Submitted:
21 January 2024
Posted:
23 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
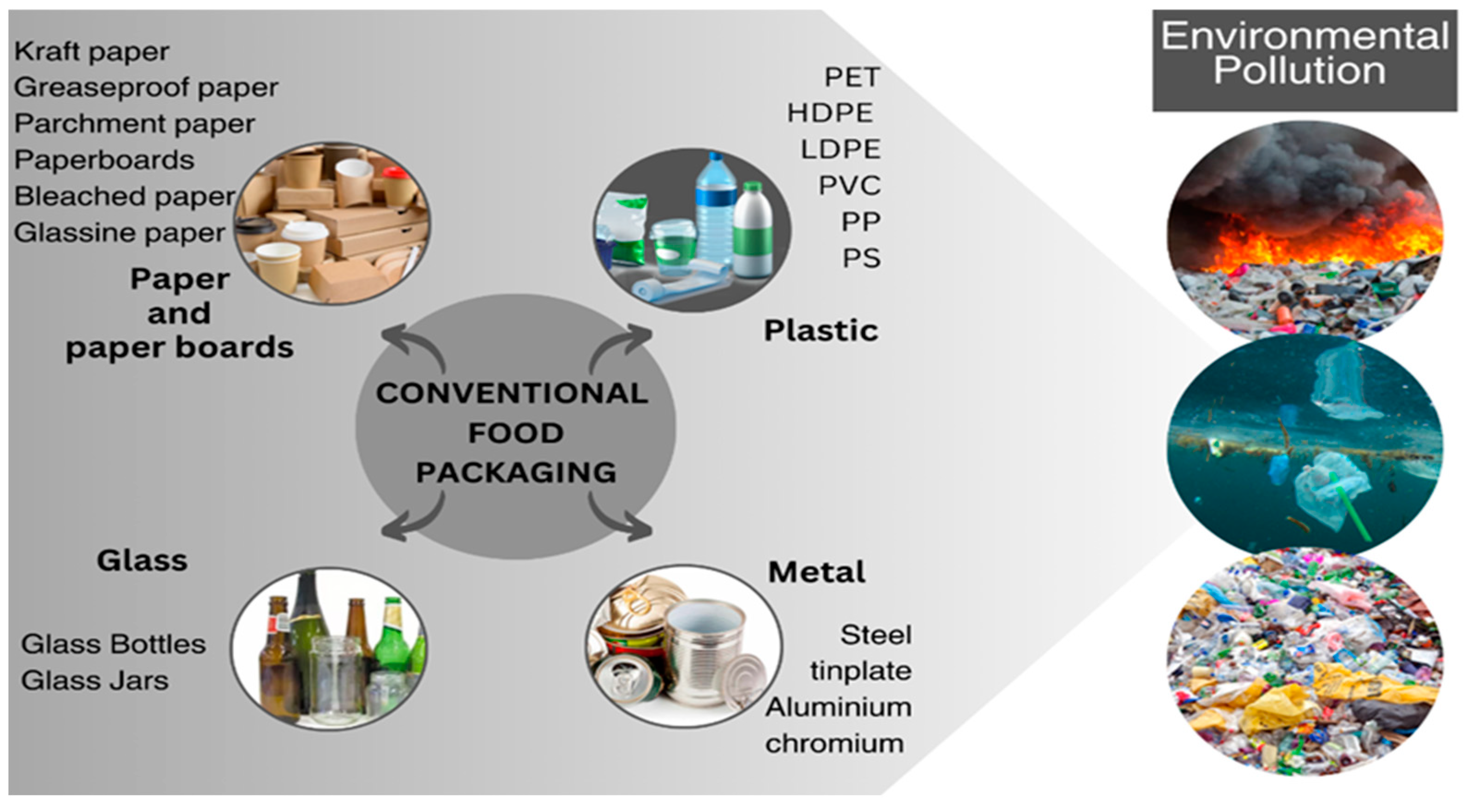
2. Conventional food packaging
2.1. Paper and paperboards
2.2. Plastics
2.3. Glass
2.4. Metal
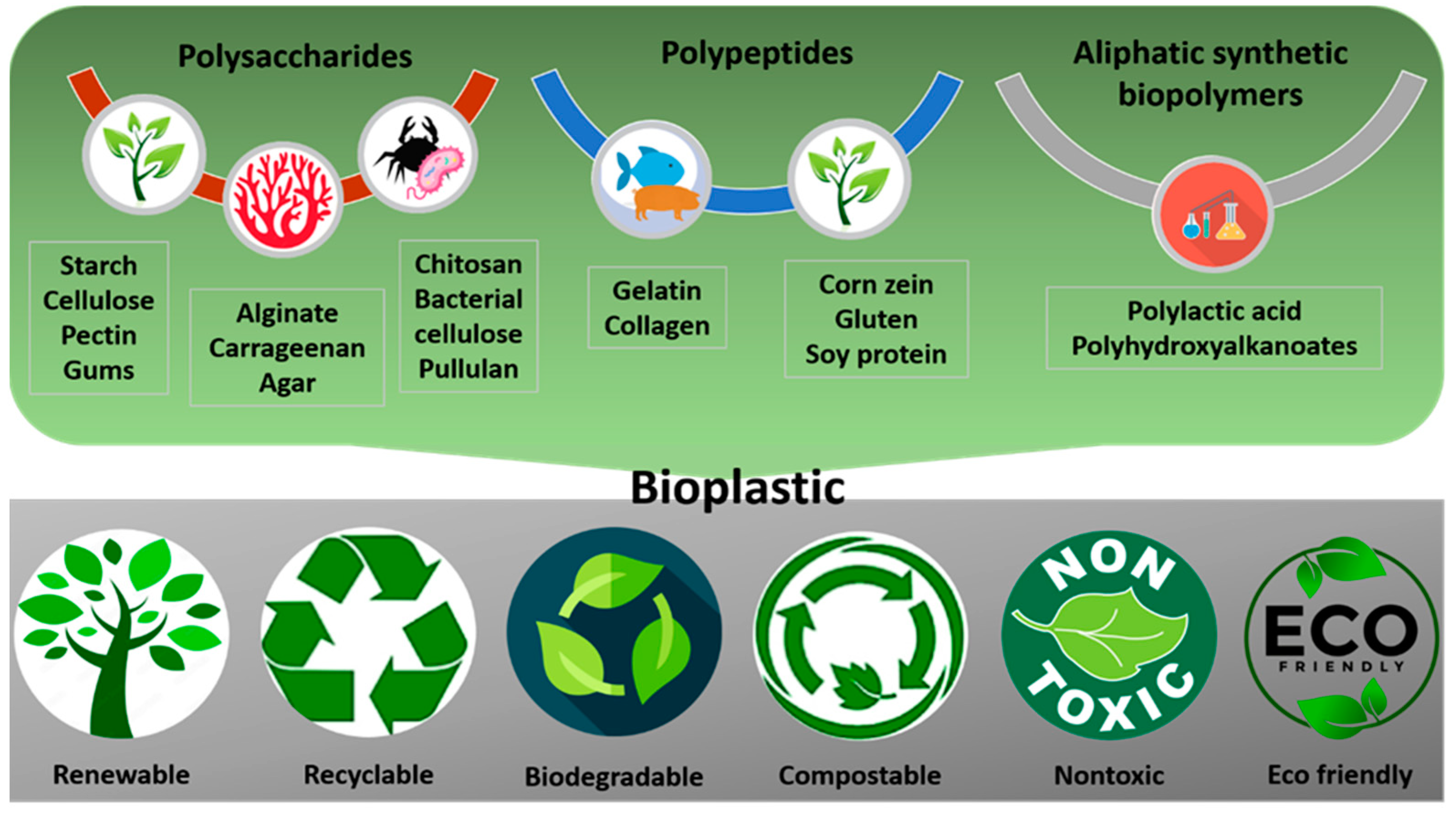
3. Biopolymers for sustainable food packaging
3.1. Polysaccharide-based biopackaging materials and applications in the food industry
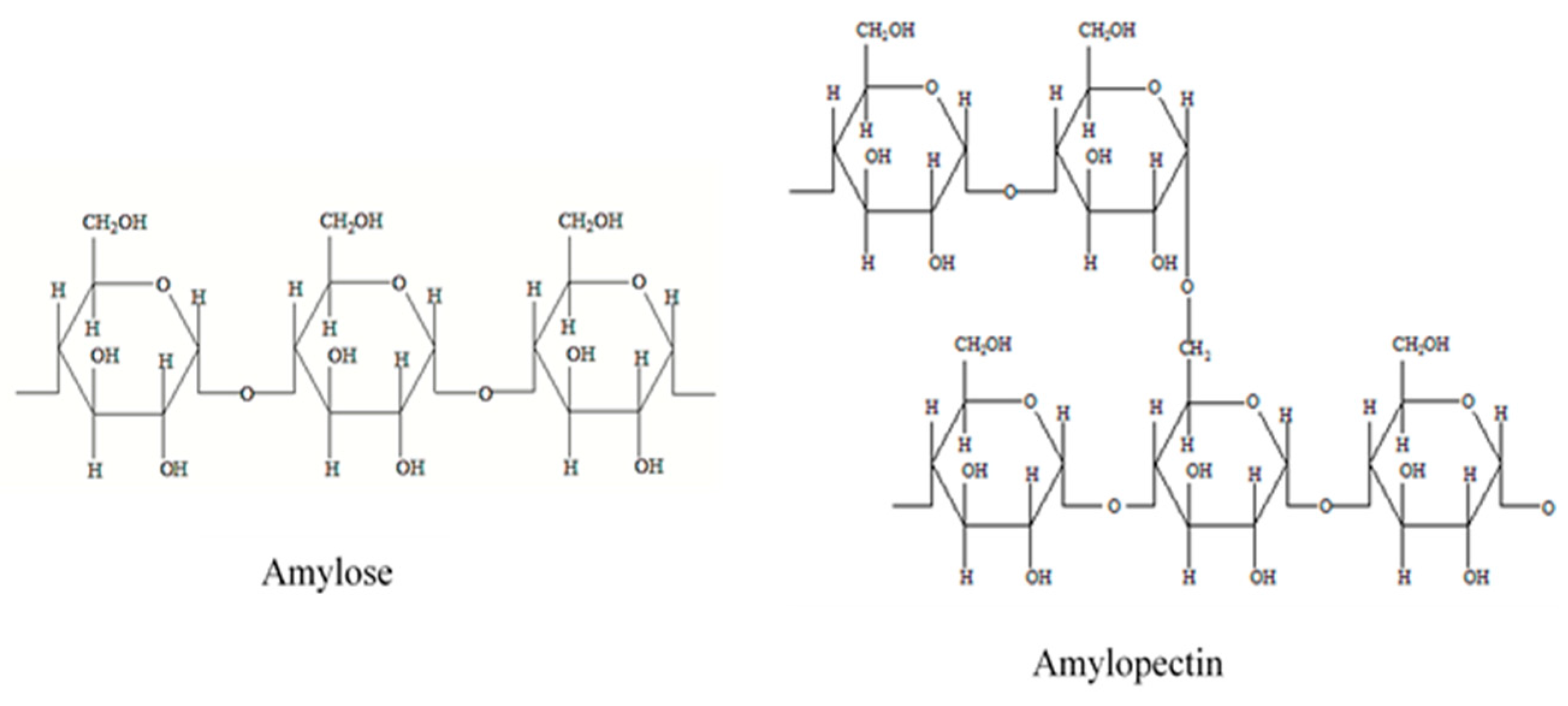
3.1.1. Starch
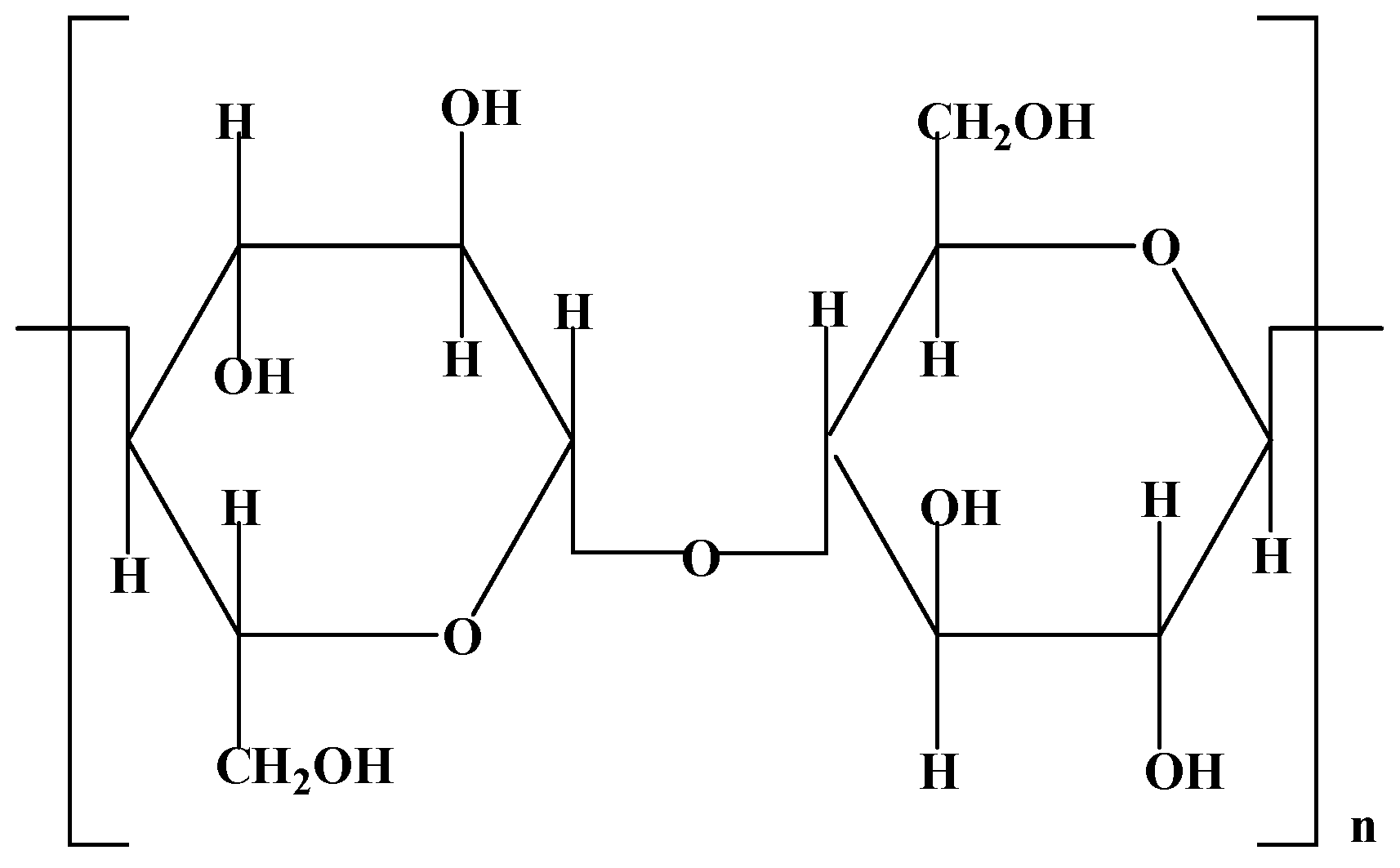
3.1.2. Cellulose
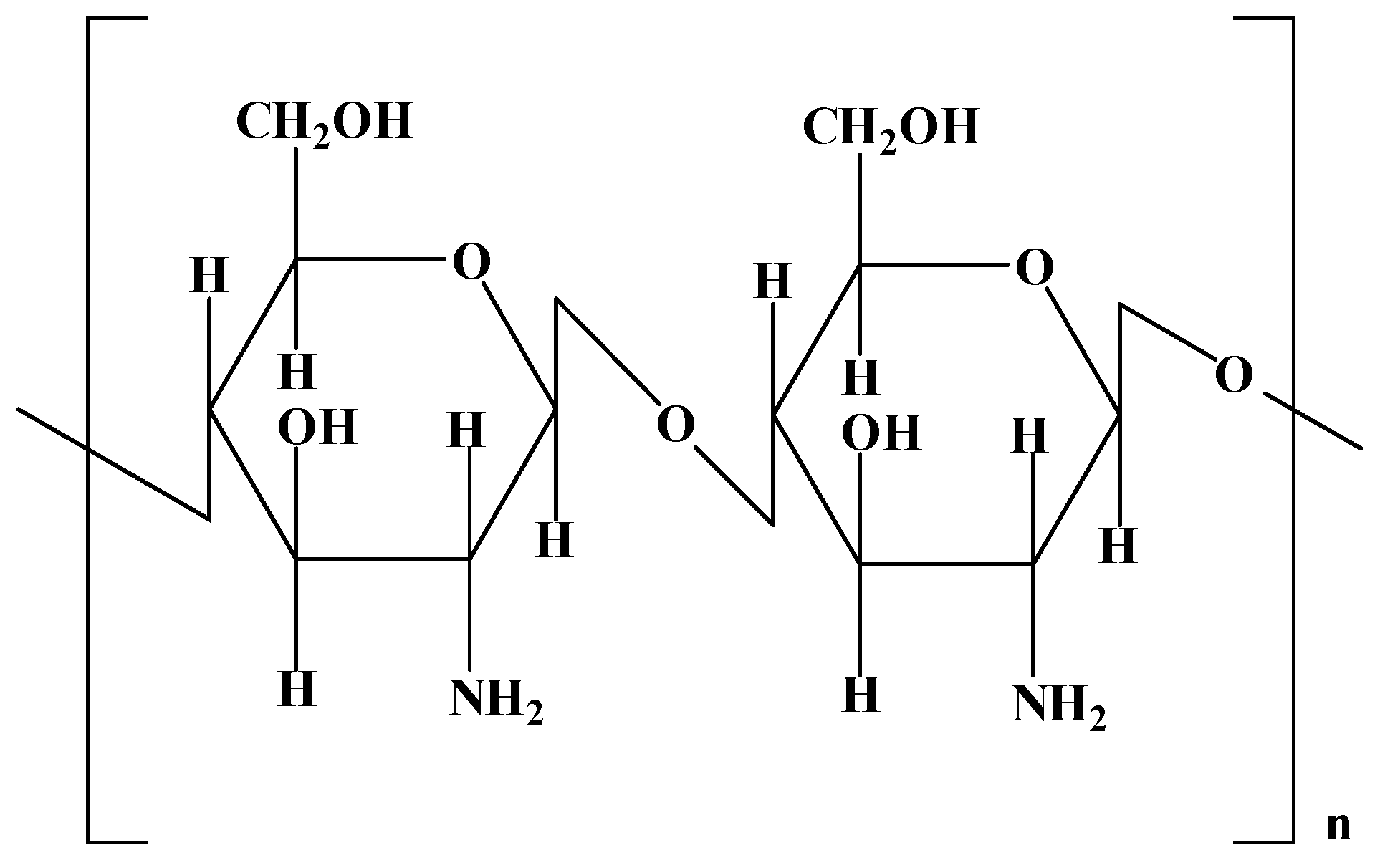
3.1.3. Chitosan
