Submitted:
23 January 2024
Posted:
24 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
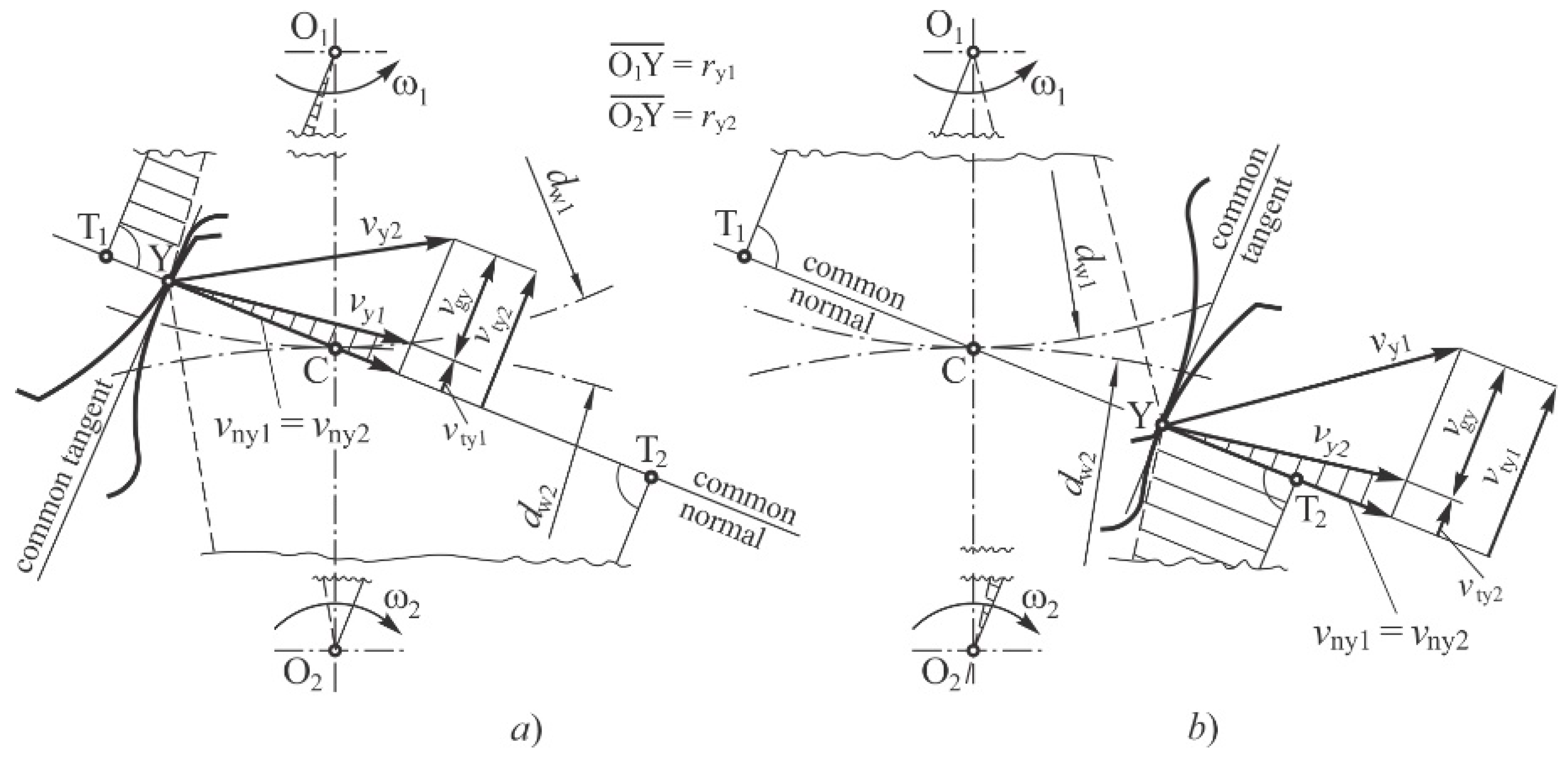
2.1. Computational modelling
2.2. Geometrical and material parameters of the analysed gear pair
2.3. FE model of gear pair
2.4. Analytical approach according to VDI 2736
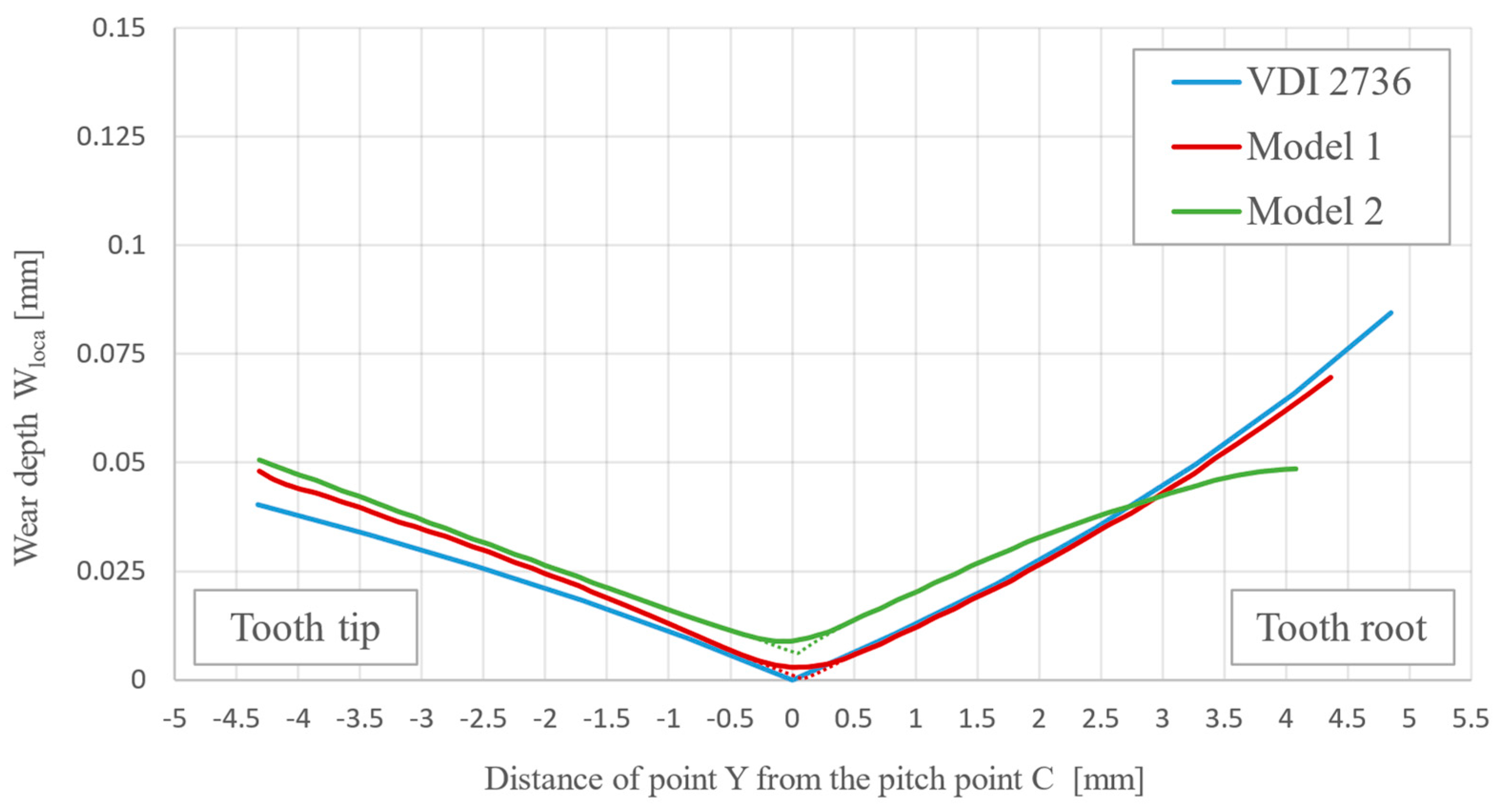
3. Results and discussion
4. Conclusions
- The proposed computational model could be used to simulate the wear