Submitted:
15 January 2024
Posted:
16 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of Pb on Contents of Pb and Endogenous Hormones in Arabis alpina
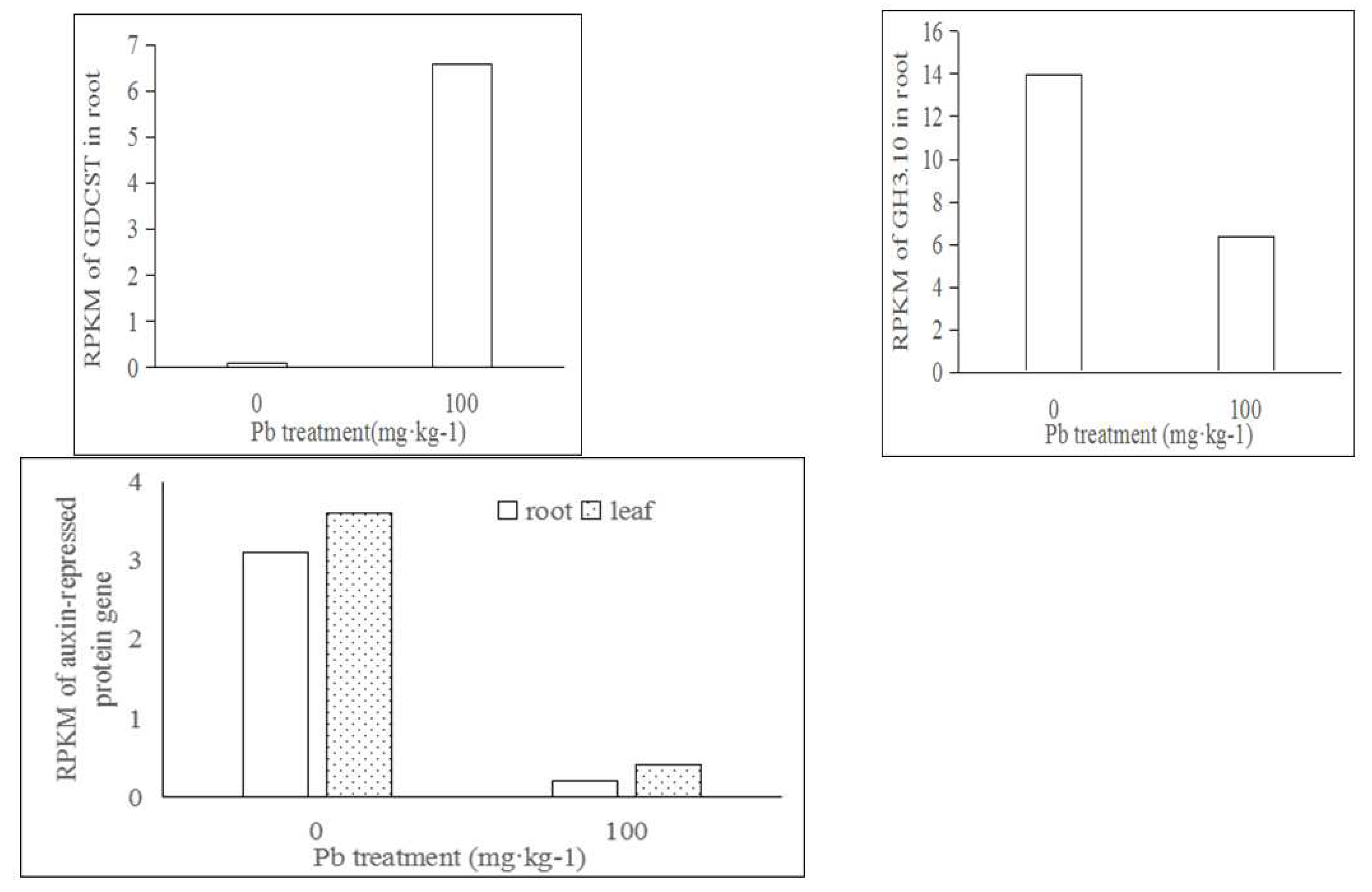
2.2. Effect of Pb on Gene Expression Related to Plant Hormones Dased on RNA-seq analysis
2.3. Effect of foliage spraying IAA on Pb contents and activities of transporters in Arabis alpina
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Experimental Design
4.3. Determination of Indicators
4.4. Calculation and Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, Y.Y.; Dong, Y.W.; Zhu, N.; Jin, H.M. Foliar application of biosynthetic nano-selenium alleviates the toxicity of Cd, Pb, and Hg in Brassica chinensis by inhibiting heavy metal adsorption and improving antioxidant system in plant. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 2022, 240, 113681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firdaus-e-Bareen; Shafiq, M.; Jamil, S. Role of plant growth regulators and a saprobic fungus in enhancement of metal phytoextraction potential and stress alleviation in pearl millet. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2012, 237–238, 186–193. [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska-Niczyporuk, A.; Baiquz, A.; Zambrzycka, E.; et al. Phytohormones as regulators of heavy metal biosorption and toxicity in green alga Chlorella vulgaris (Chlorophyceae). Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 2012, 52, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelgadir, H.A.; Jager, A.K.; Johnson, S.D.; Staden, J.V. Influence of plant growth regulators on flowering, fruiting, seed oil content and oil quality of Jatropha curcas. South African Journal of Botany 2020, 76, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, P.; Nabi, G.; Ashraf, M. Cadmium-induced oxidative damage in mustard(Brassica juncea(L.)Czern.&Coss. plants can be alleviated by salicylic acid. South African Journal of Botany 2011, 77, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.Y.; Ren, Y.F.; Wang, Y.Y.; Li, Z.J. Root morphological and physiological response of rice seedling with different to tolerance to cadmium stress. Acta Ecologica Sinica 2011, 31, 0522–0528. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.H.; Xue, Z.L.; Yang, C.Y. Effect of salicylic acid on membrane lipid peroxidation in rice seedling under copper stress. HelongjiangAgricultural Science 2013, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Orenes, A.; Alba, J.M.; Kant, M.R.; Calderon, A.A.; Ferrer, M.A. OPDA and ABA accumulation in Pb-stressed Zygophyllum fabago can be primed by salicylic acid and coincides with organ-specific differences in accumulation of phenolics. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2020, 154, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Lu, Q.Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Chen, X.Q.; Wang, X.G.; Gu, M.H. Effects of different growth regulators on cadmium accumulation by Sedum alfredii H. Journal of Agro-Environmental Science. 2014, 33, 1538–1545. