1. Introduction
Determining Young’s modulus for a material is an important objective during the design of a mechanical system. In the aeronautical industry, this becomes particularly important if you take into account the continuously increasing percentage of the parts of an aircraft made of composites. Its determination can be done experimentally or using different calculation formulas, methods for which there is a rich literature. For composite materials in particular, numerous methods have been developed to determine this value, with greater or lesser precision. The methods based on micromechanical models and those based on the theory of homogenization are based on the determination of the stress and deformation field for the respective system. Variational models generally provide upper and lower limits of the modulus of elasticity. Obviously in this case it is given by the difference between the upper and lower modulus of the module and can lead, for certain concentrations of the composite phases, to errors, sometimes significant [
1]. Such limits for an orthotropic and a transversally isotropic composite are presented in the cited work. These methods take into account particular cases of loading of the studied body and are quite imprecise [
2,
3]. Micromechanical models are theoretically more accurate, but require knowledge of the field of stresses and deformations for the respective material [
4,
5]. The results obtained in these works are developed and verified experimentally and the results agree very well [
6,
7]. Fiber-reinforced composites represent an important class of materials, with many applications in practice and as a result numerous studies have been carried out on their mechanical properties [
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16]. The studies generated numerous problems related to the methods of solving the equations obtained and the numerical results obtained [
17,
18,
19,
20]. Of course, experimental methods represent an extremely useful solution and with a very high degree of confidence, but their use requires time, equipment and costs that can sometimes be significant. For this reason, in a first phase of the design, it is more advantageous to have some estimates obtained quickly and with a satisfactory degree of confidence.
For materials that can be considered to be made up of many elementary volumes with the same topology, geometry and dimensions, the study is done for an elementary volume called a representative volume element. For this volume, the homogenized elastic coefficients are determined, which are assumed to be the coefficients of the entire material. Using this method, a composite material with short fibers is analyzed in [
21], but it can be applied in many applications to determine the elastic constants of composite materials, for example, reinforced composites with aligned cylindrical fibers.
The Finite Element Method (FEM) is a method successfully used by researchers to determine the mechanical behavior of composites. In general, this method is applied for static calculation, mainly to determine the stress and strain field inside a composite solid. In the work, the proposed method uses the dynamic analysis of the composite to study the vibrations and determine the natural frequencies of the considered specimen. The advantage of this method is that it allows obtaining fast results in a very wide class of materials, with different topologies, geometries and mechanical properties. The ability of FEM to obtain results very close to reality was demonstrated by experimental verifications [
22]. So FEM proved once again to be a useful method for studying the mechanical properties of composite materials made up of a polymer matrix reinforced with aligned cylindrical fibers [
23].
In engineering practice, situations may arise in which it is necessary to take into account other factors such as temperature and humidity. In this case, it is necessary that the classic models used also take into account these factors in obtaining some analytical relations that contain Young’s modulus. The FEM can be used in the classical mode to obtain the natural frequencies, but in the classical model the additional factors that influence the mechanical behavior of the materials must also be introduced. A very useful model for determining the elastic constants for a polymeric composite reinforced with unidirectional graphite fibers is developed in [
24]. Developments of this model are made in [
25,
26].
For the determination of Young’s modulus using experimental techniques that provide these values with high precision in laboratory conditions, useful results are presented in [
27]. Some examples for the determination of Young’s modulus for brass, copper, plexiglass and PVC illustrate the proposed experimental method. The material studied in the paper has a transversely isotropic behavior and the axial Young’s modulus is determined.
Pipes for current applications are made of rubber that is reinforced with metal braids. Due to the wide use of these elements, the interest in determining the mechanical properties is obvious. Due to the complexity and the complicated manufacturing method that introduces parameters that are difficult to control, for these types of materials the best method for determining the mechanical properties is the experimental methods.
