Submitted:
22 January 2024
Posted:
23 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
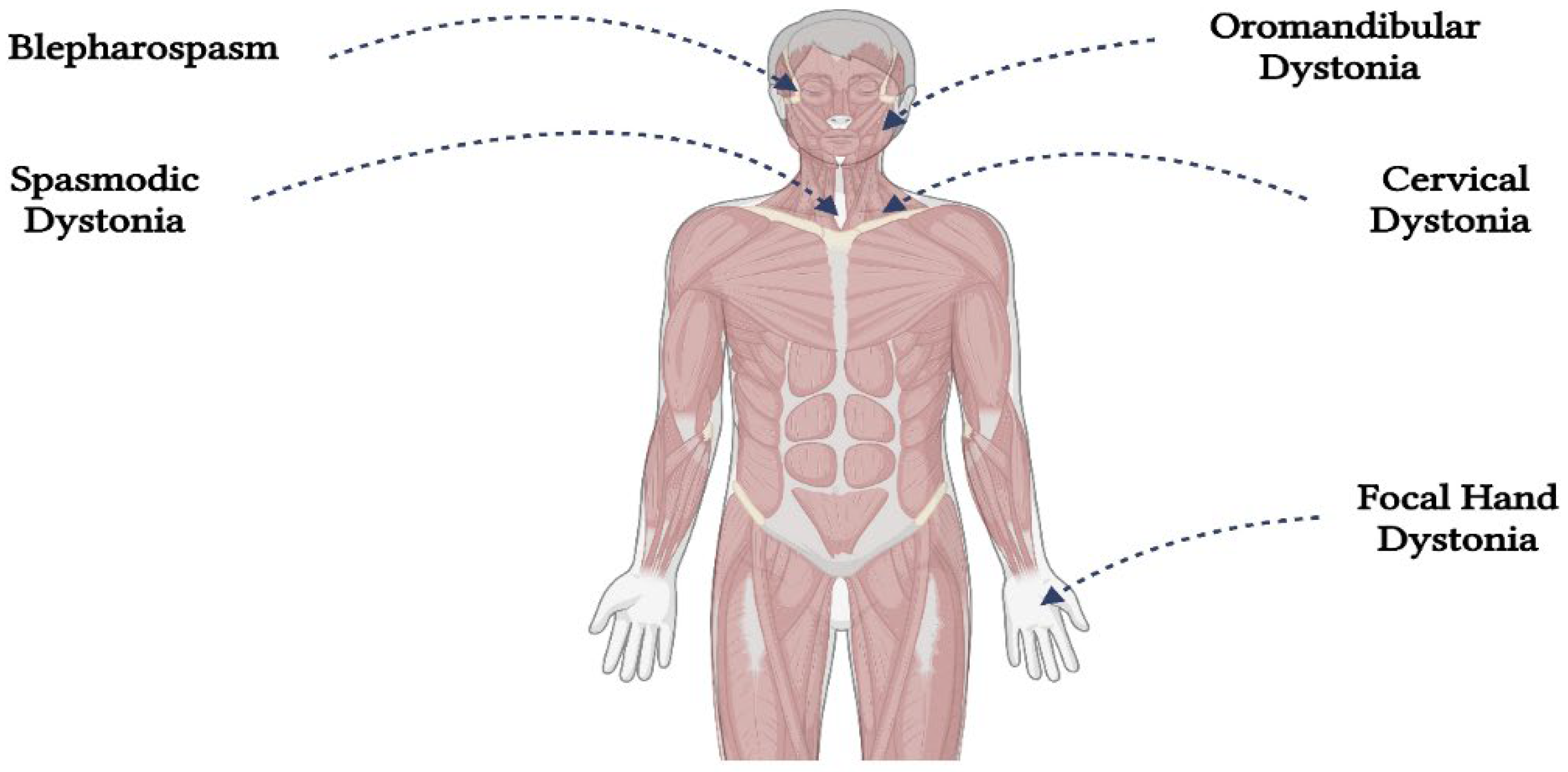
3. Classification and comorbidities in dystonia
4. Diagnostic of dystonia
5. The genetic background of dystonia
- a)
- Endoplasmic reticulum stress response - TOR1A (torsin 1A)
- b)
- Neurodevelopment - THAP1 (THAP domain-containing protein 1), KMT2B (lysine-specific methyltransferase 2B)
- c)
- Striatal dopamine signaling – GNAL (guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-activating activity polypeptide)
- d)
- Calcium homeostasis - ANO3 (anoctamin)
- e)
- Autophagy - VPS16 (PS16 core subunit of corvet and HOPS complexes)
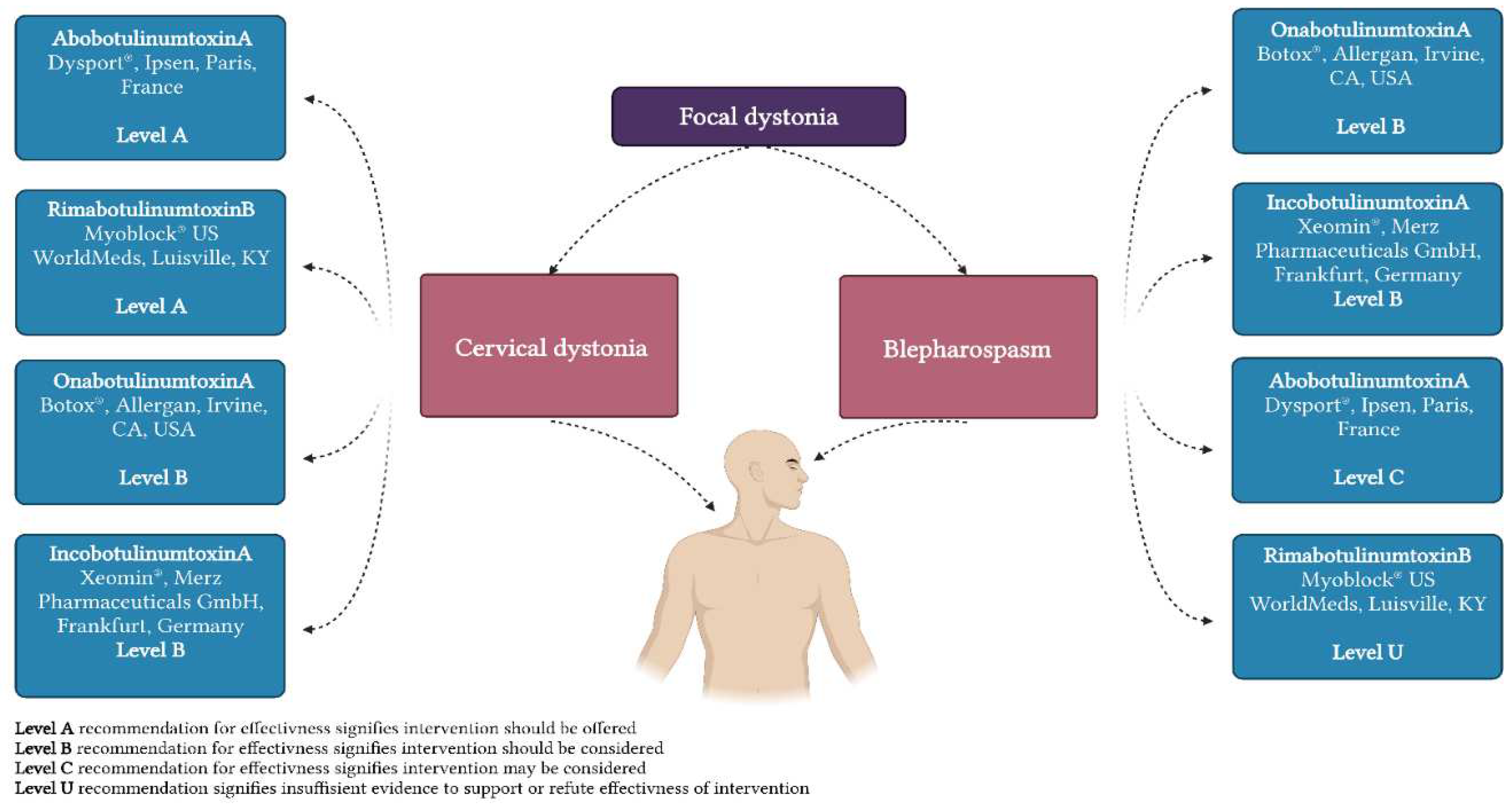
5. Treatment options for dystonia
| Primary focal dystonia |
Cervical dystonia |
Oromandibular dystonia | Blepharospasm |
Spasmodic dysphonia |
Focal hand dystonia |
| BoNT | + | + | + | + | + |
| DBS | + | +/- | +/- | - | + |
| Trihexyphenidyl | + | - | - | - | + |
| Tetrabenazine | + | - | - | - | - |
| Clonazepam | + | - | + | - | - |
| Baclofen | - | + | - | - | + |
| Levodopa | - | - | - | - | - |
| Amantadine | +/- | - | - | - | - |
| Haloperidol | - | - | - | - | - |
6. Conclusions and future perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jinnah, H.A. The Dystonias. Contin. Lifelong Learn. Neurol. 2019, 25, 976–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinnah, H.A.; Berardelli, A.; Comella, C.; DeFazio, G.; DeLong, M.R.; Factor, S.; Galpern, W.R.; Hallett, M.; Ludlow, C.L.; Perlmutter, J.S.; et al. The Focal Dystonias: Current Views and Challenges for Future Research. Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 926–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balint, B.; Mencacci, N.E.; Valente, E.M.; Pisani, A.; Rothwell, J.; Jankovic, J.; Vidailhet, M.; Bhatia, K.P. Dystonia. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primer 2018, 4, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyślerowicz, M.; Kiedrzyńska, W.; Adamkiewicz, B.; Jost, W.H.; Sławek, J. Cervical Dystonia — Improving the Effectiveness of Botulinum Toxin Therapy. Neurol. Neurochir. Pol. 2020, 54, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales, R.L.; Cuffe, L.; Regnault, B.; Trosch, R.M. Pain in Cervical Dystonia: Mechanisms, Assessment and Treatment. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2021, 21, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Qu, J.; Ye, L.; Shu, Y.; Qu, Q. Blepharospasm, Oromandibular Dystonia, and Meige Syndrome: Clinical and Genetic Update. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 630221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titi-Lartey, O.A.; Patel, B.C. Benign Essential Blepharospasm. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island (FL), 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Aramideh, M.; Ongerboer De Visser, B.W.; Brans, J.W.; Koelman, J.H.; Speelman, J.D. Pretarsal Application of Botulinum Toxin for Treatment of Blepharospasm. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1995, 59, 309–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzo, N.; Ginatempo, F.; Belvisi, D.; Defazio, G.; Conte, A.; Deriu, F.; Berardelli, A. Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Oromandibular Dystonia. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2022, 134, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramaniam, R.; Ram, S. Orofacial Movement Disorders. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 20, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Sadoughi, B. Spasmodic Dysphonia. In Advances in Oto-Rhino-Laryngology; S. Karger AG, 2020; Vol. 85, pp. 133–143. ISBN 978-3-318-06627-2. [Google Scholar]
- Huber, L.; Kassavetis, P.; Gulban, O.F.; Hallett, M.; Horovitz, S.G. Laminar VASO fMRI in Focal Hand Dystonia Patients. Dystonia 2023, 2, 10806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aránguiz, R.; Chana-Cuevas, P.; Alburquerque, D.; León, M. Distonía focales en los músicos. Neurología 2011, 26, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, S.; Pal, P.K. Dystonia in Performing Artists: Beyond Focal Hand Dystonia. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. J. Can. Sci. Neurol. 2022, 49, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenka, A.; Jankovic, J. Sports-Related Dystonia. Tremor Hyperkinetic Mov. 2021, 11, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albanese, A.; Bhatia, K.; Bressman, S.B.; DeLong, M.R.; Fahn, S.; Fung, V.S.C.; Hallett, M.; Jankovic, J.; Jinnah, H.A.; Klein, C.; et al. Phenomenology and Classification of Dystonia: A Consensus Update. Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grütz, K.; Klein, C. Dystonia Updates: Definition, Nomenclature, Clinical Classification, and Etiology. J. Neural Transm. 2021, 128, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steel, D.; Reid, K.M.; Pisani, A.; Hess, E.J.; Fox, S.; Kurian, M.A. Advances in Targeting Neurotransmitter Systems in Dystonia. In International Review of Neurobiology; Elsevier, 2023; Vol. 169, pp. 217–258. ISBN 978-0-323-99026-4. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández, I.H.; Cabrera, J.R.; Santos-Galindo, M.; Sánchez-Martín, M.; Domínguez, V.; García-Escudero, R.; Pérez-Álvarez, M.J.; Pintado, B.; Lucas, J.J. Pathogenic SREK1 Decrease in Huntington’s Disease Lowers TAF1 Mimicking X-Linked Dystonia Parkinsonism. Brain 2020, 143, 2207–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFarlane, D.G.; Dieppe, P.A. Pseudo-Rheumatoid Deformity in Elderly Osteoarthritic Hands. J. Rheumatol. 1983, 10, 489–490. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, A.; Miyatake, T. A Family with Hereditary Juvenile Dystonia-parkinsonism. Mov. Disord. 1995, 10, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetty, A.S.; Bhatia, K.P.; Lang, A.E. Dystonia and Parkinson’s Disease: What Is the Relationship? Neurobiol. Dis. 2019, 132, 104462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabresi, P.; Standaert, D.G. Dystonia and Levodopa-Induced Dyskinesias in Parkinson’s Disease: Is There a Connection? Neurobiol. Dis. 2019, 132, 104579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centen, L.M.; Van Egmond, M.E.; Tijssen, M.A.J. New Developments in Diagnostics and Treatment of Adult-Onset Focal Dystonia. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2023, 36, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, C.D. The Dystonias. Contin. Lifelong Learn. Neurol. 2022, 28, 1435–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanese, A.; Lalli, S. Is This Dystonia? Mov. Disord. 2009, 24, 1725–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Briceno, H.; Fung, V.S.C.; Bhatia, K.P.; Balint, B. Parkinsonism and Dystonia: Clinical Spectrum and Diagnostic Clues. J. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 433, 120016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalli, S.; Albanese, A. The Diagnostic Challenge of Primary Dystonia: Evidence from Misdiagnosis. Mov. Disord. 2010, 25, 1619–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postuma, R.B.; Berg, D.; Stern, M.; Poewe, W.; Olanow, C.W.; Oertel, W.; Obeso, J.; Marek, K.; Litvan, I.; Lang, A.E.; et al. MDS Clinical Diagnostic Criteria for Parkinson’s Disease: MDS-PD Clinical Diagnostic Criteria. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaenens, C.; Krystkowiak, P.; Douay, X.; Charpentier, P.; Bele, S.; Destée, A.; Sablonnière, B. Clinical and Genetic Evaluation in a French Population Presenting with Primary Focal Dystonia. Mov. Disord. 2005, 20, 822–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leube, B.; Kessler, K.R.; Goecke, T.; Auburger, G.; Benecke, R. Frequency of Familial Inheritance among 488 Index Patients with Idiopathic Focal Dystonia and Clinical Variability in a Large Family. Mov. Disord. 1997, 12, 1000–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, L.; McGovern, E.; Kimmich, O.; Molloy, A.; Beiser, I.; Butler, J.S.; Molloy, F.; Logan, P.; Healy, D.G.; Lynch, T.; et al. Epidemiological, Clinical and Genetic Aspects of Adult Onset Isolated Focal Dystonia in Ireland. Eur. J. Neurol. 2017, 24, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loens, S.; Hamami, F.; Lohmann, K.; Odorfer, T.; Ip, C.W.; Zittel, S.; Zeuner, K.E.; Everding, J.; Becktepe, J.; Marth, K.; et al. Tremor Is Associated with Familial Clustering of Dystonia. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2023, 110, 105400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, M.; Lange, L.M.; Zech, M.; Lohmann, K. Genetics and Pathogenesis of Dystonia. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2024, 19, 321932111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozelius, L.J.; Hewett, J.W.; Page, C.E.; Bressman, S.B.; Kramer, P.L.; Shalish, C.; De Leon, D.; Brin, M.F.; Raymond, D.; Corey, D.P.; et al. The Early-Onset Torsion Dystonia Gene (DYT1) Encodes an ATP-Binding Protein. Nat. Genet. 