Submitted:
23 January 2024
Posted:
23 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
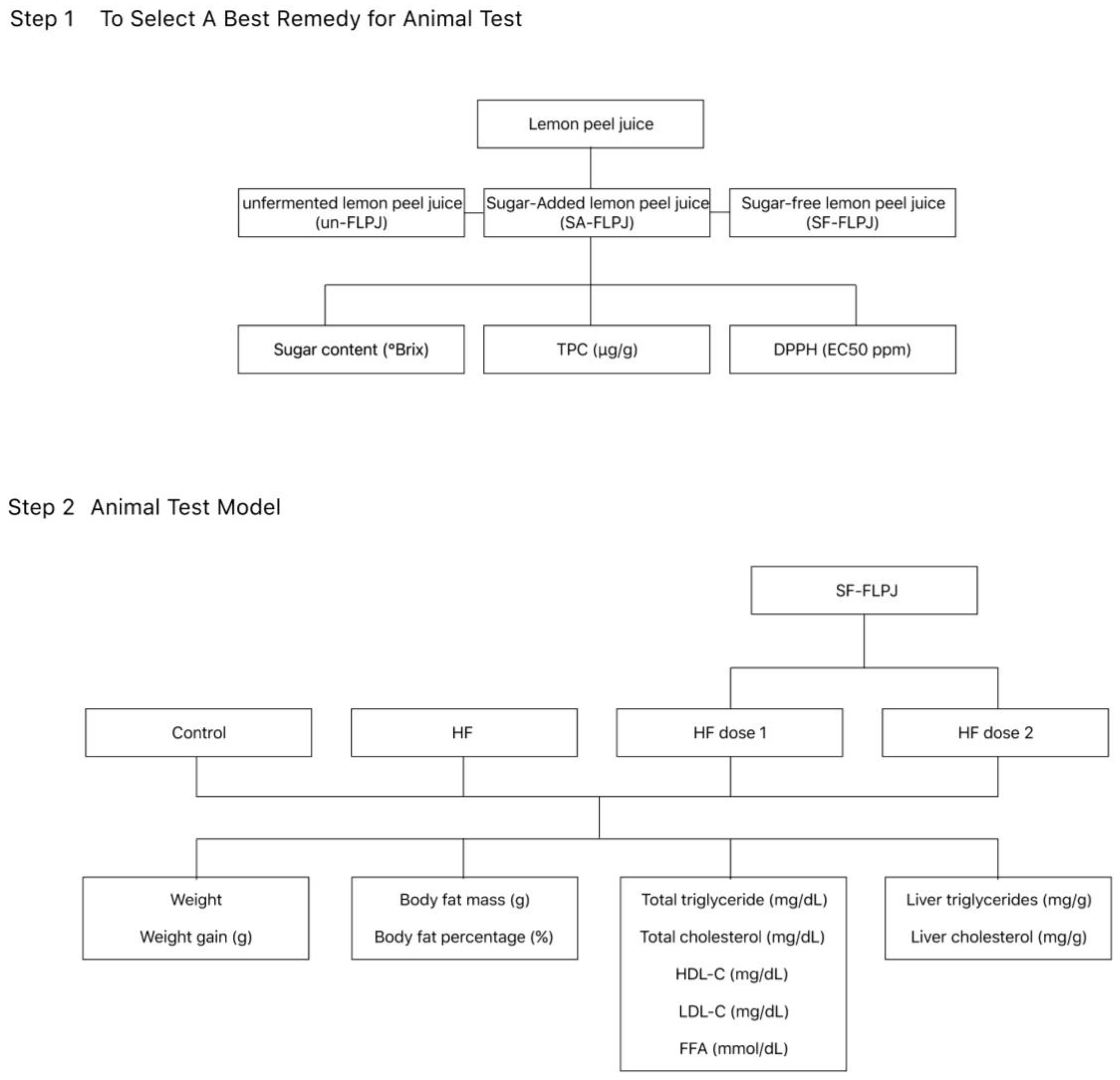
Materials and methods
Preparation of unfermented lemon peel juice (un-FLPJ), sugar-added fermented lemon peel juice (SA- FLPJ) and sugar-free fermented lemon peel juice (SF-FLPJ)
- (1)
- the preparation of un-FLPJ by smashing whole lemons, and then obtained lemon juice with smashed peel, seed and pulp.