Thus in [
28] a method is proposed for the experimental determination of Young’s modulus. For this, the Euler-Bernopulli model is used and three vibration modes are determined experimentally. Based on the obtained results, the Young’s modulus is calculated with simple relations. In the paper, an additional verification of the results is done using FEM. The experimental determination of Young’s modulus for a special type of fiber-metal laminated beams is described in [
29]. Modeling using a classic model confirms the accuracy of the results obtained. The FEM is also used to determine the mechanical properties of some types of wood, a situation in which there are insufficient data to describe the model and approximations at the model level are needed [
30]. Things become more complicated in such an analysis since wood is an orthotropic composite, so it is necessary to know several parameters to describe the constitutive law of the material. The method used was to make successive tests, with different values of the elastic constants, until the moment when the theoretical results obtained with FEM coincided with the experimental determinations. Obviously, such an approach requires effort and resources. Once these values are determined, it is possible to study more complex models for practical situations that can be encountered in practice. In [
31] such an approach is used to determine the mechanical properties of some species and types of wood material, in order to use these values for design activities. Other experimental methods performed to determine the natural frequencies for transverse and torsional vibrations that allow the determination of some of the elastic constants are presented in [
32]. The theoretical model for their determination is based on Timoshenko’s theory.
It is clear that to determine the mechanical properties of composites the best method and which has been used intensively by researchers is to experimentally measure the natural frequencies of a material specimen and using these measurements to calculate the values of the engineering constants [
33,
34,
35,
36] . But this method involves time and resources to perform the measurements, which is why the use of a quick method of determining the properties in the first design phase is desirable.
In engineering practice, the last few years have shown that composites reinforced with carbon fibers or glass have had a spectacular evolution, proving to be extremely useful in a wide range of applications. Obviously, such an evolution led to the increase of researchers’ interest in this type of material. Some applications of these fiber-reinforced materials will be presented below. Concrete is one of these materials and deserves special attention due to its extraordinary application in construction. In this field, the current practice is to reinforce the concrete with cylindrical iron fibers. The FEM proved to be in this case also an adequate method to determine the mechanical properties of the homogenized material. Using finite element modeling of a concrete block reinforced with iron bars, the elastic constants of the homogenized material were determined. These values were thus obtained by calculation, which were then verified experimentally [
37]. A very good agreement was found between the values estimated by calculation and the values determined by experimental methods. Another area where intense development is taking place is the use of natural fibers to reinforce the polymer matrix. The use of these fibers is based on both ecological considerations and the fact that they are easily obtained at a low price. However, their study is more complicated because they have a viscoelastic behavior [
38] and the developed models are generally sophisticated. The analytical methods used are more elaborate and require a greater calculation effort. The results obtained by the mentioned work were validated experimentally, the differences between the calculated and measured values being small.
Another interesting method used in the study of composite materials reinforced with glass or carbon fibers, which presents a viscoelastic behavior, is presented in [
39]. Such a material has viscoelastic behavior due to the polymer matrix material. In developing the method, the time factor must also be introduced that will describe the flow of the material if the temperature at which it is used increases. The theoretically obtained results are verified experimentally, obtaining a good agreement. Other works develop methods for calculating the elastic coefficients for different types of materials used in engineering applications [
40,
41].
In the study, a FEM model is used to calculate the natural frequencies of a bar. Two sets of boundary conditions are considered, the bar is embedded at both ends and the bar is embedded at one of the ends. The material from which the beam is made is a polymer composite reinforced with carbon fibers. Within the standard assumptions of the classical theory of straight bars, with the values determined based on the formulas provided by the literature and knowing the values of the natural pulsations determined with the FEM model, the Young’s modulus can be determined.
The FEM is used to determine the natural frequencies for a composite material, using all the information regarding the matrix material and the fiber material in the modeling. At the same time, the classical methods are considered for determining the natural frequencies for a straight bar, made of the same material, which represents the homogenized material having the properties determined by the properties of the phases used. By comparing these values and comparing with those obtained using FEM, the values for the elastic constants for the homogenized material can be obtained. The main advantage offered by this method consists in the fact that it provides quick estimates for these values. Obviously, the costs involved are also reduced. If it is compared with the experimental methods, the method is much cheaper and more convenient. Also, the time required to obtain these values is reduced. The analysis focuses on the study of longitudinal vibrations, through the conditions imposed on the displacements in the FEM allowing only the axial displacement of the bar. In this way, computing resources are optimally used. In this work, this method is used to determine Young’s modulus for a composite material reinforced with unidirectional carbon fibers. The method can be applied to a wide class of materials in order to determine the properties of the homogenized material.
