1. Introduction
The rising popularity of electric vehicles (EVs) has compelled automotive manufacturers to seek traction motors that offer remarkable torque capabilities, high power density, and a broad operational speed range. Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (IPMSMs) are among the most appealing choices as they align with these crucial traction motor requirements [
1,
2]. A higher rotor speed enables improving the power density of the motor [
3]. However, a higher motor speed can also have a damaging effect on the IPMSM rotor because the centrifugal load is quadratically proportional to speed. An IPMSM usually requires a thinner rotor bridge to improve torque performance, but it leads to an increase in stress at the rotor bridges [
4]. The rotor is also affected by electromagnetic, thermal, and other mechanical loads. Hence, evaluating the rotor for all loads is critical to ensure its structural integrity.
Furthermore, the rotor goes through fluctuating temperatures and speeds through drive cycles. The fluctuating temperature leads to changes in the electrical, electromagnetic, and mechanical properties of the materials of an IPMSM. Fluctuating speeds lead to a change in the mean and amplitude load, which should also be accounted to ensure the structural integrity of the rotor. Hence, it is critical to calculate the fatigue life of the rotor, taking into account the fluctuating speed and temperature.
The thermal management of an IPMSM motor is critical as it has an adverse effect on motor performance. As the temperature increases, the flux density of rare earth magnets decreases reversibly and, beyond a specific temperature, it may be demagnetized irreversibly [
5]. Moreover, higher temperature leads to higher copper losses and may reduce the life expectancy of coils [
6,
7]. So, ensuring a proper cooling mechanism for the IPMSM motor is critical to its performance. Electromagnetic-thermal coupled analysis coupled analysis has been used to design the motors earlier [
8,
9]. Lumped Parameter Thermal Network approach (LPTN) has been used to evaluate the thermal performance of a motor for a drive cycle because it is computationally economical.
Rotor stress due to electromagnetic, thermal, and centrifugal load calculated through finite element simulations has been compared in a few publications in the literature. Rotor stress due to thermal load and centrifugal load was much higher than stress due to electromagnetic load in [
10], whereas rotor stress due to centrifugal load was significantly higher than stress due to thermal and electromagnetic load in [
11]. Rotor fatigue has been carried out for a drive cycle considering only centrifugal load in [
12,
13]. Rotor stress considering thermal, and centrifugal load was studied for a drive cycle, and fatigue analysis was carried out using analytical calculation in [
14]. Fatigue analysis for drive cycles requires stress results for all time steps, which could be computationally expensive. An equivalent damage approach has been used to create block cycles instead of drive cycles in [
11,
15,
16]. The peak-valley extraction method has been discussed to remove the non-damaging cycles from a drive cycle in [
17].
A strain-life (E-N) approach is preferred over a stress-life (S-N) approach if the stress exceeds yield strength. The rotor laminations are made of thin electrical steel sheets, and it is usually challenging to extract their E-N fatigue material properties. In [
14] and [
18], S-N properties have been extracted for a positive stress ratio and used for fatigue life estimation. The stress-ratio here refers to the ratio of the maximum and minimum load used for fatigue testing of specimens to extract fatigue material properties. Fatigue life is affected by multiple factors, such as surface roughness, mean stress effect, and fatigue life scatter in [
19,
20,
21,
22]. The effect of surface roughness on the fatigue life of electrical steel has been studied in [
18,
23]. Surface roughness due to various cutting methods of electrical steel was discussed in [
24].
This paper proposes a thermo-mechanical fatigue workflow for an IPMSM rotor. The rotor stress due to electromagnetic, thermal, and mechanical loads is presented. A drive cycle is defined for the rotor fatigue analysis. Thermal analysis of the motor is carried out, the cooling parameters are determined to meet the magnet and coil maximum temperature limit, and the rotor temperature profile for the drive cycle is calculated. Peak-valley approach is utilized to compress the drive cycle and eliminate the non-damaging cycles. The fatigue life is then calculated using the compressed drive cycle and the rotor temperature profile.
2. Rotor Stress due to Electromagnetic, Thermal, and Mechanical loads
In an IPMSM, electromagnetic forces are generated as a result of electromechanical energy conversion. Since the rotor laminations are made of electrical steel, these forces lead to stress on the rotor lamination. The electromagnetic forces have a tangential component leading to torque and radial components, leading mainly to stator vibrations. Furthermore, operational conditions induce copper, core, and mechanical losses, which cause the rotor temperature to rise. This rise in temperature, in turn, causes thermal expansion, subjecting the rotor to thermal loading. Also, the IPMSM rotor undergoes centrifugal load because of its rotation. Stress-induced due to centrifugal load is quadratically proportional to speed. Notably, an interference fit between the shaft and the rotor also contributes to rotor stress.
2.1. Loads and Boundary Conditions
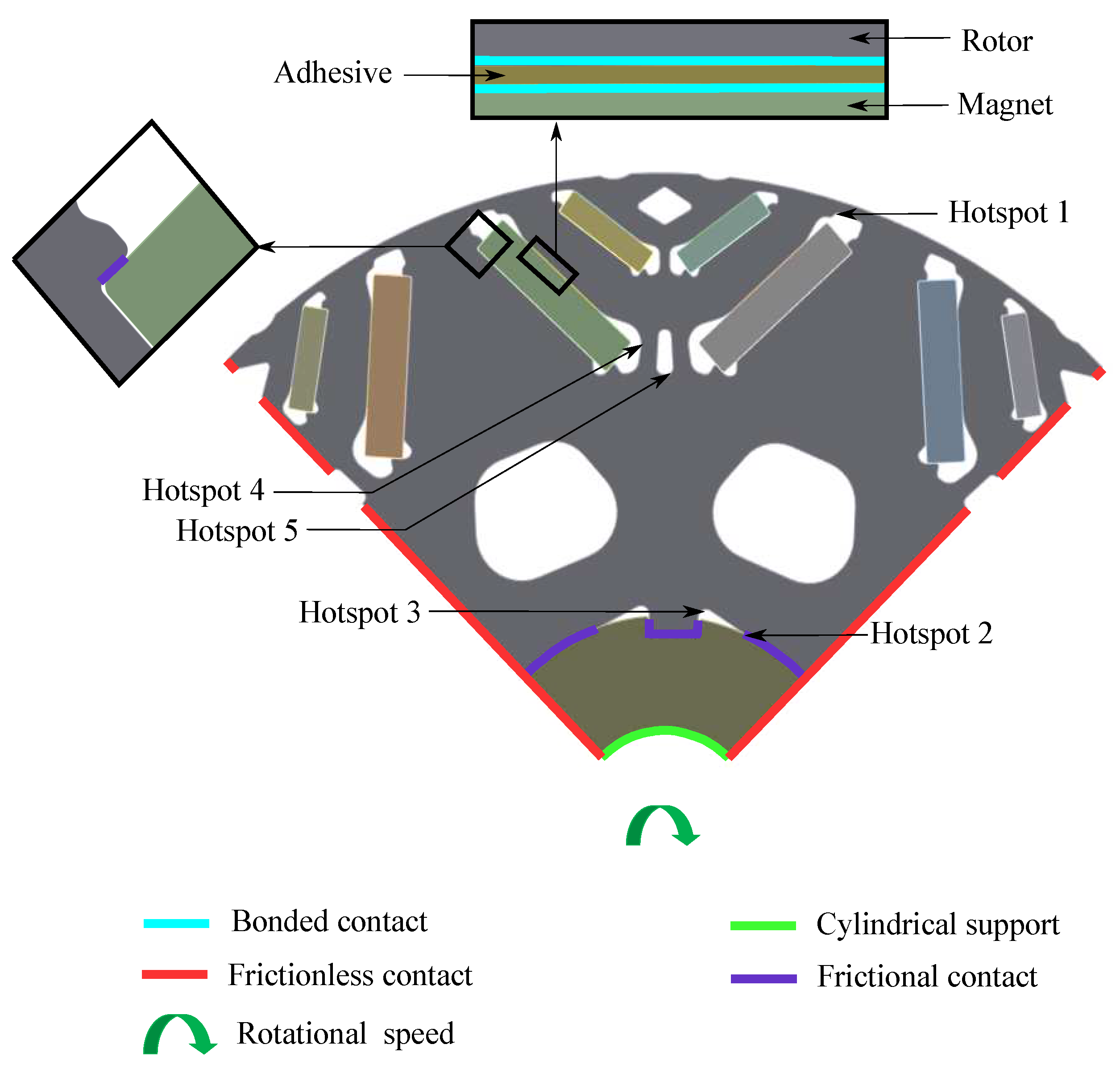
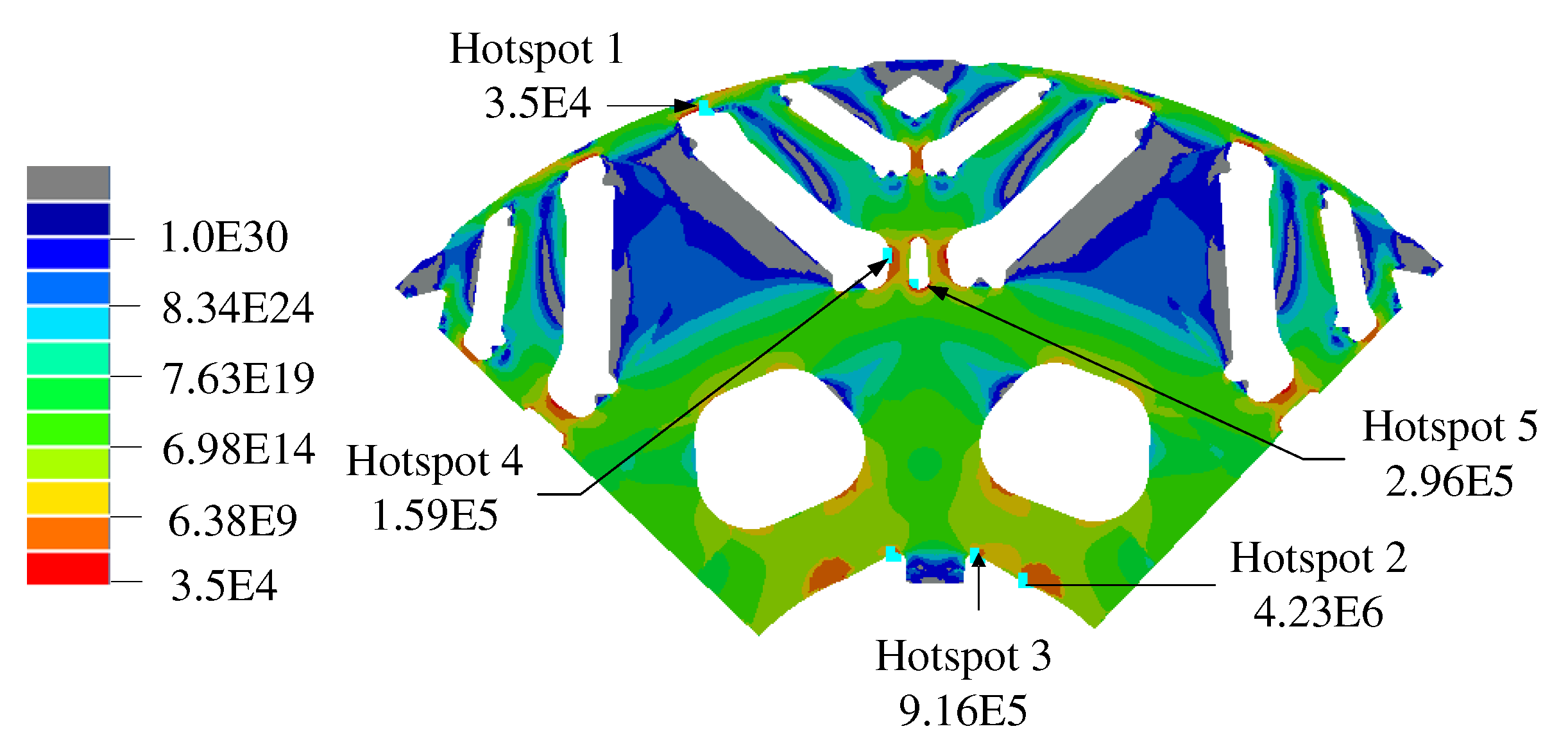
A finite element analysis is carried out on an 8-pole IPMSM rotor to analyze the rotor stress due to electromagnetic, thermal, and mechanical load. A rotor lamination quarter-symmetric model is considered for the rotor stress calculation because the rotor has four keys, as shown in
Figure 1. It also shows the loads and boundary conditions for the rotor stress analysis. During the rotor assembly, adhesive is applied at the bottom and the upper edge of the magnet. However, during real-world application, the lower adhesive layer deteriorates over time, so it has not been considered for simulation. The adhesive is modeled between the rotor and the magnet’s upper surface using bonded contact to introduce realistic stiffness to the joint. Frictional contact is defined between the rotor and outer edges of magnets to avoid singularity errors during simulation. Frictional contact is applied between the shaft and the rotor. Frictional-less contact is defined on the symmetric boundary edges of the rotor and shaft and on one face of the rotor assembly, considering it is the endmost lamination of the rotor stack. Cylindrical support is considered on the inner diameter of the shaft with a free radial degree of freedom.