behaviour of contacting mechanical elements like gears, bearings, etc.
- The use of the boundary displacement method (BDM) in the framework of PrePoMax software provides information on the geometry change that alters the operating conditions in subsequent load cycles.
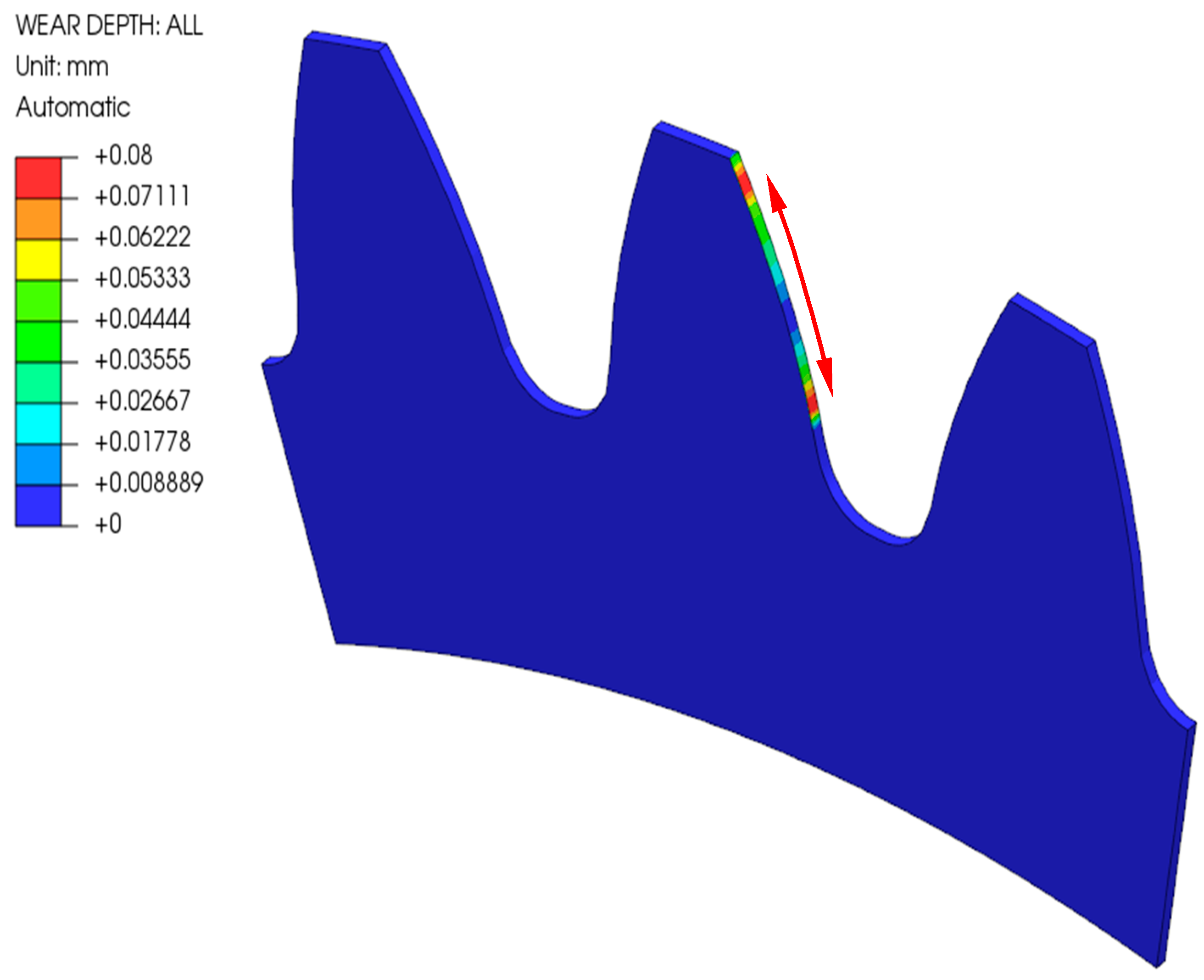
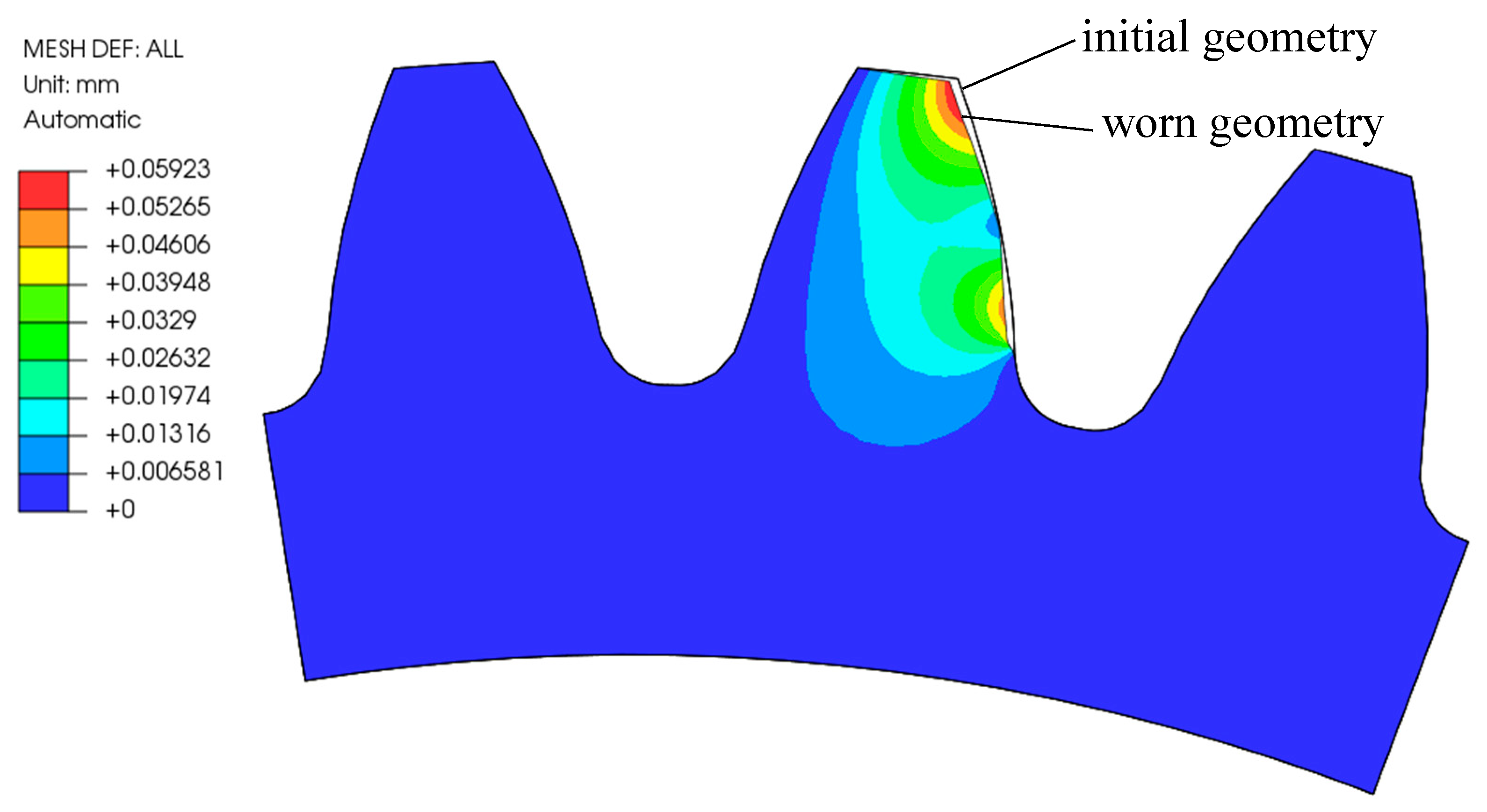
- Due to the contact problem and the formation of contact pressure peaks in the finite element mesh, it is necessary to consider mesh smoothing in the model to allow a smooth distribution of wear over the surface. This avoids additional convergence problems in the use of BDM, but it does result in the averaging of values in locations where the differences in wear between adjacent element nodes should actually be larger (such as pitch point) and is not entirely correct. The validity of the results should, therefore, be checked with a model without smoothing.