2. Materials and Methods
The main results regarding the vibrations of straight beam are briefly presented. The classic assumptions from the straight bar theory are considered valid [
42]. In our study two cases are considered: clamped beam at both ends and clamped beam at one of the ends. Based on the relationships to determine the eigenfrequencies for a beams with the mentioned boundary conditions, it is possible to determine the Young’s modulus for the homogenized material. These values represent a quick estimation for the Young’s modulus.
FEM is used to determine these natural frequencies considering the matrix and the reinforcing fibers included in it. This can be done relatively easily and accurately using this method. Knowing the relations that provide the analytical expression of the eigenfrequencies of a homogeneous beam depending on the dimensions of the beam and the Young’s modulus and having the eigenfrequencies calculated with the FEM, it is possible to obtain the Young’s modulus from these relations through simple calculations.
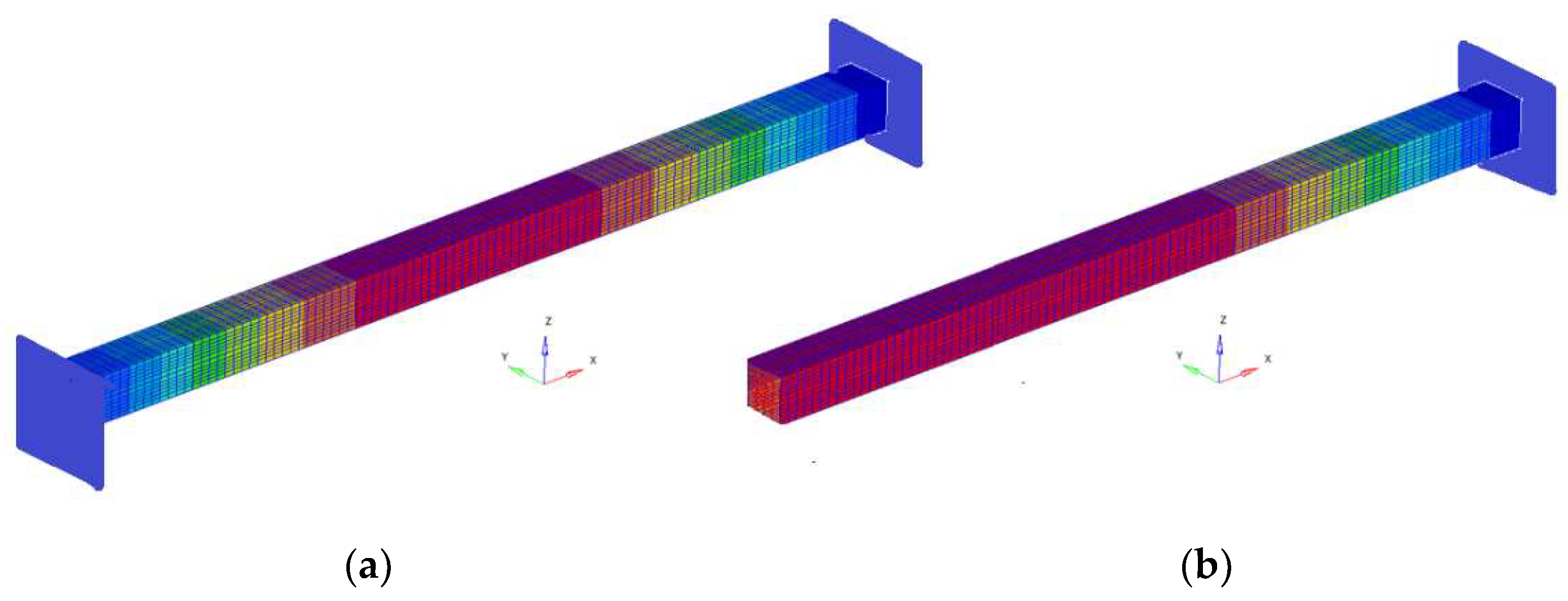
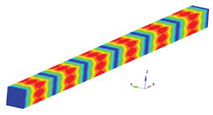
Figure 1 shows the two types of beams analyzed.
