1. Introduction
Bladder cancer (BC) is a potentially life-threatening malignancy and considered as one of the most expensive tumors in terms of treatment and medical care (1). Several metabolic pathways are involved in BC tumorigenesis, representing potential targets for therapy (2). Recent advances in molecular understanding of urothelial cancer (UC) have led to the identification of prognostic biomarkers displaying interplay between immunity and autophagy (3, 4). While Ki-67 expression is well established prognostic proliferation biomarker in BC (5), Beclin-1 and Protein kinase B (AKT) mediated pathways have been recognized as important autophagy mediators in the development and progression of UC (6, 7)). Recently proposed biomarkers, with diagnostic and predictive relevance in BC, are interleukin–1 beta (IL-1β) and IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1RA) (8). Several studies reported IL-1RA induced restoration of autophagy process and catabolism reduction in inflammation-altered human cells, while IL-1β acts more like autophagy inhibitor, especially in cancer cells (9-11). Despite the assumed value of both the IL-1β and IL-1RA status, only little is known about their (combined) prognostic value and on their correlation to cancer proliferation (Ki-67) and autophagy markers such as AKT. Therefore, the aim of the present study was to assess the expression patterns and prognostic role of IL-1ß/IL-1RA axis in invasive BC, as well as their correlation with Ki-67 and AKT in order to gain further insight in their molecular relevance in BC.
2. Results
2.1. Patients’ Characteristics
In total, 194 subjects who underwent radical cystectomy for invasive BC were retrospectively enrolled for this study. Patients were selected in two cohorts: 102 in a discovery and 92 patients in confirmatory group. First group had a median follow-up of 44.5 months and only within this cohort correlation with AKT was examined. Correlation with Ki-67 was examined within second cohort. Both groups were comparable in terms of age, gender, pathological stage, grade and metastatic disease status. The baseline characteristics for both cohorts are shown in
Table 1.
2.2. Expression Characteristics of IL-1β and IL1RA
Mean cytoplasmic expression of IL-1β and IL-1RA in BC and surrounding benign urothelium tissue was 185 and 190 vs. 120 and 110 (p=0.0001 and 0.004), respectively.