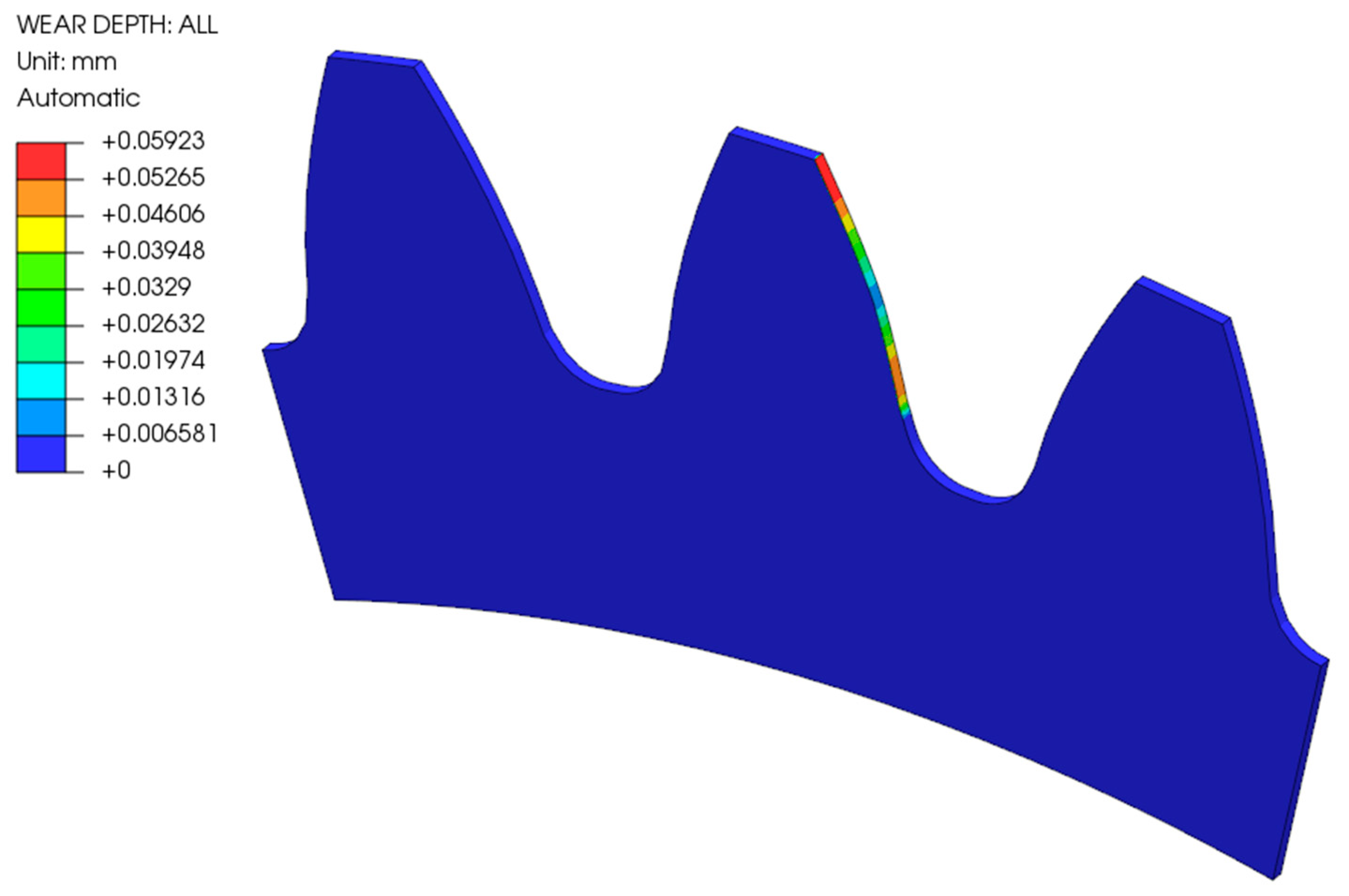
- With the computational model using a multi-step geometry update, more accurate results were obtained, which show a reduced depth of wear at the root of the tooth. In the pitch point region, a non-zero value of the wear depth appears as the number of cycles increases. The tooth deflection and the new tooth flank geometry have a major impact on this.
- The main advantage of the model, if compared to the standardised procedure according to the VDI 2736 guidelines, is the geometry updating after a certain number of loading cycles, which enables a more accurate prediction of wear behaviour under rolling/sliding loading conditions.
- In the future, a comprehensive 3D numerical model will be developed to analyse the interaction of meshing gears. This model aims to compare the results obtained from experimental testing with those derived from numerical simulations.