Consider the longitudinal vibration of a straight beam. These vibrations are described by the differential equations:
If we choose a solution under the form:
and introducing in Eq.(1) it results the differential equation that offers the amplitude of the natural vibrations (eigenfunctions):
The initial conditions, considered at the moment
are:
Eq.(3) give the solution:
where:
If we consider the beam clamped at both end the boundary conditions become:
and it results:
Taking into account notation (6) the eigenpulsations are given by the relation:
So the Young’s modulus of the homogenized material clamped at the both ends can be determined:
From Eq.(10), it results:
Now if we consider the beam clamped only on one end, the boundary conditions are:
and it results:
It obtains:
from where:
or:
The Young’s modulus of the homogenized material clamped at one both end can be determined:
From Eq.(20), it results:
Using FEM, it is possible to obtain a number of eigenpulsation which offers us more values for E. The average can be calculated in order to obtain a better estimation for E.
3. Results
In this study, a composite material made of a polymeric material reinforced with carbon fibers is considered. With the help of finite element analysis, the material is modeled considering the fibers incorporated in it. The beam’s own pulsations are determined with the help of this model. Only the longitudinal vibrations of the material are considered. On the other two directions, the nodes are blocked. This was done because when analyzing such a bar, the low modes are transverse and torsional vibration modes. The modes due to longitudinal vibrations appear at higher frequencies. The study aimed to obtain more frequencies for the longitudinal vibrations, without having to identify and eliminate the other modes of vibration. This is achieved by blocking the movement of the bar surface in the other two directions. Considering the classical model of the bar [
