Submitted:
16 January 2024
Posted:
16 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Spices, Chemicals, and Cultural Media
2.2. Bacterial Strains
2.3. Spice Extraction
2.4. Culture Media and Biogenic Amines (BAs) Extraction
2.5. Analysis of BA by HPLC after Derivatization
2.6. Chromatographic Separation
2.7. Determination of Different Bacterial Growths in Tyrosine Decarboxylase Broth (TDB)
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Bacterial Growth in Tyrosine Decarboxylase Broth
3.2. Ammonia, Trimethylamine and BAs Production in Tyrosine Decarboxylase Broth
3.2.1. Histamine Production by Food-Borne Pathogen Bacteria in Tyrosine Decarboxylase Broth
3.2.2. Tyramine Production by Food-Borne Pathogen Bacteria in Tyrosine Decarboxylase Broth
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramachandran, G. Gram-positive and gram-negative bacterial toxins in sepsis: A brief review. Virulence 2014, 5, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gourama, H. Foodborne pathogens. Food Safety Engineering 2020, 25–49. [Google Scholar]
- Özogul, Y.; Özogul, F. Biogenic amines formation, toxicity, regulations in food. Biogenic amines in food: Analysis, occurrence and toxicity 2019, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Gardini, F.; et al. Technological factors affecting biogenic amine content in foods: A review. Frontiers in microbiology 2016, 7, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsafack, P.B.; Tsopmo, A. Effects of bioactive molecules on the concentration of biogenic amines in foods and biological systems. Heliyon 2022, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalaby, A.R.; Anwar, M.M.; Sallam, E.M.; Emam, W.H. Quality and safety of irradiated food regarding biogenic amines: Ras cheese. International Journal of Food Science & Technology 2016, 51, 1048–1054. [Google Scholar]
- Jaguey-Hernandez, Y.; Aguilar-Arteaga, K.; Ojeda-Ramirez, D.; Anorve-Morga, J.; González-Olivares, L.G.; Castaneda-Ovando, A. Biogenic amines levels in food processing: Efforts for their control in foodstuffs. Food Research International 2021, 144, 110341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathod, N.B.; et al. Recent developments of natural antimicrobials and antioxidants on fish and fishery food products. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety 2021, 20, 4182–4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, S.M.; Youssef, A.M. Potential application of herbs and spices and their effects in functional dairy products. Heliyon 2019, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batiha, G.E.S.; Ogunyemi, O.M.; Shaheen, H.M.; Kutu, F.R.; Olaiya, C.O.; Sabatier, J.M.; De Waard, M. Rhus coriaria L.(Sumac), a versatile and resourceful food spice with cornucopia of polyphenols. Molecules 2022, 27, 5179. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pervez, M.K.; Ahmed, F.; Dewani, R.; Ayaz, T.; Mehboob, S.J.; Soomro, S.A. Qualitative investigation of prohibited food colors in red hot chilli & curry collected from Karachi City. Pakistan Journal of Pharmacology 2017, 34, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Modupalli, N.; Naik, M.; Sunil, C.K.; Natarajan, V. Emerging non-destructive methods for quality and safety monitoring of spices. Trends in Food Science & Technology 2021, 108, 133–147. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, A.; Chan, M.W.H.; Aslam, S.; Khan, A.; Abbas, Q.; Ali, S.; et al. Banned Sudan dyes in spices available at markets in Karachi, Pakistan. Food Additives & Contaminants: Part B 2023, 16, 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Daud, N.M.; et al. Valorisation of plant seed as natural bioactive compounds by various extraction methods: A review. Trends in Food Science & Technology 2022, 119, 201–214. [Google Scholar]
- Kuley, E.; Özogul, F. Synergistic and antagonistic effect of lactic acid bacteria on tyramine production by food-borne pathogenic bacteria in tyrosine decarboxylase broth. Food chemistry 2011, 127, 1163–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazgan, H.; et al. The antimicrobial properties and biogenic amine production of lactic acid bacteria isolated from various fermented food products. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation 2021, 45, e15085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klausen, N.K.; Huss, H.H. A rapid method for detection of histamine-producing bacteria. International Journal of Food Microbiology 1987, 5, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özogul, F. Effects of specific lactic acid bacteria species on biogenic amine production by foodborne pathogen. International journal of food science & technology 2011, 46, 478–484. [Google Scholar]
