Submitted:
20 January 2024
Posted:
22 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
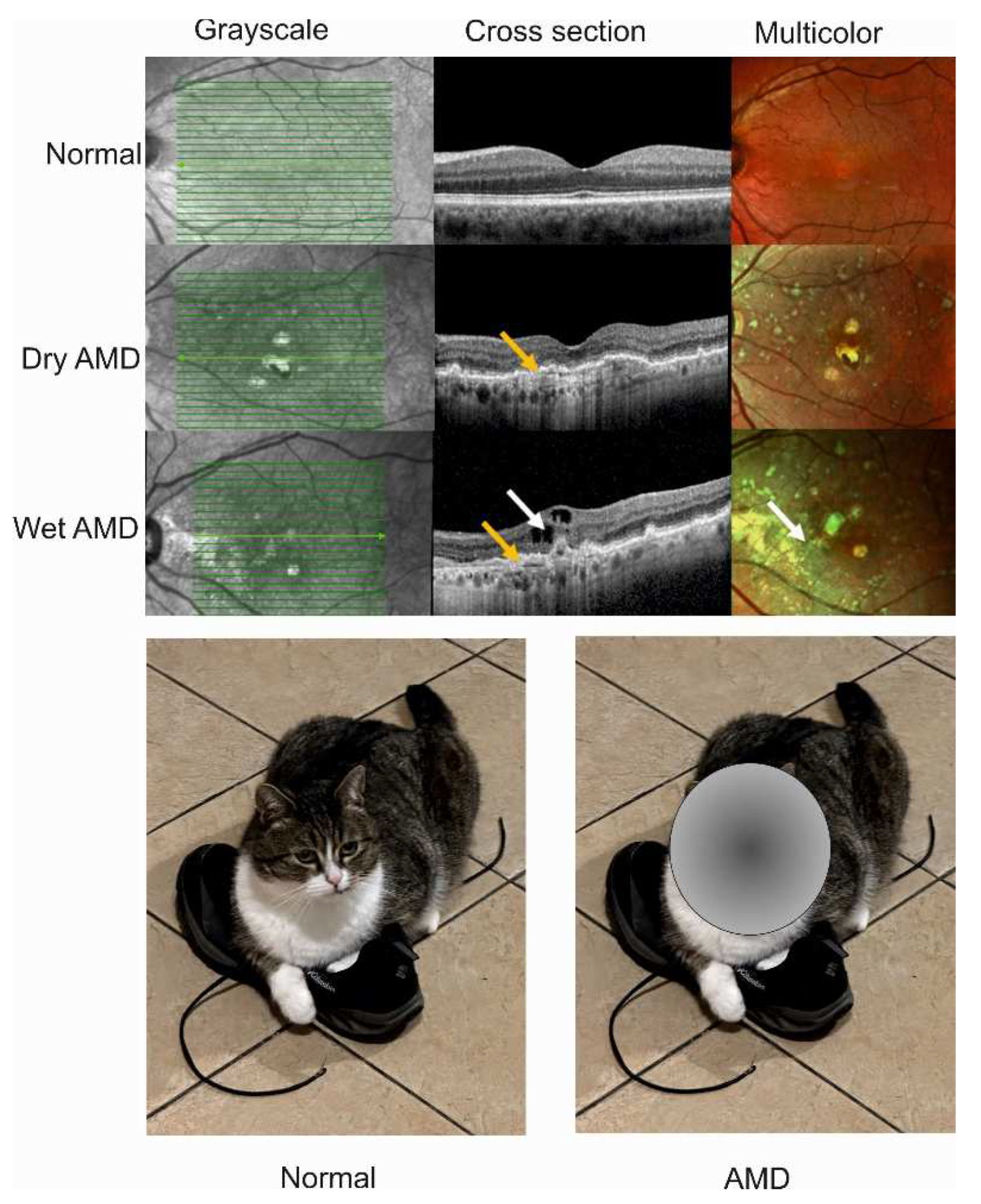
2. Wet age-related macular degeneration: pathogenesis and therapy
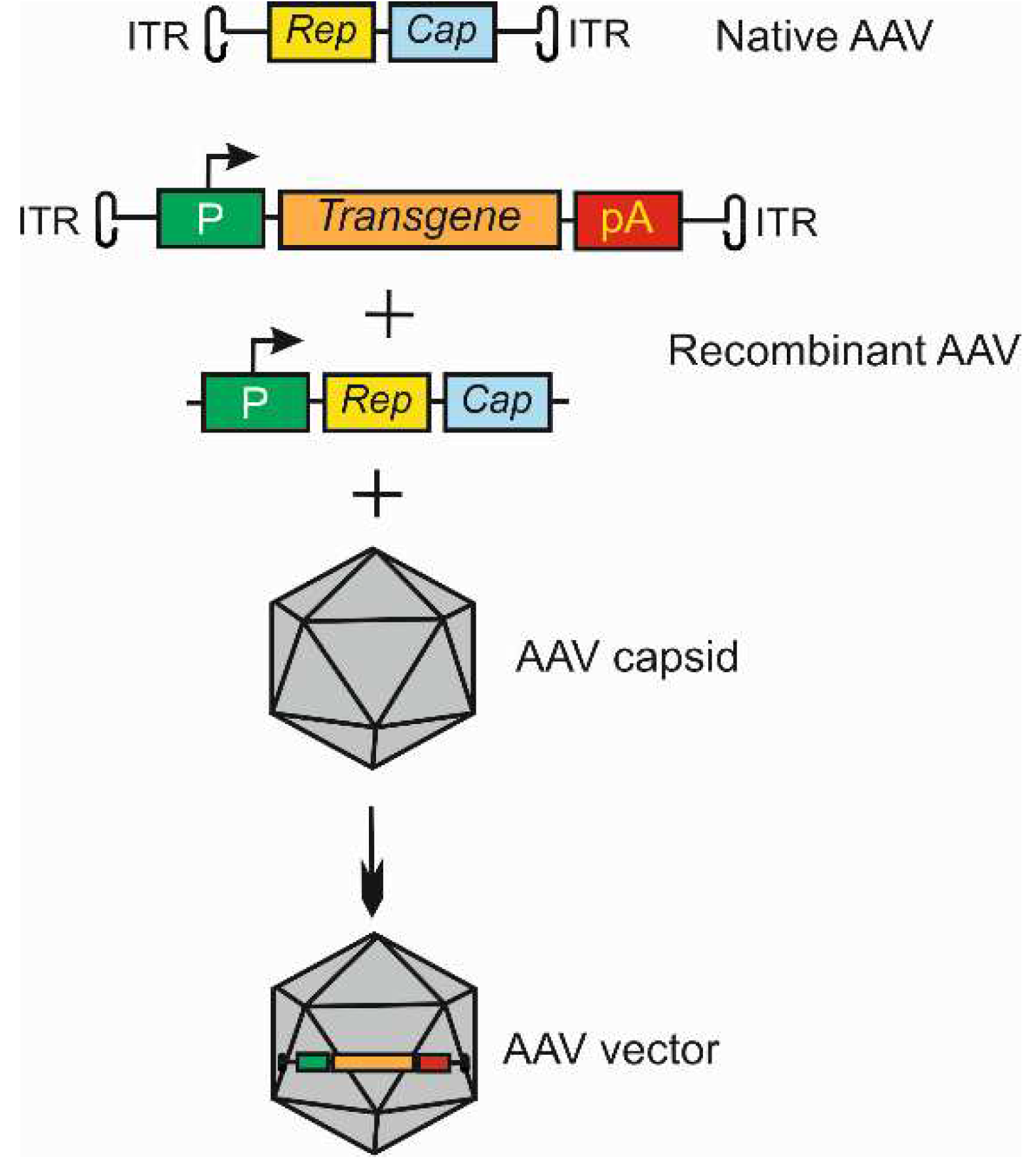
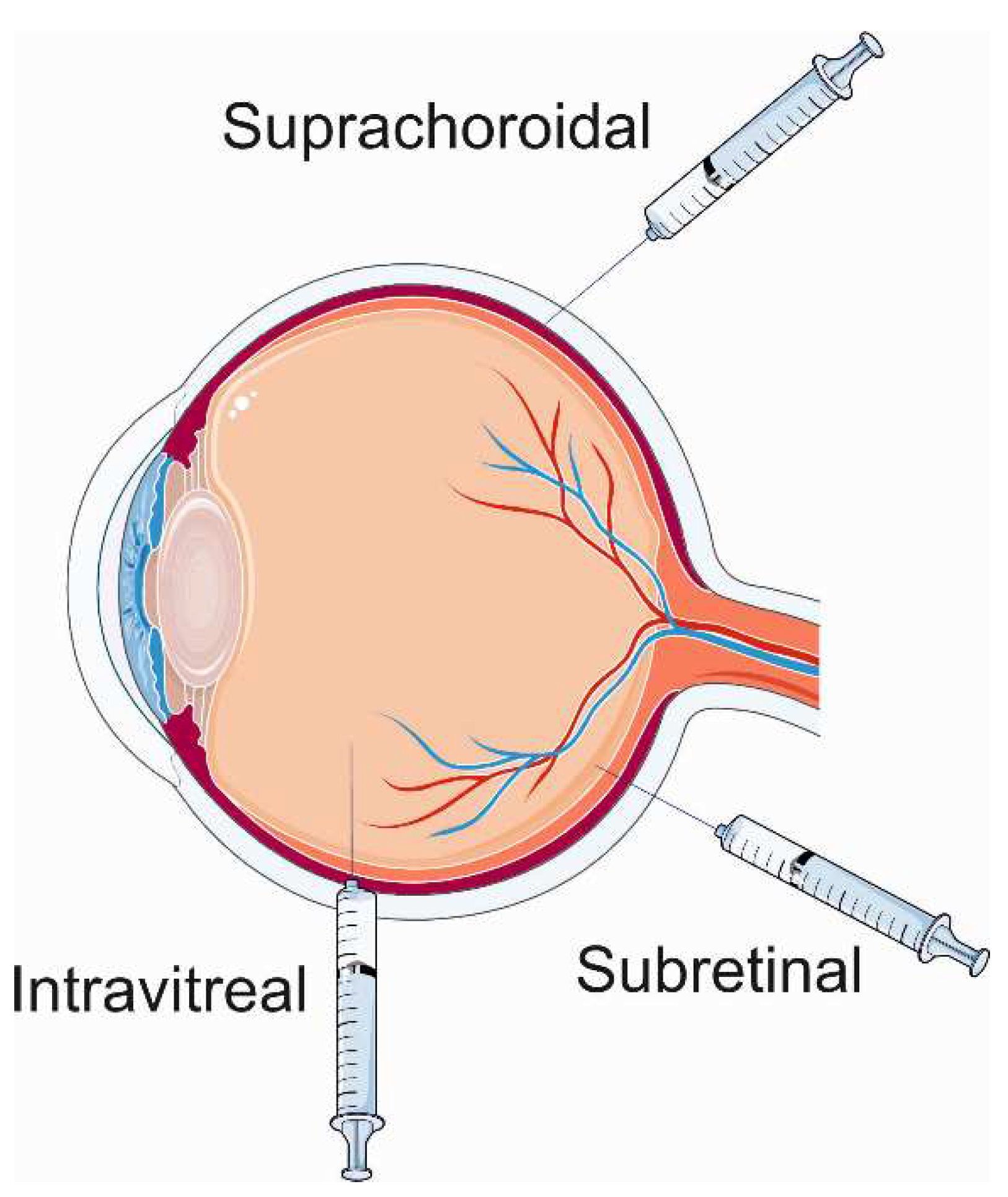
3. Gene therapy for wet age-related macular degeneration
4. Clinical trials on gene therapy for wet age-related macular degeneration
4.1. ADVM-022
4.2. RGX-314
4.2. Trials with anti-VEGFA treatment-naive patients
5. Genome editing and wet AMD
6. Conclusions, outstanding questions, and perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Flores, R.; Carneiro, Â.; Vieira, M.; Tenreiro, S.; Seabra, M.C. Age-Related Macular Degeneration: Pathophysiology, Management, and Future Perspectives. Ophthalmologica. Journal international d’ophtalmologie. International journal of ophthalmology. Zeitschrift fur Augenheilkunde 2021, 244, 495-511. [CrossRef]
- Stahl, A. The Diagnosis and Treatment of Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Dtsch Arztebl Int 2020, 117, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granstam, E.; Aurell, S.; Sjövall, K.; Paul, A. Switching anti-VEGF agent for wet AMD: evaluation of impact on visual acuity, treatment frequency and retinal morphology in a real-world clinical setting. Graefe’s Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology 2021, 259, 2085–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.W. VEGF: From Discovery to Therapy: The Champalimaud Award Lecture. Transl Vis Sci Technol 2016, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oncel, D.; Oncel, D.; Mishra, K.; Oncel, M.; Arevalo, J.F. Current Management of Subretinal Hemorrhage in Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Ophthalmologica. Journal international d’ophtalmologie. International journal of ophthalmology. Zeitschrift fur Augenheilkunde 2023, 246, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Chen, Y.; Gordon, I.; Safi, S.; Lingham, G.; Evans, J.; Keel, S.; He, M. A