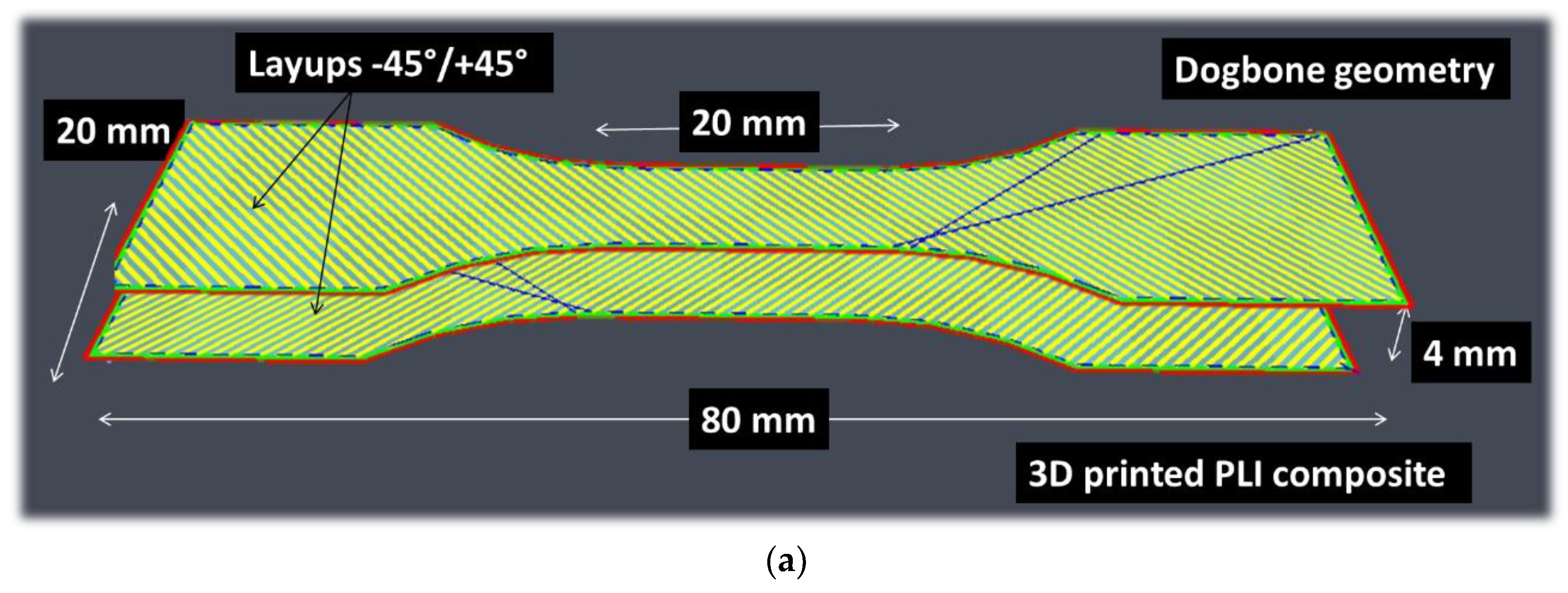
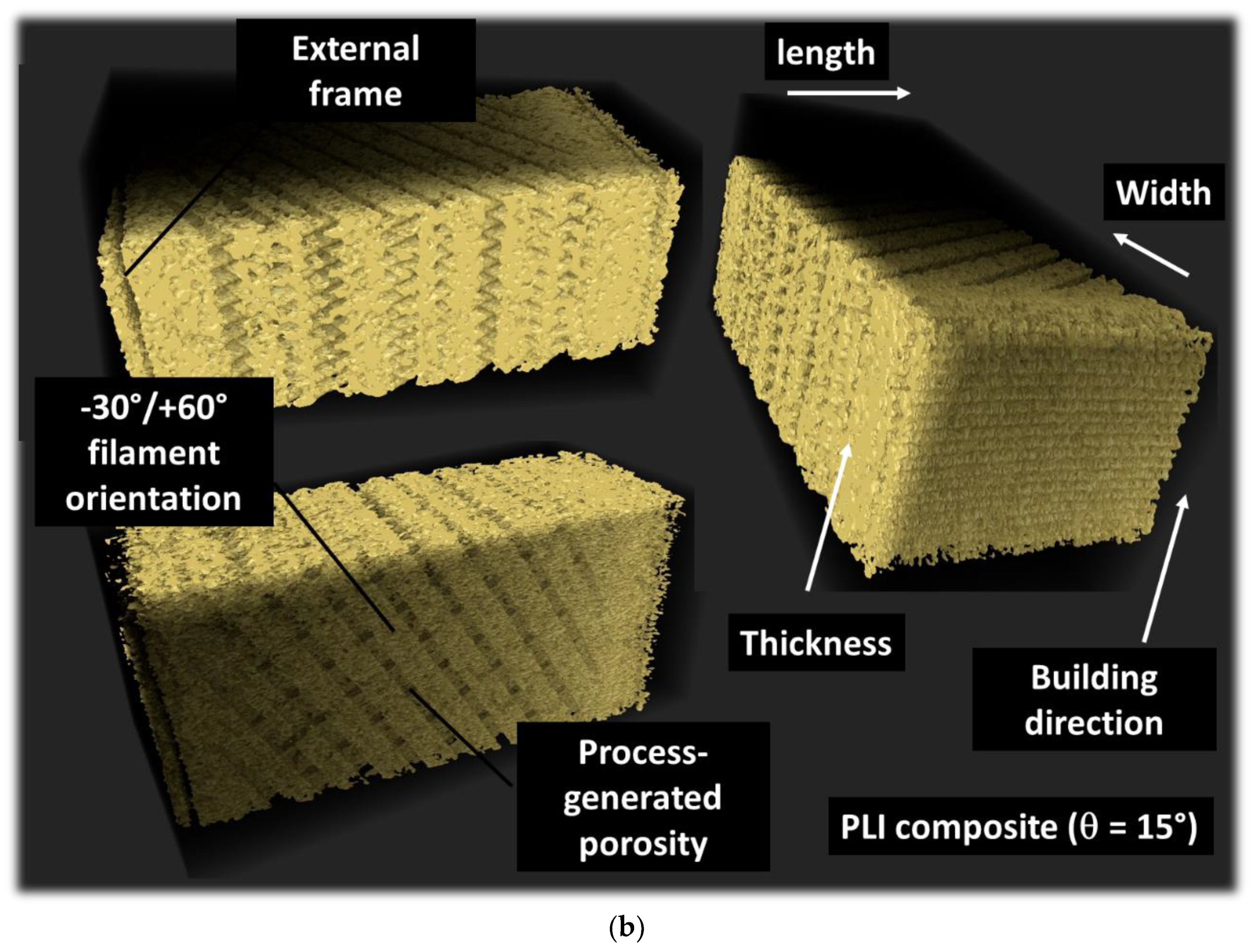
3.1.3. D Microstructure of PLI Composites
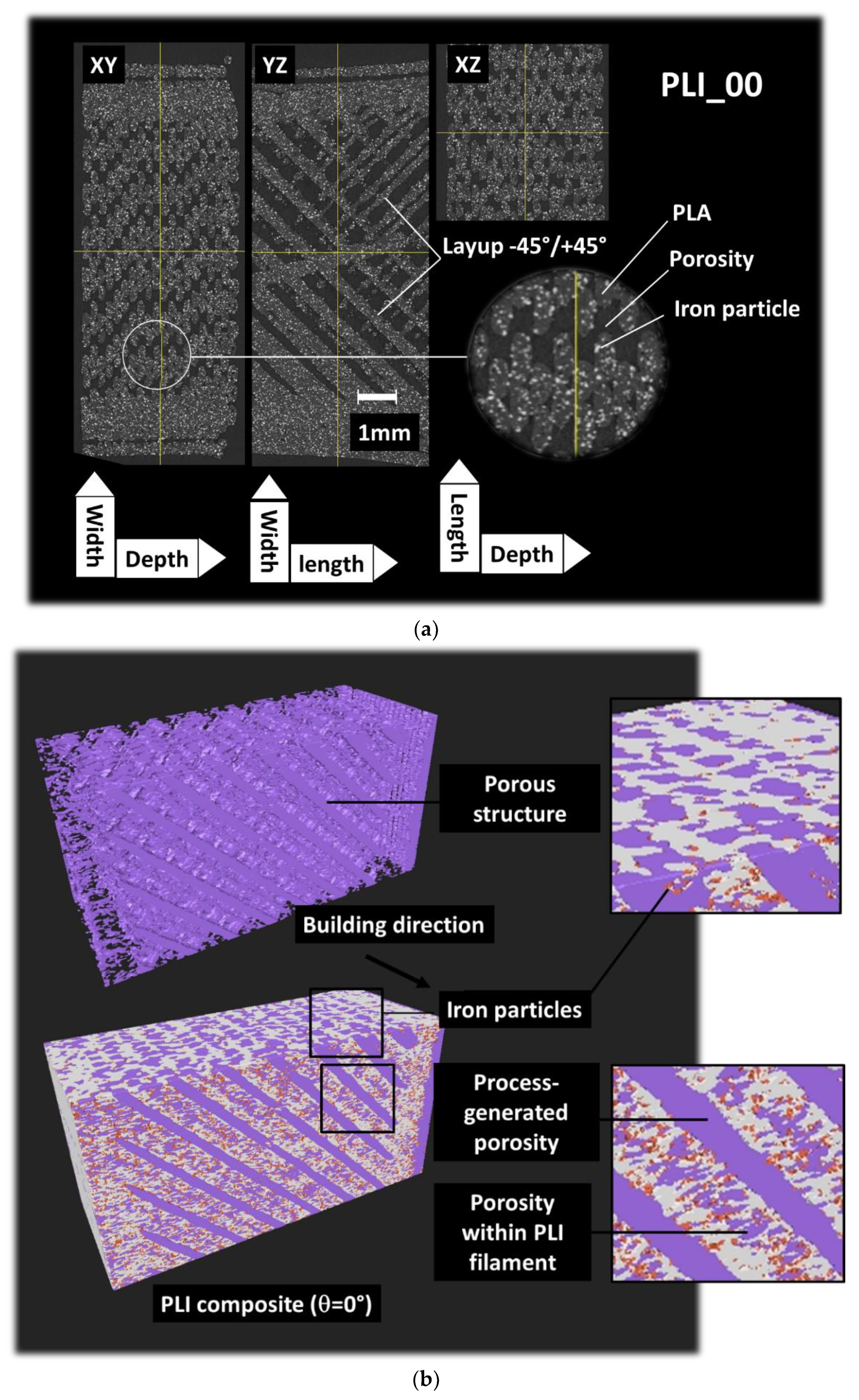
Figure 3 displays orthogonal perspectives of the PLI_00 composite, printed at a 0° angle. These perspectives result from merging two consecutive tomograms obtained along the specimen’s height. The Region of Interest typically measures 4.0 × 10 × 4.7 mm. The microstructure reveals key characteristics related to three distinct phases with varying densities: the PLA matrix, magnetic iron particles, and porosity. These phases can be discerned through a double segmentation process. The XY plane view highlights the primary features of Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF), showcasing in-plane discontinuities associated with the filament layup.
For the PLI_00 sample at a printing angle of 0° (= 0°), two main filament orientations emerge within the specimen: +45° and -45° relative to the primary dimension (length) of the sample. The spatial distribution of iron particles appears uniform without any discernible preferred orientation. Views in the XY and YZ planes reveal two main types of porosities: one associated with the raster, termed core porosity, and the other linked to the connection between the raster and external frame. Upon conversion to an 8-bit image, applying a first threshold at 60 allows the isolation of the porous structure from the rest of the specimen (
Figure 3b). A second threshold at 140 separates the iron particles from the remaining phases.
Upon closer inspection of the porosity structure, it becomes apparent that the core porosity can be categorized as process-induced porosity, and there is porosity within the filament. The latter is likely to be present prior to the printing process.
