1. Introduction
Breast cancer is now the leading cause of cancer incidence in women worldwide, accounting for one in four cancer cases and one in six cancer deaths [
1]. Although the overall prognosis for breast cancer patients is relatively good when detected early, relative to other cancers, it has a high recurrence rate after surgery [
2]. Cancer recurrence affects the patient's prognosis and quality of life, posing a critical clinical problem in later years as they often resist chemotherapy. The potential for recurrence and metastasis of breast cancer varies by subtypes, proliferative potential, and dormancy [
3,
4]. Even in the same subtype, recurrence-free survival varies from patient to patient; some patients experience recurrence within one year, while others do not see any recurrence over five years. Therefore, it is beneficial to predict whether each breast cancer patient is prone to relapse individually so that frequency of follow-up tests would be personalized. For those who experience breast cancer recurrence, it is also helpful if recurrence can be diagnosed as early as possible by sensitive tests in a patient-friendly manner. Follow-up management after the initial treatment of breast cancer, such as adjuvant or neoadjuvant therapy, has generally involved physical examination and diagnostic imaging [
5].
Simple and minimally invasive measurement of blood-based tumor markers is used for early detection of cancer and monitoring treatment response. Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and cancer antigen 15-3 (CA15-3) are, in particular, often used as tumor markers for several cancers in clinical settings [
6,
7]. CEA is a glycoprotein involved in cell adhesion and known to be elevated in many cancers [
8]. CA15-3 is known to be a glycan-containing protein antigen of the transmembrane glycoprotein MUC-1 and has been reported to be associated with breast cancer stage and survival [
9]. These two markers have been validated in a number of studies to measure changes in patients' blood to evaluate their application for early detection of cancer recurrence and monitoring treatment response[
10,
11]; however, there are little data available about the utility of these markers in asymptomatic or early-stage cancers. Although the frequent measurements of tumor markers in the blood have not been strongly recommended by several guidelines [
12,
13], developing effective biomarkers to detect breast cancer recurrence is critical, since liquid biopsy is generally more sensitive and cost-effective than diagnostic imaging.
Recently, endocan has received increasing attention as one of the blood-based biomarkers to detect various cancers. Endocan, encoded by the
ESM1 gene, is a human endothelial cell-specific molecule soluble dermatan sulfate proteoglycan known to circulate in the bloodstream [
14,
15]. Endocan expression is reportedly associated with clinicopathological parameters and poor prognosis in several cancers, including gastric cancer [
16], hepatocellular carcinoma [
17], prostate cancer [
18], bladder cancer [
19], and breast cancer [
20]. Our previous study demonstrated that an elevated expression of
ESM1 in MDA-MB-231 cells, a human triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cell line, increased cell proliferation and tumor formation, and that TNBC patients with high
ESM1 expression in primary breast cancer had significantly shorter relapse-free survival [
21]. In addition, blood endocan levels in luminal-type breast cancer patients were associated with cancer staging [
20]. Therefore, since
ESM1 negatively impacts breast cancer patients and endocan, the gene product of
ESM1, can be detected from the peripheral blood samples, the association between the status of breast cancer and blood endocan levels is clinically worth pursuing.
To bridge the gap between endocan's preclinical and clinical value as a blood-based biomarker, we sought to measure and assess the blood endocan levels in murine models of breast cancer and breast cancer patients. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to investigate the extent to which blood endocan levels in mice and patients with breast cancer are affected by the surgical removal of primary tumors and postoperative recurrence.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
In this study, MDA-MB-231BR cell line, a metastatic variant of human-derived triple-negative breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231 [
22], was used. Our previous study reported that MDA-MB-231BR cells overexpressed
ESM1 and secreted measurable amounts of endocan, which was detected from the supernatant of the conditioned medium as well as the blood of mouse models bearing MDA-MB-231BR tumor, which was not the case with MDA-MB-231 [
21]. To our knowledge, MDA-MB-231BR cell line is the only human breast cancer cell line overexpressing
ESM1 thus far, which is the reason why we used MDA-MB-231BR in this study.
MDA-MB-231BR was a kind gift from Dr. Patricia Steeg (National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, MD, U.S.A.). MDA-MB-231BR was cultured in RPMI-1640 (FujiFilm Wako Pure Chemical Corp., Osaka, Japan) with 10% fetal bovine serum (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.) and maintained under aseptic conditions of 5% CO2 at 37℃. Contamination with Mycoplasma or fungi was routinely checked and only uncontaminated cells were used. Cell line authentification was outsourced to BEX Co, Ltd. (Tokyo, Japan), and MDA-MB-231BR/mVenus-Akaluc, detailed in the next section, was confirmed to be the identical cell strain to MDA-MB-231.