- (2)
- added sugar up to 50% with un-FLPJ and then implanted cultivated yeast as SA-FLPJ;
- (3)
- the un-FLPJ was mixed with cultivated yeast as SF-FLPJ.
Detection of the lemon peel juices’ total phenol content (TPC)
Determination of the lemon peel juices’ 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical scavenging assay
Juices’ sugar content determination
Experimental animal care
Standard and high-fat diet composition
Animal study & SF-FLPJ Dosage
Data collection
Blood collection
Tissue samples collection
Determination of the TGs and TC in the rats’ livers
Statistical Analysis Methods
Assessment of the functional indicators
Animal body weight
Body fat and body fat percentage
Evaluation of the safety indicators
Blood lipids
Non-esterified free fatty acid blood levels
Liver lipids
Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, L., et al., Salvianolic acid B prevents body weight gain and regulates gut microbiota and LPS/TLR4 signaling pathway in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Food & function, 2020. 11(10): p. 8743-8756. [CrossRef]
- Organization, W.H. Obesity and overweight. 2021; Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight.
- Health, T.M.o. Prevalence of overweight and obesity among Chinese people. 2023; Available from: https://www.gender.ey.gov.tw/gecdb/Stat_Statistics_DetailData.aspx?sn=%24mQvpHYEayTTt8pmhMjRvA%40%40.
- Blüher, M., Obesity: global epidemiology and pathogenesis. Nature Reviews Endocrinology, 2019. 15(5): p. 288-298.
- Valerii, M.C., et al., Effect of a Fiber D-Limonene-Enriched Food Supplement on Intestinal Microbiota and Metabolic Parameters of Mice on a High-Fat Diet. Pharmaceutics, 2021. 13(11): p. 1753. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X., et al., Alleviating effects of walnut green husk extract on disorders of lipid levels and gut bacteria flora in high fat diet-induced obesity rats. Journal of Functional Foods, 2019. 52: p. 576-586. [CrossRef]
- Wei, T., et al., Different duck products protein on rat physiology and gut microbiota. Journal of proteomics, 2019. 206: p. 103436. [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-C., et al., The Anti-Obesity Effects of Lemon Fermented Products in 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes and in a Rat Model with High-Calorie Diet-Induced Obesity. Nutrients, 2021. 13(8): p. 2809. [CrossRef]
- Tiencheu, B., et al., Nutritional, sensory, physico-chemical, phytochemical, microbiological and shelf-life studies of natural fruit juice formulated from orange (Citrus sinensis), lemon (Citrus limon), Honey and Ginger (Zingiber officinale). Heliyon, 2021. 7(6): p. e07177. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H., et al., Extraction and comparison of cellulose nanocrystals from lemon (Citrus limon) seeds using sulfuric acid hydrolysis and oxidation methods. Carbohydrate polymers, 2020. 238: p. 116180. [CrossRef]
- Diab, K.A., In vitro studies on phytochemical content, antioxidant, anticancer, immunomodulatory, and antigenotoxic activities of lemon, grapefruit, and mandarin citrus peels. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, 2016. 17(7): p. 3559-3567.
- Makni, M., et al., Citrus limon from Tunisia: Phytochemical and physicochemical properties and biological activities. BioMed research international, 2018. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Oboh, G., et al., Antioxidant, hypolipidemic, and anti-angiotensin-1-converting enzyme properties of lemon (Citrus limon) and lime (Citrus aurantifolia) juices. Comparative Clinical Pathology, 2015. 24(6): p. 1395-1406. [CrossRef]
- Trovato, A., et al., Effects of fruit juices of Citrus sinensis L. and Citrus limon L. on experimental hypercholesterolemia in the rat. Phytomedicine, 1996. 2(3): p. 221-227. [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.-Y., et al., Effect of lemon water vapor extract (LWAE) from lemon byproducts on the physiological activity and quality of lemon fermented products. International Journal of Food Properties, 2021. 24(1): p. 264-276. [CrossRef]
- Fukuchi, Y., et al., Lemon polyphenols suppress diet-induced obesity by up-regulation of mRNA levels of the enzymes involved in β-oxidation in mouse white adipose tissue. Journal of clinical biochemistry and nutrition, 2008. 43(3): p. 201-209. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L., et al., Physicochemical characterization of five types of citrus dietary fibers. Biocatalysis and agricultural biotechnology, 2015. 4(2): p. 250-258. [CrossRef]
- Ağagündüz, D., et al., Novel candidate microorganisms for fermentation technology: From potential benefits to safety issues. Foods, 2022. 11(19): p. 3074. [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A., et al., Global regulatory frameworks for fermented foods: A review. Frontiers in Nutrition, 2022. 9. [CrossRef]
- Campbell-Platt, G., Fermented foods—a world perspective. Food research international, 1994. 27(3): p. 253-257.