- Özoğul, F. Production of biogenic amines by Morganella morganii, Klebsiella pneumoniae and Hafnia alvei using a rapid HPLC method. European Food Research and Technology 2004, 219, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazeli, M.R.; et al. Antimicrobial activities of Iranian sumac and avishan-e shirazi (Zataria multiflora) against some food-borne bacteria. Food control 2007, 18, 646–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasar-Abbas, S.; Halkman, A.K. Antimicrobial effect of water extract of sumac (Rhus coriaria L.) on the growth of some food borne bacteria including pathogens. International journal of food microbiology 2004, 97, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayne, S.; Mazza, G. Biological activities of extracts from sumac (Rhus spp.): A review. Nature precedings 2017, 1–1. [Google Scholar]
- Mostafa, A.A.; et al. Antimicrobial activity of some plant extracts against bacterial strains causing food poisoning diseases. Saudi journal of biological sciences 2018, 25, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammad Salamatullah, A.; et al. Effects of different solvents extractions on total polyphenol content, HPLC analysis, antioxidant capacity, and antimicrobial properties of peppers (red, yellow, and green (Capsicum annum L.). Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2022, 2022.
- Pundir, R.K.; Jain, P. Comparative studies on the antimicrobial activity of black pepper (Piper nigrum) and turmeric (Curcuma longa) extracts. International Journal of Applied Biology and Pharmaceutical Technology 2010, 1, 492–500. [Google Scholar]
- Tırıs, G.; Yanıkoğlu, R.S.; Ceylan, B.; Egeli, D.; Tekkeli, E.K.; Önal, A. A review of the currently developed analytical methods for the determination of biogenic amines in food products. Food Chemistry 2023, 398, 133919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallik, S.; Sharangi, A.; Sarkar, T. Phytochemicals of coriander, cumin, fenugreek, fennel and black cumin: A preliminary study. National Academy Science Letters 2020, 43, 477–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merah, O.; et al. Biochemical composition of cumin seeds, and biorefining study. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; et al. Genetic engineering approach using early Vinca alkaloid biosynthesis genes led to increased tryptamine and terpenoid indole alkaloids biosynthesis in differentiating cultures of Catharanthus roseus. Protoplasma 2018, 255, 425–435. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Reidah, I.M.; et al. HPLC–DAD–ESI-MS/MS screening of bioactive components from Rhus coriaria L.(Sumac) fruits. Food chemistry 2015, 166, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgut, A.; et al. Suppression effects of aqueous and ethanolic extracts of propolis on biogenic amine production by Morganella psychrotolerans. LWT 2020, 131, 109771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houicher, A.; et al. Control of biogenic amine production and bacterial growth in fish and seafood products using phytochemicals as biopreservatives: A review. Food Bioscience 2021, 39, 100807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathod, N.B.; et al. Recent developments in polyphenol applications on human health: A review with current knowledge. Plants 2023, 12, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhu, F. Chemical composition and biological activity of staghorn sumac (Rhus typhina). Food Chemistry 2017, 237, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, P.; et al. Sumac silver novel biodegradable nano composite for bio-medical application: Antibacterial activity. Molecules 2015, 20, 12946–12958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harich, M.; et al. Evaluation of antibacterial activity of two natural bio-preservatives formulations on freshness and sensory quality of ready to eat (RTE) foods. Food Control 2018, 85, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karsha, P.V.; Lakshmi, O.B. Antibacterial activity of black pepper (Piper nigrum Linn.) with special reference to its mode of action on bacteria. 2010.