2.2. Generation of MDA-MB-231BR/mVenus-Akaluc
Primer was designed from pcDNA3 Venus-Akaluc vector (RDB15781; Riken BioResource Research Center, Ibaraki, Japan), and Q5® High-Fidelity 2X Master Mix (New England Biolabs, MA, USA) was used to amplify the DNA. The mVenus-Akaluc primers used for PCR amplification were as follows: FW, 5’-TAG AGC TAG CGA ATT ATG GTG AGC AAG GGC GAG-3' (33 bp); and RV, 5’-ATT TAA ATT CGA ATT CCA TAG AGC CCA CCG CAT-3' (33 bp). PiggyBac™ Transposon Vector System (System Biosciences, CA, U.S.A.) was used to transfect mVenus-Akaluc DNA into MDA-MB-231BR cells stably. The PB-CMV-MCS-EF1-Puro cDNA Cloning and Expression Vector (System Biosciences) was linearized by EcoRI-HF restriction enzymes, and a purified PCR fragment of mVenus-Akaluc was incorporated into the PB-linearized vector using In-Fusion® HD Cloning Kit (Takara Bio Ltd., Shiga, Japan). The resultant PB-mVenus-Akaluc plasmid was cloned with Stellar™ Competent Cells (Takara Bio Ltd.), followed by the purification with GenElute™ Plasmid Miniprep Kit (Sigma-Aldrich), and the sequence was verified by a DNA sequencing service (Eurofins Genomics Inc., Tokyo, Japan). MDA-MB-231BR was transfected with the plasmid DNA using Lipofectamine® LTX Reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.), and stable lines, designated as MDA-MB-231BR/mVenus-Akaluc hereafter, were selected by 1 μg/mL of puromycin (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.). The basic function of MDA-MB-231BR/mVenus-Akaluc, such as cell proliferation and the visibility by fluorescence and luminescence imaging, was confirmed by Cell Counting Kit-8 assay, fluorescence microscopy, and IVIS Lumina Series III (PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, U.S.A.).
2.3. Animals
Female athymic nu/nu mice (Balb/c background, four weeks old, 17-20 g) and NOD.Cg-Prkdcscid Il2rgtm1Wjl/SzJ (NSG) mice (4 weeks old, 16-21 g) were purchased from CLEA Japan, Inc. (Tokyo, Japan) and The Jackson Laboratory Japan, Inc. (Kanagawa, Japan), respectively. The institutional animal care committee at Hoshi University approved the study protocol before the animal experiments.
2.4. Blood endocan Measurements and Luminescence Imaging of Mice Bearing Orthotopic Breast Cancer
One million MDA-MB-231BR/
mVenus-Akaluc cells were orthotopically inoculated into the mammary fat pad of mice. The tumor volume was measured and calculated in a blinded manner using a caliper:
Considering the susceptibility of mouse strain to metastatic recurrence, the primary tumor was resected from each mouse once the tumor volume exceeded 500 mm3 in nude mice and 200 mm3 in NSG mice.
Local or metastatic recurrence was visually detected by luminescence imaging with IVIS Lumina Series III after intraperitoneal injection of akaLumine n-hydrochloride (Fujifilm Wako Pure Chemical Corp.) at a dose of 1.8 nmol.
In order to quantitate endocan in the peripheral blood of nude and NSG mice, blood was collected from the tail vein_at predetermined time points. Plasma was isolated by centrifugation at 4°C, 1,200 ×g for 10 min, and stored at -80ºC until use.
2.5. Blood Collection from Breast Cancer Patients
Clinical studies on the measurement of endocan levels in the blood of breast cancer patients were approved by the Institutional Review Board from Showa University Hospital and Hoshi University, which preceded the participation of the patients in this study. Participation in the study was voluntary, and written informed consent was received from all subjects. Patients with diabetes, an infectious disease, or other types of cancer were excluded from this study because all of those conditions are known to affect blood endocan levels [
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28,
29]. The patient's blood samples were sent to a certified clinical lab for the routine measurements of tumor markers, CEA and CA15-3. CEA concentration of over 5 ng/mL and CA15-3 concentration of over 31.5 U/mL indicated positive for serum CEA and CA15-3, respectively.
Blood was collected from breast cancer patients at the Breast Center of Showa University Hospital (Tokyo, Japan) between 2020 and 2021, and the patient population is summarized in
Supplementary Tables S1 and S2. Plasma was isolated by centrifugation at 4°C, 1,200 ×
g for 10 min, and stored at -80°C until use.
2.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) for the Quantification of Endocan
Plasma samples were diluted twice with sample diluent, and endocan was quantitated using commercial ELISA kits (Lunginnov (Lille, France) for plasma from nude mice and CUSABIO (Wuhan, China) for plasma from NSG mice and humans) according to the manufacturer's instructions. The detection limit was set at 0.156 ng/mL in accordance with the protocol of the ELISA kit. Based on our previous study, an endocan level of 1.68 ng/mL or higher was considered positive for endocan [
20]. Endocan expression of breast cancer cells was confirmed negative by immunohistochemistry in the patients who showed blood endocan levels below the cutoff value (Supplementary Fig. 1) and, thus, was excluded from postsurgical endocan measurements.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
The normality of the data distribution was estimated using StatPlus:mac software (AnalystSoft Inc., Alexandria, VA, USA). Student's t-test or the Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test was used unless otherwise noted. The null hypothesis was rejected when the P-value was smaller than or equal to the significance level (α=0.05).