3.1.4. Pectin
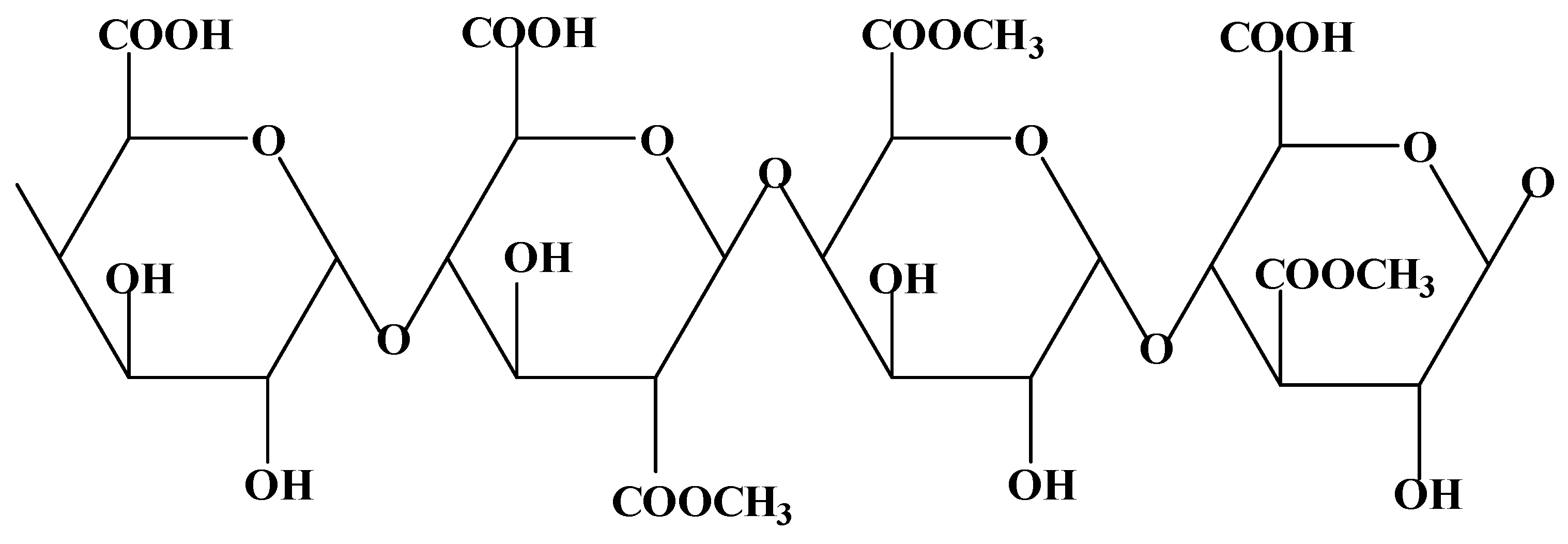
3.1.5. Alginate
3.1.6. Carrageenan
3.2. Aliphatic polymer-based food packaging
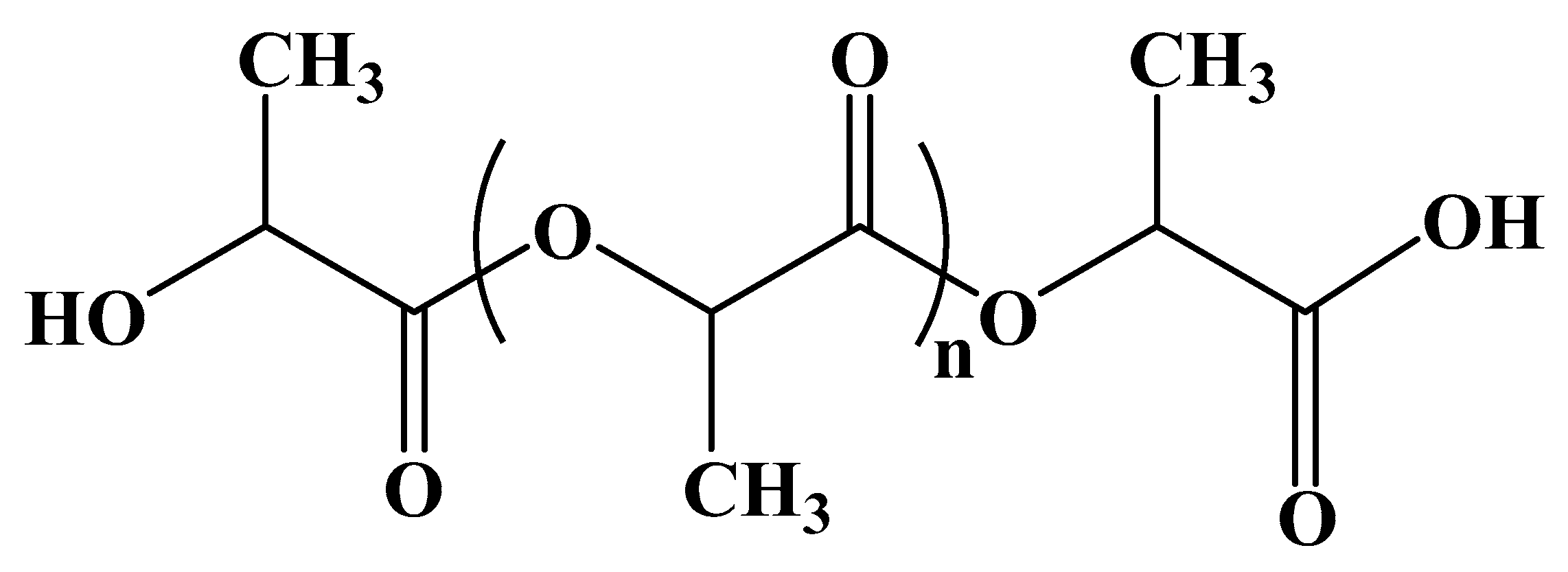
3.2.1. Polylactic acid (PLA)
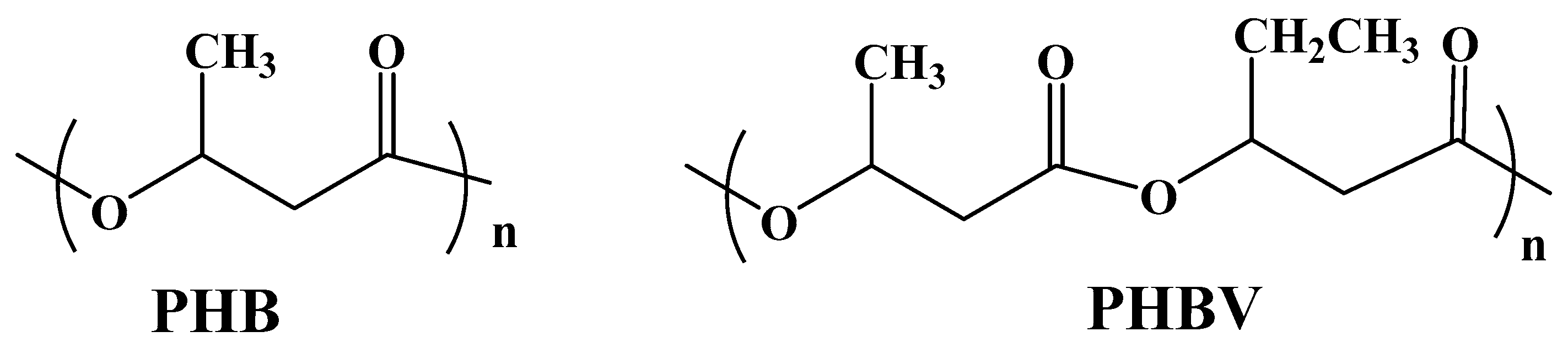
3.2.2. Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB)
4. Future perspectives of biopacking in the food industry
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Estimating the burden of foodborne diseases. https://www.who.int/activities/estimating-the-burden-of-foodborne-diseases (archived on 22 August 2023).