- Milenković, A.N.; Stanojević, L.P. Black pepper: Chemical composition and biological activities. Advanced Technologies 2021, 10, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Hu, Y.-Y.; Chen, W.-X. Antibacterial mechanism and activities of black pepper chloroform extract. Journal of Food Science and Technology 2015, 52, 8196–8203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, W.; et al. Effects of spices on the formation of biogenic amines during the fermentation of dry fermented mutton sausage. Food Chemistry 2020, 321, 126723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trifan, A.; et al. Phytochemical characterization and evaluation of the antioxidant and anti-enzymatic activity of five common spices: Focus on their essential oils and spent material extractives. Plants 2021, 10, 2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wendakoon, C.N.; Sakaguchi, M. Inhibition of amino acid decarboxylase activity of Enterobacter aerogenes by active components in spices. Journal of food protection 1995, 58, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oktariani, A.F.; Ramona, Y.; Sudaryatma, P.E.; Dewi, I.A.M.M.; Shetty, K. Role of marine bacterial contaminants in histamine formation in seafood products: A review. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, A.R.; Lee, J.H.; Mah, J.-H. Biogenic amine formation and bacterial contribution in Cheonggukjang, a Korean traditional fermented soybean food. LWT 2018, 92, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; et al. Inhibitory effects of brown algae extracts on histamine production in mackerel muscle via inhibition of growth and histidine decarboxylase activity of Morganella morganii. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 2014, 24, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakila, R.J.; Vasundhara, T.; Vijaya Rao, D. Inhibitory effect of spices on in vitro histamine production and histidine decarboxylase activity of Morganella morganii and on the biogenic amine formation in mackerel stored at 30 C. Zeitschrift für Lebensmittel-Untersuchung und Forschung 1996, 203, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, D.M.; et al. Comparative analysis of the in vitro cytotoxicity of the dietary biogenic amines tyramine and histamine. Food chemistry 2016, 197, 658–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.F.A.; et al. Reduction of biogenic amines production in chilled minced meat using antimicrobial seasonings. Journal of microbiology, biotechnology and food sciences 2021, 10, e3663–e3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Wu, Z.-y.; Zhang, W.-x. Bioinformatics analysis of amino acid decarboxylases related to four major biogenic amines in pickles. Food Chemistry 2022, 393, 133339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
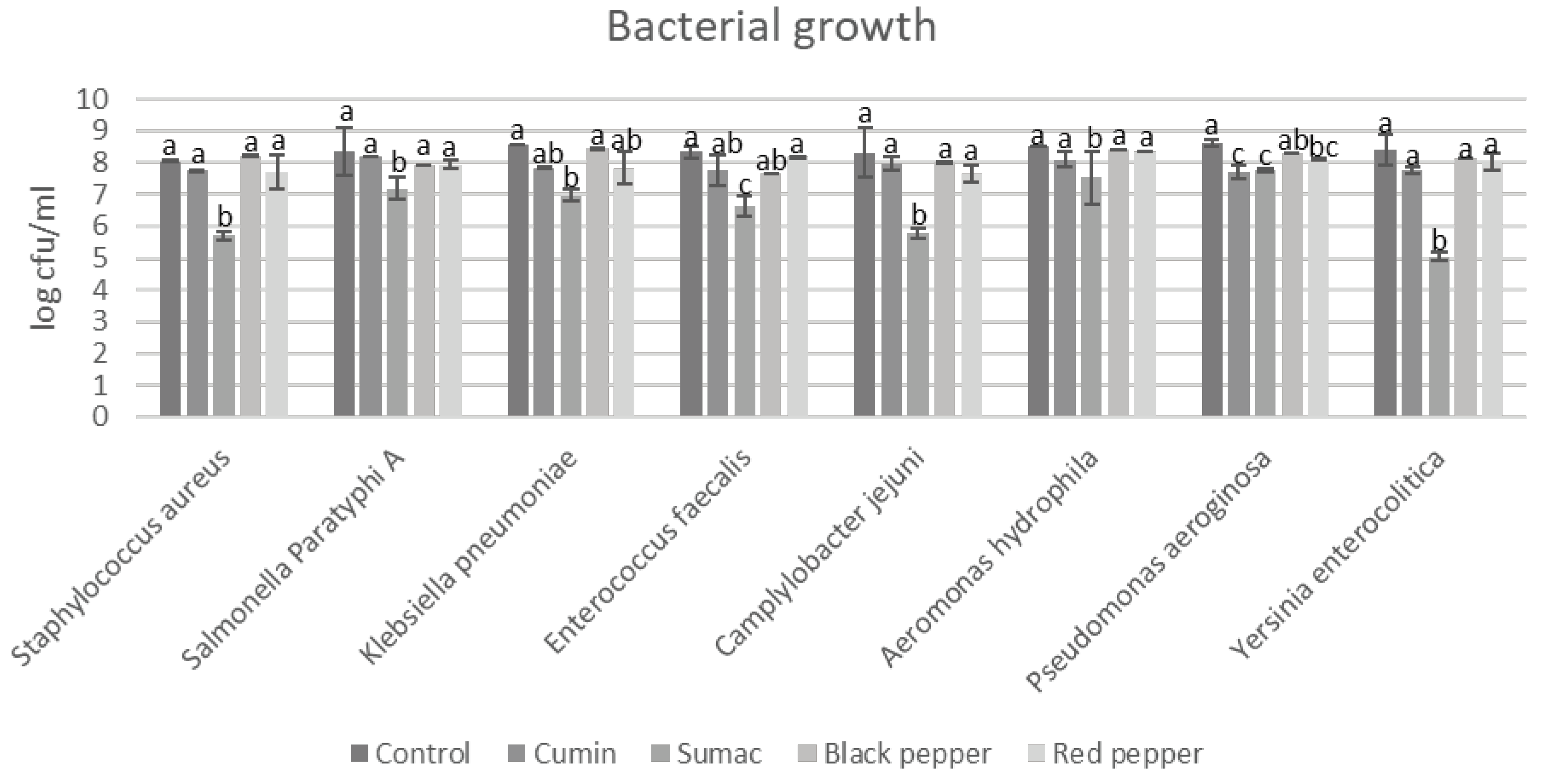
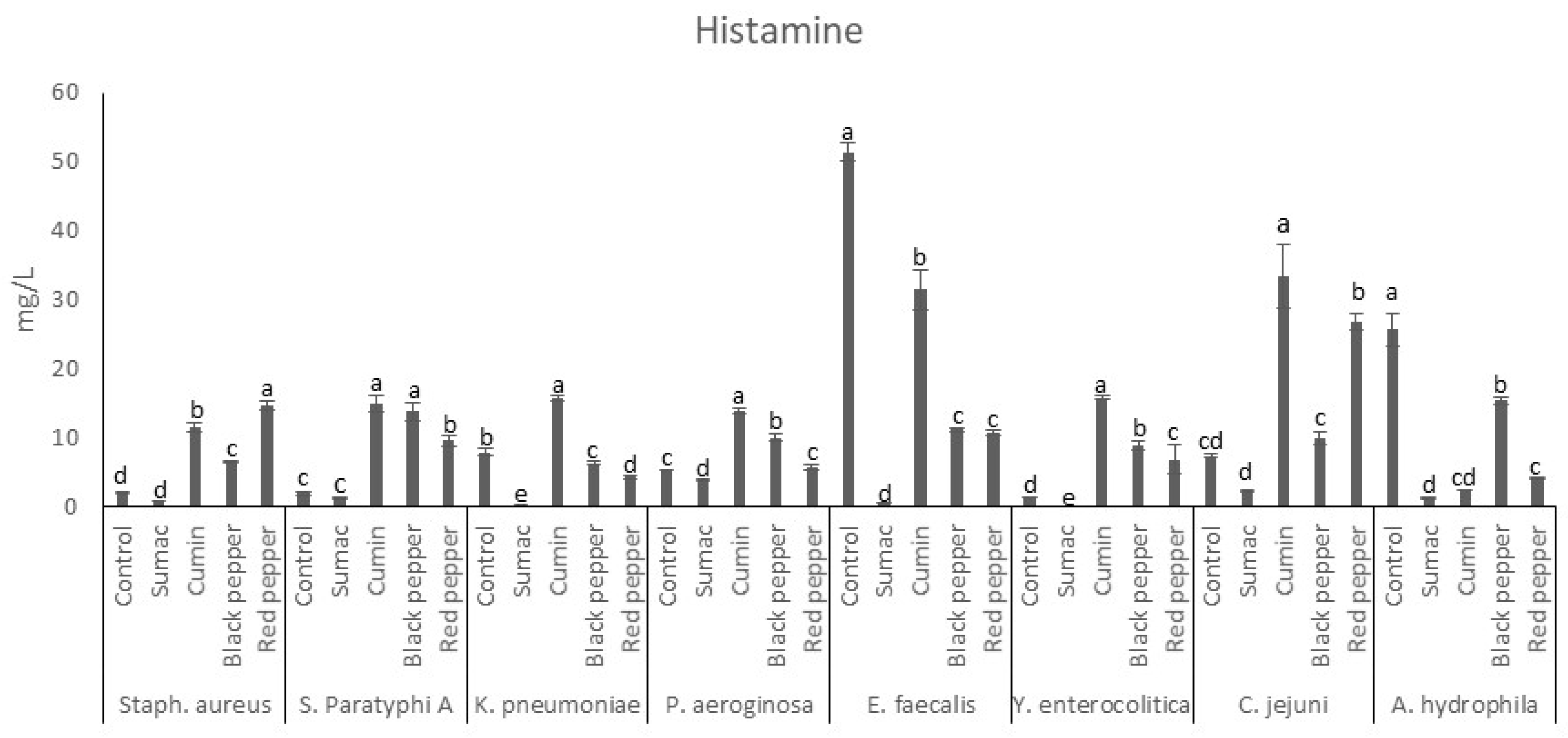
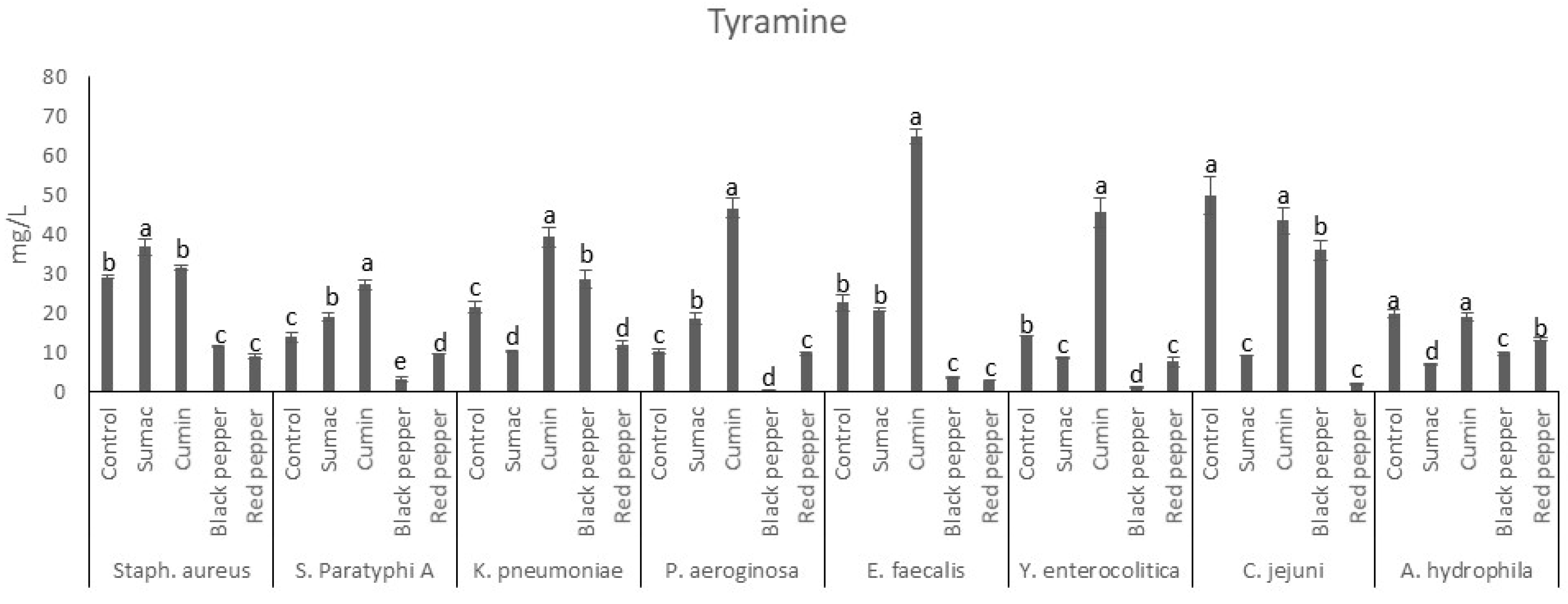
