Submitted:
18 January 2024
Posted:
19 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
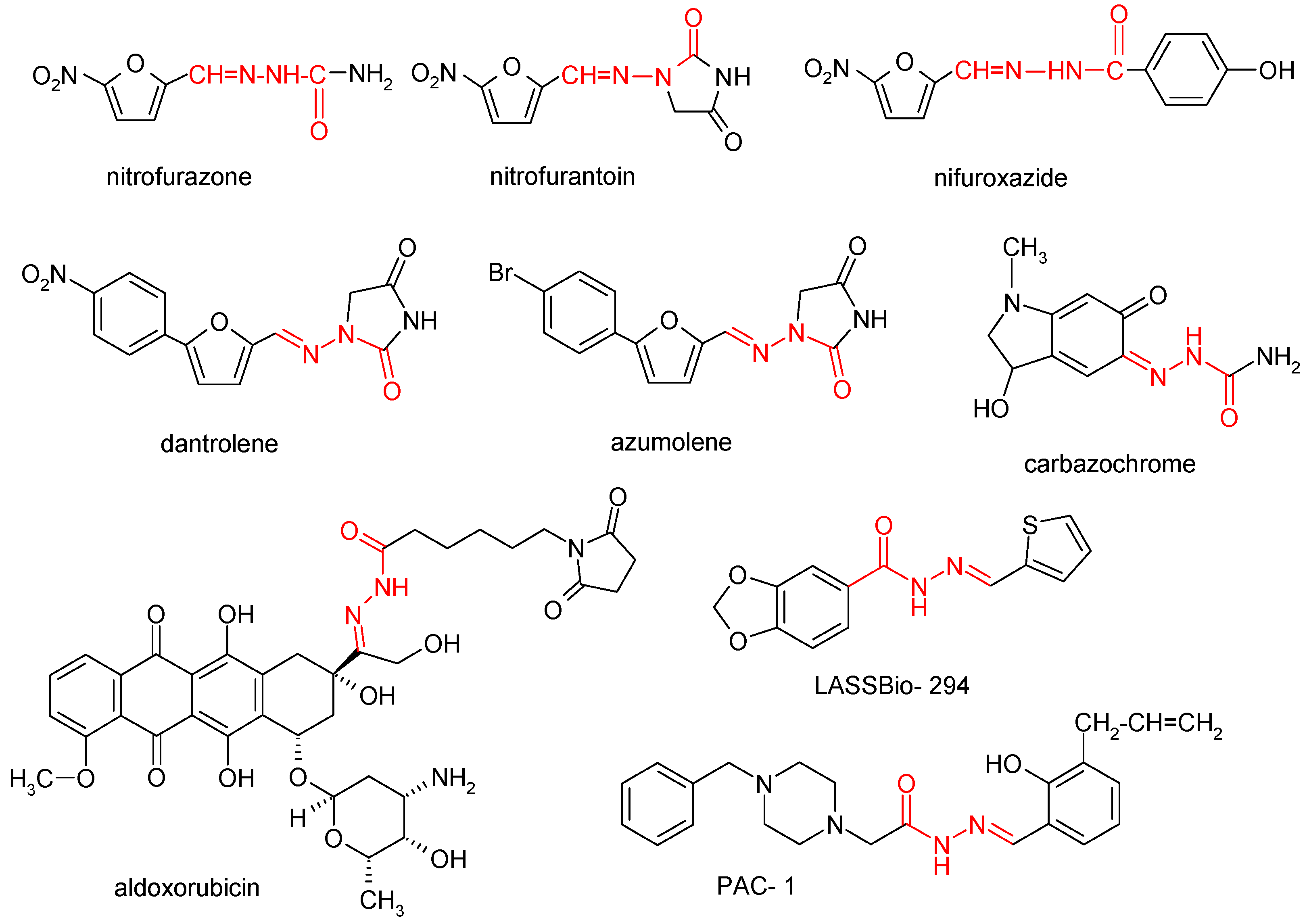
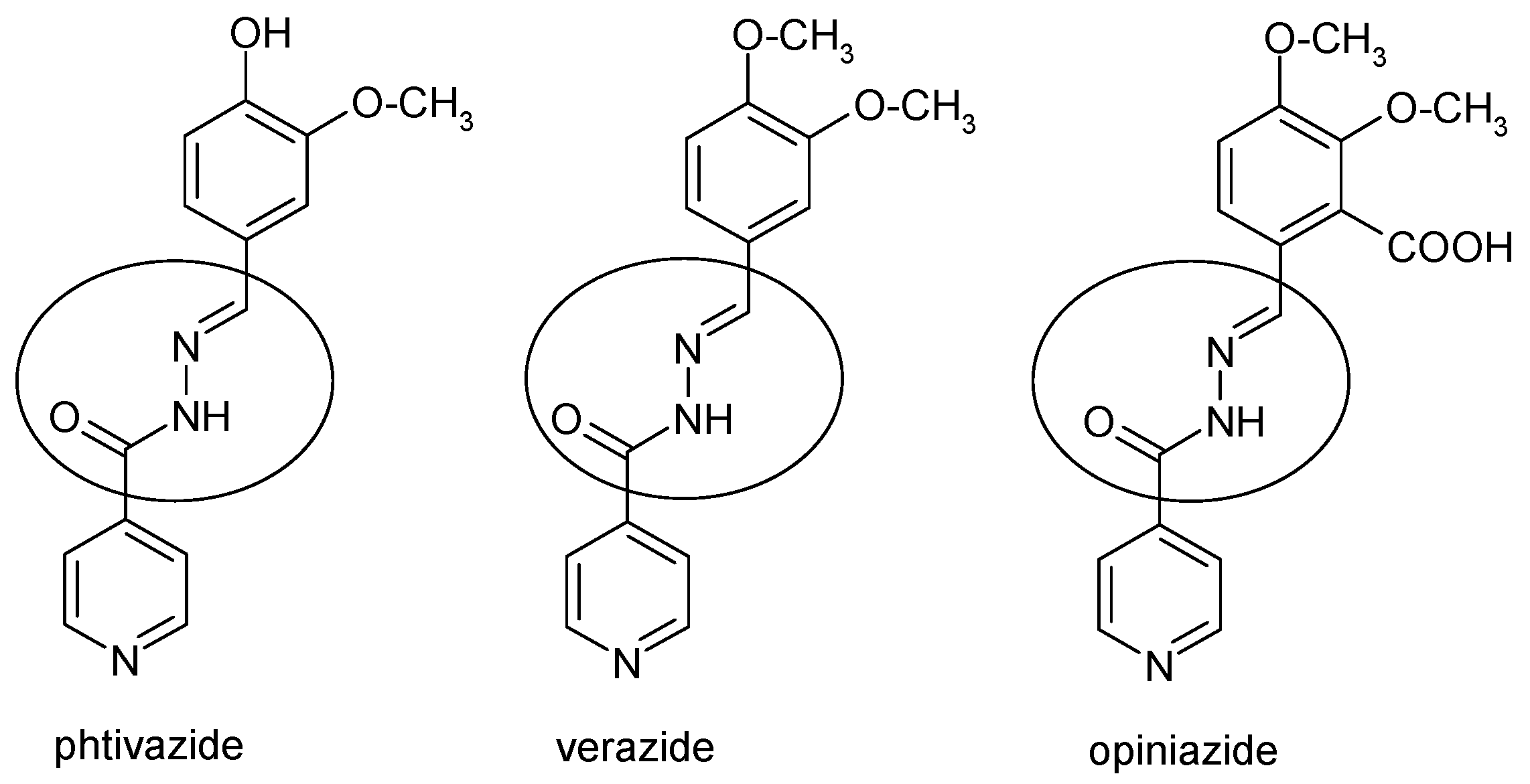
1. Introduction
2. Results
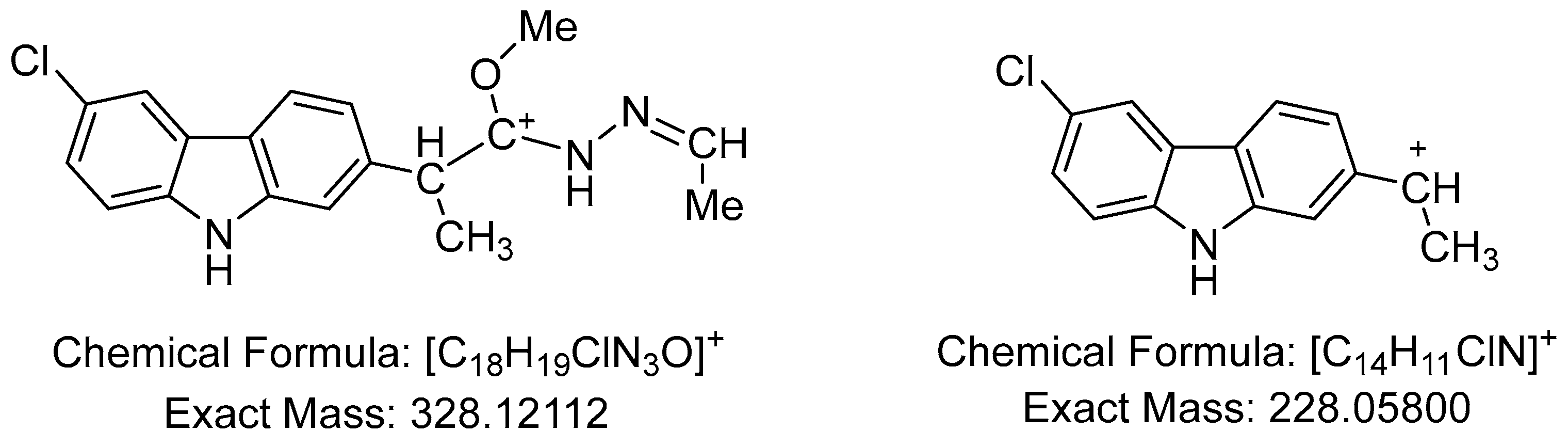
2.1. Spectral data
2.2. Tuberculostatic activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Measurements
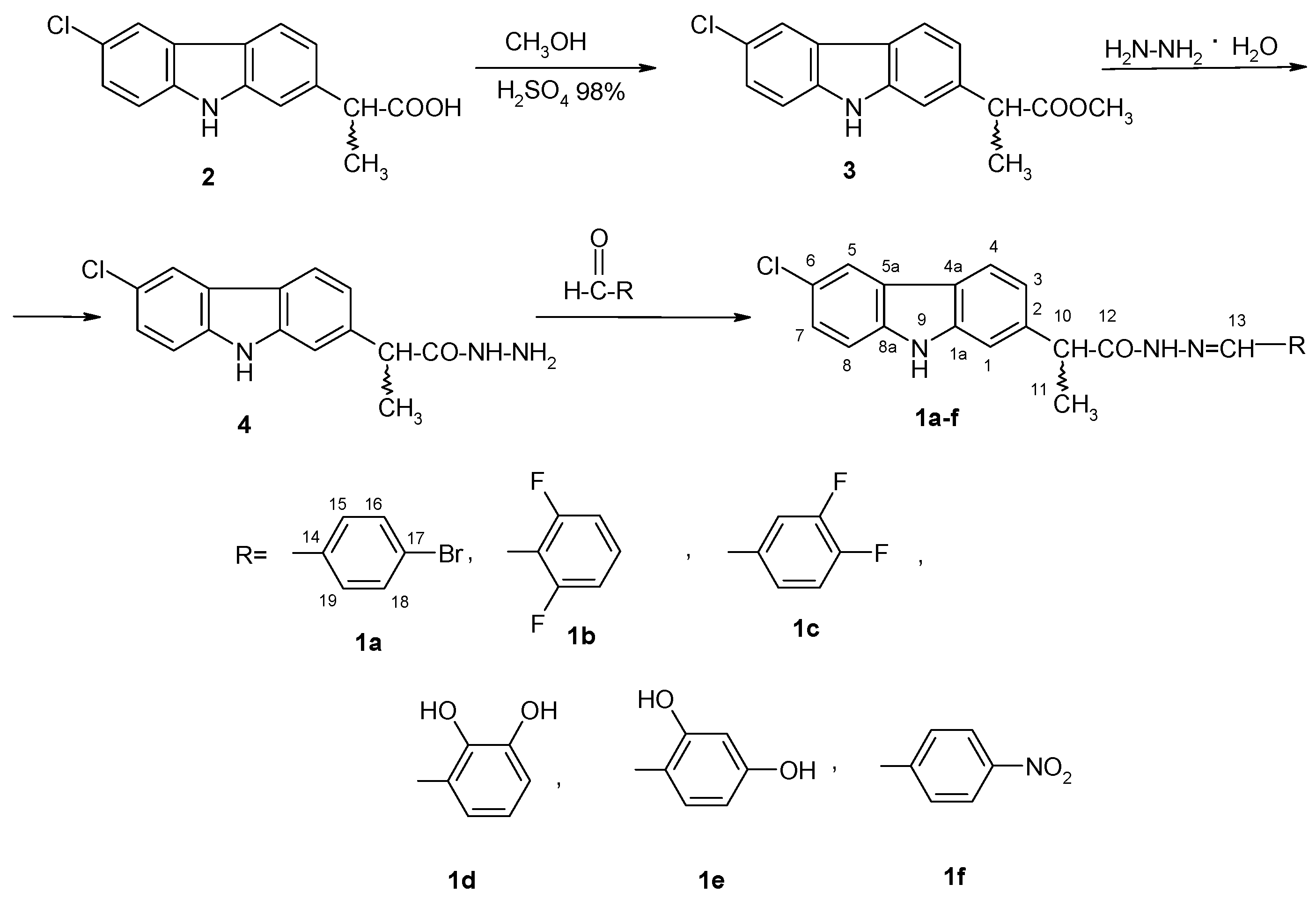
4.2. Chemistry
4.3. Tuberculostatic activity assay
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Palla, G.; Predieri, G.; Domiano, P.; Vignali, C.; Turner, W. Conformational behaviour and E/Z isomerization of N-acyl and N-aroylhydrazones. Tetrahedron 1986, 42, 3649-3654. [CrossRef]
- Munir, R.; Javid, N.; Zia-ur-Rehman, M.; Zaheer, M.; Huma, R.; Roohi, A.; Athar, M.M. Synthesis of novel N-acylhydrazones and their CN/NN bond conformational characterization by NMR spectroscopy. Molecules 2021, 26, 4908. [CrossRef]
- Kümmerle, A.E.; Schmitt, M.; Cardozo, S.V.S.; Lugnier, C.; Villa, P.; Lopes, A.B.; Romeiro, N.C.; Justiniano, H.; Martins, M.A.; Fraga, C.A.M.; et al. Design, Synthesis, and Pharmacological Evaluation of N-Acylhydrazones and Novel Conformationally Constrained Compounds as Selective and Potent Orally Active Phosphodiesterase-4 Inhibitors. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2012, 55, 7525-7545. [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rahman, H.M.; Abdel-Aziz, M.; Tinsley, H.N.; Gary, B.D.; Canzoneri, J.C.; Piazza, G.A. Design and Synthesis of Substituted Pyridazinone-1-Acetylhydrazones as Novel Phosphodiesterase 4 Inhibitors. Archiv der Pharmazie 2016, 349, 104-111. [CrossRef]
- Freitas, R.; Cordeiro, N.M.; Carvalho, P.R.; Alves, M.A.; Guedes, I.A.; Valerio, T.S.; Dardenne, L.E.; Lima, L.M.; Barreiro, E.J.; Fernandes, P.D.; et al. Discovery of naphthyl-N-acylhydrazone p38α MAPK inhibitors with in vivo anti-inflammatory and anti-TNF-α activity. Chemical biology & drug design 2018, 91, 391-397. [CrossRef]
