Submitted:
02 January 2024
Posted:
18 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
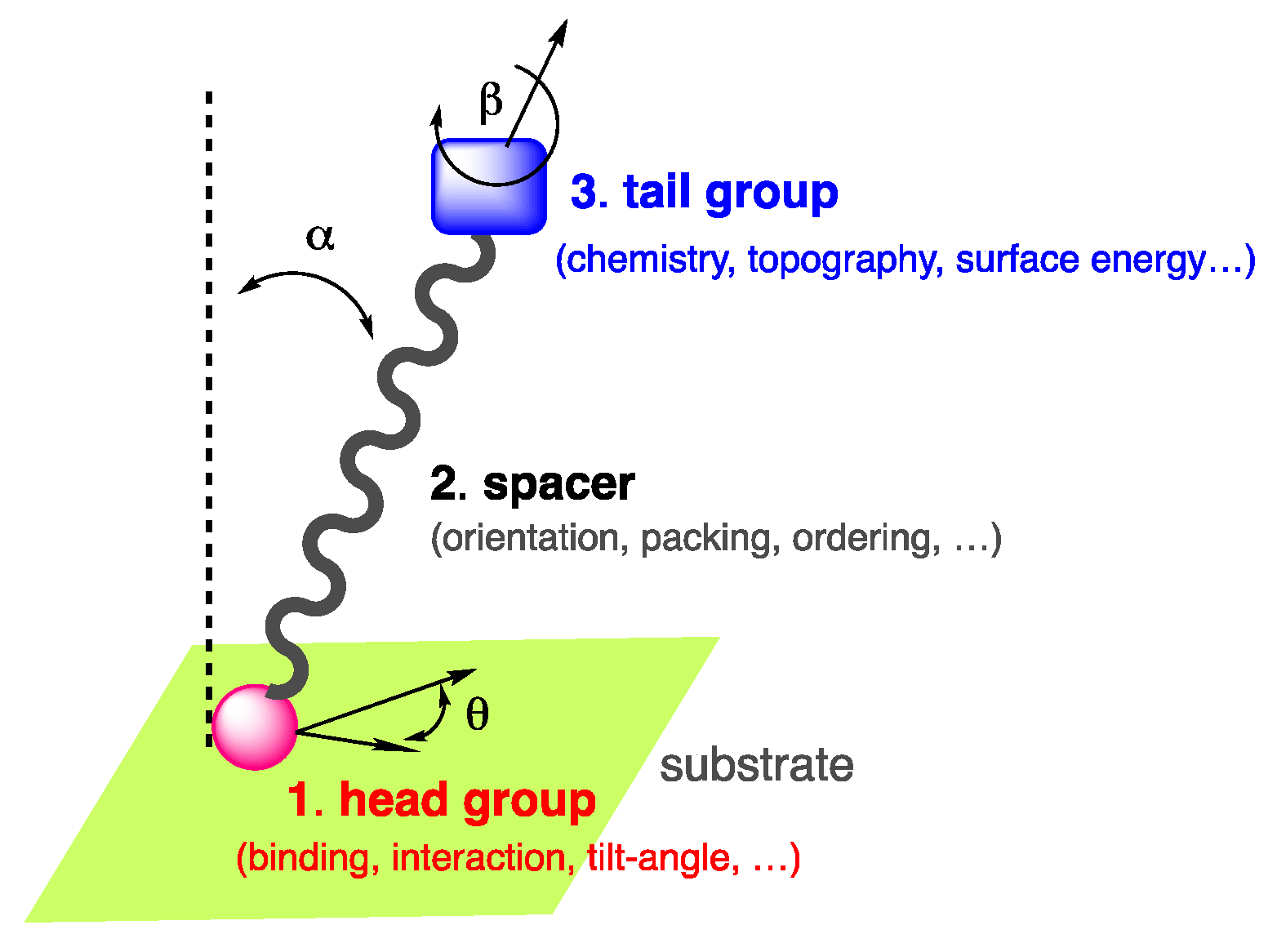
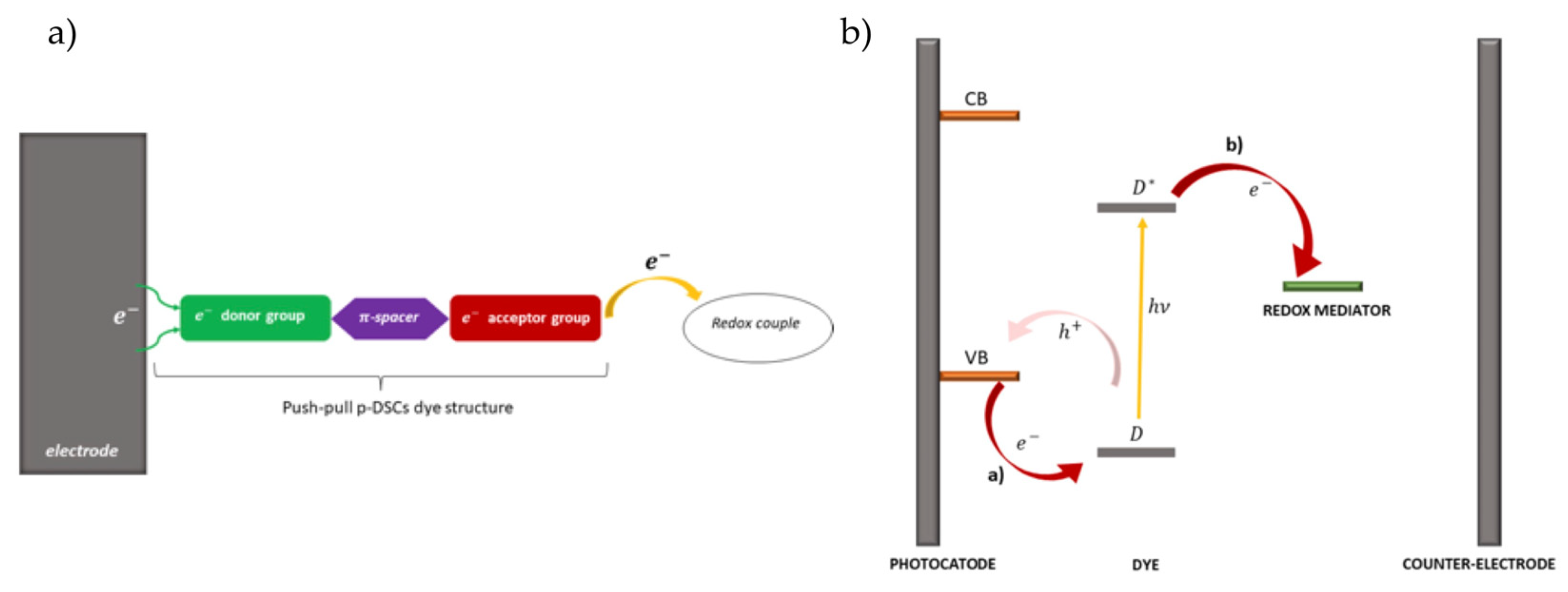
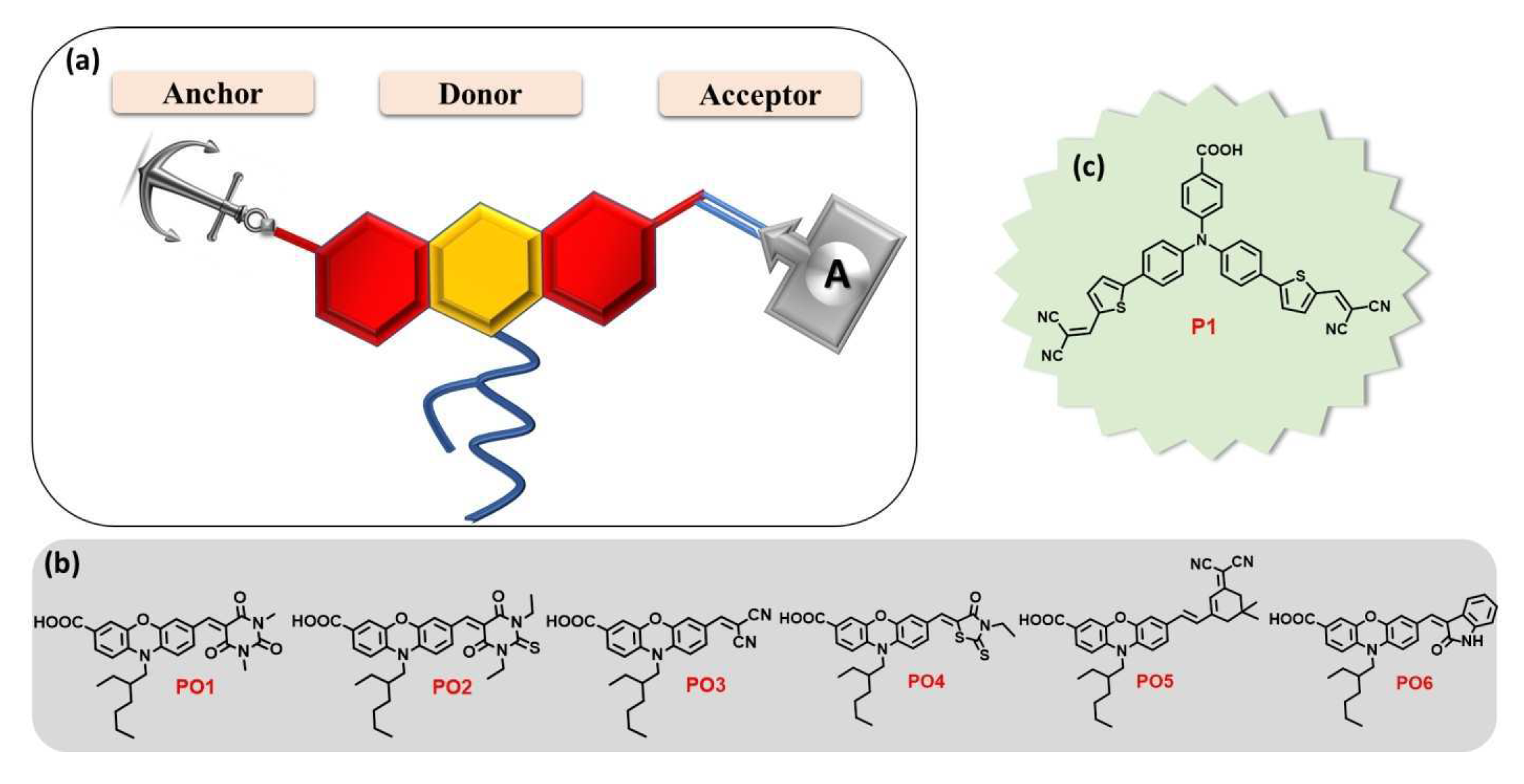
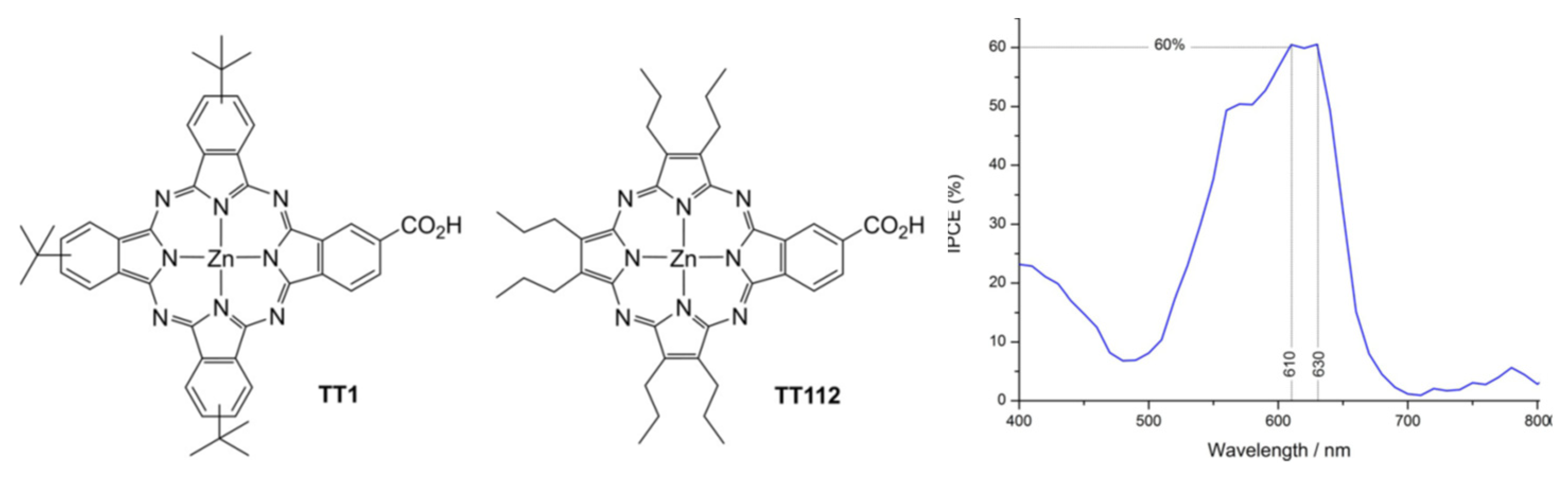
2. SAMs from push-pull chromophores for dye-sensitized solar cell applications
3. SAMs of push-pull chromophores to improve perovskite solar cell performances
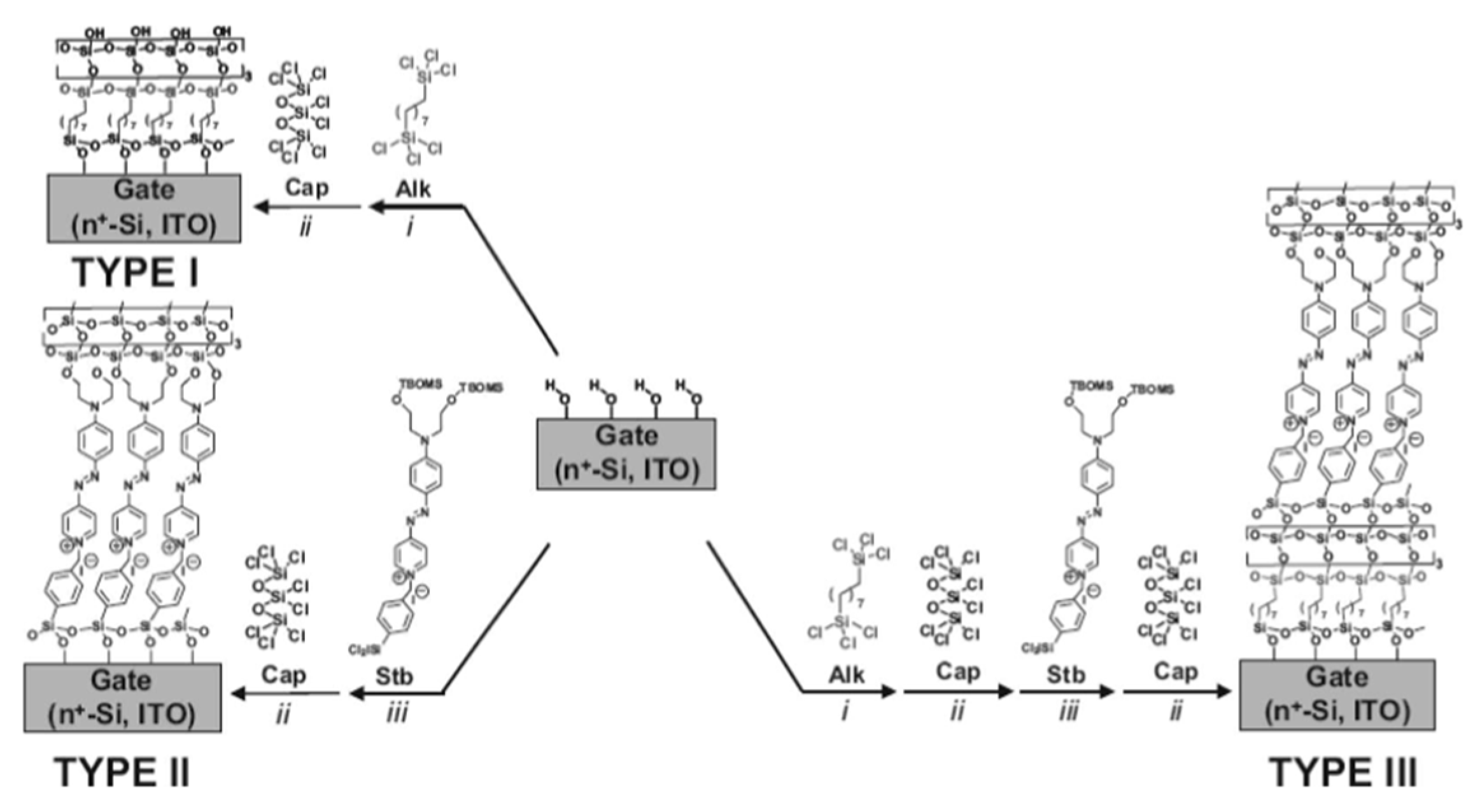
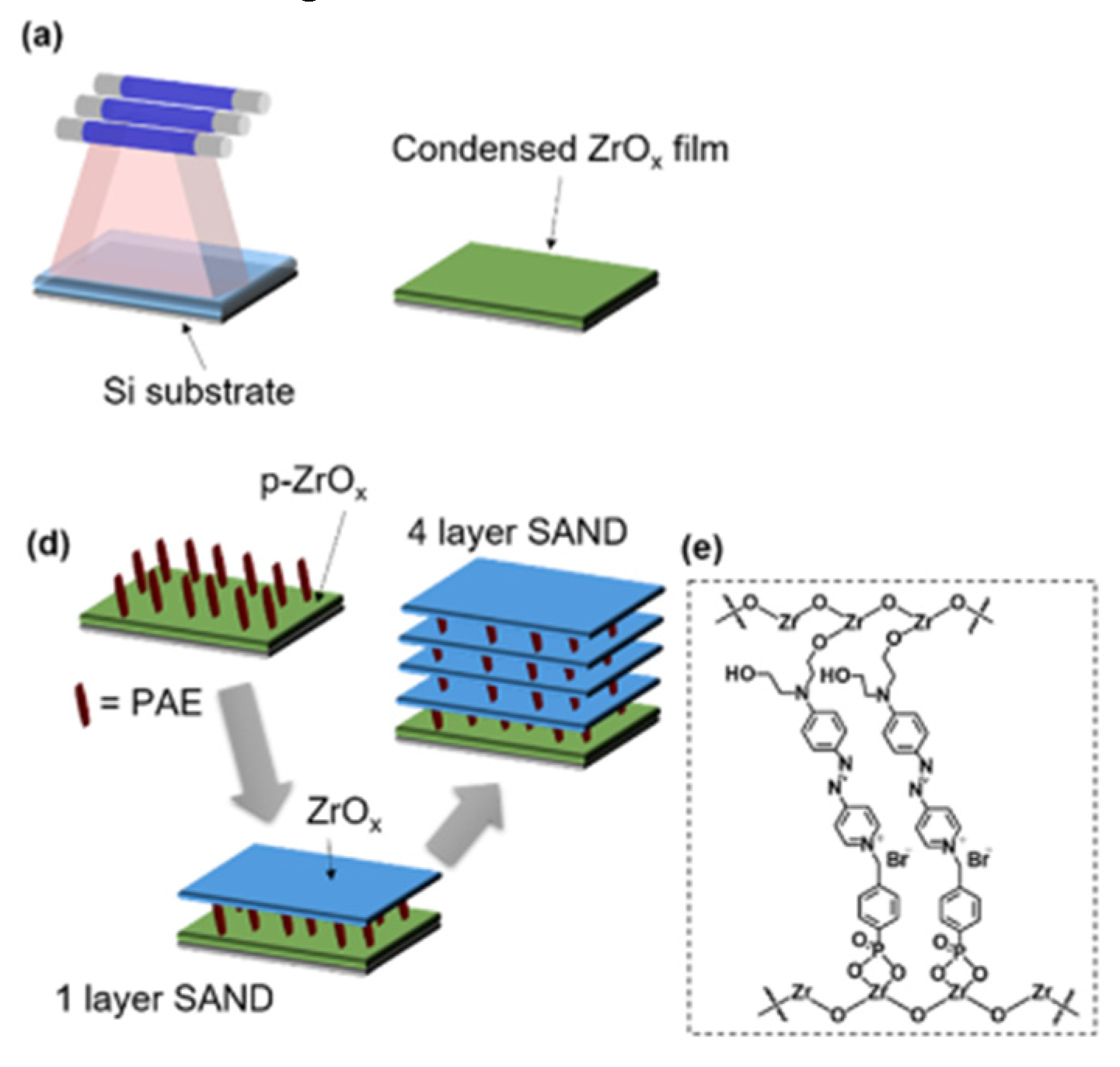
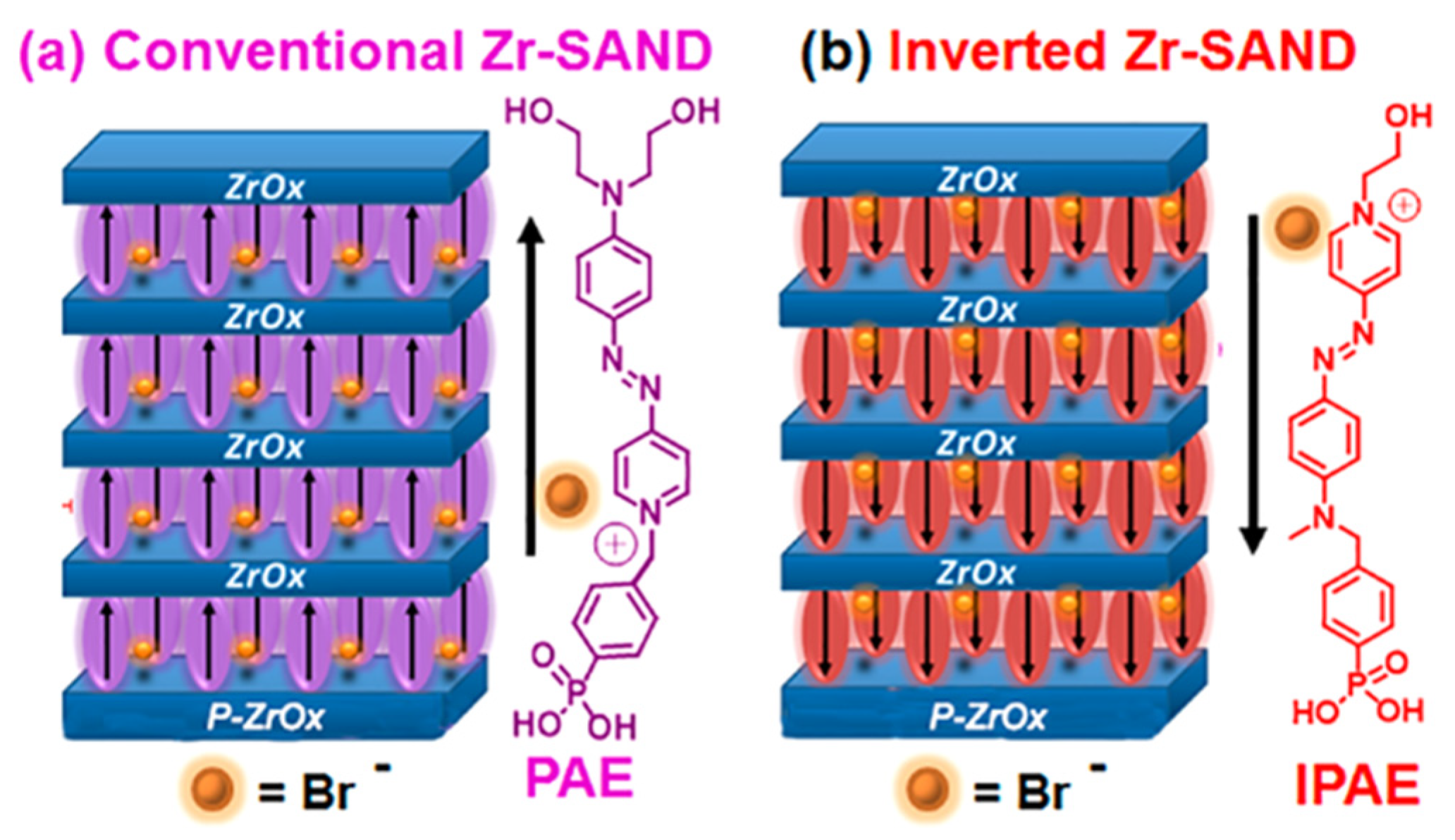
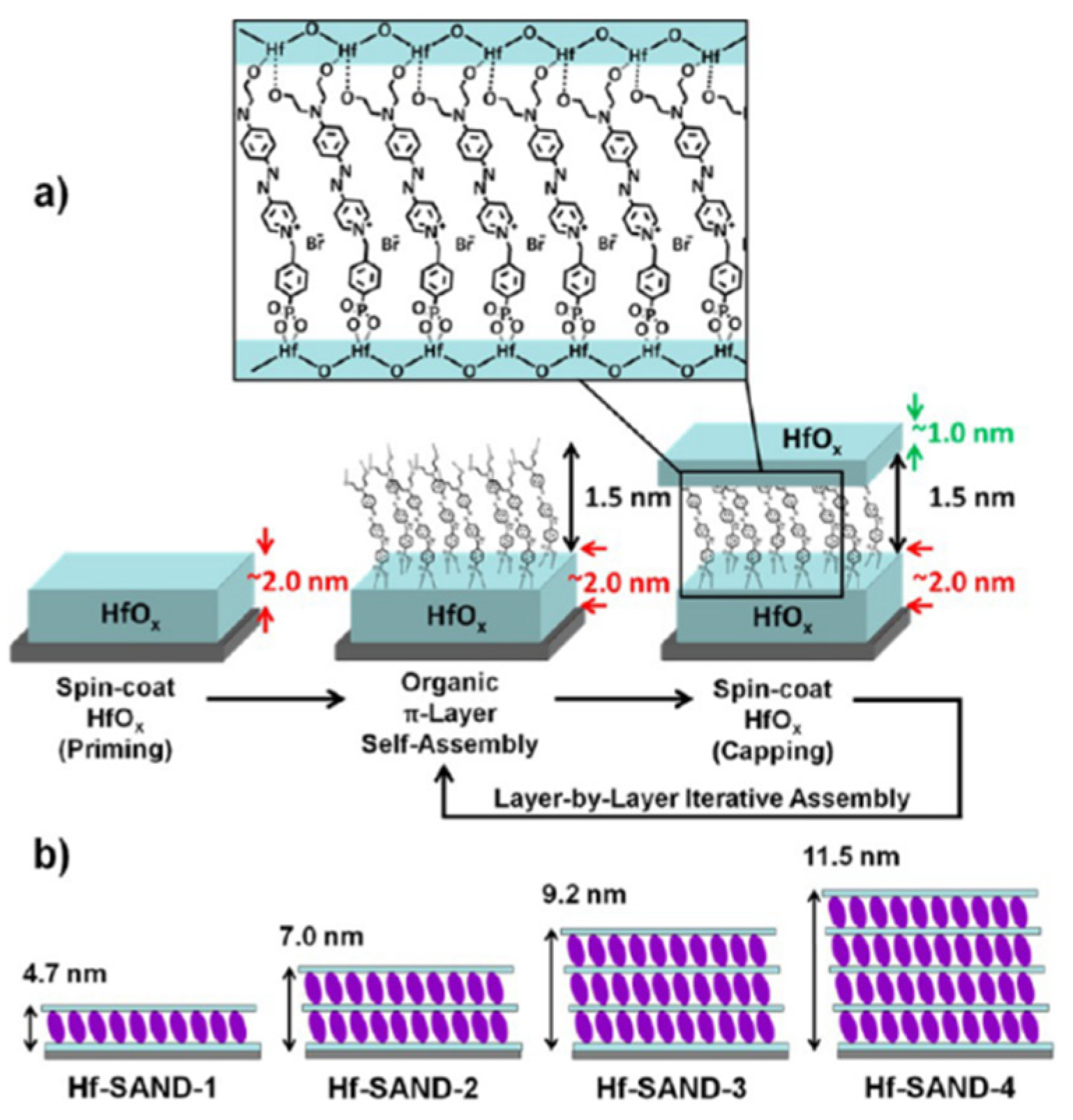
4. SAMs of push-pull chromophores as dielectric materials.
5. Various electrical and photonic properties generated by push-pull chromophores assemblies
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kelsall, R.; Hamley, I.W.; Geoghegan, M. Nanoscale science and technology, Wiley, 2005.
- Whitesides, G.M.; Grzybowski, B. Self-assembly at all scales. Science, 2002, 295, 2418–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelesko, J.A. Self-assembly: the science of things that put themselves together, Chapman & Hall/CRC, London, 2007.
- Chai, Z.; Childress, A.; Busnaina, A.A. Directed assembly of nanomaterials for making nanoscale devices and structures: mechanism and applications. ACS Nano, 2022, 16, 17641–17686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulman, A. Formation and structure of self-assembled monolayers. Chem. Rev., 1996, 96, 1533–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehn, J.-M. Supramolecular chemistry. Science 1993, 260, 1762–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blodgett, K.B. Films built by depositing successive monomolecular layers on a solid surface. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1935, 57, 1007–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- . Blodgett, K.B.; Langmuir, I. Built-up films of barium stearate and their optical properties. Phys. Rev., 1937, 51, 0964–0982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigelow, W.C.; Pickett, D.L.; Zisman, W.A. Oleophobic monolayers: films adsorbed from solution in non-polar liquids. J. Colloid Sci., 1946, 1, 513–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigelow, W.C.; Glass, E.; Zisman, W.A. Oleophobic monolayers: temperature effects and energy of adsorption. J. Colloid Sci., 1947, 2, 563–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagiv, J. Organized monolayers by adsorption. Formation and structure of oleophobic mixed monolayers on solid surfaces. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1980, 102, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuzzo, R.G.; Allara, D.L. Adsorption of bifunctional organic disulfides on gold surfaces, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1983, 105, 4481–4483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Whitesides, G.M. Soft litography. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci., 1998, 28, 153–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savig, J.; Nuzzo, R.G.; Allara, D.L.; Whitesides, G.M. Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) on solid substrates: molecular coating to control surface properties, Kavli prize in Nanoscience, 2022, https://www.kavliprize.org/prizes/nanoscience/2022.
