Submitted:
08 January 2024
Posted:
11 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Proximate Composition
2.2.5. Date Pomace Extracts Preparation
2.2.6. Total Phenolic Content (TPC) Determination
2.2.7. Total Flavonoid Determination
2.2.8. Antioxidant Activity Determinations
DPPH Scavenging Activity
ABTS Radical Scavenging Capacity
2.2.9. Simulated In Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion
Recovery Index and Bio-Accessibility Index
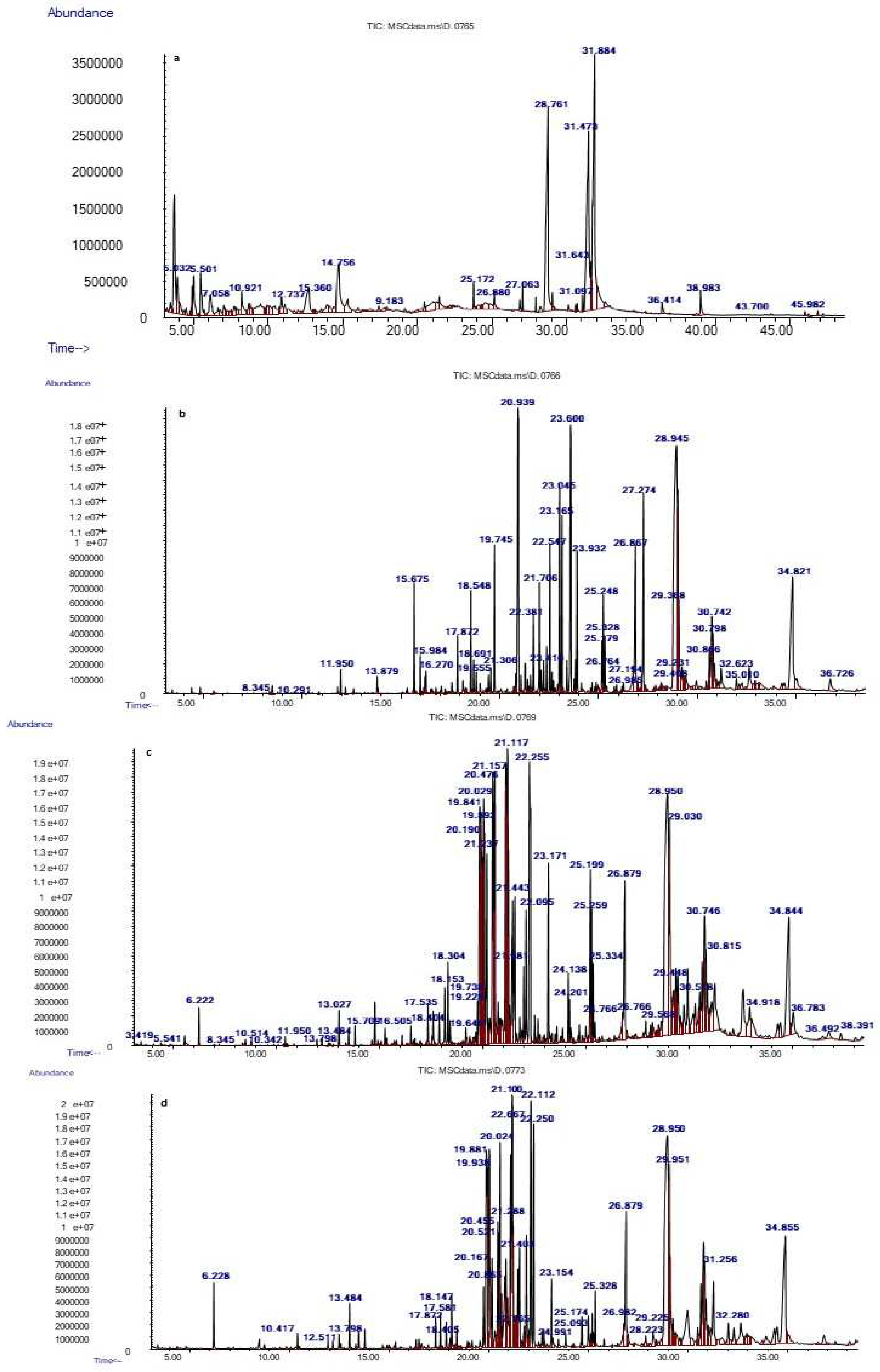
2.2.10. GC-MS Analysis of Date Pomace
2.2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Chemical Composition
3.2. Effect of the Extraction Solvent on Total Phenolic, Total Flavonoids, and Antioxidant Activity of Ruzeiz Date Pomace Powder
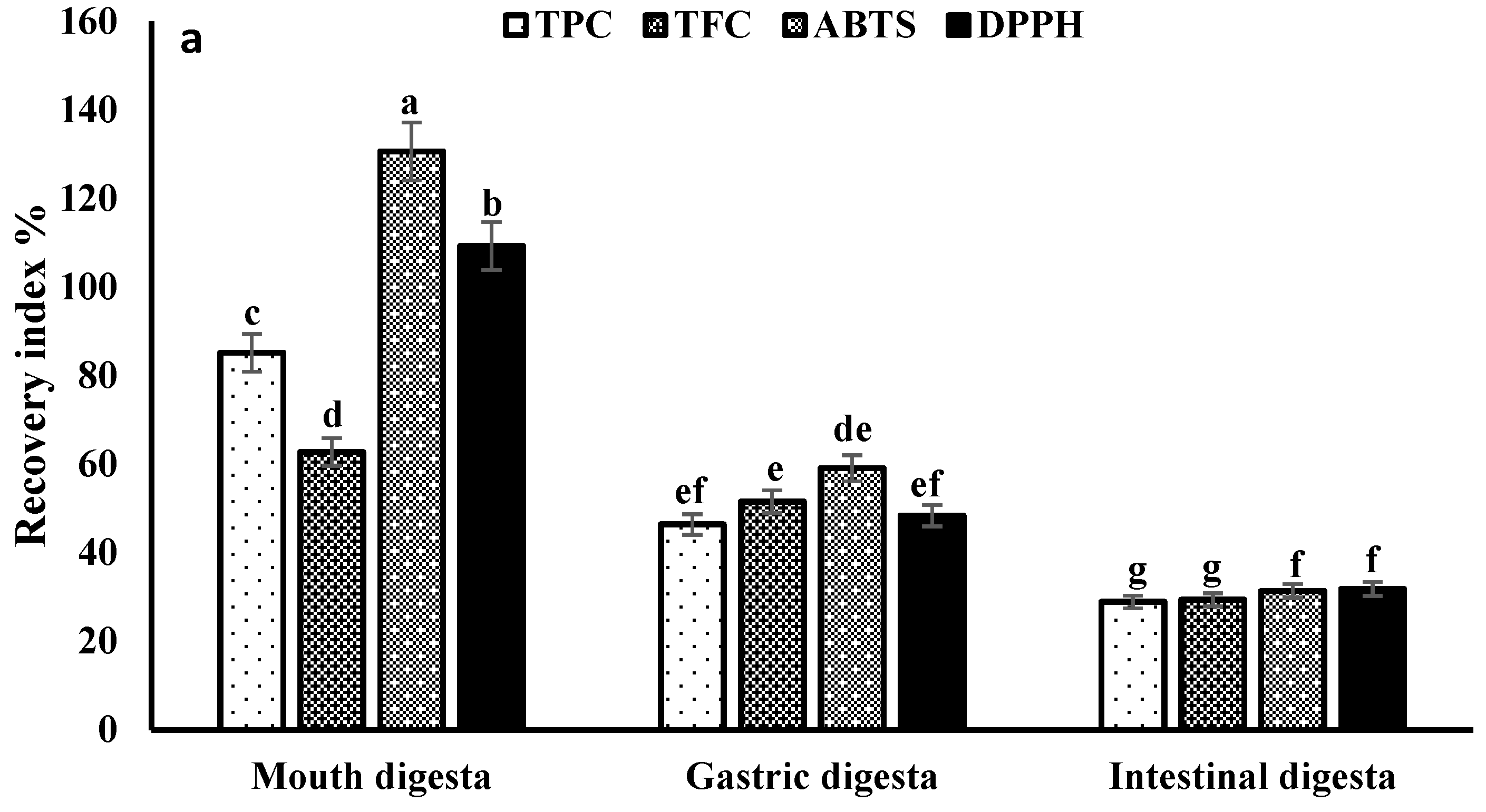
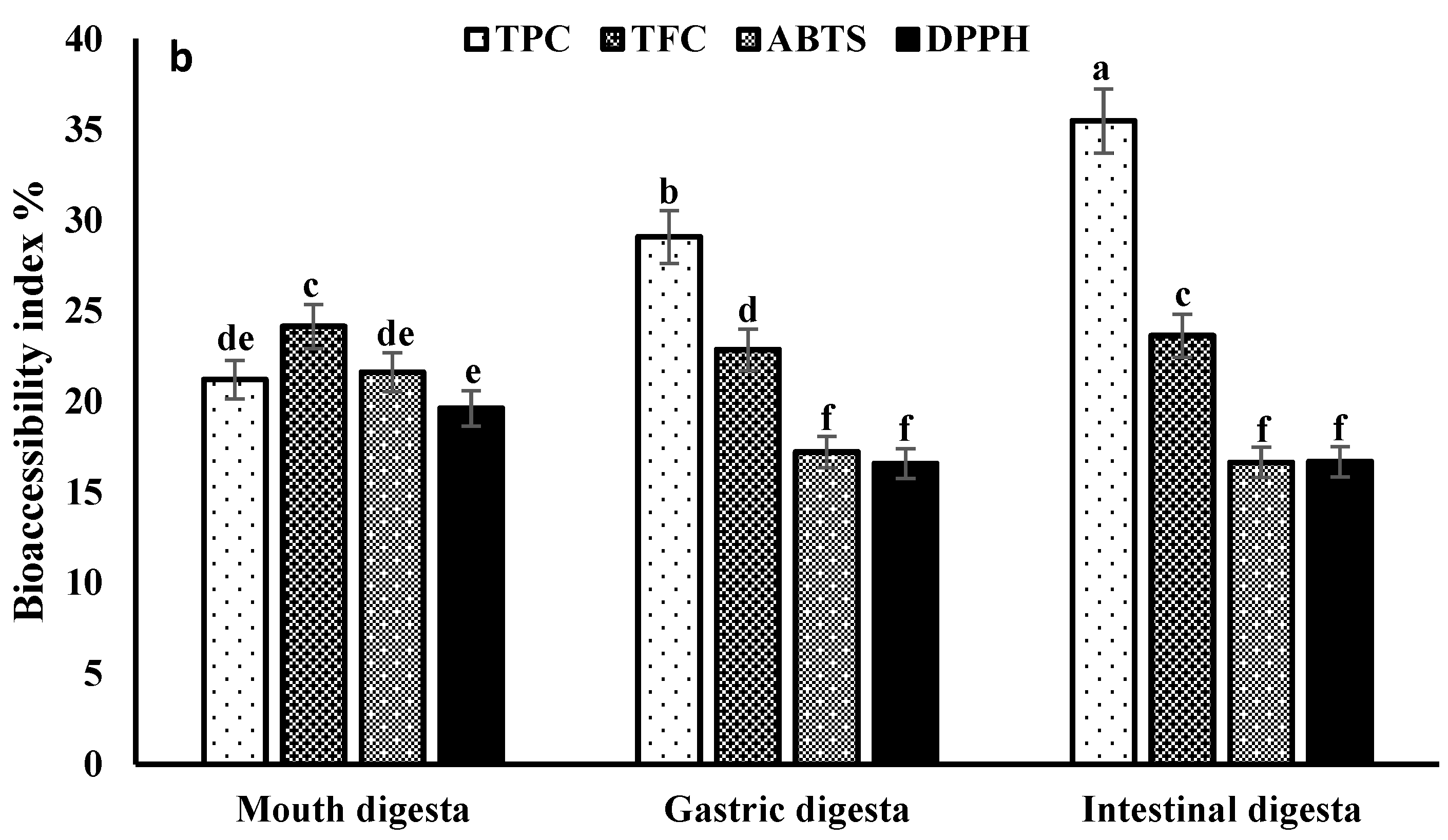
3.3. Recovery and Bio-Accessibility Index
3.4. Bioactive Compounds Stability during In Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion
3.5. Correlation between TPC, TFC, and Antioxidant Activity
3.6. Identification of RDPC Powder Phenolic Compounds during Simulated In Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion
4. Discussion
Author Declarations
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tengberg, M. Beginnings and early history of date palm garden cultivation in the Middle East. J. Arid. Environ. 2012, 86, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, S.; Khalid, N.; Khan, R.S.; Ahmed, H.; Ahmad, A. A review on chemistry and pharmacology of Ajwa date fruit and pit. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 63, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Hamid, N.A.; Mustaffer, N.H.; Maulidiani, M.; Mediani, A.; Ismail, I.S.; Tham, C.L.; Shadid, K.; Abas, F. Quality evaluation of the physical properties, phytochemicals, biological activities and proximate analysis of nine Saudi date palm fruit varieties. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2020, 19, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrabet, A.; Hammadi, H.; Rodríguez-Gutiérrez, G.; Jiménez-Araujo, A.; Sindic, M. Date palm fruits as a potential source of functional dietary fiber: A review. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2019, 25, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, A.A.; Awadelkarem, A.M.; Hossain, A.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Fawzi, M.; Ashraf, S.A. Nutritional assessment of different date fruits (Phoenix dactylifera L.) varieties cultivated in Hail province, Saudi Arabia. Biosci. Biotechnol. Res. Commun. 2018, 11, 10–21786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harrasi, A.; Rehman, N.U.; Hussain, J.; Khan, A.L.; Al-Rawahi, A.; Gilani, S.A.; Al-Broumi, M.; Ali, L. Nutritional assessment and antioxidant analysis of 22 date palm (Phoenix dactylifera) varieties growing in Sultanate of Oman. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2014, 7, S591–S598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarie, A.A.; Hassan, A.B.; Alshammari, G.M.; Yahya, M.A.; Osman, M.A. Date Industry by-Product: Date Seeds (Phoenix dactylifera L.) as Potential Natural Sources of Bioactive and Antioxidant Compounds. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echegaray, N.; Gullón, B.; Pateiro, M.; Amarowicz, R.; Misihairabgwi, J.M.; Lorenzo, J.M. Date fruit and its by-products as promising source of bioactive components: A review. Food Rev. Int. 2023, 39, 1411–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqarni, M.M.; Osman, M.A.; Al-Tamimi, D.S.; Gassem, M.A.; Al-Khalifa, A.S.; Al-Juhaimi, F.; Mohamed Ahmed, I.A. Antioxidant and antihyperlipidemic effects of Ajwa date (Phoenix dactylifera L.) extracts in rats fed a cholesterol-rich diet. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuras, M.J.; Zielińska-Pisklak, M.; Duszyńska, J.; Jabłońska, J. Determination of the elemental composition and antioxidant properties of dates (Phoenix dactyliferia) originated from different regions. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 2828–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarie, A.A.; Osman, M.A.; Alshammari, G.M.; Hassan, A.B.; Yagoub, A.E.A.; Yahya, M.A. Saudi date cultivars' seed extracts inhibit developing hepatic steatosis in rats fed a high-fat diet. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 30, 103732. [Google Scholar]