- do Amaral, D.N.; Cavalcanti, B.C.; Bezerra, D.P.; Ferreira, P.M.P.; Castro, R.d.P.; Sabino, J.R.; Machado, C.M.L.; Chammas, R.; Pessoa, C.; Sant'Anna, C.M.R. Docking, synthesis and antiproliferative activity of N-acylhydrazone derivatives designed as combretastatin A4 analogues. PLoS One 2014, 9, e85380. [CrossRef]
- Fraga, C.A.; Barreiro, E.J. Medicinal chemistry of N-acylhydrazones: new lead-compounds of analgesic, antiinflammatory and antithrombotic drugs. Current medicinal chemistry 2006, 13, 167-198. [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.Y.; Lee, J.; Ahn, S.; Yoo, M.; Lee, Y.H.; Koh, D.; Lim, Y. Design, synthesis, and evaluation of 4-chromenone derivatives combined with N-acylhydrazone for aurora kinase A inhibitor. Applied Biological Chemistry 2021, 64, 21. [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Zheng, M.; Li, H.; Yu, K.; Chen, K.; Shen, X.; Jiang, H.; et al. Discovering potent inhibitors against the beta-hydroxyacyl-acyl carrier protein dehydratase (FabZ) of Helicobacter pylori: structure-based design, synthesis, bioassay, and crystal structure determination. J Med Chem 2009, 52, 2465-2481. [CrossRef]
- Gorantla, V.; Gundla, R.; Jadav, S.S.; Anugu, S.R.; Chimakurthy, J.; Nidasanametla, S.K.; Korupolu, R. Molecular hybrid design, synthesis and biological evaluation of N-phenyl sulfonamide linked N-acyl hydrazone derivatives functioning as COX-2 inhibitors: new anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant and anti-bacterial agents. New Journal of Chemistry 2017, 41, 13516-13532. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Kunadia, A.; Lin, Y.; Fondell, J.D.; Seidel, D.; Fan, H. Identification of a strong and specific antichlamydial N-acylhydrazone. PLOS ONE 2017, 12, e0185783. [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Wu, R.; Qi, S.; Gu, C.; Si, F.; Chen, Z. Synthesis and Antibacterial Evaluation of New N-acylhydrazone Derivatives from Dehydroabietic Acid. Molecules 2012, 17, 4634-4650. [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos Fernandes, G.F.; de Souza, P.C.; Moreno-Viguri, E.; Santivañez-Veliz, M.; Paucar, R.; Pérez-Silanes, S.; Chegaev, K.; Guglielmo, S.; Lazzarato, L.; Fruttero, R.; et al. Design, Synthesis, and Characterization of N-Oxide-Containing Heterocycles with in Vivo Sterilizing Antitubercular Activity. J Med Chem 2017, 60, 8647-8660. [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, S.H.; Barreto, M.B.; Lourenço, M.C.; Henriques, M.; Candéa, A.L.; Kaiser, C.R.; de Souza, M.V. Antitubercular activity of new coumarins. Chemical biology & drug design 2011, 77, 489-493. [CrossRef]
- Rozada, A.M.; Rodrigues, F.A.; Sampiron, E.G.; Seixas, F.A.; Basso, E.A.; Scodro, R.B.; Kioshima É, S.; Gauze, G.F. Novel 4-methoxynaphthalene-N-acylhydrazones as potential for paracoccidioidomycosis and tuberculosis co-infection. Future microbiology 2019, 14, 587-598. [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos Filho, J.M.; de Queiroz, E.S.D.M.A.; Macedo, T.S.; Teixeira, H.M.P.; Moreira, D.R.M.; Challal, S.; Wolfender, J.L.; Queiroz, E.F.; Soares, M.B.P. Conjugation of N-acylhydrazone and 1,2,4-oxadiazole leads to the identification of active antimalarial agents. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry 2016, 24, 5693-5701. [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, S.A.; Kaiser, M.; Brun, R.; Silva, E.F.; Fraga, C.A. Antiprotozoal Activity of (E)-Cinnamic N-Acylhydrazone Derivatives. Molecules 2014, 19, 20374-20381. [CrossRef]
