Submitted:
10 January 2024
Posted:
11 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
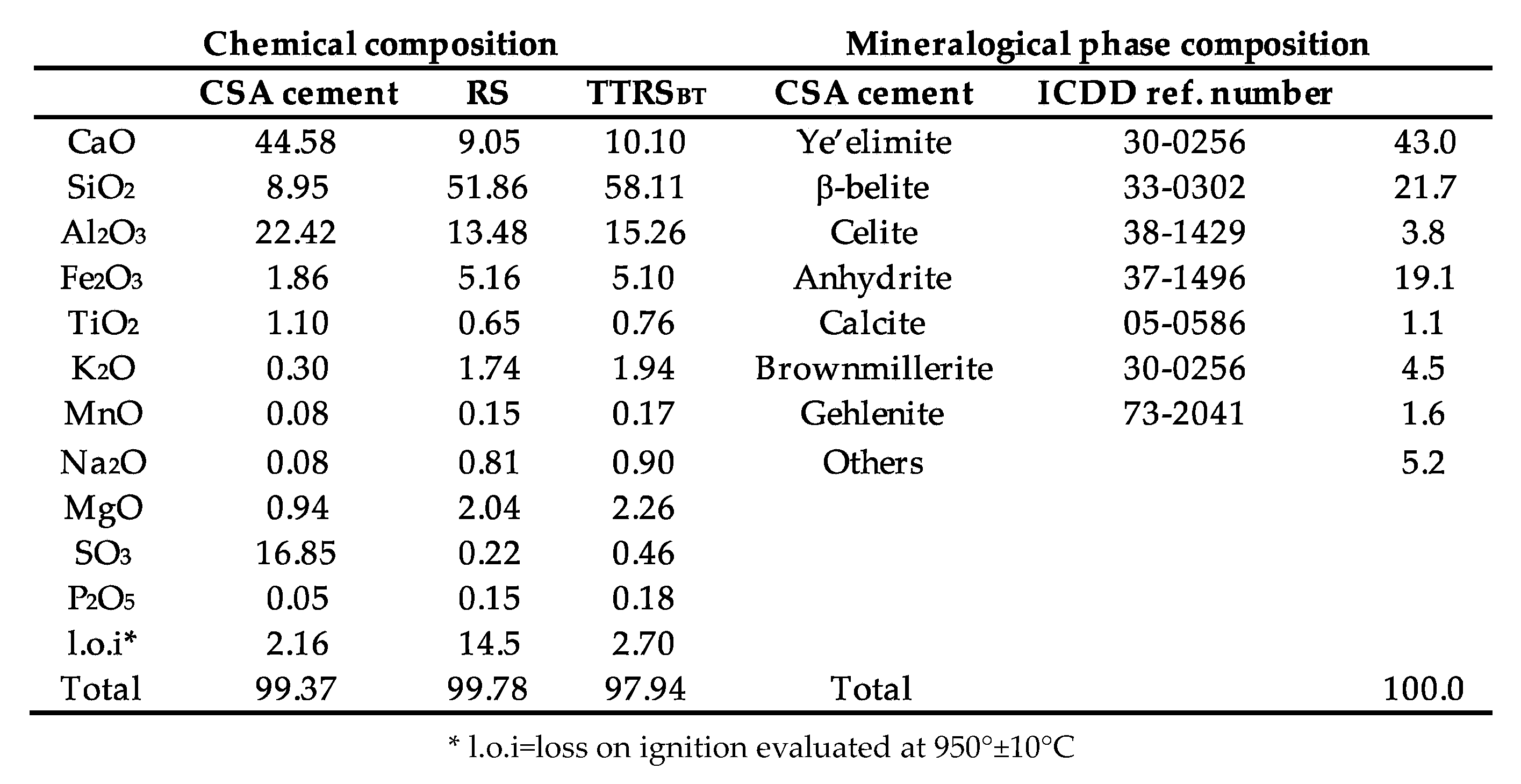
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods and Evaluation Techniques
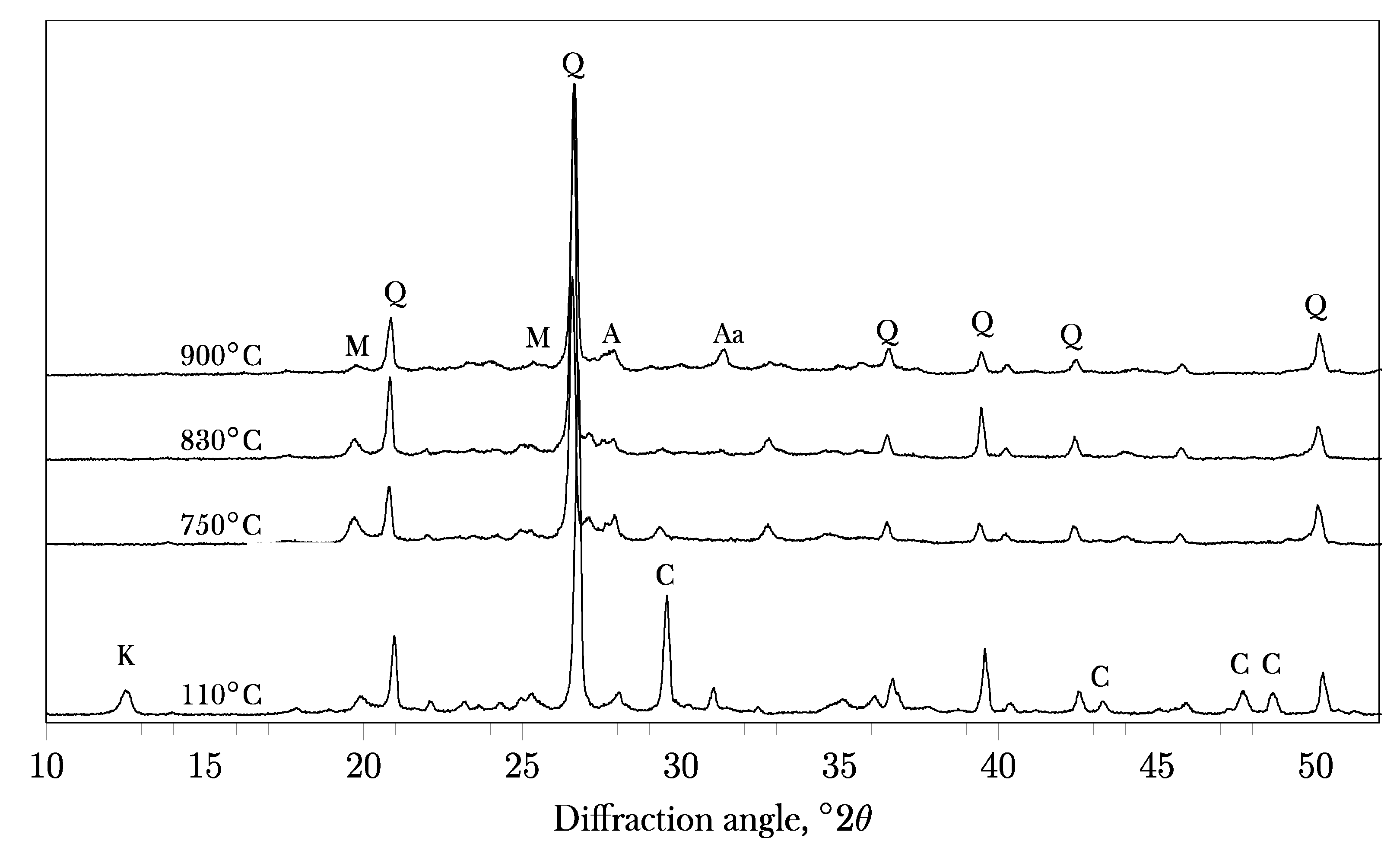
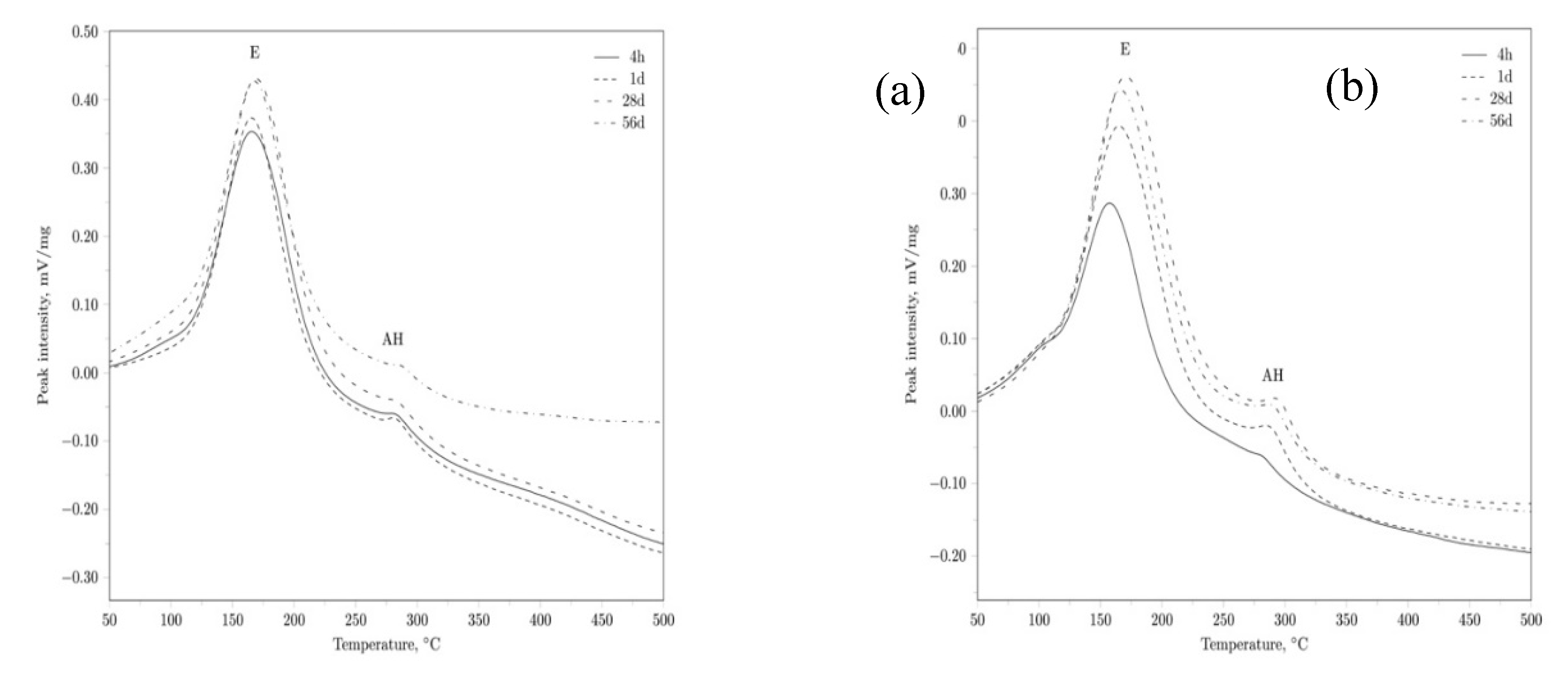
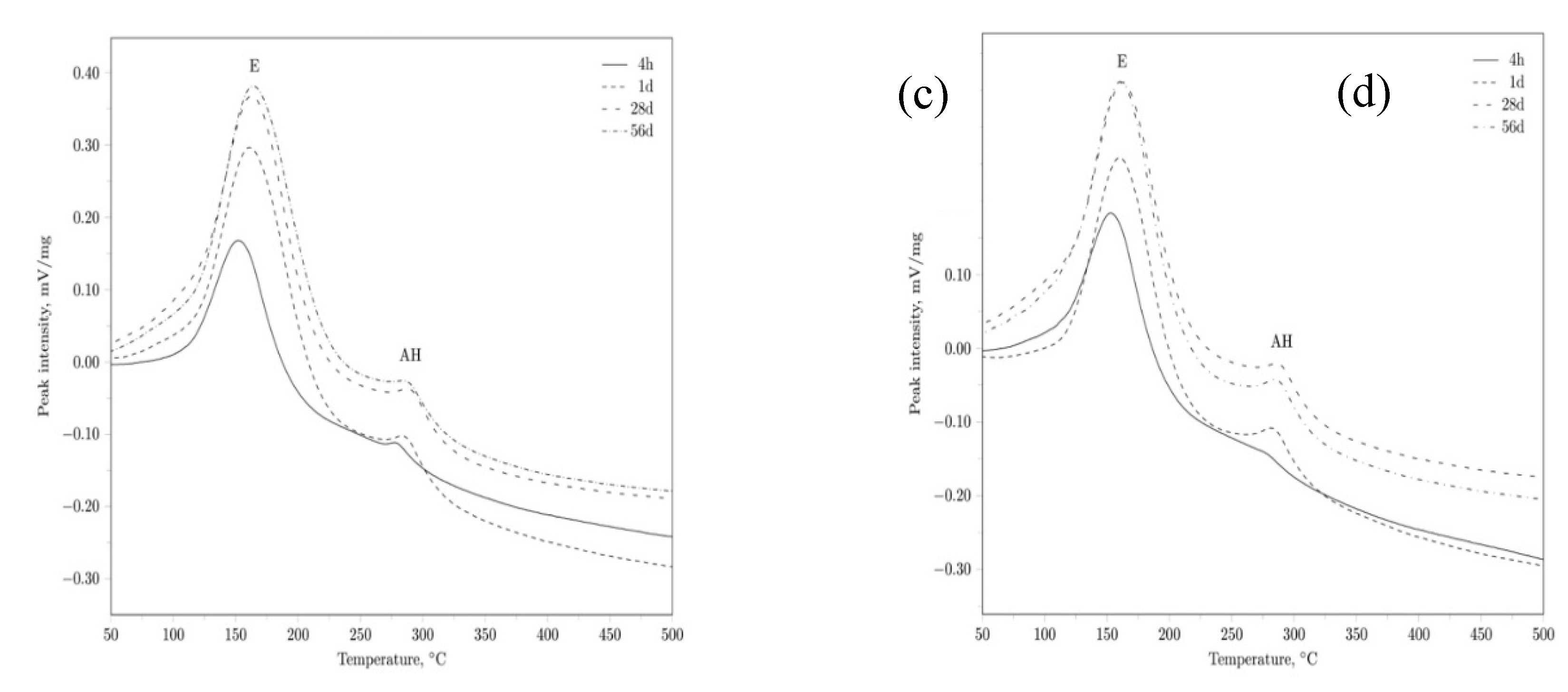
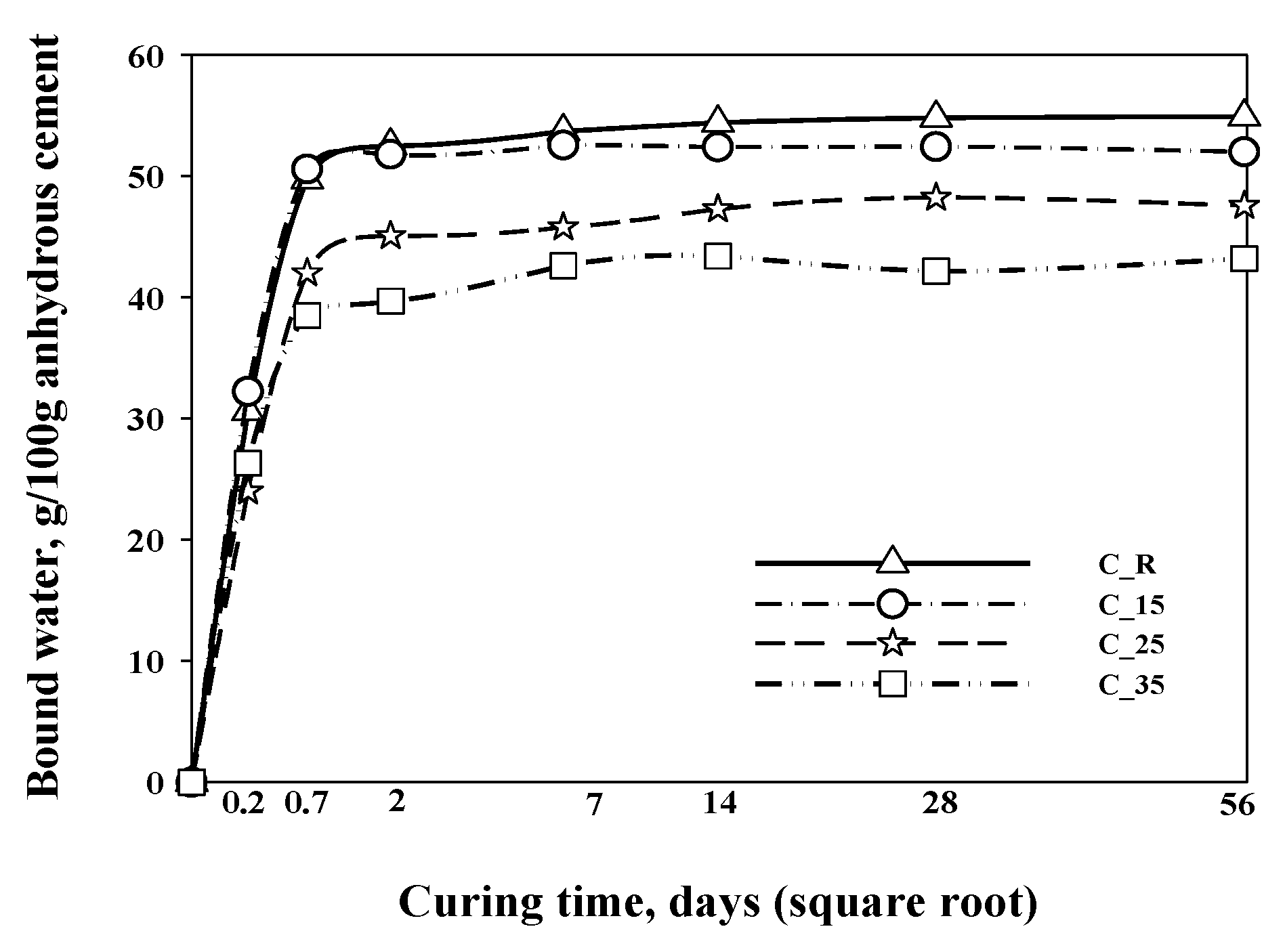
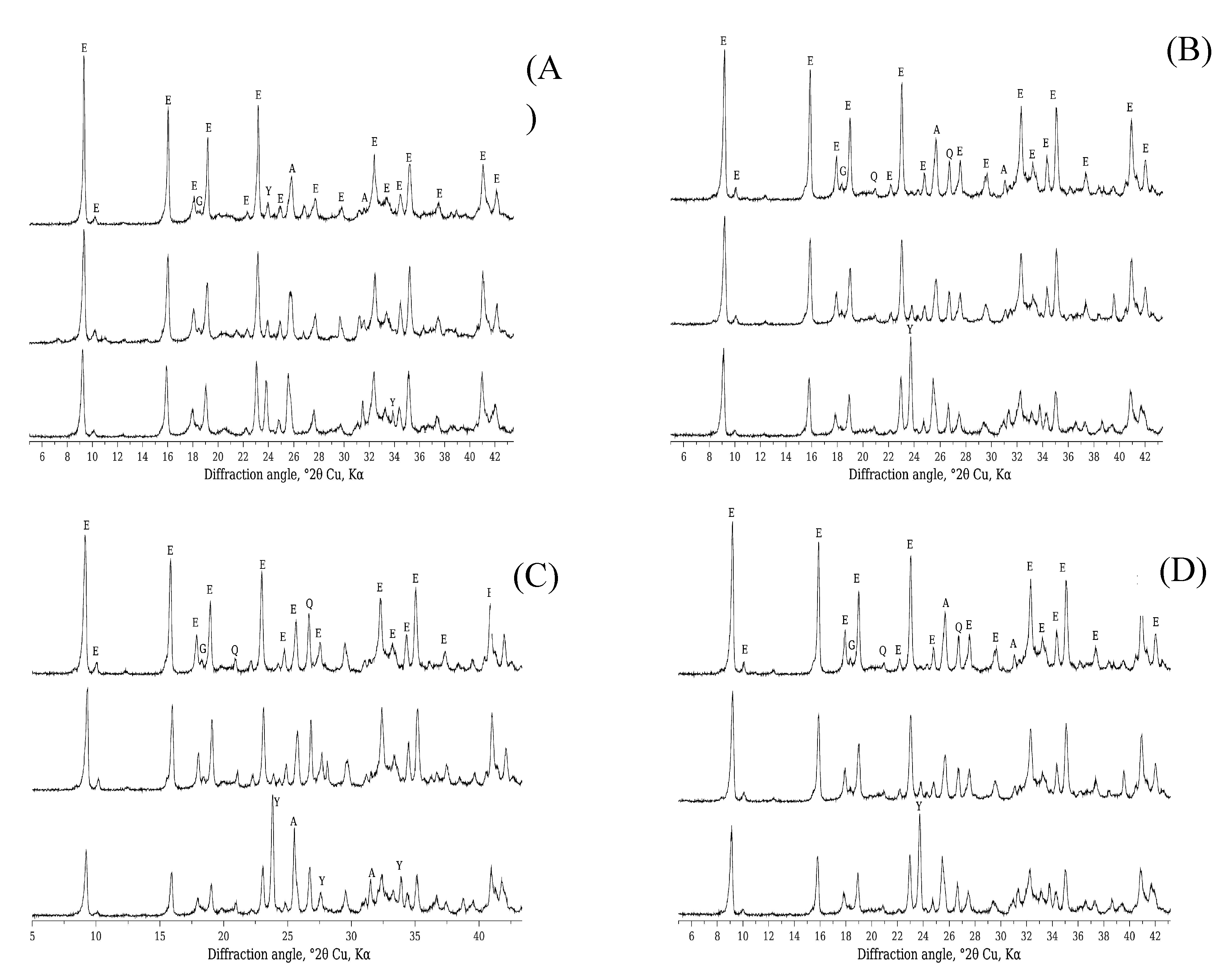
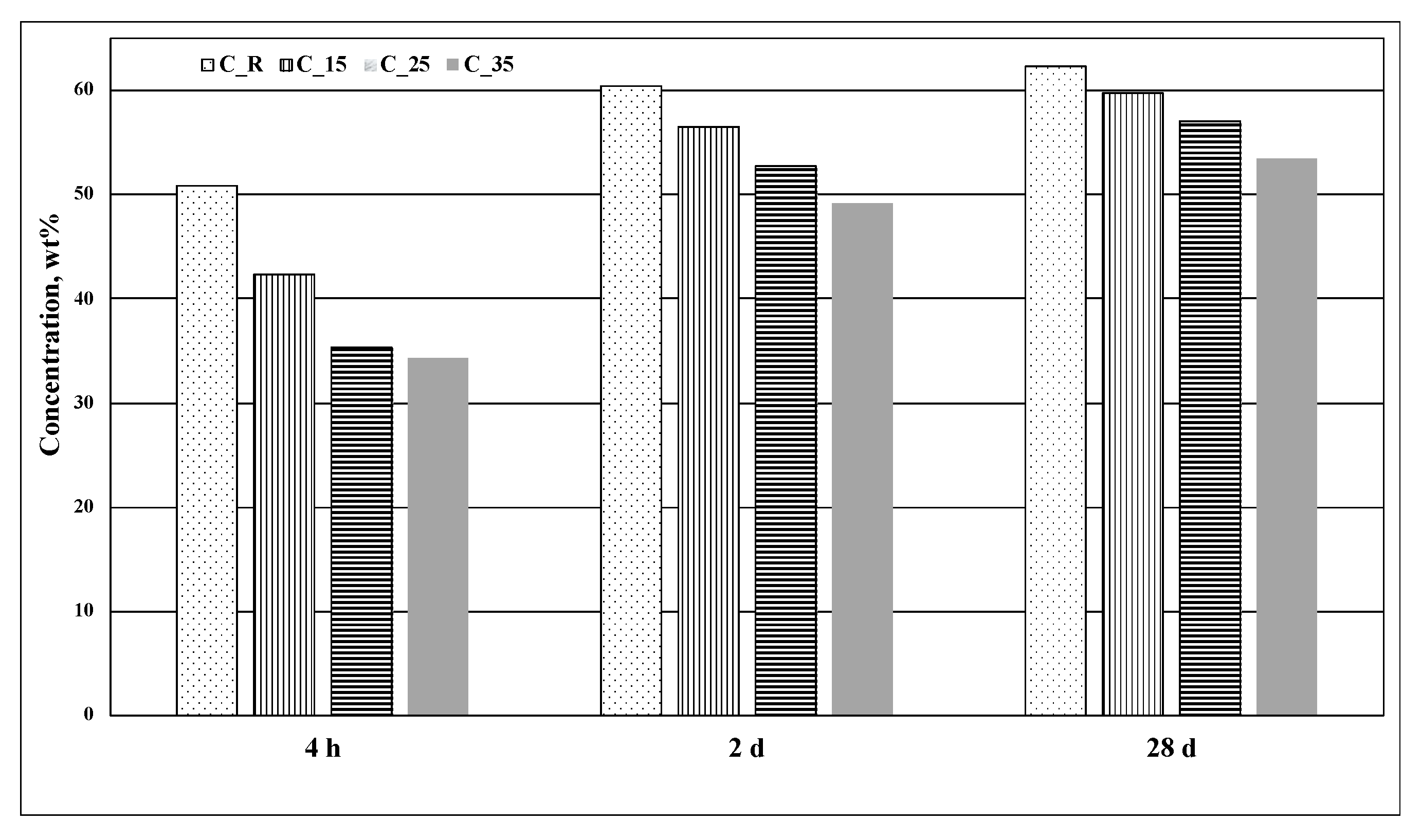
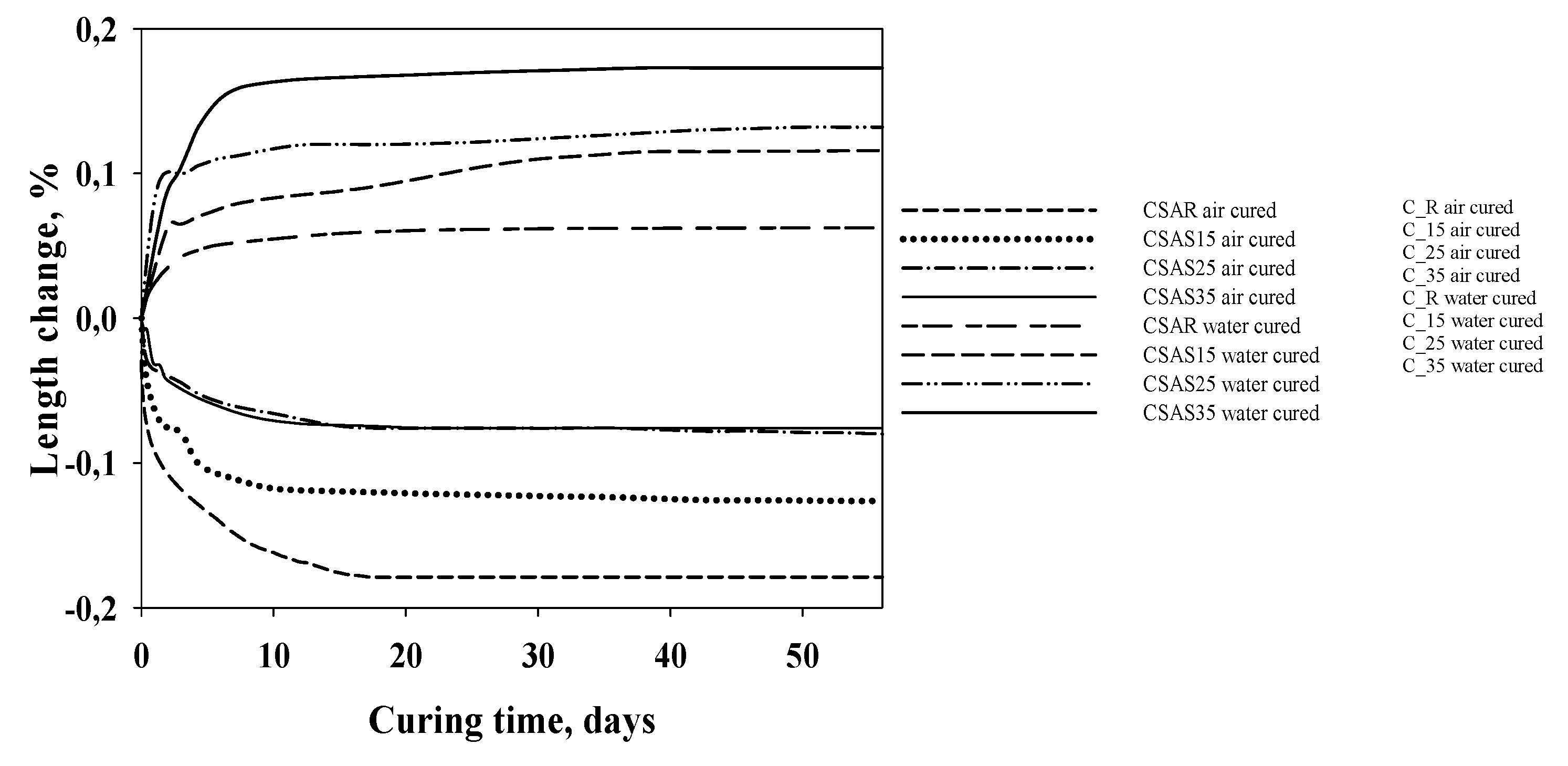
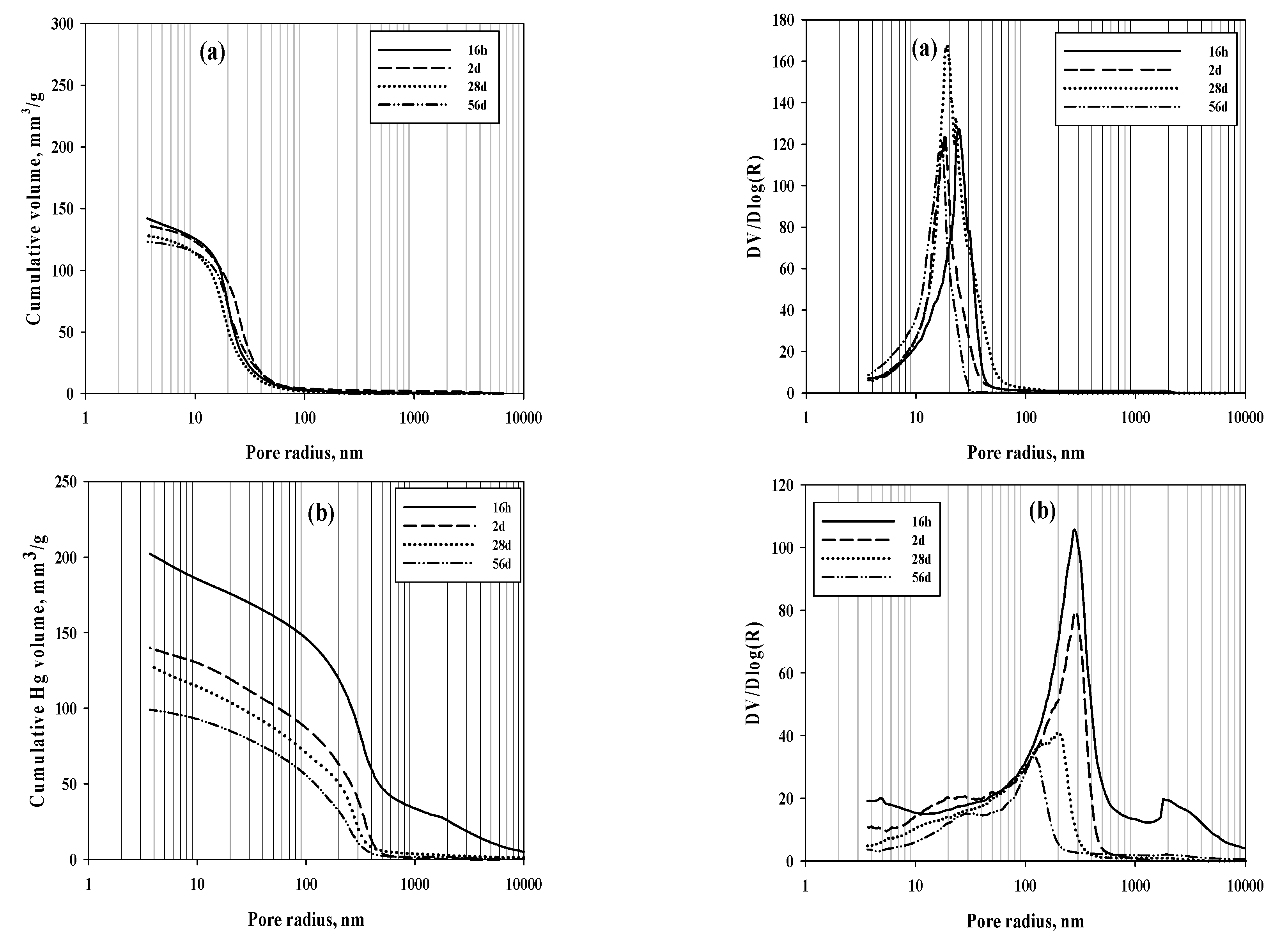
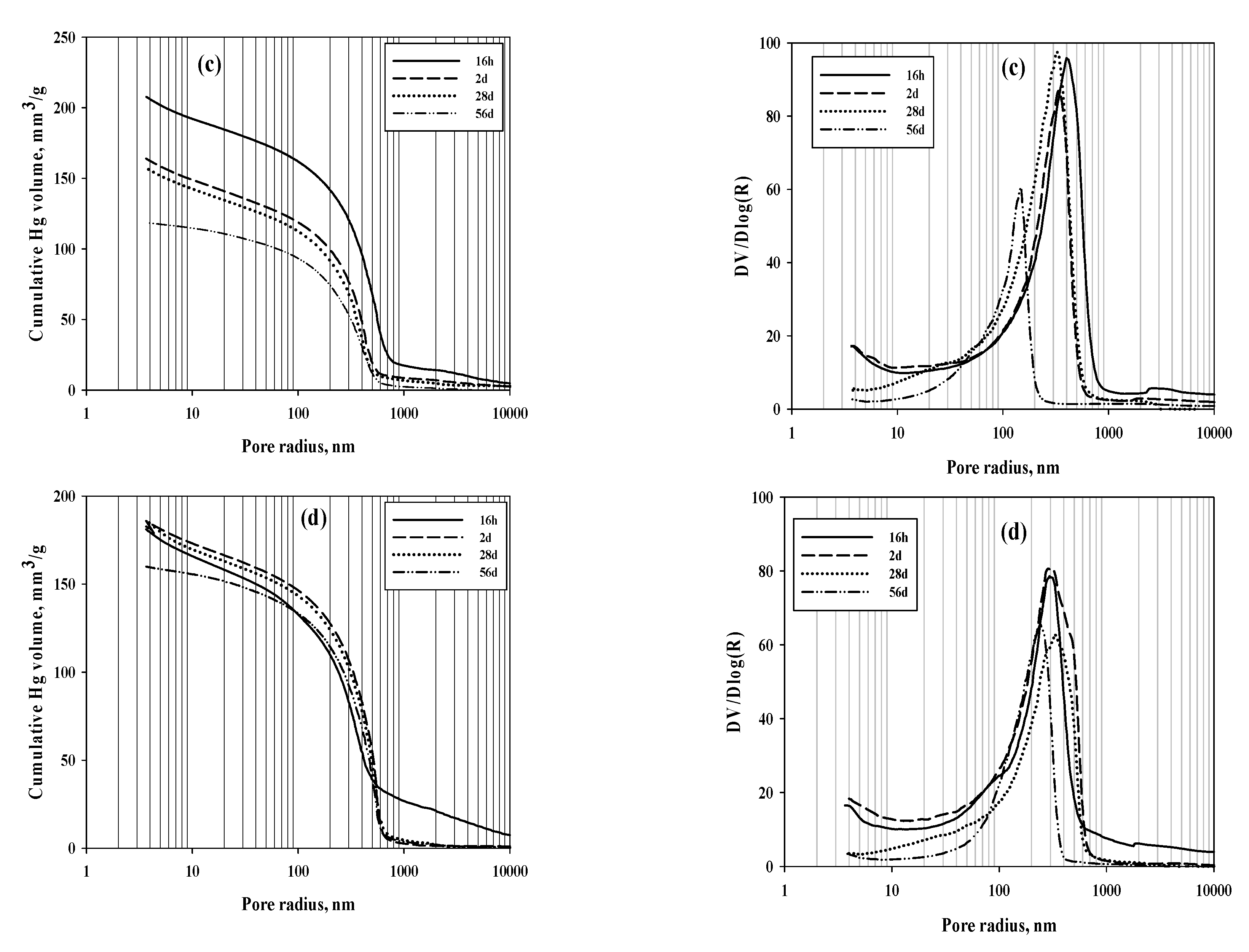
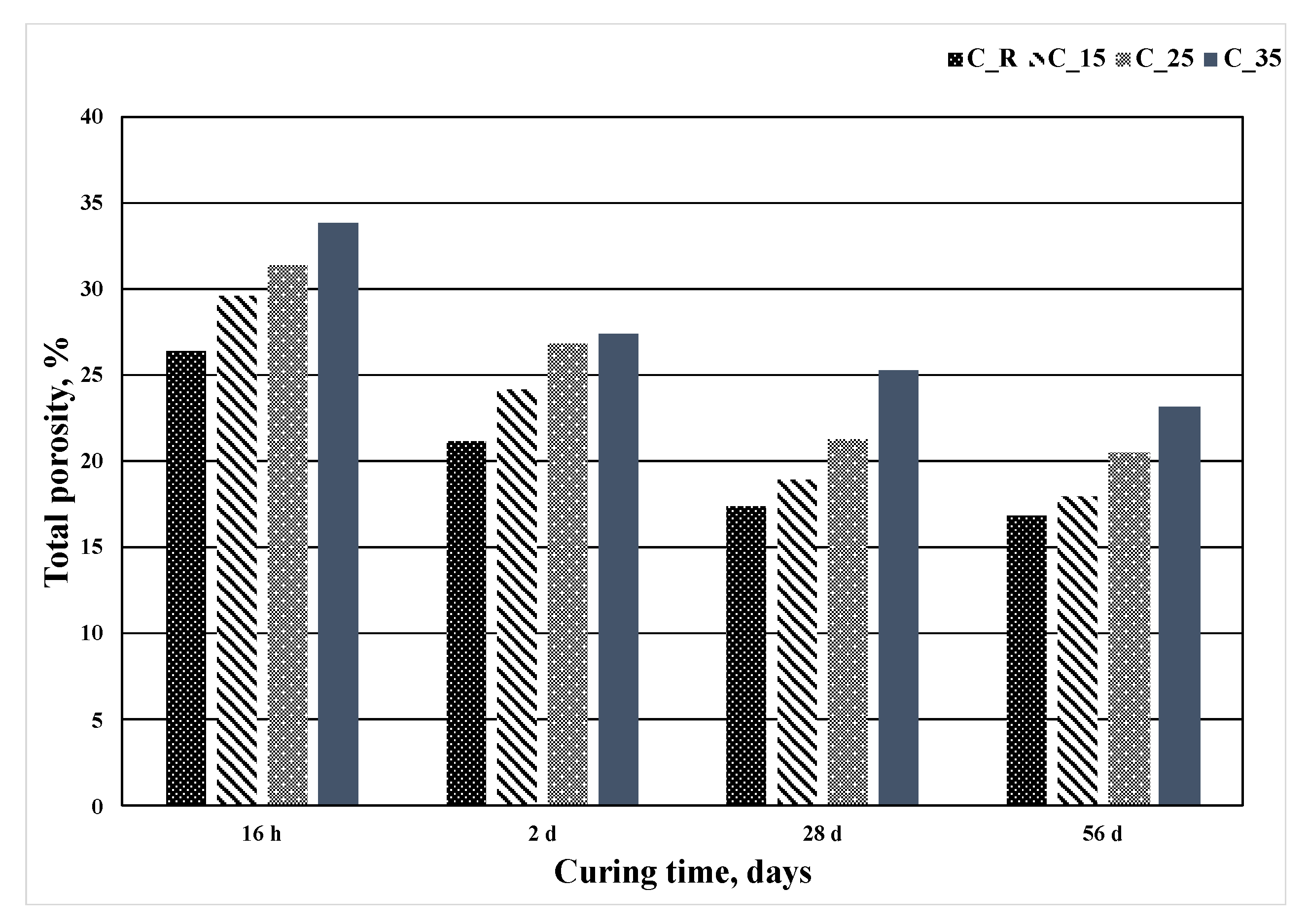
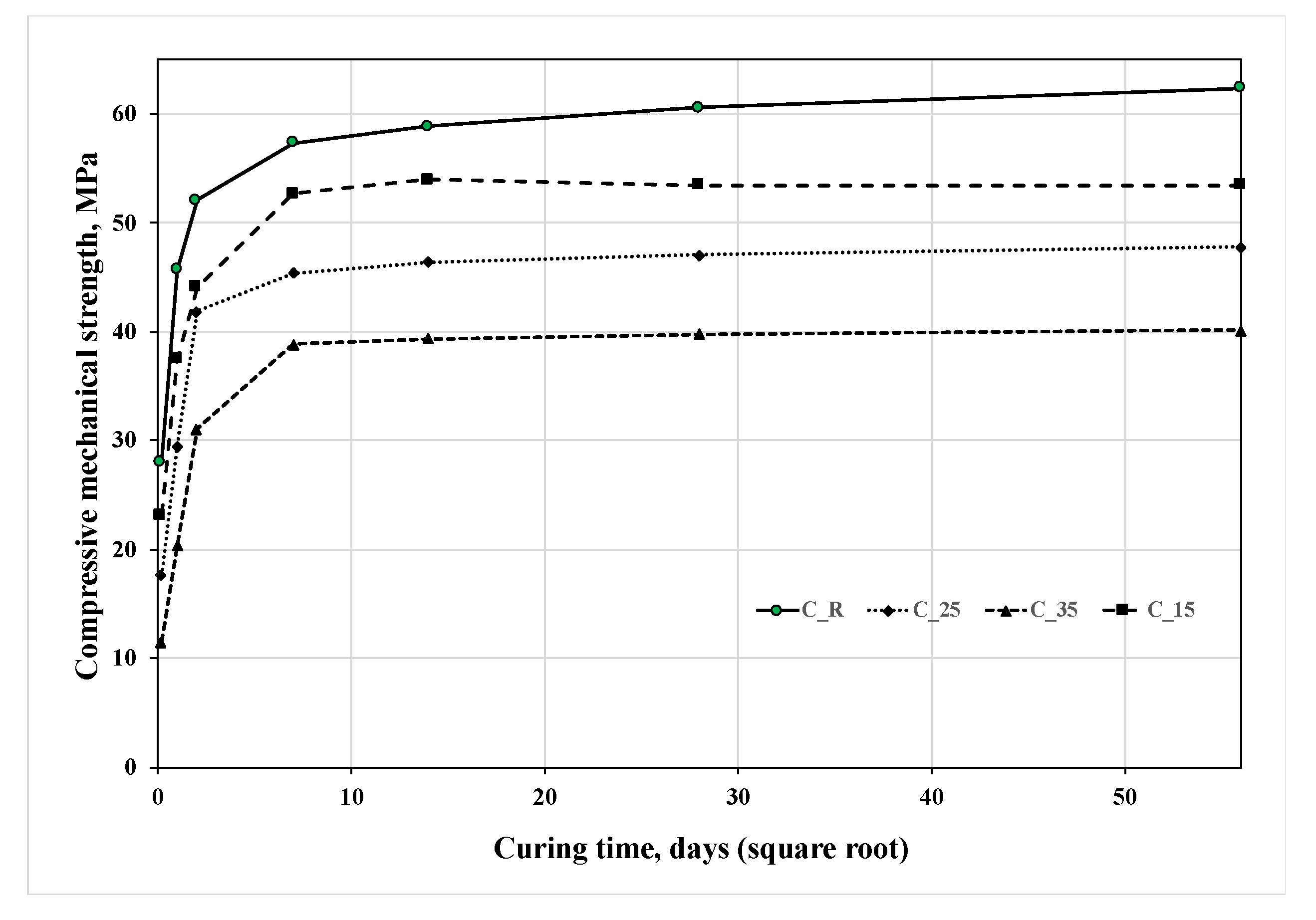
3. Results
4. Concluding remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Telesca, A.; Ibris, N.; Marroccoli, M. Use of Potabilized Water Sludge in the Production of Low-Energy Blended Calcium Sulfoaluminate Cements. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cembureau; Activity report 2022. Cembureau; The European Cement Association, 2022.
- IEA. 2023. Available online: https://www.iea.org/data-and-statistics/charts/direct-emissions-intensity-of-cement-production-in-the-net-zero-scenario-2015-2030, 2022 (accessed on 24 November 2023).
- Barcelo, L.; Kline, J.; Walenta, G.; Gartner, E. Cement and carbon emissions. Mater. Struct. 2014, 47, 1055–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M. The cement industry on the way to a low-carbon future. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 124, 105792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Qu, B.; Provis, J.L. Recent progress in low-carbon binders. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 122, 227–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartner, E.; Sui, T. Alternative cement clinkers. