chemistry 2017, 29, 572-586.
- Vartak, A.; Sucheck, S.J. Recent advances in subunit vaccine carriers. Vaccines 2016, 4, 12.
- Skwarczynski, M.; Toth, I. Non-invasive mucosal vaccine delivery: Advantages, challenges and the future. Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery 2020, 17, 435-437.
- Nahar, U.J.; Toth, I.; Skwarczynski, M. Mannose in vaccine delivery. Journal of Controlled Release 2022, 351, 284-300. [CrossRef]
- Foged, C. Subunit vaccines of the future: the need for safe, customized and optimized particulate delivery systems. Therapeutic delivery 2011, 2, 1057-1077. [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, N.; Skwarczynski, M.; Toth, I. The influence of component structural arrangement on peptide vaccine immunogenicity. Biotechnology Advances 2022, 108029. [CrossRef]
- Firdaus, F.Z.; Skwarczynski, M.; Toth, I. Developments in vaccine adjuvants. Vaccine Design: Methods and Protocols, Volume 3. Resources for Vaccine Development 2022, 145-178.
- Acosta-Coley, I.; Cervantes-Ceballos, L.; Tejeda-Benítez, L.; Sierra-Márquez, L.; Cabarcas-Montalvo, M.; García-Espiñeira, M.; Coronell-Rodríguez, W.; Arroyo-Salgado, B. Vaccines platforms and COVID-19: what you need to know. Tropical Diseases, Travel Medicine and Vaccines 2022, 8, 20. [CrossRef]
- Ura, T.; Okuda, K.; Shimada, M. Developments in viral vector-based vaccines. Vaccines 2014, 2, 624-641. [CrossRef]
- Pardi, N.; Hogan, M.J.; Porter, F.W.; Weissman, D. mRNA vaccines — a new era in vaccinology. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 2018, 17, 261-279. [CrossRef]
- Kariko, K.; Muramatsu, H.; Welsh, F.A.; Ludwig, J.; Kato, H.; Akira, S.; Weissman, D. Incorporation of pseudouridine into mRNA yields superior nonimmunogenic vector with increased translational capacity and biological stability. Mol Ther 2008, 16, 1833-1840. [CrossRef]
- Sahin, U.; Kariko, K.; Tureci, O. mRNA-based therapeutics--developing a new class of drugs. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2014, 13, 759-780. [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.C.; Sekhon, S.S.; Shin, W.R.; Ahn, G.; Cho, B.K.; Ahn, J.Y.; Kim, Y.H. Modifications of mRNA vaccine structural elements for improving mRNA stability and translation efficiency. Mol Cell Toxicol 2022, 18, 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Yi Xue, H.; Guo, P.; Wen, W.-C.; Lun Wong, H. Lipid-based nanocarriers for RNA delivery. Current pharmaceutical design 2015, 21, 3140-3147. [CrossRef]
- Chahal, J.S.; Khan, O.F.; Cooper, C.L.; McPartlan, J.S.; Tsosie, J.K.; Tilley, L.D.; Sidik, S.M.; Lourido, S.; Langer, R.; Bavari, S. Dendrimer-RNA nanoparticles generate protective immunity against lethal Ebola, H1N1 influenza, and Toxoplasma gondii challenges with a single dose. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2016, 113, E4133-E4142.
- Liu, M.A. A comparison of plasmid DNA and mRNA as vaccine technologies. Vaccines 2019, 7, 37.
- Crommelin, D.J.; Volkin, D.B.; Hoogendoorn, K.H.; Lubiniecki, A.S.; Jiskoot, W. The science is there: key considerations for stabilizing viral vector-based Covid-19 vaccines. Journal of pharmaceutical sciences 2021, 110, 627-634. [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, D.; Djearamane, S.; Fuloria, S.; Kayarohanam, S.; Subramaniyan, V.; Sekar, M.; Fuloria, N.K. A Review on DNA Vaccines in Pre-Clinical Trials Against SARS-CoV-2. Journal of Experimental Biology and Agricultural Sciences 2022, 10, 487-493.
- Shafaati, M.; Saidijam, M.; Soleimani, M.; Hazrati, F.; Mirzaei, R.; Amirheidari, B.; Tanzadehpanah, H.; Karampoor, S.; Kazemi, S.; Yavari, B. A brief review on DNA vaccines in the era of COVID-19. Future Virology 2022, 17, 49-66. [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Liang, H.; Chen, P.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Fan, S.; Wu, K.; Li, X.; Chen, W.; Qin, Y.; et al. Viral Vector Vaccine Development and Application during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1450. [CrossRef]
- SM Wold, W.; Toth, K. Adenovirus vectors for gene therapy, vaccination and cancer gene therapy. Current gene therapy 2013, 13, 421-433.
- Butt, M.H.; Zaman, M.; Ahmad, A.; Khan, R.; Mallhi, T.H.; Hasan, M.M.; Khan, Y.H.; Hafeez, S.; Massoud, E.E.S.; Rahman, M.H.; et al. Appraisal for the Potential of Viral and Nonviral Vectors in Gene Therapy: A Review. Genes (Basel) 2022, 13. [CrossRef]
- Gregory, S.M.; Nazir, S.A.; Metcalf, J.P. Implications of the innate immune response to adenovirus and adenoviral vectors. Future virology 2011, 6, 357-374. [CrossRef]
- Bavli, Y.; Chen, B.-M.; Gross, G.; Hershko, A.; Turjeman, K.; Roffler, S.; Barenholz, Y. Anti-PEG antibodies before and after a first dose of Comirnaty®(mRNA-LNP-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccine). Journal of Controlled Release 2023, 354, 316-322.
- Mabrouk, M.T.; Huang, W.C.; Martinez-Sobrido, L.; Lovell, J.F. Advanced materials for SARS-CoV-2 vaccines. Advanced Materials 2022, 34, 2107781.
- FDA. Overview of COVID-19 Vaccines. Availabe online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/different-vaccines/overview-COVID-19-vaccines.html (accessed on.
- Hou, X.; Zaks, T.; Langer, R.; Dong, Y. Lipid nanoparticles for mRNA delivery. Nature Reviews Materials 2021, 6, 1078-1094. [CrossRef]
- Tenchov, R.; Bird, R.; Curtze, A.E.; Zhou, Q. Lipid nanoparticles─ from liposomes to mRNA vaccine delivery, a landscape of research diversity and advancement. ACS nano 2021, 15, 16982-17015.
- Krammer, F. SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in development. Nature 2020, 586, 516-527.
- Nagy, A.; Alhatlani, B. An overview of current COVID-19 vaccine platforms. Computational and structural biotechnology journal 2021, 19, 2508-2517.
- Keech, C.; Albert, G.; Cho, I.; Robertson, A.; Reed, P.; Neal, S.; Plested, J.S.; Zhu, M.; Cloney-Clark, S.; Zhou, H. Phase 1–2 trial of a SARS-CoV-2 recombinant spike protein nanoparticle vaccine. New England Journal of Medicine 2020, 383, 2320-2332.
- Shalash, A.O.; Azuar, A.; Madge, H.Y.R.; Modhiran, N.; Amarilla, A.A.; Liang, B.; Khromykh, A.A.; Hussein, W.M.; Chappell, K.J.; Watterson, D.; et al. Peptide-Based Vaccine against SARS-CoV-2: Peptide Antigen Discovery and Screening of Adjuvant Systems. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14. [CrossRef]
- Shalash, A.O.; Toth, I.; Skwarczynski, M. The potential of developing a protective peptide-based vaccines against SARS-CoV-2. Drug Dev Res 2022, 83, 1251-1256. [CrossRef]
- Pandey, M.; Ozberk, V.; Eskandari, S.; Shalash, A.O.; Joyce, M.A.; Saffran, H.A.; Day, C.J.; Lepletier, A.; Spillings, B.L.; Mills, J.L. Antibodies to neutralising epitopes synergistically block the interaction of the receptor-binding domain of SARS-CoV-2 to ACE 2. Clinical & Translational Immunology 2021, 10, e1260.
- Shalash, A.O.; Hussein, W.M.; Skwarczynski, M.; Toth, I. Key considerations for the development of safe and effective SARS-CoV-2 subunit vaccine: A peptide-based vaccine alternative. Advanced Science 2021, 8, 2100985.