- Love, J.C.; Estroff, L.A.; Kriebel, J.K.; Nuzzo, R.G.; Whitesides, G.M. Self-assembled monolayers of thiolates on metals as a form of nanotechnology. Chem. Rev., 2005, 105, 1103–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bain, C.D.; Whitesides, G.M. Formation of monolayers by the coadsorption of thiols on gold: variation in the length of the alkyl chain. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1989, 111, 7164–7175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claridge, S.A.; Liao, W.-S.; Thomas, J.C.; Zhao, Y.; Cao, H.H.; Cheunkar, S.; Serino, A.C.; Andrews, A.M.; Weiss, P.S. From the bottom up: dimensional control and characterization in molecular monolayers. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 2725–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariga, K. Organized Organic Ultrathin Films: Fundamentals and Applications, John Wiley & Sons, New Jersy, Ariga, Kat., 2012.
- Rogalska, E.; Bilewicz, R.; Brigaud, T.; El Moujahid, C.; Foulard, G.; Portella, C.; Stébé, M.J. Formation and properties of Langmuir and Gibbs monolayers: a comparative study using hydrogenated and partially fluorinated amphiphilic derivatives of mannitol, Chem. Phys. Lipids, 2000, 105, 71–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Oyola-Reynoso, S.; Thuo, M. The Porter-Whitesides discrepancy: revisiting odd-even effects in wetting properties of n-alkanethiolate SAMs. Coatings, 2015, 5, 1034–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Katzbach, S.; Asyuda, A.; Das, S.; Terfort, A.; Zharnikov, M. Effect of substitution on the charge transport properties of oligophenylenethiolate self-assembled monolayers. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022, 24, 27693–27704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aswal, D.K.; Lenfant, S.; Guerin, D.; Yakhmi, J.V.; Vuillaume, D. Self-assembled monolayers on silicon for molecular electronics, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2006, 568, 84–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cegiełka, D.M.; Kozieł, K.; Zharnikov, M.; Cyganik, P. Molecular engineering of technologically relevant surfaces- carboxylic acids on naturally oxidized aluminium, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2023, 636, 157798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamun, A.H.A.; Hahn, J.R. Effect of immersion temperature on self-assembled monolayers of octanethiol on Au(111). Surf. Sci., 2012, 606, 664–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzam, W. Effect of immersion time temperature on structure of the self-assembled monolayer of 1,2-diphenyldiselenide on gold surface, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2016, 180, 432–439. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, N.-S.; Kang, H.; Seong, S.; Noh, J. Effect of immersion time on the structure of octanethiol self-assembled monolayers on Au(111) at elevated solution temperature. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc., 2019, 40, 1152–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Luais, E.; Darwish, N.; Ciampi, S.; Thordarson, P.; Gooding, J.J. Studies on the effect of solvents on self-assembled monolayers formed from organophosphonic acids on indium tin oxide. Langmuir 2012, 28, 9487–9495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.-S.; Chang, W.-H.; Chang, C.-C.; Chien, Y.-H.; Fang, J.-S.; Cheng, Y.-L. Structural models and barrier properties of amine-terminated trialkoxysilane monolayers incubated in nonpolar vs. polar protic solvents. Mater. Chem. Phys., 2021, 274, 125113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunker, B.C.; Carpick, R.W.; Assink, R.A.; Thomas, M.L.; Hankins, M.G.; Voigt, J.A.; Sipola, D.; de Boer, M.P.; Gulley, G.L. The impact of solution agglomeration on the deposition of self-assembled monolayers. Langmuir, 2000, 16, 7742–7751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozlosnik, N.; Gerstenberg, M.; Larsen, N.B. Effect of solvents and concentration on the formation of a self-assembled monolayer of octodecylsiloxane on silicon(001). Langmuir 2003, 19, 1182–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vericat, C.; Vela, M.E.; Corthey, G.; Pensa, E.; Cortés, E.; Fonticelli, M.H.; Ibañez, F.; Benitez, G.E.; Carro, P.; Salvarezza, R.C. Self-assembled monolayers of thiolates on metals: a review article on sulfur-metal chemistry and surface structures. RSC Adv., 2014, 4, 27730–27754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Schubert, U.S.; Hoeppener, S. Surface chemical reactions on self-assembled silane-based monolayers. Chem. Soc. Rev., 2021, 50, 6507–6540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, S.A. Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) of carboxylic acids: an overview. Cent. Eur. J. Chem., 2011, 9, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, T.; Schmaltz, T.; Lenz, T.; Halik, M.; Meyer, B.; Clark, T. Phosphonate- and carboxylate-based self-assembled monolayers for organic devices: a theoretical study of surface binding on aluminium oxide with experimental support. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2013, 5, 6073–6080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pujari, S.P.; Scheres, L.; Marcelis, A.T.M.; Zuilhof, H. Covalent surface modification of oxide surfaces. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed, 2014, 53, 2–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, S.; Fritz, E.-C.; Ravoo, B.J. New trends in the functionalization of metallic gold: from organosulfur ligands to N-heterocyclic carbenes. Chem. Soc. Rev., 2017, 46, 2057–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, G.; Thimes, R.L.; Camden, J.P.; Jenkins, D.M. Fundamentals and applications of N-heterocyclic carbene functionalized gold surfaces and nanoparticles. Chem. Commun., 2022, 58, 13188–13197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinwangso, P.; Jamison, A.C.; Lee, T.R. Multidente adsorbates for self-assembled monolayer films. Acc. Chem. Res., 2011, 44, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilbur, J.L.; Whitesides, G.M. Self-assembly and self-assembled monolayers in micro- and nanofabrication, in Nanotechnology, edited by Timp, G., New York: Springer-Verlag, 1999, 331-369.
