Submitted:
21 January 2024
Posted:
22 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
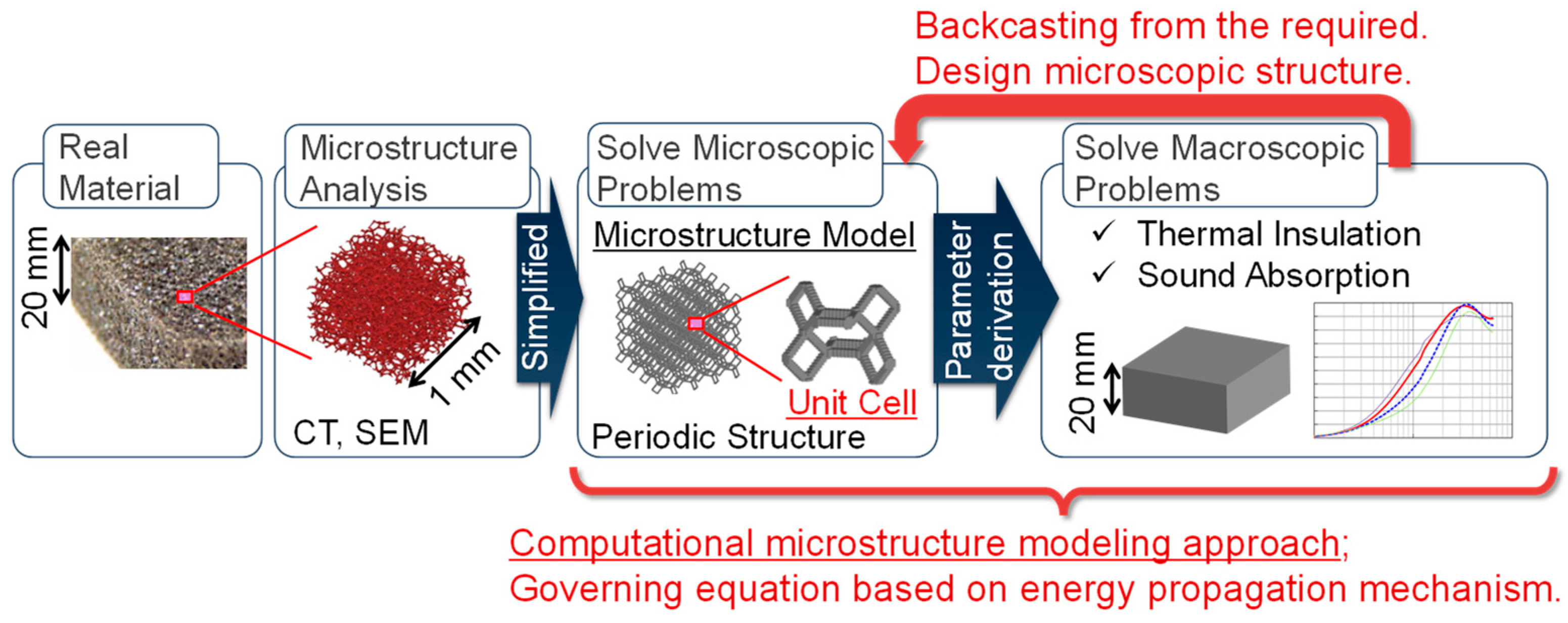
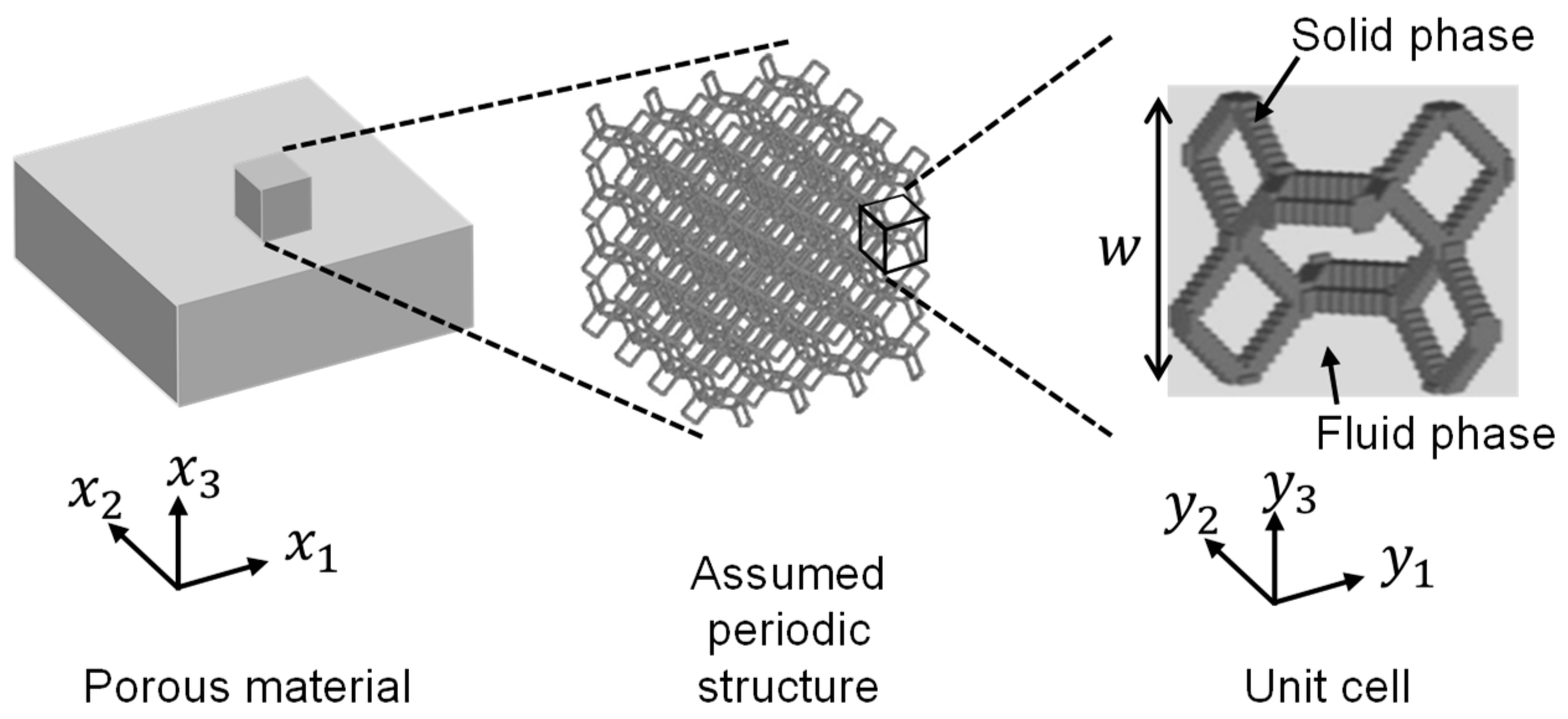
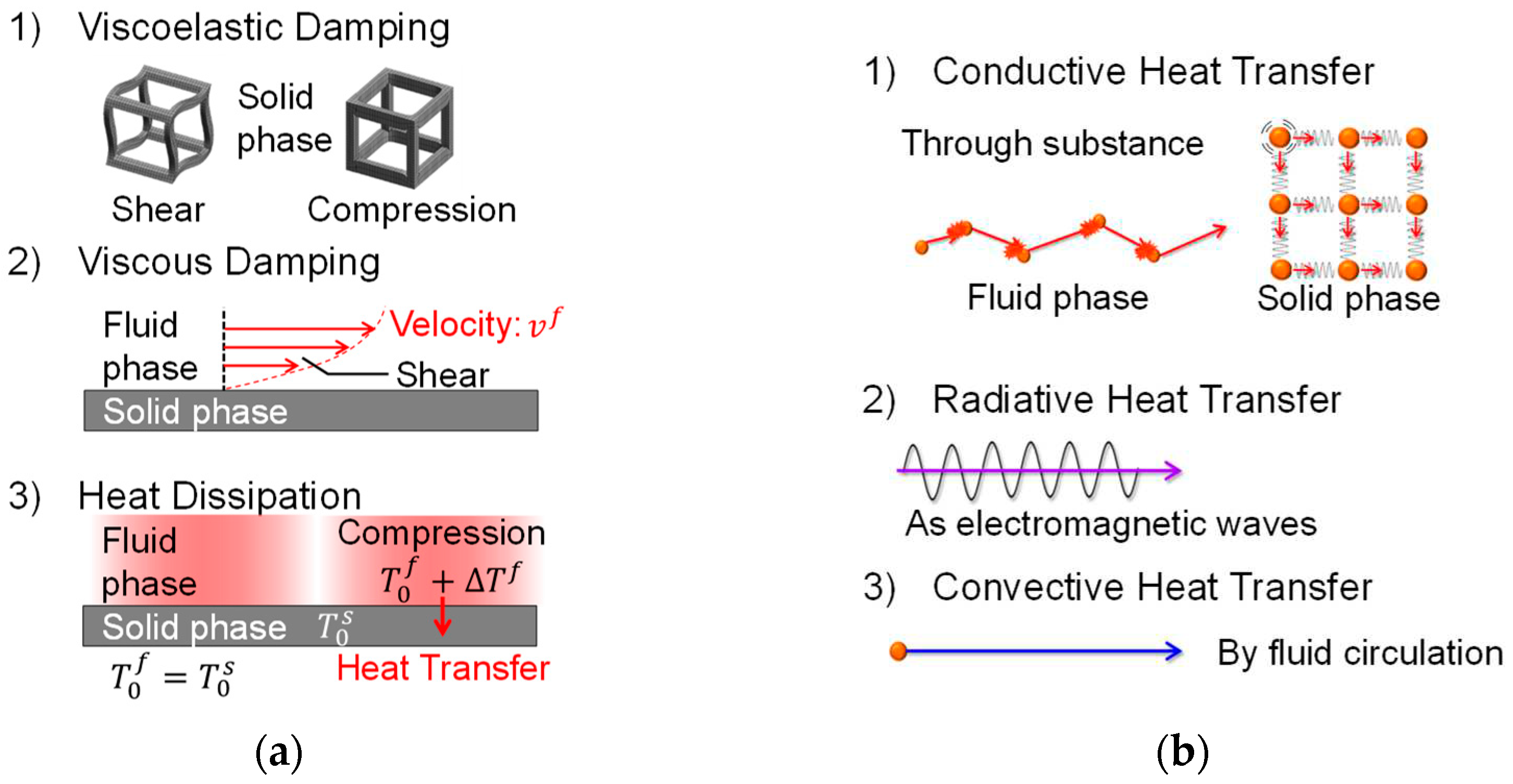
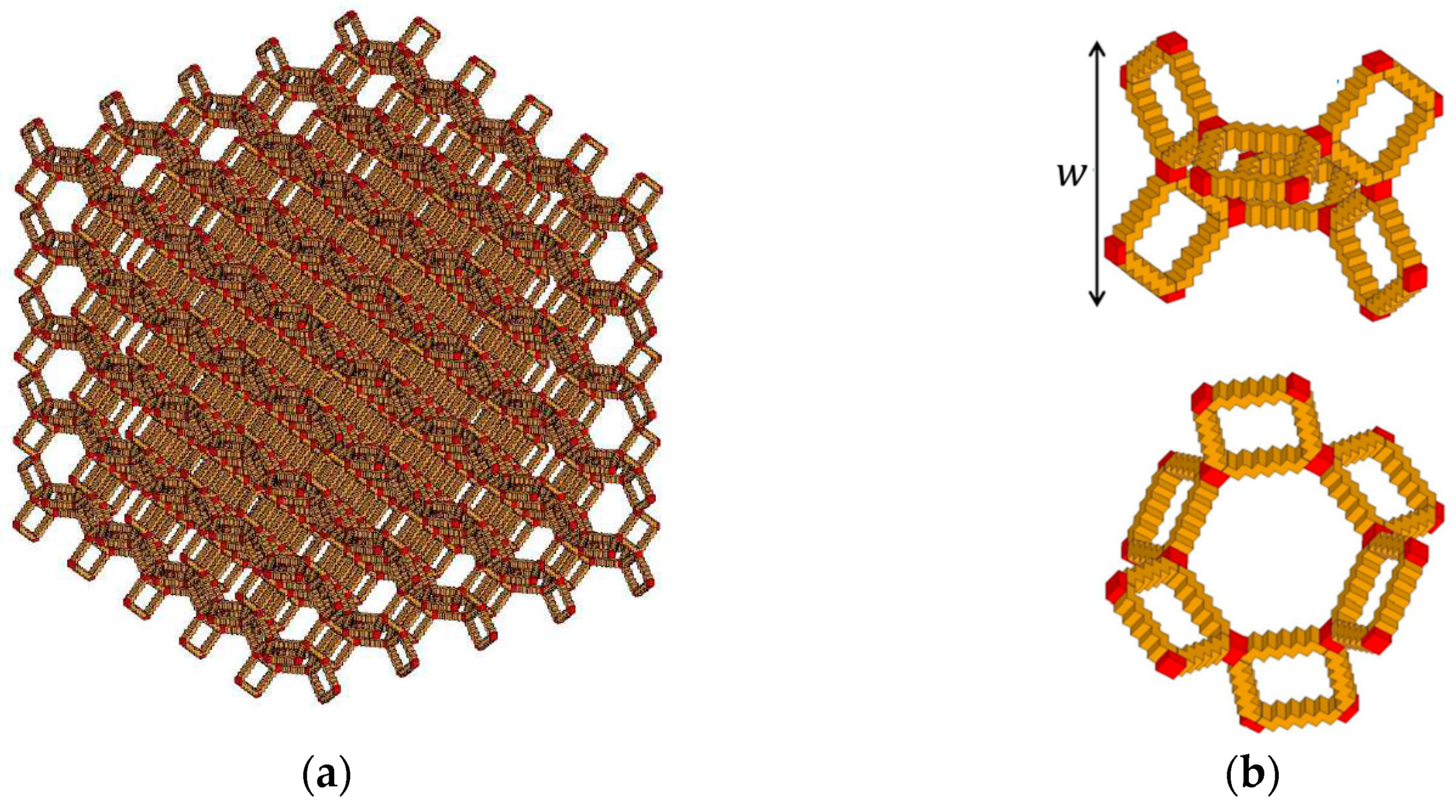
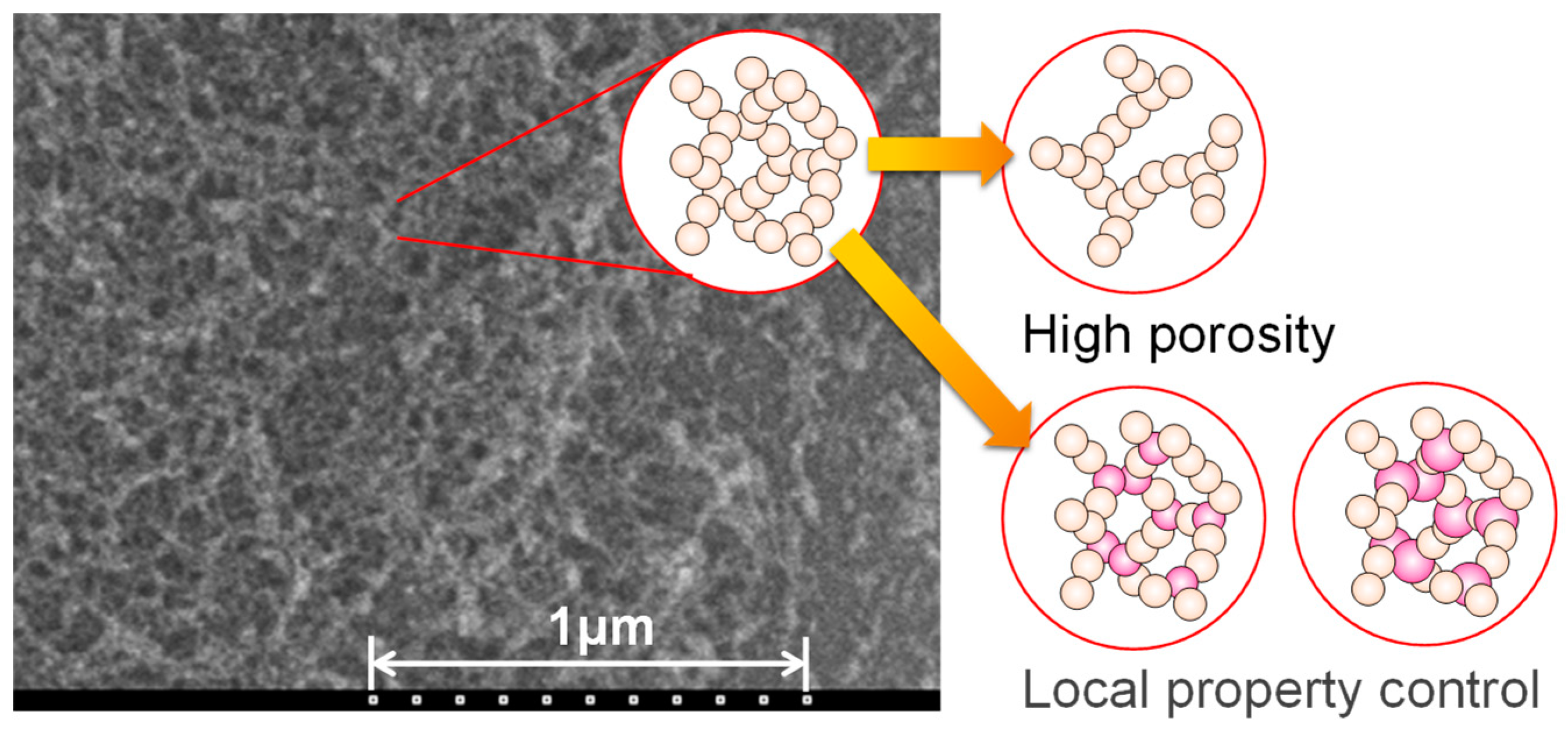
2.1. Computational microstructure modeling approach to designing porous materials
2.2. Application of computational microstructure modeling to porous materials
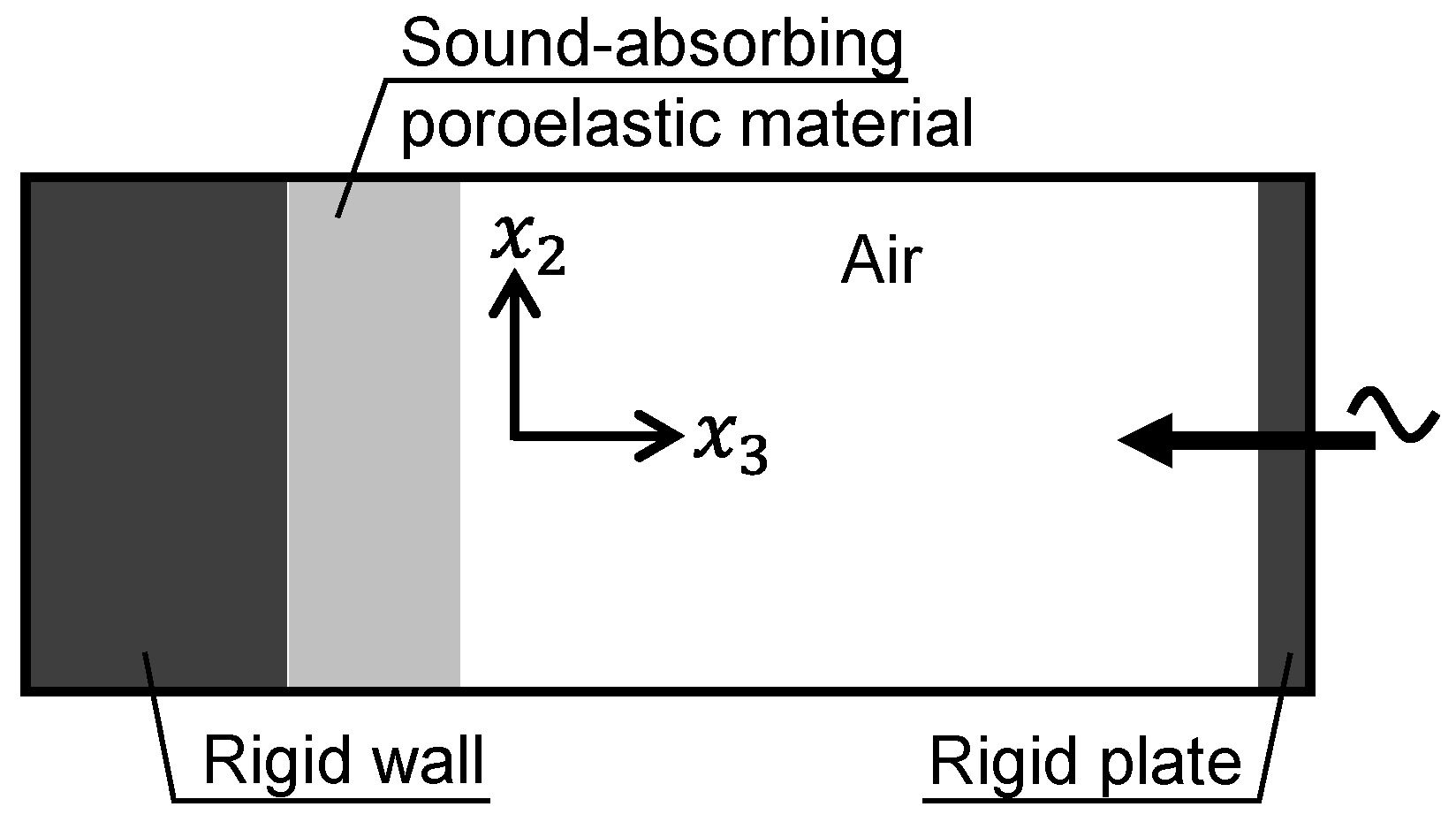
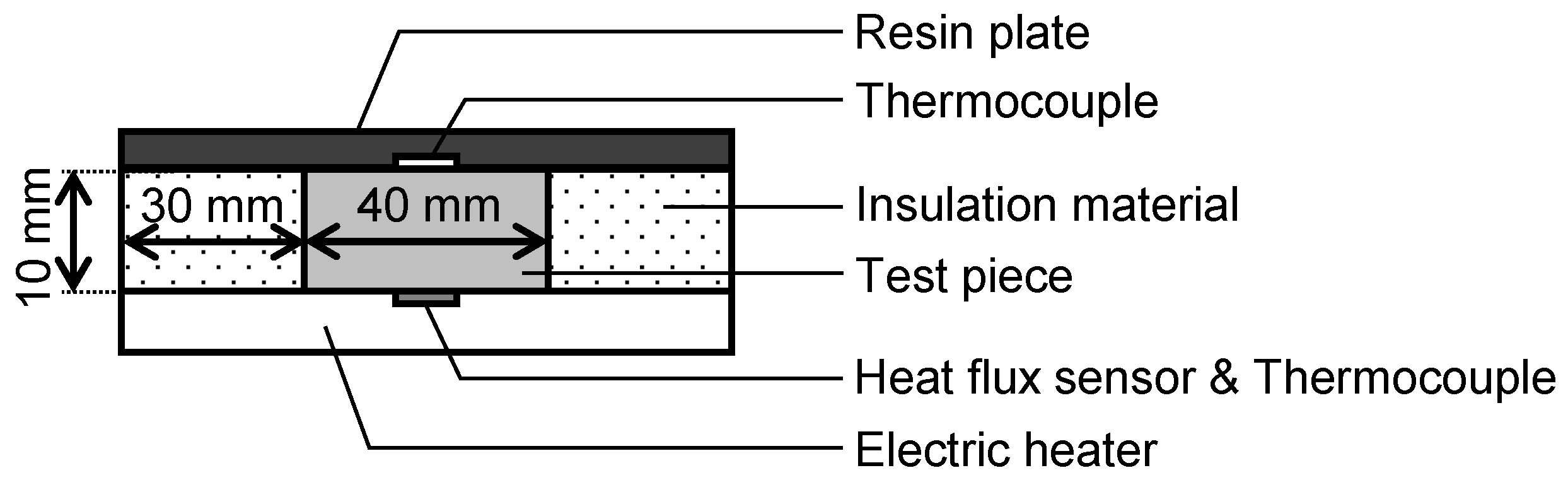
2.3. Preparation of porous materials and performance evaluation methods
3. Results and Discussion
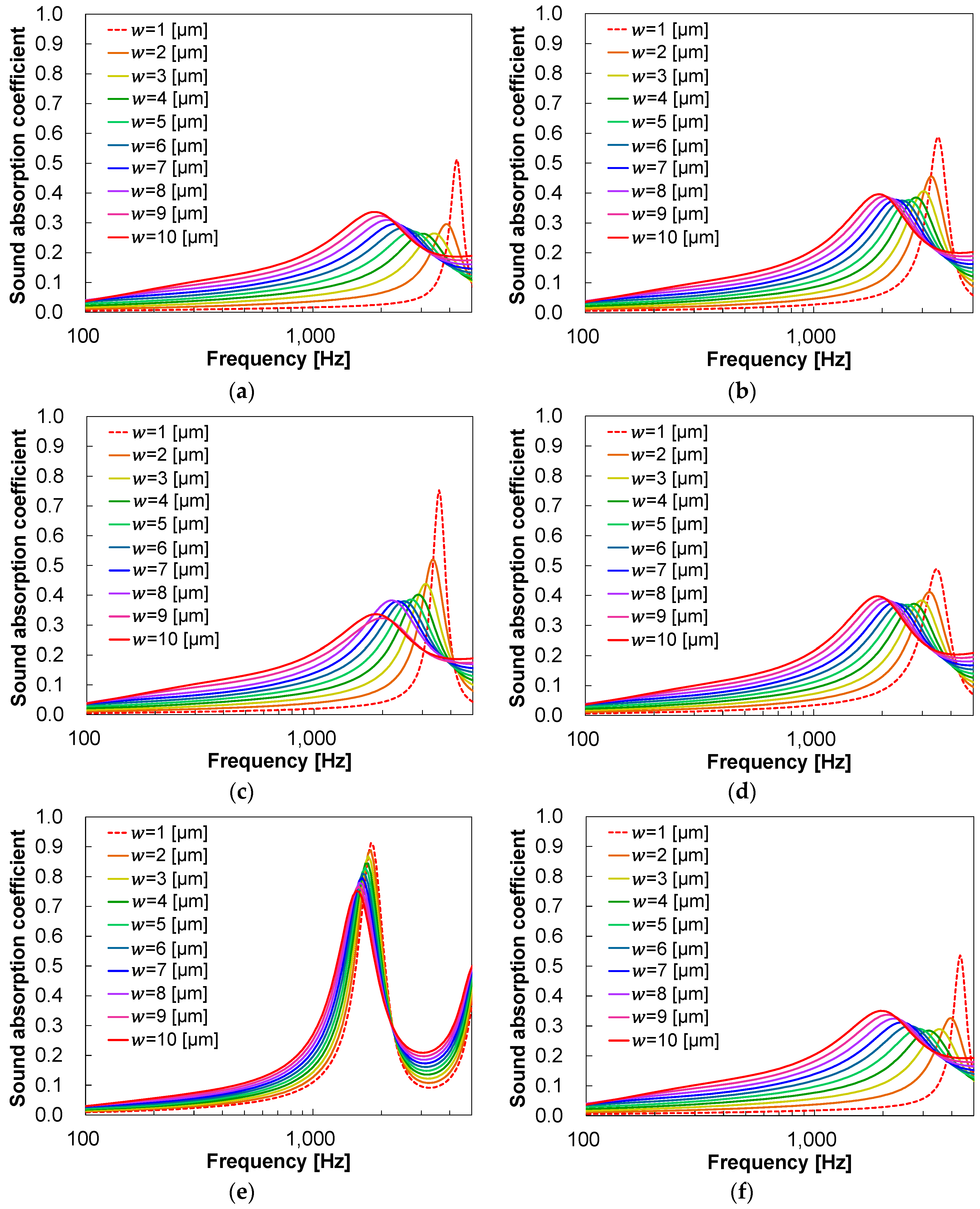