- Shalash, A.O.; Azuar, A.; Madge, H.Y.; Modhiran, N.; Amarilla, A.A.; Liang, B.; Khromykh, A.A.; Watterson, D.; Young, P.R.; Toth, I. Detection and quantification of SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain neutralization by a sensitive competitive ELISA assay. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1493.
- Sanchez-Felipe, L.; Vercruysse, T.; Sharma, S.; Ma, J.; Lemmens, V.; Van Looveren, D.; Arkalagud Javarappa, M.P.; Boudewijns, R.; Malengier-Devlies, B.; Liesenborghs, L. A single-dose live-attenuated YF17D-vectored SARS-CoV-2 vaccine candidate. Nature 2021, 590, 320-325.
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Xia, H.; Zou, J.; Muruato, A.E.; Periasamy, S.; Kurhade, C.; Plante, J.A.; Bopp, N.E. A live-attenuated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine candidate with accessory protein deletions. Nature communications 2022, 13, 4337.
- Yoon, W.; Park, Y.; Kim, S.; Bang, I.S. Development of an oral Salmonella-based vaccine platform against SARS-CoV-2. Vaccines 2022, 10, 67.
- Geng, Q.; Tai, W.; Baxter, V.K.; Shi, J.; Wan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Montgomery, S.A.; Taft-Benz, S.A.; Anderson, E.J.; Knight, A.C. Novel virus-like nanoparticle vaccine effectively protects animal model from SARS-CoV-2 infection. PLoS pathogens 2021, 17, e1009897.
- van Riel, D.; de Wit, E. Next-generation vaccine platforms for COVID-19. Nature Materials 2020, 19, 810-812. [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Nazari, M. New Generation Vaccines for COVID-19 Based on Peptide, Viral Vector, Artificial Antigen Presenting Cell, DNA or mRNA. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol 2022, 14, 30-36. [CrossRef]
- Chavda, V.P.; Bezbaruah, R.; Deka, K.; Nongrang, L.; Kalita, T. The Delta and Omicron variants of SARS-CoV-2: what we know so far. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1926.
- Chugh, A.; Khurana, N.; Verma, K.; Sehgal, I.; Rolta, R.; Vats, P.; Phartyal, R.; Salaria, D.; Kaushik, N.; Choi, E.H. Changing dynamics of SARS-CoV-2: a global challenge. Applied Sciences 2022, 12, 5546.
- Harvey, W.T.; Carabelli, A.M.; Jackson, B.; Gupta, R.K.; Thomson, E.C.; Harrison, E.M.; Ludden, C.; Reeve, R.; Rambaut, A.; Consortium, C.-G.U. SARS-CoV-2 variants, spike mutations and immune escape. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2021, 19, 409-424.
- Chakraborty, C.; Bhattacharya, M.; Sharma, A.R.; Dhama, K. Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 variants XD, XE, and XF: The emergence of recombinant variants requires an urgent call for research–Correspondence. International journal of surgery (London, England) 2022, 102, 106670.
- Thomson, E.C.; Rosen, L.E.; Shepherd, J.G.; Spreafico, R.; da Silva Filipe, A.; Wojcechowskyj, J.A.; Davis, C.; Piccoli, L.; Pascall, D.J.; Dillen, J. The circulating SARS-CoV-2 spike variant N439K maintains fitness while evading antibody-mediated immunity. BioRxiv 2020, 2020.2011. 2004.355842.
- Zhou, W.; Xu, C.; Wang, P.; Luo, M.; Xu, Z.; Cheng, R.; Jin, X.; Guo, Y.; Xue, G.; Juan, L. N439K variant in spike protein alter the infection efficiency and antigenicity of SARS-CoV-2 based on molecular dynamics simulation. Frontiers in cell and developmental biology 2021, 9, 697035.
- Guan, Q.; Sadykov, M.; Nugmanova, R.; Carr, M.J.; Arold, S.T.; Pain, A. The genomic variation landscape of globally-circulating clades of SARS-CoV-2 defines a genetic barcoding scheme. biorxiv 2020, 2020.2004. 2021.054221.
- Ashwaq, O.; Manickavasagam, P.; Haque, S.M. V483A: An emerging mutation hotspot of SARS-CoV-2. Future Virology 2021, 16, 419-429.
- Chen, J.; Wang, R.; Wang, M.; Wei, G.-W. Mutations strengthened SARS-CoV-2 infectivity. Journal of molecular biology 2020, 432, 5212-5226.
- Hu, J.; He, C.-L.; Gao, Q.-Z.; Zhang, G.-J.; Cao, X.-X.; Long, Q.-X.; Deng, H.-J.; Huang, L.-Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, K. D614G mutation of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein enhances viral infectivity. BioRxiv 2020, 2020.2006. 2020.161323.
- Hou, Y.J.; Chiba, S.; Halfmann, P.; Ehre, C.; Kuroda, M.; Dinnon III, K.H.; Leist, S.R.; Schäfer, A.; Nakajima, N.; Takahashi, K. SARS-CoV-2 D614G variant exhibits efficient replication ex vivo and transmission in vivo. Science 2020, 370, 1464-1468.
- Sixto-López, Y.; Correa-Basurto, J.; Bello, M.; Landeros-Rivera, B.; Garzón-Tiznado, J.A.; Montaño, S. Structural insights into SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and its natural mutants found in Mexican population. Scientific Reports 2021, 11, 4659.
- Zhang, L.; Jackson, C.B.; Mou, H.; Ojha, A.; Rangarajan, E.S.; Izard, T.; Farzan, M.; Choe, H. The D614G mutation in the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein reduces S1 shedding and increases infectivity. BioRxiv 2020.
- Zhang, L.; Jackson, C.B.; Mou, H.; Ojha, A.; Peng, H.; Quinlan, B.D.; Rangarajan, E.S.; Pan, A.; Vanderheiden, A.; Suthar, M.S. SARS-CoV-2 spike-protein D614G mutation increases virion spike density and infectivity. Nature communications 2020, 11, 6013.
- Ren, W.; Lan, J.; Ju, X.; Gong, M.; Long, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Yu, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhong, J.; Zhang, R. Mutation Y453F in the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 enhances interaction with the mink ACE2 receptor for host adaption. PLoS Pathogens 2021, 17, e1010053.
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, F.; Luo, B.; Yuan, Y.; Xia, B.; Ma, X.; Yang, T.; Yu, F. The ORF8 protein of SARS-CoV-2 mediates immune evasion through down-regulating MHC-Ι. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2021, 118, e2024202118.
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Luo, B.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, F.; Yang, T.; Yu, F.; Liu, J.; Liu, B. The ORF8 protein of SARS-CoV-2 mediates immune evasion through potently downregulating MHC-I. biorxiv 2020, 2020.2005. 2024.111823.
- Cosar, B.; Karagulleoglu, Z.Y.; Unal, S.; Ince, A.T.; Uncuoglu, D.B.; Tuncer, G.; Kilinc, B.R.; Ozkan, Y.E.; Ozkoc, H.C.; Demir, I.N. SARS-CoV-2 mutations and their viral variants. Cytokine & growth factor reviews 2022, 63, 10-22.
- Ou, J.; Zhou, Z.; Dai, R.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, S.; Wu, X.; Lan, W.; Ren, Y.; Cui, L.; Lan, Q. V367F mutation in SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD emerging during the early transmission phase enhances viral infectivity through increased human ACE2 receptor binding affinity. Journal of virology 2021, 95. [CrossRef]
- Hirabara, S.M.; Serdan, T.D.; Gorjao, R.; Masi, L.N.; Pithon-Curi, T.C.; Covas, D.T.; Curi, R.; Durigon, E.L. SARS-COV-2 variants: differences and potential of immune evasion. Frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology 2022, 11, 1401. [CrossRef]
- Tandel, D.; Gupta, D.; Sah, V.; Harinivas Harshan, K. N440K variant of SARS-CoV-2 has higher infectious fitness. BioRxiv 2021, 2021.2004. 2030.441434.
- Gan, H.H.; Twaddle, A.; Marchand, B.; Gunsalus, K.C. Structural modeling of the SARS-CoV-2 spike/human ACE2 complex interface can identify high-affinity variants associated with increased transmissibility. Journal of Molecular Biology 2021, 433, 167051.