- Lee, S.H.; Rho, W.-Y.; Park, S.J.; Kim, J.; Kwon, O.S.; Jun, B.-H. Multifunctional self-assembled monolayers via microcontact printing and degas-driven flow guided patterning. Sci. Rep., 2018, 8, 16763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Bennett, R.K.A.; Xu, Y.; Rather, A.M.; Li, S.; Cheung, T.C.; Bhanji, A.; Kreder, M.J.; Daniel, D.; Adera, S.; Aizenberg, J.; Wang, X. Wettability-based ultrasensitive detection of amphiphiles through directed concentration at disordered regions in self-assembled monolayers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A, 2022, 119, e2211042119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, R.; Mao, Y.; Shen, Y.; Chen, L. Self-assembled monolayers for batteries. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2021, 143, 12897–12912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrara, S.; Rouvier, F.; Auditto, S.; Brunel, F.; Jeanneau, C.; Camplo, M.; Sergent, M.; About, I.; Bolla, J.-M.; Raimundo, J.-M. Nanoarchitectonics of electrically activable phosphonium self-assembled monolayers to efficiently kill and tackle bacterial infections on demand. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2022, 23, 2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, F.; Roldán-Carmona, C.; Sohail, M.; Nazeeruddin, M.K. Applications of self-assembled monolayers for perovskite solar cells interface engineering to address efficiency and stability. Adv. Energy Mater., 2020, 10, 2002989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Tao, L.; Xian, W.; Arbaugh, T.; Li, Y. Molecular self-assembled monolayers anomalously enhance thermal conductance across polymer-semiconductor interfaces. Nanoscale, 2022, 14, 17681–17693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casalini, S.; Bortolotti, C.A.; Leonardi, F.; Biscarini, F. Self-assembled monolayers in organic electronics, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2017, 46, 40–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- .Singh, M.; Kaur, N.; Comini, E. Role of self-assembled monolayers in electronic devices. J. Mater. Chem. C, 2020, 8, 3938–3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussey, K.A.; Hadyniak, S.E.; Johnston Jr, R.J. Patterning and development of photoreceptors in the human retina. Front. Cell Dev. Biol., 2022, 10, 878350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borchert, J.W.; Peng, B.Y.; Letzkus, F.; Burghartz, J.N.; Chan, P.K.L.; Zojer, K.; Ludwigs, S.; Klauk, H. Small contact resistance and high-frequency operation of flexible low-voltage inverted coplanar organic transistors. Nat. Commun., 2019, 10, 1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauter, E.; Terfort, A.; Zharnikov, M. Pronounced solvent effect on the composition of binary self-assembled monolayers with embedded dipole moments. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2020, 124, 28596–28604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Husein, T.; Schuster, S.; Egger, D.A.; Kind, M.; Santowski, T.; Wiesner, A.; Chiechi, R.; Zojer, E.; Terfort, A.; Zharnikov, M. The effect of embedded dipoles in aromatic self-assembled monolayers. Adv. Func. Mater., 2015, 25, 3943–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzam, W.; Subaihi, A. Influence of an alkyl spacer on the formation and structure of 4-fluorobenthiol and 4-fluorobenzenemethanethiol self-assembled monolayers on Au (111). Surf. Interfaces, 2020, 20, 100544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khasbaatar, A.; Xu, Z.; Lee, J.-H.; Campillo-Alvarado, G.; Hwang, C.; Onusaitis, B.N.; Diao, Y. From solution to thin film: molecular assembly of p-conjugated systems ans impact on (opto-electronic properties. Chem. Rev., 2023, 123, 8395–8487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ouyang, C.; Huo, F.; He, W.; Cao, A. Progress in the enhancement of electro-optic coefficients and orientation stability for organic second-order nonlinear optical materials. Dyes Pigm., 2020, 181, 108509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadenne, V.; Grenier, B.; Praveen, C.; Marsal, P.; Valmalette, J.C.; Patrone, L.; Raimundo, J.-M. Combined SERS/DFT studies of push-pull chromophores self-assembled monolayers: insights of their surface orientation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2019, 21, 25865–25871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burěs, F. Fundamental aspects of property tuning in push-pull molecules. RSC Adv., 2014, 4, 58826–58851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klikar, M.; Solanke, P.; Tydlitát; Burěs, F. Alphabet-inspired design of (hetero)aromatic push-pull chromophores. Chem. Rec., 2016, 16, 1886–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gámez-Valenzuela, S.; Neusser, D.; Benitez-Martin, C.; Najera, F.; Guadix, J.A.; Moreno-Yruela, C.; Villacampa, B.; Ponce Ortiz, R.; Ludwigs, S.; Andreu, R.; Ruiz Delgado, M.C. V-shaped pyranylidene/triphenylamine-based chromophores with enhanced photophysical, electrochemical and nonlinear optical properties. Mater. Adv., 2021, 2, 4255–4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinin, A.A.; Islamova, L.N.; Sharipova, S.M.; Fazleeva, G.M.; Gaysin, A.I.; Shmelev, A.G.; Simanchuk, A.E.; Turgeneva, S.A.; Sharipova, A.V.; Mukhtarov, A.S.; Vakhonina, T.A.; Forminykh, O.D.; Mikerin, S.L.; Balakina, M.Y. Quadratic nonlinear optical response of composite polymer materials based on push-pull quinoxaline chromophores with various groups in the aniline donor moiety. New J. Chem., 2023, 47, 2296–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malytskyi, V.; Simon, J.J.; Patrone, L.; Raimundo, J.