Submitted:
23 January 2024
Posted:
24 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
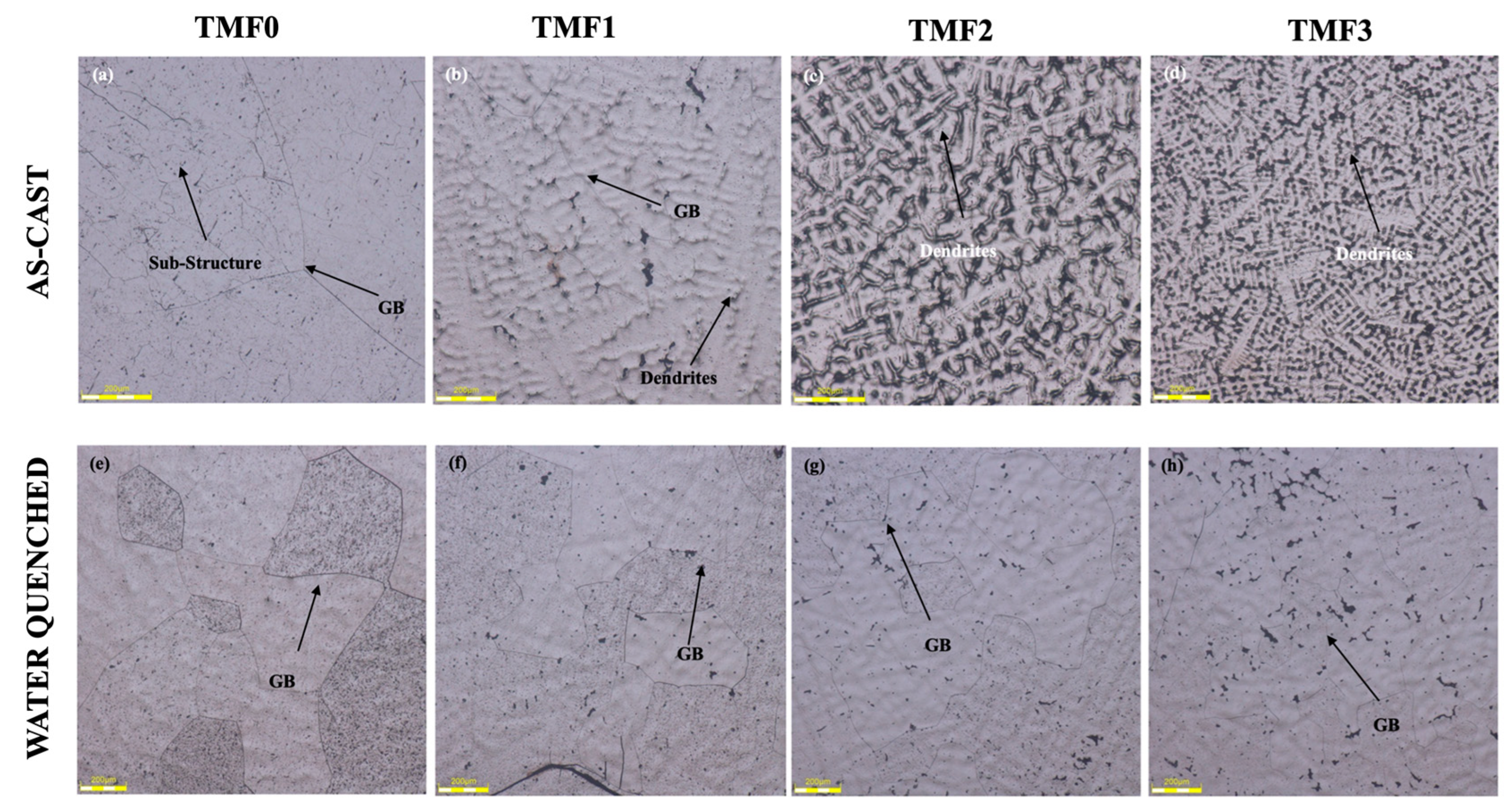
3.1. Microstructural evolution
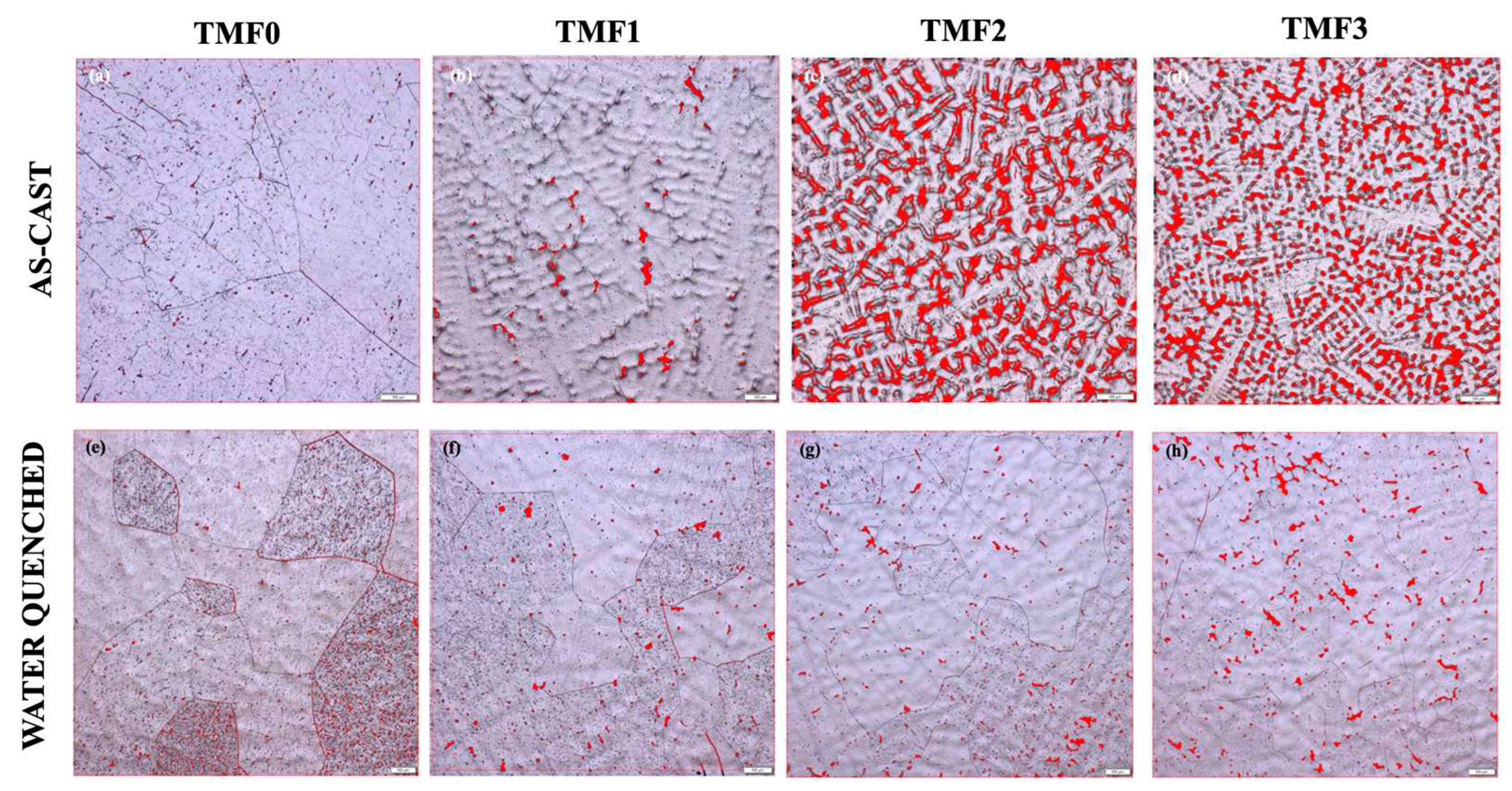
3.2. Porosity Measurements