Systematic Review of Clinical Practice Guidelines for Age-related Macular Degeneration. Ophthalmic Epidemiol 2023, 30, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasiak, J.; Chojnacki, J.; Szczepanska, J.; Fila, M.; Chojnacki, C.; Kaarniranta, K.; Pawlowska, E. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate, an Active Green Tea Component to Support Anti-VEGFA Therapy in Wet Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Zhao, J.; Sun, X. Resistance to anti-VEGF therapy in neovascular age-related macular degeneration: a comprehensive review. Drug design, development and therapy 2016, 10, 1857–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bainbridge, J.W.; Smith, A.J.; Barker, S.S.; Robbie, S.; Henderson, R.; Balaggan, K.; Viswanathan, A.; Holder, G.E.; Stockman, A.; Tyler, N.; et al. Effect of gene therapy on visual function in Leber’s congenital amaurosis. The New England journal of medicine 2008, 358, 2231–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauswirth, W.W.; Aleman, T.S.; Kaushal, S.; Cideciyan, A.V.; Schwartz, S.B.; Wang, L.; Conlon, T.J.; Boye, S.L.; Flotte, T.R.; Byrne, B.J.; et al. Treatment of leber congenital amaurosis due to RPE65 mutations by ocular subretinal injection of adeno-associated virus gene vector: short-term results of a phase I trial. Hum Gene Ther 2008, 19, 979–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, A.M.; Simonelli, F.; Pierce, E.A.; Pugh, E.N., Jr.; Mingozzi, F.; Bennicelli, J.; Banfi, S.; Marshall, K.A.; Testa, F.; Surace, E.M.; et al. Safety and efficacy of gene transfer for Leber’s congenital amaurosis. The New England journal of medicine 2008, 358, 2240–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunbar, C.E.; High, K.A.; Joung, J.K.; Kohn, D.B.; Ozawa, K.; Sadelain, M. Gene therapy comes of age. Science (New York, N.Y.) 2018, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacein-Bey-Abina, S.; von