- Potential future advancements of the existing Archard’s wear model could include incorporating a contact stress-dependent wear coefficient, as demonstrated in prior research. Currently, the wear coefficient remains constant throughout the analysis. Additionally, the model could be enhanced by establishing a relationship between the wear parameter and wear depth in order to account for diverse surface improvement techniques.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pogačnik, A.; Tavčar, J. An Accelerated Multilevel Test and Design Procedure for Polymer Gears. Mater. Des. 2015, 65, 961–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matkovič, S.; Pogačnik, A.; Kalin, M. Wear-Coefficient Analyses for Polymer-Gear Life-Time Predictions: A Critical Appraisal of Methodologies. Wear 2021, 480–481, 203944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratović, E.; Muminović, A.; Delić, M.; Pervan, N.; Muminović, A.J.; Šarić, I. Potential and Design Parameters of Polyvinylidene Fluoride in Gear Applications. Polymers (Basel). 2023, 15, 4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosangthum, N.; Krataitong, R.; Wila, P.; Koiprasert, H.; Buncham, K.; Kansuwan, P.; Manonukul, A.; Sheppard, P. Dry Rolling-Sliding Wear Behavior of ER9 Wheel and R260 Rail Couple under Different Operating Conditions. Wear 2023, 518–519, 204636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Guo, L.C.; Maiorino, M.; Liu, J.P.; Ding, H.H.; Lewis, R.; Meli, E.; Rindi, A.; Liu, Q.Y.; Wang, W.J. Comparison of Wear and Rolling Contact Fatigue Behaviours of Bainitic and Pearlitic Rails under Various Rolling-Sliding Conditions. Wear 2020, 460–461, 203455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, H.; Zhu, C.; Ge, Y. Simulation of the Fatigue-Wear Coupling Mechanism of an Aviation Gear. Friction 2021, 9, 1616–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.T.; Guo, L.C.; Shi, L.B.; Cai, Z.B.; Li, Q.L.; Liu, Q.Y.; Wang, W.J. Wear and Damage Transitions of Two Kinds of Wheel Materials in the Rolling-Sliding Contact. Wear 2018, 398–399, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, X.; Pu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, L. Surface Topography and Friction Coefficient Evolution during Sliding Wear in a Mixed Lubricated Rolling-Sliding Contact. Tribol. Int. 2019, 137, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.-W.; Jun, H.-K.; Kwon, S.-J.; Lee, D.-H. Rolling Contact Fatigue and Wear of Two Different Rail Steels under Rolling–Sliding Contact. Int. J. Fatigue 2016, 83, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Fan, X.; Wei, S.; Liu, D.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, Y. Microstructure and Wear Properties of High-Speed Steel with High Molybdenum Content under Rolling-Sliding Wear. Tribol. Int. 2017, 116, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, A.; Esteves, M.; Marta, P. Friction and Wear Behaviour of Rolling–Sliding Steel Contacts. Wear 2013, 302, 1468–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archard, J.F. Contact and Rubbing of Flat Surfaces. J. Appl. Phys. 1953, 24, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flodin, A.; Andersson, S. Simulation of Mild Wear in Spur Gears. Wear 1997, 207, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flodin, A.; Andersson, S. Simulation of Mild Wear in Helical Gears. Wear 2000, 241, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wang, H. An Adhesive Wear Prediction Method for Double Helical Gears Based on Enhanced Coordinate Transformation and Generalized Sliding Distance Model. Mech. Mach. Theory 2018, 128, 58–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jbily, D.; Guingand, M.; de Vaujany, J.-P. A Wear Model for Worm Gear. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2016, 230, 1290–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunalioğlu, M.Ş.; Tuç, B. Theoretical and Experimental Investigation of Wear in Internal Gears. Wear 2014, 309, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.; Kolivand, M.; Kahraman, A. Prediction of Surface Wear of Hypoid Gears Using a Semi-Analytical Contact Model. Mech. Mach. Theory 2012, 52, 180–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.; Kolivand, M.; Kahraman, A. An Approximate Method to Predict Surface Wear of Hypoid Gears Using Surface Interpolation. Mech. Mach. Theory 2014, 71, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Wang, Z.; Kubo, A. Hypoid Gear Integrated Wear Model and Experimental Verification Design and Test. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2020, 166, 105228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Qiao, B.; Yang, L.; Luo, W.; Yang, Z.; Chen, X. Fault Mechanism and Dynamic Modeling of Planetary Gear with Gear Wear. Mech. Mach. Theory 2021, 155, 104098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Qiao, B.; Yang, L.; Luo, W.; Chen, X. Evaluating the Influence of Tooth Surface Wear on TVMS of Planetary Gear Set. Mech. Mach. Theory 2019, 136, 206–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Põdra, P.; Andersson, S. Simulating Sliding Wear with Finite Element Method. Tribol. Int. 1999, 32, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundvall, O.; Klarbring, A. PREDICTION OF TRANSMISSION ERROR IN SPUR GEARS AS A CONSEQUENCE OF WEAR *. Mech. Struct. Mach. 2001, 29, 431–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundvall, O.; Klarbring, A. SIMULATION OF WEAR BY USE OF A NONSMOOTH NEWTON METHOD—A SPUR GEAR APPLICATION1-2 * †. Mech. Struct. Mach. 2001, 29, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, P.; Kahraman, A.; Anderson, N.E. A Surface Wear Prediction Methodology for Parallel-Axis Gear Pairs. J. Tribol. 2004, 126, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Kahraman, A. Interactions between Nonlinear Spur Gear Dynamics and Surface Wear. J. Sound Vib. 2007, 307, 662–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Dong, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z. Time-Varying Mesh Stiffness Model of a Modified Gear–Rack Drive with Tooth Friction and Wear. J. Brazilian Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2022, 44, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huangfu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Ma, H.; Han, H.; Chen, K. Effects of Tooth Modifications on the Dynamic Characteristics of Thin-Rimmed Gears under Surface Wear. Mech. Mach. Theory 2020, 150, 103870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J. Investigation on Coupling Effects between Surface Wear and Dynamics in a Spur Gear System. Tribol. Int. 2016, 101, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zheng, X.; Yu, Y. A Calculation Method for Tooth Wear Depth Based on the Finite Element Method That Considers the Dynamic Mesh Force. Machines 2022, 10, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, T.; Velex, P. Static and Dynamic Simulations of Mild Abrasive Wear in Wide-Faced Solid Spur and Helical Gears. Mech. Mach. Theory 2010, 45, 911–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trobentar, B.; Glodež, S.; Flašker, J.; Zafošnik, B. The Influence of Surface Coatings on the Tooth Tip Deflection of Polymer Gears. Mater. Tehnol. 2016, 50, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VDI 2736, Thermoplastic Gear Wheels, German Standard; 2019.