43], the relationship between Young’s modulus and the natural pulsation can be written. If the natural pulsation was calculated with FEM, then it is easy to obtain the Young’s modulus. Several determinations of the natural pulsations are considered in order to obtain a better estimate for the modulus of elasticity. This way of estimating Young’s modulus has the advantage of simplicity. The methods that can be used today are relatively imprecise and time- and resource-consuming. Experimental methods also involve careful preparation, time and resources. For the two bars with different boundary conditions, eigenfrequencies and eigenmodes were determined. Based on the values obtained in the calculation, the longitudinal Young’s modulus was calculated [
44,
45,
46,
47,
48,
49,
50].
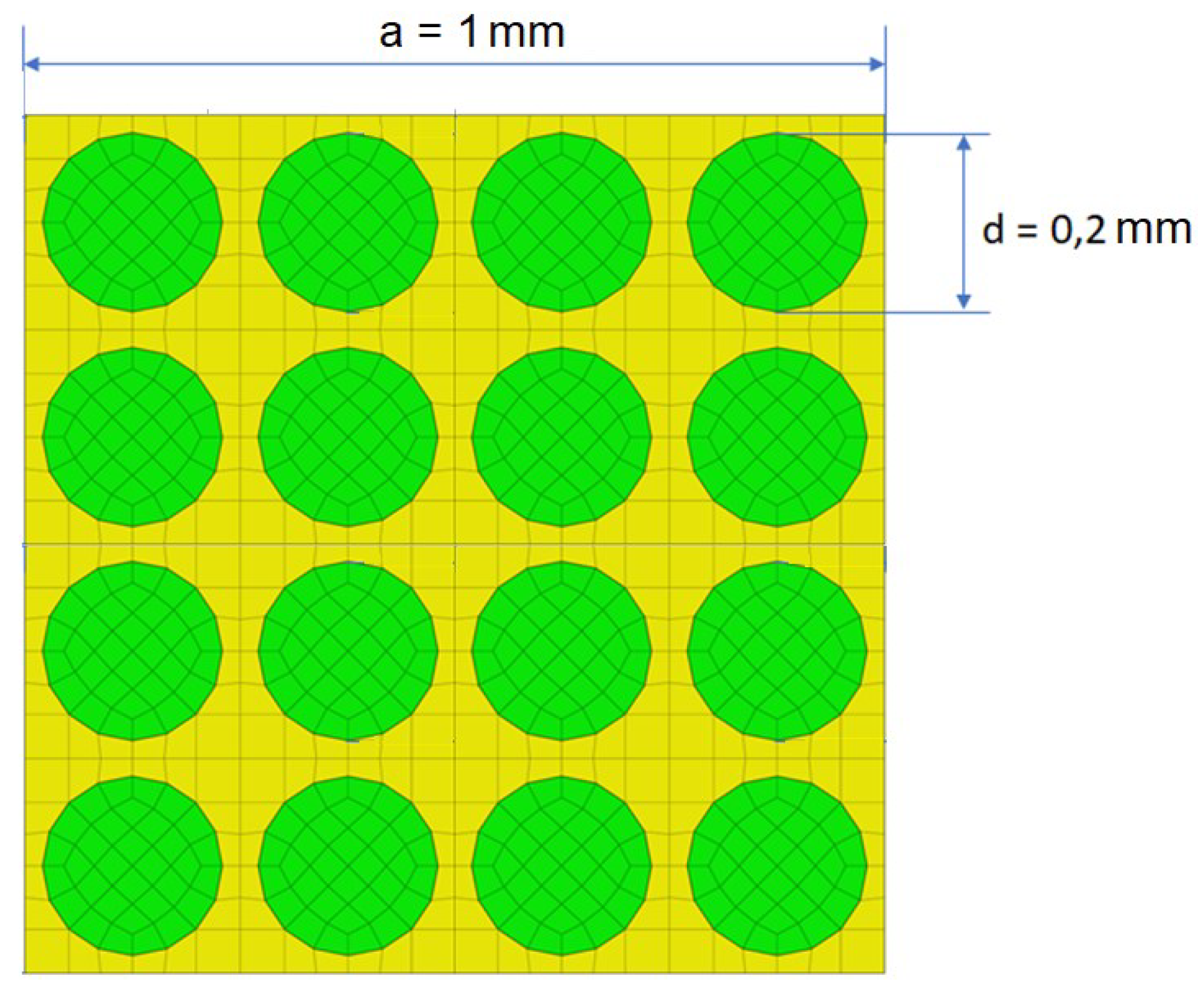
The model considered in the calculations is presented in
Figure 2 and is represented by a specimen with a square section, with a length of 10 mm and a side of 1 mm, inside which are incorporated 16 cylindrical carbon fibers aligned along the x axis. The considered dimensions can be found on the figure. It was considered for carbon fiber that the Young’s modulus has the value of 86,960 GPa. For the polymer matrix, the Young’s modulus was considered to be 4,140 GPa. The density taken in the calculations is 1850 kg/m3 for the polymer matrix and 2000 kg/m3 for the reinforcing carbon fibers. The Poisson’s ratio for the matrix was taken to be 0.22 and 0.34 for the carbon fibers. Based on these data, the FEM model was built with the help of which the eigenfrequencies were determined.