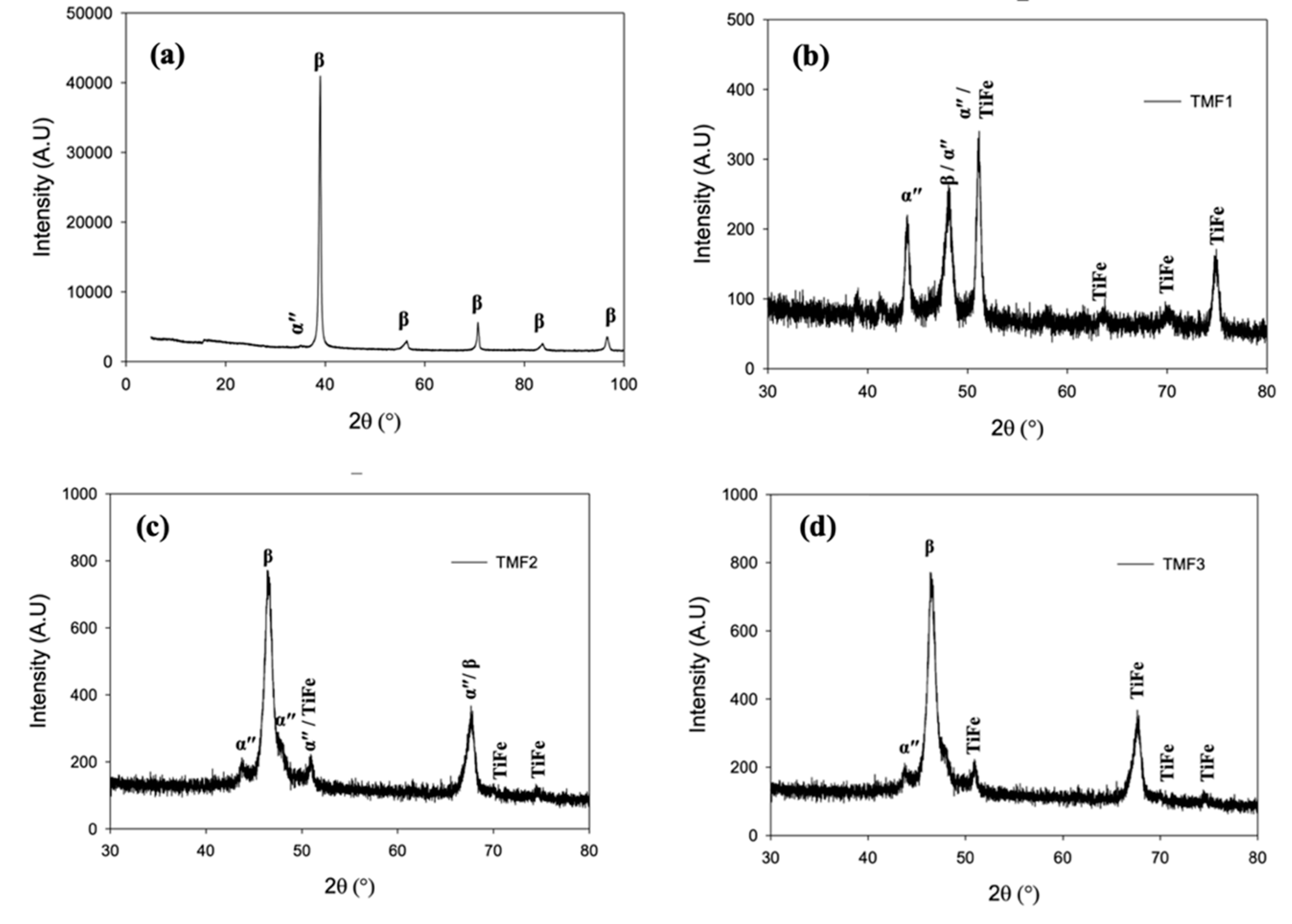
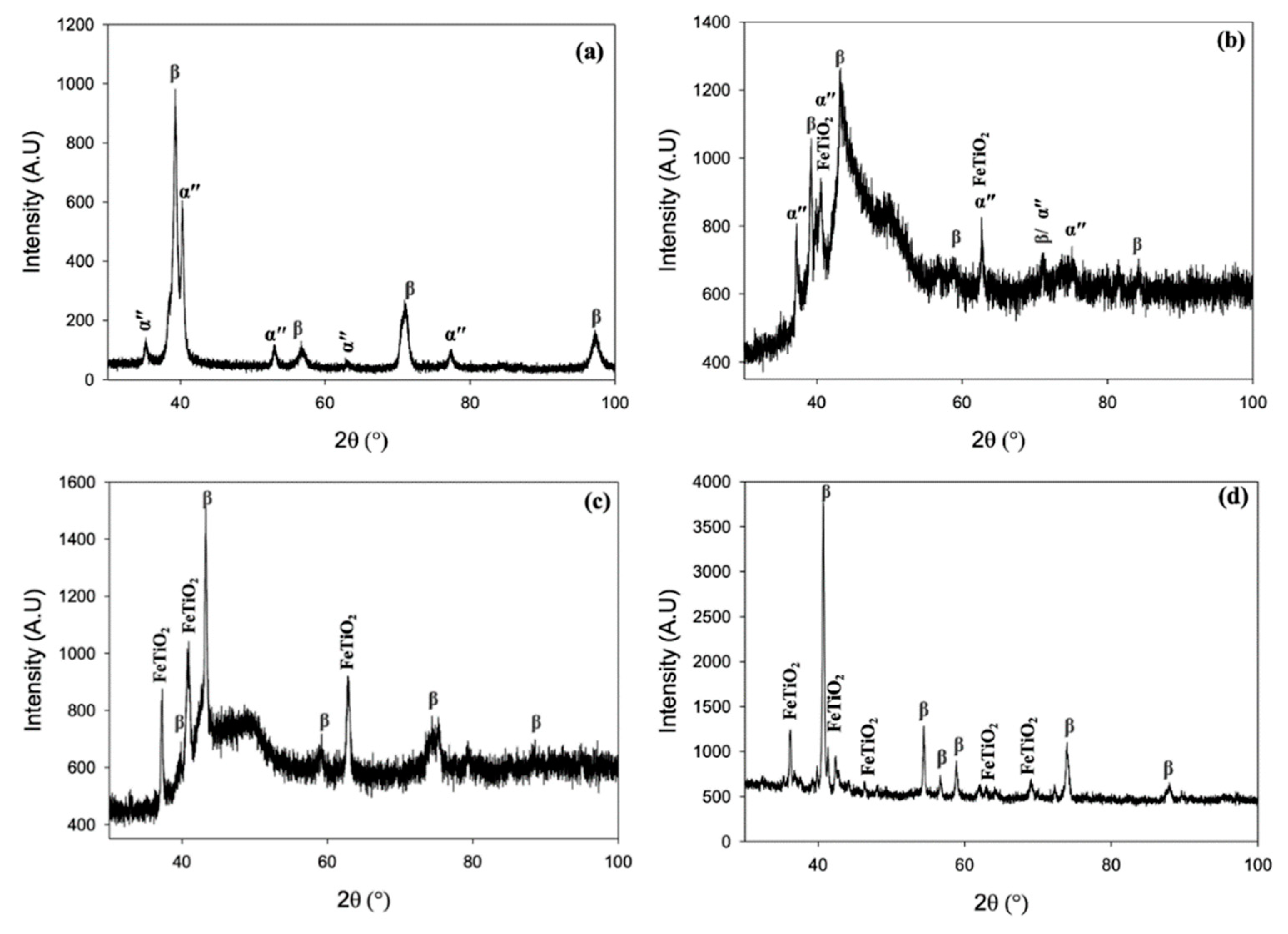
3.3. Phase analysis
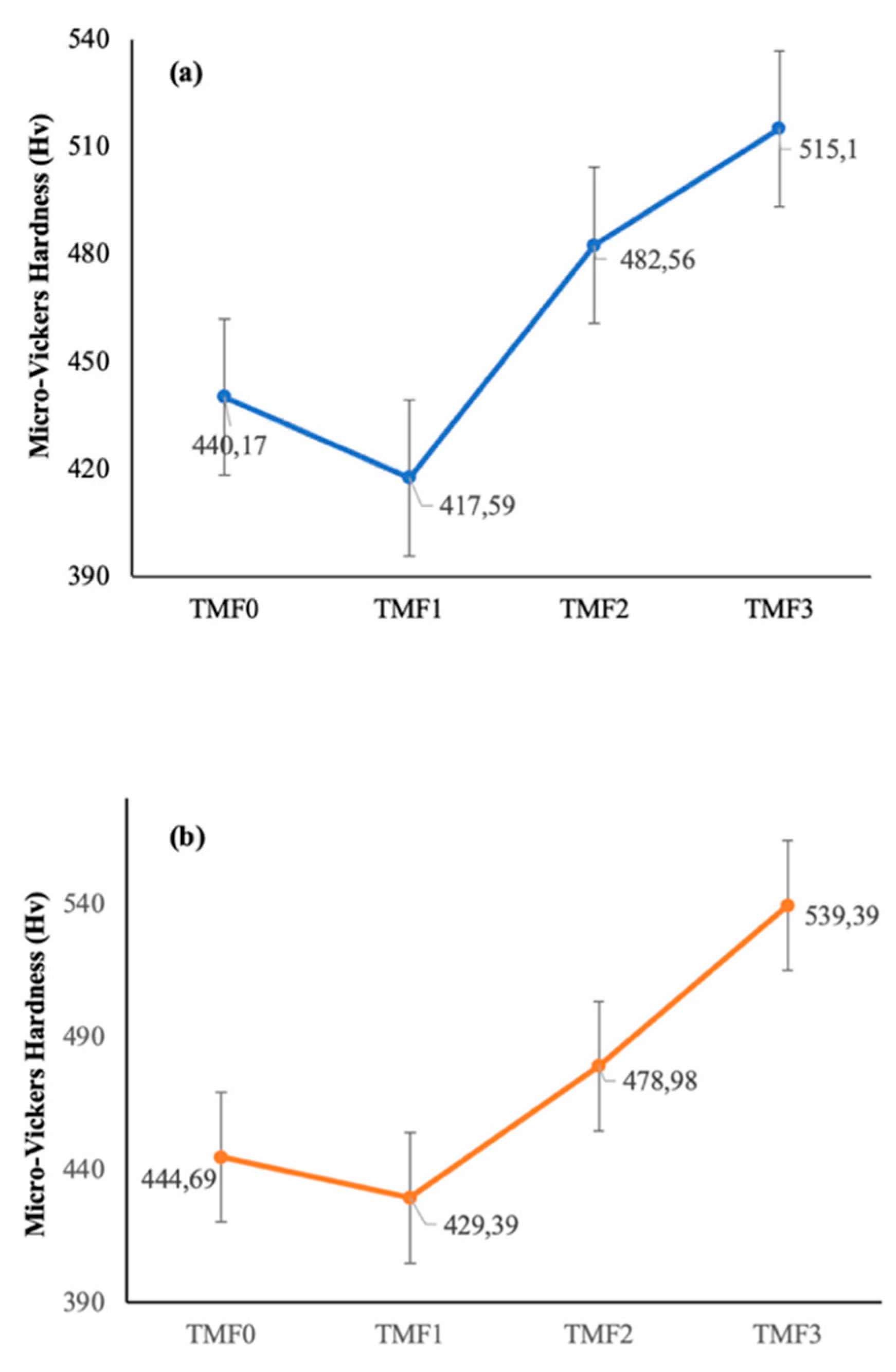
3.4. Micro-Vickers Hardness
3.5. Tensile Properties
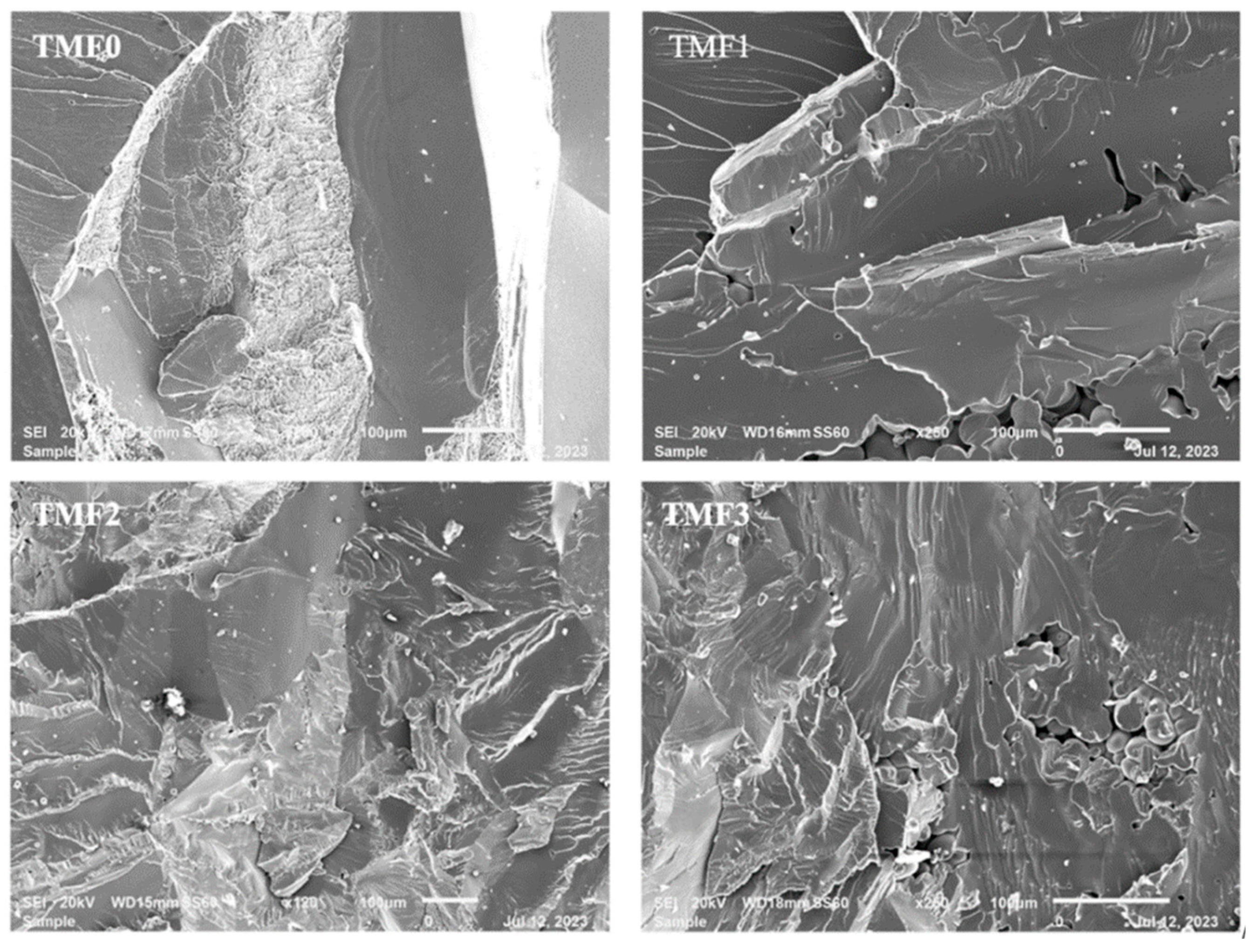
