Submitted:
27 May 2025
Posted:
28 May 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Current PFAS Detection Methods
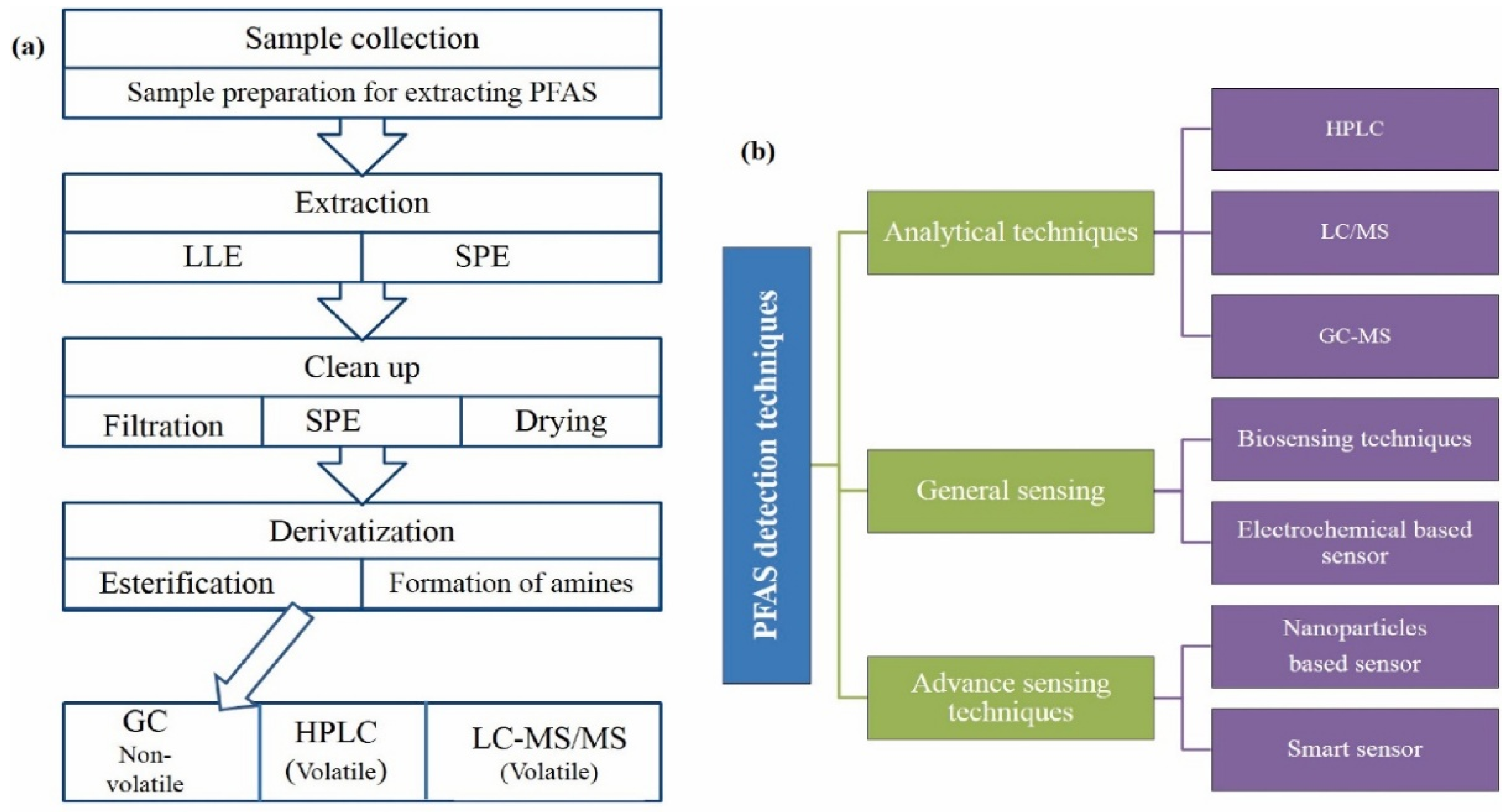
2.1. PFAS Sample Preparation and Extraction
2.2. Analysis of PFAS via Chromatography
2.3. PFAS Detection by Sensors
2.4. Nanomaterial Based Sensor
2.5. PFAS Detection by Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy
3. Conclusions
References
- R. C. Buck et al., “Perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the environment: terminology, classification, and origins,” Integrated environmental assessment and management, vol. 7, no. 4, pp. 513–541, 2011.
- C. Zhang, K. Yan, C. Fu, H. Peng, C. J. Hawker, and A. K. Whittaker, “Biological utility of fluorinated compounds: from materials design to molecular imaging, therapeutics and environmental remediation,” Chemical Reviews, vol. 122, no. 1, pp. 167–208, 2021.