1997, 17, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Huang, J.; Yang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Pan, L.; Jin, L. Genetic Spectrum and Clinical Features in a Cohort of Chinese Patients with Isolated Dystonia. Clin. Genet. 2023, 103, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holla, V.V.; Prasad, S.; Neeraja, K.; Kamble, N.; Yadav, R.; Pal, P.K. Late Adulthood Onset DYT-THAP1 Secondary to a Novel Splice Site Mutation-A Report from India. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2020, 78, 36–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, L.M.; Junker, J.; Loens, S.; Baumann, H.; Olschewski, L.; Schaake, S.; Madoev, H.; Petkovic, S.; Kuhnke, N.; Kasten, M.; et al. Genotype–Phenotype Relations for Isolated Dystonia Genes: MDSGene Systematic Review. Mov. Disord. 2021, 36, 1086–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.J.; Woo, K.A.; Kim, H.-J.; Jeon, B. Late-Onset Dystonia With THAP1 Mutation (DYT6) in South Korea: A Case Report and Literature Review. J. Clin. Neurol. Seoul Korea 2023, 19, 198–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Closas, A.M.F.D.; Lohmann, K.; Tan, A.H.; Ibrahim, N.M.; Lim, J.L.; Tay, Y.W.; Muthusamy, K.A.; Ahmad-Annuar, A.B.; Klein, C.; Lim, S.-Y. A KMT2B Frameshift Variant Causing Focal Dystonia Restricted to the Oromandibular Region After Long-Term Follow-Up. J. Mov. Disord. 2023, 16, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erro, R.; Bhatia, K.P.; Hardy, J. GNAL Mutations and Dystonia. JAMA Neurol. 2014, 71, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salamon, A.; Nagy, Z.F.; Pál, M.; Szabó, M.; Csősz, Á.; Szpisjak, L.; Gárdián, G.; Zádori, D.; Széll, M.; Klivényi, P. Genetic Screening of a Hungarian Cohort with Focal Dystonia Identified Several Novel Putative Pathogenic Gene Variants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zech, M.; Gross, N.; Jochim, A.; Castrop, F.; Kaffe, M.; Dresel, C.; Lichtner, P.; Peters, A.; Gieger, C.; Meitinger, T.; et al. Rare Sequence Variants in ANO3 and GNAL in a Primary Torsion Dystonia Series and Controls. Mov. Disord. 2014, 29, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steel, D.; Zech, M.; Zhao, C.; Barwick, K.E.S.; Burke, D.; Demailly, D.; Kumar, K.R.; Zorzi, G.; Nardocci, N.; Kaiyrzhanov, R.; et al. Loss-of-Function Variants in HOPS Complex Genes VPS16 and VPS41 Cause Early Onset Dystonia Associated with Lysosomal Abnormalities. Ann. Neurol. 2020, 88, 867–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.-X.; Jiang, L.-T.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.-L.; Pan, Y.-G.; Pan, L.-Z.; Nie, Z.-Y.; Wan, X.-H.; Jin, L.-J. Mutation Screening of VPS16 Gene in Patients with Isolated Dystonia. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2021, 83, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, B.D.; Groth, C.L.; Sillau, S.H.; Pirio Richardson, S.; Norris, S.A.; Junker, J.; Brüggemann, N.; Agarwal, P.; Barbano, R.L.; Espay, A.J.; et al. Risk of Spread in Adult-Onset Isolated Focal Dystonia: A Prospective International Cohort Study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2020, 91, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hok, P.; Veverka, T.; Hluštík, P.; Nevrlý, M.; Kaňovský, P. The Central Effects of Botulinum Toxin in Dystonia and Spasticity. Toxins 2021, 13, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Flynn, L.C.; Simonyan, K. Short- and Long-Term Central Action of Botulinum Neurotoxin Treatment in Laryngeal Dystonia. Neurology 2022, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakin, E.; Simpson, D.M. Botulinum Toxin Therapy in Writer’s Cramp and Musician’s Dystonia. Toxins 2021, 13, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, G.S.; Rodrigues, F.B.; Marques, R.E.; Castelão, M.; Ferreira, J.; Sampaio, C.; Moore, A.P.; Costa, J. Botulinum Toxin Type A Therapy for Blepharospasm. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Castaneda, J.; Jankovic, J. Long-Term Efficacy, Safety, and Side Effect Profile of Botulinum Toxin in Dystonia: A 20-Year Follow-Up. Toxicon 2014, 90, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, F.B.; Duarte, G.S.; Marques, R.E.; Castelão, M.; Ferreira, J.; Sampaio, C.; Moore, A.P.; Costa, J. Botulinum Toxin Type A Therapy for Cervical Dystonia. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, D.M.; Hallett, M.; Ashman, E.J.; Comella, C.L.; Green, M.W.; Gronseth, G.S.; Armstrong, M.J.; Gloss, D.; Potrebic, S.; Jankovic, J.; et al. Practice Guideline Update Summary: Botulinum Neurotoxin for the Treatment of Blepharospasm, Cervical Dystonia, Adult Spasticity, and Headache: Report of the Guideline Development Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2016, 86, 1818–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erro, R.; Picillo, M.; Pellecchia, M.T.; Barone, P. Improving the Efficacy of Botulinum Toxin for Cervical Dystonia: A Scoping Review. Toxins 2023, 15, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jinnah, H.A.; Comella, C.L.; Perlmutter, J.; Lungu, C.; Hallett, M. Longitudinal Studies of Botulinum Toxin in Cervical Dystonia: Why Do Patients Discontinue Therapy? Toxicon 2018, 147, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessler, K.R.; Skutta, M.; Benecke, R. Long-Term Treatment of Cervical Dystonia with Botulinum Toxin A: Efficacy, Safety, and Antibody Frequency. J. Neurol. 1999, 246, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, E.; Banerjee, P.S.; Asghar, A.; Gupta, N.K.; Mosahebi, A. Botulinum Toxin Type A Immunogenicity across Multiple Indications: An Overview Systematic Review. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2022, 149, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellows, S.; Jankovic, J. Immunogenicity Associated with Botulinum Toxin Treatment. Toxins 2019, 11, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albanese, A.; Asmus, F.; Bhatia, K.P.; Elia, A.E.; Elibol, B.; Filippini, G.; Gasser, T.; Krauss, J.K.; Nardocci, N.; Newton, A.; et al. EFNS Guidelines on Diagnosis and Treatment of Primary Dystonias. Eur. J. Neurol. 2011, 18, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Zheng, Z.