3. Results
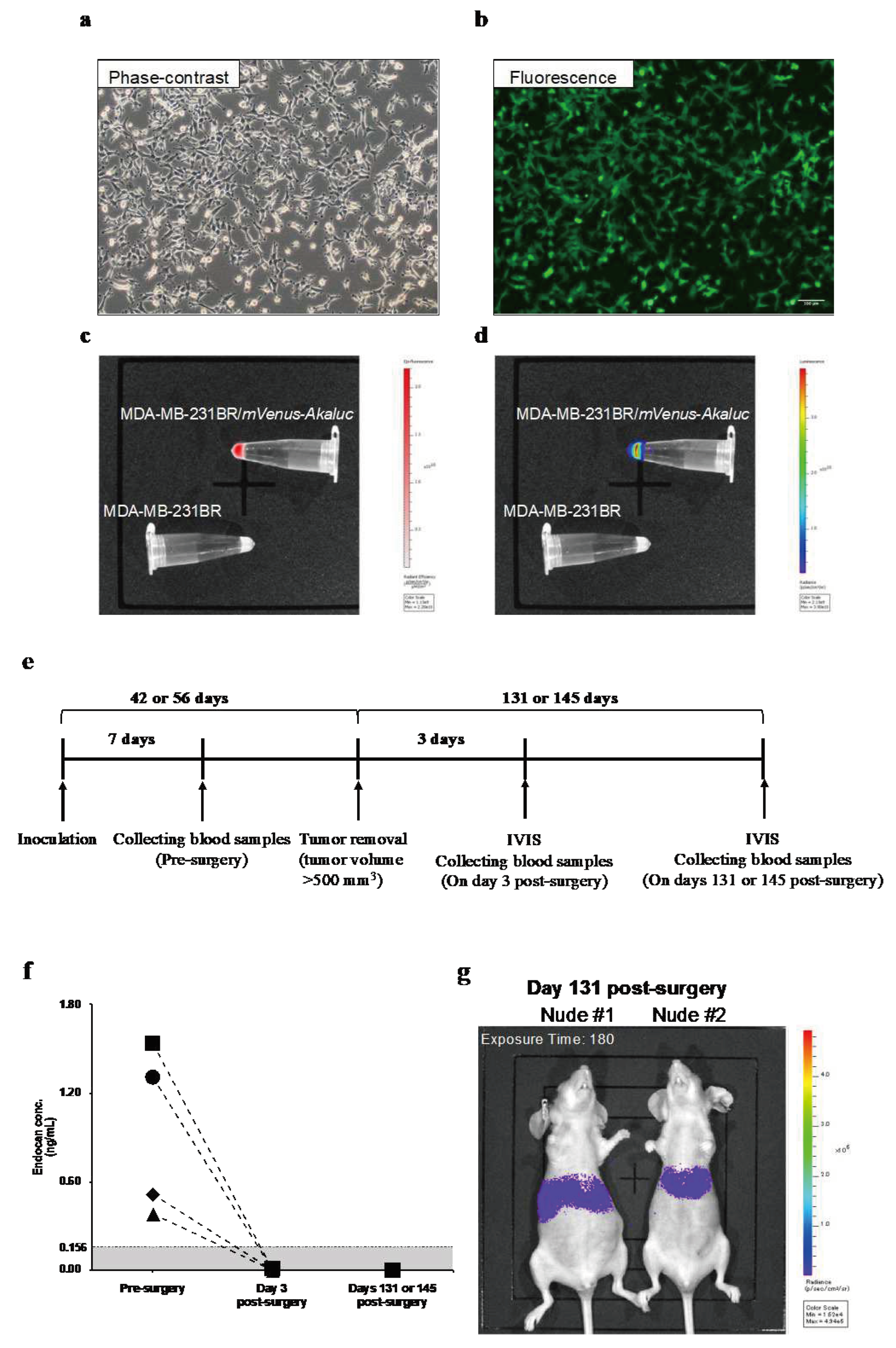
3.1. Blood Endocan Levels Dropped Below the Detection Limit After the Surgical Removal of Primary Breast Tumors from Nude Mice
MDA-MB-231BR/
mVenus-Akaluc was generated to noninvasively visualize tumor recurrence and metastasis. Fluorescence and luminescence imaging confirmed the expressions of mVenus fluorescent protein (
Figure 1b,c) and Akaluc enzyme (
Figure 1d) in MDA-MB-231BR/
mVenus-Akaluc. The doubling time of the generated cell line was 22.7 ± 1.9 h, while that of non-transfected original cells (MDA-MB-231BR) was 21.8 ± 2.1 h (
P=0.444), confirming that the transfection of
mVenus-
Akaluc with PiggyBac™ Transposon Vector System did not affect cell proliferation.
At seven days after inoculation of the MDA-MB-231BR/
mVenus-Akaluc, tumor volume reached 56-110 mm
3, and blood endocan levels were 0.73 ng/mL (range; 0.38-1.54) (
Figure 1f). When the tumor was resected, plasma endocan levels were below the detection limit of the ELISA kit three days after the surgery. Although weak luminescent signals were detected 131 and 145 days after surgery (
Figure 1g), blood endocan levels remained below the detection limit (
Figure 1f).