Electromagnetic forces are calculated in Ansys Maxwell for the peak torque condition and applied to the rotor as body force density in Ansys Mechanical. Centrifugal load is applied considering the maximum rotational speed about the central axis of the rotor assembly. The rotor assembly temperature is considered 150 °C to apply the thermal load. The interference between the shaft and rotor is considered 30 micrometers to observe the impact of interference fit.
20SW1200 electric steel is considered for rotor lamination [
25], G48UH for magnets [
26], hot rolled steel for shaft, and an epoxy-based adhesive [
27] for the rotor stress analysis. A global mesh size of 0.4 mm is considered, and hotspots are refined to 0.09 mm to achieve stress convergence. Linear mechanical properties are used for the analysis, and pseudo stresses are used for comparison.
2.2. Stress Analysis Results
2.2.1. Individual load cases
First, the loads acting on the rotor are applied in isolation on the rotor to understand their impact on the rotor stress.
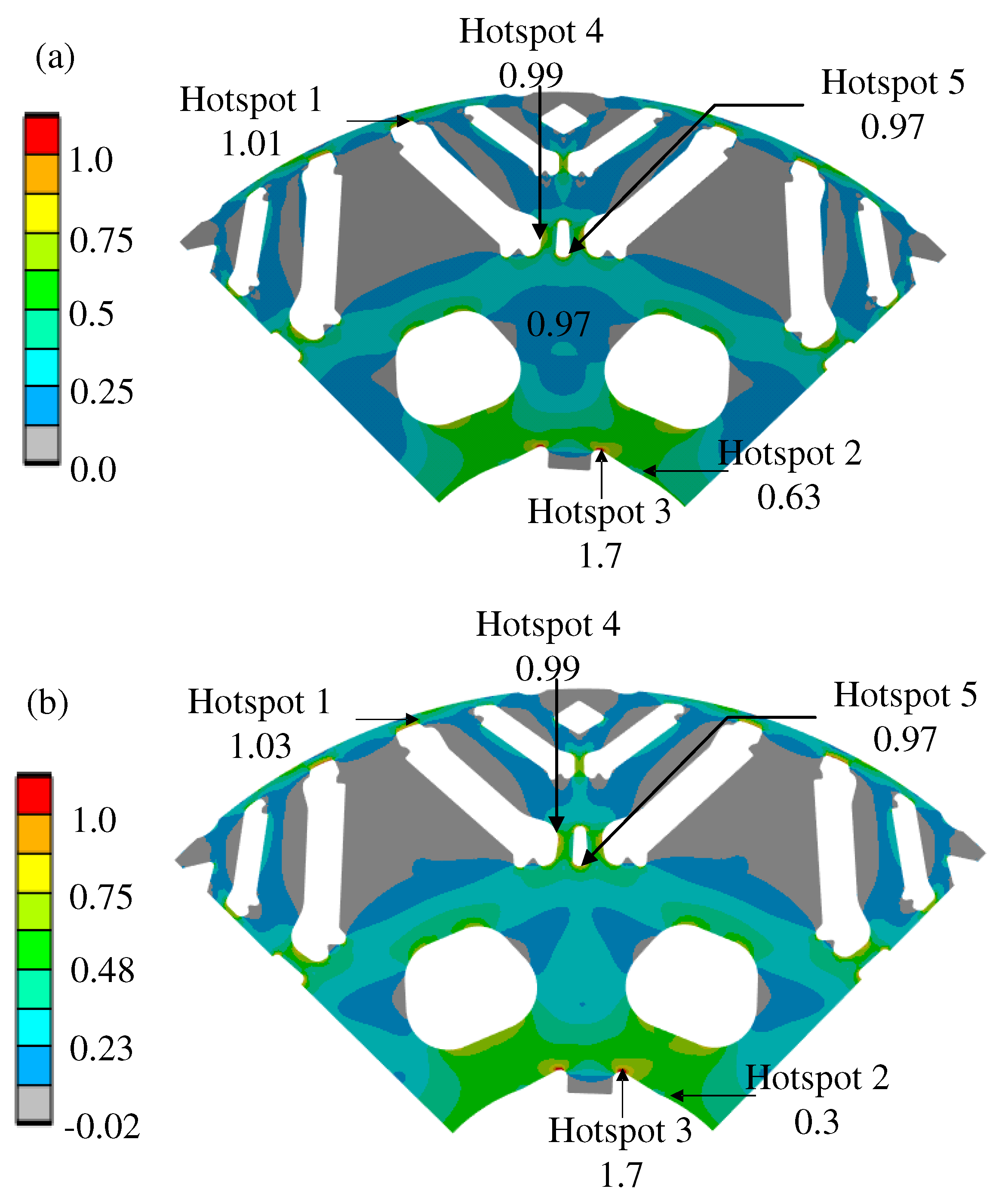
Figure 1 shows the hotspots for various loads. A hotspot refers to a critical location with high stress for the specific load case.
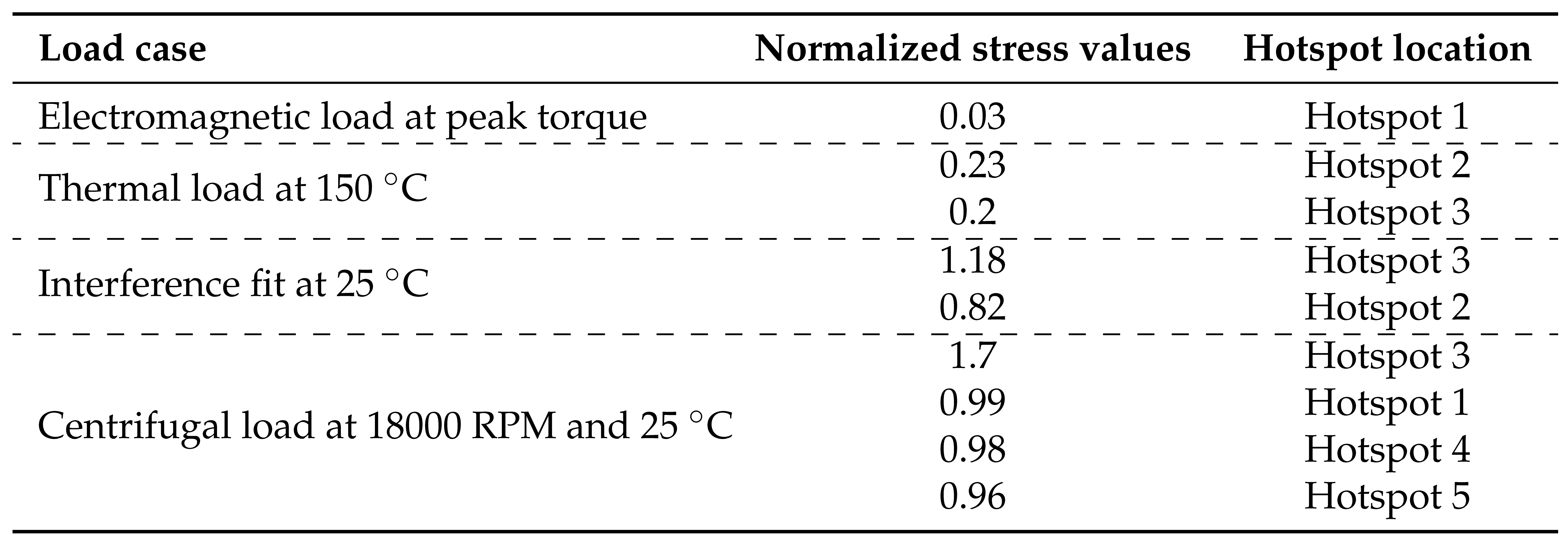
Table 1 shows the stress due to various loads, which are normalized with respect to the yield strength of the electrical steel at room temperature. A stress value above one means the stress is above the yield strength of the material.
Electromagnetic load induces low-stress levels around the air flux barriers situated near the outer diameter of the rotor. Thermal load leads to stress around 20-25 % of yield strength, with the highest stress occurring in close proximity to the interface between the rotor and shaft. If adhesives are considered on the upper and lower edges of the magnet, as in the case of a new motor, high-stress levels could also be observed around the bridges, potentially increasing with a higher adhesive modulus of elasticity. The current simulation model, which is based on a single lamination, does not account for thermal stress due to axial constraints that could be introduced by the stacking method used, such as bolting, welding, or interlocking. The interference fit between the rotor and shaft also leads to high-stress levels close to the rotor and shaft interface. Stress induced due to thermal load and interference fit may significantly elevate the mean stress within the rotor, potentially leading to decreased fatigue life, particularly at hotspots near the rotor and shaft interface.
Under centrifugal load at maximum rotor speed, multiple stress hotspots emerge at air flux barriers and in close proximity to the rotor and shaft interface. Notably, these regions show stress levels that approach or surpass the yield strength of the material.
2.2.2. Combined load cases
Next, a stress analysis is carried out considering the rotor speed of 18000 RPM, a 30-micron interference fit between the rotor and shaft, and the rotor, shaft, and magnet temperature at 150 °C.