- Sobitan, A.; Mahase, V.; Rhoades, R.; Williams, D.; Liu, D.; Xie, Y.; Li, L.; Tang, Q.; Teng, S. Computational saturation mutagenesis of SARS-CoV-1 spike glycoprotein: Stability, binding affinity, and comparison with SARS-CoV-2. Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences 2021, 8, 784303.
- Weisblum, Y.; Schmidt, F.; Zhang, F.; DaSilva, J.; Poston, D.; Lorenzi, J.C.; Muecksch, F.; Rutkowska, M.; Hoffmann, H.-H.; Michailidis, E. Escape from neutralizing antibodies by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein variants. elife 2020, 9, e61312.
- Deng, X.; Garcia-Knight, M.A.; Khalid, M.M.; Servellita, V.; Wang, C.; Morris, M.K.; Sotomayor-González, A.; Glasner, D.R.; Reyes, K.R.; Gliwa, A.S. Transmission, infectivity, and neutralization of a spike L452R SARS-CoV-2 variant. Cell 2021, 184, 3426-3437. e3428.
- Chakraborty, C.; Sharma, A.R.; Bhattacharya, M.; Lee, S.-S. A detailed overview of immune escape, antibody escape, partial vaccine escape of SARS-CoV-2 and their emerging variants with escape mutations. Frontiers in Immunology 2022, 13, 801522.
- Baum, A.; Fulton, B.O.; Wloga, E.; Copin, R.; Pascal, K.E.; Russo, V.; Giordano, S.; Lanza, K.; Negron, N.; Ni, M. Antibody cocktail to SARS-CoV-2 spike protein prevents rapid mutational escape seen with individual antibodies. Science 2020, 369, 1014-1018.
- Planas, D.; Veyer, D.; Baidaliuk, A.; Staropoli, I.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Rajah, M.M.; Planchais, C.; Porrot, F.; Robillard, N.; Puech, J. Reduced sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 variant Delta to antibody neutralization. Nature 2021, 596, 276-280.
- Alenquer, M.; Ferreira, F.; Lousa, D.; Valério, M.; Medina-Lopes, M.; Bergman, M.-L.; Gonçalves, J.; Demengeot, J.; Leite, R.B.; Lilue, J. Signatures in SARS-CoV-2 spike protein conferring escape to neutralizing antibodies. PLoS pathogens 2021, 17, e1009772.
- Lu, L.; Chu, A.W.-H.; Zhang, R.R.; Chan, W.-M.; Ip, J.D.; Tsoi, H.-W.; Chen, L.-l.; Cai, J.-P.; Lung, D.C.; Tam, A.R. The impact of spike N501Y mutation on neutralizing activity and RBD binding of SARS-CoV-2 convalescent serum. EBioMedicine 2021, 71.
- Borges, V.; Isidro, J.; Cortes-Martins, H.; Duarte, S.; Vieira, L.; Leite, R.; Gordo, I.; Caetano, C.P.; Nunes, B.; Sá, R. On the track of the D839Y mutation in the SARS-CoV-2 Spike fusion peptide: emergence and geotemporal spread of a highly prevalent variant in Portugal. medRxiv 2020, 2020.2008. 2010.20171884.
- Cavallo, L.; Oliva, R. D936Y and other mutations in the fusion core of the SARS-Cov-2 spike protein heptad repeat 1 undermine the Post-Fusion assembly. BioRxiv 2020, 2020.2006. 2008.140152.
- Barrett, C.T.; Neal, H.E.; Edmonds, K.; Moncman, C.L.; Thompson, R.; Branttie, J.M.; Boggs, K.B.; Wu, C.-Y.; Leung, D.W.; Dutch, R.E. Effect of clinical isolate or cleavage site mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein on protein stability, cleavage, and cell–cell fusion. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2021, 297.
- Rahman, M.S.; Hoque, M.N.; Islam, M.R.; Islam, I.; Mishu, I.D.; Rahaman, M.M.; Sultana, M.; Hossain, M.A. Mutational insights into the envelope protein of SARS-CoV-2. Gene reports 2021, 22, 100997.
- Timmers, L.F.S.M.; Peixoto, J.V.; Ducati, R.G.; Bachega, J.F.R.; de Mattos Pereira, L.; Caceres, R.A.; Majolo, F.; da Silva, G.L.; Anton, D.B.; Dellagostin, O.A. SARS-CoV-2 mutations in Brazil: from genomics to putative clinical conditions. Scientific reports 2021, 11, 11998.
- Mou, K.; Abdalla, M.; Wei, D.Q.; Khan, M.T.; Lodhi, M.S.; Darwish, D.B.; Sharaf, M.; Tu, X. Emerging mutations in envelope protein of SARS-CoV-2 and their effect on thermodynamic properties. Informatics in medicine unlocked 2021, 25, 100675.
- Wu, H.; Xing, N.; Meng, K.; Fu, B.; Xue, W.; Dong, P.; Tang, W.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, G.; Luo, H. Nucleocapsid mutations R203K/G204R increase the infectivity, fitness, and virulence of SARS-CoV-2. Cell host & microbe 2021, 29, 1788-1801. e1786. [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.; Islam, M.R.; Alam, A.R.U.; Islam, I.; Hoque, M.N.; Akter, S.; Rahaman, M.M.; Sultana, M.; Hossain, M.A. Evolutionary dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein and its consequences. Journal of medical virology 2021, 93, 2177-2195.
- Bartolini, B.; Rueca, M.; Gruber, C.E.M.; Messina, F.; Carletti, F.; Giombini, E.; Lalle, E.; Bordi, L.; Matusali, G.; Colavita, F. SARS-CoV-2 phylogenetic analysis, Lazio region, Italy, February–march 2020. Emerging infectious diseases 2020, 26, 1842.
- Troyano-Hernáez, P.; Reinosa, R.; Holguín, Á. Evolution of SARS-CoV-2 envelope, membrane, nucleocapsid, and spike structural proteins from the beginning of the pandemic to September 2020: a global and regional approach by epidemiological week. Viruses 2021, 13, 243. [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Peng, P.; Cao, X.; Wu, K.; Chen, J.; Wang, K.; Tang, N.; Huang, A.-l. Increased immune escape of the new SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern Omicron. Cellular & Molecular Immunology 2022, 19, 293-295.
- Lohr, B.; Niemann, D.; Verheyen, J. Bamlanivimab treatment leads to rapid selection of immune escape variant carrying the E484K mutation in a B. 1.1. 7-infected and immunosuppressed patient. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2021, 73, 2144-2145. [CrossRef]
- Jangra, S.; Ye, C.; Rathnasinghe, R.; Stadlbauer, D.; Alshammary, H.; Amoako, A.A.; Awawda, M.H.; Beach, K.F.; Bermúdez-González, M.C.; Chernet, R.L. SARS-CoV-2 spike E484K mutation reduces antibody neutralisation. The Lancet Microbe 2021, 2, e283-e284.
- Jangra, S.; Ye, C.; Rathnasinghe, R.; Stadlbauer, D.; Krammer, F.; Simon, V.; Martinez-Sobrido, L.; Garcia-Sastre, A.; Schotsaert, M.; Group, P.S. The E484K mutation in the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein reduces but does not abolish neutralizing activity of human convalescent and post-vaccination sera. MedRxiv 2021.
- Cui, Z.; Liu, P.; Wang, N.; Wang, L.; Fan, K.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, K.; Chen, R.; Feng, R.; Jia, Z. Structural and functional characterizations of infectivity and immune evasion of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron. Cell 2022, 185, 860-871. e813.
- Vogt, A.-C.S.; Augusto, G.; Martina, B.; Chang, X.; Nasrallah, G.; Speiser, D.E.; Vogel, M.; Bachmann, M.F.; Mohsen, M.O. Increased receptor affinity and reduced recognition by specific antibodies contribute to immune escape of SARS-CoV-2 variant omicron. Vaccines 2022, 10, 743.
- Li, G.; Zhou, Z.; Du, P.; Yu, M.; Li, N.; Xiong, X.; Huang, H.; Liu, Z.; Dai, Q.; Zhu, J. The SARS-CoV-2 spike L452R-E484Q variant in the Indian B. 1.617 strain showed significant reduction in the neutralization activity of immune sera. Precision Clinical Medicine 2021, 4, 149-154. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; VanBlargan, L.A.; Bloyet, L.-M.; Rothlauf, P.W.; Chen, R.E.; Stumpf, S.; Zhao, H.; Errico, J.M.; Theel, E.S.; Liebeskind, M.J. Landscape analysis of escape variants identifies SARS-CoV-2 spike mutations that attenuate monoclonal and serum antibody neutralization. BioRxiv 2020, 2020.2011. 2006.372037.