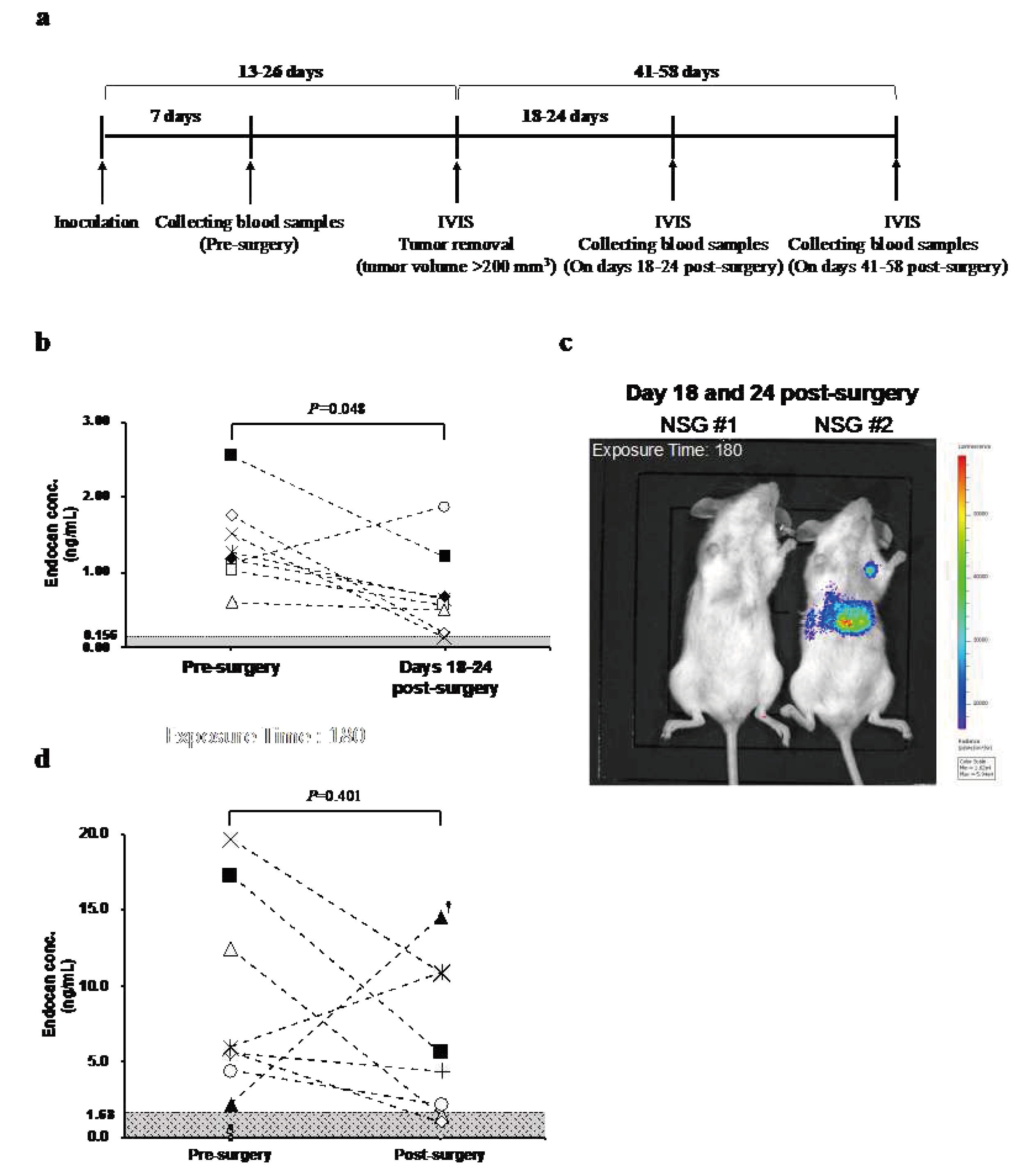
3.2. Blood Endocan Levels Showed a Similar Pattern in NSG mice and Breast Cancer Patients After the Surgical Removal of the Primary Breast Tumor
Since elevation of blood endocan levels in the status of recurrence or metastasis was not observed in nude mice, more susceptible NSG mice were used in a similar experiment (
Figure 2a). At seven days after inoculation of MDA-MB-231BR/
mVenus-Akaluc, tumor size reached 77-147 mm
3 and endocan was detected in all eight mice (range; 0.60-2.54). When the tumor was resected, blood endocan levels dropped in all but one mouse (
Figure 2b). Luminescence imaging displayed weak luminescence signals in distant organs in some mice (
Figure 2c).
To investigate how blood endocan levels respond to tumor resection in the clinical setting, we measured the blood endocan levels of 16 breast cancer patients pre- and post-surgery. Eight patients tested positive for endocan; the endocan level for pre-surgery ranged from 2.24 to 19.64 ng/mL. Blood endocan levels decreased after the surgery except for two patients (
Figure 2d).
