Submitted:
18 January 2024
Posted:
18 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Rokoko Smartsuit
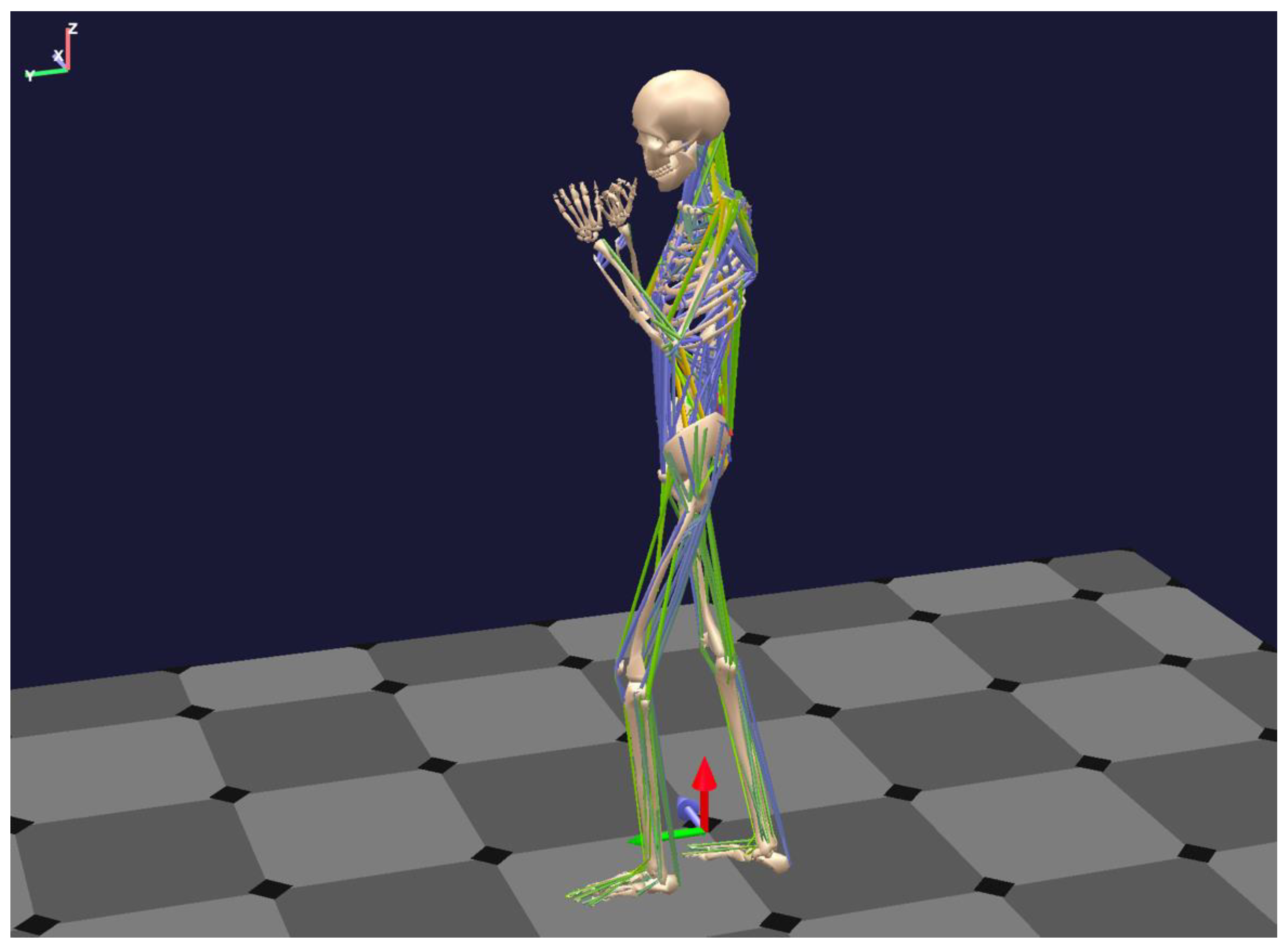
2.2. Biomechanics of Bodies (BoB)
2.3. Statistics
2.4. Operational Tactical Procedures (OTP)
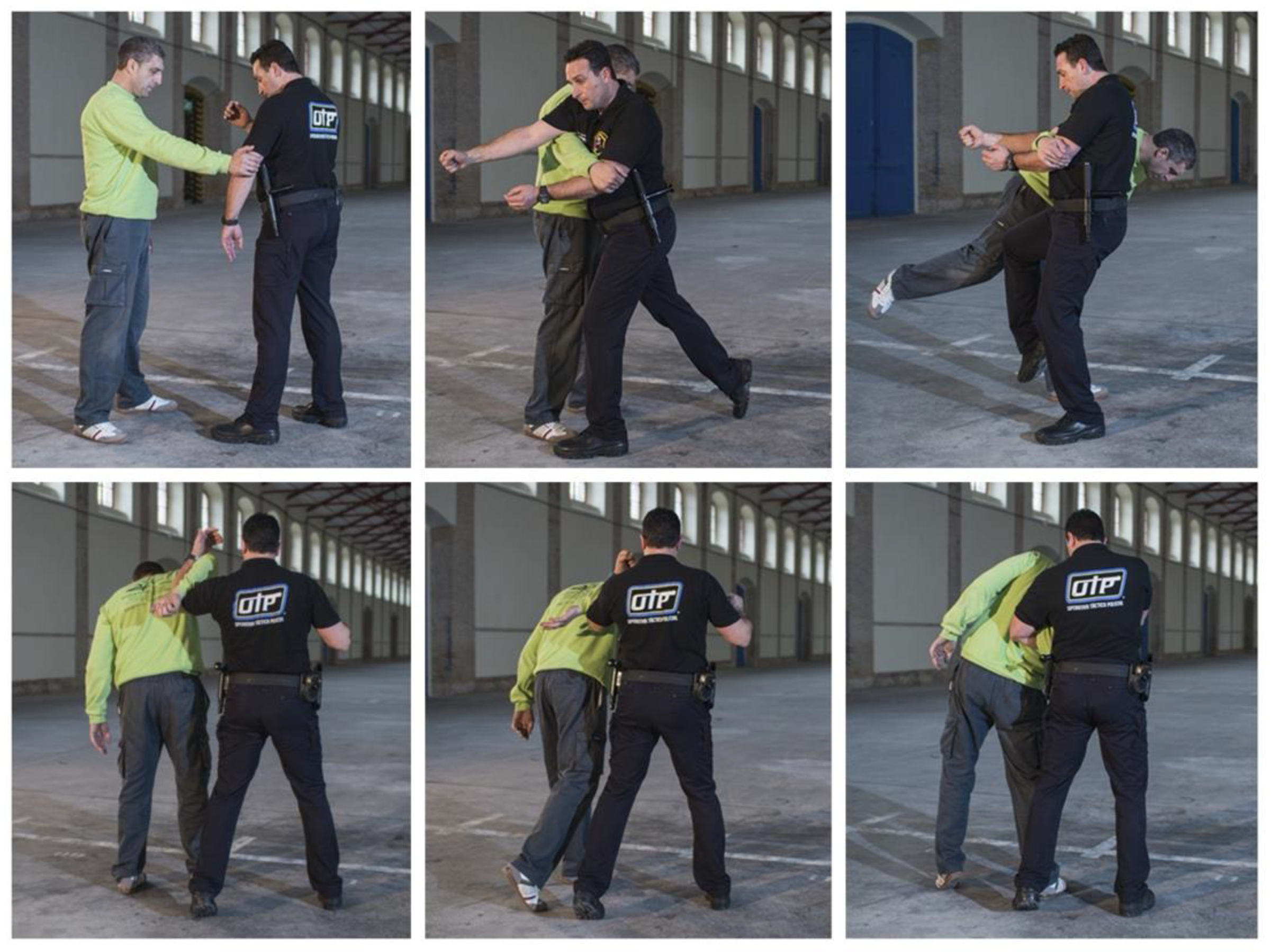

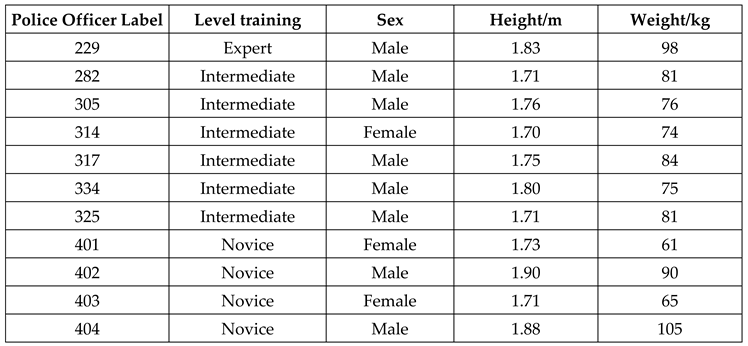
2.5. The subjects who performed the corresponding tests were:
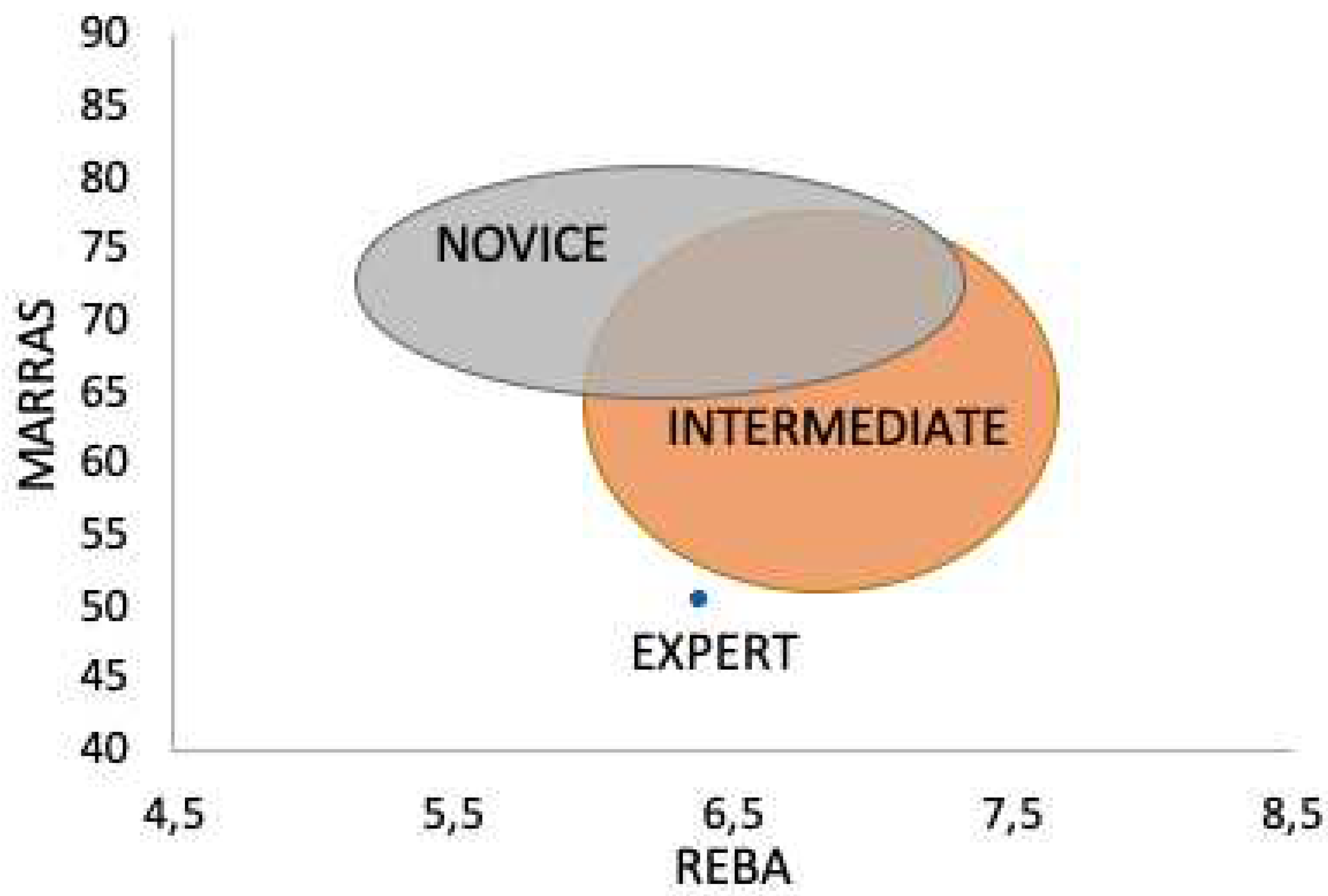
3. Results and discussion
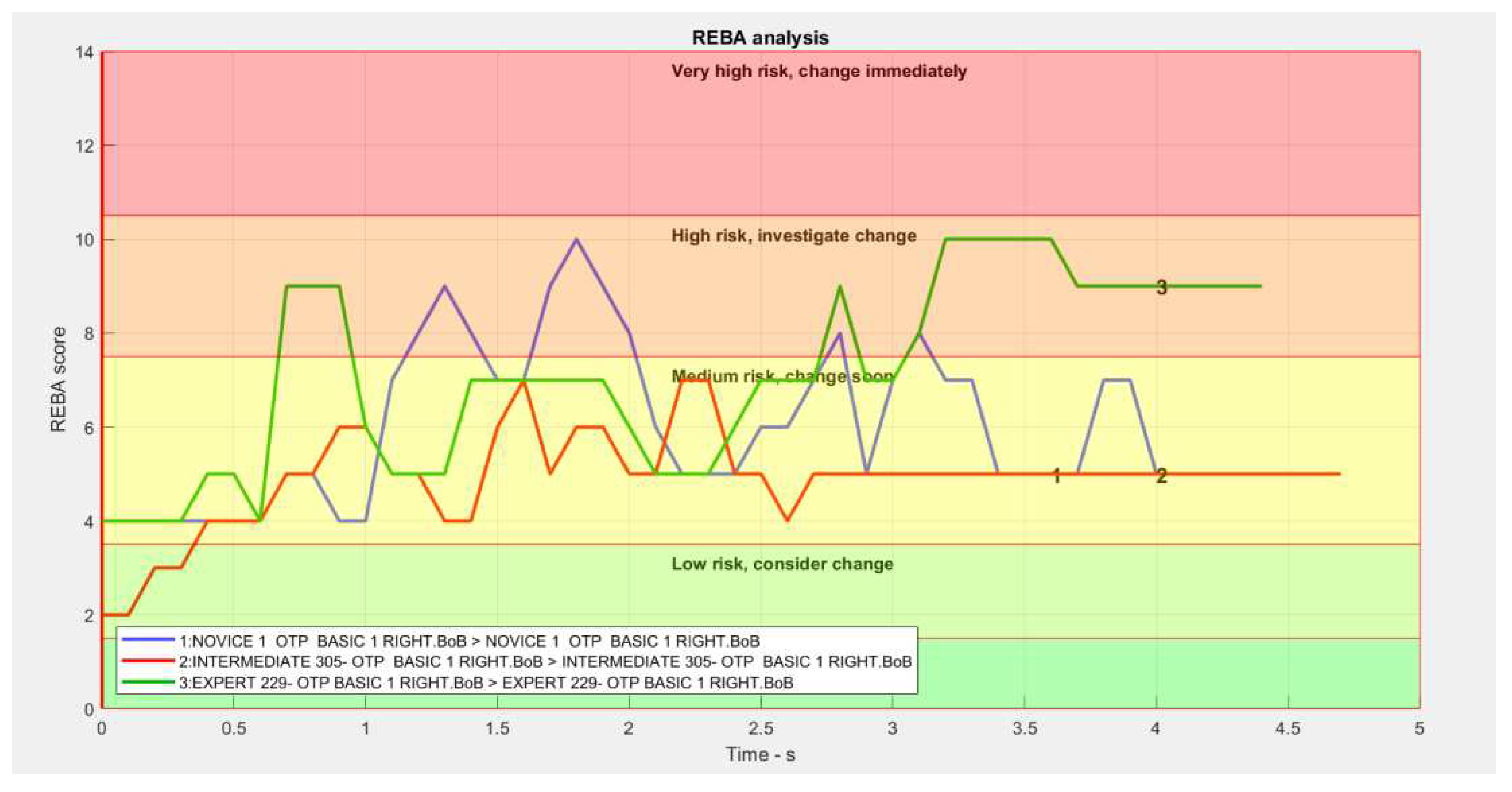
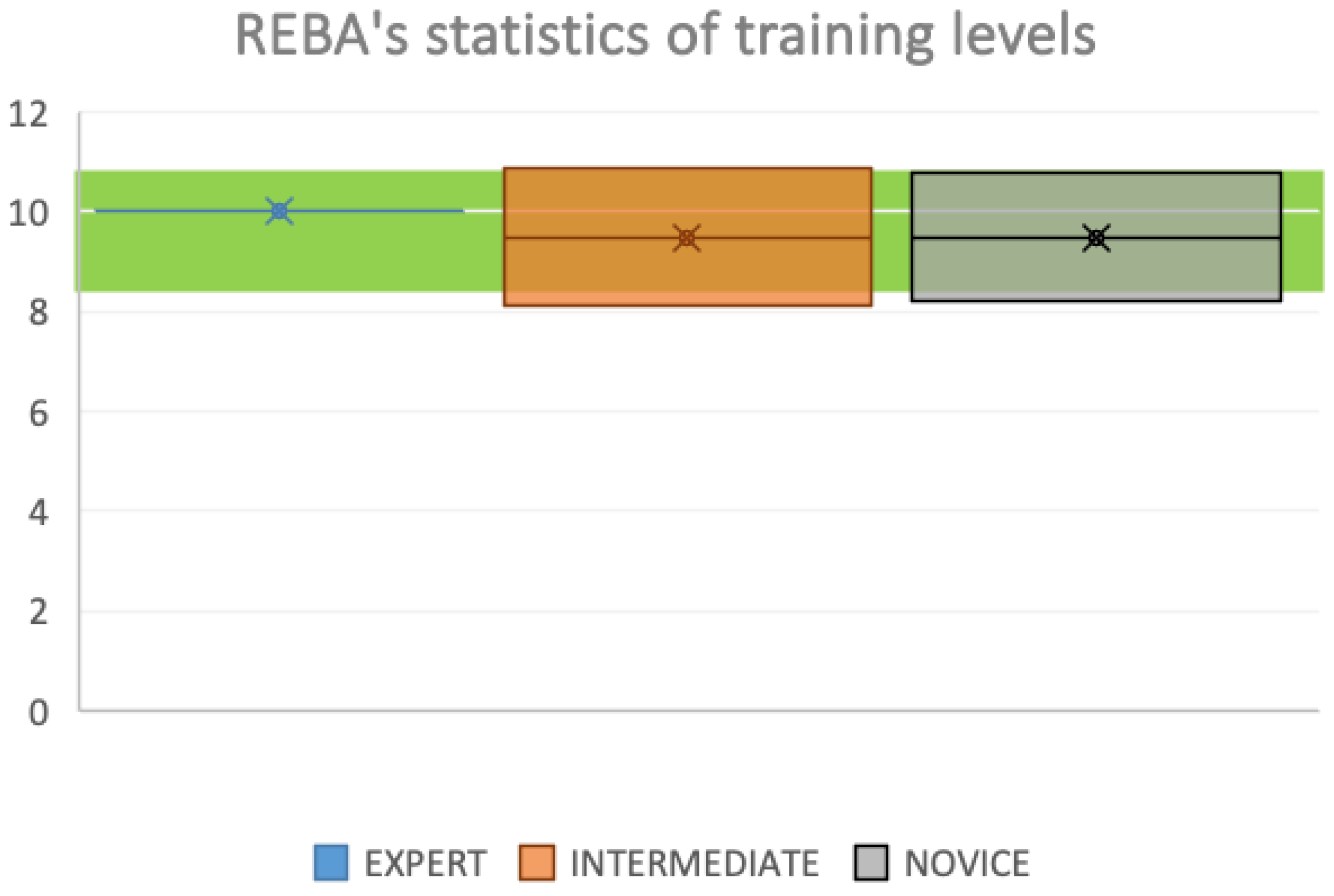
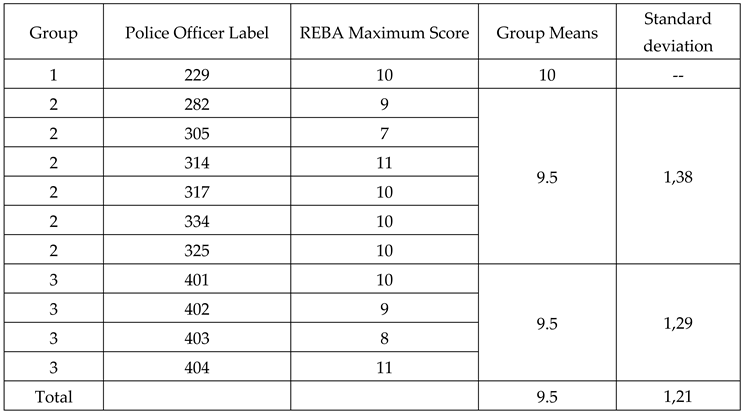
3.1. REBA (Rapid Entire Body Assessment)
3.1.1. Normality Analysis.
3.1.2. ANOVA
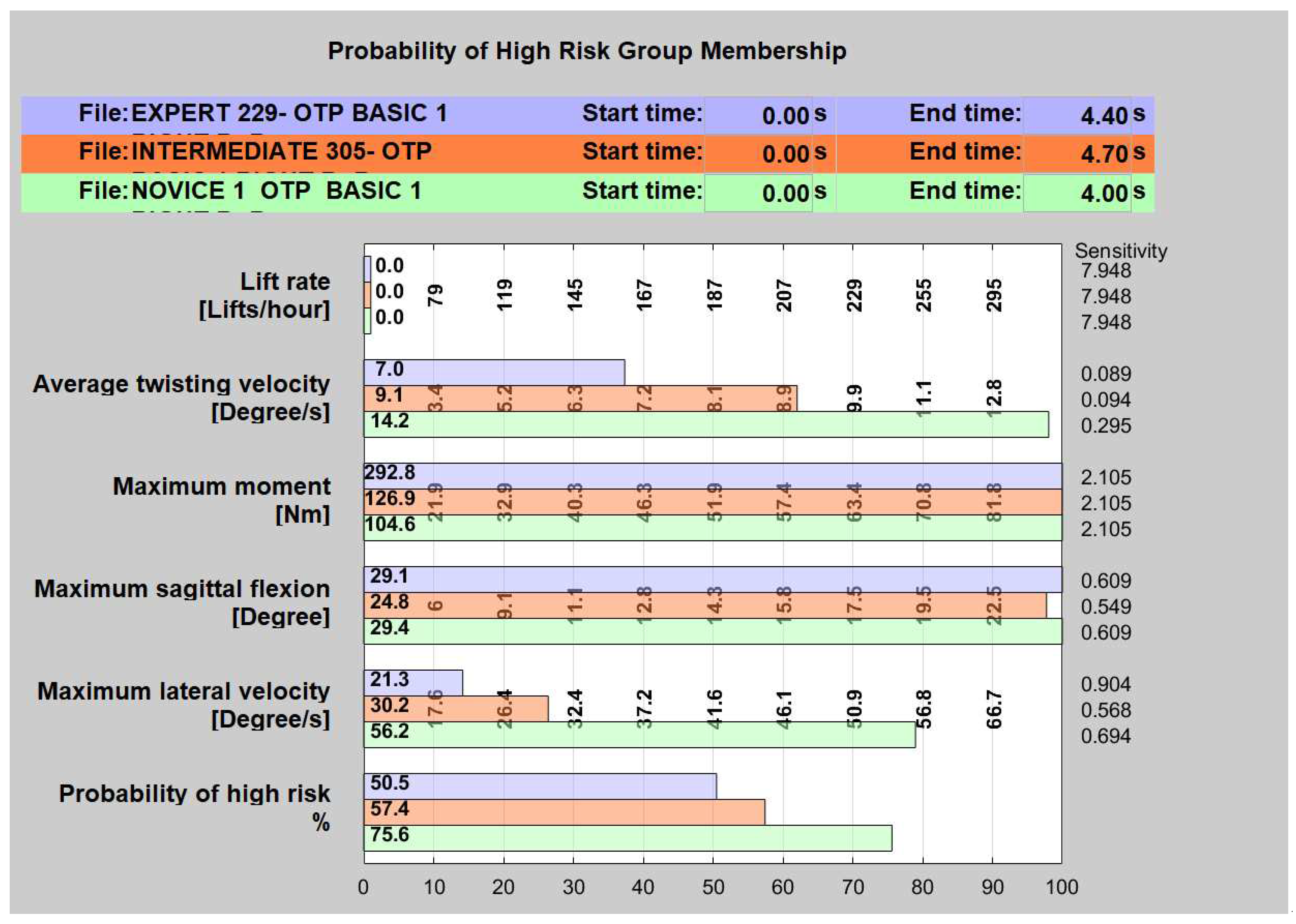
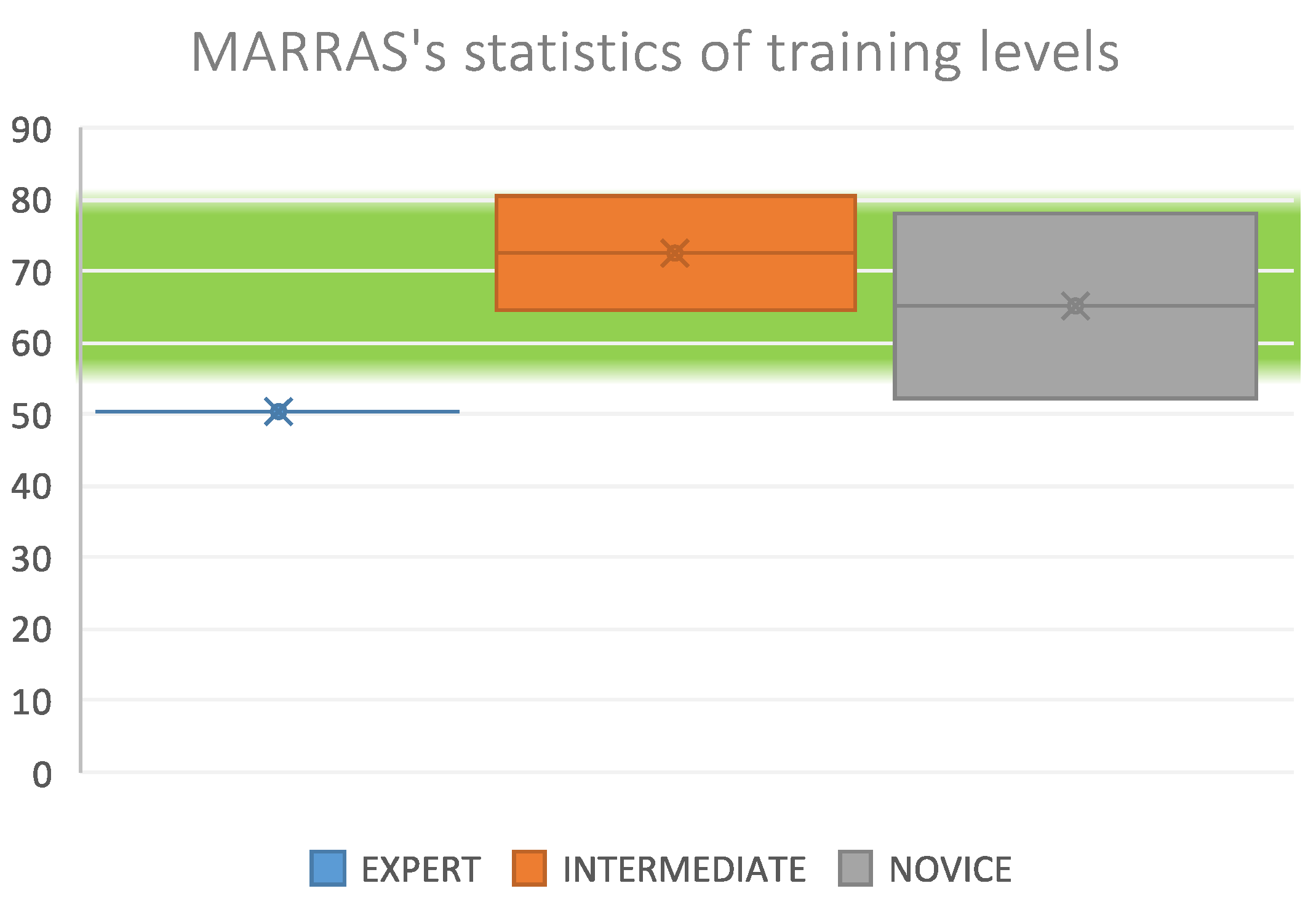
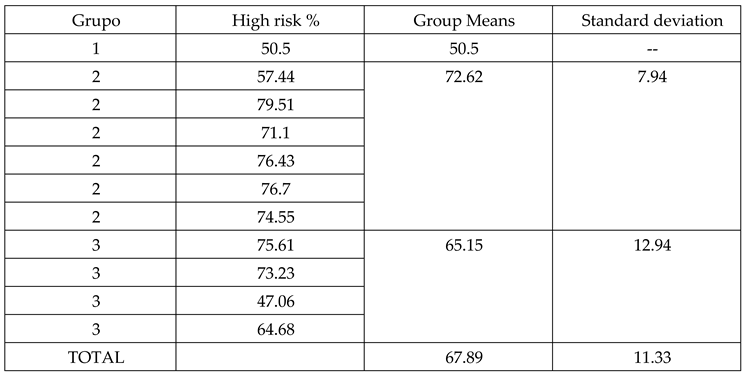
3.2. Marras method (Probability of High Risk Group Membership)
3.2.1. Normality Analysis
3.2.2. Kruskal-Wallis contrast test
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BoB | Biomechanics of Bodies |
| IESPA | Instituto de Emergencias y Seguridad Pública de Andalucía |