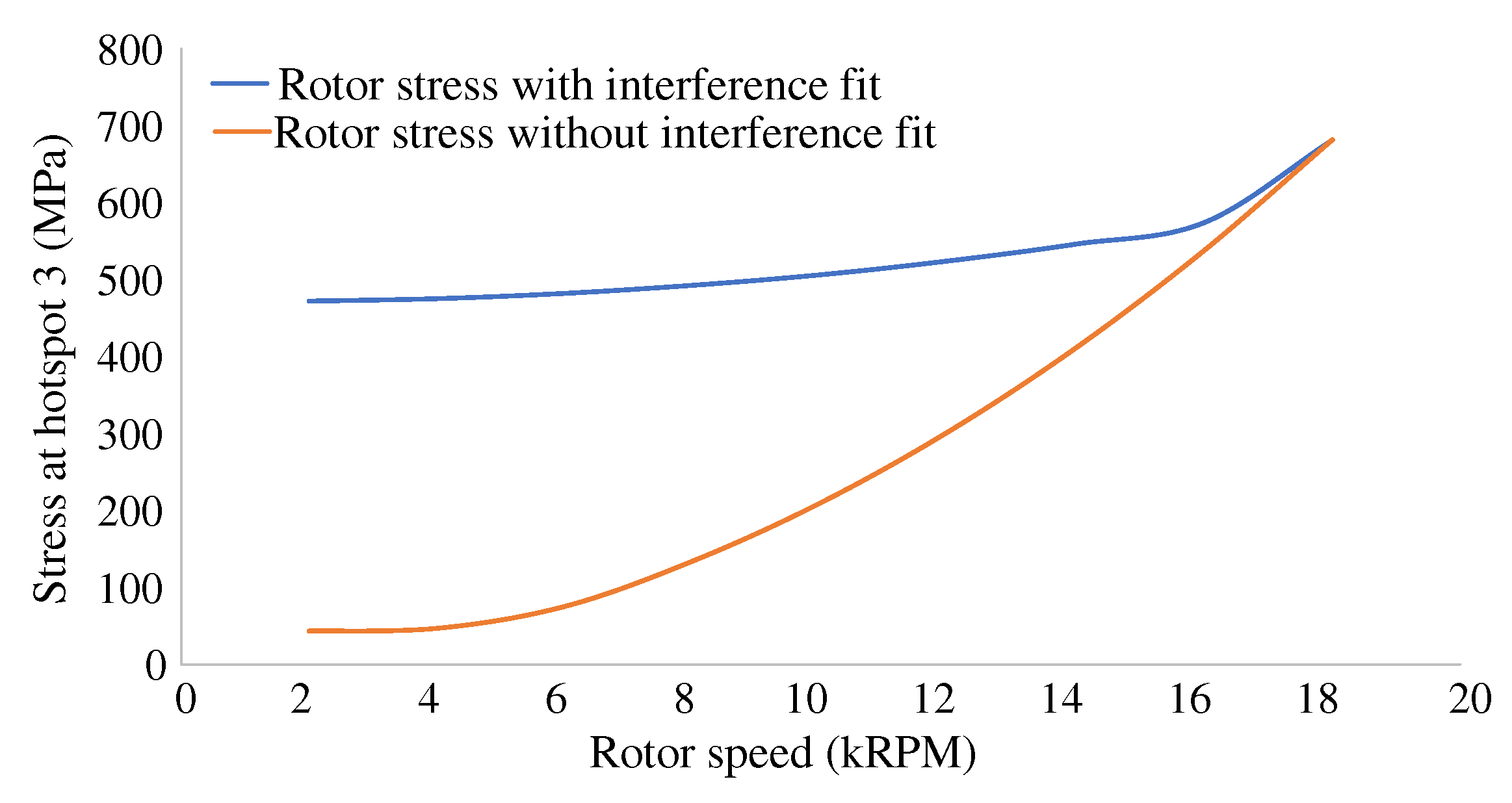
The Von-misses stress levels at hotspot 3 due to thermal and centrifugal loads, considering scenarios with and without an interference fit are compared in
Figure 2. When the interference fit is taken into account, the stress at hotspot 3 maintains a relatively constant value for the majority of the speed range. It is only after reaching a speed of 16000 RPM then the centrifugal load begins to exert greater influence, surpassing the effects of the interference fit. This observation implies that hotspot 3 has high mean stress during a drive cycle as compared to hotspots 1, 4, and 5.
In
Figure 3, Von-misses and Maximum Principal stress normalized to yield strength are compared for all hotspots. Von-misses stress, which is based on maximum distortion energy theory, is observed for ductile materials such as electrical steels because it ensures no permanent deformation if the induced stress is below the yield strength.
Induced stress on a component can also be classified as tension or compressive. Tensile stress is due to the pulling nature of the load, whereas compressive stress is due to the compressive behavior of the load. Experiments suggest that compressive mean stress is favorable and tensile mean stress is unfavorable to fatigue life [
21]. Therefore, it is a good practice to check the Maximum Principal stress because there can be hotspots with high Von-misses stress and compressive behavior, which may lead to a superior fatigue life as compared to high Von-misses stress and tensile behavior.
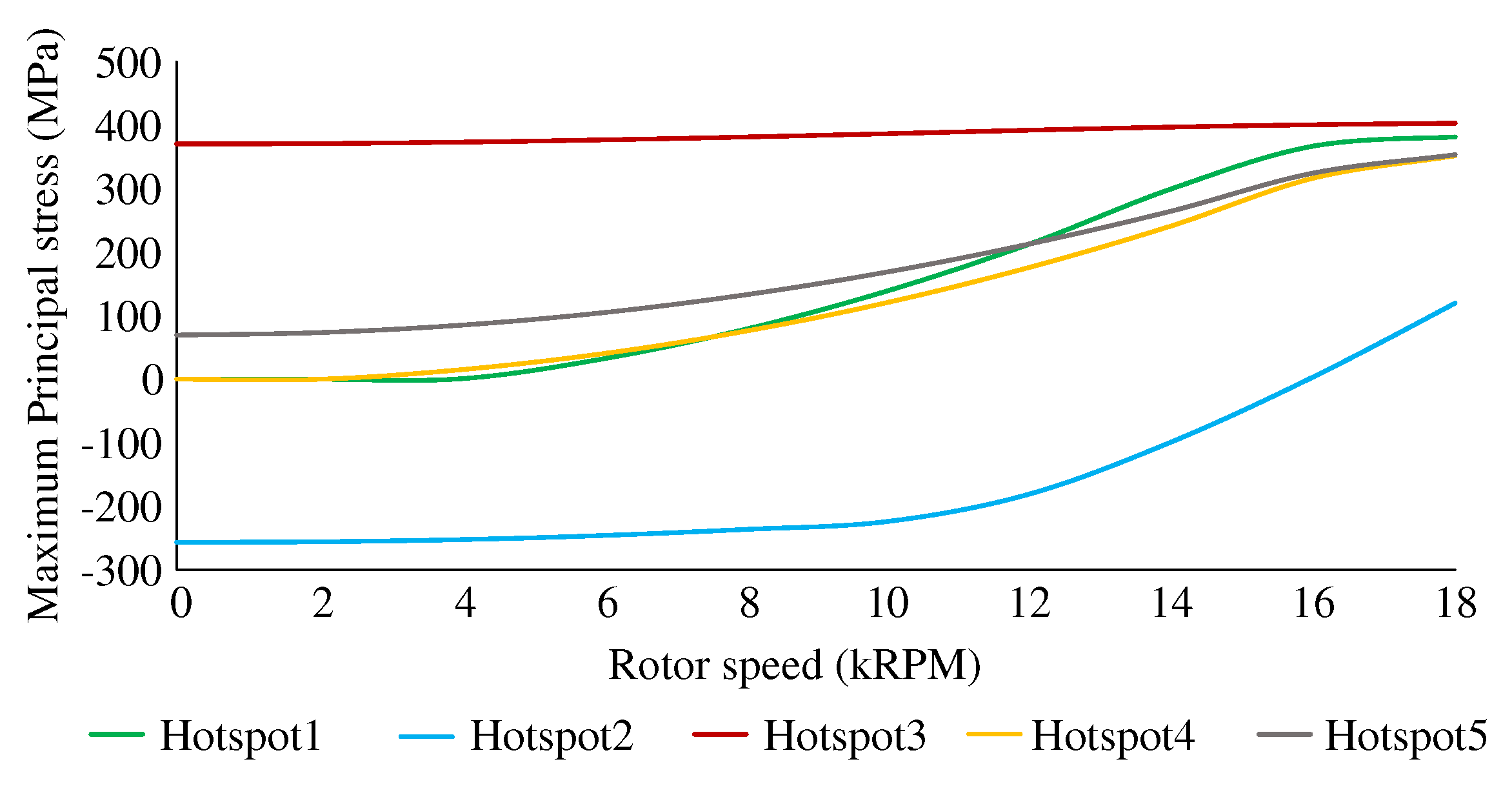
As shown in
Figure 3(a) and
Figure 3(b), all hotspots have high Von-misses stress, and all of them are under tensile conditions at the maximum speed of the rotor. The Maximum Principal stress is positive when the stress has a tensile behavior. As shown in
Figure 4, the initial temperature and interference fit has negligible impact on hotspots 1 and 4, a minor tensile effect on hotspot 5, a significant tensile effect on hotspot 3, and a significant compressive effect on hotspot 2. As the centrifugal force increases with speed, the centrifugal load overpowers stress due to interference fit at hotspot 2, leading to tensile Maximum Principal stress at higher speeds, as shown in
Figure 4.
3. Drive Cycle Design for Thermo-mechanical Fatigue Analysis of a Rotor
The drive cycle holds significant importance for the design and development of any motor as it defines a crucial target for motor operating points. These drive cycles are typically derived from real-world usage patterns. In the context of this paper, a daily transient velocity drive cycle is created using generic drive cycles to replicate the real-world usage pattern and assess the rotor fatigue life [
28].
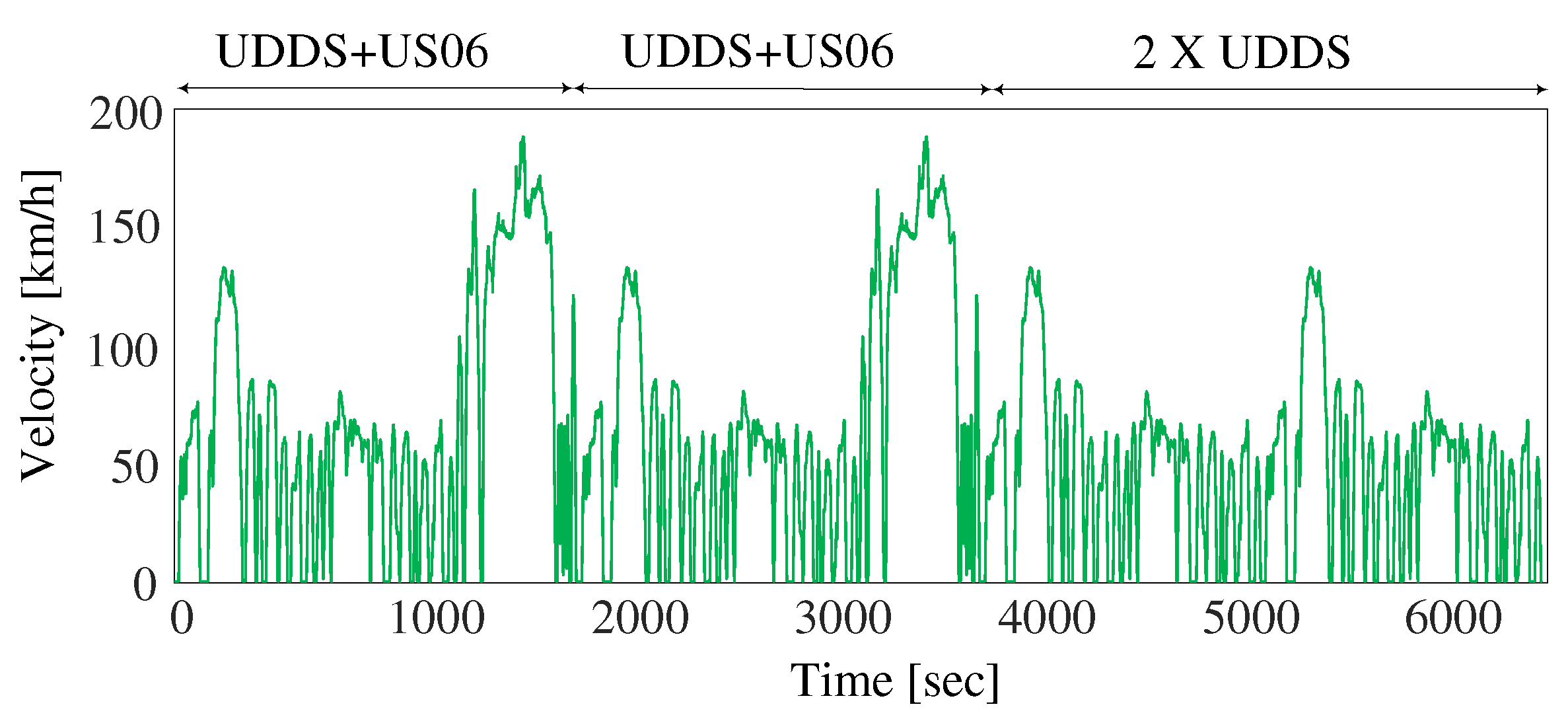
It is assumed that that vehicle is driven for a round-trip commute to the workplace, followed by an evening excursion. The round-trip office commute is represented through a combined sequence of the Urban Dynamometer Driving Schedule (UDDS) and the US06 Emission Test Cycle. Similarly, the evening excursion is represented by a UDDS cycle. The drive cycle is scaled by 50 percent to make it more demanding for durability requirements.