- Alves, M.S.D.; das Neves, R.N.; Sena-Lopes, Â.; Domingues, M.; Casaril, A.M.; Segatto, N.V.; Nogueira, T.C.M.; de Souza, M.V.N.; Savegnago, L.; Seixas, F.K.; et al. Antiparasitic activity of furanyl N-acylhydrazone derivatives against Trichomonas vaginalis: in vitro and in silico analyses. Parasites & Vectors 2020, 13, 59. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Kadyan, K.; Duhan, M.; Sindhu, J.; Singh, V.; Saharan, B.S. Design, synthesis, conformational and molecular docking study of some novel acyl hydrazone based molecular hybrids as antimalarial and antimicrobial agents. Chemistry Central Journal 2017, 11, 115. [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.K.C.; Teixeira, J.S.; Moreira, D.R.M.; da Silva, T.F.; Barreiro, E.J.L.; de Freitas, H.F.; Pita, S.; Teles, A.L.B.; Guimarães, E.T.; Soares, M.B.P. In Vitro, In Vivo and In Silico Effectiveness of LASSBio-1386, an N-Acyl Hydrazone Derivative Phosphodiesterase-4 Inhibitor, Against Leishmania amazonensis. Frontiers in pharmacology 2020, 11, 590544. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Ye, J.; Lian, W.; Zhang, M.; Li, B.; Liu, A.; Hu, A. Microwave-assisted synthesis, characterization and bioassay of acylhydrazone derivatives as influenza neuraminidase inhibitors. Medicinal Chemistry Research 2017, 26, 3216-3227. [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, D.A.; Ferreira-Silva, G.; Ferreira, A.C.; Fernandes, R.A.; Kwee, J.K.; Sant'Anna, C.M.; Ionta, M.; Fraga, C.A. Design, Synthesis, and Pharmacological Evaluation of Novel N-Acylhydrazone Derivatives as Potent Histone Deacetylase 6/8 Dual Inhibitors. J Med Chem 2016, 59, 655-670. [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, N.M.; Freitas, R.H.; Fraga, C.A.; Fernandes, P.D. Discovery of Novel Orally Active Tetrahydro-Naphthyl-N-Acylhydrazones with In Vivo Anti-TNF-α Effect and Remarkable Anti-Inflammatory Properties. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0156271. [CrossRef]