3.1. Predicted sound absorption coefficients
3.2. Performance evaluation results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, K.; van Dommelen, J.A.W.; Geers, M.G.D. Investigation of the effects of the microstructure on the sound absorption performance of polymer foams using a computational homogenization approach. Eur J Mech A Solids 2017, 61, 330–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; van Dommelen, J.A.W.; Göransson, P.; Geers, M.G.D. A homogenization approach for characterization of the fluid–solid coupling parameters in Biot׳s equations for acoustic poroelastic materials. J Sound Vib 2015, 351, 251–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieliński, T.G. Microstructure-based calculations and experimental results for sound absorbing porous layers of randomly packed rigid spherical beads. J Appl Phys 2014, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrot, C.; Chevillotte, F.; Tan Hoang, M.; Bonnet, G.; Bécot, F.-X.; Gautron, L.; Duval, A. Microstructure, transport, and acoustic properties of open-cell foam samples: experiments and three-dimensional numerical simulations. J Appl Phys 2012, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-Y.; Leamy, M.J.; Nadler, J.H. Frequency band structure and absorption predictions for multi-periodic acoustic composites. J Sound Vib 2010, 329, 1809–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.S.; Tiwari, J.; Rai, A.; Hun, D.E.; Howard, D.; Desjarlais, A.O.; Francoeur, M.; Feng, T. Solid and gas thermal conductivity models improvement and validation in various porous insulation materials. Int J Therm Sci 2023, 187, 108164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Huang, B.; Cao, B.-Y. Vibrational modes with long mean free path and large volumetric heat capacity drive higher thermal conductivity in amorphous zeolitic imidazolate Framework-4. Mater Today Phys 2021, 21, 100516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Bao, H.; Zhang, G.; Wu, Y.; Ruan, X. Molecular dynamics simulations of lattice thermal conductivity and spectral phonon mean free path of PbTe: bulk and nanostructures. Comput Mater Sci 2012, 53, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Katsura, D.; Kubota, H. Optimization of microstructure of sound-absorbing poroelastic material by homogenization method. In JSAE Annual Congress (Spring) Proceedings, 2018; p. 20185332.
- Yamakawa, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Katsura, D. Acoustic modelling technique of internal structures of a sound-absorbing foamed resin by homogenization method. In JSAE Congress (Autumn) Proceedings, 2019; p. 20196290.