Generic drive cycles are constructed based on vehicle velocity to evaluate overall vehicle performance. So, the daily transient velocity drive cycle shown in
Figure 5 is converted to the daily motor speed profile using the vehicle wheel diameter and the gear reduction ratio between the electric motor and the wheels. The daily transient velocity drive cycle is then used to conduct the thermal analysis of the motor, and the daily motor speed profile is used to carry out thermo-mechanical fatigue analysis of the rotor.
4. Motor Thermal Management and Temperature Profile Estimation for a Drive Cycle
Maintaining the magnet and coil temperatures below critical thresholds through an effective cooling mechanism holds a pivotal role in optimizing motor performance. In addition, driving dynamics change continuously and rapidly for a drive cycle, which impacts thermal performance significantly. In turn, this leads to fluctuation in rotor assembly temperature throughout the drive cycle. The rotor assembly temperature fluctuation leads to variations in mechanical and fatigue properties. Therefore, it is critical to evaluate the rotor assembly temperature for the drive cycle. Ansys Motor-CAD is opted at this stage to calculate the rotor temperature profile for a given drive cycle.
First, the Electromagnetic (EM) analysis is carried out to calculate the motor loss, and a loss model is built for the entire speed range. Then, a hybrid cooling system is modeled for the thermal management of the motor, which consists of a cooling water jacket, oil spray on end windings, and oil flow through the shaft.
The initial motor temperature, the inlet water temperature, and the inlet oil temperature are considered based on normal operating conditions. The average electric motor temperature is expected to be around 100 C under normal operating conditions. Typically, a vehicle-level cooling system for an electric drive train may consist of an electric motor heat exchanger, which supplies coolant at around 65-67 C. Therefore, the inlet water temperature is considered 70 C, assuming a 3-5 C rise until the coolant reaches the inlet of the motor water jacket. For a hybrid cooling system, the coolant passes through the water jacket to an oil cooler, leading to the oil cooler temperature around 75-77 C. Assuming a rise of 3-5 C of the oil until it reaches the oil spray and shaft inlet, 80 C is considered for oil inlet temperature.
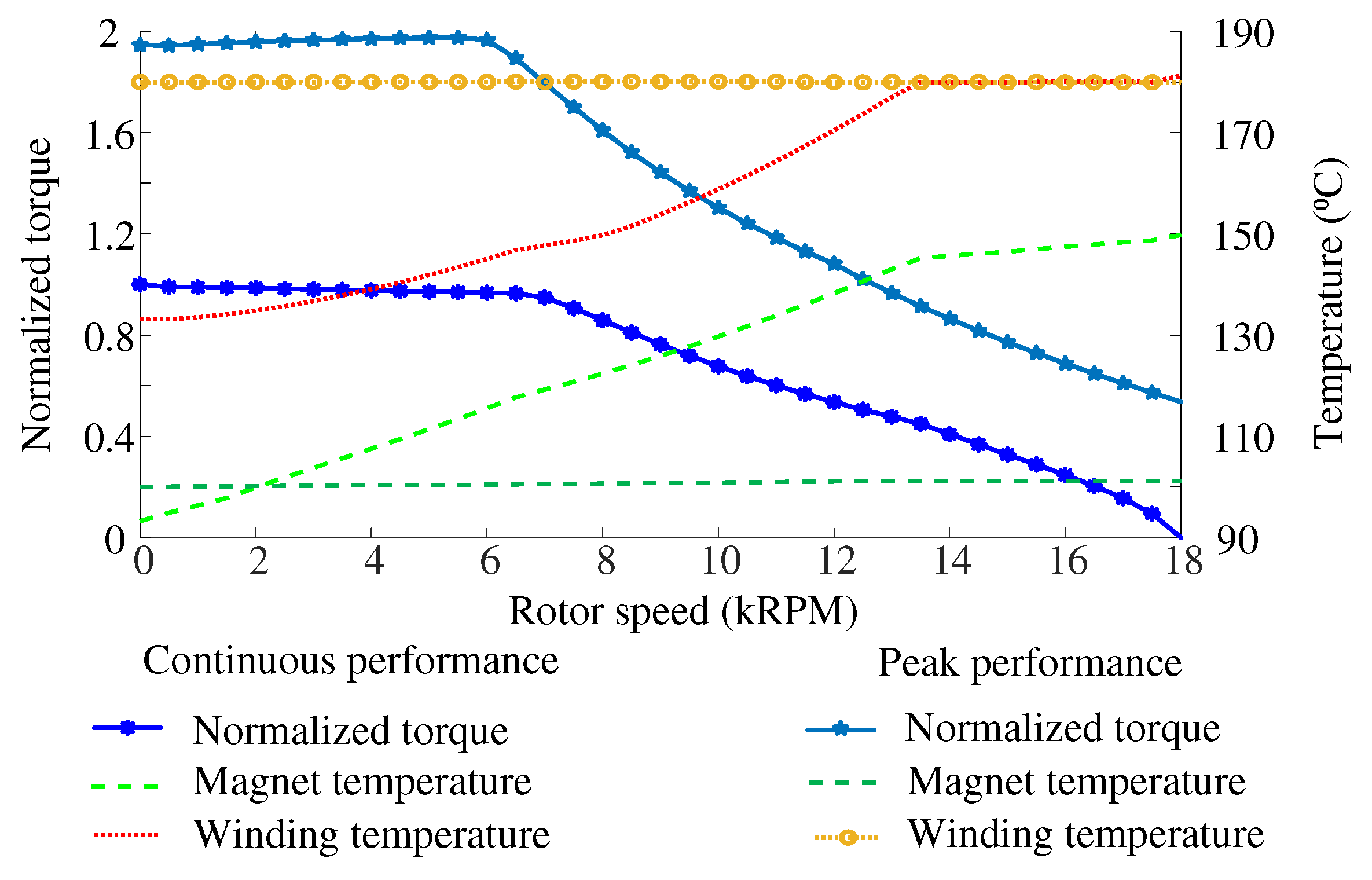
Simulations are conducted for the entire speed range for 30 seconds of peak power operation to ensure that the heat capacity of the motor is sufficient, and for steady-state conditions to ensure that the heat dissipation capacity is sufficient for continuous operation. The volume flow rate of the coolant is 12 LPM for the water jacket, and 3 LPM for oil spray, and 3 LPM for oil flow through the shaft to maintain the magnet and coil temperature below 150
C and 180
C [
29], respectively. The per unit torque, magnet, and coil temperature for continuous and peak performance and the entire speed range after the tuning of the cooling model are shown in
Figure 6.
The magnet and winding temperature during operation depend on their losses, heat flux from adjacent components, and initial temperature conditions. During a 30-second peak power operation, there’s insufficient time for heat to transfer between components. As a result, the magnet temperature remains closer to its initial condition, mainly because magnet losses are negligible. In contrast, during steady-state continuous operation, the magnet temperature tends to be higher due to heat accumulation. The winding and core losses increase with speed, so the magnet temperature increases with an increase in speed.
The winding temperature during the 30-second peak power operation across various speeds is consistently at 180 C, primarily due to the high current applied to the conductors. This temperature serves as a limiting factor for peak power operation, and the current is optimized to keep the winding temperature within limits while delivering maximum power. In steady-state continuous operation, the lower current at lower speeds keeps the winding temperature lower. However, as speed increases, copper losses rise, causing the winding temperature to gradually approach the maximum allowable limit.