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 114, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tregambi, C.; Solimene, R.; Montagnaro, F.; Salatino, P.; Marroccoli, M.; Ibris, N.; Telesca, A. Solar-driven production of lime for ordinary Portland cement formulation. Sol. Energy 2018, 173, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartner, E.; Hirao, H. A review of alternative approaches to the reduction of CO2 emissions associated with the manufacture of the binder phase in concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 78, 126–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juenger, M.C.G.; Winnefeld, F.; Provis, J.L.; Ideker, J.H. Advances in alternative cementitious binders. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 1232–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dung, N.T.; Unluer, C. Advances in the hydration of reactive MgO cement blends incorporating different magnesium carbonates. Constr. Build. Mat. 2021, 294, 123573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaunsali, P.; Vaishnav, K. Calcium-sulfoaluminate-belite cements: opportunities and challenge. The Indian Concr. J. 2020, 94, 18–25. [Google Scholar]
- Gastaldi, D.; Bertola, F.; Irico, S.; Paul, G.; Canonico, F. Hydration behavior of cements with reduced clinker factor in mixture with sulfoaluminate binder. Cem. Concr. Res. 2021, 139, 106261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boháč, M.; Staněk, T.; Zezulová, A.; Rybová, A.; Kubátová, D.; Novotný, R. Early Hydration of Activated Belite-Rich Cement. Adv. Mat. Res. 2019, 1151, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, G.; Marroccoli, M.; Nobili, M.; Telesca, A.; Valenti, G.L. The use of oil well-derived drilling waste and electric arc furnace slag as