- Polo-Cerón, D.; Hincapié-Otero, M.M.; Joaqui-Joaqui, A. Synthesis and characterization of four N-acylhydrazones as potential O, N, O donors for Cu2+: An experimental and theoretical study. Universitas Scientiarum 2021, 26, 193-215. [CrossRef]
- Thiago Moreira, P.; Arthur Eugen, K. Hydrazone-Based Small-Molecule Chemosensors. In Computational Biology and Chemistry, Payam, B., Nicola, B., Eds.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, 2020; p. Ch. 6.
- Guay, D.R. An update on the role of nitrofurans in the management of urinary tract infections. Drugs 2001, 61, 353-364. [CrossRef]
- McOsker, C.C.; Fitzpatrick, P.M. Nitrofurantoin: mechanism of action and implications for resistance development in common uropathogens. The Journal of antimicrobial chemotherapy 1994, 33 Suppl A, 23-30. [CrossRef]
- Basile, M.; Gidaro, S.; Pacella, M.; Biffignandi, P.M.; Gidaro, G.S. Troxerutin-carbazochrome combination versus placebo in the treatment of posthemorrhoidectomy symptoms: a single-center, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Current Therapeutic Research 2002, 63, 527-535. [CrossRef]
- Passali, G.C.; De Corso, E.; Bastanza, G.; Di Gennaro, L. An old drug for a new application: carbazochrome-sodium-sulfonate in HHT. Journal of clinical pharmacology 2015, 55, 601-602. [CrossRef]
- Krause, T.; Gerbershagen, M.U.; Fiege, M.; Weisshorn, R.; Wappler, F. Dantrolene--a review of its pharmacology, therapeutic use and new developments. Anaesthesia 2004, 59, 364-373. [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, J.C.R.; Hiene, M.A.C.; Salgado, H.R.N. Physico-chemical characterization and analytical development for sodium azumolene, a potential drug designed to fight malignant hyperthermia. Journal of Analytical & Bioanalytical Techniques 2013, 1-6.