| AMN | PUT | CAD | SPD | TRP | PHEN | SPM | SER | TMA | DOP | AGM | Group | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC29213) |
808.05±68.56a 84.60±5.66c 323.35±17.46b 344.10±34.97b 419.86±30.89b |
15.85±0.54b 5.64±0.22c 81.09±4.21a 15.77±1.13b 8.34±0.48c |
3.42±0.21cd 2.01±0.32d 27.99±2.27a 16.87±0.97b 6.22±0.40c |
16.70±1.36b 2.10±0.20c 90.42±8.11a 1.01±0.01c 15.25±1.27b |
0.28±0.01c 0.00±0.00c 17.80±0.27a 0.28±0.03c 5.80±0.18b |
0.25±0.01b 0.00±0.00b 12.77±0.51a 0.00±0.00b 0.41±0.01b |
16.16±0.37c 5.50±0.13d 42.13±1.91b 9.32±0.07d 69.93±3.29a |
7.69±0.25d 95.31±1.66a 34.03±2.62b 14.27±1.37c 8.99±0.60d |
3.21±0.03d 3.96±0.21d 22.34±0.09b 12.79±0.34c 30.01±2.15a |
95.24±1.63c 190.39±13.94b 503.00±0.34a 494.54±16.05a 24.37±1.38d |
39.18±0.27c 42.49±3.77c 71.83±1.28b 111.65±8.84a 47.11±1.62c |
C SUM CUM BP RP |
|
Salmonella Paratyphi A (NCTC13) |
836.47±62.76a 71.51±5.94c 286.12±5.54b 78.34±0.79c 287.30±18.56b |
21.49±1.04b 1.44±0.02c 57.39±4.55a 5.89±0.39c 4.23±0.07c |
4.39±0.40c 1.73±0.04d 27.41±1.19a 3.07±0.13cd 7.86±0.42b |
22.24±2.08b 5.34±0.48c 60.55±2.34a 0.00±0.00d 21.25±2.47b |
0.00±0.00b 0.00±0.00b 16.54±0.67a 0.16±0.02b 0.77±0.01b |
0.00±0.00b 0.00±0.00b 12.81±0.85a 0.00±0.00b 0.97±0.10b |
17.81±1.53c 2.96±0.16e 58.75±0.63b 7.28±0.74d 112.37±2.42a |
31.40±2.52b 82.42±2.93a 23.96±0.51c 8.56±0.35d 19.71±1.09c |
18.65±0.92a 4.24±0.09c 17.17±1.29a 3.29±0.16c 14.36±1.09b |
468.63±41.47a 355.11±30.40b 482.23±37.95a 45.24±4.30c 322.84±21.54b |
70.90±5.82a 26.40±1.56c 80.87±6.91a 32.90±1.59bc 43.26±1.82b |