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, W.J.; Gao, W.; Liu, H.E.; Nie, Z.J.; Qin, S.Y.; Li, C.; Sui, F.Q.; Zhao, P. Effects of plant growth regulator on growth and cadmium uptake and accumulation in wheat seedlings. Journal of Henan Agricultural University 2021, 55, 1036–1044. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, P.H.; Jiang, Y.J.; Tang, X.W.; Thanh, H.N.; Tong, Y.A.; Gao, P.C.; Han, W.S. Enhancing of Phytoremediation Efficiency Using Indole-3-Acetic Acid (IAA). Soil and Sediment Contamination: An International Journal 2015, 24, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.M.; Wang, D.S.; Hu, F.; Li, H.X.; Ma, L.; Xu, L. Exogenous IAA treatment enhances phytoremediation of soil contaminated with phenanthrene by promoting soil enzyme activity and increasing microbial biomass. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2016, 23, 10656–10664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, F.; Bano, A.; Fuller, M.P. The improved phytoextraction of lead (Pb) and the growth of maize (Zea mays L.):The role of plant growth regulators(GA3 and IAA) and EDTA alone and in combinations. Chemosphere 2010, 80, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fässler, E.; Evangelou, M.W.; Robinson, B.H.; et al. Effects of indole-3-acetic acid(IAA) on sunflower growth and heavy metal uptake in combination with ethylene diamine disuccinic acid(EDDS). Chemosphere 2010, 80, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, R.J.; He, E.K.; Tang, Y.T.; Hu, P.J.; Ying, R.R. How Phytohormone IAA and Chelator EDTA affect lead uptake by Zn/Cd hyperaecumulator Pictis divaricata. International Journal of Phytoremediation 2011, 13, 1024–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Wang, Z.X.; Xiang, Y.Z.; Ren, J.; Luo, G.J.; Liu, F. Effects of Indole-3-acetic Acid and L-glutamic Acid N, N-diacetic Acid on the Growth and Heavy Metal Uptake by Solanum nigrum L. in Cd-Pb Contaminated Soil. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University (Natural Science) 2022, 37, 145–151. [Google Scholar]
- Uraguchi, S.; Fujiwara, T. Rice breaks ground for cadmium-free cereals. Current opinion in plant biology 2013, 16, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, B.; Zhang, W.W.; Yang, H.Q. Abscisic acid decreases cell death in Malus hupehensis Rehd. under Cd stress by reducing root Cd2+ infux and leaf Transpiration. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation 2022, 41, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, Z.R.; Zu, Y.Q. Transport protein CAXs and HMAs related to cadmium absorbing and transferring of plant: A review. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin 2020, 36, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.Y.; Bovet, L.; Maeshima, M.; Lee, Y. The ABC transporter AtPDR8 is a cadmium extrusion pump conferring heavy metal resistance. The plant journal 2007, 50, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strader, L.C.; Bartel, B. The Arabidopsis pleiotropicdrug resistance8/abcg36 ATP binding cassette transporter modulates sensitivity to the auxin