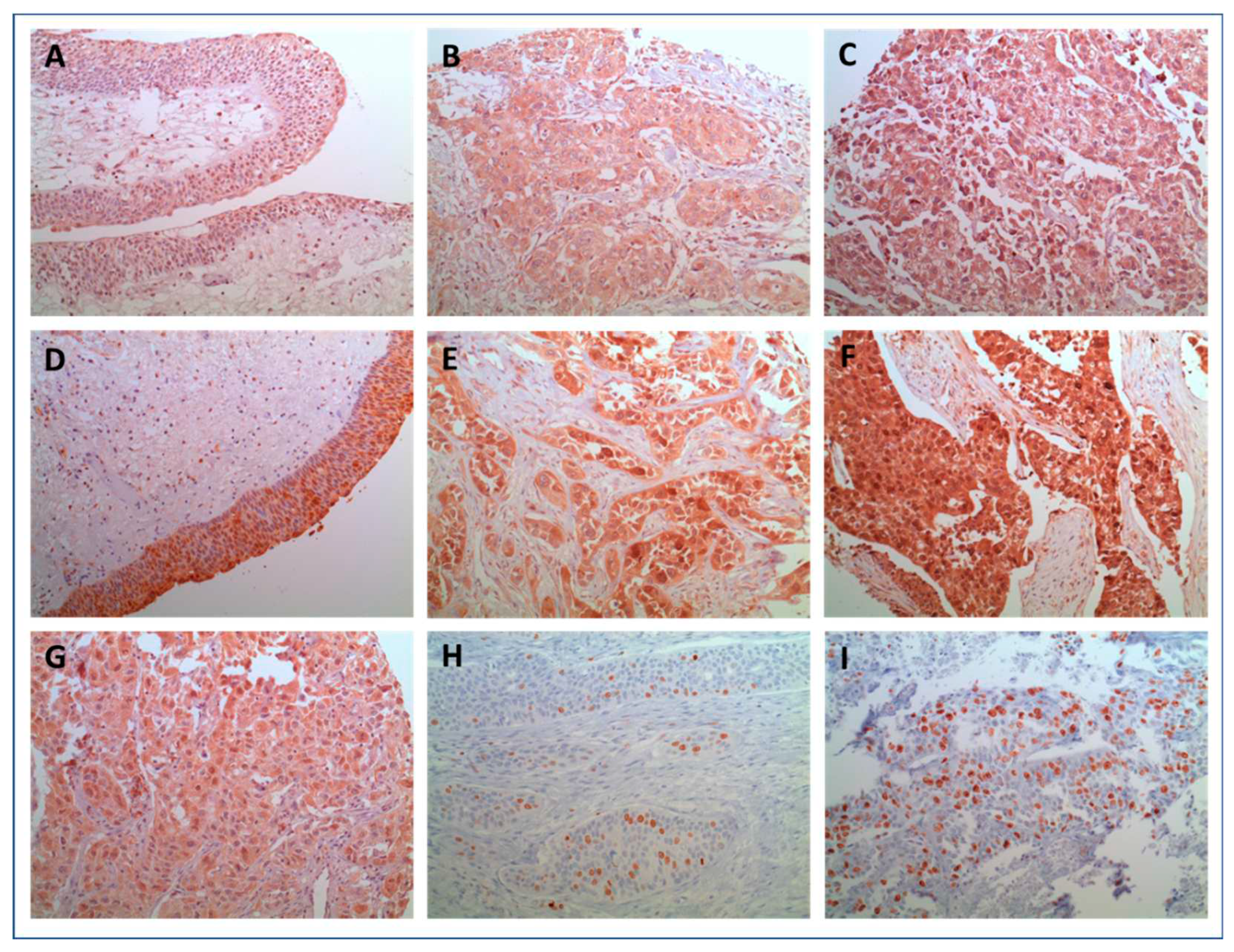
Figure 1 (A-F) shows representative histological images of IL-1β and IL-1RA expression in histopathological benign and malignant urothelium. Although heterogeneity was observed with regard to the cytoplasmatic distribution and intensity of expression in BC, staining for both, IL-1ß and IL-1RA in benign controls was predominantly of low intensity. Figure 2A and 2B Illustrate differences in intensity of IL-1 expression pattern between normal and malignant tissue. Only few benign urothelial tissues showed high expression levels of both, IL-1β (H-score: 240) and IL-1RA (H-score: 280). In summary, both, Il-1ß as well as IL-1RA were significantly overexpressed in invasive UC compared to benign urothelium (both p<0.005). These findings could be reproduced in the confirmatory cohort (all p<0.05).
2.3. Correlation of IL-1 Axis with histopathologic Parameters
Table 2 summarizes the correlation of IL-1β and IL-1RA expression with histopathologic variables in univariate analysis. Expression patterns were predictive of pathological stage (≥T2), nodal or distant metastasis (N+, M+). Strong IL-1β expression was observed in patients with vascular (210 vs. 183, p<0.02) and with lymphatic invasion (210 vs. 180, <0.05), as well as in G3 UC (193 vs. 188, <0.04). Expression of IL-1RA did not correlate with tumor stage, lymphovascular invasion, N+ or M+ status. Nevertheless, significant association of low expression of IL-1RA and high-grade UC (p=0.002) was determined, which led to positive correlation between IL-1 beta/IL-1RA ratio and tumor grade (p=0.002). Furthermore, G3 UC showed lower median IL1-RA expression compared to G2 (185 vs. 250, <0.003) and IL-1 beta/IL-1RA ratio was consequently significantly higher in G3 UC (1.10 vs. 0.66, p=0.001).
2.4. Combined Scores and Clinical Data
Clinical parameters were compared with combined biomarker scores ‘Ki-67+ and IL-1ß+’ and ‘Ki-67+ or IL-1ß+’ as well as and/or IL-1RA, respectively. Statistical significance could be demonstrated in ‘Ki-67+ and IL-1ß+’ for vascular invasion and in ‘Ki-67+ or IL-1ß+’ and (higher) tumor grade (
Table 3).
2.5. Correlation of IL-1 Axis with Ki-67 and AKT Expression
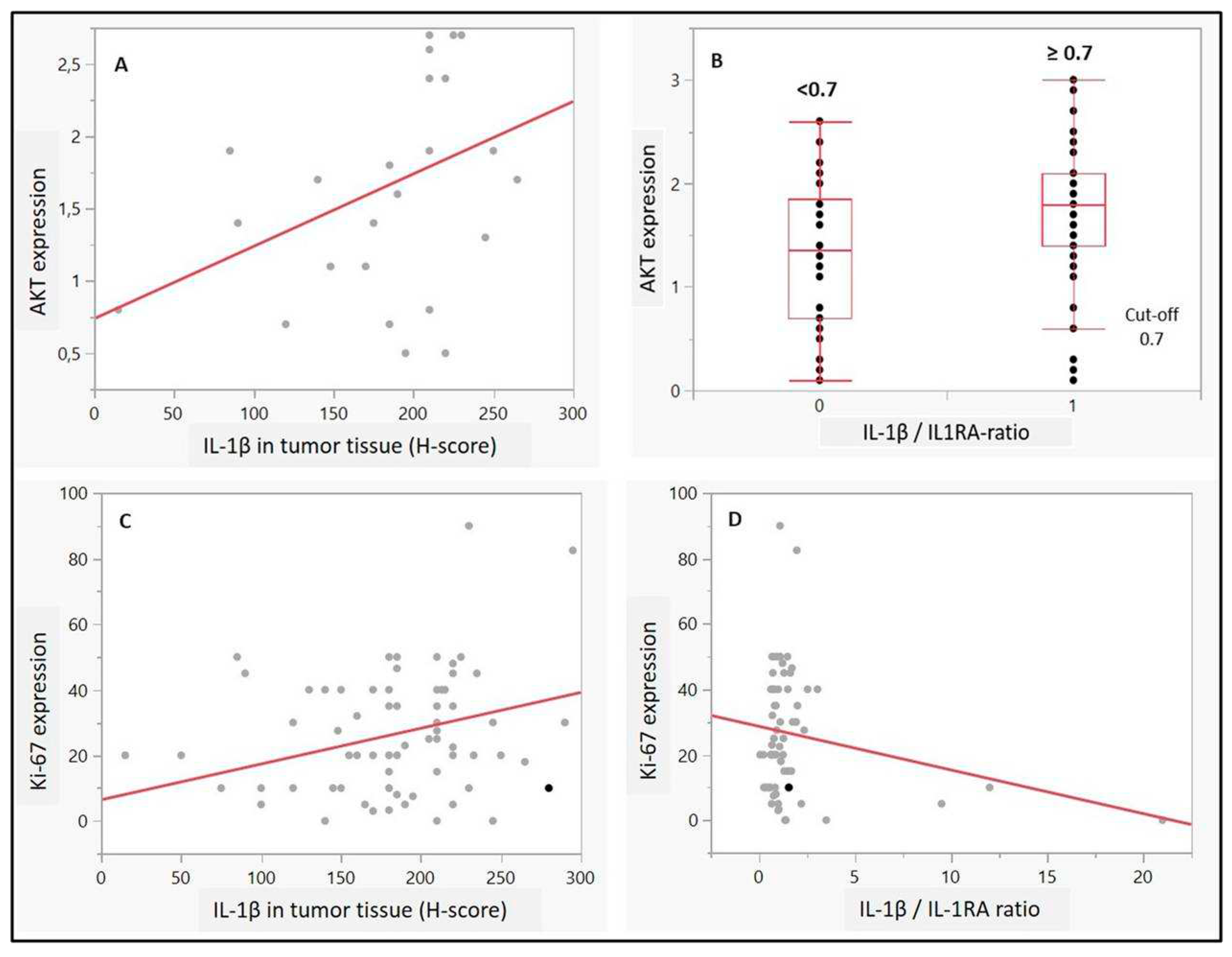