| IMU | Inertial Measurement Units |
| OTP | Operational Tactical Procedures |
| PITS | Physical Intervention Techniques |
| UOF | Use of force |
| REBA | Rapid Entire Body Assessment |
References
- Untrained police officers with 35 daily attacks on authority: "You seek self-defense" El Español (National newspaper) Available online:. Available online: https://www.elespanol.com/reportajes/20230903/policias-sin-entrenamiento-atentados-diarios-autoridad-defensa-personal-buscas/791171253_0.html (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Strömmer, E.M.F., Leith, W., Zeegers, M.P., Freeman, M. D.; Injuries Due to Law Enforcement Use of Force in the United States, 2006-2015: Trends in Severity and by Race. J. Racial and Ethnic Health Disparities (2023). [CrossRef]
- Staller, M.S., Koerner, S., Heil, V., Klemmer I., Abraham A., Poolton J.; The Structure and Delivery of Police Use of Force Training: A German Case Study. Eur J Secur Res 7, 87–112 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Kleygrewe, L., Oudejans, R.R.D., Koedijk, M., Hutter, R.I.V.; Police Training in Practice: Organization and Delivery According to European Law Enforcement Agencies. Front. Psychol. 12:798067. (2022). [CrossRef]
- Dulsky C.C., Renzi C.P., McLaurin N.N., Wang T., Chen L.S., Walters M.R., Tanaka H.; J Sports Med. Effects of supra high-intensity interval training in police officers. Phys Fitness. 2023 Apr;63(4):543-549. [CrossRef]
- Staller M. S., Koerner, S., Bennell C., Suss, J.; Editorial: Police education and training revisited: Drawbacks and advances. Frontiers in Psychology. (2022). [CrossRef]
- Boxer, P., Brunson, R. K., Gaylord-Harden, N., Kahn, K., Patton, D. U., Richardson, J., Algrim, K.; Addressing the inappropriate use of force by police in the United States and beyond: A behavioral and social science perspective. Aggressive Behavior, 47(5), 502–512. (2021). [CrossRef]
- Granholm-Valmari, E., Ghazinour, M., Nygren, U., Gilenstam, K. ; Exploring the life contexts of patrolling police officers in the European Union–A scoping review. Scandinavian Journal of Occupational Therapy, 30(5), 585-603. (2023). [CrossRef]