precursor indole-3-butyric acid. The Plant Cell 2009, 21, 1992–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukumar, P.; Maloney, G.S.; Muday, G.K. Localizes induction of the ATP-binding cassette B19 auxin transporter enhances adventitious root formation in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology 2013, 162, 1392–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peto, A.; Lehotai, N.; Lozano-Juste, J. Involvement of nitric oxide and auxin in signal transduction of copper-induced morphological responses in Arabidopsis seedlings. Annals of Botany 2011, 108, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolbert, Z.; Pet, A.; Lehotai, N.; Feigl, G.; Erdei, L. Long-term copper(Cu2+) exposure impacts on auxin, nitric oxide(NO) metabolism and morphology of Arabidopsis thaliana L. Plant Growth Regulator 2012, 68, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.R.; Ikka, T.; Sawaki, Y.; et al. Comparative transcriptomic characterization of aluminum, sodium chloride,cadmium and copper rhizotoxicities in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biology 2009, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Yue, R.; Tao, S.; et al. Genome-wide identification,expression analysis of auxin-responsive GH3 family genes in maize (Zea mays L.) under abiotic stresses. Journal of Plant Biology 2015, 57, 783–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Wang, Q.; Zou, Y.J.; Ma, M.N.; Jing, G.Q.; Ma, F.W.; Li, C. Silencing MdGH3-2/12 in apple reduces cadmium resistance via the regulation of AM colonization. Chemosphere 2021, 269, 129407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Zhou, N.N.; Wang, G.; Xiao, L.T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z. Effect of Lead Pollution on the content of endogenous hormones in cucumber leaves. Ecology and Environment 2007, 16, 1446–1446. [Google Scholar]
- He, B.; Chen, X.Q.; Xin, Z.B.; Lu, Q.Y.; Shi, Q.; Gu, M.H.; Wang, Z.L. Effects of four plant growth regulators on growth and cadmium accumulation in rice. Acta Ecologica Sinica 2016, 36, 6863–6871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Guo, H.C.; Li, J.; Zhang, G.H.; Shi, L.C. Effects of lead stress on growth morphology and endogenous hormone of potato seedlings. Acta Agricultural Boreali-occidentalis Sinica 2019, 28, 1830–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.K.; Zhang, C.Y.; Wang, Y.; Ai, Y.M.; Xu, X.Y.; Feng, J.P.; Feng, W.Y.; Song, L.P.; Li, X.P.; Zhou, J.H. Effects of different auxin content on physiological and biochemical characteristics of Cinnamomum camphora seedling in Cd polluted soil. Journal of Northeast Forestry University 2023, 51, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sytar, O.; Kumari, P.; Yadav, S.; Brestic, M.; Rastogi, A. Phytohormone priming: regulator for heavy metal stress in plants. J. Plant Growth Regul 2019, 38, 739–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. Study on the regulatory effect of exogenous methyl jasmonate on heavy metal resistance in mangrove seedlings. Shanghai: East China Normal University 2014.