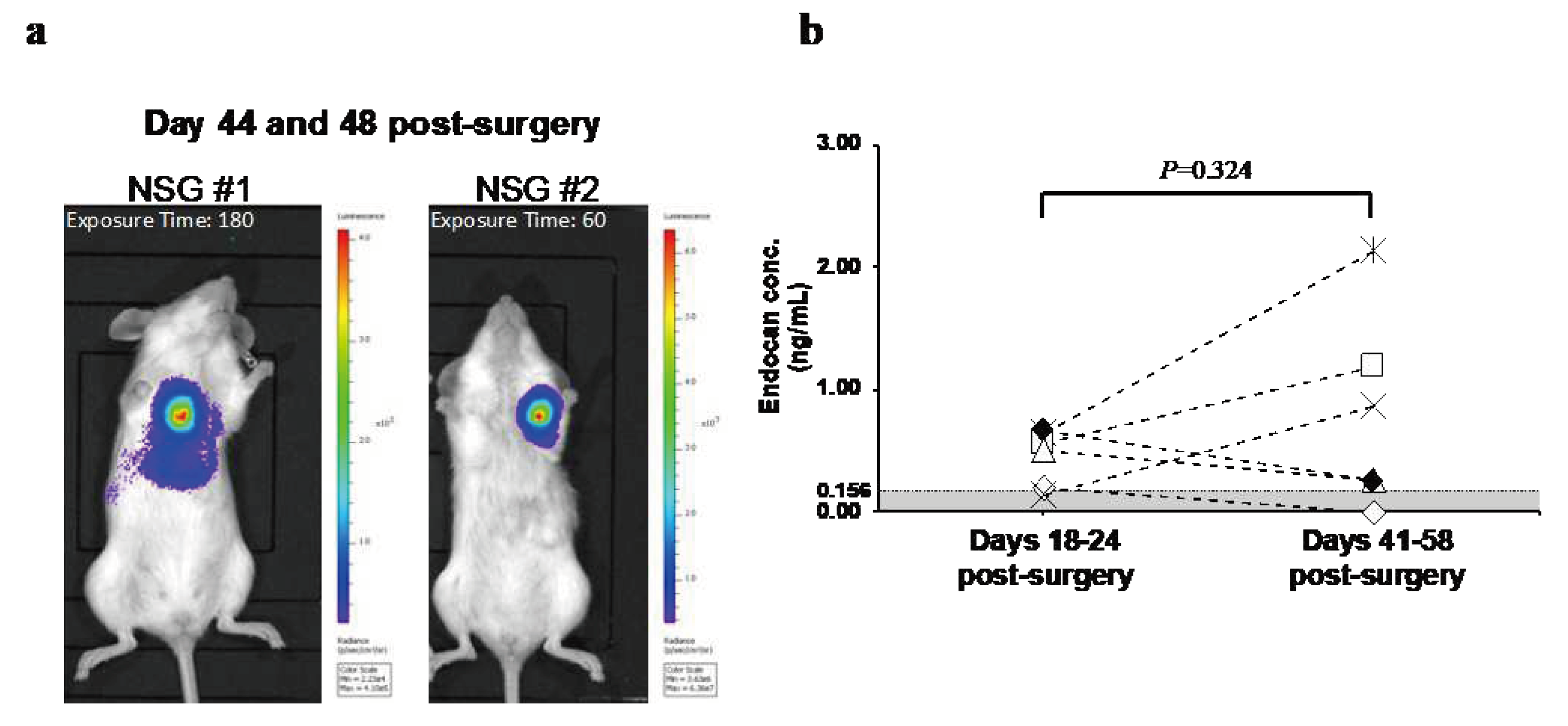
3.3. Changes in Blood Endocan Level in Response to Breast Cancer Recurrence
In order to examine the changes in blood endocan levels with the growth of metastatic recurrence, the animals were monitored until recurrent tumor burdens were evident. On days 41-58, metastatic recurrence was observed with strong luminescent signals in all mice tested (
Figure 3a). Relative to 18-24 days post-surgery, blood endocan levels increased on days 41-58 post-surgery in three out of six mice (
Figure 3b). There was no correlation between the luminescence intensity of the metastases and blood endocan levels.
We next assessed the clinical benefit of blood endocan as a blood-based biomarker for breast cancer recurrence. Endocan in the blood of the patients diagnosed with postoperative recurrence (
N=20) was measured, and the positivity rate for endocan was compared with that for CEA and CA15-3. As summarized in
Table 1, 13 patients (65%) tested positive for endocan, which was much higher than CEA-positive patients (35%) and CA15-3-positive patients (25%). Moreover, among 13 patients who tested negative for CEA, eight patients (61.5%) were positive for endocan, and among 15 patients who tested negative for CA15-3, 10 patients (66.7%) were positive for endocan.
4. Discussion
For successful clinical translation of endocan as a blood-based breast cancer biomarker, it is critical to be accurately reflected by the status of tumors. Surgical resection of primary breast tumors is expected to reduce blood endocan levels, while recurrence potentially increases blood endocan levels. As expected, the removal of primary tumors decreased blood endocan levels of the majority of tumor-bearing mice and breast cancer patients. However, most of them did not reach an undetectable level, except for nude mice. Since MDA-MB-231BR/mVenus-Akaluc cells are the only source of human endocan in animal models, a large number of cells that are sufficient for detectable levels of endocan possibly remained in the body of NSG mice.