- Sachdev, E.; Sachdev, D.; Mita, M. Aldoxorubicin for the treatment of soft tissue sarcoma. Expert opinion on investigational drugs 2017, 26, 1175-1179. [CrossRef]
- Costa, D.G.; da Silva, J.S.; Kümmerle, A.E.; Sudo, R.T.; Landgraf, S.S.; Caruso-Neves, C.; Fraga, C.A.; de Lacerda Barreiro, E.J.; Zapata-Sudo, G. LASSBio-294, A compound with inotropic and lusitropic activity, decreases cardiac remodeling and improves Ca²(+) influx into sarcoplasmic reticulum after myocardial infarction. American journal of hypertension 2010, 23, 1220-1227. [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.L.; Noël, F.; Barreiro, E.J. Cyclic GMP-dependent vasodilatory properties of LASSBio 294 in rat aorta. British journal of pharmacology 2002, 135, 293-298. [CrossRef]
- Lucas, P.W.; Schmit, J.M.; Peterson, Q.P.; West, D.C.; Hsu, D.C.; Novotny, C.J.; Dirikolu, L.; Churchwell, M.I.; Doerge, D.R.; Garrett, L.D.; et al. Pharmacokinetics and derivation of an anticancer dosing regimen for PAC-1, a preferential small molecule activator of procaspase-3, in healthy dogs. Investigational new drugs 2011, 29, 901-911. [CrossRef]
- Peterson, Q.P.; Goode, D.R.; West, D.C.; Ramsey, K.N.; Lee, J.J.; Hergenrother, P.J. PAC-1 activates procaspase-3 in vitro through relief of zinc-mediated inhibition. Journal of molecular biology 2009, 388, 144-158. [CrossRef]
- Thota, S.; Rodrigues, D.A.; Pinheiro, P.d.S.M.; Lima, L.M.; Fraga, C.A.M.; Barreiro, E.J. N-Acylhydrazones as drugs. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 2018, 28, 2797-2806. [CrossRef]
- Effenberger, K.; Breyer, S.; Ocker, M.; Schobert, R. New doxorubicin N-acyl hydrazones with improved efficacy and cell line specificity show modes of action different from the parent drug. International journal of clinical pharmacology and therapeutics 2010, 48, 485-486. [CrossRef]
- de Melo, T.R.; Chelucci, R.C.; Pires, M.E.; Dutra, L.A.; Barbieri, K.P.; Bosquesi, P.L.; Trossini, G.H.; Chung, M.C.; dos Santos, J.L. Pharmacological evaluation and preparation of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs containing an N-acyl hydrazone subunit. International journal of molecular sciences 2014, 15, 5821-5837. [CrossRef]
- Aarjane, M.; Aouidate, A.; Slassi, S.; Amine, A. Synthesis, antibacterial evaluation, in silico ADMET and molecular docking studies of new N-acylhydrazone derivatives from acridone. Arabian Journal of Chemistry 2020, 13, 6236-6245. [CrossRef]
- Lazzarini, C.; Haranahalli, K.; Rieger, R.; Ananthula Hari, K.; Desai Pankaj, B.; Ashbaugh, A.; Linke Michael, J.; Cushion Melanie, T.; Ruzsicska, B.; Haley, J.; et al. Acylhydrazones as Antifungal Agents Targeting the Synthesis of Fungal Sphingolipids. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 2018, 62, 10.1128/aac.00156-00118. [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, T.C.M.; dos Santos Cruz, L.; Lourenço, M.C.; de Souza, M.V.N. Design, synthesis and anti-tuberculosis activity of hydrazones and N-acylhydrazones containing vitamin B6 and different heteroaromatic nucleus. Letters in Drug Design & Discovery 2019, 16, 792-798. [CrossRef]
- Angelova, V.T.; Valcheva, V.; Vassilev, N.G.; Buyukliev, R.; Momekov, G.; Dimitrov, I.; Saso, L.; Djukic, M.; Shivachev, B. Antimycobacterial activity of novel hydrazide-hydrazone derivatives with 2H-chromene and coumarin scaffold. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 2017, 27, 223-227. [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, G.F.d.S.; de Souza, P.C.; Marino, L.B.; Chegaev, K.; Guglielmo, S.; Lazzarato, L.; Fruttero, R.; Chung, M.C.; Pavan, F.R.; dos Santos, J.L. Synthesis and biological activity of furoxan derivatives against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2016, 123, 523-531. [CrossRef]
- Naveen Kumar, H.S.; Parumasivam, T.; Jumaat, F.; Ibrahim, P.; Asmawi, M.Z.; Sadikun, A. Synthesis and evaluation of isonicotinoyl hydrazone derivatives as antimycobacterial and anticancer agents. Medicinal Chemistry Research 2014, 23, 269-279. [CrossRef]
- Fahmi, M.R.G.; Khumaidah, L.; Ilmiah, T.K.; Fadlan, A.; Santoso, M. 2-Thiophenecarboxylic acid hydrazide Derivatives: Synthesis and Anti-Tuberculosis Studies. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering 2018, 349, 012039. [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.D.; Dixit, S.R.; Gadag, S.; Kulkarni, V.H.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Molecular docking, synthesis, and antimycobacterial activities of pyrrolyl hydrazones and their copper complexes. Research and Reports in Medicinal Chemistry 2015, 1-14.