- M. Li et al., “Theoretical studies of perfluorochemicals (PFCs) adsorption mechanism on the carbonaceous surface,” Chemosphere, vol. 235, pp. 606–615, 2019.
- Z. Du et al., “Adsorption behavior and mechanism of perfluorinated compounds on various adsorbents—A review,” Journal of hazardous materials, vol. 274, pp. 443–454, 2014.
- J. Walkowiak-Kulikowska, “Poly/Perfluorinated Alkyl Substances (PFASs)–Synthetic Methods, Properties and Applications,” Perfluoroalkyl Substances: Synthesis, Applications, Challenges and Regulations, 2022.
- F. Dixit et al., “Removal of zwitterionic PFAS by MXenes: comparisons with anionic, nonionic, and PFAS-specific resins,” Environmental Science & Technology, vol. 56, no. 10, pp. 6212–6222, 2022.
- I. M. Militao, F. A. Roddick, R. Bergamasco, and L. Fan, “Removing PFAS from aquatic systems using natural and renewable material-based adsorbents: A review,” Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, vol. 9, no. 4, p. 105271, 2021.
- R. Mueller and V. Yingling, “History and use of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS),” Interstate Technology & Regulatory Council, 2017.
- B. Bokkers et al., “Per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in food contact materials,” 2019.
- K. A. Barzen-Hanson, “Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) and Aqueous Film-Forming Foam Impacted Sites: New PFAS Discovery and Sorption of Anionic, Zwitterionic, and Cationic PFASs,” 2017.
- F. Li et al., “Short-chain per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances in aquatic systems: Occurrence, impacts and treatment,” Chemical Engineering Journal, vol. 380, p. 122506, 2020.
- C. Fang, X. Zhang, Z. Dong, L. Wang, M. Megharaj, and R. Naidu, “Smartphone app-based/portable sensor for the detection of fluoro-surfactant PFOA,” Chemosphere, vol. 191, pp. 381–388, Jan. 2018. [CrossRef]
- J. Radjenovic, N. Duinslaeger, S. S. Avval, and B. P. Chaplin, “Facing the challenge of poly-and perfluoroalkyl substances in water: is electrochemical oxidation the answer?,” Environmental Science & Technology, vol. 54, no. 23, pp. 14815–14829, 2020.
- A. He et al., “Vital environmental sources for multitudinous fluorinated chemicals: new evidence from industrial byproducts in multienvironmental matrices in a fluorochemical manufactory,” Environmental Science & Technology, vol. 56, no. 23, pp. 16789–16800, 2022.
- H. Zhu and K. Kannan, “A pilot study of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances in automotive lubricant oils from the United States,” Environmental Technology & Innovation, vol. 19, p. 100943, 2020.
- K. L. Vorst, N. Saab, P. Silva, G. Curtzwiler, and A. Steketee, “Risk assessment of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in food: Symposium proceedings,” Trends in Food Science & Technology, vol. 116, pp. 1203–1211, 2021.
- A. F. Zakaria, N. Yahaya, M. Raznisyafiq, S. H. Loh, and S. Kamaruzaman, “Recent advances in applications of hybrid natural polymers as adsorbent for perfluorinated compounds removal–review paper,” Journal of Polymer Research, vol. 29, no. 1, pp. 1–19, 2022.
- H. A. Langberg et al., “Paper product production identified as the main source of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in a Norwegian lake: Source and historic emission tracking,” Environmental Pollution, vol. 273, p. 116259, 2021.
- Y.-C. Lin, W. W.-P. Lai, H. Tung, and A. Y.-C. Lin, “Occurrence of pharmaceuticals, hormones, and perfluorinated compounds in groundwater in Taiwan,” Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, vol. 187, no. 5, pp. 1–19, 2015.
- E. Papadopoulou et al., “Sampling strategy for estimating human exposure pathways to consumer chemicals,” Emerging Contaminants, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 26–36, 2016.
- Md. A. Ahmed, M. Hossain, and M. Islam, Prediction of Solid Waste Generation Rate and Determination of Future Waste Characteristics at South-western Region of Bangladesh Using Artificial Neural Network. KUET, Khulna, Bangladesh: WasteSafe 2017, KUET, Khulna, Bangladesh, 2017.
- T. Stoiber, S. Evans, and O. V. Naidenko, “Disposal of products and materials containing per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS): A cyclical problem,” Chemosphere, vol. 260, p. 127659, 2020.
- M. A. Ahmed and S. D. Chakrabarti, “SCENARIO OF EXISTING SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT PRACTICES AND INTEGRATED SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT MODEL FOR DEVELOPING COUNTRY WITH REFERENCE TO JHENAIDAH MUNICIPALITY, BANGLADESH,” presented at the 4 th International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2018), Khulna, Bangladesh: Department of Civil Engg., KUET, Feb. 2018.