Although luminescence signals were detected in nude mice long after the tumor resection, luminescence signals that appeared in nude mice were much weaker than those detected in NSG mice. NSG mice are more susceptible to engraftment, growth, metastasis, and recurrence of xenogeneic cancer cells than conventional immunodeficient mice, including nude mice [
30,
31], which may explain why the number of MDA-MB-231BR/
mVenus-Akaluc cells that remained in the body of nude mice was small and did not produce enough endocan detectable in the peripheral blood. In addition, there was no correlation between the luminescence intensities of recurrent tumors and blood endocan levels.
ESM1 expression levels were different in an individual cell obtained by single-cell cloning of MDA-MB-231BR/
mVenus-Akaluc cells (Supplementary Fig. 2), implying that intratumoral heterogeneity of MDA-MB-231BR/
mVenus-Akaluc cells could be responsible for the inconsistency between luminescence intensities and blood endocan levels in the NSG mouse model.
The case is more complicated for breast cancer patients, however, because various diseases, including inflammatory disease [
27], diabetes [
28], and sepsis [
29], are known to increase blood endocan levels. Although such patients were excluded from this study, unnoticeable inflammation or undeclared events might have occurred during the study, which might be why the blood endocan levels were not entirely down to below the cutoff value.
Blood endocan levels of a few individuals were increased even after the surgery, both in NSG mice and breast cancer patients. Although the blood endocan level in one patient whose blood was collected on day 29 post-surgery was increased, that in other two patients whose blood was collected on day 32 post-surgery was decreased (
Supplementary Table S3), implying that surgical inflammation was not considered to affect the postsurgical blood endocan levels. Therefore, other than one patient who ran a marathon, which might cause an increase in the blood endocan level, the day before the postsurgical blood collection, it is difficult to identify the reasons for the discrepancy with limited information and sample size.
CEA and CA15-3 have been used in clinical practice for years but are not well supported by clinical evidence [
12,
32]. Despite a limited number of patients participating in this study, endocan seems more responsive to breast cancer recurrence than CEA and CA15-3. Due to technical issues, CEA and CA15-3 in mouse models were not measured in this study, as it is necessary to obtain sufficient amounts of mouse plasma in order to quantitate all three markers by each ELISA kit. More importantly, the main objective of this study is not just to compare blood endocan with the existing biomarkers, but eventually to show the “clinical” benefit of blood endocan measurement. Since CEA and CA15-3 are routinely measured in clinical settings, we can compare blood endocan with the existing biomarkers of the same patient, which is more valuable information than preclinical comparisons for future clinical use. Still, one-fourth of the patients with breast cancer recurrence were negative for all three markers (
Supplementary Table S4). Not all breast cancer patients have primary tumors expressing endocan, and the patients with postoperative recurrence participating in this study were not prescreened by de novo endocan expression. A longitudinal study tracking endocan-positive breast cancer patients is necessary to corroborate the clinical benefit of blood endocan measurements.
In order to achieve the clinical use of blood endocan measurement for breast cancer recurrence, several possible limitations need to be addressed. First, as described above, blood endocan rises in patients with inflammatory disease, diabetes, and sepsis. Therefore, it is important to include patients without breast cancer recurrence and compare with patients with breast cancer recurrence in order to determine if blood endocan levels are specifically elevated when breast cancer recurrence occurs. However, providing conclusive evidence of “non-recurrence” in patients is challenging as physicians typically do not perform diagnostic imaging if patients do not show any abnormalities during routine follow-up, leaving the recurrence status undetermined. Since performing additional diagnostic tests to confirm “non-recurrence” may impose medical costs, potential radiation exposure from mammography, and unnecessary tissue diagnosis, this study primarily focused on the sensitivity of the blood endocan measurement and left the specificity for future studies. Generally speaking, sensitivity is more important when the consequence of missing a positive case is serious, such as in screening for a life-threatening disease, like cancer, which is the case for this study. In addition, some ELISA kits from other suppliers did not work well with measuring blood endocan in our study. Epitopes that anti-endocan antibodies recognize may vary depending on each ELISA kit supplied by manufacturers, which might be responsible for inconsistent results when ELISA kits from different suppliers were used. We have worked on developing a new alternative to ELISA for future clinical use of blood endocan measurement.