Kalle, C.; Schmidt, M.; Le Deist, F.; Wulffraat, N.; McIntyre, E.; Radford, I.; Villeval, J.L.; Fraser, C.C.; Cavazzana-Calvo, M.; et al. A serious adverse event after successful gene therapy for X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency. The New England journal of medicine 2003, 348, 255–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Tai, P.W.L.; Gao, G. Adeno-associated virus vector as a platform for gene therapy delivery. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 2019, 18, 358–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanani, A.M.; Thomas, M.J.; Aziz, A.A.; Weng, C.Y.; Danzig, C.J.; Yiu, G.; Kiss, S.; Waheed, N.K.; Kaiser, P.K. Review of gene therapies for age-related macular degeneration. Eye (Lond) 2022, 36, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, E.H.; Suh, S.; Sears, A.E.; Hołubowicz, R.; Kedhar, S.R.; Browne, A.W.; Palczewski, K. Genome editing in the treatment of ocular diseases. Experimental & molecular medicine 2023, 55, 1678–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleckenstein, M.; Keenan, T.D.L.; Guymer, R.H.; Chakravarthy, U.; Schmitz-Valckenberg, S.; Klaver, C.C.; Wong, W.T.; Chew, E.Y. Age-related macular degeneration. Nature Reviews Disease Primers 2021, 7, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acar, I.E.; Galesloot, T.E.; Luhmann, U.F.O.; Fauser, S.; Gayán, J.; den Hollander, A.I.; Nogoceke, E. Whole Genome Sequencing Identifies Novel Common and Low-Frequency Variants Associated With Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Investigative ophthalmology & visual science 2023, 64, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassmann, F.; Heid, I.M.; Weber, B.H. Recombinant Haplotypes Narrow the ARMS2/HTRA1 Association Signal for Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Genetics 2017, 205, 919–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.H.; Connor, K.M.; Lambris, J.D. The