Regarding potential associations to proliferation or autophagy, IL-1β as well as IL-1 beta/IL-1RA ratio (cut-off 0.7) was associated with higher AKT expression in the UC cells (p=0.04 and p=0.009, respectively,
Figure 3A and B). Moreover, high expression scores of Ki-67 (>15%) correlated with higher expression of IL-1β (p=0.01,
Figure 3C). Although no statistical significance was observed for IL-1RA, there was a positive trend towards correlation between high Ki-67 scores and IL-1 beta/IL-1RA ratio (p=0.08) (
Figure 3 D). Moreover, contingency analysis confirmed significant association of combined expressions of ‘Ki-67 and IL-1β’, as well as Ki-67/IL-1 ratio, with high tumor grade (p=0.02 and p=0.01, respectively, not shown).
2.6. Survival Analysis
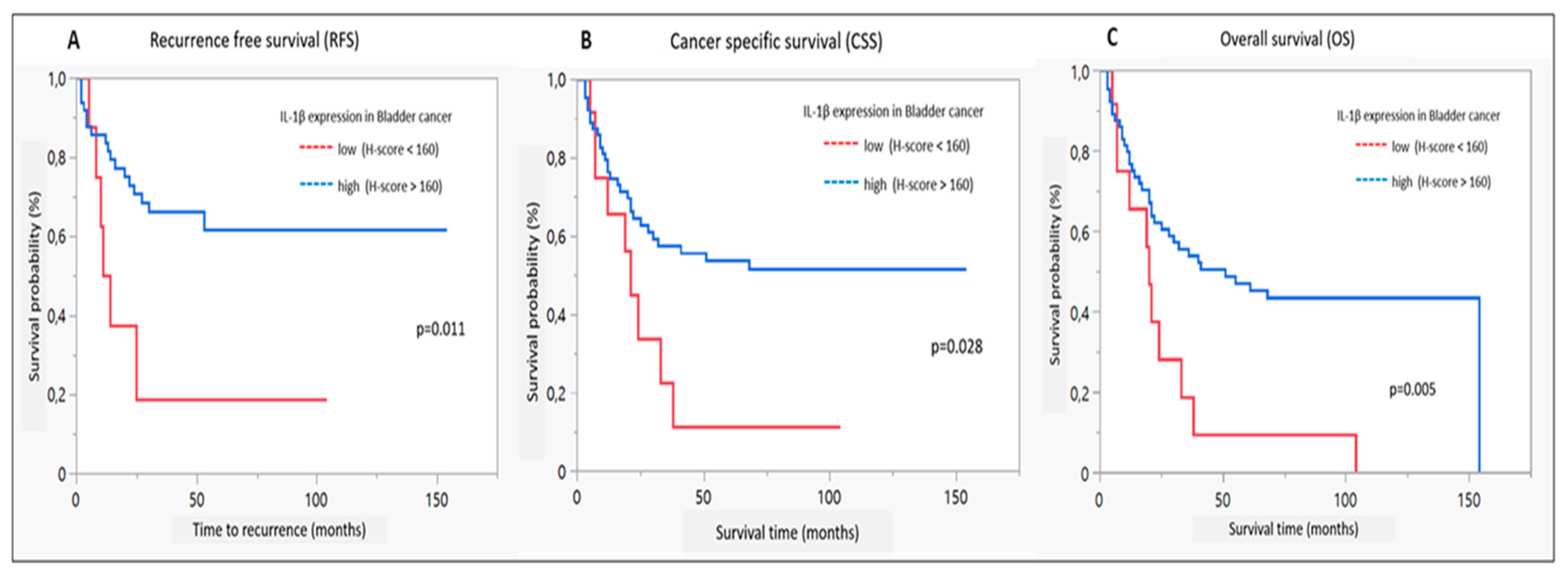
Figure 4 illustrates Kaplan-Meyer estimates for RFS, CSS and OS in dependence of IL-1β expression levels in the discovery cohort. Survival analysis revealed improved RFS, CSS as well as OS in case of IL-1ß high expression (p<0.02, <0.03 and <0.006, respectively). No significant correlation could be observed with regard to IL-1RA expression or IL-1ß/IL1RA- ratio and any of the survival outcomes.
Suppl. Figure 1A-C.
Kaplan-Meier diagrams for IL-1ß expression: A. recurrence-free survival, B. cancer specific survival and C. overall survival; red = expression <160, log rank test.
Suppl. Figure 1A-C.
Kaplan-Meier diagrams for IL-1ß expression: A. recurrence-free survival, B. cancer specific survival and C. overall survival; red = expression <160, log rank test.
2.7. Uni- and Multivariate Cox Proportional Hazard Analysis
Results are illustrated in
Table 4. In multivariate analysis, IL1ß was confirmed as an independent predictor of RFS. All investigated parameters including age, T, N+, M and G, as well as IL1-ß, were significantly associated with CSS and multivariate analyses revealed an independent impact of IL1-ß on CSS. Moreover, IL1-ß was significantly associated with OS in univariable and multivariate analyses.
3. Discussion
Intense research has been performed in recent years to identify potential biological markers predicting clinical behavior of invasive BC (21, 22). This was followed by significant improvement in our understanding of molecular biology of this malignancy. Bladder tumors are highly heterogeneous, with frequent mutations in different signaling pathways, including cell-cycle genes, receptors tyrosine