alternative raw materials in clinker production. Res. Cons. Rec. 2007, 52, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adolfsson, D.; Menad, N.; Viggh, E.; Bjorkman, B. Steelmaking slags as raw material for sulphoaluminate belite cement. Adv.Cem. Res. 2007, 19, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juenger, M.C.G.; Snellings, R.; Bernal, S.A. Supplementary cementitious materials: New sources, characterization, and performance insights. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 122, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snellings, R.; Suraneni, P.; Skibsted, J. Future and emerging supplementary cementitious materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2023, 173, 107199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telesca, A.; Marroccoli, M.; Tomasulo, M.; Valenti, G.L.; Dieter, H.; Montagnaro, F. Low-CO2 Cements from Fluidized Bed Process Wastes and Other Industrial By-Products. Comb. Sci. Tech. 2016, 188, 492–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telesca, A.; Marroccoli, M.; Pace, M.L.; Tomasulo, M.; Valenti, G.L.; Monteiro, P.J.M. A hydration study of various calcium sulfoaluminate cements. Cem. Concr. Comp. 2014, 53, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, M.K.; Rahul, A.V.; De Schutter, G.; Van Tittelboom, K. Early age hydration, rheology and pumping characteristics of CSA cement-based 3D printable concrete. Constr. Build. Mat. 2021, 275, 122136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirtoli, D.; Wyrzykowski, M.; Riva, P.; Tortelli, S.; Marchi, M.; Lura, P. Shrinkage and creep of high-performance concrete based on calcium sulfoaluminate cement. Cem. Concr. Comp. 2019, 98, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimraksa, K.; Chindaprasirt, P. 