- Katsura, D.; Yamamoto, T.; Yamakawa, K.; Hatakeyama, N.; Miura, R.; Okajima, J.; Inaba, K.; Ishizawa, Y.; Ochiai, H.; Yukawa, H.; Murashige, K.; Katagihara, J.; Tomotsu, J.; Ishimoto, T.; Ohshita, J. Development of thermal management and noise/vibration control material model technology by model-based research (MBR) 1st report. JSAE Annual Congress (Spring) Proceedings, 2021; p. 20215301.
- Yamakawa, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Katsura, D.; Inoue, M.; Hatakeyama, N.; Miura, R.; Okajima, J.; Inaba, K.; Ishizawa, Y.; Yukawa, H.; Ito, H.; Ishimoto, T.; Ohshita, J. Development of thermal management and noise/vibration control material model technology by model-based research (MBR) (2nd report). JSAE Annual Congress (Spring) Proceedings, 2022; p. 20225223.
- Yamamoto, T.; Maruyama, S.; Terada, K.; Izui, K.; Nishiwaki, S. A generalized macroscopic model for sound absorbing poroelastic media using a homogenization method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 2011, 200, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, R.P.; Mikelić, A. Homogenizing the acoustic properties of the seabed: Part I. Nonlinear Anal 2000, 40, 185–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clopeau, T.; Ferrín, J.L.; Gilbert, R.P.; Mikelić, A. Homogenizing the acoustic properties of the seabed, part II. Math Comput Modell 2001, 33, 821–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Palencia, E. Non-homogeneous Media and Vibration Theory, Lecture Notes in Physics; Volume 127; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, 