- Lei, X.; Dong, X.; Ma, R.; Wang, W.; Xiao, X.; Tian, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Ren, L. Activation and evasion of type I interferon responses by SARS-CoV-2. Nature communications 2020, 11, 3810.
- Thoms, M.; Buschauer, R.; Ameismeier, M.; Koepke, L.; Denk, T.; Hirschenberger, M.; Kratzat, H.; Hayn, M.; Mackens-Kiani, T.; Cheng, J. Structural basis for translational shutdown and immune evasion by the Nsp1 protein of SARS-CoV-2. Science 2020, 369, 1249-1255.
- Lin, J.-w.; Tang, C.; Wei, H.-c.; Du, B.; Chen, C.; Wang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, M.-x.; Cheng, L.; Kuivanen, S. Genomic monitoring of SARS-CoV-2 uncovers an Nsp1 deletion variant that modulates type I interferon response. Cell host & microbe 2021, 29, 489-502. e488.
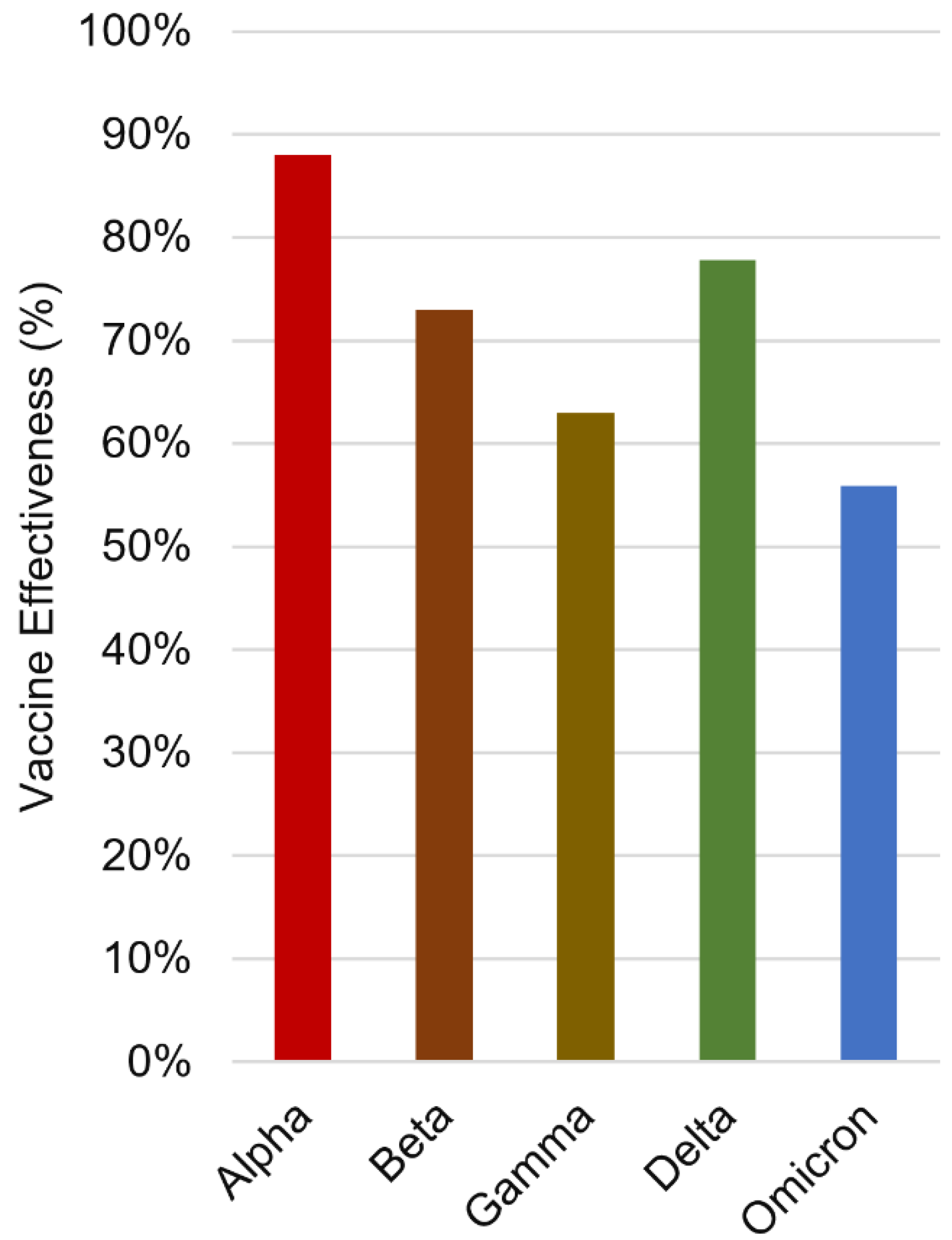
- Zeng, B.; Gao, L.; Zhou, Q.; Yu, K.; Sun, F. Effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC medicine 2022, 20, 1-15.
- Chen, Y.; Shen, H.; Huang, R.; Tong, X.; Wu, C. Serum neutralising activity against SARS-CoV-2 variants elicited by CoronaVac. The Lancet Infectious Diseases 2021, 21, 1071-1072.
- Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xie, J.; Xiao, L.; Xiang, Z. Resistance of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant to convalescent and CoronaVac vaccine plasma. Emerging Microbes & Infections 2022, 11, 425-428.
- Jin, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Zhu, F. CoronaVac: A review of efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity of the inactivated vaccine against SARS-CoV-2. Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics 2022, 18, 2096970.
- Ai, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Wan, Y.; Huang, Y.; Song, J.; Fu, Z. Omicron variant showed lower neutralizing sensitivity than other SARS-CoV-2 variants to immune sera elicited by vaccines after boost. Emerging microbes & infections 2022, 11, 337-343.