- Granholm-Valmari, E., Ghazinour, M., Nygren, U., Gilenstam, K.; A systematic review of lifestyle and health among patrolling police officers. Scandinavian Journal of Occupational Therapy, 30(5), 721-744. (2023). [CrossRef]
- Koerner, S., Staller M. S.; The Situation is Quite Different.” Perceptions of Violent Conflicts and Training Among German Police Officers. Frontiers in Education. 6 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Vera-Jiménez, J. C., Fernandez, F., Ayuso, J., Lorente-Acosta, J. A.; Evaluation of the police operational tactical procedures for reducing officer injuries resulting from physical interventions in problematic arrests. The case of the Municipal Police of Cádiz (Spain). International journal of occupational medicine and environmental health, 33(1), 35-43. (2019). [CrossRef]
- Vera-Jiménez, J. C., Lorente, J. A., González-Herrera, L., Álvarez, J. A., Ferreiro-González, M., & Ayuso, J.; A legal and forensic medicine approach to police physical intervention techniques in high-risk situations. International journal of environmental research and public health, 17(8), 2809. (2020). [CrossRef]
- Vera-Jiménez, J. C., Meléndez-Sánchez, F. L., Álvarez, J. A., Ayuso, J.; An Analysis of Biomechanical Parameters in OTP Police Physical Intervention Techniques for Occupational Risk Prevention. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(11), 6615. (2022). [CrossRef]
- Duarte, J. D. R. D. S., Ferraz, A. D. F.; Studies on martial arts, fights and sports combat with police: a systematic review. Scientific Electronic Archives, 15(3). (2022). [CrossRef]
- Vera-Jiménez, J. C., Villero-Carro, D., González-Herrera, L., Álvarez, J. A., Ayuso, J.; A Multidisciplinary Vision of the Criminal, Social and Occupational Risk Consequences of the Use of Police Force. Safety, 9(3), 50. (2023). [CrossRef]
- Vera-Jiménez, J. C., Villero-Carro, D., Pastor-Fernandez, A., Shippen, J., Ferreiro-González, M., Vera-Jurado, J. C., Ayuso, J. Comparison of traditional physical intervention techniques vs. operational tactical procedures and techniques in the use of force during police arrests. Safety, 9(2), 39. (2023). [CrossRef]