- S. Garg et al., “A review on the sources, occurrence and health risks of per-/poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) arising from the manufacture and disposal of electric and electronic products,” Journal of Water Process Engineering, vol. 38, p. 101683, 2020.
- D. Page, J. Vanderzalm, A. Kumar, K. Y. Cheng, A. H. Kaksonen, and S. Simpson, “Risks of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) for sustainable water recycling via aquifers,” Water, vol. 11, no. 8, p. 1737, 2019.
- M. A. Ahmed and S. M. Moniruzzaman, “A STUDY ON PLASTIC WASTE RECYCLING PROCESS IN KHULNA CITY,” presented at the 4 th International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2018), Khulna, Bangladesh: Department of Civil Engg., KUET, Feb. 2018.
- C. Berg et al., “Developing innovative treatment technologies for PFAS-containing wastes,” Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association, vol. 72, no. 6, pp. 540–555, 2022.
- M. A. Ahmed, P. Roy, M. H. Shah, D. P. Argha, D. Datta, and R. H. Riyad, “Recycling of cotton dust for organic farming is a pivotal replacement of chemical fertilizers by composting and its quality analysis,” ERT, vol. 4, no. 2, Art. no. 2, Jun. 2021. [CrossRef]
- P. Roy, Md. A. Ahmed, and Md. H. Shah, “Biogas generation from kitchen and vegetable waste in replacement of traditional method and its future forecasting by using ARIMA model,” Waste Dispos. Sustain. Energy, vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 165–175, Jun. 2021. [CrossRef]
- C. Zhang et al., “Turning Waste into Wealth: An Efficient Platform for Capturing, Recycling and Reusing Perfluorinated Compounds,” 2023.
- M. A. Ahmed, D. B. P. Argha, M. R. Rashid, and R. H. Riyad, “Forms, Importance and Sources of Dissolved Organic Nitrogen (DON) in the Environment: A Review,” SVU-International Journal of Engineering Sciences and Applications, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 18–27, Dec. 2024. [CrossRef]
- M. N. Goukeh and N. Alamdari, “Removal of Contaminants in Stormwater via Subsurface-Flow Wetlands: A Review with Focus on Nutrients, Heavy Metals, and PFAS,” Journal of Environmental Engineering, vol. 150, no. 3, p. 03124001, 2024.
- K. Sivagami et al., “Electrochemical-based approaches for the treatment of forever chemicals: Removal of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from wastewater,” Science of The Total Environment, vol. 861, p. 160440, 2023.
- J. Kearns, “The role of chemical exposures in reducing the effectiveness of water–sanitation–hygiene interventions in Bangladesh, Kenya, and Zimbabwe,” Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Water, vol. 7, no. 5, p. e1478, 2020.
- P. Roy, M. A. Ahmed, and A. Kumer, “AN OVERVIEW OF HYGIENE PRACTICES AND HEALTH RISKS RELATED TO STREET FOODS AND DRINKING WATER FROM ROADSIDE RESTAURANTS OF KHULNA CITY OF BANGLADESH,” EJERE, vol. 3, no. 2, Art. no. 2, Dec. 2019, Accessed: Aug. 08, 2023. [Online]. Available online: https://dergipark.org.tr/en/pub/ejere/issue/49620/590483.
- M. Dettori, A. Arghittu, G. Deiana, P. Castiglia, and A. Azara, “The revised European Directive 2020/2184 on the quality of water intended for human consumption. A step forward in risk assessment, consumer safety and informative communication,” Environmental Research, vol. 209, p. 112773, 2022.
- R. del V. Patrocinio and W. H. Organization, “Keeping our water clean: the case of water contamination in the Veneto Region, Italy,” 2017.
- S. Modak, H. Mokarizadeh, E. Karbassiyazdi, A. Hosseinzadeh, and M. R. Esfahani, “The AI-assisted removal and sensor-based detection of contaminants in the aquatic environment,” in Artificial Intelligence and Data Science in Environmental Sensing, Elsevier, 2022, pp. 211–244.
- A. Hosseinzadeh, A. Altaee, X. Li, and J. L. Zhou, “Machine learning-based modeling and analysis of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances controlling systems in protecting water resources,” Current Opinion in Chemical Engineering, vol. 42, p. 100983, 2023.
- D. B. P. Argha and M. A. Ahmed, “A Machine Learning Approach to Understand the Impact of Temperature and Rainfall Change on Concrete Pavement Performance Based on LTPP Data,” SVU-International Journal of Engineering Sciences and Applications, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 150–155, Jun. 2024. [CrossRef]
- J. Roostaei, S. Colley, R. Mulhern, A. A. May, and J. M. Gibson, “Predicting the risk of GenX contamination in private well water using a machine-learned Bayesian network model,” Journal of Hazardous Materials, vol. 411, p. 125075, 2021.