- Han, J.; Ruiz-Garcia, L.; Qian, J.-P.; Yang, X.T. Food Packaging: A Comprehensive Review and Future Trends. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 1–18. [CrossRef]
- Goswami, B. The Role of Food Packaging. In Global Challenges and Innovation In Science and Management, 1st ed.; Rami, A., Jha, P., Shah, P., Eds.; Kaav publications: Delhi, India, 2019; pp. 157–167.
- Ncube, L. K.; Ude, A. U.; Ogunmuyiwa, E. N.; Zulkifli, R.; Beas, I. N. Environmental Impact of Food Packaging Materials: A Review of Contemporary Development from Conventional Plastics to Polylactic Acid Based Materials. Materials (Basel). 2020, 13, 1–24. [CrossRef]
- Nemat, B.; Razzaghi, M.; Bolton, K.; Rousta, K. The Potential of Food Packaging Attributes to Influence Consumers’ Decisions to Sort Waste. Sustain. 2020, 12, 2234. [CrossRef]
- Asgher, M.; Qamar, S. A.; Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H. M. N. Bio-Based Active Food Packaging Materials: Sustainable Alternative to Conventional Petrochemical-Based Packaging Materials. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109625. [CrossRef]
- Nesic, A.; Cabrera-Barjas, G.; Dimitrijevic-Brankovic, S.; Davidovic, S.; Radovanovic, N.; Delattre, C. Prospect of Polysaccharide-Based Materials as Advanced Food Packaging. Molecules. 2020, 25, 1–35. [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, S.; Yaqoob, M.; Aggarwal, P. An Overview of Biodegradable Packaging in Food Industry. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2021, 4, 503–520. [CrossRef]
- Thulasisingh, A.; Kumar, K.; Yamunadevi, B.; Poojitha, N.; SuhailMadharHanif, S.; Kannaiyan, S. Biodegradable Packaging Materials. Polym. Bull. 2021, 79, 4467–4496. [CrossRef]
- Cruz, R. M. S.; Krauter, V.; Krauter, S.; Agriopoulou, S.; Weinrich, R.; Herbes, C.; Scholten, P. B. V; Uysal-Unalan, I.; Sogut, E.; Kopacic, S.; Lahti, J.; Rutkaite, R.; Varzakas, T. Bioplastics for Food Packaging: Environmental Impact, Trends and Regulatory Aspects. Food 2022, 11, 1–39. [CrossRef]
- Deshwal, G. K.; Panjagari, N. R.; Alam, T. An Overview of Paper and Paper Based Food Packaging Materials: Health Safety and Environmental Concerns. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 4391–4403. [CrossRef]
- Marsh, K.; Bugusu, B. Food Packaging - Roles, Materials, and Environmental Issues. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, 39–55. [CrossRef]
- Fahmy, Y.; Fahmy, T. y A.; Mobarak, F.; El-Sakhawy, M.; Fadl, M. Agricultural Residues (Wastes) for Manufacture of Paper, Board, and Miscellaneous Products: Background Overview and Future Prospects. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 2017, 10, 424–448.
- Ferdous, T.; Ni, Y.; Quaiyyum, M. A.; Uddin, M. N.; Jahan, M. S. Non-Wood Fibers: Relationships of Fiber Properties with Pulp Properties. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 21613–21622. [CrossRef]
- Pydimalla, M.; Reddy, K. Effect of Pulping, Bleaching and Refining Process on Fibers for Paper Making - A Review. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 310–316.
- Hubbe, M. A.; Pruszynski, P. Greaseproof Paper Products: A Review Emphasizing Ecofriendly Approaches. BioResources 2020, 15, 1978–2004. [CrossRef]
- Jasmani, L.; Ainun, Z. M. A.; Adnan, S.; Ibrahim, R.; Sapuan, S. M.; Ilyas, R. A. Sustainable Paper-Based Packaging. In Bio-BasedPackaging: Material, Environmental and Economic Aspects, 1st ed.; Sapuan, S.M., Ilyas, R.A., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd, 2021; 225–244. [CrossRef]
- Verma, M. K.; Shakya, S.; Kumar, P.; Madhavi, J.; Murugaiyan, J.; Rao, M. V. R. Trends in Packaging Material for Food Products: Historical Background, Current Scenario, and Future Prospects. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 4069–4082. [CrossRef]
- Fadiji, T.; Coetzee, C.; Pathare, P.; Opara, U. L. Susceptibility to Impact Damage of Apples inside Ventilated Corrugated Paperboard Packages: Effects of Package Design. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2016, 111, 286–296. [CrossRef]
- Oloyede, O. O.; Lignou, S. Sustainable Paper-Based Packaging: A Consumer’s Perspective. foods 2021, 10, 1–18.
- Jadhav, S. V; Sonone, S. S.; Sankhla, M. S.; Kumar, R. Health Risks of Newspaper Ink When Used as Food Packaging Material. Lett. Appl. NanoBioScience 2021, 10, 2614–2623. [CrossRef]
- Tajeddin, B.; Arabkhedri, M. Polymers and Food Packaging. In Polymer Science and Innovative Applications; 2020; 525–543. [CrossRef]
- Silva, N.; Blumberga, D. Why Biopolymer Packaging Materials Are Better. Environ. Clim. Technol. 2019, 23, 366–384. [CrossRef]
- Sid, S.; Mor, R. S.; Kishore, A.; Sharanagat, V. S. Bio-Sourced Polymers as Alternatives to Conventional Food Packaging Materials: A Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 115, 87–104. [CrossRef]
- Alabi, O. A.; Ologbonjaye, K. I.; Awosolu, O.; Alalade, O. E. Public and Environmental Health Effects of Plastic Wastes Disposal: A Review. J. Toxicol. risk Assess. 2019, 5, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Worm, B.; Lotze, H. K.; Jubinville, I.; Wilcox, C.; Jambeck, J. Plastic as a Persistent Marine Pollutant. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2017, 42, 1–26. [CrossRef]
- Nistico, R. Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) in the Packaging Industry. Polym. Test. 2020, 90, 106707. [CrossRef]
- Mendes, A. C.; Pedersen, G. A. Perspectives on Sustainable Food Packaging: – Is Bio-Based Plastics a Solution? Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 112, 839–846. [CrossRef]
- Cruz, R. M. S.; Rico, B. P. M.; Vieira, M. C. Food Packaging and Migration. In Food Quality and Shelf Life; Elsevier Inc., 2019; pp 281–301. [CrossRef]
- Lewandowski, K. A Brief Review of Poly (Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Recycling. Polymers (Basel). 2022, 14, 1–14.
- Katsara, K.; Kenanakis, G.; Alissandrakis, E.; Papadakis, V. M. Low-Density Polyethylene Migration from Food Packaging on Cured Meat Products Detected by Micro-Raman Spectroscopy. Microplastics 2022, 1, 428–439. [CrossRef]
- Sadighara, P.; Akbari, N.; Mostashari, P.; Yazdanfar, N.; Shokri, S. The Amount and Detection Method of Styrene in Foods: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Food Chem. X. 2022, 13, 100238. [CrossRef]
- Tajeddin, B.; Ahmadi, B.; Sohrab, F.; Chenarbon, H. A. Polymers for Modified Atmosphere Packaging Applications. In Food Packaging and Preservation; Elsevier Inc., 2018; pp 457–499. [CrossRef]
- Geyer, R.; Jambeck, J. R.; Law, K. L. Production, Use, and Fate of All Plastics Ever Made. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700782.
- Kehinde, O.; Ramonu, O. J.; Babaremu, K. O.; Justin, L. D. Plastic Wastes: Environmental Hazard and Instrument for Wealth Creation in Nigeria. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05131. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Verma, A.; Shome, A.; Sinha, R.; Sinha, S.; Jha, P. K.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, P.; Shubham; Das, S.; Sharma, P.; Prasad, P. V. V. Impacts of Plastic Pollution on Ecosystem Services, Sustainable Development Goals, and Need to Focus on Circular Economy and Policy Interventions. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1–40. [CrossRef]
- Proshad, R.; Kormoker, T.; Islam, M. S.; Haque, M. A.; Rahman, M. M.; Mithu, M. M. R. Toxic Effects of Plastic on Human Health and Environment: A Consequences of Health Risk Assessment in Bangladesh. Int. J. Heal. 2017, 6, 1. [CrossRef]
- Krammer, J. Exploring the Last Phases of Product Development;From Kitchen to Plant Production, LUND UNIVERSITY, 2017.
- Yaris, A.; Sezgin, A. C. Food Packaging : Glass and Plastic. In Researches On Science and Art in 21st Century Turkey; 2017; Vol. 8, pp 735–740.
- Testa, M.; Malandrino, O.; Sessa, M. R.; Supino, S.; Sica, D. Long-Term Sustainability from the Perspective of Cullet Recycling in the Container Glass Industry: Evidence from Italy. Sustain. 2017, 9. [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Selke, S. E. Food Packaging. In Food Processing: Principles and Applications, Second Edition; 2014; pp 249–273.
- Dunn, T. J. Food Packaging. Kirk-Othmer Encycl. Chem. Technol. 2017, 1–24. [CrossRef]
- Deshwal, G. K.; Panjagari, N. R. Review on Metal Packaging: Materials, Forms, Food Applications, Safety and Recyclability. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 2377–2392. [CrossRef]
- Debeaufort, F. Metal Packaging. In Packaging Materials and Processing for Food, Pharmaceuticals and Cosmetics; 2021; Vol. 13, pp 75–104. [CrossRef]
- Sand, C. K. The Role of Metal in Food Packaging. Food Technol. 2021, July, 1–7.
- Pandey, S.; Mishra, K. K.; Ghosh, P.; Singh, A. K.; Jha, S. K. Characterization of Tin-Plated Steel. Front. Mater. 2023, January. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Chen, L.; McClements, D. J.; Yang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, F.; Miao, M.; Tian, Y.; Jin, Z. Starch-Based Biodegradable Packaging Materials: A Review of Their Preparation, Characterization and Diverse Applications in the Food Industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 114 (July 2020), 70–82. [CrossRef]
- Orzan, G.; Cruceru, A. F.; Teodora, C.; Chivu, R. Consumers’ Behavior Concerning Sustainable Packaging: An Exploratory Study on Romanian Consumers. sustainability 2018. [CrossRef]
- Udayakumar, G. P.; Muthusamy, S.; Selvaganesh, B.; Sivarajasekar, N.; Rambabu, K.; Banat, F.; Sivamani, S.; Sivakumar, N.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Show, P. L. Biopolymers and Composites: Properties, Characterization and Their Applications in Food, Medical and Pharmaceutical Industries. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105322. [CrossRef]
- Baranwal, J.; Barse, B.; Fais, A.; Delogu, L. G.; Kumar, A. Biopolymer: A Sustainable Material for Food and Medical Applications. Polymers (Basel). 2022, 14, 1–22.