- Zhang, X.M.; Wang, H.J.; Wang, H.B. Advances in biosynthesis and degradation of indoleacetic acid in plants under heavy metal stress. Chinese Journal of Ecology 2017, 36, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.Q.; Zhang, C.B. Advance in regulation of heavy metals on nonselective cation channels: A review. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment 2017, 34, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colebrook, E.H.; Thomas, S.G.; Phillips, A.L.; Hedden, P. The role of gibberellin signalling in plant response to abiotic stress. Journal of experimental biology 2014, 217, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgher, M.; Khan, MIR. ; Anjum, N.A.; Khan, N. Minimising toxicity of cadmium in plants role of plant growth regulators. Proto plasma 2015, 252, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potters, G.; Pasternak, T.P.; Guisez, Y.; Jansen, M. A.Different stresses,similar morphogenic responses: Integrating a plethora of pathways. Plant, Cell & Environment 2009, 32, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tognetti, V.B.; Van Aken, O.; Morreel, K. Perturbation in indole-3-butyric acid homeostasis by the UDP-glucosyltransferase UTG74E2 modulates Arabidopsis architecture and water stress tolerance. The Plant Cell 2010, 22, 2660–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilfoyle, T.J.; Ulmasov, T.; Hagen, G. The ARF family of transcription factors and their role in plant hormone-responsive transcription. Cellular and molecular life sciences 1998, 54, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, M.; Kaur, N.; Garg, R.; Thakur, J.K.; Tyagi, A.K.; Khurana, J.P. Structure and expression analysis of early auxin-responsive Aux/IAA gene family in rice (Oryza sativa). Funct. Integr. Genom 2006, 6, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, M.; Kaur, N.; Tyagi, A.K.; Khurana, J.P. The auxin-responsive GH3 gene family in rice (Oryza sativa). Funct. Integr. Genom. 2006, 6, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Tyagi, A.K.; Khurana, J.P. Genome-wide analysis,evolutionary expansion,and expression of early auxin-responsive SAUR gene family in rice (Oryza sativa). Genomics 2006, 88, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, W. M.; Kepinski, S.; Rouse, D.; Leyse, O.; Estelle, M. Auxin regulates SCF[TIR1]-dependent degradation of AUX/IAA proteins. Nature 2001, 414, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Agarwal, P.; Tyagi, A.K.; Sharma, A.K. Genome-wide investigation and expression analysis suggest diverse roles of auxin-responsive GH3 genes during development and response to different stimuli in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). Molecular Genetics & Genomics 2012, 287, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Han, C.T.; Hur, Y. Molecular characterization of the Brassica rapa auxin-repressed, superfamily genes, Br ARP1 and Br DRM1. Molecular Biology Reports 2013, 40, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Huang, D.; Niu, D.S.; Deng, J.; Ma, F.W.; Liu, C.H. Overexpression of auxin response gene MdIAA24 enhanced cadmium tolerance in apple (Malus domestica). Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 2021, 225, 112734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, K.; Ueda, J.; Komaki, M.K.; Bell, C.J.; Shimura, Y. Requirement of auxin polar transport system in early stages of Arabidopsis floral bud formation. Plant Cell 1991, 72, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, B.; Murphy, A.S.; Spalding, E.P. Multidrug resistance-like genes of Arabidopsis required for auxin transport and auxin-mediated development. Plant Cell 2001, 13, 2441–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swarup, K.; Benkova, E.; Swarup, R.; Casimiro, T.; Peret, B.; Yang, Y.; Parry, G.; Nielsen, E.; De Smet, I.; Vanneste, S.; Levesque, M.P.; Carrier, D.; James, N.; Calvo, V.; Ljung, K.; Kramer, E.; Roberts, R.; Graham, N.; Marillonnet, S.; Patel, K.; Jones, J.D.; Taylor, C.G.; Schachtman, D.P.; May, S.; Sandberg, G.; Benfeg, P.; Friml, J.; Kerr, I.; Beeckman, T.; Laplaze, I.; Bennett, M.J. The auxin influx carrier LAX3 promotes lateral root emergence. Nature Cell Biology 2008, 10, 946–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Tao, Y.; Chen, X.; Zou, Y.; Lei, C.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, M.; Lu, Z.; Xu, J.; Cheng, Z. Identification of a new rice Blast resistance gene, Pid3, by genomewide comparison of paired nucleotide-binding site-Leucine-rich repeat genes and their pseudogene alleles between the two sequenced rice genomes. Genetics 2009, 182, 1303–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.W.; Kim, K.A.; Park, S.C.; Jeong, M.J.; Byun, M.O.; Kwon, H.B. Expression profiles of hot pepper (Capsicum annuum) genes under cold stress conditions. J Biosci. 2005, 30, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Chai, T.Y.; Zhang, Y.X. Upstream promoter sequences of Arabidopsis GH3 gene family. Journal of the Graduate School of the Chinese Academy of Sciences 2010, 27, 847–852. [Google Scholar]