- Bhiman, J.N.; Richardson, S.I.; Lambson, B.E.; Kgagudi, P.; Mzindle, N.; Kaldine, H.; Crowther, C.; Gray, G.; Bekker, L.-G. Novavax NVX-COV2373 triggers neutralization of Omicron sub-lineages. Scientific Reports 2023, 13, 1222. [CrossRef]
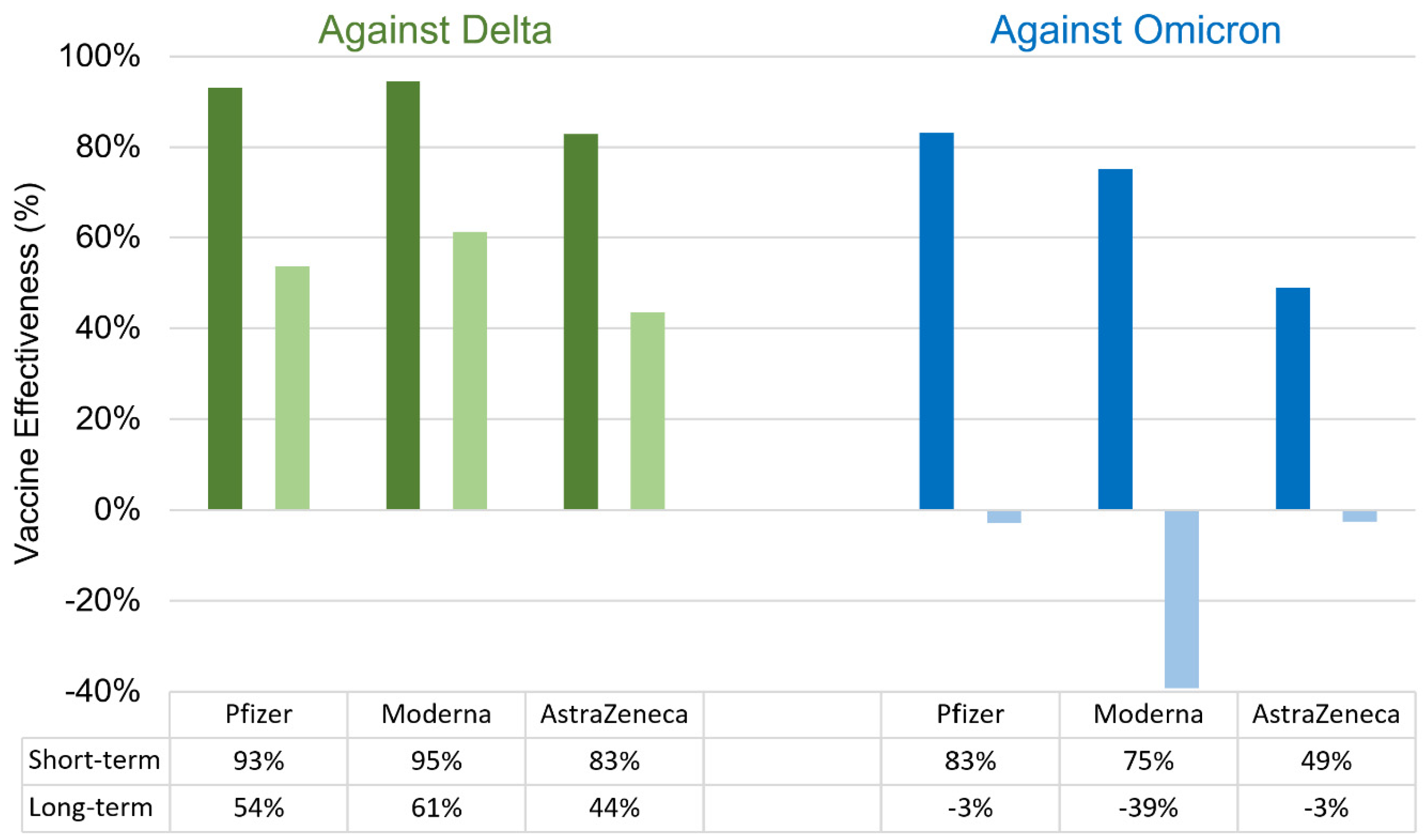
- Bruxvoort, K.J.; Sy, L.S.; Qian, L.; Ackerson, B.K.; Luo, Y.; Lee, G.S.; Tian, Y.; Florea, A.; Aragones, M.; Tubert, J.E. Effectiveness of mRNA-1273 against delta, mu, and other emerging variants of SARS-CoV-2: test negative case-control study. bmj 2021, 375.
- Tseng, H.F.; Ackerson, B.K.; Luo, Y.; Sy, L.S.; Talarico, C.A.; Tian, Y.; Bruxvoort, K.J.; Tubert, J.E.; Florea, A.; Ku, J.H. Effectiveness of mRNA-1273 against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron and Delta variants. Nature medicine 2022, 28, 1063-1071.
- Lustig, Y.; Zuckerman, N.; Nemet, I.; Atari, N.; Kliker, L.; Regev-Yochay, G.; Sapir, E.; Mor, O.; Alroy-Preis, S.; Mendelson, E. Neutralising capacity against Delta (B. 1.617. 2) and other variants of concern following Comirnaty (BNT162b2, BioNTech/Pfizer) vaccination in health care workers, Israel. Eurosurveillance 2021, 26, 2100557. [CrossRef]
- Lauring, A.S.; Tenforde, M.W.; Chappell, J.D.; Gaglani, M.; Ginde, A.A.; McNeal, T.; Ghamande, S.; Douin, D.J.; Talbot, H.K.; Casey, J.D. Clinical severity of, and effectiveness of mRNA vaccines against, covid-19 from omicron, delta, and alpha SARS-CoV-2 variants in the United States: prospective observational study. Bmj 2022, 376.
- Paul, P.; El-Naas, A.; Hamad, O.; Salameh, M.A.; Mhaimeed, N.; Laswi, I.; Abdelati, A.A.; AlAnni, J.; Khanjar, B.; Al-Ali, D. Effectiveness of the pre-Omicron COVID-19 vaccines against Omicron in reducing infection, hospitalization, severity, and mortality compared to Delta and other variants: A systematic review. Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics 2023, 19, 2167410. [CrossRef]
- Chenchula, S.; Karunakaran, P.; Sharma, S.; Chavan, M. Current evidence on efficacy of COVID-19 booster dose vaccination against the Omicron variant: A systematic review. Journal of Medical Virology 2022, 94, 2969-2976.
- Andrews, N.; Stowe, J.; Kirsebom, F.; Toffa, S.; Rickeard, T.; Gallagher, E.; Gower, C.; Kall, M.; Groves, N.; O’Connell, A.-M. Covid-19 vaccine effectiveness against the Omicron (B. 1.1. 529) variant. New England Journal of Medicine 2022, 386, 1532-1546.
- Atmar, R.L.; Lyke, K.E.; Deming, M.E.; Jackson, L.A.; Branche, A.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Rostad, C.A.; Martin, J.M.; Johnston, C.; Rupp, R.E. Homologous and heterologous Covid-19 booster vaccinations. New England Journal of Medicine 2022, 386, 1046-1057. [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, K.; Prasad, N.; Dascomb, K.; Irving, S.A.; Yang, D.-H.; Gaglani, M.; Klein, N.P.; DeSilva, M.B.; Ong, T.C.; Grannis, S.J. Effectiveness of homologous and heterologous COVID-19 booster doses following 1 Ad. 26. COV2. S (Janssen [Johnson & Johnson]) vaccine dose against COVID-19–associated emergency department and urgent care encounters and hospitalizations among adults—VISION Network, 10 states, December 2021–March 2022. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report 2022, 71, 495.
- Çağlayan, D.; Süner, A.F.; Şiyve, N.; Güzel, I.; Irmak, Ç.; Işik, E.; Appak, Ö.; Çelik, M.; Öztürk, G.; Alp Çavuş, S.; et al. An analysis of antibody response following the second dose of CoronaVac and humoral response after booster dose with BNT162b2 or CoronaVac among healthcare workers in Turkey. J Med Virol 2022, 94, 2212-2221. [CrossRef]
- Thye, A.Y.-K.; Tan, L.T.-H.; Law, J.W.F.; Letchumanan, V. COVID-19 Booster Vaccines Administration in Different Countries. Progress In Microbes & Molecular Biology 2021, 4. [CrossRef]
- Jara, A.; Undurraga, E.A.; Zubizarreta, J.R.; González, C.; Pizarro, A.; Acevedo, J.; Leo, K.; Paredes, F.; Bralic, T.; Vergara, V. Effectiveness of homologous and heterologous booster doses for an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine: a large-scale prospective cohort study. The Lancet Global Health 2022, 10, e798-e806.
- Regev-Yochay, G.; Gonen, T.; Gilboa, M.; Mandelboim, M.; Indenbaum, V.; Amit, S.; Meltzer, L.; Asraf, K.; Cohen, C.; Fluss, R. 4th dose COVID mRNA vaccines’ immunogenicity & efficacy against omicron VOC. MedRxiv 2022, 2022.2002. 2015.22270948.
- Bowen, J.E.; Addetia, A.; Dang, H.V.; Stewart, C.; Brown, J.T.; Sharkey, W.K.; Sprouse, K.R.; Walls, A.C.; Mazzitelli, I.G.; Logue, J.K.; et al. Omicron spike function and neutralizing activity elicited by a comprehensive panel of vaccines. Science 2022, 377, 890-894. [CrossRef]
- Kawasuji, H.; Morinaga, Y.; Tani, H.; Saga, Y.; Yamada, H.; Yoshida, Y.; Takegoshi, Y.; Kaneda, M.; Murai, Y.; Kimoto, K. Efficacy of the wild-type/Omicron BA. 1 bivalent vaccine as the second booster dose against Omicron BA. 2 and BA. 5. medRxiv 2022, 2022.2011. 2015.22282328. [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Kurhade, C.; Patel, S.; Kitchin, N.; Tompkins, K.; Cutler, M.; Cooper, D.; Yang, Q.; Cai, H.; Muik, A. Improved neutralization of Omicron BA. 4/5, BA. 4.6, BA. 2.75. 2, BQ. 1.1, and XBB. 1 with bivalent BA. 4/5 vaccine. BioRxiv 2022, 2022.2011. 2017.516898.