- Z. Lin and W.-C. Chou, “Machine learning and artificial intelligence in toxicological sciences,” Toxicological Sciences, vol. 189, no. 1, pp. 7–19, 2022.
- S. Rainieri, N. Conlledo, T. Langerholc, E. Madorran, M. Sala, and A. Barranco, “Toxic effects of perfluorinated compounds at human cellular level and on a model vertebrate,” Food and Chemical Toxicology, vol. 104, pp. 14–25, 2017.
- D. Longpré, L. Lorusso, C. Levicki, R. Carrier, and P. Cureton, “PFOS, PFOA, LC-PFCAS, and certain other PFAS: A focus on Canadian guidelines and guidance for contaminated sites management,” Environmental Technology & Innovation, vol. 18, p. 100752, 2020.
- US EPA, “Drinking water health advisory for perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS).” Office of Water (4304T), Health and Ecological Criteria, 2016.
- A. L. Hagstrom et al., “Yale School of Public Health Symposium: an overview of the challenges and opportunities associated with per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS),” Science of the Total Environment, vol. 778, p. 146192, 2021.
- A. Nadal, I. Quesada, E. Tuduri, R. Nogueiras, and P. Alonso-Magdalena, “Endocrine-disrupting chemicals and the regulation of energy balance,” Nature Reviews Endocrinology, vol. 13, no. 9, pp. 536–546, 2017.
- M. Trojanowicz and M. Koc, “Recent developments in methods for analysis of perfluorinated persistent pollutants,” Microchimica Acta, vol. 180, no. 11, pp. 957–971, 2013.
- B. M.b. et al., “Detection of PFAS via surface-enhanced Raman scattering: Challenges and future perspectives,” Sustainable Chemistry for the Environment, vol. 3, p. 100031, Sep. 2023. [CrossRef]
- L. T. Miaz et al., “Temporal trends of suspect-and target-per/polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), extractable organic fluorine (EOF) and total fluorine (TF) in pooled serum from first-time mothers in Uppsala, Sweden, 1996–2017,” Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts, vol. 22, no. 4, pp. 1071–1083, 2020.
- S. Ganesan, C. Chawengkijwanich, M. Gopalakrishnan, and D. Janjaroen, “Detection methods for sub-nanogram level of emerging pollutants—Per and polyfluoroalkyl substances,” Food and Chemical Toxicology, vol. 168, p. 113377, Oct. 2022. [CrossRef]
- L. Wang, H. Sun, L. Yang, C. He, W. Wu, and S. Sun, “Liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry analysis of perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acids and perfluorooctanesulfonate in bivalve shells: Extraction method optimization,” Journal of chromatography A, vol. 1217, no. 4, pp. 436–442, 2010.
- M. D. Malinsky, C. B. Jacoby, and W. K. Reagen, “Determination of perfluorinated compounds in fish fillet homogenates: method validation and application to fillet homogenates from the Mississippi River,” Analytica chimica acta, vol. 683, no. 2, pp. 248–257, 2011.
- J. Janda, K. Nödler, H.-J. Brauch, C. Zwiener, and F. T. Lange, “Robust trace analysis of polar (C2-C8) perfluorinated carboxylic acids by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: method development and application to surface water, groundwater and drinking water,” Environmental Science and Pollution Research, vol. 26, no. 8, pp. 7326–7336, 2019.
- Y. Wan et al., “Perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs) in water and sediment from the coastal regions of Shandong peninsula, China,” Environmental monitoring and assessment, vol. 189, no. 3, pp. 1–14, 2017.
- Y. Cao et al., “1000-fold preconcentration of per-and polyfluorinated alkyl substances within 10 minutes via electrochemical aerosol formation,” Analytical chemistry, vol. 91, no. 22, pp. 14352–14358, 2019.
- S. X. L. Goh and H. K. Lee, “Automated bundled hollow fiber array-liquid-phase microextraction with liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometric analysis of perfluorinated compounds in aqueous media,” Analytica chimica acta, vol. 1019, pp. 74–83, 2018.
- C. Moreta and M. T. Tena, “Determination of perfluorinated alkyl acids in corn, popcorn and popcorn bags before and after cooking by focused ultrasound solid–liquid extraction, liquid chromatography and quadrupole-time of flight mass spectrometry,” Journal of Chromatography A, vol. 1355, pp. 211–218, 2014.