-M. Thiophene-based push–pull chromophores for small molecule organic solar cells (SMOSCs). RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 354–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymakers, J.; Krysova, H.; Artemenko, A.; Cermak, J.; Nicley, S.S.; Verstappen, P.; Gielen, S.; Kromka, A.; Haenen, K.; Kavan, L.; Maes, W.; Rezek, B. Functionalization of boron-doped diamond with a push–pull chromophore via Sonogashira and CuAAC chemistry. RSC Adv., 2018, 8, 33276–33290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unny, D.; Kandregula, G.R.; Sivanadanam, J.; Ramanujam, K. Molecular engineering of pyrene carbazole dyes with a single bond and double bond as the mode of linkage. New J. Chem., 2020, 44, 16511–16525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindh, L.; Gordivska, O.; Persson, S.; Michaels, H.; Fan, H.; Chábera, P.; Rosemann, N.W.; Kumar Gupta, A.; Benesperi, I.; Uhlig, J.; Prakash, O.; Sheibani, E.; Kjaer, K.S.; Boschloo, G.; Yartsev, A.; Freitag, M.; Lomoth, R.; Persson, P.; Wärnmark, K. Dye-sensitized solar cells based on Fe N-heterocyclic carbene photosensitizers with improved rod-like push-pull functionality. Chem. Sci., 2021, 12, 16035–16053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, R.D.; Algahtani, L.S.; Mallows, J.; Flint, H.V.; Waddell, P.G.; Woodford, O.J.; Gibson, E.A. Pentafluorosulfanyl-functionalised BODIPY push–pull dyes for p-type dye-sensitized solar cells. Sustain. Energy Fuels, 2023, 7, 1494–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauvel, S.; Riquelme, A.J.; Castán, J.-M. A.; Mwalukuku, W.M.; Kervella, Y.; Challuri, V.K.; Sauvage, F.; Narbey, S.; Maldivi, P.; Demadrille, R. Push-pull photochromic dyes for semi-transparent solar cells with light-adjustable optical properties and high color-rendering index. Chem. Sci., 2023, 14, 8497–8506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D'Annibale, V.; Chen, C.G.; Bonomo, M.; Dini, D.; D'Abramo, M. P1 push-pull dye as a case study in QM/MM theoretical characterization for dye-sensitized solar cell organic chromophores. ChemistrySelect, 2023, 8, e20220490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwell, G.J.; Tyrell, W.D.; Whittam, A.J. Molecular rectification: seld-assembled monoloayers in which donor-(p-bridge)-acceptor moities are centrally located and symmetrically coupled to both gold electrodes. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126, 7102–7110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- . Malytskyi, V.; Gadenne, V.; Ksari, Y.; Patrone, L.; Raimundo, J.-M. Synthesis and characterization of thiophene-based push-pull chromophores for tuning the electrical and optical properties of surfaces with controlled SAM formation. Tetrahedron 2017, 73, 5738–5744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellaha, I.M.; El-Shafei, A. Synthesis and characterization of novel tetra anchoring A2-D-D-D-A2 architecture sensitizers for efficient dye-sensitized solar cells. Sol. Energy, 2020, 198, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholamrezaie, F.; Kirkus, M.; Mathijissen, S.G.J.; de Leeuw, D.M.; Meskers, S.C.J. Photophysics of self-assembled monolayers of a π-conjugated quinquethiophene derivative. J. Phys. Chem. A, 2012, 116, 7645–7650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraghavan, R.K.; Gholamrezaie, F.; Meskers, S.C.J. Photovoltaic effect in self-assembled molecular monolayers on gold: influence of orbital energy level alignment on short-circuits current generation. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2013, 117, 16820–16829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keremane, K.S.; Planchat, A.; Pellegrin, Y.; Jacquemin, D.; Odobel, F.; Adhikari, A.V. Push-pull phenoxazine-based sensitizers for p-type DSSCs: effect of acceptor units on photovoltaic performance. Chem. Sus. Chem.; 2022, 15, e202200520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, D.; Sarkar, U. Designing of PC31BM-based acceptors for dye-sensitized solar cell. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2022, e4419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, F.M.; Latif, M.K.A.; Khalek, A.A.A. Theoretical investigation on the influence of electron-accepting substitutions in modulating the optoelectronic properties of dye-sensitized solar cells. Mol. Phys. 2023, e2245060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avhad, K.; Jadhav, M.; Patil, D.; Chowdhury, T.H.; Bedja, I.; Sekar, N. Rhodanine-3-acetic acid containing D-π-A push-pull chromophores: Effect of methoxy group on the performance of dye-sensitized solar cells. Org. Electron., 2019, 65, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belen Marco, A.; Martinez de Baroja, N.; Andres-Castan, J.M.; Franco, S.; Andreu, R.; Villacampa, B.; Orduna, J.; Garin, J. Pyranylidene/thienothiophene-based organic sensitizers for dye-sensitized solar cells. Dyes Pigm., 2019, 161, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gümüşgöz Çelik, G.; Tunç, G.; Lafzi, F.; Saracoglu, N.; Seçkin Arslan, B.; Nebioğlu, M.; Şişman, I.; Gül Gürek, A. Influence of spacer and donor groups as tetraphenylethylene or triphenylamine in asymmetric zinc phthalocyanine dyes for dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A, 2023, 444, 114962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabelsi, S.; Kouki, N.; Seydou, M.; Maurel, F.; Tangour, B. Intramolecular path determination of active electrons on push-pull oligocarbazole dyes-sensitized solar cells. ChemistryOpen, 2019, 8, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dovaa, D.; Cauteruccioa, S.; Manfredib, N.; Pragerc, S.; Dreuwc, A.; Arnaboldia, S.; Mussinia, P.R.; Licandroa, E.; Abbotto, A. An unconventional helical push-pull system for solar cells. Dyes Pigm., 2019, 161, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.W.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, H.G.; Gil Cha, H.; Lee, D.H.; Jae Ko, M. Effects of structure and electronic properties of D-π-A organic dyes on photovoltaic performance of dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Energy Chem., 2021, 54, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yang, X.; Cai, B.