- Younas, A.; Naqvi, S.A.; Khan, M.R.; Shabbir, M.A.; Jatoi, M.A.; Anwar, F.; Inam-Ur-Raheem, M.; Saari, N.; Aadil, R.M. Functional food and nutra-pharmaceutical perspectives of date (Phoenix dactylifera L.) fruit. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Sohaimy, S.; Abdelwahab, A.; Brennan, C.S.; Aboul-Enein, A. Phenolic content, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Egyptian date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) fruits. 2015.
- Al-Sayyed, H.F.; Takruri, H.R.; Shomaf, M.S. The effect of date palm fruit (Phoenix dactylifera L.) on 7, 12-dimethylbenz (α) anthracene (DMBA)-induced mammary cancer in rats. Res. Opin. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2014, 4, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Zangiabadi, N.; Asadi-Shekaari, M.; Sheibani, V.; Jafari, M.; Shabani, M.; Asadi, A.R.; Tajadini, H.; Jarahi, M. Date fruit extract is a neuroprotective agent in diabetic peripheral neuropathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: A multimodal analysis. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2011, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Environment, M.o. Water and Agriculture, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Year book (2022).https://www.mewa.gov.sa/en/Pages/default.aspx.
- National center for palm and dates (N.c.p.d). Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.. (2018).https://www.mewa.gov.sa/en/Partners/Pages/ncpd.aspx.