- G. W. Curtzwiler, P. Silva, A. Hall, A. Ivey, and K. Vorst, “Significance of Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Food Packaging,” Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management, vol. 17, no. 1, pp. 7–12, 2021. [CrossRef]
- C. A. Moody, W. C. Kwan, J. W. Martin, D. C. Muir, and S. A. Mabury, “Determination of perfluorinated surfactants in surface water samples by two independent analytical techniques: liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry and 19F NMR,” Analytical chemistry, vol. 73, no. 10, pp. 2200–2206, 2001.
- G. N. Hebert, M. A. Odom, S. C. Bowman, and S. H. Strauss, “Attenuated total reflectance FTIR detection and quantification of low concentrations of aqueous polyatomic anions,” Analytical chemistry, vol. 76, no. 3, pp. 781–787, 2004.
- S. Na, R. Hai, X. Wang, N. Li, and D. Chen, “Concentrations and seasonal variations of perfluorinated compounds in sludge from three wastewater treatment plants in China,” Analytical Letters, vol. 53, no. 15, pp. 2400–2412, 2020.
- M. Wu et al., “Analysis of perfluorinated compounds in human serum from the general population in Shanghai by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS),” Chemosphere, vol. 168, pp. 100–105, 2017.
- J. Wu, M. Junaid, Z. Wang, W. Sun, and N. Xu, “Spatiotemporal distribution, sources and ecological risks of perfluorinated compounds (PFCs) in the Guanlan River from the rapidly urbanizing areas of Shenzhen, China,” Chemosphere, vol. 245, p. 125637, 2020.
- J. Wang, Y. Shi, and Y. Cai, “A highly selective dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction approach based on the unique fluorous affinity for the extraction and detection of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances coupled with high performance liquid chromatography tandem–mass spectrometry,” Journal of Chromatography A, vol. 1544, pp. 1–7, 2018.
- Guohong Deng, Yu Zhang, Xuegang Luo, and Jiayi Yang, “Direct extraction of U(VI) from a simulated saline solution by alkali-activated collagen fiber,” Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, vol. 318, no. 2, pp. 1109–1118, 2018.
- N. Park, Y. Kho, and J. Kim, “Levels of Perfluorinated Compounds in Liquid Milk Products in Korea,” Journal of Food Hygiene and Safety, vol. 36, no. 4, pp. 310–315, 2021.
- T. E. Lockwood, M. Talebi, A. Minett, S. Mills, P. A. Doble, and D. P. Bishop, “Micro solid-phase extraction for the analysis of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances in environmental waters,” Journal of Chromatography A, vol. 1604, p. 460495, 2019.
- M. Zhang et al., “Bioaccumulation and human exposure of perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs) in vegetables from the largest vegetable production base of China,” Environment international, vol. 135, p. 105347, 2020.
- L. Zheng et al., “Core-shell quantum dots coated with molecularly imprinted polymer for selective photoluminescence sensing of perfluorooctanoic acid,” Talanta, vol. 194, pp. 1–6, Mar. 2019. [CrossRef]
- L. Xiang et al., “Determination of trace perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acids in edible crop matrices: matrix effect and method development,” Journal of agricultural and food chemistry, vol. 65, no. 39, pp. 8763–8772, 2017.
- G. Riviere et al., “Food risk assessment for perfluoroalkyl acids and brominated flame retardants in the French population: results from the second French total diet study,” Science of the Total Environment, vol. 491, pp. 176–183, 2014.
- S. Dalahmeh, S. Tirgani, A. J. Komakech, C. B. Niwagaba, and L. Ahrens, “Per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in water, soil and plants in wetlands and agricultural areas in Kampala, Uganda,” Science of the Total Environment, vol. 631, pp. 660–667, 2018.
- H. Chen et al., “Occurrence and inputs of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) from rivers and drain outlets to the Bohai Sea, China,” Environmental Pollution, vol. 221, pp. 234–243, 2017.
- V. Naresh and N. Lee, “A review on biosensors and recent development of nanostructured materials-enabled biosensors,” Sensors, vol. 21, no. 4, p. 1109, 2021.