Challenges and Promise of Complement Therapeutics for Ocular Diseases. Front Immunol 2019, 10, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrielle, P.H.; Maitrias, S.; Nguyen, V.; Arnold, J.J.; Squirrell, D.; Arnould, L.; Sanchez-Monroy, J.; Viola, F.; O’Toole, L.; Barthelmes, D.; et al. Incidence, risk factors and outcomes of submacular haemorrhage with loss of vision in neovascular age-related macular degeneration in daily clinical practice: data from the FRB! registry. Acta Ophthalmol 2022, 100, e1569–e1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferris, F.L., 3rd; Wilkinson, C.P.; Bird, A.; Chakravarthy, U.; Chew, E.; Csaky, K.; Sadda, S.R. Clinical classification of age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmology 2013, 120, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasiak, J.; Watala, C.; Tuuminen, R.; Kivinen, N.; Koskela, A.; Uusitalo-Järvinen, H.; Tuulonen, A.; Winiarczyk, M.; Mackiewicz, J.; Zmorzyński, S.; et al. Expression of VEGFA-regulating miRNAs and mortality in wet AMD. Journal of cellular and molecular medicine 2019, 23, 8464–8471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curcio, C.A. Soft Drusen in Age-Related Macular Degeneration: Biology and Targeting Via the Oil Spill Strategies. Investigative ophthalmology & visual science 2018, 59, Amd160–amd181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.W.; Im, S.; Jun, H.O.; Lee, K.; Park, Y.J.; Kim, J.H.; Park, W.J.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, J.H. Dry age-related macular degeneration like pathology in aged 5XFAD mice: Ultrastructure and microarray analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 40006–40018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobbs, S.D.; Pierce, K. Wet Age-Related Macular Degeneration (Wet AMD). In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing Copyright © 2023, StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island (FL), 2023.