- Tassi, E.; Pouget, J.E.L.; Petruzzelli, G. The effects of exogenous plant growth regulators in the phytoextraction of heavy metals. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.L.; Li, H.; Ma, C.F.; Zhang, Y.L.; Polle, A.; Rennenberg, H.; Cheng, X.Q.; Luo, Z.B. Overexpression of bacterial g-glutamylcysteine synthetase mediates changes in cadmium influx, allocation and detoxification in poplar. New Phytol. 2015, 205, 240–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downes, B.P.; Crowell, D.N. Cytokinin regulates the expression of a soybean β-expansin gene by a post-transcriptional mechanism. Plant Mol. Biol. 1998, 37, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.W.; Shi, G.X.; Xu, Q.S. Effects of Cd2+ polluted water on the activities of antioxidant enzymes and ultrastructure in roots of Alternanthera philoxeroides. Plant Physiology Communication 2003, 9, 211–214. [Google Scholar]
- Uraguchi, S.; Mori, S.; Kuramata, M. Root-to-shoot Cd translocation via the xylem is the major process determining shoot and grain cadmium accumulation in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 60, 2677–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemianowski, O.; Mills, R.F.; Williams, L.E.; Antosiewicz, D.M. Expression of the P1B-type ATPase AtHMA4 in tobacco modifies Zn and Cd root to shoot partitioning and metal tolerance. lant biotechnology journal 2011, 9, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.T.; Wan, H.X.; Qin, S.J.; He, J.L.; Lyu, D.G.; Li, H.F. Net cadmium flux and gene expression in relation to differences in cadmium accumulation and translocation in four apple rootstocks. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2016, 130, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.B.; Lin, W.W.; Tang, W.X.; Takahashi, K.; Pan, X.; Dai, J.W.; Ren, H.; Zhu, X.Y.; Pan, S.Q.; Zheng, H.Y. TMK based cell surface auxin signaling activates cell wall acidification in Arabidopsis. Nature 2023, 599, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.Y.; Shigaki, T.; Williams, K.A.; Han, J.S.; Kim, C.K.; Hirschi, K.D.; Park, S. Expression of an Arabidopsis Ca2+/H+ antiporter CAX1 variant in petunia enhances cadmium tolerance and accumulation. Plant Physiol. 2011, 168, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.R.; Sheng, Q.R. Effects of ABA and IAA on the Behavior of Stomata of Rice Crop Cultivated in Aerobic Soil Condition. Scientia Agricultural Sinica 2003, 36, 1450–1455. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.M.; Dang, Z.; Chen, N.C.; Xu, S.G.; Xie, Z.Y. Enhanced phytoextraction of heavy metal contaminated soil by chelating agents and auxin indole-3-acetic acid. Environmental Science 2007, 28, 2085–2088. [Google Scholar]
| Parts | Pb2+ treatment concentration (mg·kg-1) | Pb content(mg·kg-1) | |||
| F1-Pb | F2-Pb | F3-Pb | Total | ||
| Leaves | 0 | 5.38±1.41b | 4.42±1.39b | 3.39±1.43b | 17.55±7.17c |
| 100 | 44.77±7.27a | 6.07±0.12b | 4.43±1.41b | 248.22±29.59b | |
| 300 | 42.28±13.58a | 13.02±1.26a | 15.01±4.65a | 614.32±64.68a | |
| Roots | 0 | 3.62±0.98b | 3.09±0.25b | 1.53±0.56b | 22.23±1.22c |
| 100 | 67.52±13.98a | 5.78±1.55a | 2.15±0.91b | 337.86±95.59b | |
| 300 | 66.10±24.80a | 5.41±1.06a | 21.42±0.58a | 600.09±33.09a | |
| Parts | Pb treatment concentration (mg·kg-1) | Auxin | Gibberellin | Abscisic acid | Cytokinin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leaves | 0 | 82.25±38.74c | 2.04±0.43b | 3.86±0.34b | 183.31±14.38b |
| 100 | 563.68±96.60a | 3.40±0.74a | 5.59±1.18a | 340.72±63.48a | |
| 300 | 331.08±13.10b | 4.04±0.52a | 3.34±0.82b | 347.16±61.24a | |
| Roots | 0 | 237.42±17.78b | 2.31±0.62b | 3.12±0.35b | 238.79±32.83b |
| 100 | 655.73±278.92a | 3.27±0.45b | 6.14±2.36a | 366.17±21.51a | |
| 300 | 413.70±46.53a | 3.77±0.83a | 3.42±0.56b | 421.63±33.02a |
| Treatments | Leaves (mg·kg-1) |
Apoplast sap(mg·kg-1) | Symplast sap(mg·kg-1) | Xylem sap(µg·L-1) | Phloem sap(mg·L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | 30.36±1.64b | 0.11±0.01a | 0.19±0.06b | 6.94±2.10a | 0.21±0.04a |
| Pb+IAA | 39.41±1.20a | 0.10±0.01a | 4.64±0.21a | 7.29±1.99a | 0.16±0.03a |
| Parts | Treatments | CAX(U·mL-1) | HMA(ng·mL-1) | ABC(U·mL-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leaves | Pb | 888.02±24.14a | 501.75±0.48a | 1797.23±53.13a |
| Pb+IAA | 764.87±16.85b | 464.04±18.57b | 1756.26±79.18a | |
| Roots | Pb | 862.05±97.89b | 478.36±7.58b | 1846.90±26.66a |
| Pb+IAA | 961.31±23.13a | 521.45±8.90a | 1420.23±104.61b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