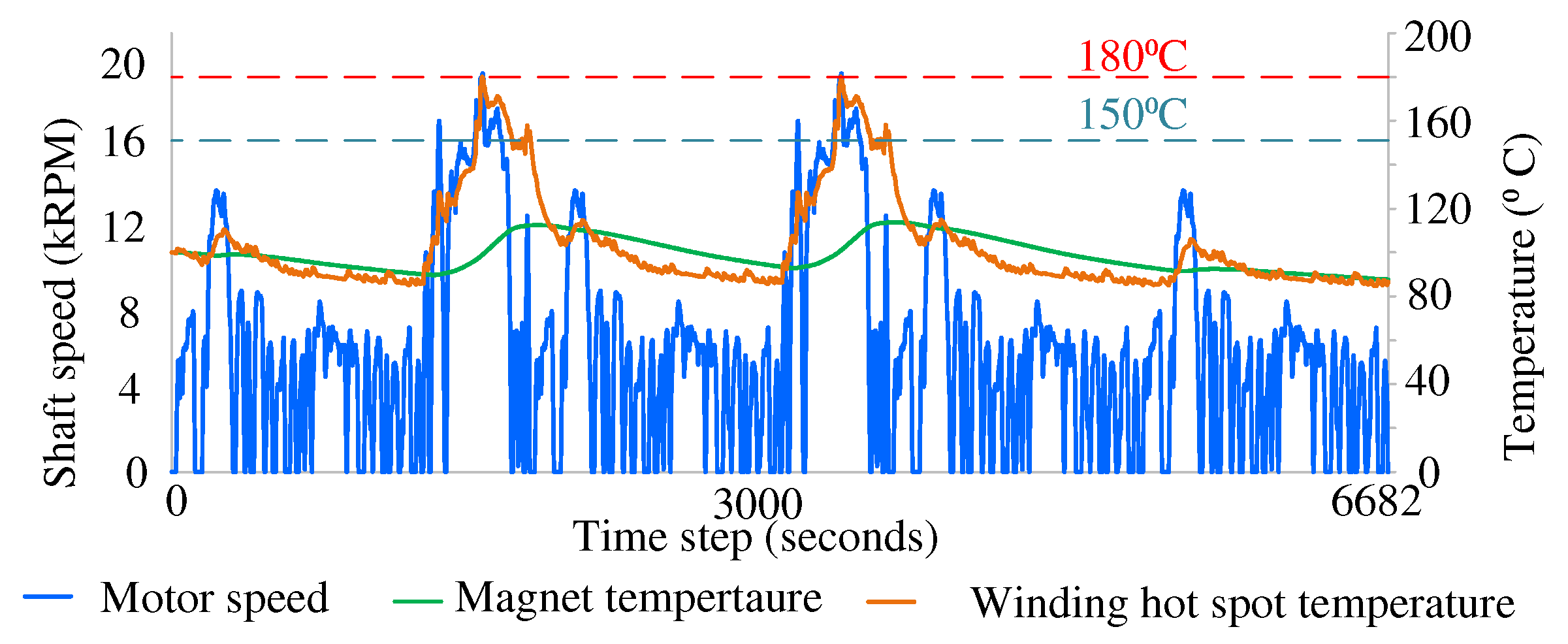
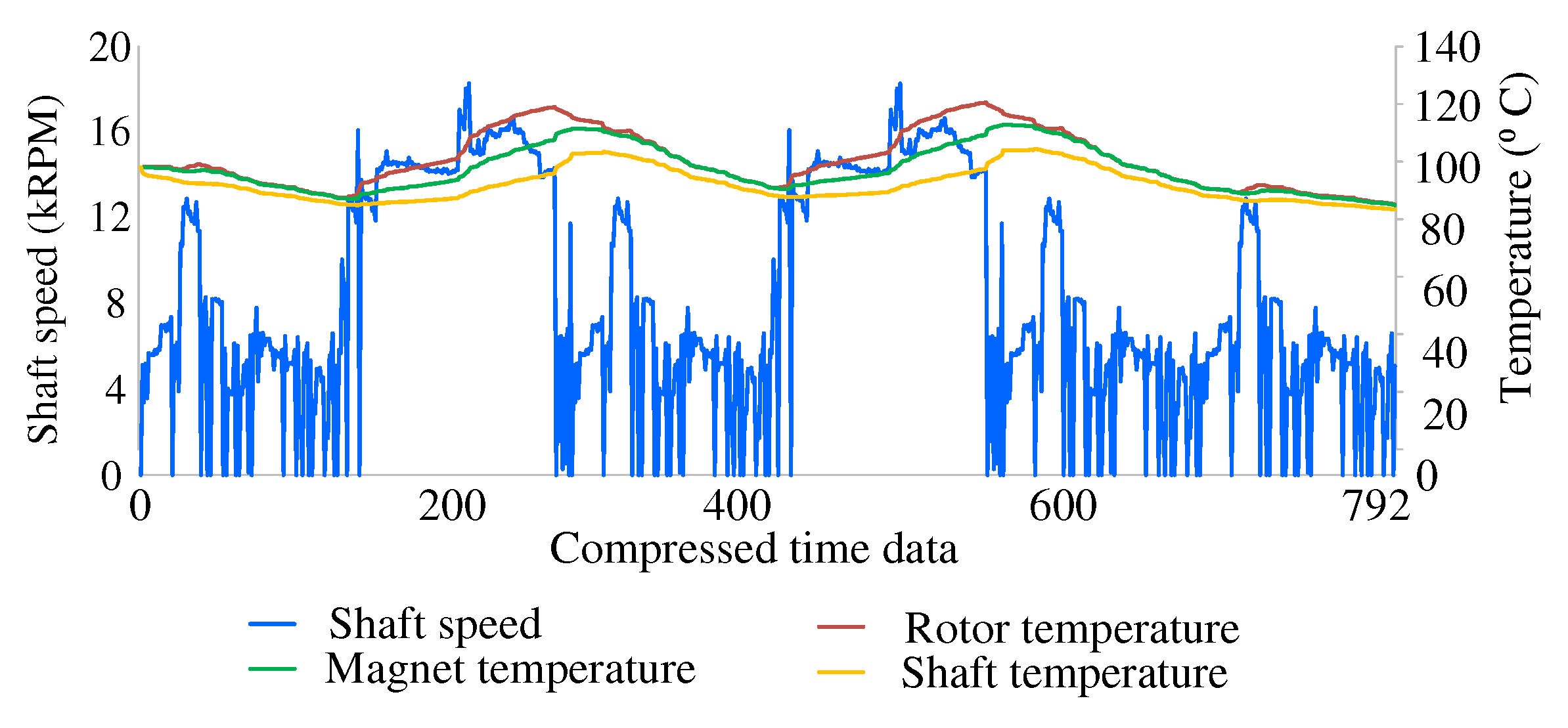
Figure 7 shows the rotor temperature profile for the daily drive cycle. The temperatures are calculated from the thermal model of the motor by applying the electromagnetic motor losses. In order to capture the worst-case scenario, the rotor temperature is calculated without any vehicle stops.
5. Accelerated Fatigue Life Approach
Estimating stress and fatigue for a drive cycle can be computationally expensive as it requires stress and fatigue life estimation at each time step. Deterministic events like drive cycles have defined loads for each time step. Accelerated fatigue life approaches such as load amplification, peak valley extraction, and block cycles can be used to accelerate fatigue life estimation for deterministic events [
17]. In this paper, the peak valley extraction method is applied to remove the non-damaging time steps from the drive cycle, which is then used to carry out rotor stress and fatigue analysis.
The stress values only at troughs and crests of the drive cycle are critical for the fatigue life estimation [
30,
31]. Therefore, the intermediate rotor speed values can be removed, and consequently, a compressed drive cycle can be used for rotor fatigue to reduce the simulation time. The Peak Valley approach conserves the load amplitude and sequence information but does not conserve the frequency information [
30]. Frequency information is critical if dynamic inertial loads induce stress. Dynamic inertial loads are caused by self-weight under resonance, and their intensity depends on frequency. In the case of rotor assembly, the natural frequency is much higher than the frequency of centrifugal force fluctuation acting on the rotor [
16]. The dynamic effects can be neglected if the excitation frequency is twice the system’s natural frequency [
32].
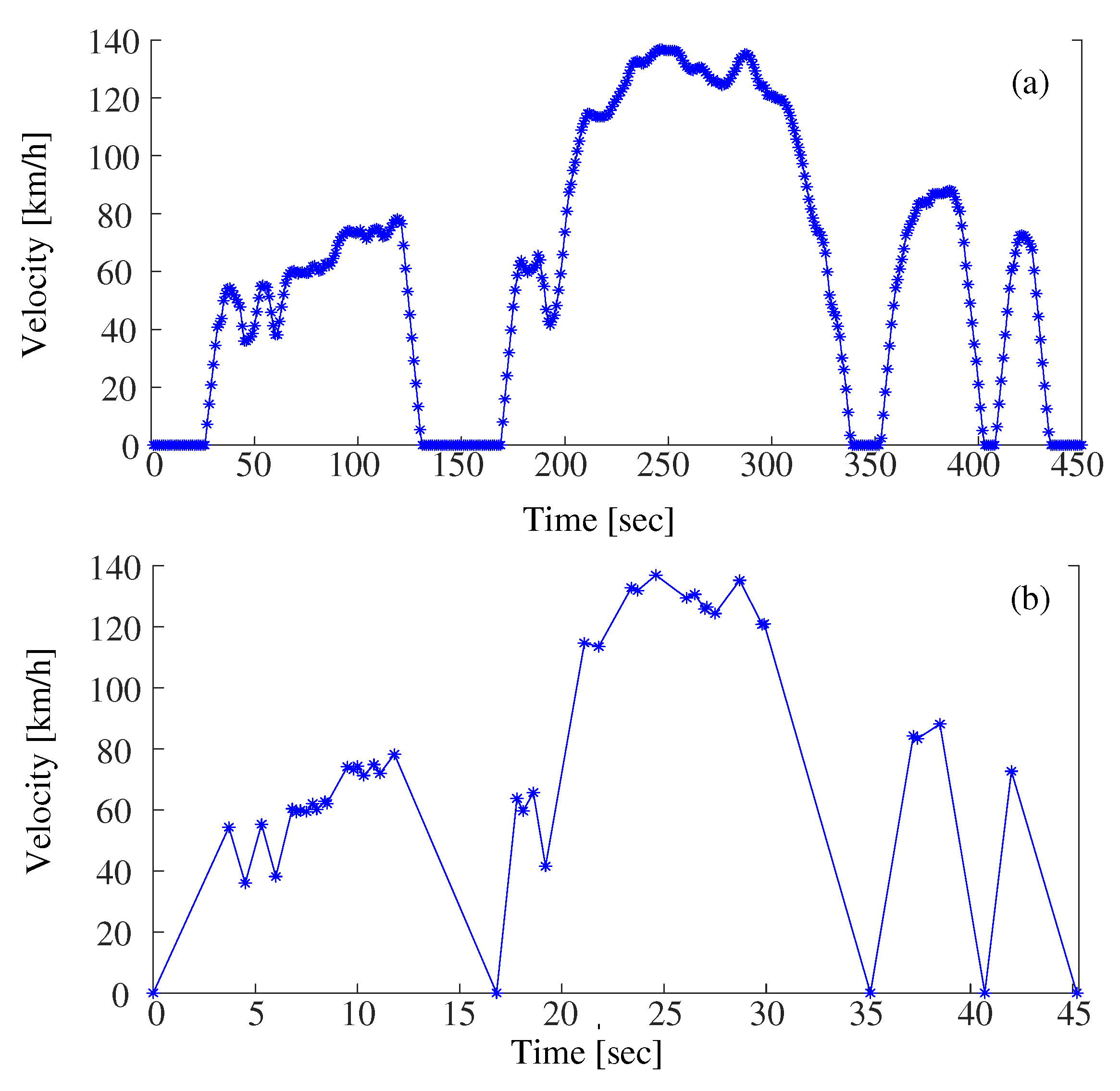
nCode GlyphWorks is used to remove the non-damaging time steps from the daily rotor speed profile. Three consecutive data points are checked to see if the middle data point is greater or not than the adjacent data point, and then the non-peak or non-valley point is discarded. The first 450 time steps data from the original daily rotor speed profile is compressed to 45 time steps data in the compressed drive cycle as shown in
Figure 8a,b. The full drive cycle data is compressed from 6682 time steps to 792 steps. The rotor temperature calculated earlier for the original drive cycles is also updated based on the compressed drive cycle.
6. Rotor Stress Analysis for a Drive Cycle
So far, we explored the effect of different loads on rotor laminations, developed the rotor temperature profile for the drive cycle, and compressed the drive cycle to reduce the simulation time. This section presents the calculations for the prediction of the stress the rotor experiences throughout the drive cycle. This is important to determine how long the rotor can last before developing a crack. In an electric motor, the rotor stress can be induced due to the combined thermal load, interference fit, and centrifugal load, which are all considered in this paper. The stress induced by the electromagnetic load is much smaller than the other loads and it is not considered for rotor stress analysis.
For the stress analysis, the boundary conditions presented in
Figure 1 are applied. The centrifugal load used in the stress analysis is based on the daily motor speed profile, and the rotor, magnet, and shaft temperature profiles are based on the daily velocity drive cycle shown in
Figure 9.
Material nonlinearity should be accounted for plastic deformations when the stress induced during a drive cycle is higher than the yield strength. Besides, finite element analysis with nonlinear material characteristics is preferred for structures with complicated boundary conditions, materials, and loading conditions [
33].