- Karampelas, M.; Malamos, P.; Petrou, P.; Georgalas, I.; Papaconstantinou, D.; Brouzas, D. Retinal Pigment Epithelial Detachment in Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Ophthalmol Ther 2020, 9, 739–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaikitmongkol, V.; Bressler, S.B.; Bressler, N.M. Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD): Non-neovascular and Neovascular AMD. In Albert and Jakobiec’s Principles and Practice of Ophthalmology, Albert, D.M., Miller, J.W., Azar, D.T., Young, L.H., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2022; pp. 3565-3617.
- Yang, Z.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Hartnett, M.E. VEGFA activates erythropoietin receptor and enhances VEGFR2-mediated pathological angiogenesis. The American journal of pathology 2014, 184, 1230–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt-Erfurth, U.; Chong, V.; Loewenstein, A.; Larsen, M.; Souied, E.; Schlingemann, R.; Eldem, B.; Monés, J.; Richard, G.; Bandello, F. Guidelines for the management of neovascular age-related macular degeneration by the European Society of Retina Specialists (EURETINA). The British journal of ophthalmology 2014, 98, 1144–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Huang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhang, X.; Ma, H.; Ren, G.; Shi, F.; Kuang, L.; Yan, S.; et al. Factors for Visual Acuity Improvement After Anti-VEGF Treatment of Wet Age-Related Macular Degeneration in China: 12 Months Follow up. Front Med (Lausanne) 2021, 8, 735318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauwvlieghe, A.M.; Dijkman, G.; Hooymans, J.M.; Verbraak, F.D.; Hoyng, C.B.; Dijkgraaf, M.G.; Peto, T.; Vingerling, J.R.; Schlingemann, R.O. Comparing the Effectiveness of Bevacizumab to Ranibizumab in Patients with Exudative Age-Related Macular Degeneration. The BRAMD Study. PloS one 2016, 11, e0153052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringel, M.J.; Tang, E.M.; Tao, Y.K. Advances in multimodal imaging in ophthalmology. Ther Adv Ophthalmol 2021, 13, 25158414211002400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talib, M.; van Schooneveld, M.J.; van Duuren, R.J.G.; Van Cauwenbergh, C.; Ten Brink, J.B.; De Baere, E.; Florijn, R.J.; Schalij-Delfos, N.E.; Leroy, B.P.; Bergen, A.A.; et al. Long-Term Follow-Up of Retinal Degenerations Associated With LRAT Mutations and Their Comparability to Phenotypes Associated With RPE65 Mutations. Transl Vis Sci Technol 2019, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulcha, J.T.; Wang, Y.; Ma, H.; Tai, P.W.L.; Gao, G. Viral vector platforms within the gene therapy landscape. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy 2021, 6, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viral Vector Systems for Gene Therapy: A Comprehensive Literature Review of Progress and Biosafety Challenges. Applied Biosafety 2020, 25, 7–18. [CrossRef]
- Kessler, P.D.; Podsakoff, G.M.; Chen, X.; McQuiston, S.A.; Colosi, P.C.; Matelis, L.A.; Kurtzman, G.J.; Byrne, B.J. Gene delivery to skeletal muscle results in sustained expression and systemic delivery of a therapeutic protein. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 1996, 93, 14082–14087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drouin, L.M.; Agbandje-McKenna, M. Adeno-associated virus structural biology as a tool in vector development. Future Virol 2013, 8, 1183–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.; Bu, W.; Bhatia, S.; Hare, J.; Somasundaram, T.; Azzi, A.; Chapman, M.S. The atomic structure of adeno-associated virus (AAV-2), a vector for human gene therapy. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2002, 99, 10405–10410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zengel, J.; Carette, J.E. Structural and cellular biology of adeno-associated virus attachment and entry. Adv Virus Res 2020, 106, 39–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, A.; Mietzsch, M.; Agbandje-McKenna, M. Understanding capsid assembly and genome packaging for adeno-associated viruses. Future Virol 2017, 12, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillay, S.; Zou, W.; Cheng, F.; Puschnik, A.S.; Meyer, N.L.; Ganaie, S.S.; Deng, X.; Wosen, J.E.; Davulcu, O.; Yan, Z.; et al. Adeno-associated Virus (AAV) Serotypes Have Distinctive Interactions with Domains of the Cellular AAV Receptor. J Virol 2017, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, A.C.; Weitzman, M.D. Adeno-Associated Virus Genome Interactions Important for Vector Production and Transduction. Hum Gene Ther 2020, 31, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessis, N.; GarciaCozar, F.J.; Boissier, M.C. Immune responses to gene therapy vectors: influence on vector function and effector mechanisms. Gene Ther 2004, 11 Suppl 1, S10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotin, R.M.; Siniscalco, M.; Samulski, R.J.; Zhu, X.D.; Hunter, L.; Laughlin, C.A.; McLaughlin, S.; Muzyczka, N.; Rocchi, M.; Berns, K.I. Site-specific integration by adeno-associated virus. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 1990, 87, 2211–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, H.K.E.; Isalan, M.; Mielcarek, M. Gene Therapy Advances: A Meta-Analysis of AAV Usage in Clinical Settings. Front Med (Lausanne) 2021, 8, 809118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, G.A.; Shalaev, E.; Karami, T.K.; Cunningham, J.; Slater, N.K.H.; Rivers, H.M. Pharmaceutical Development of AAV-Based Gene Therapy Products for the Eye. Pharmaceutical research 2018, 36, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Smet, M.D.; Lynch, J.L.; Dejneka, N.S.; Keane, M.; Khan, I.J. A Subretinal Cell Delivery Method via Suprachoroidal Access in Minipigs: Safety and Surgical Outcomes. Investigative ophthalmology & visual science 2018, 59, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naftali Ben Haim, L.; Moisseiev, E. Drug Delivery via the Suprachoroidal Space for the Treatment of Retinal Diseases. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.Y.; Fujioka, J.K.; Gholamian, T.; Zaharia, M.; Tran, S.D. Suprachoroidal Injection: A Novel Approach for Targeted Drug Delivery. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2023, 16, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladha, R.; Caspers, L.E.; Willermain, F.; de Smet, M.D. Subretinal Therapy: Technological Solutions to Surgical and Immunological Challenges. Front Med (Lausanne) 2022, 9, 846782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, W.J.; da Cruz, N.F.S.; Lima, L.H.; Emerson, G.G.; Rodrigues, E.B.; Melo, G.B. Mechanisms of sterile inflammation after intravitreal injection of antiangiogenic drugs: a narrative review. International journal of retina and vitreous 2021, 7, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, R.R.; Kompella, U.B. Intravitreal, Subretinal, and Suprachoroidal Injections: Evolution of Microneedles for Drug Delivery. Journal of ocular pharmacology and therapeutics: the official journal of the Association for Ocular Pharmacology and Therapeutics 2018, 34, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiser, P.D. Retinal pigment epithelium 65 kDa protein (RPE65): An update. Progress in retinal and eye research 2022, 88, 101013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grishanin, R.; Vuillemenot, B.; Sharma, P.; Keravala, A.; Greengard, J.; Gelfman, C.; Blumenkrantz, M.; Lawrence, M.; Hu, W.; Kiss, S.; et al. Preclinical Evaluation of ADVM-022, a Novel Gene Therapy Approach to Treating Wet Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Molecular therapy: the journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy 2019, 27, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalkara, D.; Byrne, L.C.; Klimczak, R.R.; Visel, M.; Yin, L.; Merigan, W.H.; Flannery, J.G.; Schaffer, D.V. In vivo-directed evolution of a new adeno-associated virus for therapeutic outer retinal gene delivery from the vitreous. Science translational medicine 2013, 5, 189ra176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelfman, C.M.; Grishanin, R.; Bender, K.O.; Nguyen, A.; Greengard, J.; Sharma, P.; Nieves, J.; Kiss, S.; Gasmi, M. Comprehensive Preclinical Assessment of ADVM-022, an Intravitreal Anti-VEGF Gene Therapy for the Treatment of Neovascular AMD and Diabetic Macular Edema. Journal of ocular pharmacology and therapeutics: the official journal of the Association for Ocular Pharmacology and Therapeutics 2021, 37, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, S.; Oresic Bender, K.; Grishanin, R.N.; Hanna, K.M.; Nieves, J.D.; Sharma, P.; Nguyen, A.T.; Rosario, R.J.; Greengard, J.S.; Gelfman, C.M.; et al. Long-Term Safety Evaluation of Continuous Intraocular Delivery of Aflibercept by the Intravitreal Gene Therapy Candidate ADVM-022 