5. Conclusions
This study is the first report on the effect of the surgical resection of primary breast tumors and recurrence on blood endocan levels, and our findings are consistent with the earlier reports for low-grade glioma [
33] and renal cell carcinoma [
23]. More importantly, the current study did demonstrate that blood endocan measurement could detect breast cancer recurrence with a higher probability compared to conventional tumor markers, CEA and CA15-3, in a limited number of patients (
N = 20). Although this study deals with only a limited number of patients, this positive finding is worth being validated by future large-scale studies, which would strengthen the robustness of the findings. According to clinicaltrials.gov search, many clinical trials regarding endocan levels in the peripheral blood of patients suffering from various diseases are ongoing or completed, which warrants the application of blood endocan measurements to breast cancer. Taken together, our findings indicate that blood endocan could be a more sensitive marker than CEA or CA15-3 in breast cancer patients with postoperative recurrence.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org. Figure S1. Pathological assessment of endocan expression in primary breast tumors removed by the surgery. Figure S2. Difference in ESM1 expression of MDA-MB-231BR/mVenus-Akaluc obtained by limiting dilution cloning. Table S1. Clinical characteristics of breast cancer patients whose blood was collected before and after the surgery. Table S2. Clinical characteristics of breast cancer patients with postoperative recurrence. Table S3. Effect of the interval between the surgery and the blood collection on changes in blood endocan levels. Table S4. Endocan, CEA, and CA15-3 concentrations in the blood samples of patients with postoperative breast cancer recurrence.
Funding
This research was supported by JSPS KAKENHI, grant number JP19K07760.
Authors' contributions
Conceptualization, SN and YKato; Data curation, KD, YKanada, AN and KT; Formal analysis, KD, TY and HO; Funding acquisition, YKato; Investigation, KD, YKanada, AN, HO and YKato; Methodology, KD, YKanada, AN, KT, KI, TY, FS and YK; Project administration, SN and YKato; Resources, YKanada, AN and KT; Supervision, KI, FS, SN and YKato; Validation, KI; Writing – original draft, KD; Writing – review & editing, FS, SN and YKato. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The institutional animal care committee of Hoshi University approved the animal experiments (Protocol #: 19-083). Clinical studies were approved by the Institutional Review Board from Showa University Hospital (#2880) and Hoshi University (#2019-12, #2021-04).
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was taken from each volunteer with the assistance of Showa University Hospital.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. Yosuke Sasaki for his technical assistance. We pay special tribute to Dr. Katsuhide Igarashi, who passed away before publishing this study.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests..
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN sstimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Disibio, G.; French, S.W. Metastatic patterns of cancers: Results from a large autopsy study. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2008, 132, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moossdorff, M.; Vane, M.L.G.; van Nijnatten, T.J.A.; van Maaren, M.C.; Goorts, B.; Heuts, E.M.; Strobbe, L.J.A.; Smidt, M.L. Conditional local recurrence risk: The effect of event-free years in different subtypes of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2021, 186, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dittmer, J. Mechanisms governing metastatic dormancy in breast cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 2017, 44, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burstein, H.J.; Winer, E.P. Primary care for survivors of breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2000, 343, 1086–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, L.; Fritsche, H.; Mennel, R.; Norton, L.; Ravdin, P.; Taube, S.; Somerfield, M.R.; Hayes, D.F.; Bast, R.C., Jr.; American Society of Clinical, Oncology. American Society of Clinical Oncology 2007 update of recommendations for the use of tumor markers in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2007, 25, 5287–5312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safi, F.; Kohler, I.; Rottinger, E.; Suhr, P.; Beger, H.G. Comparison of CA 15-3 and CEA in diagnosis and monitoring of breast cancer. Int J Biol Markers. 1989, 4, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunnet, M.; Sorensen, J.B. Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) as tumor marker in lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2012, 76, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebeling, F.G.; Stieber, P.; Untch, M.; Nagel, D.; Konecny, G.E.; Schmitt, U.M.; Fateh-Moghadam, A.; Seidel, D. Serum CEA and CA 15-3 as prognostic factors in primary breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 2002, 86, 1217–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolini, A.; Tartarelli, G.; Carpi, A.; Metelli, M.R.; Ferrari, P.; Anselmi, L.; Conte, M.; Berti, P.; Miccoli, P. Intensive post-operative follow-up of breast cancer patients with tumour markers: CEA, TPA or CA15.3 vs MCA and MCA-CA15.3 vs CEA-TPA-CA15.3 panel in the early detection of distant metastases. BMC Cancer. 2006, 6, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Li, H. Assessing Clinical Significance of Serum CA15-3 and Carcinoembryonic Antigen (CEA) Levels in Breast Cancer Patients: A Meta-Analysis. Med Sci Monit. 2016, 22, 3154–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatcheressian, J.L.; Hurley, P.; Bantug, E.; Esserman, L.J.; Grunfeld, E.; Halberg, F.; Hantel, A.; Henry, N.L.; Muss, H.B.; Smith, T.J.; et al. Breast cancer follow-up and management after primary treatment: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol. 2013, 31, 961–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, F.; Kyriakides, S.; Ohno, S.