- Adeyeye, O. A.; Sadiku, E. R.; Babu Reddy, A.; Ndamase, A. S.; Makgatho, G.; Sellamuthu, P. S.; Perumal, A. B.; Nambiar, R. B.; Fasiku, V. O.; Ibrahim, I. D.; Agboola, O.; Kupolati, W. K.; Daramola, O. O.; Machane, M. J.; Jamiru, T. The Use of Biopolymers in Food Packaging. In Green Biopolymers and their Nanocomposites; Springer Singapore, 2019; pp 137–158. [CrossRef]
- Teixeira-Costa, B.; Andrade, C. Natural Polymers Used in Edible Food Packaging—History, Function and Application Trends as a Sustainable Alternative to Synthetic Plastic. Polysaccharides 2021, 3, 32–58. [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, D.; Nayak, S. K.; Anis, A.; Ray, S. S.; Kim, D.; Hanh Nguyen, T. T.; Pal, K. Introduction of Biopolymers: Food and Biomedical Applications. In Biopolymer-Based Formulations: Biomedical and Food Applications; Elsevier Inc., 2020; pp 1–45. [CrossRef]
- Dassanayake, R. S.; Acharya, S.; Abidi, N. Biopolymer-Based Materials from Polysaccharides: Properties, Processing, Characterization and Sorption Applications. In Advanced Sorption Process Applications; 2019; pp 1–24. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, B.; Li, C.; Xu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Liang, D.; Huang, C. Comprehensive Review of Polysaccharide-Based Materials in Edible Packaging: A Sustainable Approach; 2021; Vol. 10. [CrossRef]
- Kong, I.; Degraeve, P.; Pui, L. P. Polysaccharide-Based Edible Films Incorporated with Essential Oil Nanoemulsions: Physico-Chemical, Mechanical Properties and Its Application in Food Preservation—A Review. Foods 2022, 11. [CrossRef]
- Katiyar, V.; Gupta, R.; Ghosh, T. Advances in Sustainable Polymers; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Pal, K.; Sarkar, P.; Anis, A.; Wiszumirska, K.; Jarzębski, M. Polysaccharide-based Nanocomposites for Food Packaging Applications. Materials (Basel). 2021, 14, 1–38. [CrossRef]
- Tadini, C. C. Bio-Based Materials from Traditional and Nonconventional Native and Modified Starches; Elsevier Inc., 2017. [CrossRef]
- Cazon, P.; Velazquez, G.; Ramirez, J. A.; Vázquez, M. Polysaccharide-Based Films and Coatings for Food Packaging: A Review. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 68, 136–148. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hu, P.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Q.; Wei, C. Progress in High-Amylose Cereal Crops through Inactivation of Starch Branching Enzymes. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Jayarathna, S.; Andersson, M.; Andersson, R. Recent Advances in Starch-Based Blends and Composites for Bioplastics Applications. Polymers (Basel). 2022, 14. [CrossRef]
- Gunawardene, O. H. P.; Gunathilake, C.; Amaraweera, S. M.; Fernando, N. M. L.; Wanninayaka, D. B.; Manamperi, A.; Kulatunga, A. K.; Rajapaksha, S. M.; Dassanayake, R. S.; Fernando, C. A. N.; Manipura, A. Compatibilization of Starch/Synthetic Biodegradable Polymer Blends for Packaging Applications: A Review. J. Compos. Sci. 2021, 5, 1–33. [CrossRef]
- Diyana, Z. N.; Jumaidin, R.; Selamat, M. Z.; Ghazali, I.; Julmohammad, N.; Huda, N.; Ilyas, R. A. Physical Properties of Thermoplastic Starch Derived from Natural Resources and Its Blends: A Review. Polymers (Basel). 2021, 13, 5–20. [CrossRef]
- Lauer, M. K.; Smith, R. C. Recent Advances in Starch-Based Films toward Food Packaging Applications: Physicochemical, Mechanical, and Functional Properties. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 3031–3083. [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, L. do V.; Arias, C. I. L. F.; Maniglia, B. C.; Tadini, C. C. Starch-Based Biodegradable Plastics: Methods of Production, Challenges and Future Perspectives. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 38, 122–130. [CrossRef]
- Onyeaka, H.; Obileke, K.; Makaka, G.; Nwokolo, N. Current Research and Applications of Starch-Based Biodegradable Films for Food Packaging. Polymers (Basel). 2022, 14, 83–102. [CrossRef]
- Issa, A.; Ibrahim, S. A.; Tahergorabi, R. Impact of Sweet Potato Starch-Based Nanocomposite Films Activated with Thyme Essential Oil on the Shelf-Life of Baby Spinach Leaves. Foods 2017, 6 (6), 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Baek, S. K.; Kim, S.; Song, K. Bin. Cowpea Starch Films Containing Maqui Berry Extract and Their Application in Salmon Packaging. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2019, 22, 100394. [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Gao, H. X.; He, Q.; Zeng, W. C. Potato Starch-Based Film Incorporated with Tea Polyphenols and Its Application in Fruit Packaging. Polymers (Basel). 2023, 15, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A. V.; Alvarez-Perez, O. B.; Rojas, R.; Aguilar, C. N.; Garrigós, M. C. Impact of Olive Extract Addition on Corn Starch-Based Active Edible Films Properties for Food Packaging Applications. Foods 2020, 9, 1–20. [CrossRef]
- Behera, L.; Mohanta, M.; Thirugnanam, A. Environmental Technology & Innovation Intensification of Yam-Starch Based Biodegradable Bioplastic Film with Bentonite for Food Packaging Application. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 25, 102180. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Hou, X.; Cui, Q.; Wu, H.; Shen, G.; Luo, Q.; Li, S.; Liu, X.; Li, M.; Zhou, M.; Zhu, X.; Chen, A.; Zhang, Z. Starch-Based Film Functionalized with Zanthoxylum Armatum Essential Oil Improved the Shelf Life of Beef Sauce. Lwt 2023, 183, 114930. [CrossRef]
- Bangar, S. P.; Whiteside, W. S.; Ozogul, F.; Dunno, K. D.; Cavender, G. A.; Dawson, P. Development of Starch-Based Films Reinforced with Cellulosic Nanocrystals and Essential Oil to Extend the Shelf Life of Red Grapes. Food Biosci. 2022, 47. [CrossRef]
- Marichelvam, M. K.; Manimaran, P.; Sanjay, M. R.; Siengchin, S.; Geetha, M.; Kandakodeeswaran, K.; Boonyasopon, P.; Gorbatyuk, S. Extraction and Development of Starch-Based Bioplastics from Prosopis Juliflora Plant: Eco-Friendly and Sustainability Aspects. Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 2022, 5, 100296. [CrossRef]
- Tafa, K. D.; Satheesh, N.; Abera, W. Mechanical Properties of Tef Starch Based Edible Films: Development and Process Optimization. Heliyon 2023, 9. [CrossRef]
- Ardjoum, N.; Chibani, N.; Shankar, S.; Salmieri, S.; Djidjelli, H.; Lacroix, M. Incorporation of Thymus Vulgaris Essential Oil and Ethanolic Extract of Propolis Improved the Antibacterial, Barrier and Mechanical Properties of Corn Starch-Based Films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 224, 578–583. [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Singh, P. K.; Pattnaik, R.; Kumar, S.; Ojha, S. K.; Srichandan, H.; Parhi, P. K.; Jyothi, R. K.; Sarangi, P. K. Biochemistry, Synthesis, and Applications of Bacterial Cellulose: A Review. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Janjarasskul, T.; Krochta, J. M. Edible Packaging Materials. Annu. Rev. ofFood Sci. Technol. 2016, 1, 415–448. [CrossRef]
- Torres-Giner, S.; Figueroa-Lopez, K. J.; Melendez-Rodriguez, B.; Prieto, C.; Pardo-Figuerez, M.; Lagaron, J. M. Emerging Trends in Biopolymers for Food Packaging. In Sustainable Food Packaging Technology; Athanassiou, A., Ed.; 2021; pp 1–33. [CrossRef]
- Yemenicioglu, A.; Farris, S.; Turkyilmaz, M.; Gulec, S. A Review of Current and Future Food Applications of Natural Hydrocolloids. Iternational J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 1, 1–18. [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C. Industrial-Scale Production and Applications of Bacterial Cellulose. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 1–19. [CrossRef]
- Atta, O. M.; Manan, S.; Ul-Islam, M.; Ahmed, A. A. Q.; Ullah, M. W.; Yang, G. Development and Characterization of Plant Oil-Incorporated Carboxymethyl Cellulose/Bacterial Cellulose/Glycerol-Based Antimicrobial Edible Films for Food Packaging Applications. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2022, 5, 973–990. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Guo, H.; Luo, W.; Chen, G.; Xiao, N.; Xiao, G.; Liu, C. Development of Functional Hydroxyethyl Cellulose-Based Composite Films for Food Packaging Applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1–15. [CrossRef]
- Yaradoddi, J. S.; Banapurmath, N. R.; Ganachari, S. V.; Soudagar, M. E. M.; Mubarak, N. M.; Hallad, S.; Hugar, S.; Fayaz, H. Biodegradable Carboxymethyl Cellulose Based Material for Sustainable Packaging Application. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Romao, S.; Bettencourt, A.; Ribeiro, I. A. C. Novel Features of Cellulose-Based Films as Sustainable Alternatives for Food Packaging. Polymers (Basel). 2022, 14, 1–27.
- Moradian, S.; Almasi, H.; Moini, S. Development of Bacterial Cellulose-Based Active Membranes Containing Herbal Extracts for Shelf-Life Extension of Button Mushrooms (Agaricus Bisporus). J. Food Process. Preserv. 2018, 42. [CrossRef]
- Al-Moghazy, M.; Mahmoud, M.; Nada, A. A. Fabrication of Cellulose-Based Adhesive Composite as an Active Packaging Material to Extend the Shelf Life of Cheese. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 160, 264–275. [CrossRef]
- Yordshahi, A. S.; Moradi, M.; Tajik, H.; Molaei, R. Design and Preparation of Antimicrobial Meat Wrapping Nanopaper with Bacterial Cellulose and Postbiotics of Lactic Acid Bacteria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 321, 108561. [CrossRef]
- Aydogdu, A.; Sumnu, G.; Sahin, S. Fabrication of Gallic Acid Loaded Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose Nanofibers by Electrospinning Technique as Active Packaging Material. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 208, 241–250. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ahmed, S.; Sameen, D. E.; Wang, Y.; Lu, R.; Dai, J.; Li, S.; Qin, W. A Review of Cellulose and Its Derivatives in Biopolymer-Based for Food Packaging Application. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 112, 532–546. [CrossRef]
- Florez, M.; Guerra-Rodríguez, E.; Cazon, P.; Vazquez, M. Chitosan for Food Packaging: Recent Advances in Active and Intelligent Films. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 124. [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshi, R.; Rhim, J. W. Chitosan-Based Biodegradable Functional Films for Food Packaging Applications. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 62, 102346. [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarek, M. B.; Struszczyk-Swita, K.; Li, X.; Szczęsna-Antczak, M.; Daroch, M. Enzymatic Modifications of Chitin, Chitosan, and Chitooligosaccharides. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7. [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Meng, X.; Meng, J.; Khan, M. I. H.; Dai, L.; Khan, A.; An, X.; Zhang, J.; Huq, T.; Ni, Y. Chitosan as A Preservative for Fruits and Vegetables: A Review on Chemistry and Antimicrobial Properties. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2019, 4, 11–21. [CrossRef]
- Luangapai, F.; Peanparkdee, M.; Iwamoto, S. Biopolymer Films for Food Industries: Properties, Applications, and Future Aspects Based on Chitosan. Rev. Agric. Sci. 2019, 7, 59–67. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Mukherjee, A.; Dutta, J. Chitosan Based Nanocomposite Films and Coatings: Emerging Antimicrobial Food Packaging Alternatives. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 97, 196–209. [CrossRef]
- Malm, M.; Liceaga, A. M.; Martin-gonzalez, F. S.; Jones, O. G.; Garcia-bravo, J. M.; Kaplan, I. Development of Chitosan Films from Edible Crickets and Their Performance as a Bio-Based Food Packaging Material. polysaccharides 2021, 744–758.
- Zehra, A.; Wani, S. M.; Jan, N.; Bhat, T. A.; Rather, S. A.; Malik, A. R.; Hussain, S. Z. Development of Chitosan - Based Biodegradable Films Enriched with Thyme Essential Oil and Additives for Potential Applications in Packaging of Fresh Collard Greens. Sci. Rep. 2022, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-cruz, S.; Enrique, M.; Jes, D.; Del-toro-s, C. L.; Gassos-ortega, L. E. Effect of Chitosan–Tomato Plant Extract Edible Coating on the Quality, Shelf Life, and Antioxidant Capacity of Pork during Refrigerated Storage. Coatings 2019, 9, 1–16.