- Scheaffer, S.M.; Lee, D.; Whitener, B.; Ying, B.; Wu, K.; Liang, C.-Y.; Jani, H.; Martin, P.; Amato, N.J.; Avena, L.E. Bivalent SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines increase breadth of neutralization and protect against the BA. 5 Omicron variant in mice. Nature medicine 2023, 29, 247-257.
- Zeng, W.; Liu, G.; Ma, H.; Zhao, D.; Yang, Y.; Liu, M.; Mohammed, A.; Zhao, C.; Yang, Y.; Xie, J. Biochemical characterization of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein. Biochemical and biophysical research communications 2020, 527, 618-623.
- Chow, S.C.; Ho, C.Y.; Tam, T.T.; Wu, C.; Cheung, T.; Chan, P.K.; Ng, M.H.; Hui, P.; Ng, H.-K.; Au, D.M. Specific epitopes of the structural and hypothetical proteins elicit variable humoral responses in SARS patients. Journal of clinical pathology 2006, 59, 468-476. [CrossRef]
- Grifoni, A.; Sidney, J.; Zhang, Y.; Scheuermann, R.H.; Peters, B.; Sette, A. A sequence homology and bioinformatic approach can predict candidate targets for immune responses to SARS-CoV-2. Cell host & microbe 2020, 27, 671-680. e672.
- Rouzbahani, A.K.; Kheirandish, F.; Hosseini, S.Z. Design of a multi-epitope-based peptide vaccine against the S and N proteins of SARS-COV-2 using immunoinformatics approach. Egypt J Med Hum Genet 2022, 23, 16. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.; Qureshi, R.; Sagurthi, S.R.; Qureshi, I.A. Designing of nucleocapsid protein based novel multi-epitope vaccine against SARS-COV-2 using immunoinformatics approach. International journal of peptide research and therapeutics 2021, 27, 941-956. [CrossRef]
- Crooke, S.N.; Ovsyannikova, I.G.; Kennedy, R.B.; Poland, G.A. Immunoinformatic identification of B cell and T cell epitopes in the SARS-CoV-2 proteome. Scientific reports 2020, 10, 14179.
- Bai, L.; Zhao, Y.; Dong, J.; Liang, S.; Guo, M.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Huang, Z.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Z. Coinfection with influenza A virus enhances SARS-CoV-2 infectivity. Cell research 2021, 31, 395-403.
- Zhang, L.; Jiang, Y.; He, J.; Chen, J.; Qi, R.; Yuan, L.; Shao, T.; Zhao, H.; Chen, C.; Chen, Y. Intranasal influenza-vectored COVID-19 vaccine restrains the SARS-CoV-2 inflammatory response in hamsters. Nature Communications 2023, 14, 4117.
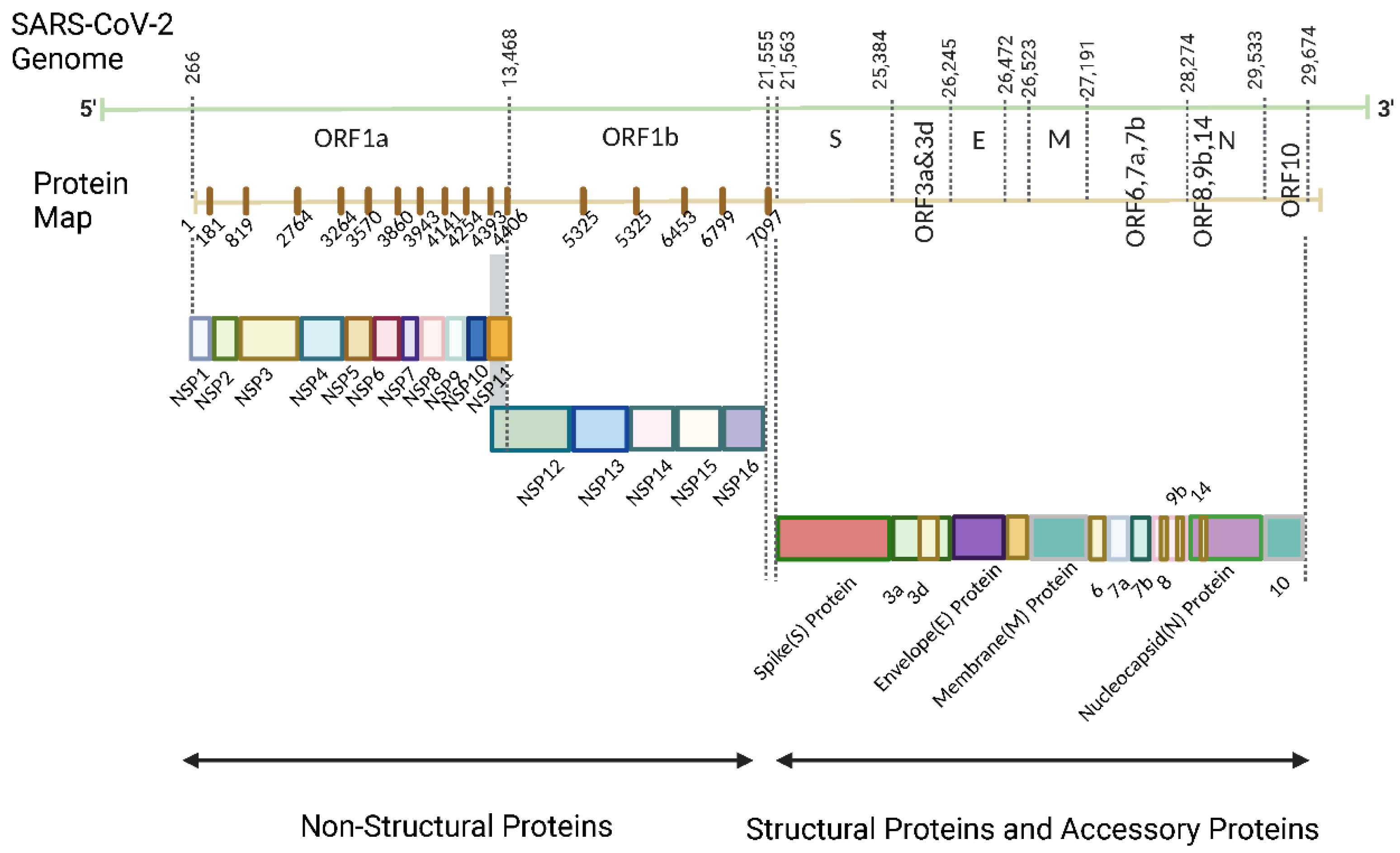
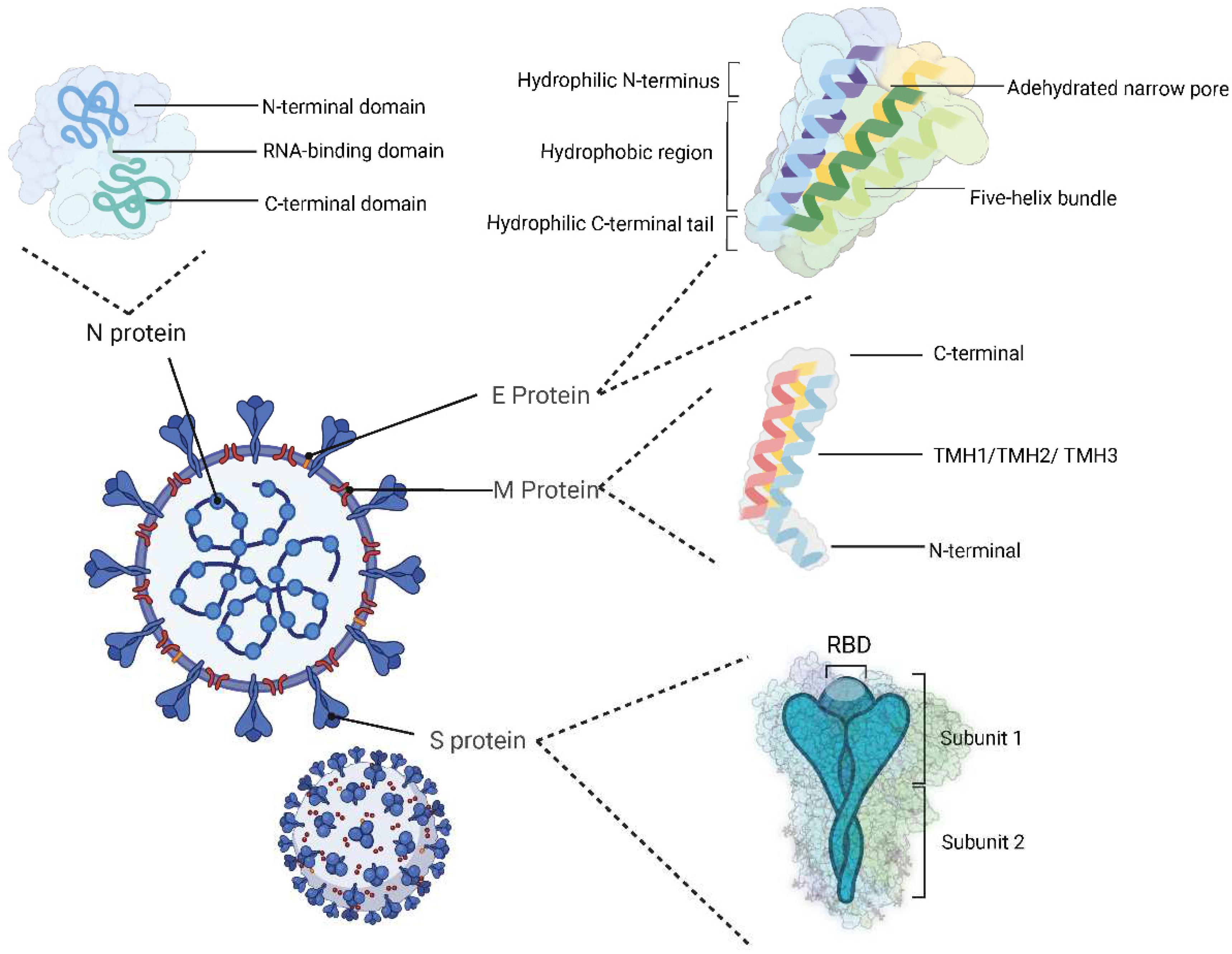
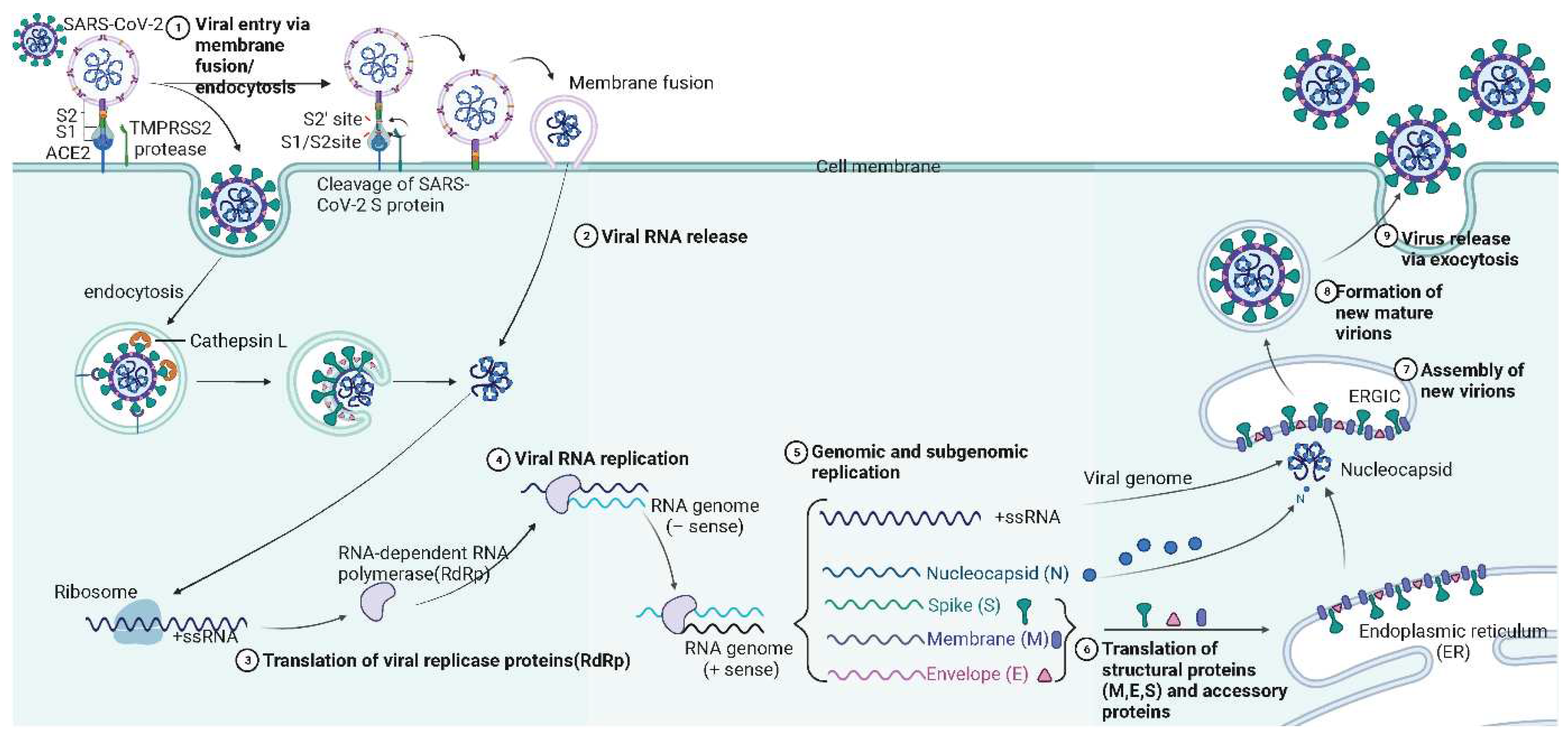
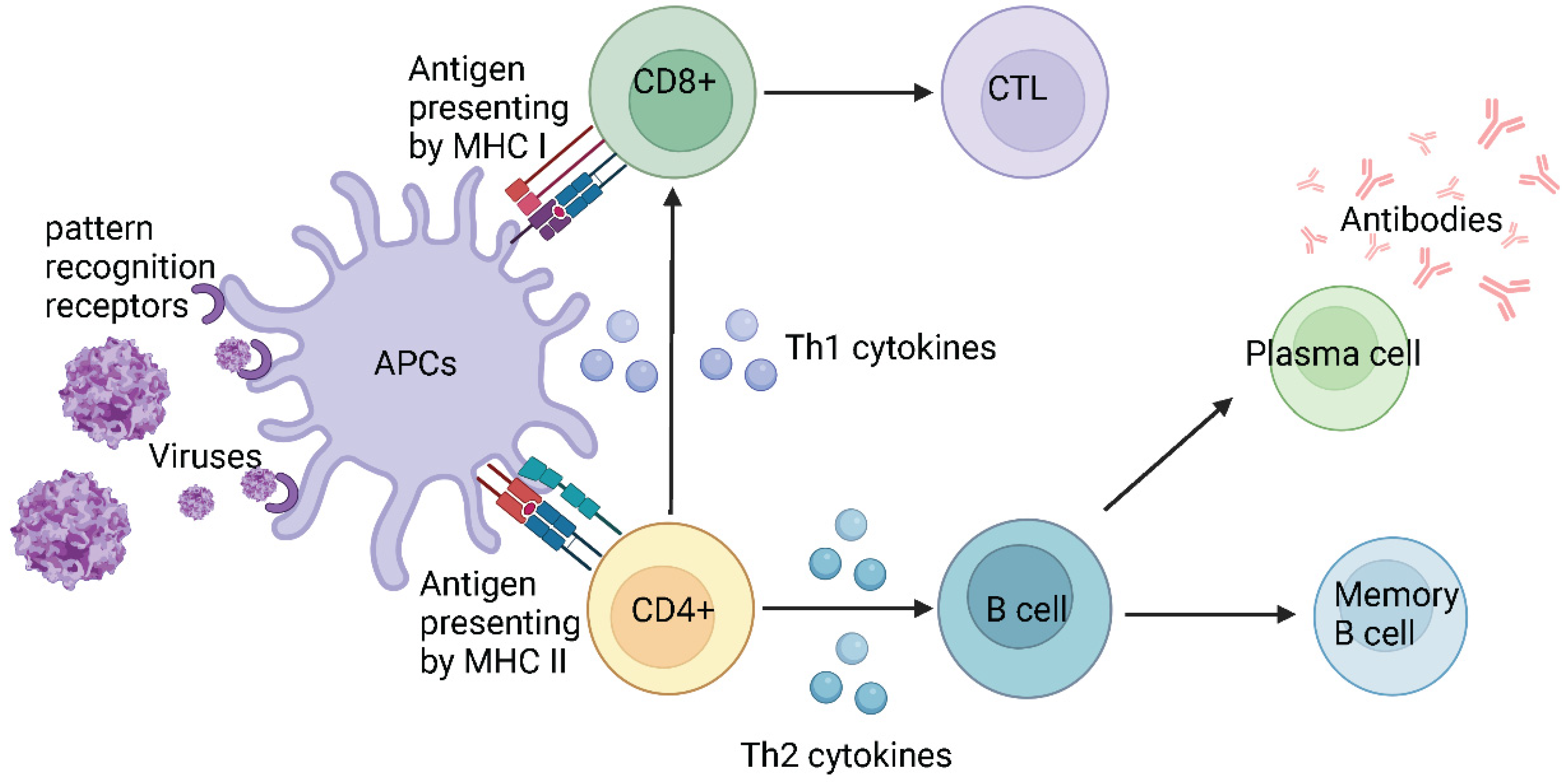
| Name | Range on genome | Function | Sequence Reference Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nsp1 | 1-180 | Leader protein host RNA inhibitor (degrade the host RNA)[25] |
YP_009725297.1 |
| Nsp2 | 181-818 | Disruption of signaling in host cells (predicted based on SARS-CoV)[26] | YP_009725298.1 |