The density of the homogenized material, which is a necessary quantity for performing the calculations, is obtained with the relation:
Here, the density of the fiber is , the density of the matrix is , the ratio of the fiber is and the ratio of the matrix is , ().
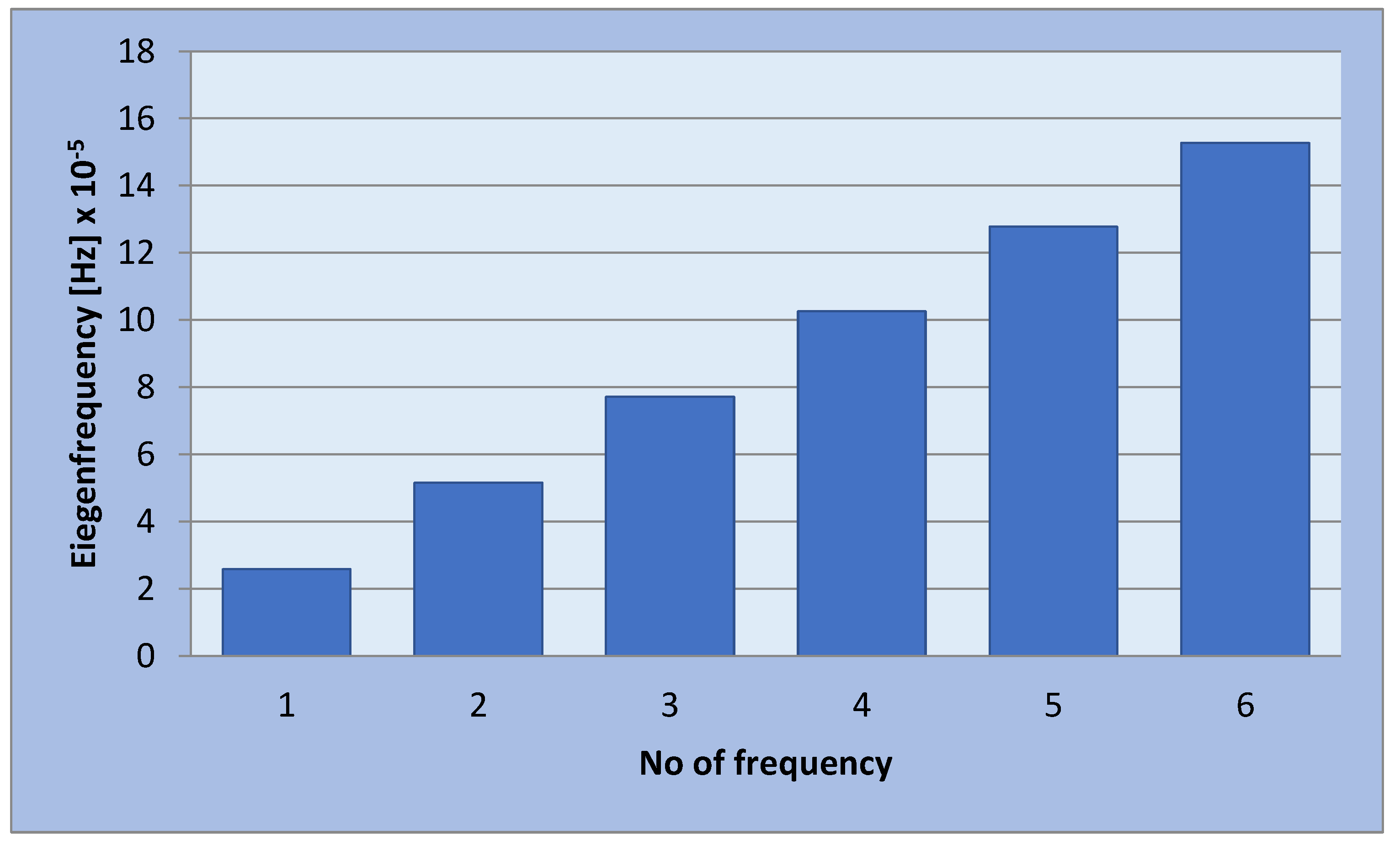
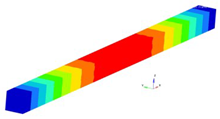
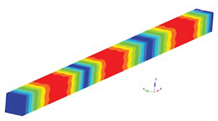
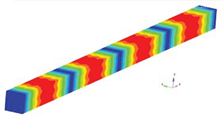
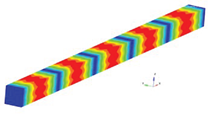
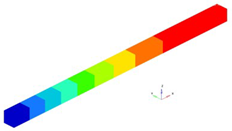
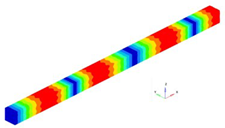
The eigenmodes for the longitudinal vibrations, for the first six eigenfrequencies are represented in
Table 1. Based on the relationships that give us the Young’s modulus depending on the eigenpulsation values, this quantity can now be determined. The results of the calculations are presented in
Table 1. In conclusion, if we know the length of the beam specimen considered, the density of the homogenized material, the number of the eigenmode considered and the eigenfrequency for this mode, calculated with FEM for a model that reproduces the two phases of the composite, we can determine Young’s modulus. This module can be determined for each frequency. It is reasonable to average the values obtained for several natural frequencies obtained by FEM calculation. In the work, we considered two boundary conditions for the bar specimen. First, the bar clamped at both ends is considered, then the bar clamped at one of the ends and free at the other end.
If it is taken into account that
where
is the natural frequency corresponding to the natural pulsation, the expression for the modulus of elasticity is obtained [
46]:
if the bar is clamped at both ends and
if the bar is clamped at one end.