1980. Volume 127; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, T.; Maruyama, S.; Terada, K.; Izui, K.; Nishiwaki, S. Prediction of sound absorption coefficients of poroelastic media by the homogenization method. In 40th International Congress and Exposition on Noise Control Engineering 2011, INTER-NOISE, 2011; Volume 2011; pp. 1989–1996.
- Kanamori, K.; Aizawa,M. ; Nakanishi, K.; Hanada, T. New transparent methylsilsesquioxane aerogels and xerogels with improved mechanical properties. Adv Mater 2007, 19, 1589–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, S.; Sakuma, W.; Yasui, H.; Daicho, K.; Saito, T.; Fujisawa, S.; Isogai, A.; Kanamori, K. Nanocellulose xerogels with high porosities and large specific surface areas. Front Chem 2019, 7, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
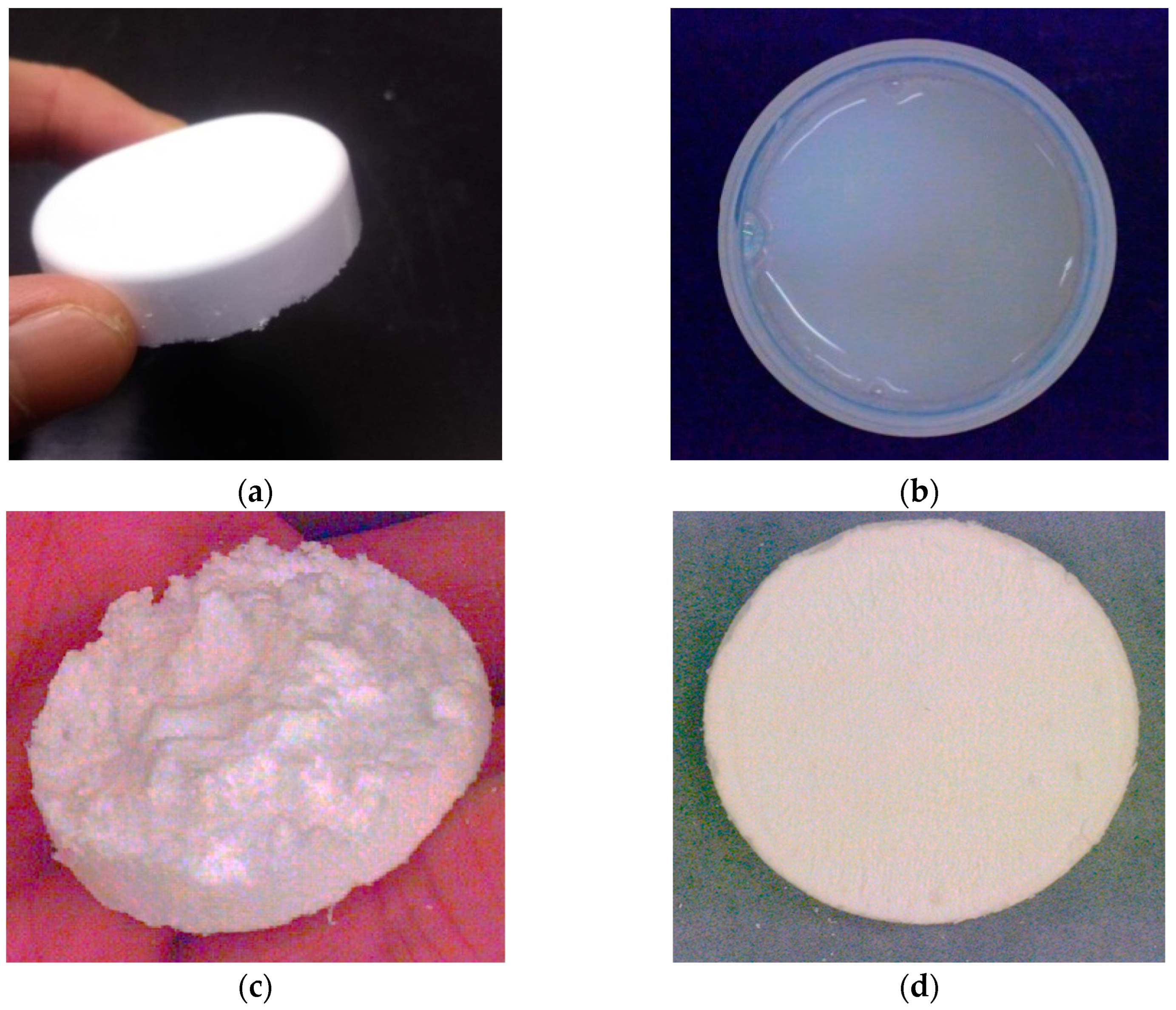
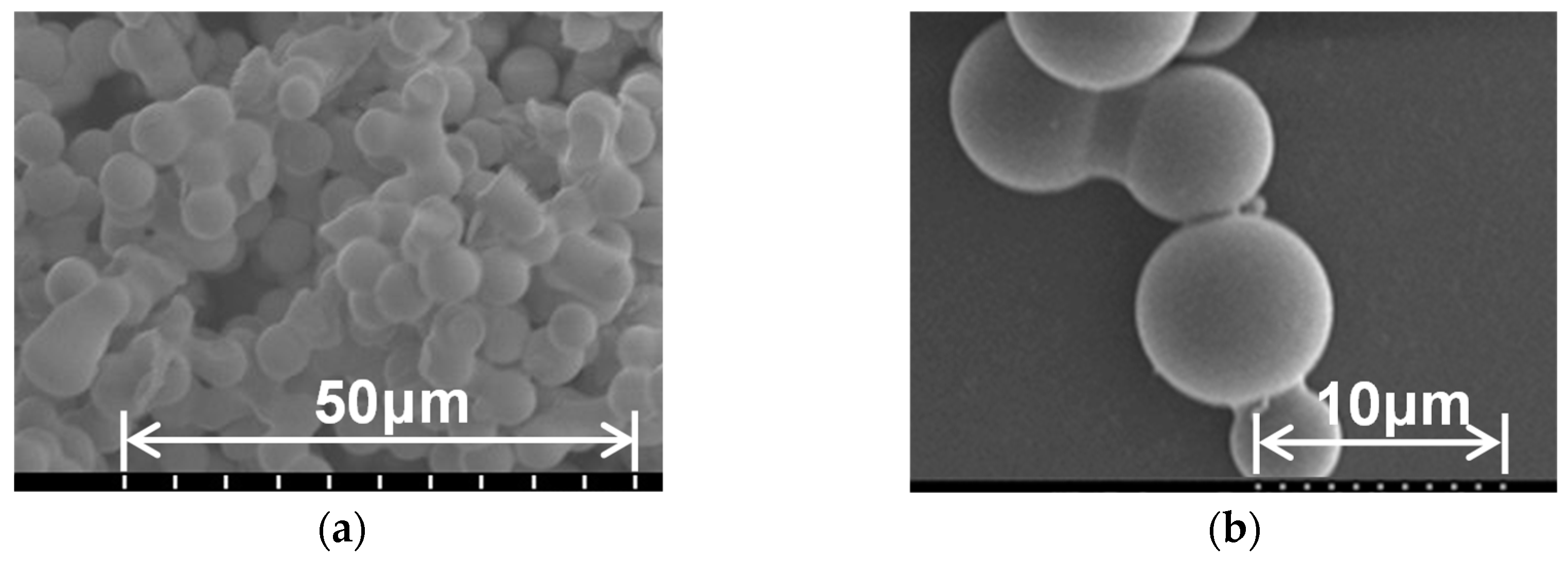
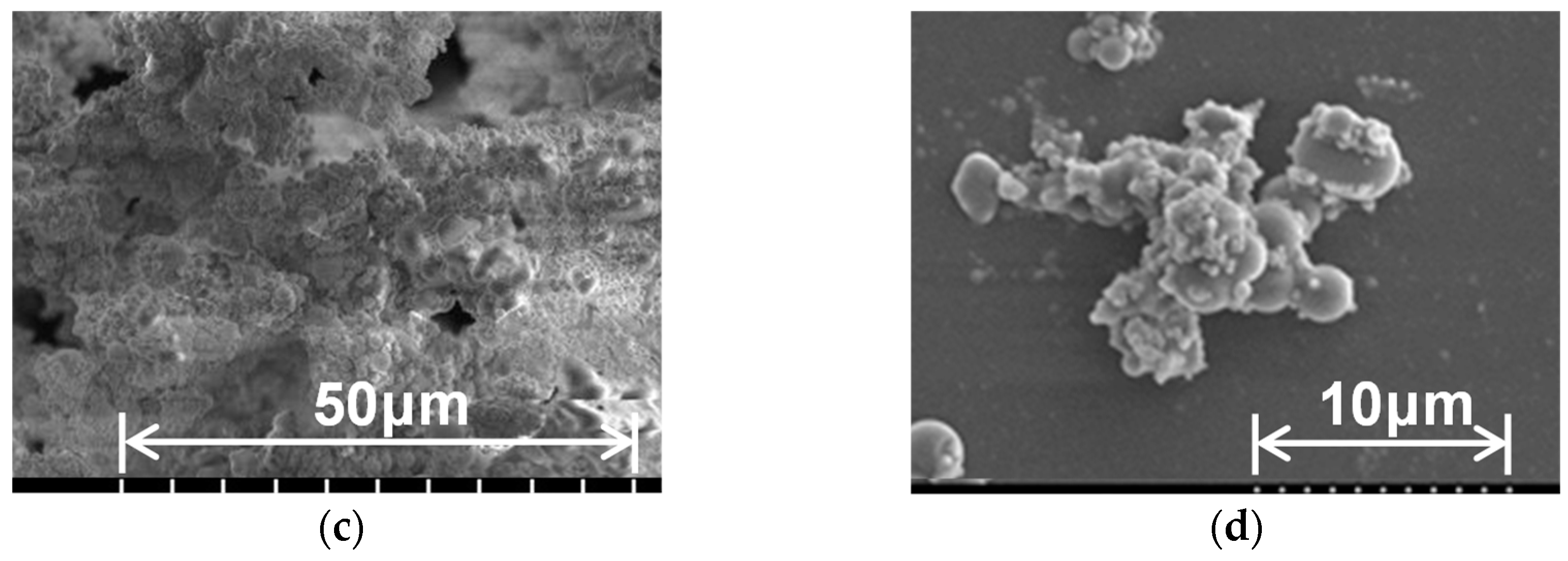
| Young’s modulus (GPa) |
Poisson’s ratio |
Density (kg/m3) |
Loss factor |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glass | 71.6 | 0.23 | 2,200 | 0.002 |
| Rubber 1 | 0.1 | 0.35 | 1,100 | 0.3 |
| Rubber 2 | 0.1 | 0.35 | 1,100 | 0.1 |
| Rubber 3 | 0.1 | 0.35 | 1,100 | 0.5 |
| Rubber 4 | 0.01 | 0.35 | 1,100 | 0.3 |
| Rubber 5 | 1 | 0.35 | 1,100 | 0.3 |
| 500–3,150 Hz Average α(-) @ w = 1 μm |
1,000–5,000 Hz Average α(-) @ w = 1 μm |
500–3,150 Hz Average α(-) @ w = 10 μm |
1,000–5,000 Hz Average α(-) @ w = 10 μm |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glass | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.23 | 0.25 |