- S. Singh, V. Kumar, D. S. Dhanjal, S. Datta, R. Prasad, and J. Singh, “Biological Biosensors for Monitoring and Diagnosis,” in Microbial Biotechnology: Basic Research and Applications, J. Singh, A. Vyas, S. Wang, and R. Prasad, Eds., in Environmental and Microbial Biotechnology. Singapore: Springer, 2020, pp. 317–335. [CrossRef]
- A. Herrera-Chacon, X. Cetó, and M. del Valle, “Molecularly imprinted polymers—towards electrochemical sensors and electronic tongues,” Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, vol. 413, no. 24, pp. 6117–6140, Apr. 2021. [CrossRef]
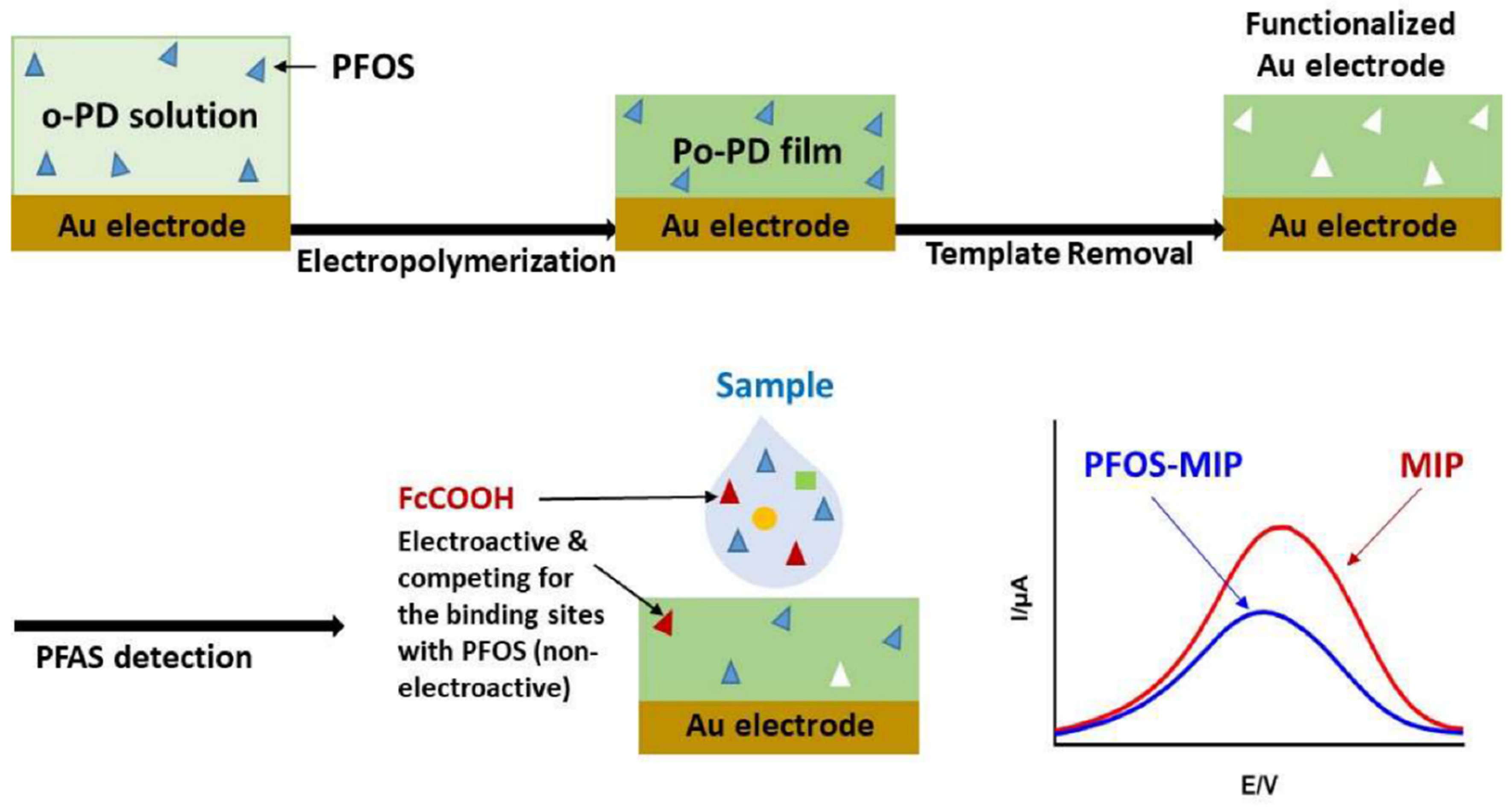
- N. Karimian, A. M. Stortini, L. M. Moretto, C. Costantino, S. Bogialli, and P. Ugo, “Electrochemosensor for Trace Analysis of Perfluorooctanesulfonate in Water Based on a Molecularly Imprinted Poly(o-phenylenediamine) Polymer,” ACS Sens., vol. 3, no. 7, pp. 1291–1298, Jul. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Q. Liu, A. Huang, N. Wang, G. Zheng, and L. Zhu, “Rapid fluorometric determination of perfluorooctanoic acid by its quenching effect on the fluorescence of quantum dots,” Journal of Luminescence, vol. 161, pp. 374–381, May 2015. [CrossRef]
- M. Takayose, K. Akamatsu, H. Nawafune, T. Murashima, and J. Matsui, “Colorimetric Detection of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) Utilizing Polystyrene-Modified Gold Nanoparticles,” Analytical Letters, vol. 45, no. 18, pp. 2856–2864, Nov. 2012. [CrossRef]
- S. Chen, A. Li, L. Zhang, and J. Gong, “Molecularly imprinted ultrathin graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets–Based electrochemiluminescence sensing probe for sensitive detection of perfluorooctanoic acid,” Analytica Chimica Acta, vol. 896, pp. 68–77, Oct. 2015. [CrossRef]
- N. Cennamo et al., “A Molecularly Imprinted Polymer on a Plasmonic Plastic Optical Fiber to Detect Perfluorinated Compounds in Water,” Sensors, vol. 18, no. 6, Art. no. 6, Jun. 2018. [CrossRef]