- Wang, K.; Lim, P. N.; Tong, S. Y.; Thian, E. S. Development of Grapefruit Seed Extract-Loaded Poly ( ε -Caprolactone )/ Chitosan Films for Antimicrobial Food Packaging. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2019, 22, 100396. [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, X.; Jiang, Q.; Yu, D.; Xu, Y.; Wang, B.; Xia, W. Development and Properties of Bacterial Cellulose, Curcumin, and Chitosan Composite Biodegradable Films for Active Packaging Materials. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 260, 117778. [CrossRef]
- Al-Hilifi, S. A.; Al-Ibresam, O. T.; Al-Hatim, R. R.; Al-Ali, R. M.; Maslekar, N.; Yao, Y.; Agarwal, V. Development of Chitosan/Whey Protein Hydrolysate Composite Films for Food Packaging Application. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7. [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Mao, L.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y. Development of Chitosan/Poly (Vinyl Alcohol) Active Films Reinforced with Curcumin Functionalized Layered Clay towards Food Packaging. Prog. Org. Coatings 2023, 182, 9–10. [CrossRef]
- De Carli, C.; Aylanc, V.; Mouffok, K. M.; Santamaria-Echart, A.; Barreiro, F.; Tomás, A.; Pereira, C.; Rodrigues, P.; Vilas-Boas, M.; Falcão, S. I. Production of Chitosan-Based Biodegradable Active Films Using Bio-Waste Enriched with Polyphenol Propolis Extract Envisaging Food Packaging Applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 213, 486–497. [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, C.; de Mello, J. M. M.; Dalcanton, F.; Macuvele, D. L. P.; Padoin, N.; Fiori, M. A.; Soares, C.; Riella, H. G. Mechanical, Thermal and Antimicrobial Properties of Chitosan-Based-Nanocomposite with Potential Applications for Food Packaging. J. Polym. Environ. 2020, 28, 1216–1236. [CrossRef]
- Karkar, B.; Patır, İ.; Eyüboğlu, S.; Şahin, S. Development of an Edible Active Chitosan Film Loaded with Nigella Sativa L. Extract to Extend the Shelf Life of Grapes. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2023, 50. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Yadav, S.; Pramanik, J.; Sivamaruthi, B. S.; Jayeoye, T. J.; Prajapati, B. G.; Chaiyasut, C. Chitosan-Based Composites: Development and Perspective in Food Preservation and Biomedical Applications. Polymers (Basel). 2023, 15. [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C. T. Pectic Polysaccharides in Plants: Structure, Biosynthesis, Functions, and Applications. In Extracellular Sugar-Based Biopolymers Matrices; Springer Nature, 2019; pp 487–514. [CrossRef]
- Aguirre-Joya, J. A.; De Leon-Zapata, M. A.; Alvarez-Perez, O. B.; Torres-León, C.; Nieto-Oropeza, D. E.; Ventura-Sobrevilla, J. M.; Aguilar, M. A.; Ruelas-Chacón, X.; Rojas, R.; Ramos-Aguiñaga, M. E.; Aguilar, C. N. Basic and Applied Concepts of Edible Packaging for Foods; Elsevier Inc., 2018. [CrossRef]
- Vanitha, T.; Khan, M. Role of Pectin in Food Processing and Food Packaging. In Pectins - Extraction, Purification, Characterization and Applications; Masuelli, M., Ed.; 2020; pp 1-. [CrossRef]
- Lara-Espinoza, C.; Carvajal-Millan, E.; Balandran-Quintana, R.; Lopez-Franco, Y.; Rascon-Chu, A. Pectin and Pectin-Based Composite Materials: Beyond Food Texture. Molecules 2018, 23, 1–35. [CrossRef]
- Raghav, P. K.; Agarwal, N.; Saini, M. Edible Coating of Fruits and Vegetables: A Review. Int. J. Sci. Res. Mod. Educ. 2016, 1, 188–204.
- Gouveia, T. I. A.; Biernacki, K.; Castro, M. C. R.; Gonçalves, M. P.; Souza, H. K. S. A New Approach to Develop Biodegradable Films Based on Thermoplastic Pectin. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 97, 105175. [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A. C. S. de; Ferreira, L. F.; Begali, D. de O.; Ugucioni, J. C.; Neto, A. R. de S.; Yoshida, M. I.; Borges, S. V. Thermoplasticized Pectin by Extrusion/Thermo-Compression for Film Industrial Application. J. Polym. Environ. 2021, 29, 2546–2556. [CrossRef]
- Mellinas, C.; Ramos, M.; Jiménez, A.; Garrigós, M. C. Recent Trends in the Use of Pectin from Agro-Waste Residues as a Natural-Based Biopolymer for Food Packaging Applications. Materials (Basel). 2020, 13. [CrossRef]
- Valdes, A.; Burgos, N.; Jimenez, A.; Garrigos, M. C. Natural Pectin Polysaccharides as Edible Coatings. Coatings 2015, 5, 865–886. [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, R. A.; Veras, J. M. L.; Sousa, T. L. de; Farias, P. M. de; Filho, J. G. de O.; Bertolo, M. R. V.; Egea, M. B.; Placido, G. R. Pequi Mesocarp: A New Source of Pectin to Produce Biodegradable Film for Application as Food PackagingAnunciação Veras, July Maendra Lopes de SOUSA, Tainara Leal de FARIAS, Patrícia Marques de OLIVEIRA FILHO, Josemar Gonçalves Bertolo, Mirella Romanelli V. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 42. [CrossRef]
- Pereira, D. G. M.; Vieira, J. M.; Vicente, A. A.; Cruz, R. M. S. Development and Characterization of Pectin Films with Salicornia Ramosissima: Biodegradation in Soil and Seawater. Polymers (Basel). 2021, 13. [CrossRef]
- Sadadekar, A. S.; Shruthy, R.; Preetha, R.; Kumar, N.; Pande, K. R.; Nagamaniammai, G. Enhanced Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Properties of Nano Chitosan and Pectin Based Biodegradable Active Packaging Films Incorporated with Fennel (Foeniculum Vulgare) Essential Oil and Potato (Solanum Tuberosum) Peel Extracts. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 60, 938–946. [CrossRef]
- Sood, A.; Saini, C. S. Utilization of Peel of White Pomelo for the Development of Pectin Based Biodegradable Composite Films Blended with Casein and Egg Albumen. Food Chem. Adv. 2022, 1, 100054. [CrossRef]
- Shivangi, S.; Dorairaj, D.; Negi, P. S.; Shetty, N. P. Development and Characterisation of a Pectin-Based Edible Film That Contains Mulberry Leaf Extract and Its Bio-Active Components. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 121, 107046. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, W.; Pu, Y.; Chen, L.; Cao, J.; Jiang, W. Development and Characterization of a Novel Active and Intelligent Film Based on Pectin and Betacyanins from Peel Waste of Pitaya (Hylocereus Undatus). Food Chem. 2023, 404. [CrossRef]
- Kannan, A.; Dheeptha, M.; Sistla, Y. S. Development of Pectin and Sodium Alginate Composite Films with Improved Barrier and Mechanical Properties for Food-Packaging Applications. Eng. Proc. 2023, 37. [CrossRef]
- Teleky, B.-E.; Mitrea, L.; Plamada, D.; Nemes, S. A.; Lavinia-florina, C.; Pascuta, M. S.; Varvara, R.; Szabo, K. Development of Pectin and Poly (Vinyl Alcohol ) -Based Active Packaging Enriched with Itaconic Acid and Apple Pomace-Derived Antioxidants. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1–21.
- Han, H. S.; Song, K. Bin. Antioxidant Activities of Mandarin (Citrus Unshiu) Peel Pectin Films Containing Sage (Salvia Officinalis) Leaf Extract. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 3173–3181. [CrossRef]
- Nisar, T.; Wang, Z. C.; Yang, X.; Tian, Y.; Iqbal, M.; Guo, Y. Characterization of Citrus Pectin Films Integrated with Clove Bud Essential Oil: Physical, Thermal, Barrier, Antioxidant and Antibacterial Properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 670–680. [CrossRef]
- Parreidt, T. S.; Müller, K.; Schmid, M. Alginate-Based Edible Films and Coatings for Food Packaging Applications. Foods 2018, 7, 1–38. [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A. R. V.; Alves, V. D.; Coelhoso, I. M. Polysaccharide-Based Membranes in Food Packaging Applications. Membranes (Basel). 2016, 6, 1–17. [CrossRef]
- Castro-Yobal, M. .; Contreras-Oliva, A.; Saucedo-Rivalcoba, V.; Rivera-Armenta, J. L.; Hernández-Ramírez, G.; Salinas-Ruiz, J.; Herrera-Corredor, A. Evaluation of Physicochemical Properties of Film-Based Alginate for Food Packing Applications. E-Polymers 2021, 21, 82–95. [CrossRef]
- Kruk, K.; Winnicka, K. Alginates Combined with Natural Polymers as Valuable Drug Delivery Platforms. Mar. Drugs 2022, 21, 1–33. [CrossRef]
- Kontominas, M. G. Use of Alginates as Food Packaging Materials. Foods 2020, 9. [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S. G. Alginates –A Seaweed Product: Its Properties and Applications. In Properties and Applications of Alginates; 2021; pp 225–240.
- Kocira, A.; Kozłowicz, K.; Panasiewicz, K.; Staniak, M.; Szpunar-Krok, E.; Hortyńska, P. Polysaccharides as Edible Films and Coatings: Characteristics and Influence on Fruit and Vegetable Quality—a Review. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1–38. [CrossRef]
- Anis, A.; Pal, K. Essential Oil-Containing Polysaccharide-Based Edible Films and Coatings for Food Security Applications. Polymers (Basel). 2021, 13, 575. [CrossRef]
- Parreidt, T. S.; Lindner, M.; Rothkopf, I.; Schmid, M.; Müller, K. The Development of a Uniform Alginate-Based Coating for Cantaloupe and Strawberries and the Characterization of Water Barrier Properties. Foods 2019, 8. [CrossRef]
- Puscaselu, R.; Gutt, G.; Amariei, S. The Use of Edible Films Based on Sodium Alginate in Meat Product Packaging: An Eco-Friendly Alternative to Conventional Plastic Materials. Coatings 2020, 10. [CrossRef]
- Nair, M. S.; Saxena, A.; Kaur, C. Effect of Chitosan and Alginate Based Coatings Enriched with Pomegranate Peel Extract to Extend the Postharvest Quality of Guava (Psidium Guajava L.). Food Chem. 2018, 240, 245–252. [CrossRef]
- Dulta, K.; Koşarsoy Agçeli, G.; Thakur, A.; Singh, S.; Chauhan, P.; Chauhan, P. K. Development of Alginate-Chitosan Based Coating Enriched with ZnO Nanoparticles for Increasing the Shelf Life of Orange Fruits (Citrus Sinensis L.). J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 3293–3306. [CrossRef]
- Bazargani-Gilani, B. Activating Sodium Alginate-Based Edible Coating Using a Dietary Supplement for Increasing the Shelf Life of Rainbow Trout Fillet during Refrigerated Storage (4 ± 1 °C). J. Food Saf. 2018, 38, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Mahcene, Z.; Khelil, A.; Hasni, S.; Akman, P. K.; Bozkurt, F.; Birech, K.; Goudjil, M. B.; Tornuk, F. Development and Characterization of Sodium Alginate Based Active Edible Films Incorporated with Essential Oils of Some Medicinal Plants. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 145, 124–132. [CrossRef]
- Alves, Z.; Ferreira, N. M.; Mendo, S.; Ferreira, P.; Nunes, C. Design of Alginate-based Bionanocomposites with Electrical Conductivity for Active Food Packaging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22. [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, S. Z.; Tong, W. Y.; Leong, C. R.; Rashid, S. A.; Rozman, N. A. S.; Hamid, N. H. M.; Karim, S.; Tumin, N. D.; Muda, S. A.; Yacob, L. S. Development of Cinnamaldehyde Loaded-Alginate Based Film for Food Packaging. Asia-Pacific J. Mol. Biol. Biotechnol. 2021, 29, 18–25. [CrossRef]
- Bata Gouda, M. H.; Zhang, C.; Peng, S.; Kong, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Luo, H.; Yu, L. Combination of Sodium Alginate-Based Coating with L-Cysteine and Citric Acid Extends the Shelf-Life of Fresh-Cut Lotus Root Slices by Inhibiting Browning and Microbial Growth. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2021, 175, 111502. [CrossRef]
- Montone, A. M. I.; Malvano, F.; Pham, P. L.; Cinquanta, L. C.; Capparelli, R.; Capuano, F.; Albanese, D. Alginate-based Coatings Charged with Hydroxyapatite and Quercetin for Fresh-cut Papaya Shelf Life. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 5307–5318.
- Ramakrishnan, R.; Kulandhaivelu, S. V.; Roy, S. Alginate/Carboxymethyl Cellulose/Starch- Based Active Coating with Grapefruit Seed Extract to Extend the Shelf Life of Green Chilli. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 199, 99.
- Feng, S.; Tang, Q.; Xu, Z.; Huang, K.; Li, H.; Zou, Z. Development of Novel Co-MOF Loaded Sodium Alginate Based Packaging Films with Antimicrobial and Ammonia-Sensitive Functions for Shrimp Freshness Monitoring. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 135. [CrossRef]
- Jeevahan, J.; Studies, A.; Govindaraj, M. A Brief Review on Edible Food Packaging Materials. J. Glob. Eng. Probl. Solut. 2017, 1, 9–19.