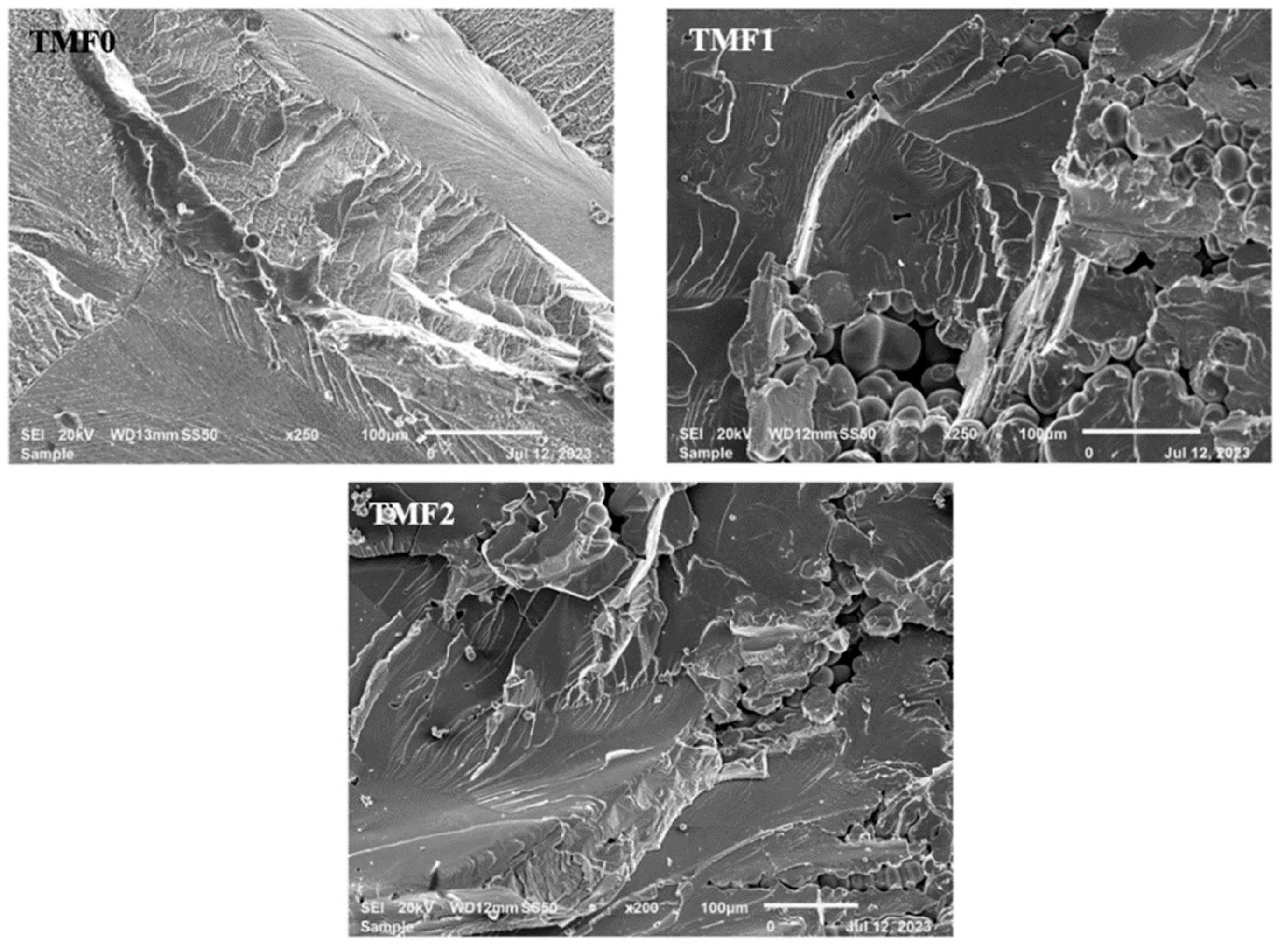
3.6. Fracture Surfaces
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- M. Niinomi and M. Nakai, “Titanium-based biomaterials for preventing stress shielding between implant devices and bone,” International Journal of Biomaterials. 2011. [CrossRef]
- Niinomi,M; Nakai, M.; and Hieda,J. “Development of new metallic alloys for biomedical applications,” Acta Biomaterialia, vol. 8, no. 11. Elsevier Ltd., 2012. pp. 3888–3903. [CrossRef]
- Biesiekierski, A.; Wang, J.; and Wen, C. “A brief review of biomedical Shape Memory Alloys by powder metallurgy,” in Key Engineering Materials, Trans Tech Publications Ltd., 2012. pp. 195–200. [CrossRef]
- Bazaka, O.; Bazaka, K.; Kingshott, P.; Crawford, RJ.; and Ivanova, EP. “Metallic Implants for Biomedical Applications.” [Online]. Available: http://books.rsc.org/books/edited-volume/chapter-pdf/1609069/bk9781788017534-00001.pdf.