14 - sulfoaluminate cement-based concrete. In Eco-Efficient Repair and Rehabilitation of Concrete Infrastructures; Pacheco-Torgal, F., Melchers, R.E., Shi, X., Belie, N.D., Tittelboom, K.V., S´aez, A., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing, 2018; pp. 355–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertola, F.; Gastaldi, D.; Irico, S.; Paul, G.; Canonico, F. Influence of the amount of calcium sulfate on physical/mineralogical properties and carbonation resistance of CSA-based cements. Cem. Concr. Res. 2022, 151, 106634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Ye, H.; Yuan, Q.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Zhou, D. Factors influencing the hydration, dimensional stability, and strength development of the OPC-CSA-Anhydrite ternary system. Mat. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Okoronkwo, M.U.; Kumar, A.; Ma, H. Durability of calcium sulfoaluminate cement concrete. J. Zhejiang Univ. - Sci. 2020, 21, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I.A.; Hargis, C.W.; Juenger, M.C.G. Understanding expansion in calcium sulfoaluminate-belite cements. Cem. Concr. Res. 2012, 42, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhan, S.; Tang, X.; Xu, Q.; Qian, K. Pore Solution Chemistry of Calcium Sulfoaluminate Cement and Its Effects on Steel Passivation. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobili, A.; Belli, A.; Giosué, C.; Telesca, A.; Marroccoli, M.; Tittarelli, F. Calcium sulfoaluminate, geopolimeric, and cementitious mortars for structural applications. Environments 2017, 4, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiventerä, J.; Piekkari, K.; Isteri, V.; Ohenoja, K.; Tanskanen, P.; Illikainen, M. Solidification/stabilization of gold mine tailings using calcium sulfoaluminate-belite cement. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 239, 118008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ao, Y.; Rahul, A.V.; Mohan, M.K.; De Schutter, G; Van Tittelboom, K. Recent progress and technical challenges in using calcium sulfoaluminate (CSA) cement. Cem. Concr. Comp. 2023, 137, 104908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, L.; Coffetti, D.; Crotti, E. An holistic approach to a sustainable future in concrete construction. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 442, 012024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Wang, W.; Mao, Y.; Yuan, X.; Song, Z.; Sun, J.; Zhao, X. Comparative life cycle assessment of sulfoaluminate clinker production derived from industrial solid wastes and conventional raw materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 116, 1314–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marroccoli, M.; Montagnaro, F.; Telesca, A.; Valenti, G.L. Environmental implications of the manufacture of calcium sulfoaluminate-based cements. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Sustainable Construction Materials and Technologies, Ancona, Italy, 28–30 June 2010; Zachar, J., Claisse, P., Naik, T.R., Ganjiam, E., Eds.; UWM Center for By-Products Utilization: Milwaukee, WI, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- El-Alfi, E.A.; Gado, R.A. Preparation of calcium sulfoaluminate-belite cement from marble sludge waste. Constr. Build. Mat. 2016, 113, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isteri, V.; Ohenoja, K.; Hanein, T.; Kinoshita, H.; Tanskanen, P.; Illikainen, M.; Fabritius, T. Production and properties of ferrite-rich CSAB cement from metallurgical industry residues. Sci. Tot. Env. 2020, 712, 