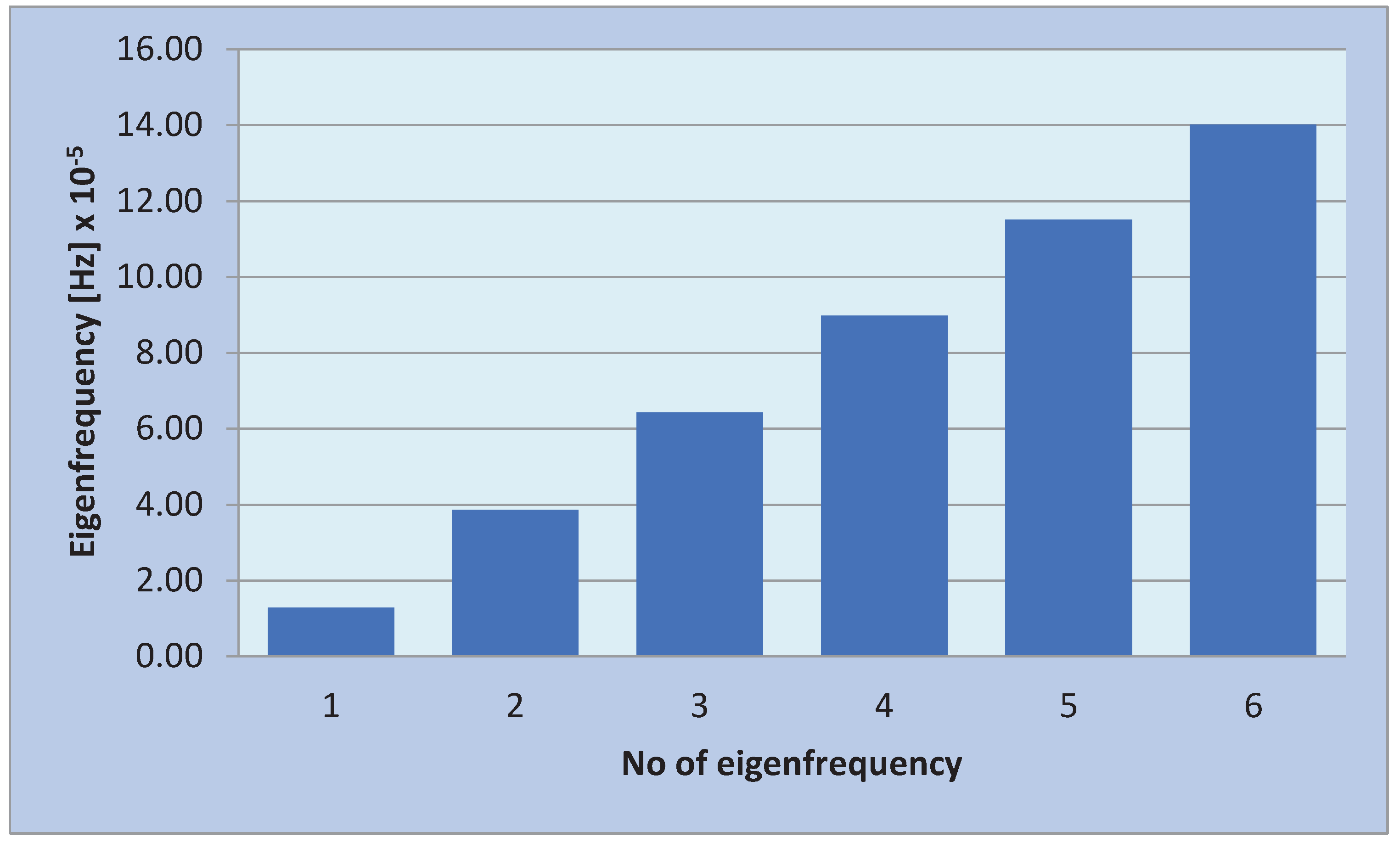
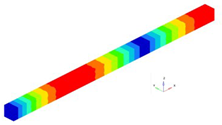
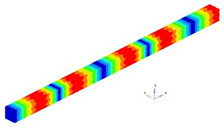
A representation of the eigenfrequencies for beam clamped at one end is made in
Figure 3.