| Rubber 1 | 0.08 | 0.12 | 0.25 | 0.27 |
| Rubber 2 | 0.06 | 0.10 | 0.23 | 0.25 |
| Rubber 3 | 0.09 | 0.13 | 0.25 | 0.28 |
| Rubber 4 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.31 | 0.39 |
| Rubber 5 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.23 | 0.25 |
| Original PMS Xerogel |
Diluted PMS Xerogel |
CNF PMS Xerogel |
Hydrophobic CNF PMS Xerogel |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTAB/g | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Urea/g | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 |
| Acetic acid/ml | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| CNF dispersion/g | 0 | 0 | 1.0 | 0.2 |
| MTMS/ml | 3.0 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| DMDMS/ml | 2.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
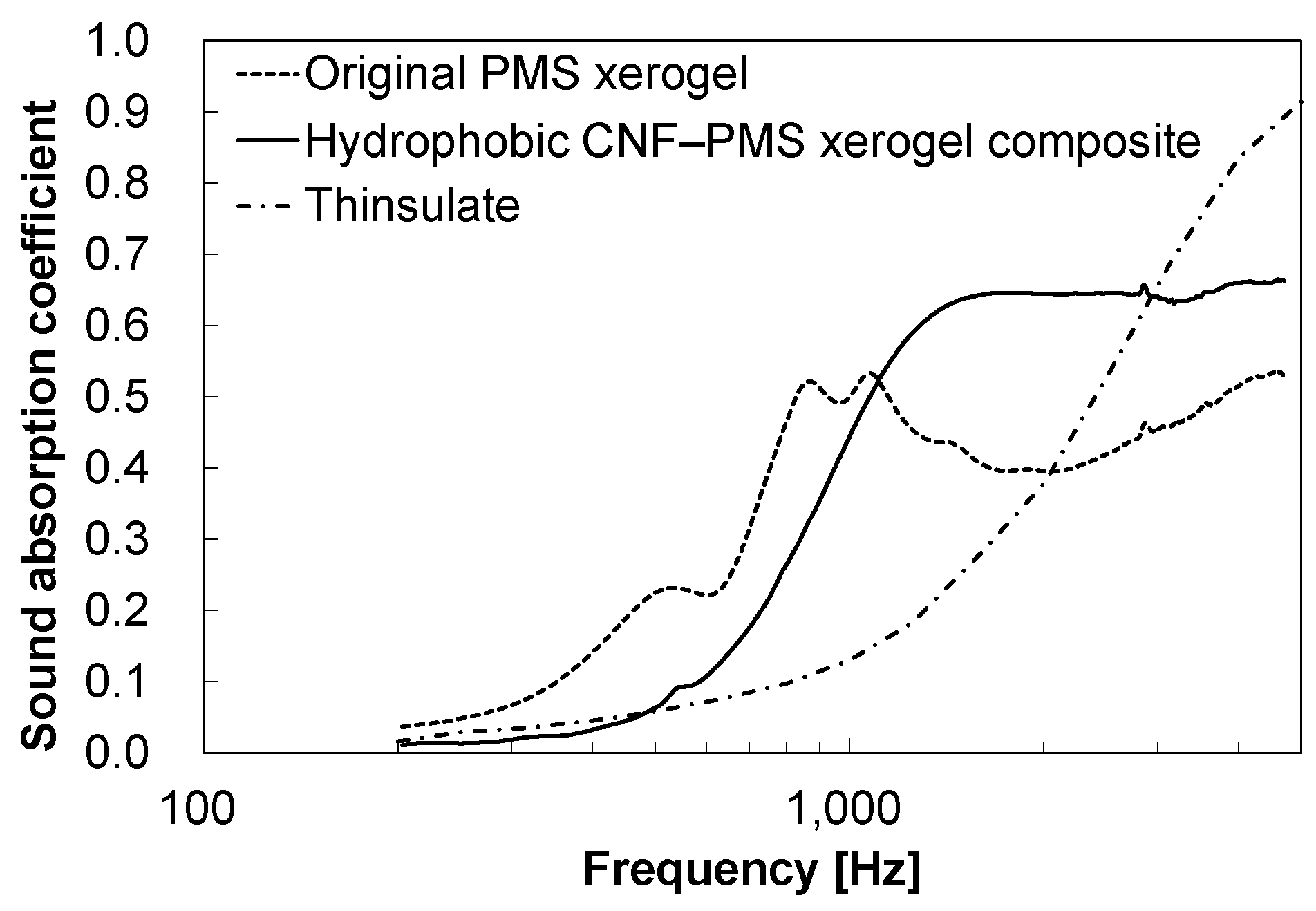
| Original PMS Xerogel |
Hydrophobic CNF PMS Xerogel |
3MTM ThinsulateTM |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Porosity [%] | 89.5 | 93.2 | - |
| Pore size distribution Peak size [μm] |
8.1 | - | - |
| Thickness [mm] | 10 | 8 | 10 |
| Flow resistivity [N s/m4] |
1.35E+06 | 5.54E+05 | - |
| Bulk Density [kg/m3] |
168.2 | 88.4 | - |
| Young's modulus [Pa] |
3.0E+04 | 1.5E+03 | - |
| Loss factor | 0.250 | 0.939 | - |
| 500–3,150 Hz Average Sound absorption coefficient |
0.39 | 0.45 | 0.27 |
| 1,000–5,000 Hz Average Sound absorption coefficient |
0.43 | 0.62 | 0.49 |
| Thermal conductivity [W/(m·K)] |
0.0371 (0.0248) |
0.0378 (0.0252) |
0.0536 (0.0358) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