- Lin, A.-D.; Kuang, J.-H. Dynamic Interaction between Contact Loads and Tooth Wear of Engaged Plastic Gear Pairs. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2008, 50, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borovinšek, M. Exploit the Power of the CalculiX FEM Solver Using a Modern Graphical Interface 2023.
- CALCULIX, V. 2. 2. A Free Software Three-Dimensional Structural Finite Element Program 2023.
- The Wear of Metals under Unlubricated Conditions. Proc. R. Soc. London. Ser. A. Math. Phys. Sci. 1956, 236, 397–410. [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Cao, L.; Li, R. Numerical Simulation of Sliding Wear Based on Archard Model. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Mechanic Automation and Control Engineering; IEEE, June 2010; pp. 325–329. [Google Scholar]
- Perron, N.; Dellinger, N.; Prévereaud, Y.; Balat-Pichelin, M. 3D Mesh Displacement Strategy to Simulate the Thermal Degradation of Materials under Atmospheric Reentry Conditions. Acta Astronaut. 2022, 199, 293–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, G.A.; Douglass, R.W.; Zardecki, A. Mesh Enhancement; PUBLISHED BY IMPERIAL COLLEGE PRESS AND DISTRIBUTED BY WORLD SCIENTIFIC PUBLISHING CO., 2005; ISBN 978-1-86094-487-1.
- Borovinšek, M. Downloads - PrePoMax 2023.
- Bončina, T.; Polanec, B.; Zupanič, F.; Glodež, S. Wear Behaviour of Multilayer Al-PVD-Coated Polymer Gears. Polymers (Basel). 2022, 14, 4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincenzo Vullo Gears: Geometric and Kinematic Design; Springer Verlag, 2020.