| Nsp3 | 819-2763 | Papain-like protease Promotion of RNA replication and transcription[27] Cleavage of proteins involved in the host innate immune immunity[28] |
YP_009725299.1 |
| Nsp4 | 2764-3263 | Membrane remodeling (Binding to nsp3) | YP_009725300.1 |
| Nsp5 | 3264-3569 | 3C-like proteinase Mediates cleavages downstream of nsp4 Cleavage of proteins related to the host innate immune response[28] |
YP_009725301.1 |
| Nsp6 | 3570-3859 | Limitation of autophagic flux[29,30] Transmembrane domain |
YP_009725302.1 |
| Nsp7 | 3860-3942 | Forms a complex with RdRp for genome replication[31] | YP_009725303.1 |
| Nsp8 | 3943-4140 | Combine with RdRp[31] Subunit of SARS-CoV-2 polymerase complex[32] |
YP_009725304.1 |
| Nsp9 | 4141-4253 | RNA binding subunit[33] | YP_009725305.1 |
| Nsp10 | 4254-4392 | Regulator of viral replicase function Activation of methyltransferase activity as a co-factor[34] |
YP_009725306.1 |
| Nsp11 | 4393-4405 | Unknown | YP_009725312.1 |
| Nsp12 | 4393-5324 | RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp)[35] | YP_009725307.1 |
| Nsp13 | 5325-5925 | Helicase[36] | YP_009725308.1 |
| Nsp14 | 5926-6452 | Exonuclease[36] | YP_009725309.1 |
| Nsp15 | 6453-6798 | Endoribonuclease[36] | YP_009725310.1 |
| Nsp16 | 6799-7096 | 2′-O-methyltransferase Immune evasion related[37] |
YP_009725311.1 |
| Vaccine | Developers & (Country) | Vaccine Type | Doses | Injection Interval* | Vaccination Restrictions** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comirnaty | Pfizer-BioNTech (USA & Germany) |
mRNA | 2 | 21 days | All individuals aged 6 months and above |
| Spikevax | Moderna, NIAID (USA) | mRNA | 2 | 28 days | All individuals aged 6 months and above |
| Johnson & Johnson vaccine | Janssen Pharmaceuticals Johnson & Johnson (USA) | Viral vector | 1 | - | 18 and above |
| Vaxzevria | AstraZeneca, University of Oxford (UK) | Viral vector | 2 | 28 days | 18 and above |
| CONVIDECIA | CanSino Biologics Inc. (China) |
Viral vector | 1 | - | 18 and above |
| CoronaVac | Sinovac (China) |
Inactivated (Vero Cells) | 2 | 14 days | 18 and above; Further assessment for pregnant women is needed |
| BBIBP-CorV (Vero Cells) | Sinopharm (China) |
Inactivated (Vero Cells) | 2 | 21 days | 18 and above; Further assessment for pregnant women is needed |
| BBV152/COVAXIN | Bharat Biotech (India) |
Inactivated | 2 | 28 days | 18 and above; recommended for pregnant woman only when the benefits of vaccination outweigh the potential risks |
| VLA2001 | Valneva SE (France) |
Inactivated | 2 | 28 days | 18 to 50 years |
| Nuvaxovid | Novavax (U.S) |
Protein Subunit vaccine | 2 | 21 days | 12 and above; recommended for pregnant woman only when the benefits of vaccination outweigh the potential risks |