- Karbowiak, T.; Debeaufort, F.; Champion, D.; Voilley, A. Wetting Properties at the Surface of Iota-Carrageenan-Based Edible Films. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 294, 400–410. [CrossRef]
- Janjarasskul, T.; Krochta, J. M. Edible Packaging Materials. 2016, No. April 2010. [CrossRef]
- Bhat, K. M.; R, J.; Sharma, A.; Rao, N. N. Carrageenan-Based Edible Biodegradable Food Packaging: A Review. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 5, 69–75.
- Li, F.; Liu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhe, T.; Guo, Z.; Sun, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, L. Copper Sulfide Nanoparticle-Carrageenan Films for Packaging Application. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 109, 106094. [CrossRef]
- Sedayu, B. B.; Cran, M. J.; Bigger, S. W. A Review of Property Enhancement Techniques for Carrageenan-Based Films and Coatings. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 216, 287–302. [CrossRef]
- Simona, J.; Dani, D.; Petr, S.; Marcela, N.; Jakub, T.; Bohuslava, T. Edible Films from Carrageenan/Orange Essential Oil/Trehalose—Structure, Optical Properties, and Antimicrobial Activity. Polymers (Basel). 2021, 13, 1–19. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Chen, S.; Su, J.; Zhu, M.; Zhou, M.; Chen, T.; Han, Y. Recent Advances in Carrageenan-Based Films for Food Packaging Applications. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9. [CrossRef]
- Martiny, T. R.; Raghavan, V.; de Moraes, C. C.; da Rosa, G. S.; Dotto, G. L. Bio-Based Active Packaging: Carrageenan Film with Olive Leaf Extract for Lamb Meat Preservation. Foods 2020, 9 , 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Avila, L. B.; Barreto, E. R. C.; de Souza, P. K.; Silva, B. D. Z.; Martiny, T. R.; Moraes, C. C.; Morais, M. M.; Raghavan, V.; da Rosa, G. S. Carrageenan-Based Films Incorporated with Jaboticaba Peel Extract: An Innovative Material for Active Food Packaging. Molecules 2020, 25. [CrossRef]
- Duan, N.; Li, Q.; Meng, X.; Wang, Z.; Wu, S. Preparation and Characterization of K-Carrageenan/Konjac Glucomannan/TiO2 Nanocomposite Film with Efficient Anti-Fungal Activity and Its Application in Strawberry Preservation. Food Chem. 2021, 364, 130441. [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.; Ramos, A.; Luís, Â.; Amaral, M. E. Production and Characterization of K-Carrageenan Films Incorporating Cymbopogon Winterianus Essential Oil as New Food Packaging Materials. Foods 2023, 12. [CrossRef]
- Panatarani, C.; Praseptiangga, D.; Widjanarko, P. I.; Azhary, S. Y.; Nurlilasari, P.; Rochima, E.; Joni, I. M. Synthesis, Characterization, and Performance of Semi-Refined Kappa Carrageenan-Based Film Incorporating Cassava Starch. Membranes (Basel). 2023, 13. [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y. H.; Bang, Y. J.; Yoon, K. S.; Priyadarshi, R.; Rhim, J. W. Pine Needle (Pinus Densiflora) Extract-Mediated Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and the Preparation of Carrageenan-Based Antimicrobial Packaging Films. J. Nanomater. 2022, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, K.; Kumar, S.; Bhat, Z. F.; Naqvi, Z.; Mungure, T. E.; Bekhit, A. E. D. A. Functionalization of Carrageenan Based Edible Film Using Aloe Vera for Improved Lipid Oxidative and Microbial Stability of Frozen Dairy Products. Food Biosci. 2021, 43, 101336. [CrossRef]
- You, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Jin, Y.; Wei, M.; Wang, X. Development of Highly Stable Color Indicator Films Based on κ-Carrageenan, Silver Nanoparticle and Red Grape Skin Anthocyanin for Marine Fish Freshness Assessment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 216, 655–669. [CrossRef]
- Pinto, L.; Bonifacio, M. A.; De Giglio, E.; Santovito, E.; Cometa, S.; Bevilacqua, A.; Baruzzi, F. Biopolymer Hybrid Materials: Development, Characterization, and Food Packaging Applications. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2021, 28, 100676. [CrossRef]
- Khodaei, D.; Álvarez, C.; Mullen, A. M. Biodegradable Packaging Materials from Animal Processing Co-Products and Wastes: An Overview. Polymers (Basel). 2021, 13. [CrossRef]
- Galgano, F.; Condelli, N.; Favati, F.; Di Bianco, V.; Perretti, G.; Caruso, M. C. Biodegradable Packaging and Edible Coating for Fresh-Cut Fruits and Vegetables. Ital. J. Food Sci. 2015, 27, 1–20. [CrossRef]
- Maurizzi, E.; Bigi, F.; Quartieri, A.; De Leo, R.; Volpelli, L. A.; Pulvirenti, A. The Green Era of Food Packaging: General Considerations and New Trends. Polymers (Basel). 2022, 14. [CrossRef]
- Naser, A. Z.; Deiab, I.; Darras, B. M. Poly (Lactic Acid) (PLA) and Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs), Green Alternatives to Petroleum-Based Plastics: A Review. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 17151–17196. [CrossRef]
- Farah, S.; Anderson, D. G.; Langer, R. Physical and Mechanical Properties of PLA, and Their Functions in Widespread Applications — A Comprehensive Review. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 367–392. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S. Polylactic Acid (PLA) and Its Composites: An Eco-friendly Solution for Packaging. In Sustainable Food Packaging Technology; 2021; pp 107–132. [CrossRef]
- Marano, S.; Laudadio, E.; Minnelli, C.; Stipa, P. Tailoring the Barrier Properties of PLA: A State-of-the-Art Review for Food Packaging Applications. Polymers (Basel). 2022, 14. [CrossRef]
- Torres-giner, S.; Figueroa-lopez, K. J.; Melendez-rodriguez, B.; Prieto, C.; Pardo-figuerez, M.; Lagaron, J. M. Emerging Trends in Biopolymers for Food Packaging. In Sustainable Food PackagingTechnology; 2021; pp 1–32.
- Mohamad, N.; Mazlan, M. M.; Tawakkal, I. S. M. A.; Talib, R. A.; Kian, L. K.; Fouad, H.; Jawaid, M. Development of Active Agents Filled Polylactic Acid Films for Food Packaging Application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 1451–1457. [CrossRef]
- Khanjari, A.; Esmaeili, H.; Hamedi, M. Shelf-Life Extension of Minced Squab Using Poly-Lactic Acid Films Containing Cinnamomum Verum Essential Oil. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023, 385, 109982. [CrossRef]
- Ardjoum, N.; Chibani, N.; Shankar, S.; Fadhel, Y. Ben; Djidjelli, H.; Lacroix, M. Development of Antimicrobial Films Based on Poly(Lactic Acid) Incorporated with Thymus Vulgaris Essential Oil and Ethanolic Extract of Mediterranean Propolis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 185, 535–542. [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Hao, Y.; Liu, B.; Chen, Y.; Li, L. Development and Application of Poly (Lactic Acid)/Poly (Butylene Adipate-Co-Terephthalate)/Thermoplastic Starch Film Containing Salicylic Acid for Banana Preservation. Foods 2023, 12, 3397. [CrossRef]
- Hernández-García, E.; Vargas, M.; Torres-Giner, S. Quality and Shelf-Life Stability of Pork Meat Fillets Packaged in Multilayer Polylactide Films. Foods 2022, 11. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Huang, C.; Xu, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhao, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. Synthesis and Characterization of Antibacterial Polylactic Acid Film Incorporated with Cinnamaldehyde Inclusions for Fruit Packaging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 4547–4555. [CrossRef]
- Suwanamornlert, P.; Kerddonfag, N.; Sane, A.; Chinsirikul, W.; Zhou, W.; Chonhenchob, V. Poly (Lactic Acid)/Poly (Butylene-Succinate-Co-Adipate) (PLA/PBSA) Blend Films Containing Thymol as Alternative to Synthetic Preservatives for Active Packaging of Bread. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2020, 25, 100515. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Cheng, R.; Wang, B.; Zeng, J.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Kang, L.; Cheng, Z.; Gao, W.; Chen, K. Biodegradable Sandwich-Architectured Films Derived from Pea Starch and Polylactic Acid with Enhanced Shelf-Life for Fruit Preservation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 251, 117117. [CrossRef]
- Wongthanaroj, D.; Jessmore, L. A.; Lin, Y.; Bergholz, T. M.; Stark, N. M.; Sabo, R. C.; Matuana, L. M. Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Poly (Lactic Acid)/Cellulose Nanocrystal Nanocomposite Films for the Preservation of Oxygen-Sensitive Food. Appl. Food Res. 2022, 2, 100222. [CrossRef]
- Nasution, H.; Harahap, H.; Julianti, E.; Safitri, A.; Jaafar, M. Smart Packaging Based on Polylactic Acid: The Effects of Antibacterial and Antioxidant Agents from Natural Extracts on Physical – Mechanical Properties, Colony Reduction , Perishable Food Shelf Life , and Future Prospective. Polymers (Basel). 2023, 15. [CrossRef]
- Gabor, D.; Tita, O. Biopolymers Used in Food Packaging: A Review. Acta Univ. Cibiniensis Ser. E Food Technol. 2012, XVI (2), 3–19.
- Manikandan, N. A.; Pakshirajan, K.; Pugazhenthi, G. Preparation and Characterization of Environmentally Safe and Highly Biodegradable Microbial Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) Based Graphene Nanocomposites for Potential Food Packaging Applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 154, 866–877. [CrossRef]
- Pawar, P. A; Purwar, A. H. Bioderadable Polymers in Food Packaging. Am. J. Eng. Res. 2013, No. 05, 151–164.
- Garcia-Garcia, D.; Quiles-Carrillo, L.; Balart, R.; Torres-Giner, S.; Arrieta, M. P. Innovative Solutions and Challenges to Increase the Use of Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate) in Food Packaging and Disposables. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 178. [CrossRef]
- Yeo, J. C. C.; Muiruri, J. K.; Thitsartarn, W.; Li, Z.; He, C. Recent Advances in the Development of Biodegradable PHB-Based Toughening Materials: Approaches, Advantages and Applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 92, 1092–1116. [CrossRef]
- Rech, C. R.; Brabes, K. C. S.; Silva, B. E. B.; Martines, M. A. U.; Silveira, T. F. S.; Alberton, J.; Amadeu, C. A. A.; Caon, T.; Arruda, E. J.; Martelli, S. M. Antimicrobial and Physical–Mechanical Properties of Polyhydroxybutyrate Edible Films Containing Essential Oil Mixtures. J. Polym. Environ. 2021, 29, 1202–1211. [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S. V. G.; Pakshirajan, K.; Pugazhenthi, G. Facile Fabrication and Characterization of Novel Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Poly (3-Hydroxybutyrate)/Essential Oil Composites for Potential Use in Active Food Packaging Applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 252, 98. [CrossRef]
- Fiorentini, C.; Bassani, A.; Zaccone, M.; Luana, M.; Díaz, E.; Apodaca, D.; Spigno, G. Active Coated PLA-PHB Film with Formulations Containing a Commercial Olive Leaf Extract to Improve Quality Preservation of Fresh Pork Burgers. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2023, 102, 85–90. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Dong, Q.; Gao, H.; Han, Y.; Li, L. Enhanced Mechanical and Antioxidant Properties of Biodegradable Poly (Lactic) Acid-Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate-Co-4-Hydroxybutyrate) Film Utilizing α-Tocopherol for Peach Storage. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2021, 34, 187–199. [CrossRef]
- Iglesias-Montes, M. L.; Soccio, M.; Siracusa, V.; Gazzano, M.; Lotti, N.; Cyras, V. P.; Manfredi, L. B. Chitin Nanocomposite Based on Plasticized Poly (Lactic Acid)/Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate) (PLA/PHB) Blends as Fully Biodegradable Packaging Materials. Polymers (Basel). 2022, 14. [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Walton, W. C.; Wang, L.; Li, L.; Wang, Y. Characterization of Polylactic Acids-Polyhydroxybutyrate Based Packaging Film with Fennel Oil, and Its Application on Oysters. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2019, 22. [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Chatli, A. S.; Mehndiratta, H. K. Development of Starch Based Edible Films. Int. J. Dev. Res. 2018, 8, 23501–23506.