- C Borresen, E., et al., Fermented foods: patented approaches and formulations for nutritional supplementation and health promotion. Recent patents on food, nutrition & agriculture, 2012. 4(2): p. 134-140.
- Steinkraus, K.H., Nutritional significance of fermented foods. Food Research International, 1994. 27(3): p. 259-267. [CrossRef]
- Liu, B., et al., Changes in organic acids, phenolic compounds, and antioxidant activities of lemon juice fermented by Issatchenkia terricola. Molecules, 2021. 26(21): p. 6712.
- Hashemi, S.M.B., et al., Fermented sweet lemon juice (Citrus limetta) using Lactobacillus plantarum LS5: Chemical composition, antioxidant and antibacterial activities. Journal of Functional Foods, 2017. 38: p. 409-414.
- Chen, Y.J.L., et al., Fermented citrus lemon reduces liver injury induced by carbon tetrachloride in rats. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2018. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L., R. Orthofer, and R.M. Lamuela-Raventós, [14] Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of folin-ciocalteu reagent, in Methods in enzymology. 1999, Elsevier. p. 152-178. [CrossRef]
- Ou, B., M. Hampsch-Woodill, and R.L. Prior, Development and validation of an improved oxygen radical absorbance capacity assay using fluorescein as the fluorescent probe. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry, 2001. 49(10): p. 4619-4626. [CrossRef]
- Reeves, P.G., Components of the AIN-93 diets as improvements in the AIN-76A diet. The Journal of nutrition, 1997. 127(5): p. 838S-841S. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J., et al., Plant proteins differently affect body fat reduction in high-fat fed rats. Preventive Nutrition and Food Science, 2012. 17(3): p. 223.
- Floch, J., A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J. biol. Chem., 1957. 226: p. 497-509.
- 潘文涵, Survey on changes in national nutrition and health status. 2022.
- Jeon, Y.B., J.J. Lee, and H.C. Chang, Characterization of juice fermented with Lactobacillus plantarum EM and its cholesterol-lowering effects on rats fed a high-fat and high-cholesterol diet. Food Science & Nutrition, 2019. 7(11): p. 3622-3634.
- Hubert, J., et al., Effects of fermentation on the phytochemical composition and antioxidant properties of soy germ. Food Chemistry, 2008. 109(4): p. 709-721. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-S., et al., Fermentation affects the antioxidant activity of plant-based food material through the release and production of bioactive components. Antioxidants, 2021. 10(12): p. 2004. [CrossRef]
- Chanbai, C., Antioxidant activities of lactic acid bacteria fermentedlemon juice, in International Master's Degree Program in Food Science 2015, National Pingtung University of Science and Technology: Pingtung County. p. 62.