- Peppoloni, L., Filippeschi, A., Ruffaldi, E., Avizzano, C.A.; (WMSDs Issue) A Novel Wearable System for the Online Assessment of Risk for Biomechanical Load in Repetitive Efforts. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2016, 52, 1–11. (2016). [CrossRef]
- Phipps, P. Case Study: Wearables Pilot Program Drives Reduction in Warehouse Hazards. Occupational Health & Safety, (2022). Available online: https://ohsonline.com/articles/2022/07/13/wearables-pilot-program.aspx (accessed on 8 January 2024).
- Shippen, J., & May, B. BoB – Biomechanics in MATLAB. In Proceedings of 11th International Conference BIOMDLORE (pp. 11-13). Vilnius Gediminas Technical University. (2016). [CrossRef]
- S.N. NTP 601: Evaluation of Working Conditions: Postural Load. REBA method (Rapid Entire Body Assessment). National Institute of Safety and Hygiene at Work (INSHT). 2001. Available online: https://www.studocu.com/ca-es/document/universitat-oberta-de-catalunya/prevencion-de-riesgos-derivados-de-la-organizacion-y-la-carga-de-trabajo/ntp-601-evaluacion-de-las-condiciones-de-trabajo-carga-postural-metodo-reba-rapid-entire-body-assessment/20730183 (accessed on 8 January 2024).
- Marras, W.S., Lavender, S.A., Leurgans, S.E., Rajulu, S.L., Allread, W.G., Fatallah, F.A., Ferguson, S.A.; The Role of Dynamics Three-Dimensional Trunk Motion in Occupationally-Related Low Back Disorder. Spine 18(5), 617-628. (1993). [CrossRef]
- WHO. Musculoskeletal Health. Available online: https://iea.cc/what-is-ergonomics (accessed on 8 January 2024).
- Driscoll, T., Jacklyn, G., Orchard, J., Passmore, E., Vos, T., Freedman, G., Lim, S., Punnett, L. The global burden of occupation-ally related low back pain: Estimates from the Global Burden of Disease 2010 study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 975–981 (2013). [CrossRef]
- ILO. Global Trends on Occupational Accidents and Diseases. World Day for Safety and Health at Work. 2015. Available online: https://www.ilo.org/legacy/english/osh/en/story_content/external_files/fs_st_1-ILO_5_en.pdf (accessed on 8 January 2024).
- Tompa, E., Mofidi, A., van den Heuvel, S., van Bree, T., Michaelsen, F., Jung, Y., Porsch, L., van Emmerik, M.; The Value of Occupational Safety and Health and the Societal Costs of Work-Related Injuries and Diseases; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, (2019). [CrossRef]
- Hassani, M., Hesampour, R., Bartnicka, J., Monjezi, N., Ezbarami S.M.; Evaluation of working conditions, work postures, musculoskeletal disorders and low back pain among sugar production workers. Work. 2022;73(1):273-289. (2022). [CrossRef]
- 27. Campo, G., Cegolon, L., De Merich, D., Fedeli, U., Pellicci, M., Heymann, W.C., Pavanello, S., Guglielmi, A., Mastrangelo, G.; The Italian National Surveillance System for Occupational Injuries: Conceptual Framework and Fatal Outcomes, 2002–2016. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, 17, 7631. (2020). [CrossRef]
 |
 |
 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