- Bordei, A.T.; Nuță, D.C.; Musat, G.C.; Missir, A.V.; Caproiu, M.T.; Dumitrascu, F.; Zarafu, I.; Ionita, P.; Badiceanu, C.D.; Limban,C.L. Microwave assisted synthesis and spectroscopic characterization of some novel Schiff bases of carprofen hydrazide. Farmacia 2019, 67, 955-962. [CrossRef]
- Avram, S.; Udrea, A.M.; Nuta, D.C.; Limban, C.; Balea, A.C.; Caproiu, M.T.; Dumitrascu, F.; Buiu, C.; Bordei, A.T. Synthesis and Bioinformatic Characterization of New Schiff Bases with Possible Applicability in Brain Disorders. Molecules 2021, 26. [CrossRef]
- Bordei, A.T.; Limban, C.; Nuta, D.C.; Zarafu, I.; Denes, M.; Marutescu, L.; Chifiriuc, M.C.; Popa, M.; Arama, C. Recent advances in the study of derivatives of (EZ)-N'-benzylidene-(2RS)-2-(6-chloro-9h-carbazol-2-yl)propanohydrazide. Farmacia 2022, 70, 589-595. [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Chibale, K. Strategies to Combat Multi-Drug Resistance in Tuberculosis. Accounts of Chemical Research 2021, 54, 2361-2376. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L. Antibiotic resistance mechanisms in M. tuberculosis: an update. Archives of toxicology 2016, 90, 1585-1604. [CrossRef]
- Bendre, A.D.; Peters, P.J.; Kumar, J. Tuberculosis: Past, present and future of the treatment and drug discovery research. Current research in pharmacology and drug discovery 2021, 2, 100037. [CrossRef]
- Riccardi, G.; Pasca, M.R.; Buroni, S. Mycobacterium tuberculosis: drug resistance and future perspectives. Future microbiology 2009, 4, 597-614. [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D.; Maiti, A.K.; Alenazy, R.; Joseph, B. In silico Approach to Identify Potent Bioactive Compounds as Inhibitors against the Enoyl-acyl Carrier Protein (acp) Reductase Enzyme of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Iacobino, A.; Fattorini, L.; Giannoni, F. Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis 2020: Where We Stand. Applied Sciences 2020, 10. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yew, W.W. Mechanisms of drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: update 2015. The international journal of tuberculosis and lung disease : the official journal of the International Union against Tuberculosis and Lung Disease 2015, 19, 1276-1289. [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Dwivedi, S.P.; Gaharwar, U.S.; Meena, R.; Rajamani, P.; Prasad, T. Recent updates on drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Journal of applied microbiology 2020, 128, 1547-1567. [CrossRef]
- Ozma, M.A.; Lahouty, M.; Abbasi, A.; Rezaee, M.A.; Kafil, H.S.; Asgharzadeh, M. Effective bacterial factors involved in the dissemination of tuberculosis. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Dhameliya, T.M.; Vekariya, D.D.; Patel, H.Y.; Patel, J.T. Comprehensive coverage on anti-mycobacterial endeavour reported during 2022. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2023, 255, 115409. [CrossRef]
- Palomino, J.C.; Martin, A. Drug resistance mechanisms in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Antibiotics 2014, 3, 317-340. [CrossRef]
- Khawbung, J.L.; Nath, D.; Chakraborty, S. Drug resistant Tuberculosis: A review. Comparative immunology, microbiology and infectious diseases 2021, 74, 101574. [CrossRef]
- Mabhula, A.; Singh, V. Drug-resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: where we stand. MedChemComm 2019, 10, 1342-1360. [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Ualiyeva, D.; Jamal, K.; Ali, B.; Ahmad, F.; Sapkota, S.; Boadi Amissah, O.; Ndip Ndip Bate, P. Molecular diagnostics and potential therapeutic options for mycobacterium tuberculosis: Where we stand. Medicine in Omics 2023, 8, 100022. [CrossRef]
- Mirnejad, R.; Asadi, A.; Khoshnood, S.; Mirzaei, H.; Heidary, M.; Fattorini, L.; Ghodousi, A.; Darban-Sarokhalil, D. Clofazimine: A useful antibiotic for drug-resistant tuberculosis. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie 2018, 105, 1353-1359. [CrossRef]
- Raghu, M.S.; Kumar, C.B.P.; Kumar, K.Y.; Prashanth, M.K.; Alshahrani, M.Y.; Ahmad, I.; Jain, R. Design, synthesis and molecular docking studies of imidazole and benzimidazole linked ethionamide derivatives as inhibitors of InhA and antituberculosis agents. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 2022, 60, 128604. [CrossRef]