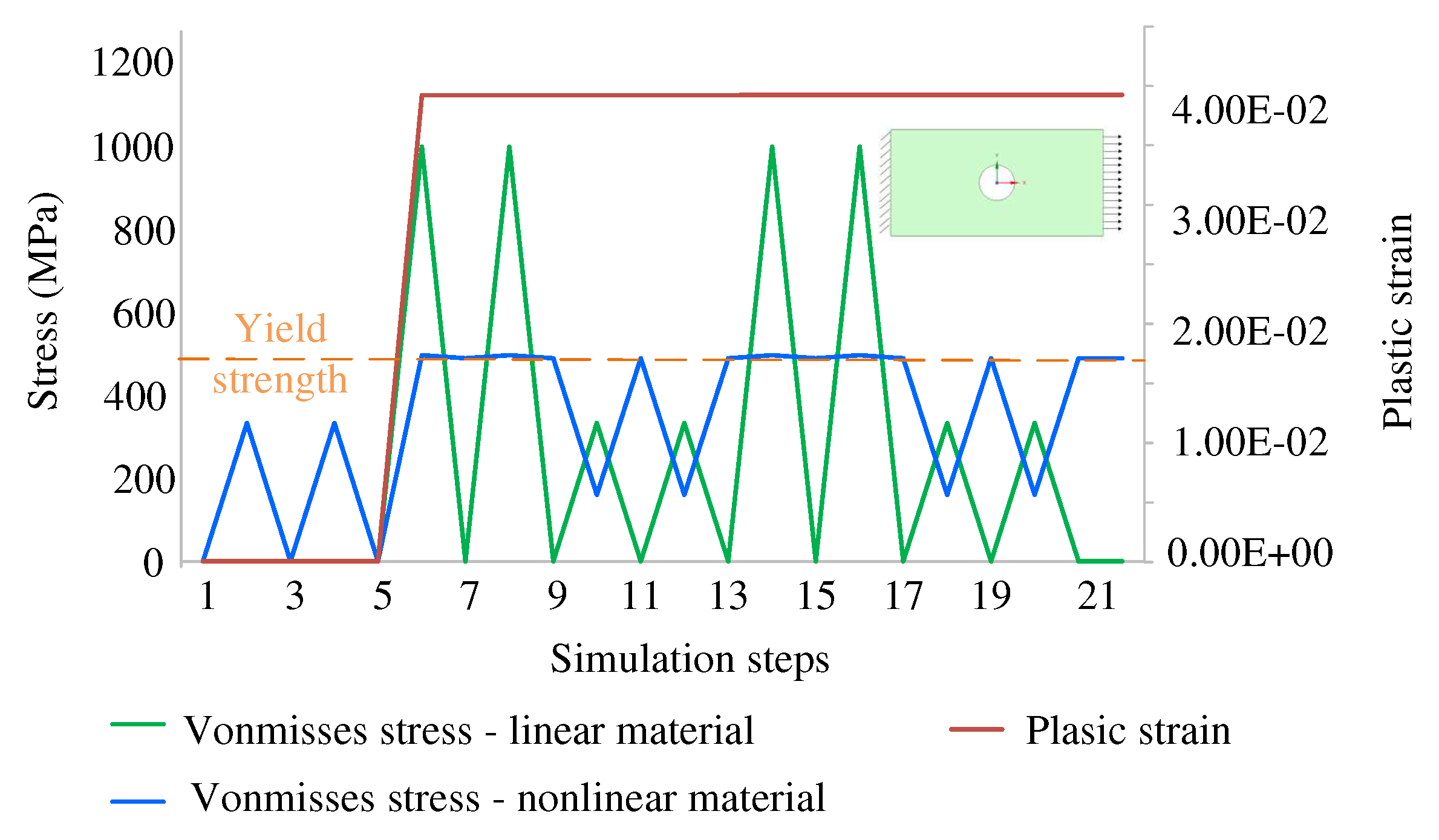
In order to comprehend the stress difference between a linear and nonlinear material, a simple geometry of a plate with a hole is investigated. The inset in
Figure 10 shows the geometry considered. This geometry was chosen for this investigation because it resembles the stress hot spots of a rotor air flux barrier with notches. A variable pulsating load is applied at one end, and the other end is fixed. As shown in
Figure 10, the stress induced with linear and nonlinear material properties match when the stress is below the yield strength. Variation above the yield strength is due to the difference in the characteristics of the linear and nonlinear materials [
16]. Plastic strain induced when the stress is higher than the yield strength is called a permanent set, and it remains permanent even when the stress after that reduces below the yield strength. Once the stress is beyond the yield strength of the material, the permanent set causes deviation in stress prediction even for the instances where the stress is below the yield strength.
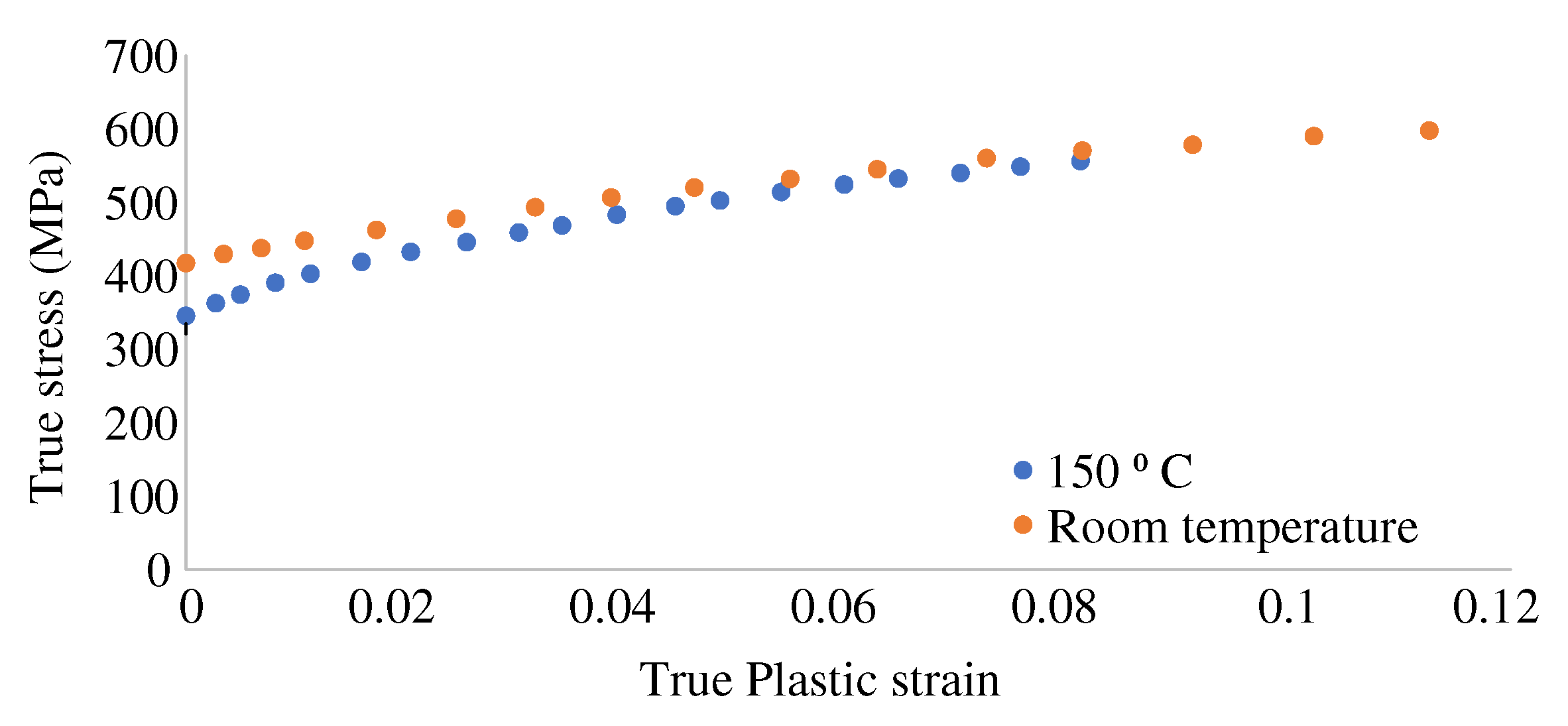
Ansys Mechanical is used for the stress analysis for the daily rotor speed profile. Mechanical properties are required at least for two temperatures to carry out the thermo-mechanical simulation. The 27PNX1350 electrical steel is selected for the analysis, whose mechanical properties, along with the nonlinear stress-strain curve, are available at room temperature and at 150
C [
14]. Since the object of investigation is rotor lamination failure, nonlinear material is used only for the electrical steel. The true stress-true plastic strain curve in
Figure 11 is used to model material nonlinearity as per the requirement of the finite element software. The adhesive modulus of elasticity is used from [
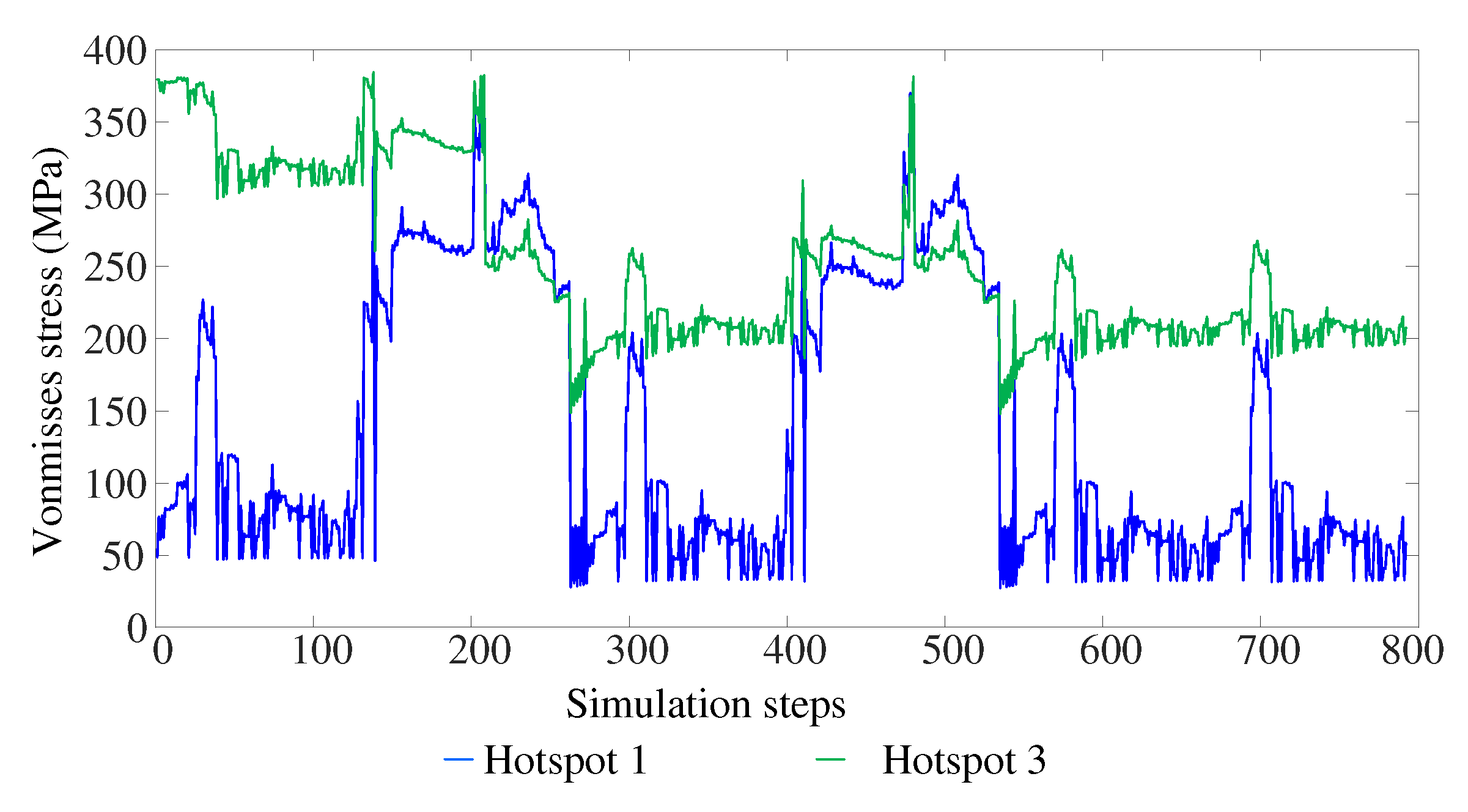
27]. The Von-misses rotor stress for the hotspots 1 and 3 in
Figure 1 is shown in
Figure 12. it is evident that the interference fit significantly impacts regions near the interface between the rotor and shaft. Consequently, the mean stress levels are considerably higher at hotspot 3 compared to hotspot 1 over the entire duration of the daily rotor speed profile. In contrast, the amplitude stress experienced at hotspot 1 is notably higher compared to hotspot 3.