- Oladzad, S.; Fallah, N.; Mahboubi, A.; Afsham, N.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Date fruit processing waste and approaches to its valorization: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 340, 125625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadum, H.; Hamid, A.; Abas, F.; Ramli, N.S.; Mohammed, A.K.S.; Muhialdin, B.J. Applications of date (Phoenix dactylifera l.) fruits as bioactive ingredients in functional foods. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 12, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, E.A.; Abdalla, I.G.; Alfawaz, M.A.; Mohammed, M.A.; Al Maiman, S.A.; Osman, M.A.; Yagoub, A.E.A.; Hassan, A.B. Effects of extraction solvents on the total phenolic content, total flavonoid content, and antioxidant activity in the aerial part of root vegetables. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Yang, S.; Huang, Y.; Huang, J.; Li, Y. Effect of in vitro gastrointestinal digestion on phenolic compounds and antioxidant properties of soluble and insoluble dietary fibers derived from hulless barley. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Aguilar, G.A.; Blancas-Benítez, F.J.; Sáyago-Ayerdi, S.G. Polyphenols associated with dietary fibers in plant foods: Molecular interactions and bioaccessibility. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2017, 13, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullon, B.; Pintado, M.E.; Fernández-López, J.; Pérez-Álvarez, J.A.; Viuda-Martos, M. In vitro gastrointestinal digestion of pomegranate peel (Punica granatum) flour obtained from co-products: Changes in the antioxidant potential and bioactive compounds stability. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 19, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouayed, J.; Hoffmann, L.; Bohn, T. Total phenolics, flavonoids, anthocyanins and antioxidant activity following simulated gastro-intestinal digestion and dialysis of apple varieties: Bioaccessibility and potential uptake. Food Chem. 2011, 128, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AOAC, B.A.M. Association of official analytical chemists. Off. Methods Anal. 1990, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Prosky, L.; Asp, N.-G.; Schweizer, T.F.; Devries, J.W.; Furda, I. Determination of insoluble, soluble, and total dietary fiber in foods and food products: Interlaboratory study. J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem. 1988, 71, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Farsi, M.A.; Lee, C.Y. Optimization of phenolics and dietary fibre extraction from date seeds. Food Chem. 2008, 108, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterhouse, A.L. Determination of total phenolics. Curr. Protoc. Food Anal. Chem. 2002, 6, I1–1. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.-O.; Jeong, S.W.; Lee, C.Y. Antioxidant capacity of phenolic phytochemicals from various cultivars of plums. Food Chem. 2003, 81, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.-T.; Wu, J.-H.; Wang, S.-Y.; Kang, P.-L.; Yang, N.-S.; Shyur, L.-F. Antioxidant activity of extracts from Acacia confusa bark and heartwood. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 3420–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thaipong, K.; Boonprakob, U.; Crosby, K.; Cisneros-Zevallos, L.; Byrne, D.H. Comparison of ABTS, DPPH, FRAP, and ORAC assays for estimating antioxidant activity from guava fruit extracts. J. Food Compost. Anal. 2006, 19, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Chi, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, B. In vitro evaluation of the bioaccessibility of phenolic acids in different whole wheats as potential prebiotics. Lwt 2019, 100, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, N.; Macià, A.; Romero, M.-P.; Reguant, J.; Motilva, M.-J. Matrix composition effect on the digestibility of carob flour phenols by an in-vitro digestion model. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.P. Identification of essential oil components by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. 5 online ed. Gruver TX USA: Texensis Publ.