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Hagfeldt, A.; Sun, L. Supramolecular Co-adsorption on TiO2 to enhance the efficiency of dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2021, 9, 13697–13703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffeis, V.; Dogan, H.; Cassette, E.; Jousselme, B.; Gustavsson, T. Role of electronic relaxation in the injection process of organic push–pull dyes in complete dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2019, 10, 5076–5081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.; Kim, T.W.; Kim, S.; Oh, I.; Wonneberger, H.; Yoon, K.; Kwak, M.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Li, C.; Müllen, K.; Ihee, H. Molecular-level understanding of excited states of N-annulated rylene dye for dye-sensitized solar sells. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2020, 124, 22993–23003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, K.; Alsaleh, A.Z.; Neeraj; Rathi, P.; Sharma, A.; Sankar, M.; D’Souza, F. Synthesis, spectral, electrochemical and photovoltaic studies of A3B porphyrinic dyes having peripheral donors. Chem. Phys. Chem., 2019, 20, 2627–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirak, K.; Can, M.; Özsoy, C.; Yiğit, M.Z.; Gültekin, B. Synthesis and photovoltaic characterization of triarylamine-substituted quinoxaline push-pull push-pull dyes to improve the performance of dye-sensitized solar cells. Turk. J. Chem., 2017, 41, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Ariza, J.; Urbani, M.; Graetzel, M.; Rodriguez-Morgade, M.S.; Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Torres, T. An unsymmetrical, push–pull porphyrazine for dye-sensitized solar cells. ChemPhotoChem., 2017, 1, 164–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, D.-P.; Fernández-Ariza, J.; Urbani, M.; Sauvage, F.; Torres, T.; Rodríguez-Morgade, M.S. Tuning the acceptor unit of push–pull porphyrazines for dye-sensitized solar cells. Molecules, 2021, 26, 2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.J.; Kinoshita, T.; Ng, D.K.P. Push–pull distyryl boron dipyrromethenes as near-infrared sensitizers for dye-sensitized solar cells. Asian J. Org. Chem., 2017, 6, 1476–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbani, M.; Ragoussi, M.E.; Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Torres, T. Phthalocyanines for dye-sensitized solar cells. Coord. Chem. Rev., 2019, 381, 1–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazal, B.; Azizi, K.; Ewies, E.F.; Youssef, A.S.A.; Mwalukuku, V.M.; Demadrille, R.; Torres, T.; Makhseed, S. Push–pull zinc phthalocyanine bearing hexa-tertiary substituted carbazolyl donor groups for dye-sensitized solar cells. Molecules, 2020, 25, 1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chindeka, F.; Mashazi, P.; Britton, J.; Oluwole, D.O.; Mapukata, S.; Nyokong, T. Fabrication of dye-sensitized solar cells based on push-pull asymmetrical substituted zinc and copper phthalocyanines and reduced graphene oxide nanosheets. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A, 2020, 399, 112612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbani, M.; Gratzel, M.; Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Torres, T. Meso-substituted porphyrins for dye-sensitized solar cells. Chem. Rev., 2014, 114, 12330–12396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birel, O.; Nadeem, S.; Duman, H. Porphyrin-based dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs): a review. J. Fluoresc., 2017, 27, 1075–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Liu, S.; Wang, M. Push-pull zinc porphyrins as light-harvesters for efficient dye-sensitized solar cells. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashino, T.; Imahori, H. Porphyrins as excellent dyes for dye-sensitized solar cells: recent developments and insights. Dalton Trans., 2015, 44, 448–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Li, X.; Ågren, H.; Xie, Y. Branched and linear alkoxy chains-wrapped push-pull porphyrins for developing efficient dye-sensitized solar cells. Dyes Pigm., 2017, 137, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashino, T.; Kawamoto, K.; Sugiura, K.; Fujimori, Y.; Tsuji, Y.; Kurotobi, K.; Ito, S.; Imahori, H. Effects of bulky substituents of push–pull porphyrins on photovoltaic properties of dye-sensitized solar cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2016, 8, 15379–15390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yella, A.; Lee, H.-W.; Tsao, H.N.; Yi, C.; Chandiran, A.K.; Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Diau, E.W.-G.; Yeh, C.-Y.; Zakeeruddin, S.M.; Gratzel, M. Porphyrin-sensitized solar cells with cobalt (II/III)–based redox electrolyte exceed 12 percent efficiency. Science, 2011, 334, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higashino, T.; Iiyama, H.; Nishimura, I.; Imahori, H. Exploration on the combination of push-pull porphyrin dyes and copper(I/II) redox shuttles toward high-performance dye-sensitized solar cells. Chem. Lett., 2020, 49, 936–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, J.C.; Li, R.; Ci, C.G. Different metal upper porphyrin based self-assembly sensitizers for application in efficient dye-sensitized solar cells. Polyhedron, 2022, 211, 115573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashino, T.; Sugiura, K.; Namikawa, K.; Imahori, H. Energy level tuning of push-pull porphyrin sensitizer by trifluoromethyl group for dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Porphyr. Phthalocyanines 2023, 27, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Webre, W.A.; Thomas, M.B.; Moss, A.; Hancock, S.N.; Schaffner, J.; D'Souza, F.; Wang, H. β-Functionalized push–pull opp-dibenzoporphyrins as sensitizers for dye-sensitized solar cells: the role of the phenylethynyl bridge. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019, 7, 10712–10722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- . Mattew, S.; Yella, A.; Gao, P.; Humphry-Baker, R.; Curchod, B.F.E.; Ashari-Astani, N.; Tavernelli, I.; Rothlisberger, U.; Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Gratzel, M. Dye-sensitized solar cells with 13% efficiency achieved through the molecular engineering of porphyrin sensitizers. Nat. Chem., 2014, 6, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yella, A.; Mai, C.-L.; Zakeeruddin, S.M.; Chang, S.-N.; Hsieh, C.-H.; Yeh, C.-Y.; Gratzel, M. Molecular engineering of push–pull porphyrin dyes for highly efficient dye-sensitized solar cells: the role of benzene spacers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed,. 2014, 53, 2973–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotakis, S.; Giannoudis, E.; Charisiadis, A.; Paravatou, R.; Lazaridi, M.-E.; Kandyli, M.; Ladomenou, K.; Angaridis, P.A.; Bertrand, H.; Sharma, G.D.; Coutsolelos, A.G. Increased efficiency of dye-sensitized solar cells by incorporation of a π-spacer in donor–acceptor zinc porphyrins bearing cyanoacrylic acid as an anchoring group. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 20-21, 2369–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
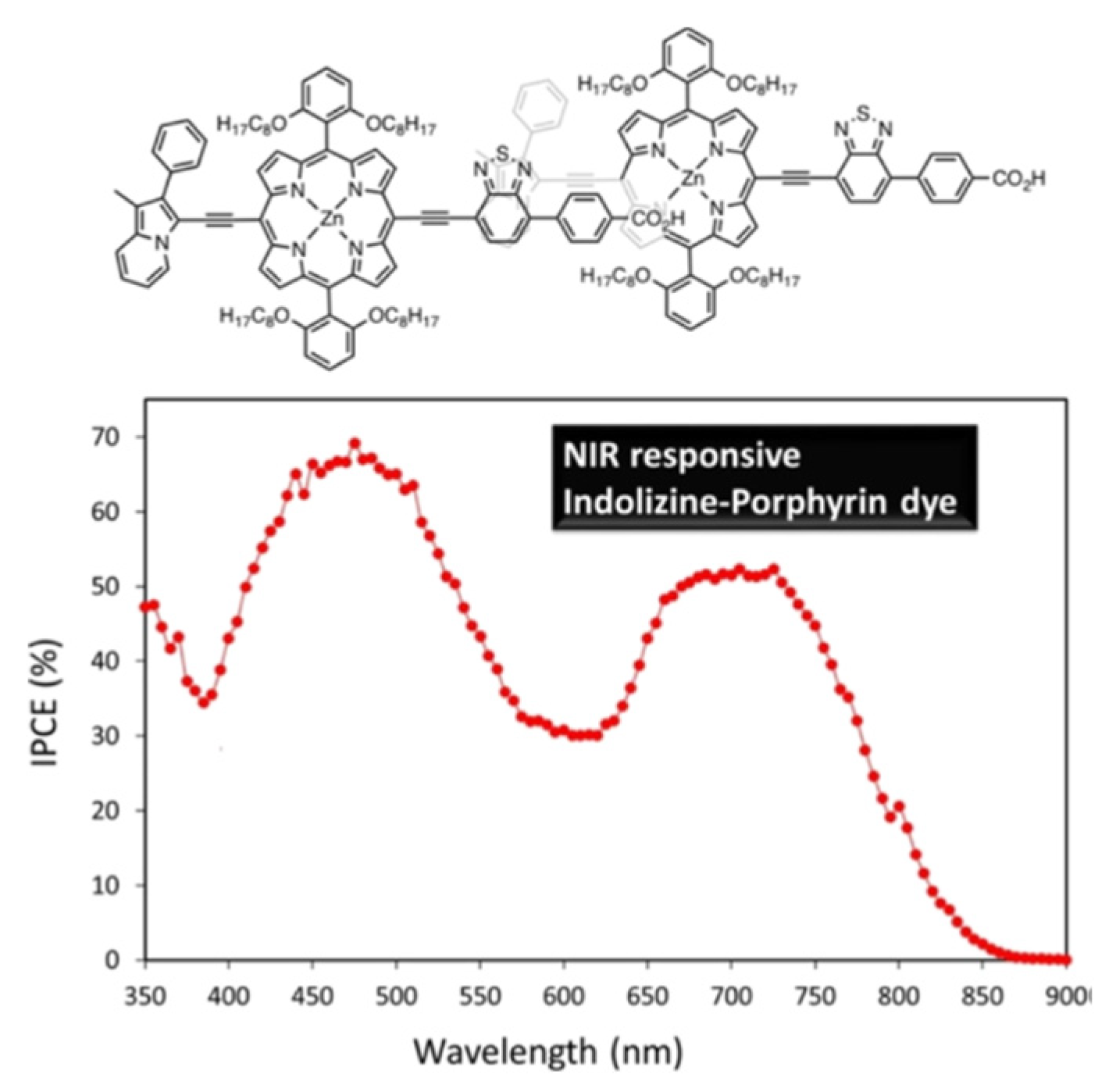
- Cheema, H.; Baumann, A.; Loya, E.K.; Brogdon, P.; McNamara, L.E.; Carpenter, C.A.; Hammer, N.I.; Mathew, S.; Risko, C.; Delcamp, J.H. Near-infrared-absorbing indolizine-porphyrin push–pull dye for dye-sensitized solar cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019, 11, 16474–16489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milan, R.; Selopal, G.S.; Cavazzini, M.; Orlandi, S.; Boaretto, R.; Caramori, S.; Concina, I.; Pozzi, G. Zinc phthalocyanines as light harvesters for SnO2-based solar cells: a case study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
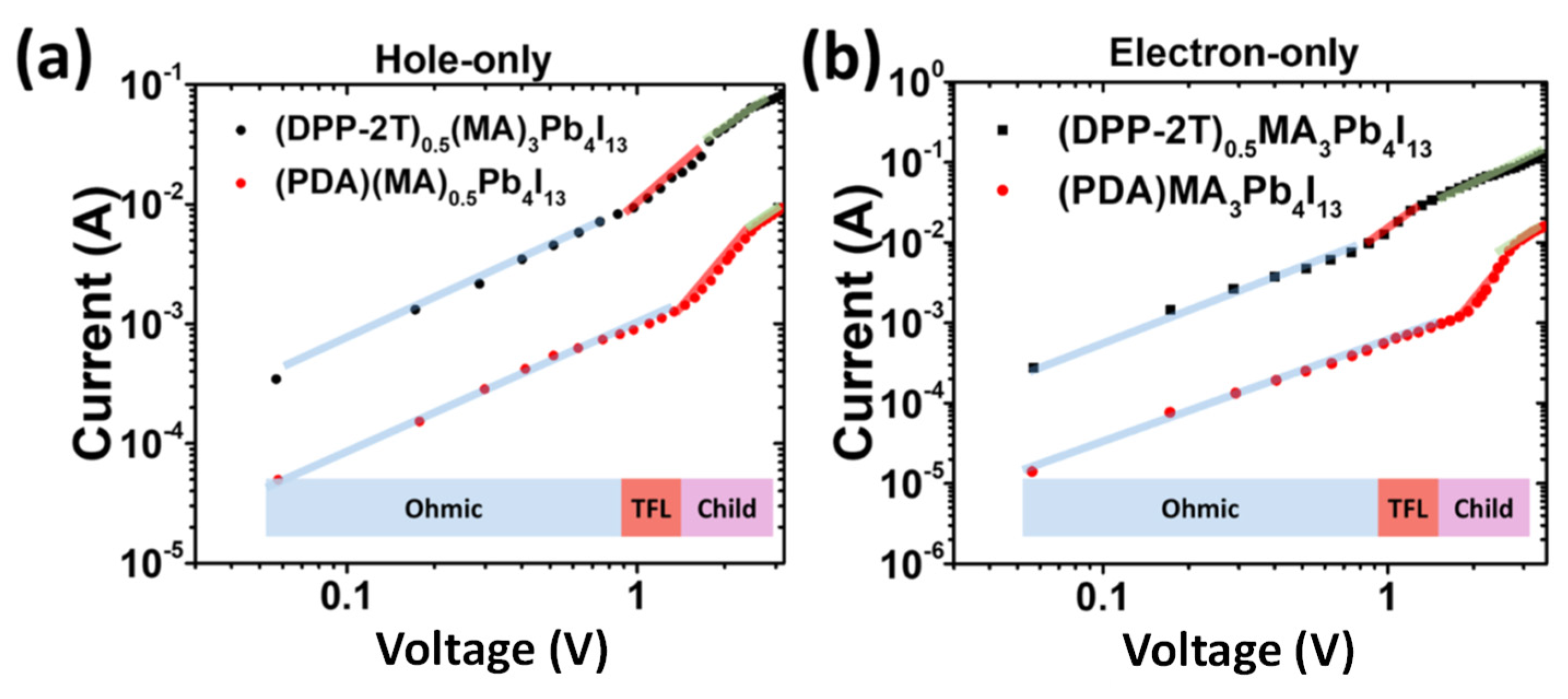
- Liu, C.; Fang, Z.; Sun, J.; Shang, M.; Zheng, K.; Yang, W.; Ge, Z. Donor-acceptor-donor type organic spacer for regulating the quantum wells of Dion-Jacobson 2D perovskites. Nano Energy, 2022, 93, 106800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkini, K.; Verykios, A.; Balis, N.; Kaltzoglou, A.; Papadakis, M.; Adamis, K.S.; Armadorou, K.-K.; Soultati, A.; Drivas, C.; Gardelis, S.; Petsalakis, I.D.; Palilis, L.C.; Fakharuddin, A.; Haider, M.I.; Bao, X.; Kennou, S.; Argitis, P.; Schmidt-Mende, L.; Coutsolelos, A.G.; Falaras, P.; Vasilopoulou, M. Enhanced Organic and Perovskite Solar Cell Performance through Modification of the Electron-Selective Contact with a Bodipy−Porphyrin Dyad, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12, 1120–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
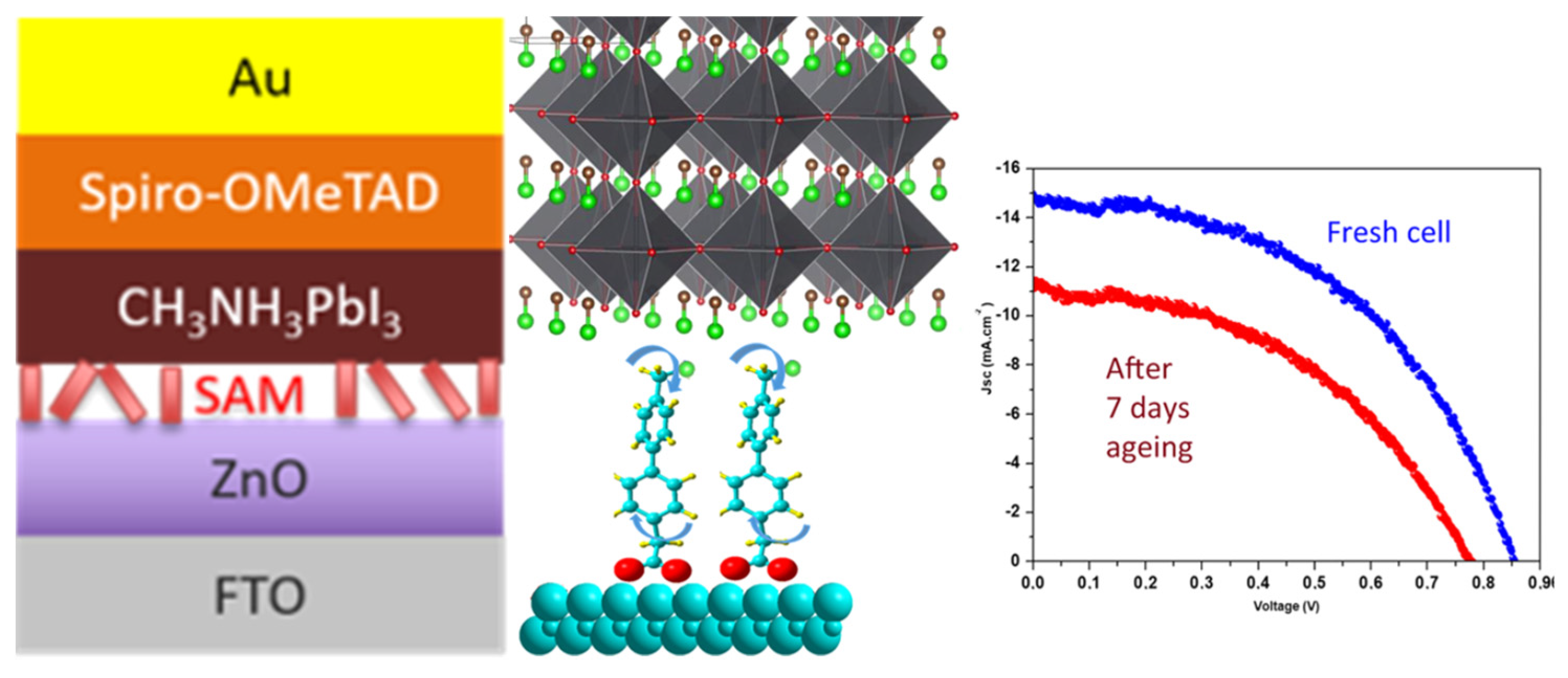
- Kouki, H.; Pitié, S.; Torkhani, A.; Mamèche, F.; Decorse, P.; Seydou, M.; Kouki, F.; Lang, P. Tailor-Made Amino-Based Self-Assembled Monolayers Grafted on Electron Transport ZnO Layers: Perovskite Solar Cell Performance and Modified Interface Relationship, ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2022, 5, 1635–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
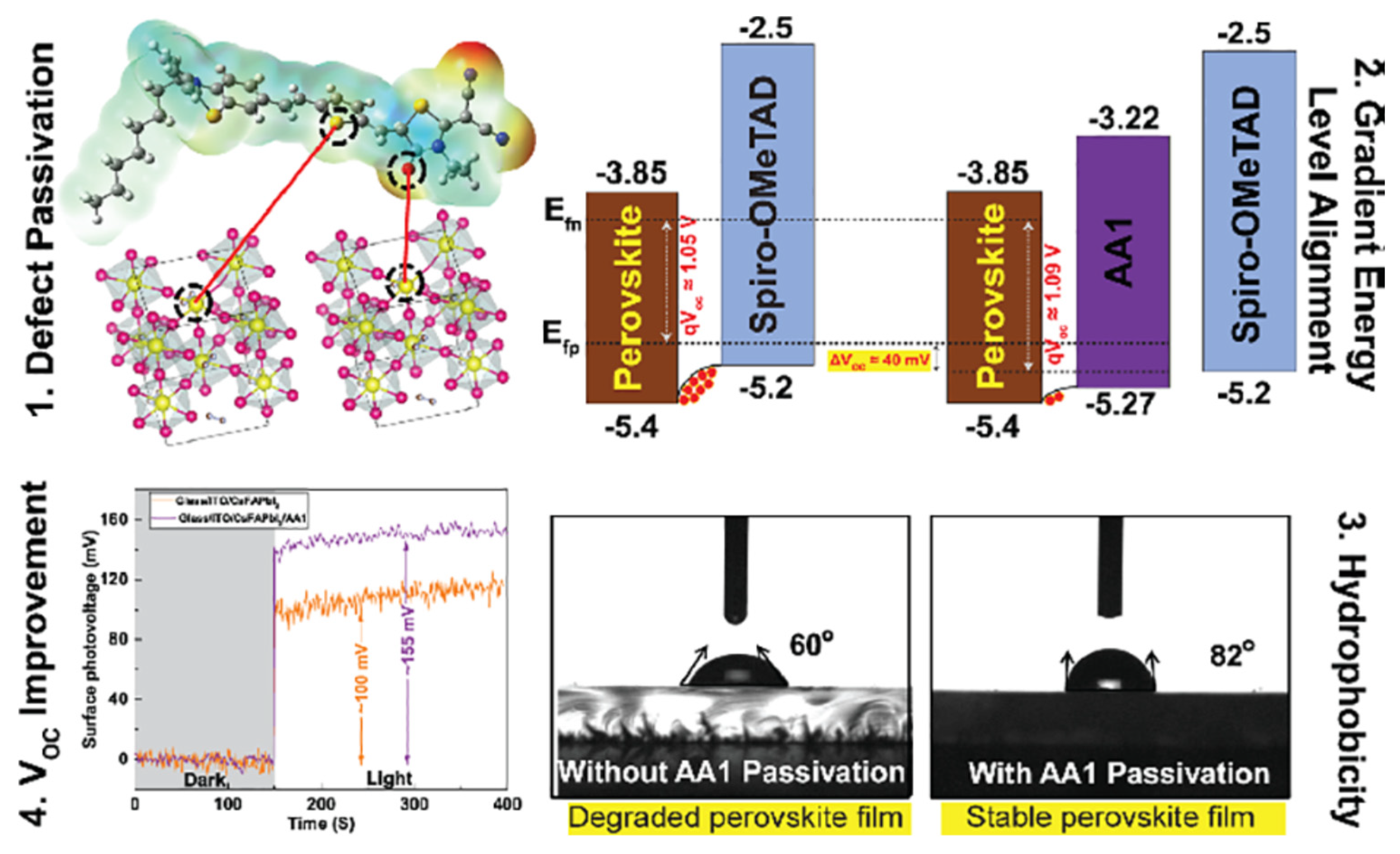
- Alagumalai, A.; Rajendran, M.V.; Ganesan, S.; Menon, V.S.; Raman, R.K.; Chelli, S.M.; Vijayasayee, S.M.; Gurusamy Thangavelu, S.A.; Krishnamoorthy, A. Interface Modification with Holistically Designed Push−Pull D−π−A Organic Small Molecule Facilitates Band Alignment Engineering, Efficient Defect Passivation, and Enhanced Hydrophobicity in Mixed Cation Planar Perovskite Solar Cells. ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2022, 5, 6783–6796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Su, H.; Pu, Y.; Guo, M.; Zhai, P.; Liu, L.; Fu, H. 3D Polydentate Complexing Agents for Passivating Defects and Modulating Crystallinity for High-Performance Perovskite Solar Cells. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2023, 33, 2212577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
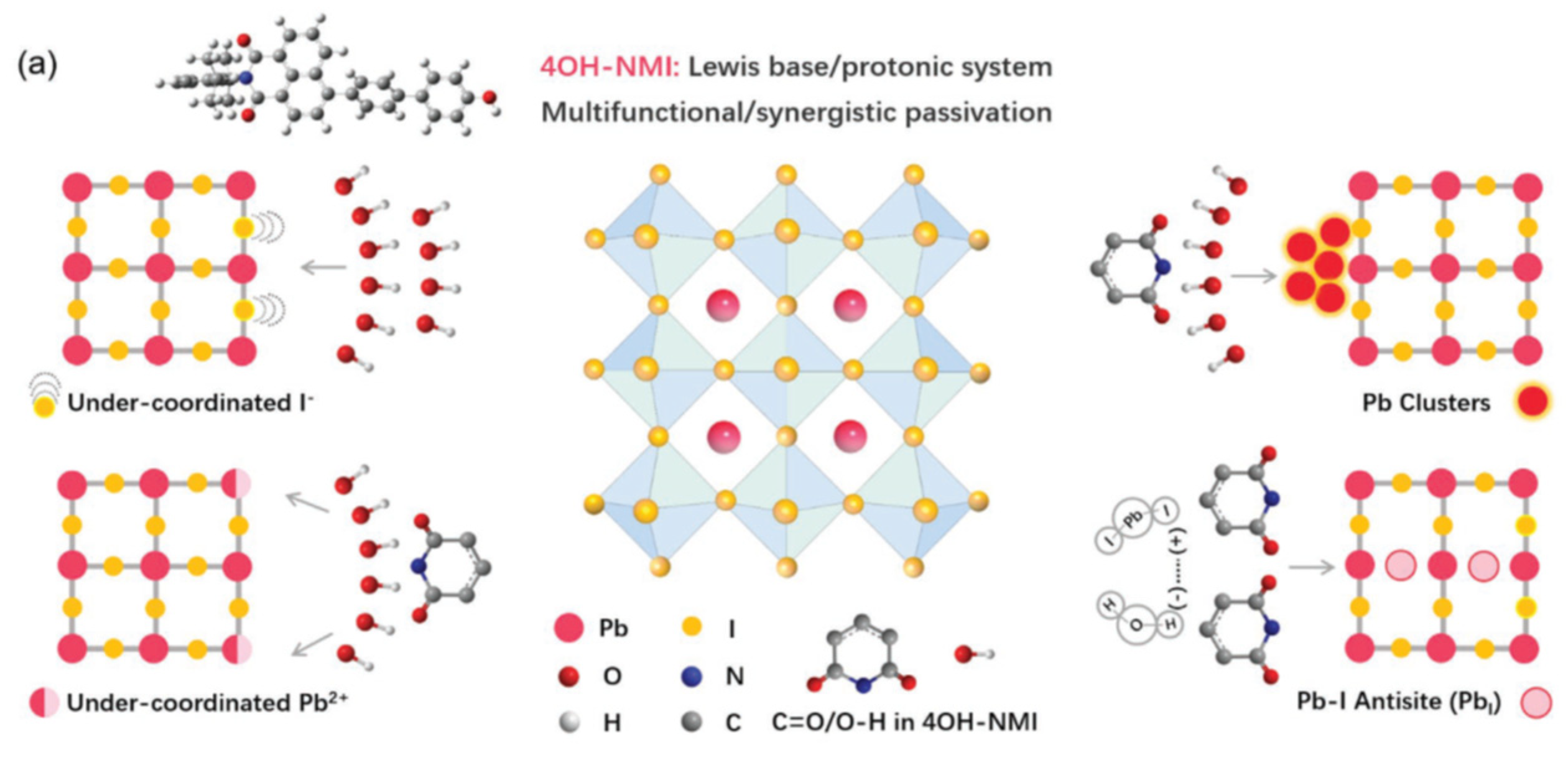
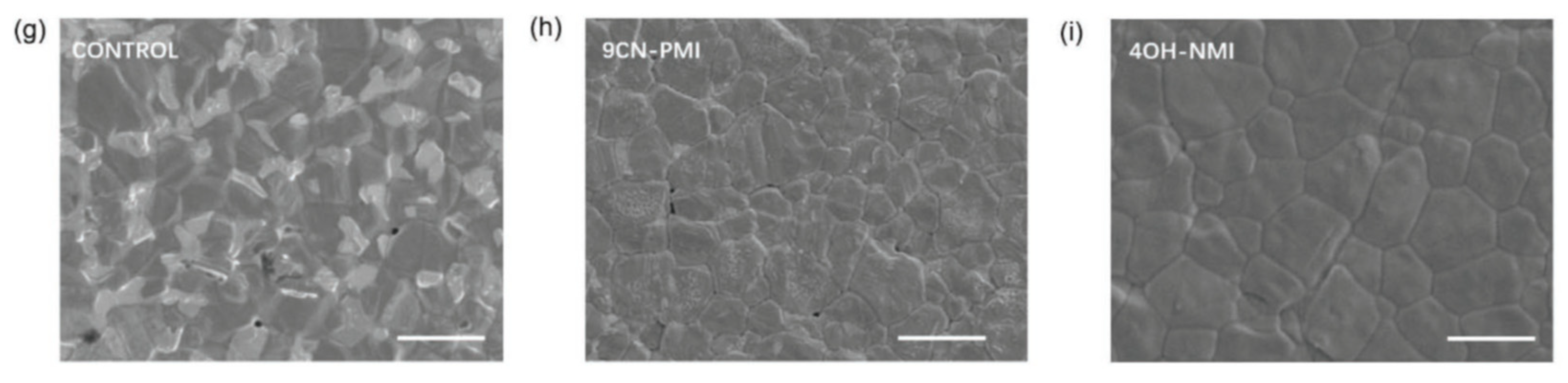
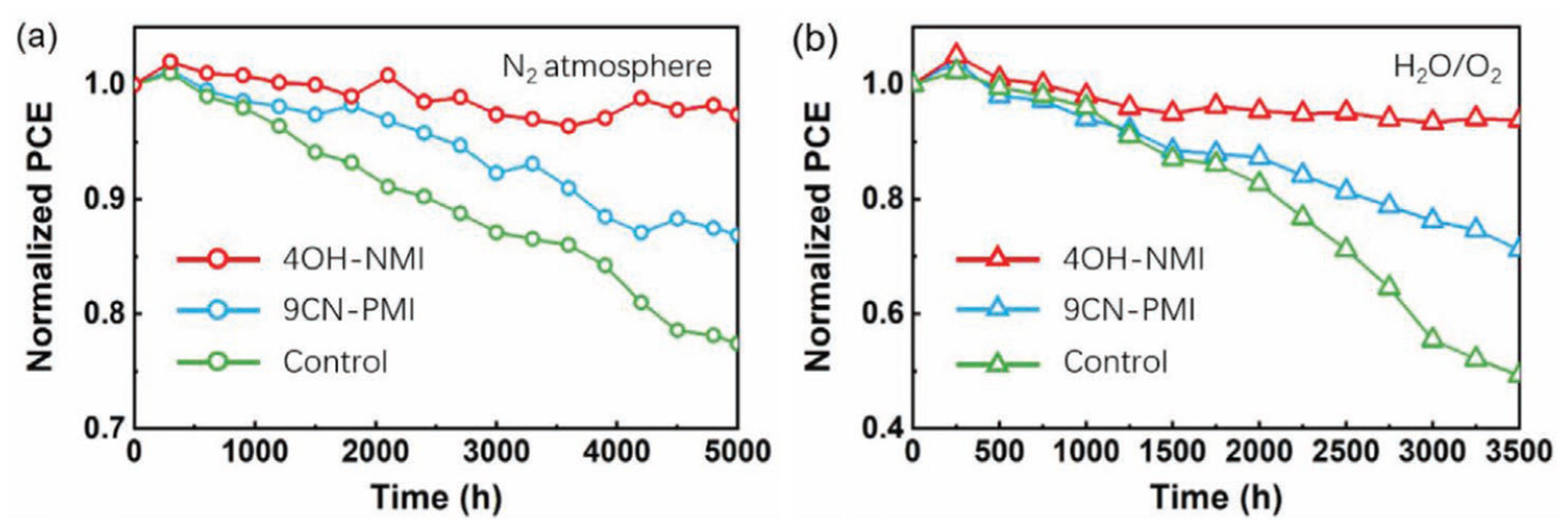
- Zhang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Li, Z.; Qiao, L.; Xiong, Q.; Deng, L.; Zhang, Z.; Long, R.; Zhou, Q.; Du, Y.; Lan, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Li, C.; Müllen, K.; Gao, P. Marked Passivation Effect of Naphthalene-1,8-Dicarboximides in High-Performance Perovskite Solar Cells. Adv. Mater., 2021, 33, 2008405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, M.-H.; Facchetti, A.; Marks, T.J. σ-π Molecular Dielectric Multilayers for Low-Voltage Organic Thin-Film Transistors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2005, 102, 4678–4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiBenedetto, S.A.; Frattarelli, D.; Ratner, M.A.; Facchetti, A.; Marks, T.J. Vapor Phase Self-Assembly of Molecular Gate Dielectrics for Thin Film Transistors. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130, 7528–7529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lu, N.; Liu, M. Effect of dipole layer on the density-of-states and charge transport in organic thin film transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2013, 103, 253303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkenasy, G.; Cahen, D.; Cohen, R.; Shanzer, A.; Vilan, A. Molecular engineering of semiconductor surfaces and devices. Acc Chem Res., 2002, 35, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahen, D.; Naaman, R.; Vager, Z. The Cooperative Molecular Field Effect. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2005, 15, 1571–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- .Salinas, M.; Jäger, C.M.; Amin, A.Y.; Dral, P.O.; Meyer-Friedrichsen, T.; Hirsch, A.; Clark, T.; Halik, M. The Relationship between Threshold Voltage and Dipolar Character of Self-Assembled Monolayers in Organic Thin-Film Transistors. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 12648–12652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Yu, X.; Zeng, L.; Wang, B.; Takai, A.; Di Carlo, G.; Bedzyk, M.J.; Marks, T.J.; Facchetti, A. Ultraviolet Light-Densified Oxide-Organic Self-Assembled Dielectrics: Processing Thin-Film Transistors at Room Temperature. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 13, 3445–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-H.; Heo, J.-S.; Kim, T.-H.; Park, S.; Yoon, M.-H.; Kim, J.; Oh, M.S.; Yi, G.-R.; Noh, Y.-Y.; Park, S.K. Flexible Metal-Oxide Devices Made by Room-Temperature Photochemical Activation of Sol–Gel Films. Nature, 2012, 489, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Di Carlo, G.; Turrisi, R.; Zeng, L.; Stallings, K.; Huang, W.; Bedzyk, M.J.; Beverina, L.; Marks, T.J.; Facchetti, A. The Dipole Moment Inversion Effects in Self-Assembled Nanodielectrics for Organic Transistors. Chem. Mater., 2017, 29, 9974–9980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Wang, B.; Chen, Y.; Facchetti, A.; Marks, T.J.; Balogun, O. Cross-Plane Thermal Conductance of Phosphonate-Based Self-Assembled Monolayers and Self-Assembled Nanodielectrics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12, 34901–34909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everaerts, K.; Emery, J.D.; Jariwala, D.; Karmel, H.J.; Sangwan, V.K.; Prabhumirashi, P.L.; Geier, M.L.; McMorrow, J.J.; Bedzyk, M.J.; Facchetti, A.; Hersam, M.C.; Marks, T.J. Ambient-Processable High Capacitance Hafnia-Organic Self-Assembled Nanodielectrics. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 8926–8939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veres, J.; Ogier, S.; Lloyd, G.; de Leeuw, D. Gate Insulators in Organic Field-Effect Transistors. Chem. Mater., 2004, 16, 4543–4555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, G.G.; Acton, O.; Ma, H.; Ka, J.W.; Jen, A.K.-Y. Study on the Formation of Self-Assembled Monolayers on Sol−Gel Processed Hafnium Oxide as Dielectric Layers. Langmuir, 2009, 25, 2140–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.; Kline, R.J.; Fischer, D.A.; Lin, E.K.; Heeney, M.; McCulloch, I.; DeLongchamp, D.M. The Effect of Interfacial Roughness on the Thin Film Morphology and Charge Transport of High-Performance Polythiophenes. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2008, 18, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-G.; Kim, H.S.; Ha, Y.-G.; He, J.; Kanatzidis, M.G.; Facchetti, A.; Marks, T.J. High-Performance Solution-Processed Amorphous Zinc−Indium−Tin Oxide Thin-Film Transistors. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 10352–10364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaboson, J.M.P.; Wang, Q.H.; Emery, J.D.; Lipson, A.L.; Bedzyk, M.J.; Elam, J.W.; Pellin, M.J.; Hersam, M.C. Seeding Atomic Layer Deposition of High- k Dielectrics on Epitaxial Graphene with Organic Self-Assembled Monolayers. ACS Nano, 2011, 5, 5223–5232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stallings, K.; Smith, J.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, L.; Wang, B.; Di Carlo, G.; Bedzyk, M.J.; Facchetti, A.; Marks, T.J. Self-Assembled Nanodielectrics for Solution-Processed Top-Gate Amorphous IGZO Thin-Film Transistors. ACS App. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 13, 15399–15408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hupfer, M.L.; Kaufmann, M.; Roussille, L.; Preiß, J.; Weiß, D.; Hinrichs, K.; Deckert, V.; Dietzek, B.; Beckert, R.; Presselt, M. Arylic ve rsus Alkylic-Hydrophobic Linkers Determine the Supramolecular Structure and Optoelectronic Properties of Tripodal Amphiphilic Push−Pull Thiazoles. Langmuir, 2019, 35, 2561–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malytskyi, V.; Simon, J.-J.; Patrone, L.; Raimundo, J.-M. Synthesis, self-assembly and characterization of a novel push–pull thiophene-based chromophore on a gold surface. RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 26308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lissau, H.; Frisenda, R.; Olsen, S.T.; Jevric, M.; Parker, C.R.; Kadziola, A.; Hansen, T.; van der Zant, H.S.J.; Nielsen, M.B.; Mikkelsen, K.V. Tracking molecular resonance forms of donor–acceptor push–pull molecules by single-molecule conductance experiments. Nature Comm. 2015, 6, 10233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandl, T.; El Abbassi, M.; Stefani, D.; Frisenda, R.; Harzmann, G.D.; van der Zant, H.S.J.; Mayor, M. Enhanced Separation Concept (ESC): Removing the Functional Subunit from the Electrode by Molecular Design. Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2019, 5334–5343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-X.; Dong, X.-M.; Yu, M.-N.; Liu, W.; Nie, Y.-J.; Zhang, J.; Xie, L.-H.; Xu, C.-X.; Liu, J.-Q.; Huang, W. A Bio-Inspired Molecular Design Strategy toward 2D Organic Semiconductor Crystals with Superior Integrated Optoelectronic Properties. Small, 2021, 17, 2102060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wen, L.; Zhou, W.; Lv, J.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, M.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Jiang, L. Asymmetric and Symmetric Dipole-Dipole Interactions Drive Distinct Aggregation and Emission Behavior of Intramolecular Charge-Transfer Molecules. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, 113, 5924–5932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, E.; Somanathan, N. Efficient white-light emission from a single polymer system with ‘‘spring-like’’ self-assemblies induced emission enhancement and intramolecular charge transfer characteristics. J. Mater. Chem. C, 2017, 5, 4763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Oh, S.; Park, S.K.; Park, S.Y. Green-Sensitive Phototransistor Based on Solution-Processed 2D n-Type Organic Single Crystal. Adv. Electron. Mater., 2019, 5, 1900478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


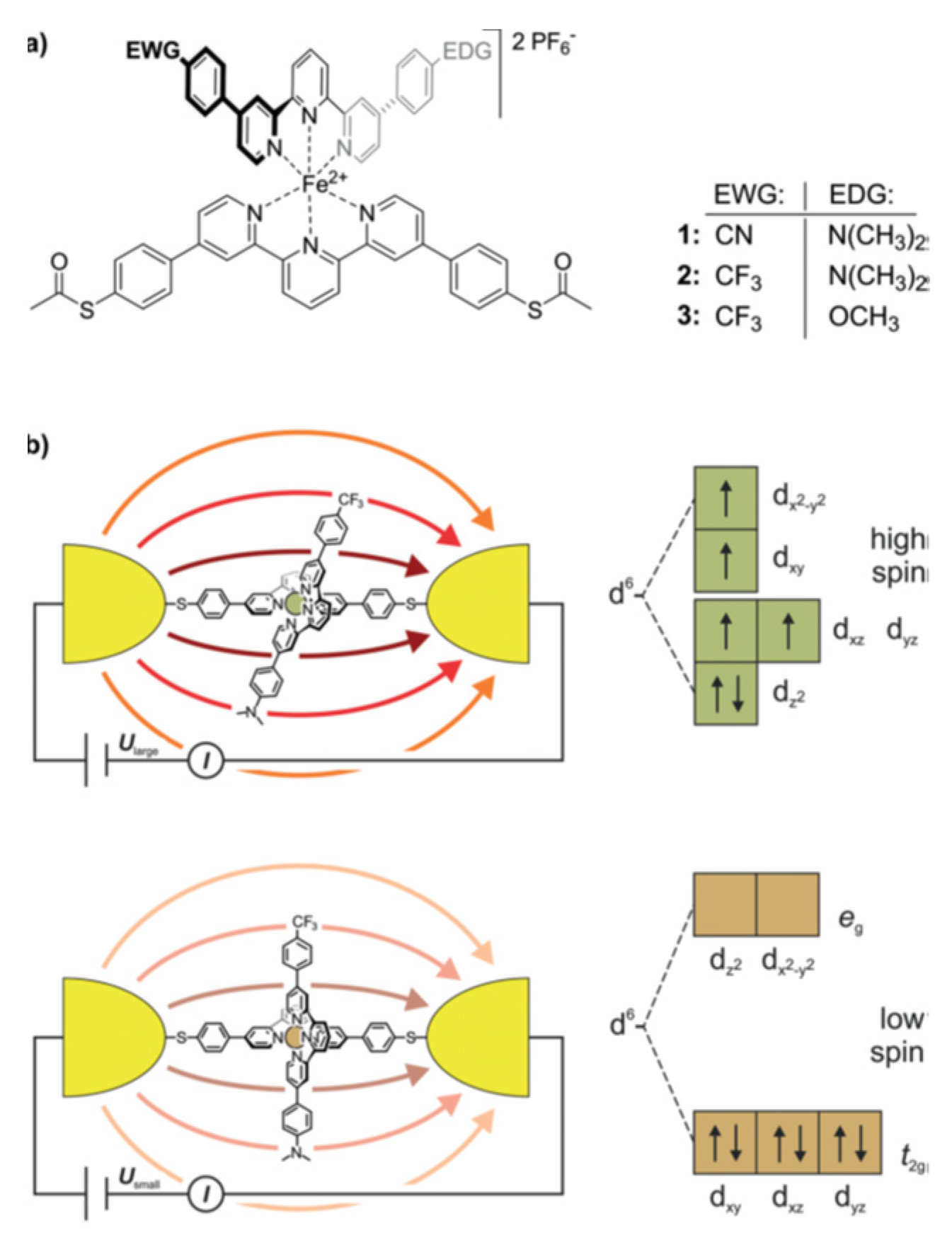
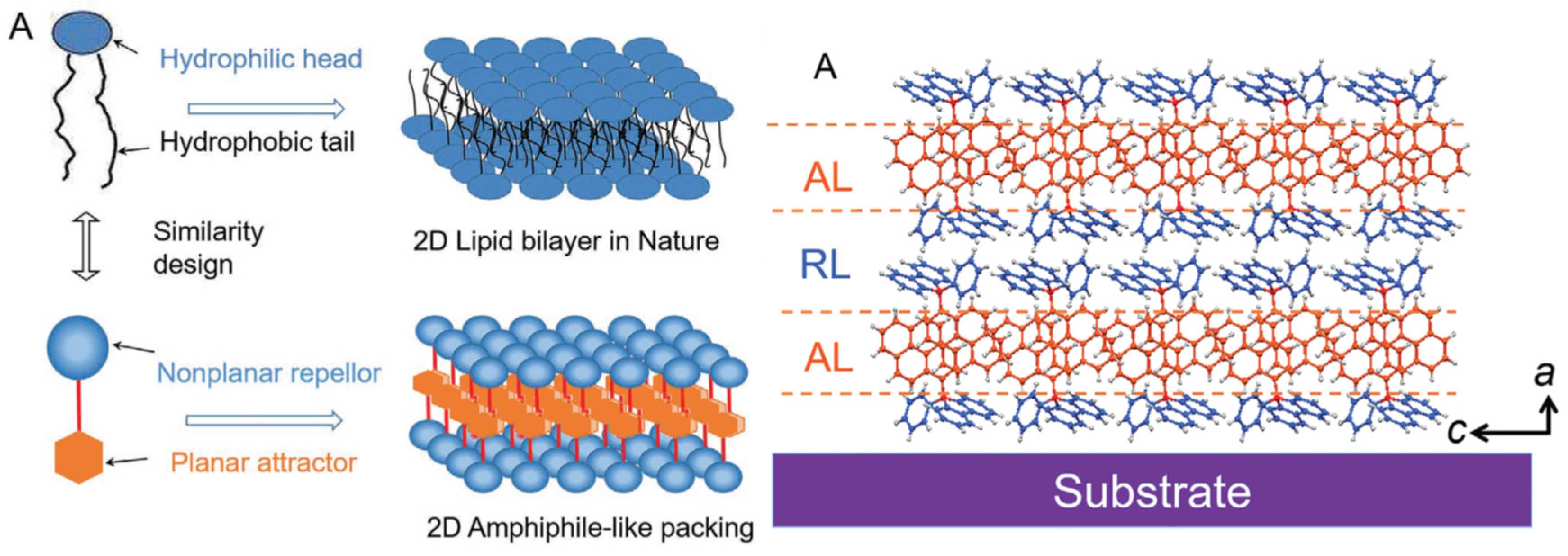
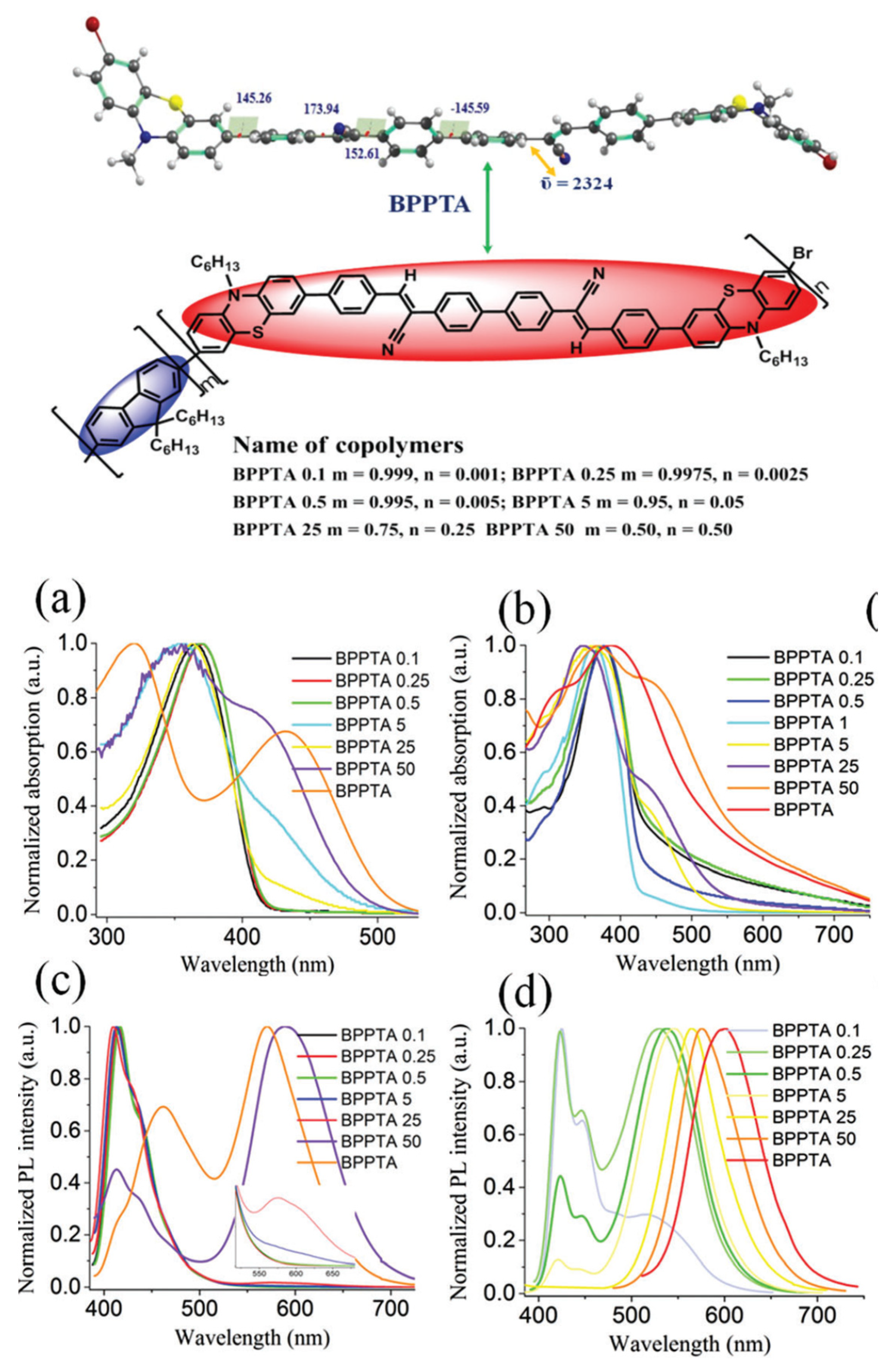
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