in Nonhuman Primates. Transl Vis Sci Technol 2021, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trichonas, G.; Kaiser, P.K. Aflibercept for the treatment of age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmol Ther 2013, 2, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanani, A.M.; Boyer, D.S.; Wykoff, C.C.; Regillo, C.D.; Busbee, B.G.; Pieramici, D.; Danzig, C.J.; Joondeph, B.C.; Major, J.C., Jr.; Turpcu, A.; et al. Safety and efficacy of ixoberogene soroparvovec in neovascular age-related macular degeneration in the United States (OPTIC): a prospective, two-year, multicentre phase 1 study. EClinicalMedicine 2024, 67, 102394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tretiakova, A.; Aleman, T.S.; Lyubarsky, A.; Zhou, E.J.; Wielechowski, E.; Ying, G.-S.; Bote, E.; Makaron, L.; Yoo, S.; Bennett, J.; et al. Subretinal delivery of RGX-314 AAV8-anti-VEGF Fab gene therapy in NHP. Investigative ophthalmology & visual science 2017, 58, 4509–4509. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Li, Q.; Li, J. Site-specific genome editing in treatment of inherited diseases: possibility, progress, and perspectives. Med Rev (2021) 2022, 2, 471–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghbalsaied, S.; Lawler, C.; Petersen, B.; Hajiyev, R.A.; Bischoff, S.R.; Frankenberg, S. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated base editors and their prospects for mitochondrial genome engineering. Gene Ther 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, R.; Brahmbhatt, N.; Sandhu, S.K.; Shah, H.; Vashi, M.; Gandhi, S.K.; Patel, P. Applications of Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR) as a Genetic Scalpel for the Treatment of Cancer: A Translational Narrative Review. Cureus 2023, 15, e50031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahul, K.; Singh, S.K.; Kumar, S.; Tewarson, V.; Hakim, M.Z.; Kaushik, K.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, B. A New Era of Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats/CRISPR-associated Protein 9 Gene Editing Technology in Cardiovascular Diseases: Opportunities, Challenges, and Perspectives. Heart Views 2023, 24, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Doudna, J.A. CRISPR technology: A decade of genome editing is only the beginning. Science (New York, N.Y.) 2023, 379, eadd8643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzalone, A.V.; Koblan, L.W.; Liu, D.R. Genome editing with CRISPR-Cas nucleases, base editors, transposases and prime editors. Nat Biotechnol 2020, 38, 824–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.; Jo, D.H.; Cho, C.S.; Shin, J.H.; Seo, J.H.; Yu, G.; Gopalappa, R.; Kim, D.; Cho, S.R.; Kim, J.H.; et al. Application of prime editing to the correction of mutations and phenotypes in adult mice with liver and eye diseases. Nat Biomed Eng 2022, 6, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, D.H.; Song, D.W.; Cho, C.S.; Kim, U.G.; Lee, K.J.; Lee, K.; Park, S.W.; Kim, D.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.S.; et al. CRISPR-Cas9-mediated therapeutic editing of Rpe65 ameliorates the disease phenotypes in a mouse model of Leber congenital amaurosis. Sci Adv 2019, 5, eaax1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeder, M.L.; Stefanidakis, M.; Wilson, C.J.; Baral, R.; Barrera, L.A.; Bounoutas, G.S.; Bumcrot, D.; Chao, H.; Ciulla, D.M.; DaSilva, J.A.; et al. Development of a gene-editing approach to restore vision loss in Leber congenital amaurosis type 10. Nat Med 2019, 25, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raguram, A.; Banskota, S.; Liu, D.R. Therapeutic in vivo delivery of gene editing agents. Cell 2022, 185, 2806–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, S.; Choi, E.H.; Leinonen, H.; Foik, A.T.; Newby, G.A.; Yeh, W.H.; Dong, Z.; Kiser, P.D.; Lyon, D.C.; Liu, D.R.; et al. Restoration of visual function in adult mice with an inherited retinal disease via adenine base editing. Nat Biomed Eng 2021, 5, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Mookherjee, S.; Chaitankar, V.; Hiriyanna, S.; Kim, J.W.; Brooks, M.; Ataeijannati, Y.; Sun, X.; Dong, L.; Li, T.; et al. Nrl knockdown by AAV-delivered CRISPR/Cas9 prevents retinal degeneration in mice. Nat Commun 2017, 8, 14716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzalone, A.V.; Gao, X.D.; Podracky, C.J.; Nelson, A.T.; Koblan, L.W.; Raguram, A.; Levy, J.M.; Mercer, J.A.M.; Liu, D.R. Programmable