C SUM CUM BP RP |
|
Klebsiella pneumoniae (ATCC700603) |
699.88±45.21a 133.15±10.39c 259.56±24.37b 181.69±7.46c 267.97±18.00b |
26.36±1.53a 16.88±1.31c 21.25±0.75b 13.18±1.03d 24.88±0.96a |
3.03±0.04c 3.10±0.13c 32.05±2.53a 8.08±0.14b 9.14±0.01b |
16.66±0.93b 12.04±0.83b 55.52±4.94a 4.67±0.23c 16.63±0.41b |
0.00±0.00b 0.00±0.00b 16.32±0.29a 0.30±0.01b 0.39±0.55b |
0.00±0.00b 0.00±0.00b 14.56±0.92a 0.00±0.00b 0.66±0.08b |
31.99±2.78a 2.39±0.02c 30.87±0.79a 11.13±0.46b 31.02±0.18a |
57.20±1.80b 65.51±3.73a 44.31±2.82c 6.27±0.60d 6.48±0.10d |
5.40±0.26b 1.70±0.04c 35.04±1.48a 5.06±0.21b 0.91±0.02c |
815.25±53.59a 434.63±38.38b 457.67±40.57b 97.64±4.07c 160.19±5.44c |
74.48±3.94b 18.67±1.33c 93.58±6.11a 25.20±1.11c 22.55±1.58c |
C SUM CUM BP RP |
|
Pseudomonas aeruginosa (ATCC27853) |
844.24±46.07a 240.06±8.52c 328.78±9.13b 166.48±6.82d 193.23±18.26d |
2.20±0.18c 1.07±0.02c 60.45±7.54a 16.40±1.12b 3.30±0.33c |
3.42±0.33c 3.26±0.26c 59.49±0.92a 3.44±0.05c 11.09±0.52b |
46.77±2.93b 2.88±0.17d 104.70±8.03a 0.77±0.10d 35.86±1.68c |
0.00±0.00c 0.00±0.00c 21.56±1.46a 0.00±0.00c 4.05±0.01b |
0.28±0.03b 0.00±0.00b 25.06±1.62a 0.00±0.00b 0.36±0.05b |
21.51±0.47c 11.87±0.39cd 67.97±3.48b 7.69±0.15d 109.52±10.36a |
16.91±0.69c 51.04±1.59a 46.76±2.20b 4.52±0.19d 14.83±0.39c |
20.83±1.54b 4.34±0.02c 48.89±0.29a 1.34±0.08d 2.01±0.07d |
668.71±55.08a 453.12±41.40b 357.57±12.44c 118.81±6.11d 175.72±4.57d |
64.32±4.17b 24.99±0.05d 92.37±4.40a 33.98±2.08c 36.93±0.56c |
C SUM CUM BP RP |