kinase, PI3K/AKT/mTOR and chromatin regulatory gene mutations (23). A number of studies have determined the important role of IL-1β in the occurrence and development of malignant tumors (13). As a member of the IL-1 family of cytokines, IL-1β may act as mediator of inflammatory response in cancer, while involved in a variety of cellular activities, including cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis. However, due to complex repercussion on the course of cancer, both tumor promoting and inhibitory functions of IL-1β have been described (24) and its specific role in BC carcinogenesis is yet to be determined. Additionally, IL1RA has been recognized as important factor in bladder carcinogenesis and high expression might be related to tumor aggressiveness (25).
In the present study, the expression patterns of IL-1β and IL1RA were assessed in invasive BC and a significant overexpression was observed when compared with normal bladder tissue. Moreover, IL-1ß expression was stronger in patients with adverse prognostic features (high-grade tumors (G3) and/or lymph-vascular invasion). Similar results have been reported in colorectal cancer (13), where higher expression of IL-1β was associated with better OS and RFS, indicating a beneficial, prognostic role in rectal cancer. In the present analysis, we observed that only IL-1β expression could be identified as an independent predictor of each RFS, CSS and OS, in multivariate analysis. IL-1RA was also significantly overexpressed in invasive BC, as compared to benign urothelium, while significant co-expression between IL-1β and IL-1RA was observed only in benign tissue. However, results showed that lower expression of IL-1RA correlates with high tumor grade (G3), which completely resembles results reported by Schneider et al. (25) indicating that adverse pathologic cancer characteristics relate to low expression of IL-1RA. Moreover, authors emphasized the potential role of IL-1RA as a therapeutic target in patients with BC. This was examined in several trials, where human competitive IL-1 inhibitor, Anakinra, decreased proliferative rate of tumors refractory to standard therapies (26, 27). In this regard, our study revealed some promising results, since both, adverse tumor features and immune response of the host were obviously strongly influenced by the expression of IL-1 axis.