- Yang, S.-Y.; Cao, L.; Kim, H.; Beak, S. E.; Song, K. Bin. Utilization of Foxtail Millet Starch Film Incorporated with Clove Leaf Oil for the Packaging of Queso Blanco Cheese as a Model Food. Starch/Staerke 2018, 70. [CrossRef]
- Aghazadeh, M.; Karim, R.; Sultan, M. T.; Paykary, M.; Johnson, S. K.; Shekarforoush, E. Comparison of Starch Films and Effect of Different Rice Starch-Based Coating Formulations on Physical Properties of Walnut during Storage Time at Accelerated Temperature. J. Food Process Eng. 2018, 41. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Wang, H.; Kang, S.; Xia, L.; Jiang, S.; Chen, M.; Jiang, S. An Active Packaging Film Based on Yam Starch with Eugenol and Its Application for Pork Preservation. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 96, 546–554. [CrossRef]
- (198) Pavinatto, A.; Mattos, A. V. de A.; Malpass, A. C. G.; Okura, M. H.; Balogh, D. T.; Sanfelice, R. C. Coating with Chitosan-Based Edible Films for Mechanical/ Biological Protection of Strawberries. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 151, 1004–1011. [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshi, R.; Sauraj; Kumar, B.; Deeba, F.; Kulshreshtha, A.; Negi, Y. S. Chitosan Films Incorporated with Apricot (Prunus Armeniaca) Kernel Essential Oil as Active Food Packaging Material. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 85, 158–166. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Pratibha; Petkoska, A. T.; Khojah, E.; Sami, R.; A. M., A.; Al-Mushhin. Chitosan Edible Films Enhanced with Pomegranate Peel Extract: Study on Physical, Biological, Thermal, and Barrier Properties. Materials (Basel). 2021, 14, 1–18.
- Salama, H. E.; Abdel Aziz, M. S. Development of Active Edible Coating of Alginate and Aloe Vera Enriched with Frankincense Oil for Retarding the Senescence of Green Capsicums. Lwt 2021, 145, 111341. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, A.; Yang, M.; Ge, Y.; Pristijono, P.; Li, J.; Xu, B.; Mi, H. Characterization of Sodium Alginate-Based Films Incorporated with Thymol for Fresh-Cut Apple Packaging. Food Control 2021, 126, 108063. [CrossRef]
- Sarengaowa; Hu, W.; Jiang, A.; Xiu, Z.; Feng, K. Effect of Thyme Oil–Alginate-Based Coating on Quality and Microbial Safety of Fresh-Cut Apples. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 2302–2311. [CrossRef]
- Ravishankar, S.; Jaroni, D.; Zhu, L.; Olsen, C.; McHugh, T.; Friedman, M. Inactivation of Listeria Monocytogenes on Ham and Bologna Using Pectin-Based Apple, Carrot, and Hibiscus Edible Films Containing Carvacrol and Cinnamaldehyde. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Romero, J.; Cruz, R. M. S.; Díez-Méndez, A.; Albertos, I. Valorization of Berries’ Agro-Industrial Waste in the Development of Biodegradable Pectin-Based Films for Fresh Salmon (Salmo Salar) Shelf-Life Monitoring. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23. [CrossRef]
- Farhan, A.; Hani, N. M. Active Edible Films Based on Semi-Refined κ-Carrageenan: Antioxidant and Color Properties and Application in Chicken Breast Packaging. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2020, 24, 100476. [CrossRef]
- Meindrawan, B.; Suyatma, N. E.; Wardana, A. A.; Pamela, V. Y. Nanocomposite Coating Based on Carrageenan and ZnO Nanoparticles to Maintain the Storage Quality of Mango. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2018, 18, 140–146. [CrossRef]
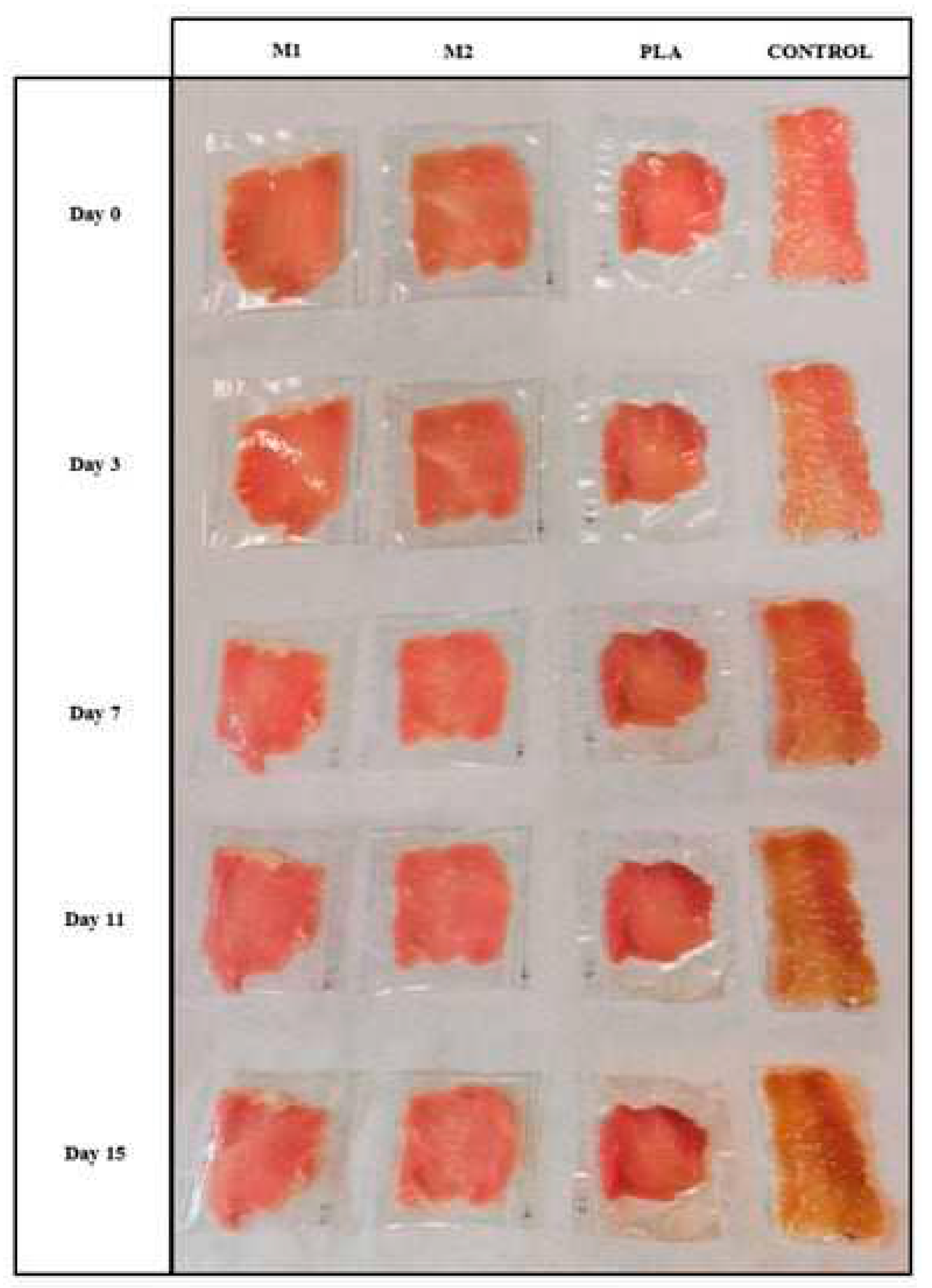
- Ma, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, Y. Development of PLA-PHB-Based Biodegradable Active Packaging and Its Application to Salmon. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2018, 31, 739–746. [CrossRef]
- Fiore, A.; Park, S.; Volpe, S.; Torrieri, E.; Masi, P. Active Packaging Based on PLA and Chitosan-Caseinate Enriched Rosemary Essential Oil Coating for Fresh Minced Chicken Breast Application. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2021, 29, 100708. [CrossRef]
- Salgado, P. R.; Di Giorgio, L.; Musso, Y. S.; Mauri, A. N. Recent Developments in Smart Food Packaging Focused on Biobased and Biodegradable Polymers. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 1–30. [CrossRef]
- Peramune, D. L.; Ranaweera, S.; Marasinghe, W. N.; Manatunga, D. C.; Jayathunge, K. G. L. R.; Dassanayake, R. S. Polysaccharides-Based Food Packaging Films: An Overview. In Food Packaging-Safety, Management and Quality; Lai, W.-F., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, 2022; pp 3–40. [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Han, F.; Zhang, S.; Li, P.; Shang, N. Novel Bio-Based Materials and Applications in Antimicrobial Food Packaging: Recent Advances and Future Trends. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22. [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, V.; Bangar, S. P.; Thaku, N.; Trif, M. Recent Advancements in Smart Biogenic Packaging: Reshaping the Future of the Food Packaging Industry. Polymers (Basel). 2022, 14. [CrossRef]
- Chausali, N.; Saxena, J.; Prasad, R. Recent Trends in Nanotechnology Applications of Bio-Based Packaging. J. Agric. Food Res. 2022, 7, 100257. [CrossRef]
- Chawla, R.; Sivakumar, S.; Kaur, H. Antimicrobial Edible Films in Food Packaging: Current Scenario and Recent Nanotechnological Advancements- a Review. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2021, 2, 100024. [CrossRef]
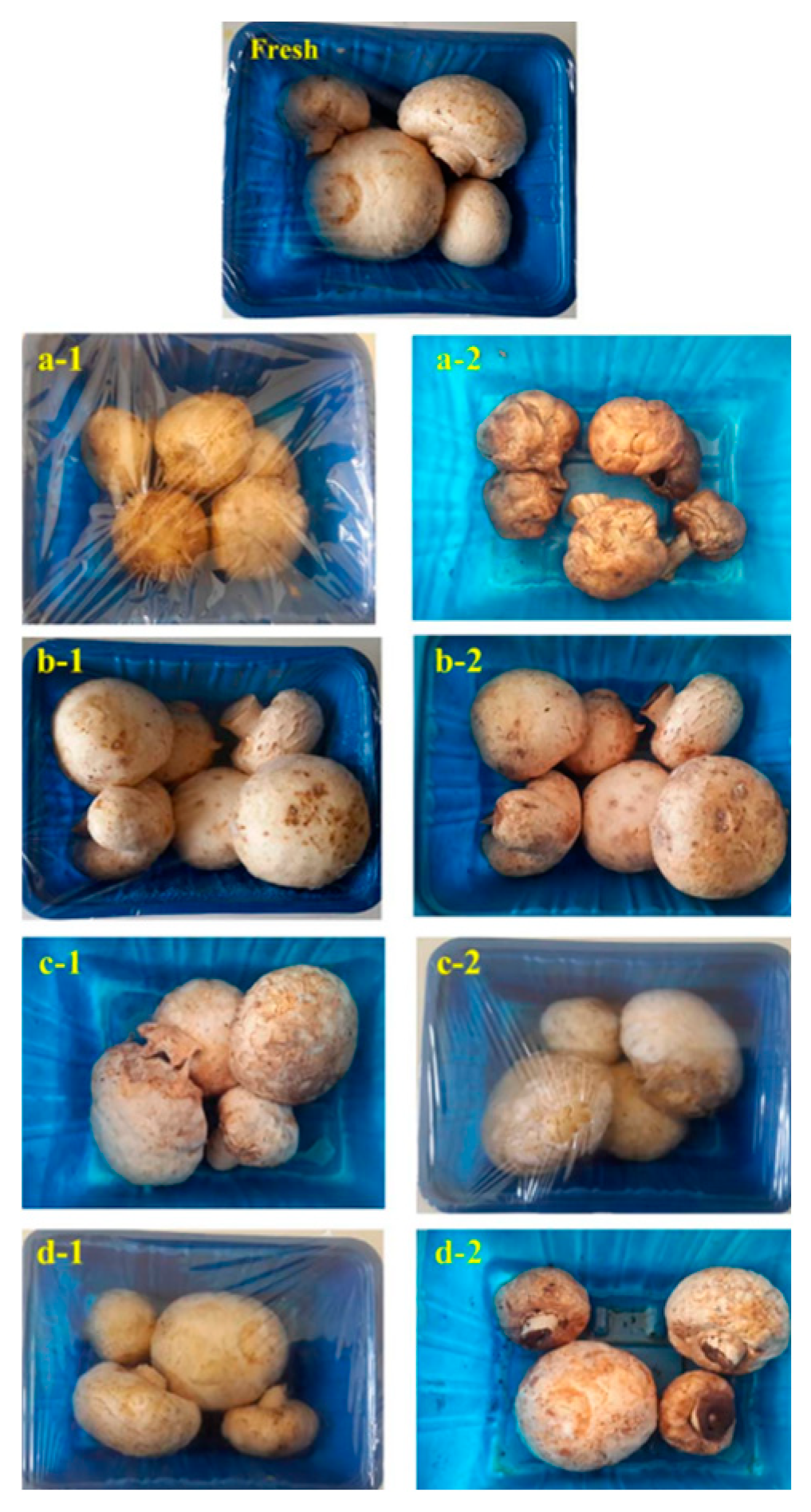

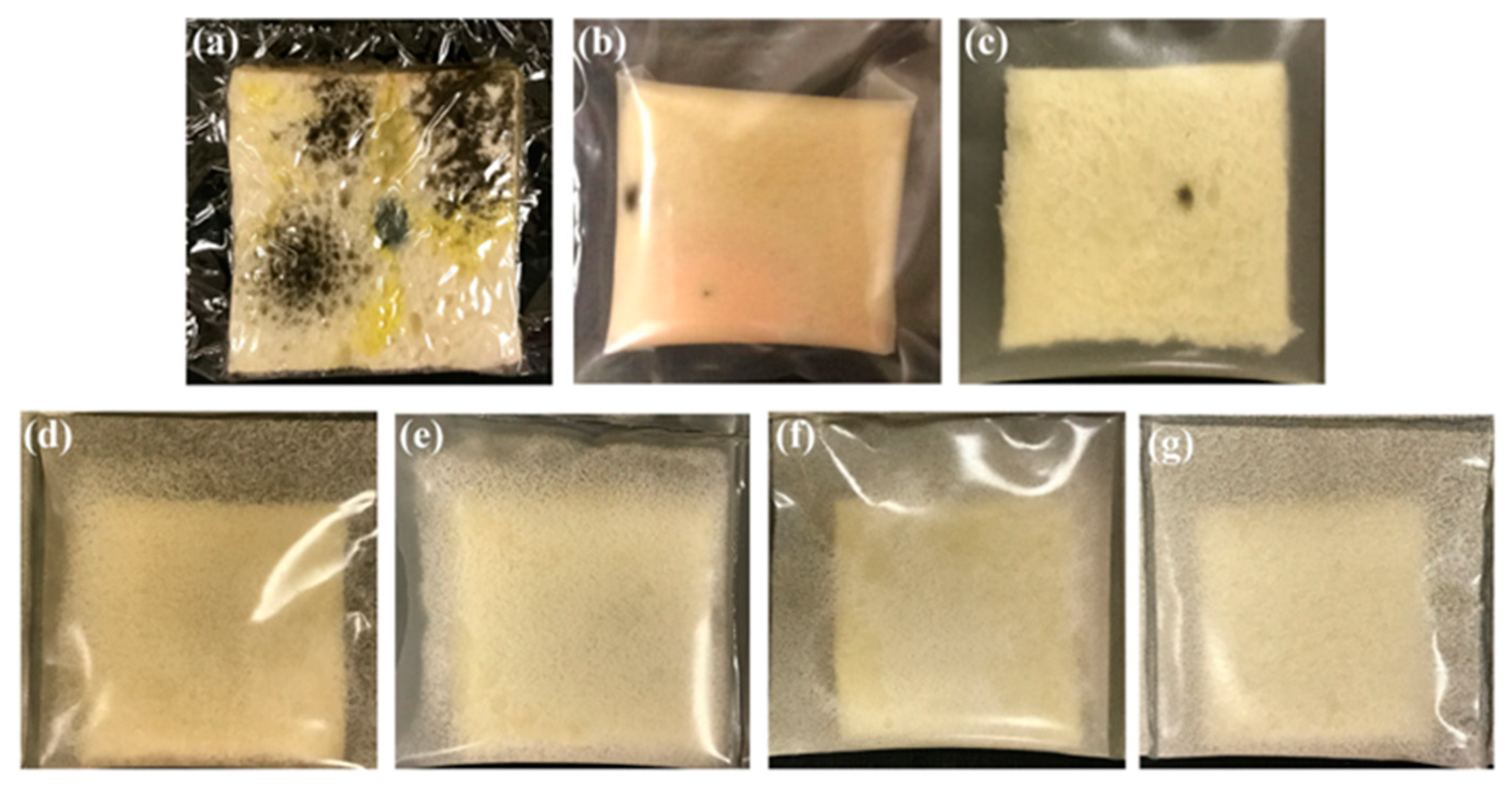
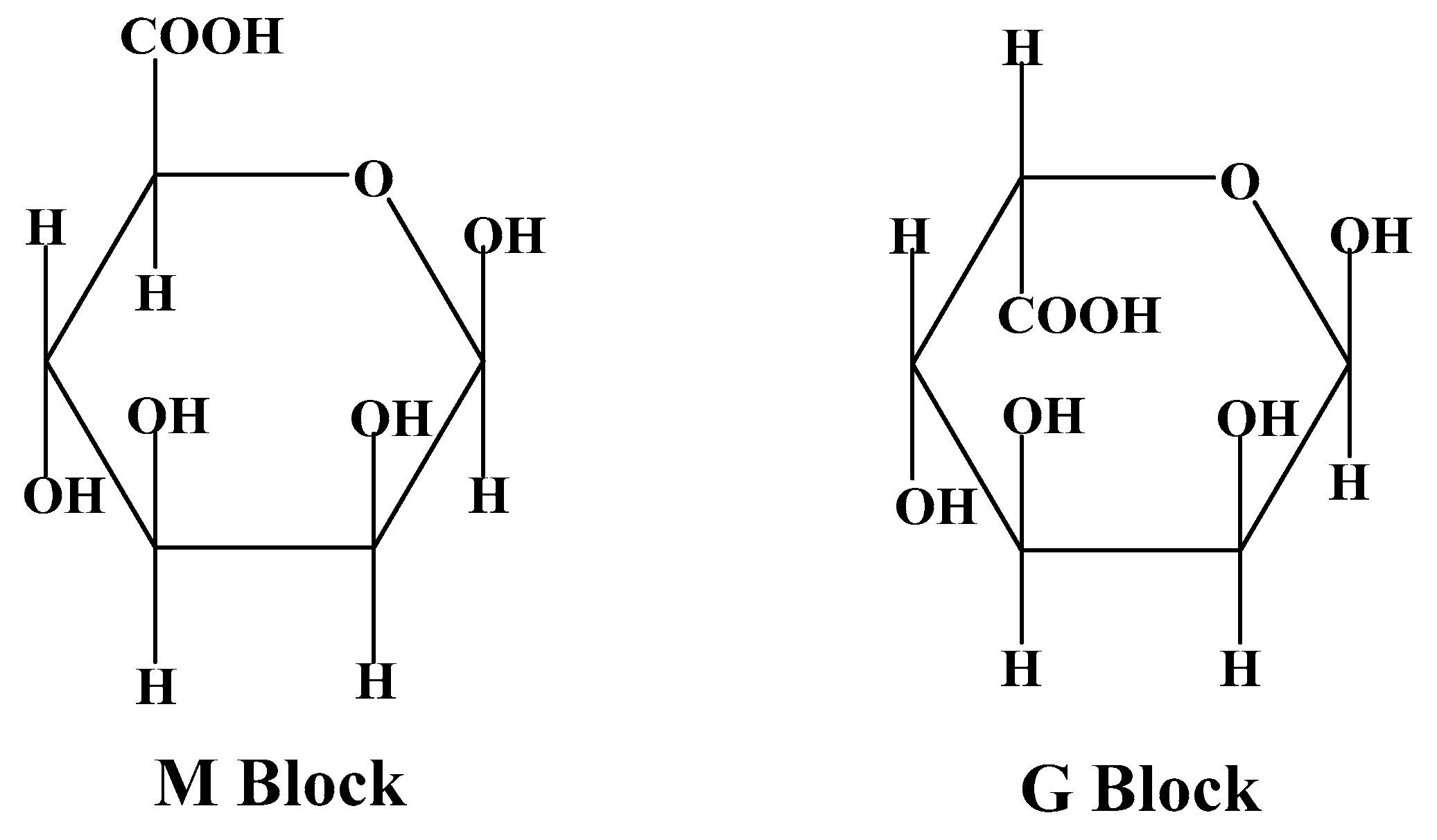