- Akahori, T.; Niinomi, M.; Fukui, H.; Ogawa, M.; and Toda, H. “Improvement in fatigue characteristics of newly developed beta type titanium alloy for biomedical applications by thermo-mechanical treatments,” in Materials Science and Engineering C, May 2005. pp. 248–254. [CrossRef]
- Niinomi, M. “Recent research and development in titanium alloys for biomedical applications and healthcare goods,” Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, vol. 4, no. 5. pp. 445–454, Sep. 2003. [CrossRef]
- Williams, DF. “On the mechanisms of biocompatibility,” Biomaterials, vol. 29, no. 20, Jul. 2008. pp. 2941–2953. [CrossRef]
- Niinomi, M. “Mechanical biocompatibilities of titanium alloys for biomedical applications,” Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, vol. 1, no. 1. Jan. 2008. pp. 30–42. [CrossRef]
- Mishra, F,T. “Mechanical and Tribological Properties and Biocompatibility of Diffusion Hardened Ti-13Nb-13Zr — A New Titanium Alloy for Surgical Implants,” In Medical applications of titanium and its alloys: the material and biological issues. ASTM International, Jan. 1996. pp. 96–113. [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Gustavson, L.; and Dumbleton, J. “Microstructure and Properties of a New Beta Titanium Alloy, Ti-12Mo-6Zr-2Fe, Developed for Surgical Implants,”. Jan. 1996. pp. 76–87. [CrossRef]
- Zardiackas, L.; Mitchell, D.; and Disegi, J. “Characterization of Ti-15Mo Beta Titanium Alloy for Orthopaedic Implant Applications,” Jan. 1996. pp. 60–75. [CrossRef]
- Gepreel, M.; Hefnawy, A.; Hussein, A.; and Kandil, S. “Effect of heat treatment on the microstructure of Ti-Nb-Ta base alloys for biomedical applications,” International Journal of Chemical and Applied Biological Sciences, vol. 1, no. 6, 2014. p. 119. [CrossRef]
- Kasuga,T.; Nogami,M.; Niinomi, M.; Hattori, T. “Bioactive calcium phosphate invert glass-ceramic coating on b-type Ti-29Nb-13Ta-4.6Zr alloy,” 2003. [CrossRef]
- Bolzoni, L.“Low-cost Fe-bearing powder metallurgy Ti alloys,” Metal Powder Report, vol. 74, no. 6, Nov. 2019. pp. 308–313. [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.; Kawakami, A.; and Cockcroft, S.L. “Beta Fleck and Segregation in Titanium Alloy Ingots.” 2006. [CrossRef]
- Devaraj A.; et al., “A low-cost hierarchical nanostructured beta-titanium alloy with high strength,” Nat Commun, vol. 7, Apr. 2016. [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Emura, S.; Min, X.; and Tsuchiya, K. “Strain-rate effect on work-hardening behavior in β-type Ti-10Mo-1Fe alloy with TWIP effect,” Materials Science and Engineering A, vol. 707, Nov. 2017. pp. 701–707. [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.et al., “High strength, low modulus and biocompatible porous Ti–Mo–Fe alloys,” Journal of Porous Materials, vol. 21, no. 6, Nov. 2014. pp. 913–919. [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, W., Zhou, L.; and Ma, C. “Formation of intermediate phases and their influences on the microstructure of high strength near-β titanium alloy,” Materials Science and Engineering: A, vol. 793, Aug. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Ruan,Y.; Mohajerani, A.; and Dao,M. “Microstructural and Mechanical-Property Manipulation through Rapid Dendrite Growth and Undercooling in an Fe-based Multinary Alloy,” Sci Rep, vol. 6, Aug. 2016. [CrossRef]
- Antoniac, V.; Saha, S.; and Roy, S.“materials Metallic Dental Implants Wear Mechanisms, Materials, and Manufacturing Processes: A Literature Review,” 2022. [CrossRef]
- Razavykia,A.; Brusa,E.; Delprete,C.; and Yavari, R. “materials An Overview of Additive Manufacturing Technologies-A Review to Technical Synthesis in Numerical Study of Selective Laser Melting”. [CrossRef]
- Elshaer, R.N.; and Ibrahim,K.M. “Study of Microstructure, Mechanical Properties, and Corrosion Behavior of As-Cast Ni-Ti and Ti-6Al-4V Alloys,” J Mater Eng Perform, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Okulov, I.V. et al., “Effect of microstructure on the mechanical properties of as-cast Ti-Nb-Al-Cu-Ni alloys for biomedical application,” Materials Science and Engineering C, vol. 33, no. 8, Dec. 2013. pp. 4795–4801. [CrossRef]
- Moshokoa, N.A.; Raganya, M.L.; Machaka, R.; Makhatha, M.E.; and Obadele, B.A. “The effect of molybdenum content on the microstructural evolution and tensile properties of as-cast Ti-Mo alloys,” Mater Today Commun, vol. 27, Jun. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.; Ju, C.; and Chern Lin, J. “Structure and properties of cast binary Ti–Mo alloys,” 1999. [CrossRef]