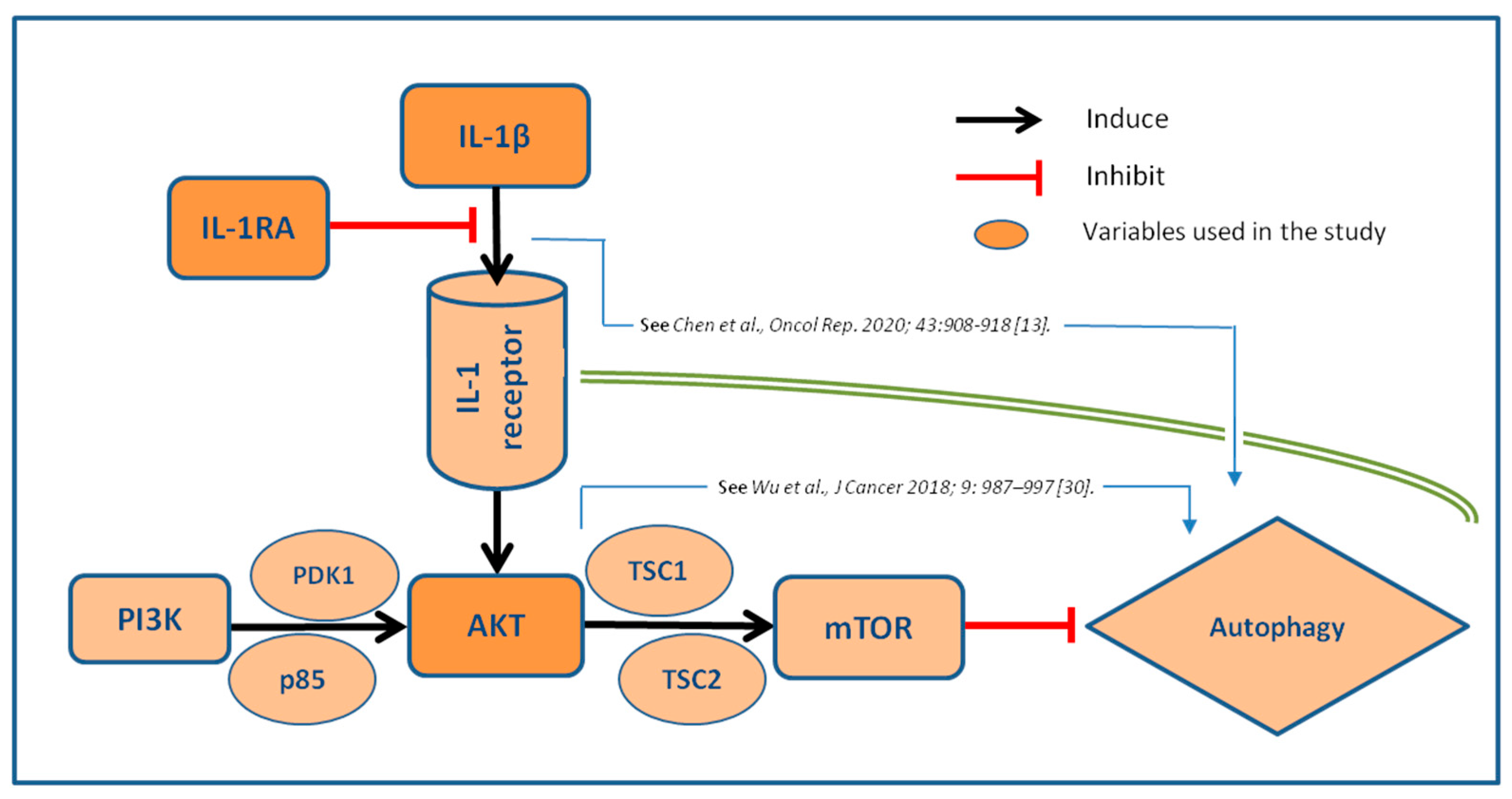
Autophagy, the major endogenous pathway for degradation, delivery and recycling of long-lived proteins and organelles, may be considered as significant tumor suppressor (6). According to recent data (28), loss of negative regulator of PI3K autophagy pathway leads to more aggressive disease and metastasis, potentially through stronger activation of AKT mechanism. This was supported by our results, where stronger expression of AKT is associated with worse tumor grade, through correlation with IL-1β. However, the interactions between IL-1 axis and autophagy markers in invasive BC are still largely unknown. Noteworthy, recent evidence suggests that IL-1β/1RA axis regulates cell proliferation, migration, clone formation and apoptosis in vitro via autophagy mechanisms (15). It seems that autophagy influences IL-1β and pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion by macrophages. Interestingly, this effect could be both, stimulatory and inhibitory (6, 29). All these data suggest that inhibition of autophagy probably increases IL-1β secretion through several mechanisms, with sequestration into autophagosomes, as the most dominant one (29, 30). This hypothesis is underlined by our results, where both, IL-1β as well as IL-1β/IL-1RA ratio correlated positively to AKT expression in BC. It is, however, still unknown the true prognostic potential of this relation, despite clear evidence that AKT pathways influence the prognostic potential of IL-1 axis in invasive BC. Proposed pathways and the interrelations of the analyzed biomarkers are illustrated in
Figure 5.