136208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I.A.; Juenger, M.C.G. Incorporation of coal combustion residuals into calcium sulfoaluminate-belite cement clinkers. Cem. Concr. Comp. 2012, 34, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isteri, V.; Ohenoja, K.; Hanein, T.; Kinoshita, H.; Kletti, H.; R¨oßler, C.; Tanskanen, P.; Illikainen, M.; Fabritius, T. Ferritic calcium sulfoaluminate belite cement from metallurgical industry residues and phosphogypsum: clinker production, scale-up, and microstructural characterisation. Cem: Concr. Res. 2022, 154, 106715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telesca, A.; Marroccoli, M.; Winnefeld, F. Synthesis and characterization of calcium sulfoaluminate cements produced by different chemical gypsums. Adv. Cem. Res. 2019, 31, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telesca, A.; Matschei, T.; Marroccoli, M. Study of eco-friendly belite-calcium sulfoaluminate cements obtained from special wastes. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluccio, S.; Beirau, T.; Pollmann, H. Maximization of the reuse of industrial residues for the production of eco-friendly CSA-belite clinker. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 208, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Qian, J.; Chai, J.; Fan, Y. Calcium sulphoaluminate cements made with phosphogypsum: production issues and material properties. Cem. Concr. Res. 2014, 48, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marroccoli, M.; Pace, M.L.; Telesca, A.; Valenti, G.L. Synthesis of calcium sulfoaluminate cements from Al2O3-rich by-products from aluminium manufacture. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Sustainable Construction Materials and Technologies, Ancona, Italy, 28–30 June 2010; Zachar, J., Claisse, P., Naik, T.R., Ganjiam, E., Eds.; UWM Center for By-Products Utilization: Milwaukee, WI, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Arjunan, P.; Silsbee, M.R.; Roy, D.M. Sulfoaluminate-belite cement from low-calcium fly ash and sulfur-rich and other industrial by-products. Cem. Concr. Res. 1999, 29, 1305–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Maté, M.; De la Torre, A.G.; Leon-Reina, L.; Aranda, M.A.G.; Santacruz, I. Hydration studies of calcium sulfoaluminate cements blended with fly ash. Cem. Concr. Res. 2013, 54, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargis, C.W.; Telesca, A.; Monteiro, P.J.M. Calcium sulfoaluminate (Ye'elimite) hydration in the presence of gypsum, calcite, and vaterite. Cem. Concr. Res. 2014, 65, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukas, H.J.; Winnefeld, F.; Tschopp, E.; Müller, C.J.; Lothenbach, B. Influence of fly ash on the hydration of calcium sulfoaluminate cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2017, 95, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.H.J.; Winnefeld, F.; Müller, C.J.; Lothenbach, B. Contribution of limestone to the hydration of calcium sulfoaluminate cement. Cem. Concr. Comp. 2015, 62, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier-Chaignat, L.; Winnefeld, F.; Lothenbach, B.; Müller, C.J. Beneficial use of limestone filler with calcium sulfoaluminate cement. Constr. Build. Mat. 2012, 26, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertola, F.; Gastaldi, D.; Canonico, F.; Paul, G. CSA and slag: Towards CSA composite binders. Adv. Cem. Res. 2019, 31, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.N.; Seo, J.; Kim, S.; Lee, H.K.; Park, S. Hydration of calcium sulfoaluminate cement blended with blast-furnace slag. Const. Build. Mater. 