- Louzguine,D.V.; Kato, H.; Louzguina,L.V.; and Inoue, A. “High-strength binary Ti-Fe bulk alloys with enhanced ductility,” J Mater Res, vol. 19, no. 12, Dec. 2004. pp. 3600–3606. [CrossRef]
- Biesiekierski, A.; Lin, J.; Li, Y.; Ping,D.; Yamabe-Mitarai, Y.; and Wen, C. “Investigations into Ti-(Nb,Ta)-Fe alloys for biomedical applications,” Acta Biomater, vol. 32, Mar. 2016. pp. 336–347. [CrossRef]
- Qi, P.; Li, B.; Wang, T.; Zhou, L.; and Nie, Z. “Microstructure and properties of a novel ternary Ti–6Zr–xFe alloy for biomedical applications,” J Alloys Compd, vol. 854, Feb. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Guo, L. et al., “On the design evolution of hip implants: A review,” Materials and Design, vol. 216. Elsevier Ltd., Apr. 01, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.W.et al., “Metastable pitting corrosion behavior and characteristics of passive film of laser powder bed fusion produced Ti–6Al–4V in NaCl solutions with different concentrations,” Corros Sci, vol. 215, May 2023. [CrossRef]
- Lee, C. M.; Ju, C.P.; and Chern Lin, J.H. “Structure-property relationship of cast Ti-Nb alloys,” J Oral Rehabil, vol. 29, no. 4, pp. 314–322, Apr. 2002. [CrossRef]
- Santos, P.F. et al., “Fabrication of low-cost beta-type Ti-Mn alloys for biomedical applications by metal injection molding process and their mechanical properties,” J Mech Behav Biomed Mater, vol. 59, Jun. 2016. pp. 497–507. [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.Y.; Cui, Y.W.; and Zhang, L.C. “Recent development in beta titanium alloys for biomedical applications,” Metals (Basel), vol. 10, no. 9, Sep. 2020. pp. 1–29. [CrossRef]
- Severino Martins, J.R.; and Grandini, C.R. “Structural characterization of Ti-15Mo alloy used as biomaterial by Rietveld method,” J Appl Phys, vol. 111, no. 8, Apr. 2012. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y. L.; Niinomi, M.; and Akahori, T. “Effects of Ta content on Young’s modulus and tensile properties of binary Ti-Ta alloys for biomedical applications,” Materials Science and Engineering: A, vol. 371, no. 1–2, Apr. 2004. pp. 283–290. [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.T.; and Welsch, G. “Young’s Modulus and Damping of Ti-6AI-4V Alloy as a Function of Heat Treatment and Oxygen Concentration,” 1990. [CrossRef]
- Dieter, G.E and Bacon D, Mechanical Metallurgy, vol. 3. New York, 1976.
- Mohan, P.; Rajak, D.K.; Pruncu, C.I.; Behera,A.; Amigó-Borrás, V.; and Elshalakany, A.B.“Influence of β-phase stability in elemental blended Ti-Mo and Ti-Mo-Zr alloys,” Micron, vol. 142, Mar. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.L. et al., “Young’s Modulus and Mechanical Properties of Ti-29Nb-13Ta- 4.6Zr in Relation to a9 Martensite.”. [CrossRef]
- Jung, H. S.; Lee, T.; Kwon, I.K.; Kim, H. S.; Hahn, S.K.; and Lee, C.S. “Surface modification of multipass caliber-rolled ti alloy with dexamethasone-loaded graphene for dental applications,” ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, vol. 7, no. 18, May 2015. pp. 9598–9607. [CrossRef]
- Moshokoa, N.; Raganya, L.; Obadele, B.A.; Machaka, R.; and Makhatha, M.E. “Microstructural and mechanical properties of Ti-Mo alloys designed by the cluster plus glue atom model for biomedical application,” International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, vol. 111, no. 5–6, Nov. 2020. pp. 1237–1246. [CrossRef]
- Niinomi, M. “Mechanical properties of biomedical titanium alloys,” 1998. [CrossRef]
- Salvador, C. A. F.; Dal Bó, M. R F.; Costa, H.; M. Taipina, O.; Lopes, E. S. N.; and Caram, R. “Solute lean Ti-Nb-Fe alloys: An exploratory study,” J Mech Behav Biomed Mater, vol. 65, Jan. 2017. pp. 761–769. [CrossRef]
- Lopes, E.S.N.; C. A. F. Salvador, C.A.F.; D. R. Andrade, D.R.; A. Cremasco, A.; K. N. Campo, K. N.; and Caram, R. “Microstructure, Mechanical Properties, and Electrochemical Behavior of Ti-Nb-Fe Alloys Applied as Biomaterials,” Metall Mater Trans A Phys Metall Mater Sci, vol. 47, no. 6, Jun. 2016. pp. 3213–3226. [CrossRef]
| Alloy Name | UTS (MPa) | E (GPa) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| TMF0 | 264 | 79 | This study |
| TMF1 | - | 74 | This study |
| TMF2 | - | - | |
| TMF3 | - | - |
| Alloy Name | UTS (MPa) | E (GPa) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| TMF0 | 411 | 66 | This study |
| TMF1 | - | - | |
| TMF2 | - | - | |
| TMF3 | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