- J. Zhang et al., “A rapid and high-throughput quantum dots bioassay for monitoring of perfluorooctane sulfonate in environmental water samples,” Environmental Pollution, vol. 159, no. 5, pp. 1348–1353, May 2011. [CrossRef]
- Y. H. Cheng et al., “Metal–Organic Framework-Based Microfluidic Impedance Sensor Platform for Ultrasensitive Detection of Perfluorooctanesulfonate,” ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, vol. 12, no. 9, pp. 10503–10514, Mar. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Z. Jiao, J. Li, L. Mo, J. Liang, and H. Fan, “A molecularly imprinted chitosan doped with carbon quantum dots for fluorometric determination of perfluorooctane sulfonate,” Microchim Acta, vol. 185, no. 10, p. 473, Sep. 2018. [CrossRef]
- S. Suarasan et al., “Doxorubicin-Incorporated Nanotherapeutic Delivery System Based on Gelatin-Coated Gold Nanoparticles: Formulation, Drug Release, and Multimodal Imaging of Cellular Internalization,” ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, vol. 8, no. 35, pp. 22900–22913, Sep. 2016. [CrossRef]
- A. Pistocchi and R. Loos, “A map of European emissions and concentrations of PFOS and PFOA,” Environmental Science & Technology, vol. 43, no. 24, pp. 9237–9244, 2009.
- J. Li et al., “Surfactant-Sensitized Covalent Organic Frameworks-Functionalized Lanthanide-Doped Nanocrystals: An Ultrasensitive Sensing Platform for Perfluorooctane Sulfonate,” ACS Omega, vol. 4, no. 14, pp. 15947–15955, Oct. 2019. [CrossRef]
- T. Tran.T et al., “Molecularly imprinted polymer modified TiO2 nanotube arrays for photoelectrochemical determination of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS),” Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, vol. 190, pp. 745–751, Jan. 2014. [CrossRef]
- T. Huang, A. McClelland, and T. H. Zeng, “Trace PFAS Detection in Water Sources Using Silver Nanoparticles for Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS),” in 2022 IEEE 22nd International Conference on Nanotechnology (NANO), Jul. 2022, pp. 342–345. [CrossRef]