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, J.; Lu, G. Deep Brain Stimulation Treating Dystonia: A Systematic Review of Targets, Body Distributions and Etiology Classifications. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 757579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filip, P.; Jech, R.; Fečíková, A.; Havránková, P.; Růžička, F.; Mueller, K.; Urgošík, D. Restoration of Functional Network State towards More Physiological Condition as the Correlate of Clinical Effects of Pallidal Deep Brain Stimulation in Dystonia. Brain Stimulat. 2022, 15, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkmann, J.; Mueller, J.; Deuschl, G.; Kühn, A.A.; Krauss, J.K.; Poewe, W.; Timmermann, L.; Falk, D.; Kupsch, A.; Kivi, A.; et al. Pallidal Neurostimulation in Patients with Medication-Refractory Cervical Dystonia: A Randomised, Sham-Controlled Trial. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupsch, A.; Benecke, R.; Müller, J.; Trottenberg, T.; Schneider, G.-H.; Poewe, W.; Eisner, W.; Wolters, A.; Müller, J.-U.; Deuschl, G.; et al. Pallidal Deep-Brain Stimulation in Primary Generalized or Segmental Dystonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 1978–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidailhet, M.; Vercueil, L.; Houeto, J.-L.; Krystkowiak, P.; Benabid, A.-L.; Cornu, P.; Lagrange, C.; Tézenas Du Montcel, S.; Dormont, D.; Grand, S.; et al. Bilateral Deep-Brain Stimulation of the Globus Pallidus in Primary Generalized Dystonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Zhao, M.; Yan, X.; Li, T.; Chen, H.; Li, J.; Cao, S.; Guo, H.; Liu, S. Bilateral Subthalamic Nucleus Deep Brain Stimulation for Refractory Isolated Cervical Dystonia. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odorfer, T.M.; Volkmann, J. Deep Brain Stimulation for Focal or Segmental Craniocervical Dystonia in Patients Who Have Failed Botulinum Neurotoxin Therapy—A Narrative Review of the Literature. Toxins 2023, 15, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirio Richardson, S.; Jinnah, H.A. New Approaches to Discovering Drugs That Treat Dystonia. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2019, 14, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-Y.; Sy, H.-N.; Wu, S.-L. Zolpidem Improves Akinesia, Dystonia and Dyskinesia in Advanced Parkinson’s Disease. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2008, 15, 955–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-hadid, O.; Jimenez-Shahed, J. An Overview of the Pharmacotherapeutics for Dystonia: Advances over the Past Decade. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2022, 23, 1927–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewczyk-Roszczenko, O.; Barlev, N.A. The Role of P53 in Nanoparticle-Based Therapy for Cancer. Cells 2023, 12, 2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batla, A.; Stamelou, M.; Bhatia, K.P. Treatment of Focal Dystonia. Curr. Treat. Options Neurol. 2012, 14, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