| WHO label* | Pango lineage** | GISAID Clade*** | Mutations in binding sites | First reported (Date/Country) |
Designation /Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alpha | B.1.1.7 | GRY | S:N501Y | Sep/2020 UK |
VOC: 18/Dec/2020 Previous VOC: 09/Mar/2022 |
| Beta | B.1.351 | GH/501Y.V2 | S:K417N,S:E484K,S:N501Y | May/2020 South Africa |
VOC: 18/Dec/2020 Previous VOC: 09/Mar/2022 |
| Gamma | P.1 | GH/501Y.V3 | S:K417T,S:E484K,S:N501Y | Nov/2020 Brazil |
VOC: 11/Jan/2021 Previous VOC: 09/Mar/2022 |
| Delta | B.1.617.2 | G/478K.V1 | S:L452R,S:T478K,S:E484Q | Oct/2020 India |
VOI: 4/Apr/2021 VOC: 11/May/2021 Previous VOC: 07/Jul/2022 |
| Omicron | B.1.1.529 | GR/484A | S:G339D,S:S371L,S:S373P,S:S375F,S:K417N, S:N440K,S:G446S,S:S477N,S:T478K,S:E484A, S:Q493R,S:G496S,S:Q498R,S:N501Y,S:Y505H |
Nov/2021 Multiple countries |
VUM: 24/Nov/2021 VOC: 26/Nov/2021 Previous VOC: 14/Mar/2023 |
| Mutations | Location | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| H49Y | NTD | Slight structural changes on the HR1 region; Increased cell entry[120] |
| V367F | RBD | Enhanced infectivity; Increased affinity to ACE2[127] |
| K417N | RBD | Immune escape[128] |
| N440K | RBD (RBM) | Higher infectious fitness; Increased affinity to ACE2[129,130] |
| S443A | RBD (RBM) | Stabilized SARS-CoV-2 S protein; Increased affinity to ACE2[130,131] |
| K444R/Q/N* | RBD (RBM) | Immune escape[132] |
| L452R | RBD (RBM) | Immune escape[133,134] |
| Y453F | RBD (RBM) | Immune escape[135] |
| G476S | RBD (RBM) | Conformational changes in the S protein; Increased affinity to ACE2[130] |
| T478K | RBD (RBM) | Immune escape[136] |
| S494P | RBD (RBM) | Immune escape[137] |
| N501Y | RBD (RBM) | Immune escape[138] |
| D839Y | S2 subunit | Structural changes on the S protein Enhanced infectivity (Prediction)[139] |
| D936Y | HR1 | Conformational stability adjustment of the pre- and/or post-fusion S protein[140] |
| S943P | HR1 | Conformational stability adjustment of the pre- and/or post-fusion S protein[140] |
| P1263L | Cytoplasmic tail | A significant increase in fusion (compared with WT)[141] |
| T9I | E protein | Destabilizing[142] |
| V62F | E protein | Highly destabilizing[142] |
| S68F | E protein | Slightly stabilizing[142,143,144] |
| R203K | N protein | Destabilized and decreased overall structural flexibility; Increased transmission and virulence of select SARS-CoV-2 variants[145,146] |
| G204R | N protein | Destabilized and decreased overall structural flexibility; Increased transmission and virulence of select SARS-CoV-2 variants[145,146] |
| D3G | M protein | A nonsynonymous substitution[147,148] |
| T175M | M protein | High antigenicity values[147,148] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