We hypothesize that IL-1β/1RA axis may express positive correlation with Ki-67 in terms of tumor potential, among patients with invasive BC. The observed interrelations IL-1β expression with Ki-67 as a reliable marker for proliferation in BC suggests a putative approach for multivariate immunohistochemical profiles integrating improved prognostic and presumably also predictive accuracy by combining several markers (19). Indeed, IL-1β high expression showed positive correlation with both, AKT and Ki-67 high staining in tumor cells, unlike IL-1 RA.
Although our analysis requires large-scale validation, it suggests a potential mechanism-based selection strategy, in which patients with higher expression of IL-1β in BC tissue may have better immune response and probably, better response to cancer treatment. This attitude has been discussed in report from Rebe et al. (24) with the conclusion that, although IL-1β has been recognized as a cancer promoter, it may also contribute the anti-tumor response, depending on tumor stage and origin.
Limitations of the study lie in its retrospective character, single center design and the reduced sample size. Inherent limitations of IHC may be seen in interobserver variability. Moreover, for the evaluation of benign urothelium, corresponding tissue from tumor-free paraffin blocks from patients with BC was analyzed. Therefore, the expression pattern of biomarkers from totally healthy urothelium may differ from that observed in the present study.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient Cohorts
Based on an institutional database, patients undergoing radical cystectomy for invasive BC (urothelial carcinoma only) from February 1996 to December 2010 were identified. From cystectomy specimen, a tissue microarray (TMA) was created, based on the identification of representative sections of tumor and normal tissue in hematoxylin and eosin staining. Furthermore, corresponding histopathological benign urothelium tissue samples from surrounding areas (n=22 and 39) were processed to a TMA and IHC stained for IL-1ß, IL-1RA, AKT and Ki-67. First group included 24 female and 78 male patients, whereas second cohort consisted of 27 female and 70 males. Tumor grade and stage were assessed according to the WHO 2016 TNM classification system by at least two pathologists experienced in urogenital pathology (12). Clinicopathological characteristics were recorded. The study was approved by the institutional review board of the University of Tubingen No. 279/2013BO2 from March 1st 2023.
4.2. Tissue Microarray (TMA) and Immunohistochemical (IHC) Staining
To obtain representative cores for TMA construction, parallel sections stained by hematoxylin and eosin were used to identify a representative core position within the specimens. IHC staining was carried out according to the antibody manufacturers' instructions. Tissue slides were incubated overnight at 4 °C with a human IL-1 beta/ IL-1F2 (AF-201, R&D systems Inc., USA) and IL-1 RA/ IL-1F3 (AF-280, R&D systems, USA) polyclonal goat immunoglobulin, respectively (13), in dilutions 1:10 and 1:300, in real antibody diluent (DAKO, Glostrup, Denmark). After three more washing steps, visualization was performed with Dako Liquid DAB-Substrat Chromogen System K3467 (DAKO, Glostrup, Denmark) and counterstaining with haematoxylin, as indicated by the manufacturer (14). Two or more cores of every invasive BC and corresponding normal bladder tissue were integrated.
4.3. Immunohistochemical Protocol
TMAs were evaluated in a blinded manner by two independent reviewers, and divergent results were reevaluated. For the results, IL-1β and IL-RA cytoplasmatic cellular staining was scored using a 4-point scale (0, no staining; 1+, light staining at high magnification; 2+, intermediate staining; 3+, dark staining of linear membrane at low magnification (15). Expressions were then quantified by the histochemical scoring system / H-score 0-300 (16) and a quotient IL-1ß/IL-1RA was built for further calculations. Microscopic analysis was performed at x100 and x400 magnifications. For AKT, epithelial zones were scored according to the intensity of staining of the cytoplasm, nucleus or membrane and the same scoring system has been used (17). Individual results were demonstrated as staining classes and compared to clinical and histopathological data of the second cohort, whereas clinical course was evaluated in the first group. Ki-67 score was expressed as the percentage of the number of immune-stained nuclei among the total number of nuclei of tumour cells, regardless of the immunostaining intensity. This counting was performed in three representative selected fields of the BC tissue section at x400 magnification (18). Ki-67 score ranged from 0-100% and its cut-off level was 15%, where ´low immunoreactivity´ was defined by nuclear staining of < 15% and ´high´ for staining ≥ 15% (19).
4.4. Patient Follow-Up
In the conformation cohort patient charts and physicians’ records were reviewed to determine clinical outcome. In general, patients were seen postoperatively at least every 3–4 months for the 1 year, semi-annually for the 2nd and 3rd year and annually thereafter. Radiological imaging including computed tomography was performed in all patients. Time to recurrence (RFS) cancer specific survival (CSS) and overall survival (OS) was assessed (20).