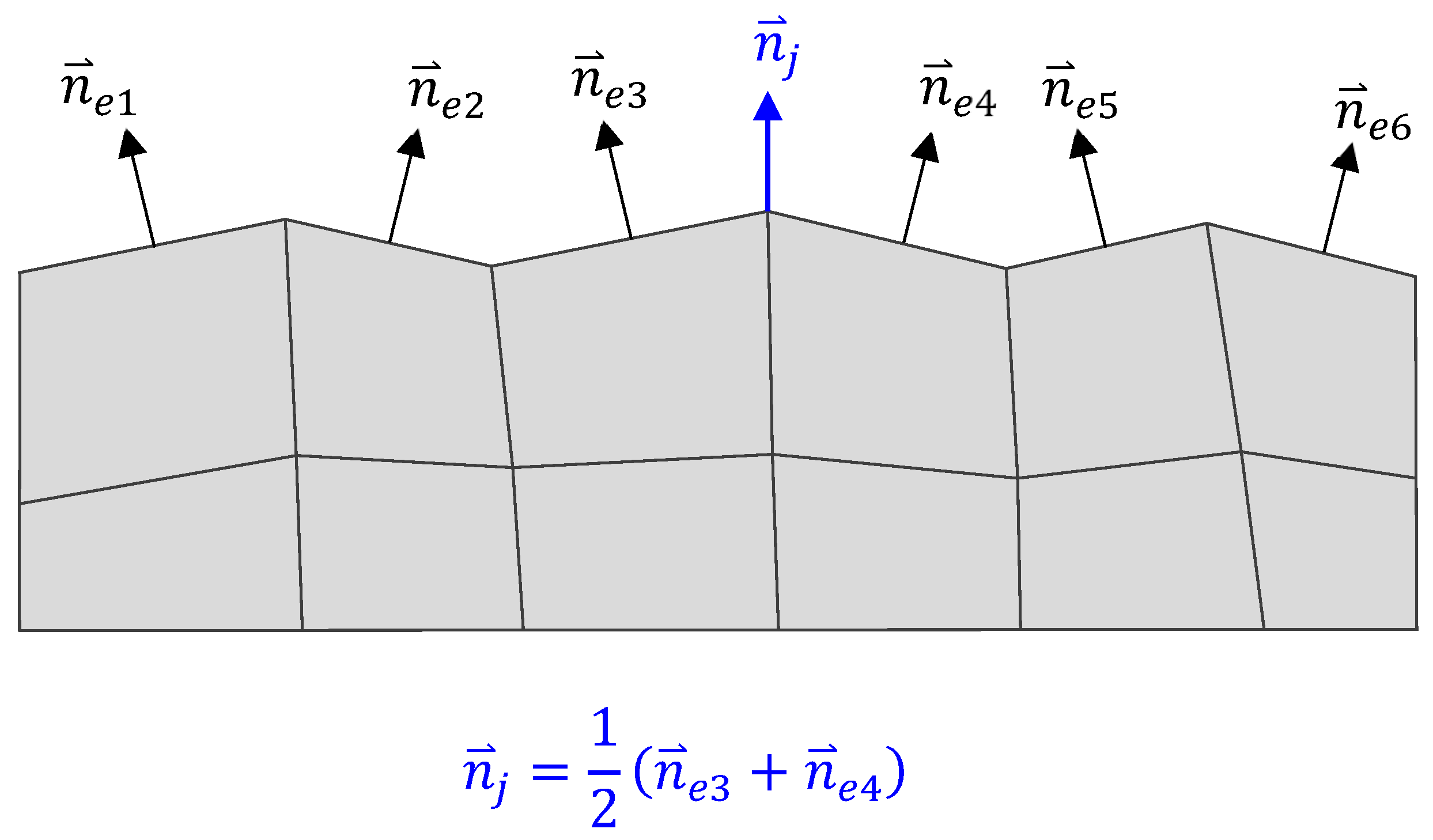
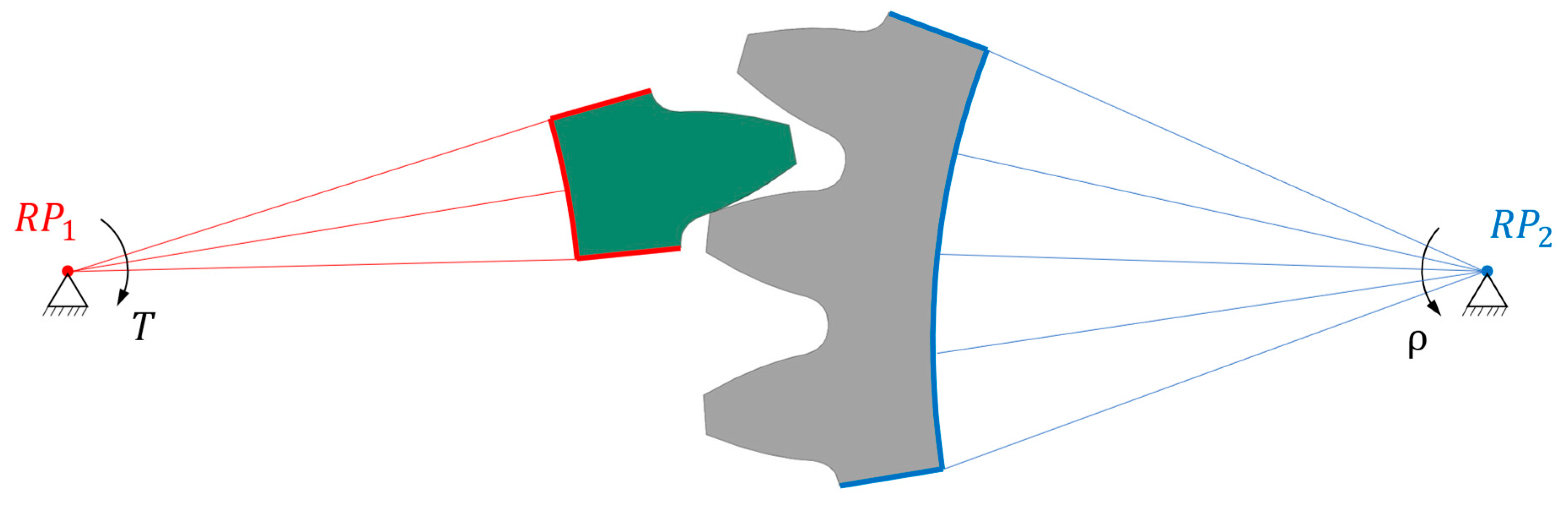
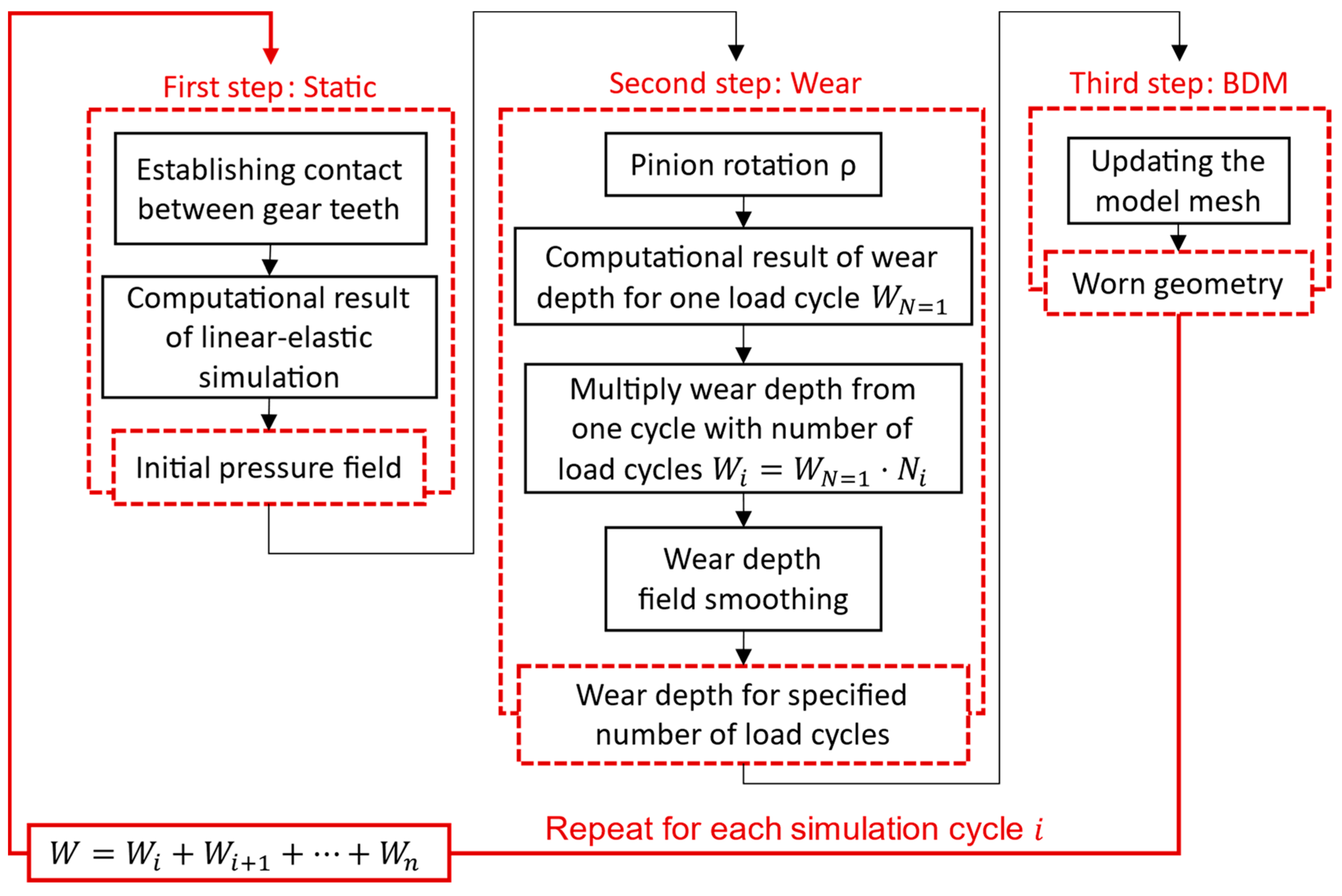
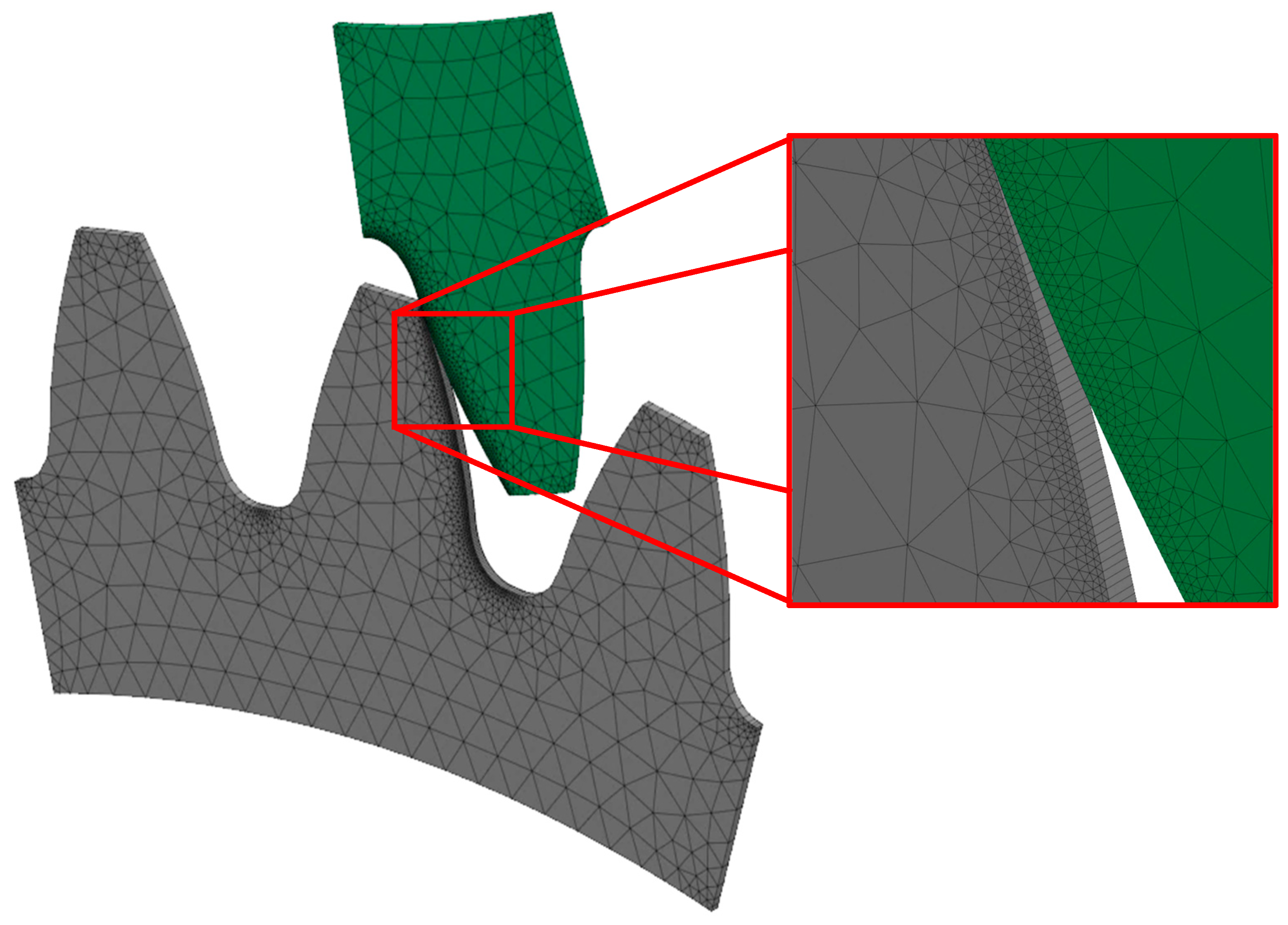
| Parameter | Tested gear | Supported gear |
| Material | POM | Steel (16MnCr5) |
| Normal module m | 2.5 mm | 2.5 mm |
| Pressure angle αn | 20° | |
| Helix angle β | 0° | |
| Number of teeth z | 36 | 36 |
| Tooth width b | 14 mm | 14 mm |
| Profile shift coefficient x | 0 | |
| Centre distance a | 90 mm | |
| Basic rack profile | ISO 53 | |
| Young’s modulus E | 2,600 MPa | 210,000 MPa |
| Poisson’s ratio ν | 0.386 | 0.280 |
| Lubrication | Dry (no lubricated) | |
| Wear coefficient kw (VDI 2736) | 3.4⋅10−6 mm3/Nm | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