|
Enterococcus faecalis (ATCC29212) |
689.23±56.42a 87.75±1.91d 290.61±7.15bc 329.76±4.75b 234.01±14.94c |
4.88±0.45c 1.46±0.05c 23.78±1.44b 26.72±2.27b 33.09±1.69a |
3.50±0.16c 2.24±0.09c 50.75±3.56a 9.12±0.11b 3.74±0.42c |
90.22±4.82a 4.43±0.04cd 0.00±0.00d 8.14±0.61c 27.99±0.94b |
0.95±0.07b 0.88±0.04b 20.35±2.08a 0.24±0.00b 0.37±0.05b |
0.35±0.01b 0.00±0.00b 15.75±0.52a 0.51±0.01b 0.00±0.00b |
7.50±0.09c 2.97±0.04d 57.36±4.62a 7.90±0.50c 41.42±0.93b |
20.98±0.94c 75.87±2.93a 25.57±0.80b 13.65±1.38d 9.92±0.71d |
36.16±2.58b 5.56±0.28d 49.73±0.54a 3.86±0.28d 10.79±0.09c |
998.43±15.67a 517.62±38.93b 532.55±25.63b 94.04±4.44c 516.60±29.40b |
55.08±4.19b 22.97±1.63d 112.61±4.92a 22.39±1.63d 43.36±1.28c |
C SUM CUM BP RP |
|
Yersinia enterocolitica (NCTC 11175) |
570.71±10.84a 55.10±1.52d 278.62±5.22b 135.34±6.13c 143.63±14.69c |
27.70±1.05a 2.81±0.27c 26.75±0.58ab 2.67±0.12c 25.85±0.65b |
4.95±0.08bc 2.27±0.00d 26.27±1.62a 1.63±0.04d 3.67±0.26c |
48.16±0.45a 0.00±0.00e 38.72±1.66b 4.41±0.15d 21.71±2.23c |
0.00±0.00c 0.00±0.00c 17.19±0.27a 0.38±0.03b 0.63±0.01b |
0.00±0.00b 0.00±0.00b 14.43±0.68a 0.00±0.00b 0.00±0.00b |
24.81±0.65c 2.59±0.11e 66.23±1.43a 8.70±0.47d 51.04±0.82b |
135.38±10.36a 14.06±0.29c 97.55±1.46b 6.28±0.44c 15.28±3.22c |
8.23±0.53b 1.28±0.08d 16.08±1.42a 1.79±0.10d 5.67±3.73c |
1159.63±114.29a 440.95±28.32c 599.80±23.20b 102.60±3.14d 214.46±120.13d |
65.27±4.36b 25.79±0.08d 97.11±1.07a 10.70±0.10e 31.45±7.25c |
C SUM CUM BP RP |
|