- Fikry, M.; Al-Awaadah, A.; Rahman, R. Production and characterization of palm date powder rich in dietary fiber. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2021, 15, 2285–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majzoobi, M.; Karambakhsh, G.; Golmakani, M.; Mesbahi, G.; Farahnaki, A. Chemical composition and functional properties of date press cake, an agro-industrial waste. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2019, 21, 1807–1817. [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekaran, M.; Bahkali, A.H. Valorization of date palm (Phoenix dactylifera) fruit processing by-products and wastes using bioprocess technology–Review. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 20, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sharnouby, G.A.; Aleid, S.M.; Al-Otaibi, M.M. Liquid sugar extraction from date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) fruits. J. Food Process Technol. 2014, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Hashim, I.; Khalil, A. Composition and functional properties of the date fruit residue a byproduct of date syrup/Debis production. Nutr. Food Technol. 2015, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Elleuch, M.; Bedigian, D.; Roiseux, O.; Besbes, S.; Blecker, C.; Attia, H. Dietary fibre and fibre-rich by-products of food processing: Characterisation, technological functionality and commercial applications: A review. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Chua, B.L.; Chow, Y.H. An insight into the extraction and fractionation technologies of the essential oils and bioactive compounds in Rosmarinus officinalis L.: Past, present and future. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, B.; Anwar, F.; Ashraf, M. Effect of extraction solvent/technique on the antioxidant activity of selected medicinal plant extracts. Molecules 2009, 14, 2167–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, C.; Kapoor, H.C. Anti-oxidant activity and total phenolic content of some Asian vegetables. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2002, 37, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belyagoubi, L.; Belyagoubi-Benhammou, N.; Atik-Bekkara, F.; Coustard, J. Effects of extraction solvents on phenolic content and antioxidant properties of Pistacia atlantica Desf fruits from Algeria. Int. Food Res. J. 2016, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Bensaci, C.; Ghiaba, Z.; Saidi, M. Effects of extraction solvents on bound phenolic contents and antioxidant activities of Tantboucht dates (Phoenix dactylifera L.) from Algeria. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2015, 7, 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, S.; Barua, B.; Sikdar, D. Phytochemical screening, phenolic content and antioxidant activity of wild date palm (Phoenix sylvestris Roxb.) fruit extracted with different solvents. Int. Food Res. J. 2017, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Kriaa, W.; Fetoui, H.; Makni, M.; Zeghal, N.; Drira, N.-E. Phenolic contents and antioxidant activities of date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) leaves. Int. J. Food Prop. 2012, 15, 1220–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wu, H.; Liu, Z.; Barrow, C.; Dunshea, F.; Suleria, H.A. Bioaccessibility and movement of phenolic compounds from tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) during in vitro gastrointestinal digestion and colonic fermentation. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 4954–4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahama, U.; Hirota, S. Interactions of flavonoids with α-amylase and starch slowing down its digestion. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunathilake, K.; Ranaweera, K.; Rupasinghe, H. Change of phenolics, carotenoids, and antioxidant capacity following simulated gastrointestinal digestion and dialysis of selected edible green leaves. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talavera, S.; Felgines, C.; Texier, O.; Besson, C.; Lamaison, J.-L.; Rémésy, C. Anthocyanins are efficiently absorbed from the stomach in anesthetized rats. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 4178–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helal, A.; Tagliazucchi, D.; Verzelloni, E.; Conte, A. Bioaccessibility of polyphenols and cinnamaldehyde in cinnamon beverages subjected to in vitro gastro-pancreatic digestion. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 7, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullon, B.; Pintado, M.E.; Barber, X.; Fernández-López, J.; Pérez-Álvarez, J.A.; Viuda-Martos, M. Bioaccessibility, changes in the antioxidant potential and colonic fermentation of date pits and apple bagasse flours obtained from co-products during simulated in vitro gastrointestinal digestion. Food Res. Int. 2015, 78, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palafox-Carlos, H.; Ayala-Zavala, J.F.; González-Aguilar, G.A. The role of dietary fiber in the bioaccessibility and bioavailability of fruit and vegetable antioxidants. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, R6–R15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, D. Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Activity of Rice–Tartary Buckwheat Composite as Affected by In Vitro Digestion. J. Chem. 2022, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafarga, T.; Villaró, S.; Bobo, G.; Simó, J.; Aguiló-Aguayo, I. Bioaccessibility and antioxidant activity of phenolic compounds in cooked pulses. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 1816–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Deng, Z.; Tang, Y.; Chen, P.X.; Liu, R.; Ramdath, D.D.; Liu, Q.; Hernandez, M.; Tsao, R. Bioaccessibility, in vitro antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of phenolics in cooked green lentil (Lens culinaris). J. Funct. Foods 2017, 32, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.X.; Dupuis, J.H.; Marcone, M.F.; Pauls, P.K.; Liu, R.; Liu, Q.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Tsao, R. Physicochemical properties and in vitro digestibility of cooked regular and nondarkening cranberry beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) and their effects on bioaccessibility, phenolic composition, and antioxidant activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 10448–10458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bas-Bellver, C.; Barrera, C.; Betoret, N.; Seguí, L. Effect of Processing and In Vitro Digestion on Bioactive Constituents of Powdered IV Range Carrot (Daucus carota, L.) Wastes. Foods 2023, 12, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbonell-Capella, J.M.; Buniowska, M.; Esteve, M.J.; Frigola, A. Effect of Stevia rebaudiana addition on bioaccessibility of bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity of beverages based on exotic fruits mixed with oat following simulated human digestion. Food Chem. 2015, 184, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.-L.; Chen, S.-G.; Zhao, Y.-Y.; Luo, C.-X.; Li, J.; Gao, Y.-Q. Total phenolic contents of 33 fruits and their antioxidant capacities before and after in vitro digestion. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 57, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosele, J.I.; Macià, A.; Romero, M.-P.; Motilva, M.-J.; Rubió, L. Application of in vitro gastrointestinal digestion and colonic fermentation models to pomegranate products (juice, pulp and peel extract) to study the stability and catabolism of phenolic compounds. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 14, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekara, A.; Shahidi, F. Bioaccessibility and antioxidant potential of millet grain phenolics as affected by simulated in vitro digestion and microbial fermentation. J. Funct. Foods 2012, 4, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Chemical composition | Mean ± SD |
|---|---|
| Moisture | 2.51 ±0.05 |
| Ash | 1.61 ± 0.06 |
| Protein | 5.85 ± 0.16 |
| Fat | 1.40 ± 0.01 |
| fiber | 66.71± 0.44 |
| Carbohydrates | 21.72± 0.16 |
| Insoluble dietary fiber | 62.9 ± 0.2 |
| Soluble dietary fiber | 3.81 ± 0.24 |
| Acid detergent fiber (ADF) | 42.51 ± 0.33 |
| Neutral detergent fiber (NDF) | 48.1 ± 0.36 |
| Calcium | 101.39 ± 2.49 |
| Potassium | 813 ± 2.12 |
| Magnesium | 41.81 ± 7.00 |
| Manganese | 0.14 ± 14 |
| Iron | 1.25 ± 0.07 |
| Zinc | 0.5 ± 0.06 |
| Solvents | TPC | TFC | DPPH | ABTS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methanol | 79 ± 1.67a* | 10.1 ± 0.92a* | 76 ± 2.11g* | 68.7 ± 2.01f* |
| Ethanol | 70.4 ± 2.41b | 9.1 ± 0.87a | 87 ± 2.47f | 77 ± 1.52e |
| Acetone | 48.4 ± 2.48d | 5.2 ± 1.23b | 150 ± 1.32d | 253.1 ± 1.15c |
| Water | 63.6 ± 1.51c | 5.6 ± 0.68b | 102 ± 2.62e | 90.8 ± 3.43d |
| Methanol: water (50:50) | 49.5 ± 1.21d | 4.1 ± 0.89b | 215 ± 2.15c | 303.5 ± 1.92b |
| Ethanol: water (50:50) | 37.2 ± 1.85e | 2.2 ± 0.49c | 258 ± 3.96b | 297.8 ± 3.19b |
| Acetone: water (50:50) | 23.5 ± 1.36f | 1.9 ± 0.25c | 383 ± 1.64a | 367 ± 1.45a |
| Sample | Assay | Control | Mouth digest | Gastric digesta | Intestinal digesta | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PF | CSF | PF | CSF | PF | CSF | |||
| Date cake | TPC | 62.80±6.38a | 53.03±5.35bA | 14.20±3.05dB | 25.90±3.62cA | 10.73±1.04dB | 14.77±2.73dA | 8.03±1.46dB |
| TFC | 5.63±0.55a | 4.80±0.26aA | 1.53±0.35cB | 4.00±0.10bA | 1.20±0.30 dB | 2.27±0.15cA | 0.70±0.10 dB | |
| DPPH | 76.63±2.12a | 67.27±1.01bA | 16.43±1.159dB | 30.73±2.02cA | 6.30±0.78eB | 20.30±4.03dA | 4.07±1.19eB | |
| ABTS | 68.73±2.01a | 70.33±2.75aA | 19.40±0.50cB | 34.00±3.02bA | 6.60±0.26 dB | 17.80±2.55cA | 3.73±2.75dB | |
| Mouth digesta | Gastric digesta | Intestinal digesta | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPC | TFC | TPC | TFC | TPC | TFC | |
| Mouth digesta | ||||||
| DPPH | 0.982** | 0.990** | 0.967** | 0.992** | 0.888* | 0.990** |
| ABTS | 0.982** | 0.989** | 0.943** | 0.992** | 0.873* | 0.986** |
| Gastric digesta | ||||||
| DPPH | 0.994** | 0.977** | 0.940** | 0.994** | 0.833* | 0.994** |
| ABTS | 0.988** | 0.970** | 0.979** | 0.984** | 0.855* | 0.995** |
| Intestinal digesta | ||||||
| DPPH | 0.980** | 0.931** | 0.951** | 0.965** | 0.762 | 0.979** |
| ABTS | 0.953** | 0.926** | 0.914* | 0.932** | 0.805 | 0.949** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