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Poortmans, P.; Rubio, I.T.; Zackrisson, S.; Senkus, E. Early breast cancer: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2019, 30, 1194–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassalle, P.; Molet, S.; Janin, A.; Heyden, J.V.; Tavernier, J.; Fiers, W.; Devos, R.; Tonnel, A.B. ESM-1 is a novel human endothelial cell-specific molecule expressed in lung and regulated by cytokines. J Biol Chem. 1996, 271, 20458–20464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechard, D.; Gentina, T.; Delehedde, M.; Scherpereel, A.; Lyon, M.; Aumercier, M.; Vazeux, R.; Richet, C.; Degand, P.; Jude, B.; et al. Endocan is a novel chondroitin sulfate/dermatan sulfate proteoglycan that promotes hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor mitogenic activity. J Biol Chem. 2001, 276, 48341–48349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Sun, M.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J. Biological and clinical implications of endocan in gastric cancer. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 10043–10049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaki, K.; Toshikuni, N.; George, J.; Minato, T.; Matsue, Y.; Arisawa, T.; Tsutsumi, M. Serum endocan as a novel prognostic biomarker in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer. 2014, 5, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslan, B.; Onuk, O.; Hazar, I.; Aydin, M.; Cilesiz, N.C.; Eroglu, A.; Nuhoglu, B. Prognostic value of endocan in prostate cancer: Clinicopathologic association between serum endocan levels and biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy. Tumori. 2017, 103, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laloglu, E.; Aksoy, H.; Aksoy, Y.; Ozkaya, F.; Akcay, F. The determination of serum and urinary endocan concentrations in patients with bladder cancer. Ann Clin Biochem. 2016, 53, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanada, Y.; Daiki, K.; Nagata, A.; Taruno, K.; Kuwayama, T.; Hashimoto, R.; Masuda, H.; Akashi-Tanaka, S.; Nakamura, S.; Kato, Y. . Clinical significance of blood endocan level in breast cancer patients. Showa Univ J Med Sci. 2023, 35, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagara, A.; Igarashi, K.; Otsuka, M.; Kodama, A.; Yamashita, M.; Sugiura, R.; Karasawa, T.; Arakawa, K.; Narita, M.; Kuzumaki, N.; et al. Endocan as a prognostic biomarker of triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2017, 161, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneda, T.; Williams, P.J.; Hiraga, T.; Niewolna, M.; Nishimura, R. A bone-seeking clone exhibits different biological properties from the MDA-MB-231 parental human breast cancer cells and a brain-seeking clone in vivo and in vitro. J Bone Miner Res. 2001, 16, 1486–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Lee, H.H.; Yoon, Y.E.; Na, J.C.; Kim, S.Y.; Cho, Y.I.; Hong, S.J.; Han, W.K. Clinical validation of serum endocan (ESM-1) as a potential biomarker in patients with renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.C.; Pan, K.F.; Lee, W.J.; Chang, J.H.; Tan, P.; Gu, C.C.; Chang, W.M.; Yang, S.F.; Hsiao, M.; Hua, K.T.; et al. Circulating proteoglycan endocan mediates EGFR-driven progression of non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 3292–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Qi, L.; Cai, Y.; Yang, P.; Xuan, G.; Jiang, Y. HULC long noncoding RNA silencing suppresses angiogenesis by regulating ESM-1 via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in human gliomas. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 14429–14440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, K.F.; Yang, Y.C.; Lee, W.J.; Hua, K.T.; Chien, M.H. Proteoglycan endocan: A multifaceted therapeutic target in Cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2022, 1877, 188672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, S.F.; Schiller, M.; Jing, D.; Li, H.; Butz, S.; Vestweber, D.; Biljes, D.; Drexler, H.C.; Nieminen-Kelha, M.; Vajkoczy, P.; et al. Esm1 modulates endothelial tip cell behavior and vascular permeability by enhancing VEGF bioavailability. Circ Res. 2014, 115, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klisic, A.; Kavaric, N.; Stanisic, V.; Vujcic, S.; Spasojevic-Kalimanovska, V.; Ninic, A.; Kotur-Stevuljevic, J. Endocan and a novel score for dyslipidemia, oxidative stress and inflammation (DOI score) are independently correlated with glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) in patients with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. Arch Med Sci. 2020, 16, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherpereel, A.; Depontieu, F.; Grigoriu, B.; Cavestri, B.; Tsicopoulos, A.; Gentina, T.; Jourdain, M.; Pugin, J.; Tonnel, A.B.; Lassalle, P. Endocan, a new endothelial marker in human sepsis. Crit Care Med. 2006, 34, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milsom, C.C.; Lee, C.R.; Hackl, C.; Man, S.; Kerbel, R.S. Differential post-surgical metastasis and survival in SCID, NOD-SCID and NOD-SCID-IL-2Rγ(null) mice with parental and subline variants of human breast cancer: Implications for host defense mechanisms regulating metastasis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iorns, E.; Drews-Elger, K.; Ward, T.M.; Dean, S.; Clarke, J.; Berry, D.; El Ashry, D.; Lippman, M. A new mouse model for the study of human breast cancer metastasis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naruse, T.; Koike, A.; Suzumura, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Ooiwa, Y.; Miwa, M.; Kojima, T.; Kanemitsu, T.; Yamamoto, S. Studies of carcinoembryonic antigen and glucoprotein antigen in sera of patients with breast cancer. J Jpn Prac Surg Soc. 1988, 49, 774–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanriverdi, T.; Kemerdere, R.; Inal, B.B.; Yuksel, O.; Emre, H.O.; Ahmedov, M.; Baran, O.; Ates, S. Serum endocan levels before and after surgery on low-grade gliomas. Surg Neurol Int. 2017, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).