4.5. Statistical Analysis
The expression of IL-1ß, IL-1RA, AKT and Ki-67 was correlated with clinicopathologic parameters at time of cystectomy by Wilcoxon Kruskal-Wallis tests, Chi-square tests or linear regression analyses, dependent on the variable’s category. Kaplan–Meier analyses were used to estimate recurrence-free (RFS), cancer-specific (CSS) and overall survival (OS) by the log-rank test. Uni- and multivariate Cox proportional hazard analyses were performed to assess the impact of IL-1β and IL-1RA together with other relevant clinical and pathologic variables. P-values <0.05 were considered significant. JMP, version 16.2 (SAS Institute, Cary, USA) was used for statistics.
5. Conclusions
We found that high expression level of IL-1β correlates with RFS, CSS and OS in bladder cancer and is an independent predictor of outcome in multivariate analysis. Moreover, both IL-1β and IL-1β/IL-1RA ratio show positive correlation to AKT and Ki-67 expression, indicating involvement in autophagy and high proliferative activity. Combined analysis of these markers may contribute to clinical decision making when defining therapeutic strategies for invasive BC.
Author Contributions
M.V.: Data curation, Analysis, Writing, Original draft preparation. J.C., S.J. Data curation, Analysis. J.H., T.T., T.L..: Data acquisition, Supervision, Reviewing and Editing. I.T.: A.S. Supervision. S.R.: Project development, Analysis, Writing, Reviewing and Editing.
Funding
Vukovic Marko is supported by EUSP scholarship grant of the European Association of Urology (S-2021-0013).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was approved by the institutional review board of the University of Tubingen No. 279/2013BO2 from March 1st 2023..
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data from this study are available by request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to ethical restrictions (IRB statement).
Acknowledgments
We thank Sieglinde Baisch and Irini Grigoriadou from Eberhard-Karls University of Tuebingen for scientific support..
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wang JZ ZW, Han J, Yang X, Zhou R, Lu HC, Yu H, Yuan WB, Li PC, Tao J, Lu, Q WJ, Yang H. The role of the HIF-1α/ALYREF/PKM2 axis in glycolysis and tumorigenesis of bladder cancer. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2021;41(7):560-75. [CrossRef]
- Huang W LY, Zhang C, Zha H, Zhou X, Fu B, Guo J, Wang G. IGF2BP3 facilitates cell proliferation and tumorigenesis via modulation of JAK/STAT signalling pathway in human bladder cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(23):13949-60. [CrossRef]
- Rausch S HJ, Teepe K, Kuehs U, Aufderklamm S, Bier S, Mischinger J, Gakis G, Stenzl A, Schwentner C, Todenhöfer T. Muscle-invasive bladder cancer is characterized by overexpression of thymidine kinase 1. Urol Oncol. 2015;33(10):426.e21-.e29. [CrossRef]
- Xia H GD, Zou W. Autophagy in tumour immunity and therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2021;21(5):281-97. [CrossRef]
- Vetterlein MW RJ, Gild P, Marks P, Soave A, Doh O, Isbarn H,, Höppner W WW, Shariat SF, Brausi M, Büscheck F, Sauter G, Fisch M, Rink, M. Impact of the Ki-67 labeling index and p53 expression status on disease-free survival in pT1 urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Transl Androl Urol. 2017;6(6):1018-26. [CrossRef]
- Liu GH ZQ, Ye YL, Wang HB, Hu LJ, Qin ZK, Zeng MS, Zeng BH. Expression of beclin 1 in bladder cancer and its clinical significance. Int J Biol Markers. 2013;28(1):56-62. [CrossRef]
- Kim H LS, Lee IK, Min SC, Sung HH, Jeong BC, Lee J, Park SH. Synergistic Effects of Combination Therapy with AKT and mTOR Inhibitors on Bladder Cancer Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(8):2825. [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto H MM, Shimizu K, Fujii N, Kobayashi K, Inoue R, Yamamoto, Y NK, Matsuyama H. Risk stratification using Bmi-1 and Snail expression is a useful prognostic tool for patients with upper tract urothelial carcinoma. Int J Urol. 2016;23(12):1030-7. [CrossRef]
- Wang F LJ, Chen X, Zheng X, Qu N, Zhang B, Xia C. IL-1β receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) combined with autophagy inducer (TAT-Beclin1) is an effective alternative for attenuating extracellular matrix degradation in rat and human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019;21(1):171. [CrossRef]
- de Luca A SS, Casagrande A, Iannitti R, Conway KL, Gresnigt MS,, Begun J PT, Joosten LA, van der Meer JW, Chamilos G, Netea MG, Xavier, RJ DC, Romani L, van de Veerdonk FL. IL-1 receptor blockade restores autophagy and reduces inflammation in chronic granulomatous disease in mice and in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111(9):3526-31. [CrossRef]