deletion, replacement, integration and inversion of large DNA sequences with twin prime editing. Nat Biotechnol 2022, 40, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzalone, A.V.; Randolph, P.B.; Davis, J.R.; Sousa, A.A.; Koblan, L.W.; Levy, J.M.; Chen, P.J.; Wilson, C.; Newby, G.A.; Raguram, A.; et al. Search-and-replace genome editing without double-strand breaks or donor DNA. Nature 2019, 576, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrieu-Soler, C.; Halhal, M.; Boatright, J.H.; Padove, S.A.; Nickerson, J.M.; Stodulkova, E.; Stewart, R.E.; Ciavatta, V.T.; Doat, M.; Jeanny, J.C.; et al. Single-stranded oligonucleotide-mediated in vivo gene repair in the rd1 retina. Molecular vision 2007, 13, 692–706. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, B.; Hawes, N.L.; Pardue, M.T.; German, A.M.; Hurd, R.E.; Davisson, M.T.; Nusinowitz, S.; Rengarajan, K.; Boyd, A.P.; Sidney, S.S.; et al. Two mouse retinal degenerations caused by missense mutations in the beta-subunit of rod cGMP phosphodiesterase gene. Vision Res 2007, 47, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.; Feng, Y.; Xu, W.; Qi, J.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.; Liu, S.; Zhang, J.; et al. Vision rescue via unconstrained in vivo prime editing in degenerating neural retinas. The Journal of experimental medicine 2023, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, T.; Park, S.W.; Jo, D.H.; Kim, D.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, H.Y.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.S. CRISPR-LbCpf1 prevents choroidal neovascularization in a mouse model of age-related macular degeneration. Nat Commun 2018, 9, 1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, S.; Yang, S.; Hu, X.; Yin, D.; Dai, Y.; Qian, X.; Wang, D.; Pan, X.; Hong, J.; Sun, X.; et al. Lentiviral delivery of co-packaged Cas9 mRNA and a Vegfa-targeting guide RNA prevents wet age-related macular degeneration in mice. Nat Biomed Eng 2021, 5, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Park, S.W.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, D.; Koo, T.; Kim, K.E.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.S. Genome surgery using Cas9 ribonucleoproteins for the treatment of age-related macular degeneration. Genome Res 2017, 27, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.H.; Sin, T.N.; Dang, B.; Ngo, T.; Lo, T.; Lent-Schochet, D.; Meleppat, R.K.; Zawadzki, R.J.; Yiu, G. CRISPR-based VEGF suppression using paired guide RNAs for treatment of choroidal neovascularization. Molecular therapy. Nucleic acids 2022, 28, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, W.L.; Su, X.; Li, X.; Cheung, C.M.; Klein, R.; Cheng, C.Y.; Wong, T.Y. Global prevalence of age-related macular degeneration and disease burden projection for 2020 and 2040: a systematic review and meta-analysis. The Lancet. Global health 2014, 2, e106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, N. VEGF and Intraocular Neovascularization: From Discovery to Therapy. Transl Vis Sci Technol 2016, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, N.; Kerbel, R.S. Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target. Nature 2005, 438, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarbin, M. Real Life Outcomes vs. Clinical Trial Results. J Ophthalmic Vis Res 2019, 14, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, A.L.; Du, S.W.; Palczewski, K. Genome editing, a superior therapy for inherited retinal diseases. Vision Res 2023, 206, 108192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogbey, D.M.; Torres, V.E.S.; Fajemisin, E.; Mpondo, L.; Ngwenya, T.; Akinrinmade, O.A.; Perriman, A.W.; Barth, S. Technological advances in the use of viral and non-viral vectors for delivering genetic and non-genetic cargos for cancer therapy. Drug Delivery and Translational Research 2023, 13, 2719–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldner, D.M.; Visser, F.; Fischer, A.J.; Bech-Hansen, N.T.; Stell, W.K. Avian Adeno-Associated Viral Transduction of the Postembryonic Chicken Retina. Translational Vision Science & Technology 2019, 8, 1–1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zin, E.A.; Ozturk, B.E.; Dalkara, D.; Byrne, L.C. Developing New Vectors for Retinal Gene Therapy. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