- Veena, K.; Raghu, M.S.; Kumar, K.Y.; Kumar, C.B.P.; Alharti, F.A.; Prashanth, M.K.; Jeon, B.-H. Design and synthesis of novel benzimidazole linked thiazole derivatives as promising inhibitors of drug-resistant tuberculosis. Journal of Molecular Structure 2022, 1269, 133822. [CrossRef]
- Acharya, P.T.; Bhavsar, Z.A.; Jethava, D.J.; Rajani, D.P.; Pithawala, E.; Patel, H.D. Synthesis, characterization, biological evaluation, and computational study of benzimidazole hybrid thiosemicarbazide derivatives. Journal of Heterocyclic Chemistry 2022, 59, 2142-2164. [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.K.; Maddipatla, S.; Gajula, S.N.R.; Ahmad, M.N.; Kaul, G.; Nanduri, S.; Sonti, R.; Dasgupta, A.; Chopra, S.; Yaddanapudi, V.M. Identification of nitrofuranylchalcone tethered benzoxazole-2-amines as potent inhibitors of drug resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis demonstrating bactericidal efficacy. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 2022, 64, 116777. [CrossRef]
- Vassiliades, S.V.; Navarausckas, V.B.; Dias, M.V.B.; Parise Filho, R. Mycobacterium tuberculosis dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors: State of Art Past 20 Years. Biointerface Research in Applied Chemistry 2023, 13. [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, M.; Nanda, B.; Kar, P.; Nanda, B.B. Intermolecular interactions of anti-tuberculosis drugs with different solvents: a review. Biointerface Research in Applied Chemistry 2022, 12, 883-892. [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Viveros, D.; Rechy-Iruretagoyena, D.A.; Díaz-Molina, R.; Vique-Sánchez, J.L. Triosephosphate Isomerase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis as Potential Target to Develop a New Anti-TB Drug. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Kancharla, S.K.; Birudaraju, S.; Pal, A.; Reddy, L.K.; Reddy, E.R.; Vagolu, S.K.; Sriram, D.; Bonige, K.B.; Korupolu, R.B. Synthesis and biological evaluation of isatin oxime ether-tethered aryl 1 H-1, 2, 3-triazoles as inhibitors of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. New Journal of Chemistry 2022, 46, 2863-2874. [CrossRef]
- Chitti, S.; Van Calster, K.; Cappoen, D.; Nandikolla, A.; Khetmalis, Y.M.; Cos, P.; Kumar, B.K.; Murugesan, S.; Sekhar, K.V.G.C. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of benzo-[d]-imidazo-[2, 1-b]-thiazole and imidazo-[2, 1-b]-thiazole carboxamide triazole derivatives as antimycobacterial agents. RSC advances 2022, 12, 22385-22401. [CrossRef]
- Shinde, S.R.; Inamdar, S.N.; Shinde, M.; Pawar, C.; Kushwaha, B.; Obakachi, V.A.; Kajee, A.; Chauhan, R.; Karpoormath, R. Discovery of oxazoline-triazole based hybrid molecules as DNA gyrase inhibitors: A new class of potential Anti-tubercular agents. Journal of Molecular Structure 2023, 1273, 134243. [CrossRef]
- El-Shoukrofy, M.S.; Atta, A.; Fahmy, S.; Sriram, D.; Mahran, M.A.; Labouta, I.M. New tetrahydropyrimidine-1, 2, 3-triazole clubbed compounds: Antitubercular activity and Thymidine Monophosphate Kinase (TMPKmt) inhibition. Bioorganic Chemistry 2023, 131, 106312. [CrossRef]
- Homorodean, D.; Moisoiu, A.; Borroni, E. Ghid național pentru rețeaua laboratoarelor TB, Ministerul Sănătății 2017.
| Mycobacterial strain | Tested compound | 2 mg/mL | 4 mg/mL | RIF | INH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. tuberculosis 2327 | 1a | 30 | 30 | <20 | <20 |
| 1b | 30-100 | 30-100 | <20 | <20 | |
| 1c | 30 | 30 | <20 | <20 | |
| 1d | 30 | 30 | <20 | <20 | |
| 1e | 30-100 | 30 | <20 | <20 | |
| 1f | 30-100 | 30-100 | <20 | <20 | |
| M. tuberculosis 2337 | 1a | 30-100 | 30 | <20 | <20 |
| 1b | 30-100 | 30 | <20 | <20 | |
| 1c | 30 | 30 | <20 | <20 | |
| 1d | 30 | 30 | <20 | <20 | |
| 1e | 30-100 | 30 | <20 | <20 | |
| 1f | 30-100 | 30-100 | <20 | <20 | |
| M. tuberculosis 1762 | 1a | 30-100 | 30-100 | <20 | >20 |
| 1b | 30-100 | 30 | <20 | >20 | |
| 1c | 30-100 | 30 | <20 | >20 | |
| 1d | 30-100 | 30 | <20 | >20 | |
| 1e | 30-100 | 30 | <20 | >20 | |
| 1f | >100 | 30-100 | <20 | >20 | |
| M. tuberculosis 309 | 1a | 30-100 | 30-100 | >20 | >20 |
| 1b | 30-100 | 30 | >20 | >20 | |
| 1c | 30-100 | 30-100 | >20 | >20 | |
| 1d | 30-100 | 30 | >20 | >20 | |
| 1e | 30-100 | 30 | >20 | >20 | |
| 1f | >100 | 30-100 | >20 | >20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