- Crişan TO PT, van de Veerdonk FL, Farcaş MF, Stoffels M, Kullberg, BJ vdMJ, Joosten LA, Netea MG. Inflammasome-independent modulation of cytokine response by autophagy in human cells. PLoS One. 2011;6(4):e18666. [CrossRef]
- Humphrey PA MH, Cubilla AL, Ulbright TM, Reuter VE. The 2016 WHO Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs-Part B: Prostate and Bladder Tumours. Eur Urol. 2016;70(1):106-19. [CrossRef]
- Chen Y YZ, Deng B, Wu D, Quan Y, Min Z. nterleukin 1β/1RA axis in colorectal cancer regulates tumor invasion, proliferation and apoptosis via autophagy. Oncol Rep. 2020;43(3):908-18. [CrossRef]
- John A GC, Bolenz C, Vidal-Y-Sy S, Bauer AT, Schneider SW, Gorzelanny, Chen Y YZ, Deng B, Wu D, Quan Y, Min Z. Bladder cancer-derived interleukin-1 converts the vascular endothelium into a pro-inflammatory and pro-coagulatory surface. BMC Cancer. 2020;2(20):1178. [CrossRef]
- Yao SJ MH, Liu GM, Gao Y, Wang W. Increased IL-1α expression is correlated with bladder cancer malignant progression. Arch Med Sci. 2020;19(1):160-70. [CrossRef]
- Lykkegaard Andersen N BA, Lelkaitis G, Nielsen S, Friis Lippert M,, M V. Virtual Double Staining: A Digital Approach to Immunohistochemical Quantification of Estrogen Receptor Protein in Breast Carcinoma Specimens. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2018;26(9):620-6. [CrossRef]
- Le Page C KI, Alam-Fahmy M, Mes-Masson AM, Saad F. Expression and localisation of Akt-1, Akt-2 and Akt-3 correlate with clinical outcome of prostate cancer patients. Br J Cancer. 2006;94(12):1906-12. [CrossRef]
- Aman NA DB, Koffi KD, Koui BS, Traore ZC, Kouyate M, Toure I, Effi, AB. Immunohistochemical Evaluation of Ki-67 and Comparison with Clinicopathologic Factors in Breast Carcinomas. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2019;20(1):73-9. [CrossRef]
- Bertz S OW, Denzinger S, Wieland WF, Burger M, Stöhr R, Link S,, Hofstädter F HA. Combination of CK20 and Ki-67 immunostaining analysis predicts recurrence, progression, and cancer-specific survival in pT1 urothelial bladder cancer. Eur Urol. 2014;65(1):218-26. [CrossRef]
- Liu Y YT, Wei YW. What is the difference between overall survival, recurrence-free survival and time-to-recurrence? Br J Surg. 2020;107(12):e634.
- Semilia M HJ, Pavone C, Bischoff T, Kühs U, Gakis G, Bedke J,, Stenzl A SC, Todenhöfer T. Expression patterns and prognostic role of transketolase-like 1 in muscle-invasive bladder cancer. World J Urol. 2015;33(10):1403-9. [CrossRef]
- Wilson F JN, Choudhury A. Biomarkers in muscle invasive bladder cancer. Adv Clin Chem. 2022;107:265-97.
- Audenet F AK, Sfakianos JP. The evolution of bladder cancer genomics: What have we learned and how can we use it? Urol Oncol. 2018;36(7):313-20. [CrossRef]
- Rébé C GF. Interleukin-1β and Cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2020;12(7):1791. [CrossRef]
- Schneider L LJ, Zhang C, Azoitei A, Meessen S, Zheng X, Cremer C,, Gorzelanny C K-GS, Brunner C, Wezel F, Bolenz C, Gunes C, John A. The Role of Interleukin-1-Receptor-Antagonist in Bladder Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(11):5875. [CrossRef]
- Waugh J PC. Anakinra: a review of its use in the management of rheumatoid arthritis. BioDrugs. 2005;19(3):189-202. [CrossRef]
- Lust JA LM, Zeldenrust SR, Dispenzieri A, Gertz MA, Witzig TE, Kumar S,, Hayman SR RS, Buadi FK, Geyer SM, Campbell ME, Kyle RA, Rajkumar SV,, Greipp PR KM, Xiong Y, Moon-Tasson LL, Donovan KA. Induction of a chronic disease state in patients with smoldering or indolent multiple myeloma by targeting interleukin 1{beta}-induced interleukin 6 production and the myeloma proliferative component. Mayo Clin Proc. 2009;84(2):114-22. [CrossRef]
- Minoli M KM, Thalmann GN, Kruithof-de Julio M, Seiler R. Evolution of Urothelial Bladder Cancer in the Context of Molecular Classifications. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(16):5670. [CrossRef]
- Iula L KI, Sabbione F, Fuentes F, Guzman M, Galletti JG, Gerber, PP OM, Geffner JR, Jancic CC, Trevani AS. Autophagy Mediates Interleukin-1β Secretion in Human Neutrophils. Front Immunol. 2018;9:269. [CrossRef]
- Wu N ZY, Xu X, Zhu Y, Song Y, Pang L, Chen Z. The anti-tumor effects of dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor BEZ235 and histone deacetylase inhibitor Trichostatin A on inducing autophagy in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Cancer. 2018;9(6):987-97. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).