Campylobacter jejuni (ATCC 33560) |
691.20±66.03a 309.57±8.03b 317.87±9.43b 168.40±9.99c 211.38±17.40c |
35.49±3.54b 7.84±0.24c 71.68±2.93a 13.43±1.16c 9.30±0.37c |
3.23±0.00c 3.27±0.01c 24.72±0.56a 13.98±0.24b 2.58±0.08c |
37.71±2.94a 4.22±0.39c 0.00±0.00d 3.96±0.12c 20.91±0.99b |
1.07±0.09b 0.00±0.00c 20.85±0.29a 0.89±0.01b 0.21±0.01c |
0.00±0.00b 0.00±0.00b 26.80±1.32a 0.00±0.00b 0.00±0.00b |
46.78±2.95b 6.34±0.21c 70.20±2.55a 7.65±0.61c 4.89±0.27c |
15.33±1.02b 11.06±1.31bc 125.78±4.12a 10.91±0.53bc 7.84±0.29c |
14.35±0.12b 6.39±0.28c 22.05±0.29a 6.23±0.32c 2.15±0.06d |
636.14±24.06a 279.47±7.78c 628.98±61.35a 16.78±1.17d 494.09±3.03b |
81.69±7.40b 19.04±1.00cd 95.69±0.04a 11.24±0.01d 26.79±0.87c |
C SUM CUM BP RP |
|
Aeromonas hydrophila (NCIMB1135) |
543.77±52.09a 99.15±2.96c 58.50±3.53c 83.68±5.21c 256.36±11.04b |
3.29±0.10b 5.71±6.63b 25.64±1.16a 1.74±0.06b 3.76±0.21b |
4.61±0.77c 5.33±0.28c 9.06±1.11b 4.57±0.14c 11.18±0.23a |
78.29±3.54a 6.36±0.44d 32.21±1.76b 1.29±0.13e 20.45±0.68c |
0.66±0.08b 0.00±0.00c 5.98±0.28a 0.28±0.02c 0.70±0.07b |
0.97±0.11b 0.00±0.00c 4.04±0.04a 0.00±0.00c 0.00±0.00c |
37.21±1.51b 6.73±0.22d 31.71±1.03c 8.91±0.19d 93.57±2.23a |
36.74±3.60b 7.36±0.17d 66.56±2.16a 5.07±0.07d 24.02±0.25c |
53.66±0.98a 2.76±0.23d 8.27±0.64b 4.89±0.42c 1.42±0.11d |
746.78±5.75a 578.68±34.14b 707.41±69.65a 57.53±4.14c 144.53±6.51c |
254.91±17.94a 51.44±1.79c 164.72±4.99b 13.96±0.95d 29.24±1.79d |
C SUM CUM BP RP |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