- B. Keskin, A. Üzer, and R. Apak, “Colorimetric sensing of ammonium perchlorate using methylene Blue−Modified gold nanoparticles,” Talanta, vol. 206, p. 120240, Jan. 2020. [CrossRef]
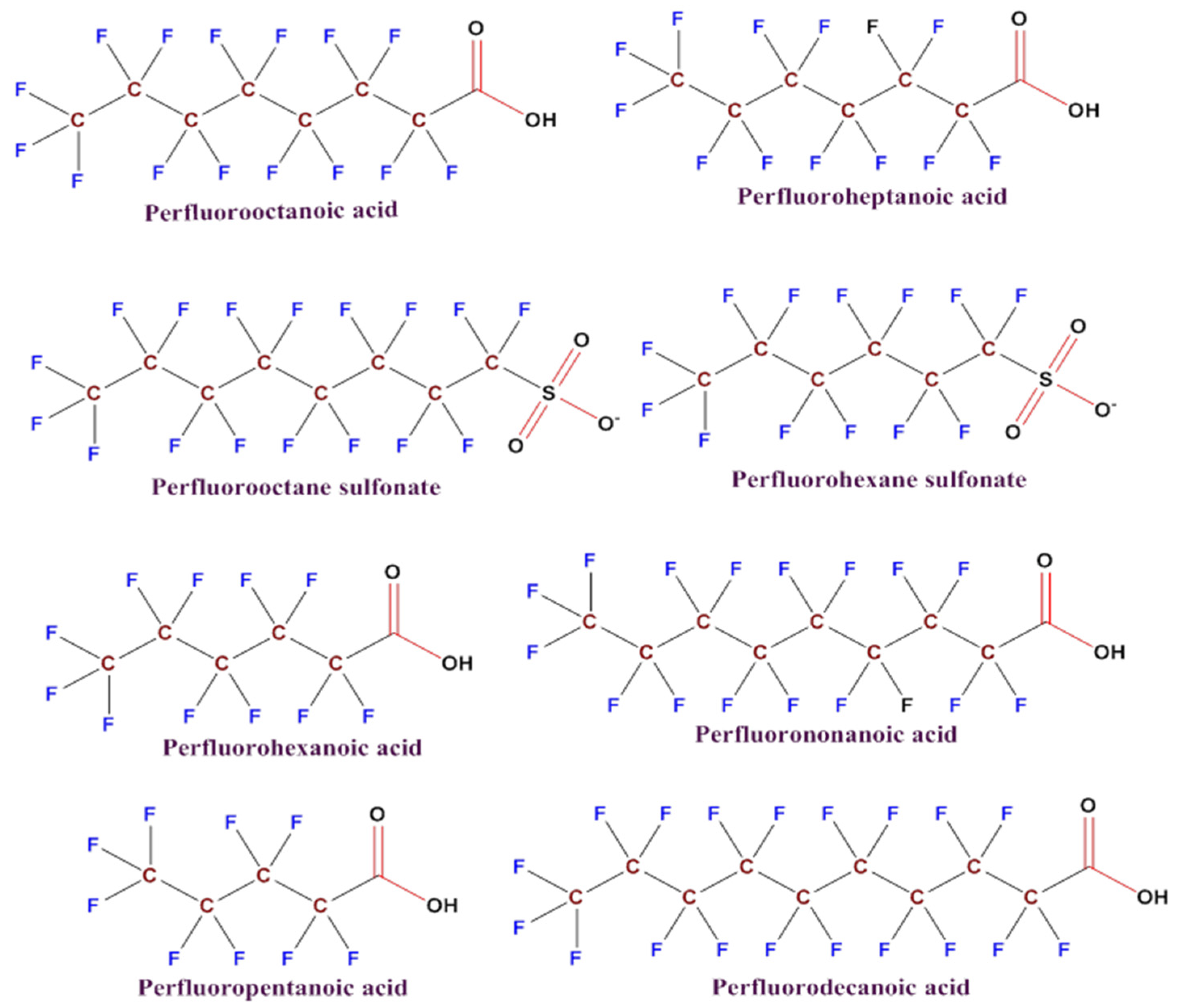
| Techniques | Samples Type | Limit of Detection (LOD) | Extraction Methods | Detected PFASs | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LC-MS/MS | Water | 0.6–8.7 ng/L | LLE | PFOA, PFOS, PFHxA, PFODA, PFHpS, PFDS | [65] |
| HPLC-MS/MS | Water | 0.01-1.15 ng/L | SPE | PFOS, PFOA, PFNA, PFHpA, PFDA, PFHxS, | [66] |
| LC-MS/MS | Milk | 0.057 ng/L (PFOA), 0.021 ng/L (PFOS) | LLE | PFNA, PFDA, PFOA, PFHpA, PFBS, PFHxS, PFOS, PFUnA | [67] |
| LC-MS/MS | Liquid Sample | 0.29–6.6 ng/L | SPE | PFOS, PFOA, PFNA, PFDA, PFBA, PFUnA, | [68] |
| LC-MS/MS | Fruits and Vegetables | 0.07 ng/g (PFOS) | SPE | PFOS, PFOA | [69] |
| HPLC-MS/MS | Sediment | 1.5–10.9 ng/L | LLE | PFOS, PFDA, PFOA, PFDoA, PFHxS, PFNA | [70] |
| HPLC-MS/MS | Cabbage, lettuce, mustard leaf, | 0.017-0.180 ng/g | Ultrasonic extraction | PFOS, PFHxS | [71] |
| LC-MS/MS | Vegetables | 0.002–3.73 ng/g | LLE | PFOS, PFOA, PFDA, PFBA, PFBS | [72] |
| HPLC-MS/MS | Surface water | 50–1790 ng/L | SPE | FOSA, MeFOSA, EtFOSA, MeFOSE | [73] |
| HPLC-MS/MS | Different Water Samples | 0.05–0.22 ng/L | SPE | PFOS and PFOA | [74] |
| Detection System | Matrix | Limit of Detection (ng/L) | Detection Range (ng/L) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spectrofluorometer | MPA-CdS QDs | 124200 | 207000–16563000 | [79] |
| Colorimetric detection | Gold nanoparticles | - | - | [80] |
| Electro chemiluminescence | Ultrathin nanosheets of carbon nitride | 10 | 20–4000 | [81] |
| Optical | Novel SPR | 210 | 0–200000 | [82] |
| Optical density | Bio-Gold Nanoparticles | 2.5 | 2.5–75 | [83] |
| Smartphone camera | Smart sensor | 0.5 | 10000–1000000 | [12] |
| Impedimetric | PFOS | 0.0005 | 0.00005–50000 | [84] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