7. Thermo-mechanical Fatigue Analysis
Once the rotor stress results are available for the daily rotor speed profile, fatigue analysis is carried out in nCode DesignLife. A temperature-dependent S-N curve for 27PNX1350 electrical steel is generated in nCode MaterialsManager. Stress amplitude intercept and slope 1 are used from the experimental data available in [
14], and endurance strength, stress at fatigue cut-off limit, and slope 2 are derived with empirical calculations [
33]. Temperature-dependent fatigue properties are used based on the rotor temperature profile to carry out the fatigue analysis at each timestep. This analysis shows how well the rotor holds up under real-world driving conditions.
7.1. Stress-life Curve Generation
In a high-cycle fatigue regime, the S-N (stress-life) curve for steel material is typically represented on a logarithmic scale, as illustrated in
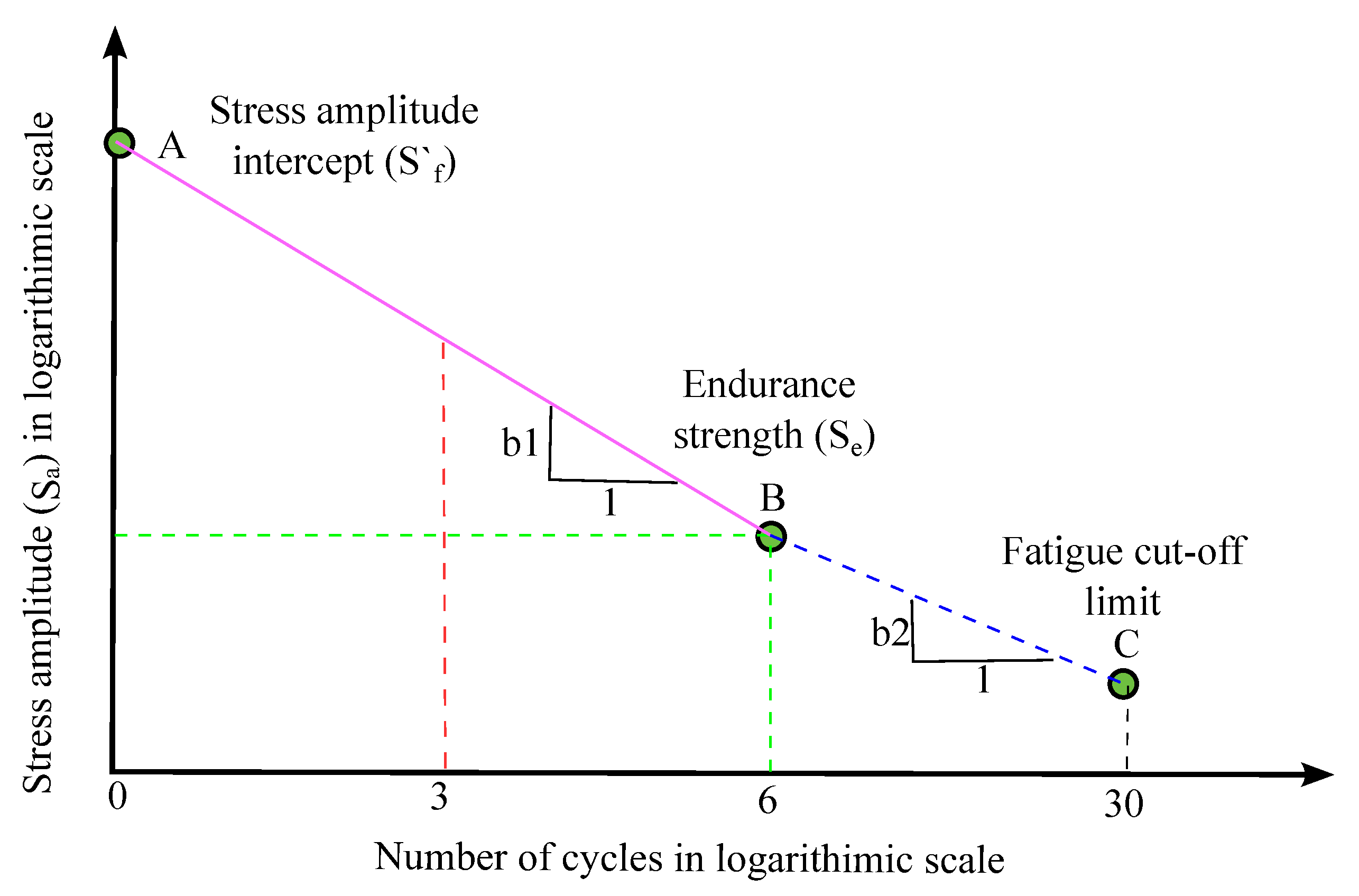
Figure 13, where the y-axis displays the stress amplitude and the x-axis shows the number of cycles till failure. High-cycle fatigue regimes are usually considered when the number of cycles exceeds
or when fatigue damage is due to little or no plastic deformation [
33]. For a constant amplitude loading, typically line AB in
Figure 13 is considered, where point A is the stress amplitude intercept and point B is called endurance strength. The line is considered horizontal after the endurance strength, which means infinite life if the induced amplitude stress is below endurance strength. The stress amplitude intercept is the stress that would lead to failure at 1 cycle, and b1 is the slope of the line AB.
In cases of variable amplitude loading, it is crucial to note that stress cycles below the endurance limit can still cause damage if some of the cycles under variable loading have stress levels above the endurance strength. To address this, the S-N curve is extended to point C, known as the cut-off point [
33]. The slope b2 is computed from the slope b1, as outlined in (
1).
The S-N curve can be expressed in equation form, as outlined in (
2),
Here, is the induced stress amplitude, is the stress amplitude intercept, b is the slope of line, and N is the cycles till failure for the induced stress amplitude.
We obtain slope
and the stress amplitude intercept from [35], which were experimentally derived using dumble-shaped specimens of thin electrical steel sheets. Subsequently, we calculate the endurance strength, the stress at the cutoff point, and the slope
using (
1) and (
2).
Table 2 consolidates the parameters used for generating the median S-N curve both at room temperature and at 150
C. The parameters applied in this analysis are based on median values derived from multiple samples of experimental data. It signifies that only fifty percent of the samples would meet the expected fatigue life under the drive cycle operation. This data forms the basis for our fatigue analysis, allowing us to assess material performance under varying load conditions of a drive cycle.
7.2. Fatigue Analysis Results
In the context of fatigue analysis, several crucial considerations extend beyond the assessment of drive cycle stress and material fatigue properties. In the high-cycles fatigue regime, mean stress has a significant effect on the fatigue behavior [
33]. The S-N curve generated for a stress ratio -1, takes into consideration the impact of stress amplitude fluctuations. To account for the influence of mean stress, the Goodman mean stress correction criteria is applied because it is considered to be the most conservative approach [
19]. Stress ratio is the ratio of maximum to minimum stress for a stress cycle. Surface roughness is another key factor that affects fatigue life. Rotor lamination can be manufactured by various manufacturing processes, such as laser cut or shear cut, which significantly influence the surface roughness of rotor lamination edges [
34,
35,
36]. The S-N curve employed in our analysis is derived from samples prepared using computer numerical control (CNC) techniques [
14], and it inherently incorporates the effects of surface roughness.
The fatigue life analysis for the rotor lamination, accounting for varying loads, a temperature-dependent S-N curve, and the Goodman mean stress correction factor, is shown in
Figure 14. The contour plot depicting fatigue life ranges from the minimum observed value up to the cutoff limit and beyond. Notably, the minimum fatigue life is observed at hotspot 1, amounting to 3.5E4 daily drive cycles, equivalent to approximately 95 years of operation. It is also observed that the fatigue life at hotspot 3 is lower than that at hotspots 1, 4, and 5. This implies that the combined effect of higher mean stress and lower amplitude stress may be less detrimental than the scenario with higher amplitude stress and lower mean stress concerning rotor fatigue under the defined drive cycle. Interestingly, hotspot 2 exhibits the highest fatigue life among all the hotspots, possibly attributed to the compressive nature of stress experienced in this region.
As previously discussed, the fatigue results presented in
Figure 14 are derived from fatigue properties based on the median value of experimental data. Estimating fatigue with it may lead to 50 percent of the samples failing under drive cycle operation. Moreover, the data is based on a limited number of samples, so confidence in the data is also low. For the design of critical components, the S-N curve should lie on the lower or safer side of the data. The curve is often modified based on the standard deviation to meet the 90% confidence and 95% reliability referred to as the R90C95 S-N curve [
37,
38]. In practical terms, this means that rotor designs based on the R90C95 S-N curve have a 90% probability that 95% of the samples will successfully complete the drive cycle operation without encountering fatigue failure.
Table 3 shows the fatigue parameters for the R90C95 S-N curve for 27PNX1350 electrical steel [
14], where the slope remains the same as the median S-N curve. The minimum fatigue life observed for rotor lamination at hotspot 3 is 1.93E4 daily drive cycles, which is approximately 44% lower than the fatigue life calculated using the median S-N curve.
8. Conclusions
This paper proposes a thermomechanical accelerated fatigue analysis approach for an IPMSM rotor. The rotor stress analysis modeling is discussed, along with the loads and boundary conditions. Then, various loads acting on the rotor are investigated. It is found that the stress induced due to thermal load, centrifugal load, and interference fit may be significantly higher than the electromagnetic stress. Then, a vehicle velocity drive cycle is created, and the thermal management of the motor is defined through simulations. It is ensured that the magnet and coil temperature is maintained below the critical temperature during continuous and peak operating conditions. Then, the peak valley extraction method is applied to remove the non-damaging cycle, which helps to reduce simulation time by approximately 90%. Then, the rotor stress analysis is carried out for the drive cycle, using a nonlinear simulation approach based on true stress-true plastic strain curve drive from a strength test of thin electrical steel. The rotor thermo-mechanical fatigue analysis is then carried out for the drive cycle using a median S-N curve and considering the mean stress effect. The minimum fatigue life observed on the rotor lamination is approximately 95 years of drive cycle operation. The rotor lamination fatigue life is also calculated for the R90C95 S-N curve, which shows a 44% reduction in fatigue life as compared to the median S-N curve.
Author Contributions
Ashish Kumar Sahu: Methodology, formal analysis, investigation, and writing-original draft. Reemon Z. Haddad: Conceptualization and methodology. Dhafar Al-Ani: Review and editing. Berker Bilgin: Review and editing.
Funding
This research was undertaken in part, thanks to funding from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC), and Stellantis N.V.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets presented in this article are unavailable for sharing due to proprietary rights held by Stellantis N.V.
Acknowledgments
The authors are particularly grateful for the technical assistance given by Dr. Mahmud Ghasemi Bijan and Mr. Prashant Modi from Stellantis Group - Global Core Engineering for E-motors and Electric Drive Modules. The authors would like to thank to ANSYS, Mathworks, and nCode for their support with Workbench, Matlab, GlyphWorks and DesignLife software in this research.