| Paper type | Properties | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kraft paper | Type of coarse paper, high strength, economical, porous, tear-resistant, rough surface, can be coated or laminated | Beverage carriers, boxes, sacks, cartons, package flour, dried fruits, sugar | [11] |
| Greaseproof paper | Translucent, machine-finished, resistant to oils | Wrap cookies, confectionaries, snack foods, high oily foods | [16] |
| Parchment paper | Made from acid-treated pulp, not heat sealable, poor air and moisture barrier properties, high wet strength, greaseproof | Layer between pastry or meat slices, labels for fatty foods, cheese wrapping | [11] |
| Glassine paper | Glassy smooth surface, transparent sheet, good grease and oil resistance, high density | Liner for baked goods, biscuits, cookies, and cooking fats |
[17] |
| Bleached paper | Soft and white, weaker compared to unbleached paper, expensive | Food labels, flour, sugar, and fruits and vegetables | [18] |
| Paperboards | Thicker than paper, rigid, foldable, and different types are available: whiteboard, liner board, food board, carton board, chipboard, and corrugated board | Rigid boxes, beverage cartons, boxes for fruits and vegetables | [18,19] |
| Plastic | Properties | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) | Good barrier to gases and moisture, resistant to heat, mineral oils, solvents, and acids, transparent, tough |
Beverage and mineral water bottles, jars, tubes, trays | [27,28] |
| High-density polyethylene (HDPE) | Good barrier to solvents and moisture, high tensile strength, opaque, high-temperature capability |
Beverage and milk bottles, shopping bags, ice cream containers | [25,29] |
| Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) | High resistance to chemicals, high strength, high oil barrier properties, good heat sealability | Bottles, food wraps | [30] |
| Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) | Good heat sealing, resistant to acid, oils, and bases, rigid, flexible, transparent | Bakery, frozen, fresh produce, meat packing, soft squeeze bottles | [31] |
| Polypropylene (PP) | High water vapor barrier, resistant to gases and odor, high strength and puncture resistance | Containers for ice cream, margarine, yogurt, snack packs, biscuit packs | [29] |
| Polystyrene (PS) | Brittle, rigid, poor barrier to moisture and gases, good insulation properties | Cutlery, food insulation boxes, meat trays, egg containers | [32,33] |
| Packaging material | Additives | Preparation method | Food sample | Properties | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Potato starch-based film | Sodium alginate Glycerol Essential oil |
Casting method | Perishable food products | Shelf-life extension and inhibit the spoilage organisms | [194] |
| Foxtail millet starch-based film | Clove leaf oil Sorbitol |
Casting method | Cheese | Reduces the lipid oxidation and microbial growth compared to LDPE | [195] |
| Rice starch-based coating | Chitosan | Coating method | Walnut | Shelf-life extension due to reduced effect of oxygen, moisture, and temperature | [196] |
| Chinese yam starch-based film | Sorbitol Glycerol Eugenol |
Casting method | Pork | Due to its superior barrier and antibacterial qualities increases the shelf-life of pork beyond 50%. | [197] |
| Chitosan-based coating | Glycerol | Coating method | Strawberry | Excellent antibacterial and antifungal activity for one week and maintain the appearance of strawberries | [198] |
| Chitosan-based film | Apricot kernel essential oil | Casting method | Sliced bread | Enhance the shelf-life of bread with antioxidant and antimicrobial activity against E. coli, B. subtilis, and fungal growth. | [199] |
| Chitosan-based films | Pomegranate peel extract Glycerol |
Casting method | Fruits and vegetables | Extend storage life and improve the quality | [200] |
| Alginate based films | Glycerol Aloe vera Frankincense oil |
Casting method | Green capsicum | Senescence retardation and resistance to the mass loss of green capsicums | [201] |
| Alginate based films | Glycerol Thymol |
Two-stage cross- linking method |
Fresh cut apple | Inhibit the growth of Staphylococcus aureus and E. coli and maintain apple weight, color, and appearance. | [202] |
| Alginate based coating | Glycerol Thyme oil |
Dipped method | Fresh cut apple | preventing bacteria growth, respiration, weight loss, and browning reaction while preserving the firmness | [203] |
| Pectin based film | Carvacrol Cinnamaldehyde | Casting method | Ham and Bologna | Improve microbial food safety | [204] |
| Pectin based film | Glycerol Berry extract |
Casting method | Salmon Fillets | Improve the shelf-life due to the antioxidant properties and barrier properties. | [205] |
| Carrageenan based film | Water extract of germinated fenugreek seeds Sorbitol |
Casting method | chicken breast | Improve the shelf-life of meat by controlling the growth of microorganisms on the surface of chicken breast. | [206] |
| Carrageenan based film | ZnO nanoparticles Glycerol |
Dipping method | Mango | Maintain firmness and delay the discoloration and decay of mango | [207] |
| PLA-PHB based films | Glycerol Cinnamaldehyde |
Casting method | Salmon | Reduce the total bacterial count on the sampler | [208] |
| PLA and chitosan-caseinate based film | Rosemary essential oil | Casting method | Fresh minced chicken breast | Provide antioxidant effects and improve the shelf-life of fresh meat products | [209] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