2021, 268, 121214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Zhang, Z.; Meng, Y.; Tang, J.; Yang, L. Effect of Flue Gas Desulfurization Gypsum on the Properties of Calcium Sulfoaluminate Cement Blended with Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag. Materials 2021, 14, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Ki_Young, Y.S.; Kang, C.; Lee, T.-K. Development of Eco-Friendly Cement Using a Calcium Sulfoaluminate Expansive Agent Blended with Slag and Silica Fume. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anger, B.; Moulin, I.; Commene, J.P.; Thery, F.; Levacher, D. Fine-grained reservoir sediments: an interesting alternative raw material for Portland cement clinker production. Eur. J. Env. Civ. Eng 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, A.; Smith, A.; Coudray, C.; Anger, B.; Colina, H.; Moulin, I.; Thery, F. Ability of Two Dam Fine-Grained Sediments to be Used in Cement Industry as Raw Material for Clinker Production and as Pozzolanic Additional Constituent of Portland-Composite Cement. Waste Biom. Val. 2017, 8, 2141–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snellings, R.; Cizer, Ö.; Horckmans, L.; Durdziński, P.T.; Dierckx, P.; Nielsen, P.; Van Balen, K.; Vandewalle, L. Properties and pozzolanic reactivity of flash calcined dredging sediments. App. Clay Sci. 2016, 129, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, S. Processing effect and reactivity assessment of artificial pozzolans obtained from clays and clay wastes: A review. Constr. Build. Mat. 2017, 140, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, H.F.W. Cement Chemistry, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1997; p. 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