Conflicts of Interest
There is no conflict of interest for this paper.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| IPMSM |
Interior permanent magnet motor |
| EV |
Electric Vehicles |
| LPTN |
Lumped Parameter Thermal Network |
| E-N |
Strain-Life |
| S-N |
Stress-Life |
| RPM |
Rotation Per Minute |
| EM |
Electromagnetic |
| UDDS |
Urban Dynamometer Driving Schedule |
References
- Yang, Y.; Castano, S.M.; Yang, R.; Kasprzak, M.; Bilgin, B.; Sathyan, A.; Dadkhah, H.; Emadi, A. Design and Comparison of Interior Permanent Magnet Motor Topologies for Traction Applications. IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification 2017, 3, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, E.; Yang, Y.; Bilgin, B.; Bakr, M.H.; Emadi, A. A Comprehensive Review of Flux Barriers in Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 149168–149181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krings, A.; Monissen, C. Review and trends in electric traction motors for battery electric and hybrid vehicles. In Proceedings of the Proc. International Conference on Electrical Machines, Gothenburg, Sweden, Nov. 2020; pp. 1807–1813. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.J.; Jung, S.Y.; Kim, Y.J. Air-Barrier Width Prediction of Interior Permanent Magnet Motor for Electric Vehicle Considering Fatigue Failure by Centrifugal Force. Journal of Electrical Engineering and Technology 2015, 10, 952–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, T. Temperature effects on torque production and efficiency of PM motors using NdFeB magnets. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications 1995, 31, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, N.; Toliyat, H.A.; Kliman, G.B. Handbook of electric motors; CRC press: Boca Raton, USA, 2017; ISBN 9781-315220826. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelrahman, S.A.; Bilgin, B. Computationally Efficient Surrogate-Based Magneto-Fluid-Thermal Numerical Coupling Approach for a Water-Cooled IPM Traction Motor. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 83692–83704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.W.; Ryu, J.Y.; Chin, J.W.; Park, S.H.; Kim, D.K.; Lim, M.S. Coupled Electromagnetic-Thermal Analysis for Predicting Traction Motor Characteristics According to Electric Vehicle Driving Cycle. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 2021, 70, 4262–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Yang, K.; Ge, H.; Magne, P.; Emadi, A. A drive cycle based electro-thermal analysis of traction inverters. In Proceedings of the Proc. IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo; 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Sikanen, E.; Nerg, J.; Heikkinen, J.E.; Tehrani, M.G.; Sopanen, J. Fatigue life calculation procedure for the rotor of an embedded magnet traction motor taking into account thermomechanical loads. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing 2018, 111, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Shang, J.; Zhao, L.; Li, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Wang, X. Failure Analysis and Accelerated Test Development for Rotor Magnetic Bridge of Electric Vehicle Drive Motor. Applied Sciences 2023, 13, 4753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindh, P.; Tehrani, M.G.; Lindh, T.; Montonen, J.H.; Pyrhönen, J.; Sopanen, J.T.; Niemelä, M.; Alexandrova, Y.; Immonen, P.; Aarniovuori, L. Multidisciplinary design of a permanent-magnet traction motor for a hybrid bus taking the load cycle into account. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics 2016, 63, 3397–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Long, R.; Pang, Y.; Lindenmo, M. Fatigue properties of an electrical steel and design of EV/HEV IPM motor rotors for durability and efficiency. SAE Technical Paper, 2010-01-1308 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Tolofari, T.I. Characterization of the Mechanical and Microstructural Properties of Thin Non-Orientated Electrical Steel Sheets. Master’s thesis, University of Waterloo, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Sahu, A.; Abdelrahman, A.; Al-Ani, D.; Bilgin, B. Fatigue life calculation and mitigation of bridge stresses in the rotor core of a delta-shape interior permanent magnet motor. In Proceedings of the Proc. IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo. IEEE; 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Sahu, A.; R. Haddad, A.; Al-Ani, D.; Bilgin, B. Fatigue life calculation and mitigation of bridge stresses in the rotor core of a delta-shape interior permanent magnet motor. In Proceedings of the Proc. IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference & Expo. IEEE; 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Halfpenny, A. Methods for accelerating dynamic durability tests. In Proceedings of the Proc. International Conference on Recent Advances in Structural Dynamics, Southampton, UK; 2006; pp. 17–19. [Google Scholar]
- Fortese, G.; Nicoletto, G.; Riva, E. Fatigue behaviour of thin Fe-Si steel sheets for electric motor production. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering. IOP Publishing; 2021; Vol. 1038, p. 012004. [Google Scholar]
- Budynas, R.G.; Nisbett, J.K. Fatigue failure resulting from variable loading. In Shigley’s Mechanical Design Engineering; Mcgraw Hill: NY, USA, 2011; ISBN 9780-073529288. [Google Scholar]
- Madayag, A.F. Metal fatigue: Theory and design; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1969; ISBN 978-0471563150. [Google Scholar]
- Dowling, N.E. Mean stress effects in stress-life and strain-life fatigue. SAE Technical Paper, 2004-04-01 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Gope, P.C. Scatter analysis of fatigue life and prediction of S–N curve. Journal of failure analysis and prevention 2012, 12, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Shang, J.; Zhao, L.; Li, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Wang, X. Failure Analysis and Accelerated Test Development for Rotor Magnetic Bridge of Electric Vehicle Drive Motor. Applied Sciences 2023, 13, 4753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayraktar, Ş.; Turgut, Y. Effects of different cutting methods for electrical steel sheets on performance of induction motors. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part B: Journal of Engineering Manufacture 2018, 232, 1287–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silicon Steel. Available online: https://www.shungesteeltrade.com (accessed on 2023-06-23).
- Sintered Neodymium-Iron-Boron Magnets- G48UH. Available online: https://www.arnoldmagnetics.com (accessed on 2023-05-19).
- Banea, M.; De Sousa, F.; Da Silva, L.; Campilho, R.; de Pereira, A.B. Effects of temperature and loading rate on the mechanical properties of a high temperature epoxy adhesive. Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology 2011, 25, 2461–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dynamometer drive schedules, vehicle and fuel emissions testing. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/ (accessed on 2021-03-02).
- Lim, D.H.; Lee, M.Y.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, S.C. Performance evaluation of an in-wheel motor cooling system in an electric vehicle/hybrid electric vehicle. Energies 2014, 7, 961–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ratal, W.; Bennebach, M.; Lin, X.; Plaskitt, R. Fatigue life modelling and accelerated test for components under variable amplitude loads. In Proceedings of the Symposium on fatigue testing and analysis under variable amplitude loading conditions, Tours, France; 2002; pp. 349–364. [Google Scholar]
- Rølvåg, T.; Haugen, B.; Bella, M.; Berto, F. Fatigue analysis of high performance race engines. Engineering Failure Analysis 2020, 112, 104514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childs, P.R. Shafts. In Mechanical design engineering handbook; Butterworth Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2013; ISBN 9780-080982830. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.L.; Barkey, M.E.; Kang, H.T. Stress-Based Uniaxial Fatigue Analysis. In Metal fatigue analysis handbook: practical problem-solving techniques for computer-aided engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2011; ISBN 9780-123852045. [Google Scholar]
- Haefele, P.; Thum, M.; Knerr, T. Life-time-assessment for rotors for electric drives. In Proceedings of the Proc. International Conference on Engineering Science and Innovative Technology, North Bangkok, Thailand; 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Radovanovic, M.; Dasic, P. Research on surface roughness by laser cut. The Annals of University Dunarea de Jos of Galati Fasicule VII, Tribology 2006, 84, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Oberg, E.; Jones, F.D.; Horton, H.L.; Ryffel, H.H.; Mccauley, C.J.; Heald, R.; Hussain, M.I. tooling and toolmaking. In Machinery’s Handbook; Industrial Press, USA: New York, USA, 2012; ISBN 9780-831129019. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, C.; Wirsching, P.; Cashman, G. Design curve to characterize fatigue strength. International Journal of Fatigue 1997, 10, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.L.; Pan, J.; Hathaway, R.; Barkey, M. Stress-Based Fatigue Analysis and Design. In Fatigue testing and analysis: theory and practice; Oxford, UK: Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2005; ISBN 978-0750677196. [Google Scholar]
Figure 1.
Loads and boundary conditions for rotor stress estimation.
Figure 1.
Loads and boundary conditions for rotor stress estimation.
Figure 2.
Effect of interference fit on Von-misses rotor stress at hotspot 3 in
Figure 1 under various rotor speeds.
Figure 2.
Effect of interference fit on Von-misses rotor stress at hotspot 3 in
Figure 1 under various rotor speeds.
Figure 3.
Normalized rotor stress under combined centrifugal load, thermal load and interference fit (a)Von-misses stress (b) Maximum Principal stress.
Figure 3.
Normalized rotor stress under combined centrifugal load, thermal load and interference fit (a)Von-misses stress (b) Maximum Principal stress.
Figure 4.
Maximum Principal stress at hotspots in
Figure 1 under combined load and under various rotor speeds.
Figure 4.
Maximum Principal stress at hotspots in
Figure 1 under combined load and under various rotor speeds.
Figure 5.
Daily transient velocity drive cycle.
Figure 5.
Daily transient velocity drive cycle.
Figure 6.
Normalized torque, magnet and coil temperature for continous and peak performance.
Figure 6.
Normalized torque, magnet and coil temperature for continous and peak performance.
Figure 7.
Magnet, winding hotspot and motor speed profile for the daily drive cycle.
Figure 7.
Magnet, winding hotspot and motor speed profile for the daily drive cycle.
Figure 8.
Vehicle velocity drive cycle (a) original (b) compressed.
Figure 8.
Vehicle velocity drive cycle (a) original (b) compressed.
Figure 9.
Compressed daily rotor speed profile and rotor, magnet and shaft temperature profile.
Figure 9.
Compressed daily rotor speed profile and rotor, magnet and shaft temperature profile.
Figure 10.
Von-misses stress for linear material, Von-misses stress and plastic strain for nonlinear material.
Figure 10.
Von-misses stress for linear material, Von-misses stress and plastic strain for nonlinear material.
Figure 11.
True stress-true plastic strain curve for electrical steel 27PNX1350 at room tempertaure and at 150 C
Figure 11.
True stress-true plastic strain curve for electrical steel 27PNX1350 at room tempertaure and at 150 C
Figure 12.
Von-misses stress at hotspot 1 and hotspot 3 for the daily rotor speed profile
Figure 12.
Von-misses stress at hotspot 1 and hotspot 3 for the daily rotor speed profile
Figure 13.
Schematic diagram for a variable amplitude S-N curve for steel
Figure 13.
Schematic diagram for a variable amplitude S-N curve for steel
Figure 14.
Fatigue life for the rotor lamination, accounting for varying loads, a temperature-dependent median S-N curve, and the Goodman mean stress correction factor.
Figure 14.
Fatigue life for the rotor lamination, accounting for varying loads, a temperature-dependent median S-N curve, and the Goodman mean stress correction factor.
Table 1.
Rotor lamination normalised stress comparision for various loads.
Table 1.
Rotor lamination normalised stress comparision for various loads.
Table 2.
Median Stress-life Parameters of 27PNX1350 at Room Temperature and 150 C.
Table 2.
Median Stress-life Parameters of 27PNX1350 at Room Temperature and 150 C.
| Parameter |
Value |
Temperature |
| Stress amplitude intercept () |
1502.3 (MPa) |
RT |
| slope 1 () |
-0.12 |
RT |
| slope 2 () |
-0.06383 |
RT |
| Endurance strength () |
286.2 (MPa) |
RT |
| Stress at fatigue cut-off limit |
8.4 (MPa) |
RT |
| Stress amplitude intercept () |
1236.7 (MPa) |
150 C |
| slope 1 () |
-0.112 |
150 C |
| slope 2 () |
-0.05932 |
150 C |
| Endurance strength () |
263.2 (MPa) |
150 C |
| Stress at fatigue cut-off limit |
9.9 (MPa) |
150 C |
Table 3.
R90C95 Stress-life Parameters of 27PNX1350 at Room Temperature and 150 C.
Table 3.
R90C95 Stress-life Parameters of 27PNX1350 at Room Temperature and 150 C.
| Parameter |
Value |
Temperature |
| Parameter |
Value |
Temperature |
| Stress amplitude intercept () |
1224 (MPa) |
RT |
| Endurance strength () |
192.5 (MPa) |
RT |
| Stress at fatigue cut-off limit |
3.7 (MPa) |
RT |
| Stress amplitude intercept () |
1195.7 (MPa) |
150 C |
| Endurance strength () |
188.2 (MPa) |
150 C |
| Stress at fatigue cut-off limit |
3.6 (MPa) |
150 C |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).