- Heydemann, A., An overview of murine high fat diet as a model for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Journal of diabetes research, 2016. 2016. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q., Y. Wu, and X. Fei, Effect of probiotics on body weight and body-mass index: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z., et al., Enhanced antioxidant activity for apple juice fermented with Lactobacillus plantarum ATCC14917. Molecules, 2018. 24(1): p. 51. [CrossRef]
- Amini, M.R., et al., Orange juice intake and lipid profile: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Journal of Nutritional Science, 2023. 12: p. e37. [CrossRef]
- Li, J., et al., High fat diet induced obesity model using four strains of mice: Kunming, C57BL/6, BALB/c and ICR. Experimental animals, 2020. 69(3): p. 326-335. [CrossRef]
- Marco, M.L., et al., Health benefits of fermented foods: microbiota and beyond. Current opinion in biotechnology, 2017. 44: p. 94-102. [CrossRef]
- Lee, H., et al., Antioxidative and cholesterol-lowering effects of lemon essential oil in hypercholesterolemia-induced rabbits. Preventive nutrition and food science, 2018. 23(1): p. 8. [CrossRef]
- Han, M., et al., Cloudy apple juice fermented by Lactobacillus prevents obesity via modulating gut microbiota and protecting intestinal tract health. Nutrients, 2021. 13(3): p. 971. [CrossRef]
- Park, S., et al., Effects of cabbage-apple juice fermented by Lactobacillus plantarum EM on lipid profile improvement and obesity amelioration in rats. Nutrients, 2020. 12(4): p. 1135. [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.-K. and C. Chae, Inducible nitric oxide distribution in the fatty liver of a mouse with high fat diet-induced obesity. Experimental Animals, 2010. 59(5): p. 595-604. [CrossRef]
- Sorrenti, V., et al., Bioactive compounds from lemon (Citrus limon) extract overcome TNF-α-induced insulin resistance in cultured adipocytes. Molecules, 2021. 26(15): p. 4411. [CrossRef]
| Group | un-FLPJ | SA-FLPJ | SF-FLPJ |
| Sugar content (°Brix) | 8.6±0.01 a | 26.96±0.09 b | 6.53±0.12 c |
| Group | un-FLPJ | SA-FLPJ | SF-FLPJ |
| TPC (µg/g) | 422.62±0.01 a | 368.96±0.33 b | 1292.58±1.07 c |
| DPPH (EC50 ppm) | 22581.86±0.4 a | 27946.90±1.96 b | 19117.66±2.41 c |
| Group | Control | HF | HF dose 1 | HF dose 2 |
| Week number | Weight | |||
| W 0 | 349.0±11.9 a | 348.7±11.3 a | 348.7±13.7 a | 347.0±18.3 a |
| W 1 | 362.6±10.0 a | 372.3±11.5 a | 372.3±11.5 a | 379.1±8.1 a |
| W 2 | 394.3±13.0 a | 418.3±14.2 b | 418.3±14.2 b | 421.3±12.2 b |
| W 3 | 415.1±14.0 a | 450.3±16.2 c | 450.3±16.2 c | 452.8±15.8 c |
| W 4 | 430.9±15.4 a | 481.8±20.9 c | 481.8±20.9 c | 477.6±14.1 c |
| W 5 | 454.5±13.8 a | 510.4±22.1 c | 510.4±22.1 c | 502.8±18.6 c |
| W 6 | 475.8±14.4 a | 539.9±14.5 c | 537.8±22.2 c | 527.0±21.4 c |
| W 7 | 491.7±15.6 a | 565.8±23.0 c | 565.8±23.0 c | 544.8±25.5 c |
| W 8 | 507.3±18.3 a | 582.0±25.6 c | 582.0±25.6 c | 560.6±24.2 b |
| Weight gain (g) | ||||
| 158.3±15.1 a | 234.5±14.9 d | 233.3±20.2 d | 210.4±26.3 c | |
| Group | Control | HF | HF dose 1 | HF dose 2 |
| Body fat mass (g) | 21.116±3.125 a | 39.230±7.073 c | 37.220±7.340 c | 30.645±6.927 b |
| Body fat percentage# (%) | 4.156±0.563 a | 6.733±1.247 c | 6.408±1.315 c | 5.472±1.211 b |
| Test items | Group # | |||
| Control | HF | HF dose 1 | HF dose 2 | |
| Total triglyceride (mg/dL) | 46.7±7.0 a | 100.1±31.1 b | 61.9±18.3 a | 52.8±14.1 a |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 58.2±8.6b c | 65.7±11.8 c | 56.2±9.0 b | 55.8±10.5 b |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | 12.03±2.33 a | 12.35±2.59 a | 11.47±2.75 a | 10.48±2.03 a |
| LDL-C (mg/dL) | 6.62±1.23 a | 7.14±1.91 a | 6.01±1.51 a | 6.38±1.04 a |
| FFA (mmol/L) | 0.40±0.05 a | 0.54±0.08 a | 0.49±0.06 a | 0.52±0.11 a |
| Test items | Group | |||
| Control | HF | HF dose 1 | HF dose 2 | |
| Liver triglycerides (mg/g) | 23.77±8.04 a | 75.55±16.52 c | 69.43±15.82 b | 55.62±19.78 b |
| Liver cholesterol (mg/g) | 2.32±0.61 a | 6.11±1.90 c | 5.48±1.22 b | 4.92±1.17 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