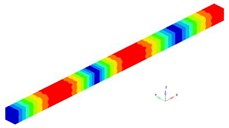
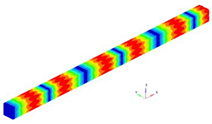
It is found that the values obtained for the bar clamped at one end are closer to each other than in the first case, when the bar is clamped at both ends. The eigenfrequencies for beam clamped at one end are represented in
Figure 4.
The law of mixtures gives us the value 54.950 GPa
4. Discussion
The values of the elastic constants that define the constitutive law of a composite made of a polymer matrix reinforced with glass or carbon fibers can be determined by several analytical methods developed by researchers, which are however very laborious. Most of these methods assume the determination of the stress field and deformations in the specimen considered representative of the material. The bounding methods for the elastic constants, proposed by some of the researchers, lead to less precise results. Sometimes when edge methods are used, for certain phase concentrations these methods can lead to practical results. Experimental methods represent the most reliable methods of determining these elastic constants, but they involve significant time and resources.
In the paper one showed that the FEM can be a simple and sufficiently precise method for a quick estimation of some of the elastic constants. In this work, we dealt with the modulus of elasticity, but it is obvious that other constants can be determined, if suitable models are used. The classical theories of the straight bar were used to analytically determine the natural frequencies and these values were compared with those obtained from the exact model elaborated with FEM. Thus, with the help of simple formulas, we managed to calculate Young’s modulus. We can conclude that the presented method has the advantage of speed, simplicity and accessibility to obtain quick estimates for the values of the elastic constants in the design phases of a mechanical system. The accuracy of the results can be improved by considering a FEM model with many elements, which will more precisely describe the existing situation for each practical application [
48,
49,
50]. So there are many methods for determining the elastic constants of a composite material, but most of them are laborious and require many calculations. The ones that stand out for their simplicity offer upper and lower bounds for the elastic constants that lead to significant errors. The method proposed in the work uses the determination of the natural frequencies for the homogenized bar using the classical theory of straight bars. FEM is also used to determine these natural frequencies, on the real system. This method gives fast and accurate estimates of Young’s modulus, important data in a design process. Obviously, the bar assumptions of the theory of straight bars must be respected. The errors that may appear are due to the FEM, within the limits accepted by the approximation method and the deviation from the classical assumptions. The method allows obtaining fast and useful results.
Obviously, the need to know the mechanical properties expressed by the elastic constants of the materials is a main objective in the case of designing a mechanical system. Within these materials, polymer composites reinforced with aligned cylindrical fibers are distinguished, mainly due to their numerous practical applications. Obviously, experimental measurements provide the most reliable results, but this operation is expensive and takes time. That is why the existence of fast methods for estimating these properties is required depending on the properties of the component phases. This has been intensively studied and numerous calculation models have been proposed. Based on the micromechanical models, analytical formulas were determined to determine the engineering constants. But this approach implies the determination of the stress and deformation field for the studied system. The same requirement is involved if the homogenization theory is used. Other theoretical models have been proposed that involve the knowledge of particular loading situations but that provide upper and lower bounds for the elastic constants, which means significant errors when determining these constants that can sometimes be far from the real values [
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13]. The method used in the present work is to consider the homogenized material and to determine with the classical calculation methods the natural frequencies of such a homogenized bar. With the FEM, the values of the natural frequencies for the real system, consisting of the matrix material and the reinforcing fibers, are determined. Comparing the two values, Young’s modulus can be easily determined. In this way, fast and accurate estimates are obtained for this quantity [59]. In practice, complex situations may arise, determined by practical applications, in which effects may appear that cannot be neglected, such as thermal effects, humidity, etc. In order to solve such problems, the classical models must be improved to be able to take into account these effects, which introduce new parameters. And they must be taken into account in these calculations,
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.I., M.L.S. and S.V.; methodology, C.I., M.L.S. and S.V.; software, C.I.; validation, C.I., M.L.S. and S.V.; formal analysis, C.I., M.L.S. and S.V ; investigation, S.V.; resources, C.I., M.L.S. and S.V.; data curation, C.I.; writing—original draft preparation, S.V.; writing—review and editing, S.V.; visualization, C.I., M.L.S. and S.V.; supervision, C.I., M.L.S. and S.V.; project administration, M.L.S.; funding acquisition, C.I., M.L.S. and S.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.