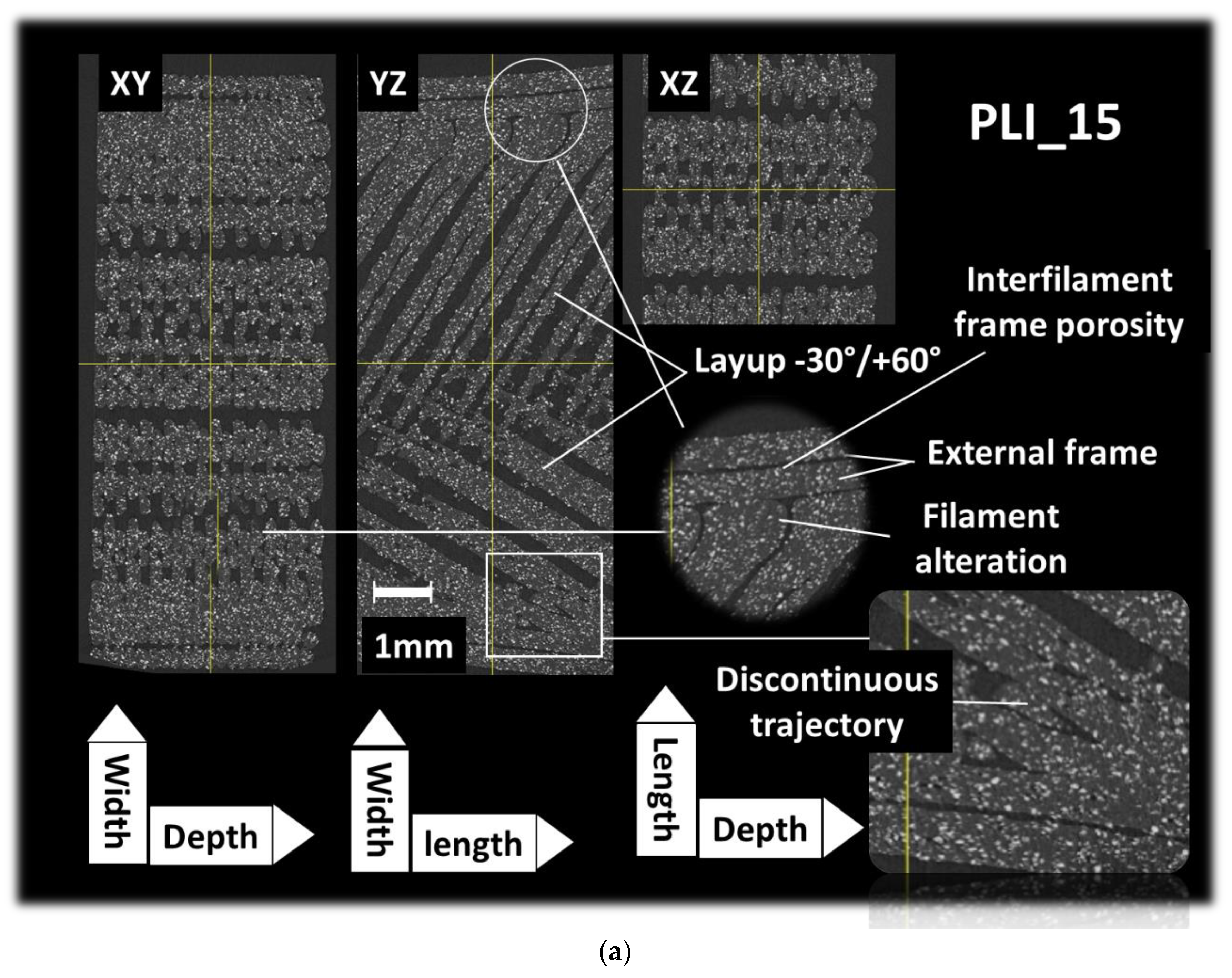
Figure 4a presents analogous orthogonal perspectives of the PLI sample, this time with a printing angle of 15°. Similar mesoscopic porosity is observed, but discerning its magnitude relative to the 0° printing angle is challenging. Much like the previous case, process-induced porosity significantly impacts the cohesion of the core structure. The porosity within the frame, composed of two filaments aligned in the primary direction of the specimen, is also accentuated. The necking effect results in a disruption along this direction.
Furthermore, a change in the tool trajectory near the specimen’s edge introduces a deceleration that modifies the lateral dimensions of the filaments. Lastly, the altered printing angle reveals regions where the print resolution falls short of adequately filling the space with filaments as small as the nozzle diameter of 0.4 mm.
Figure 4b illustrates perspective views of the porous structure within the entire Region of Interest (ROI) under a printing angle of 15°. On the right side, surface porosity aligned with the building direction contributes to the rough finishing surface of the sample, serving as an indicator of the construction direction. On the left side, noticeable distinctions are evident in the morphology of porosities within the frame and the core of the specimen. The former results from changes in filament orientation relative to the raster, while the latter is associated with filament crossings following the sequence of -30°/+60° (as observed in the perspective view at the bottom of
Figure 4b).
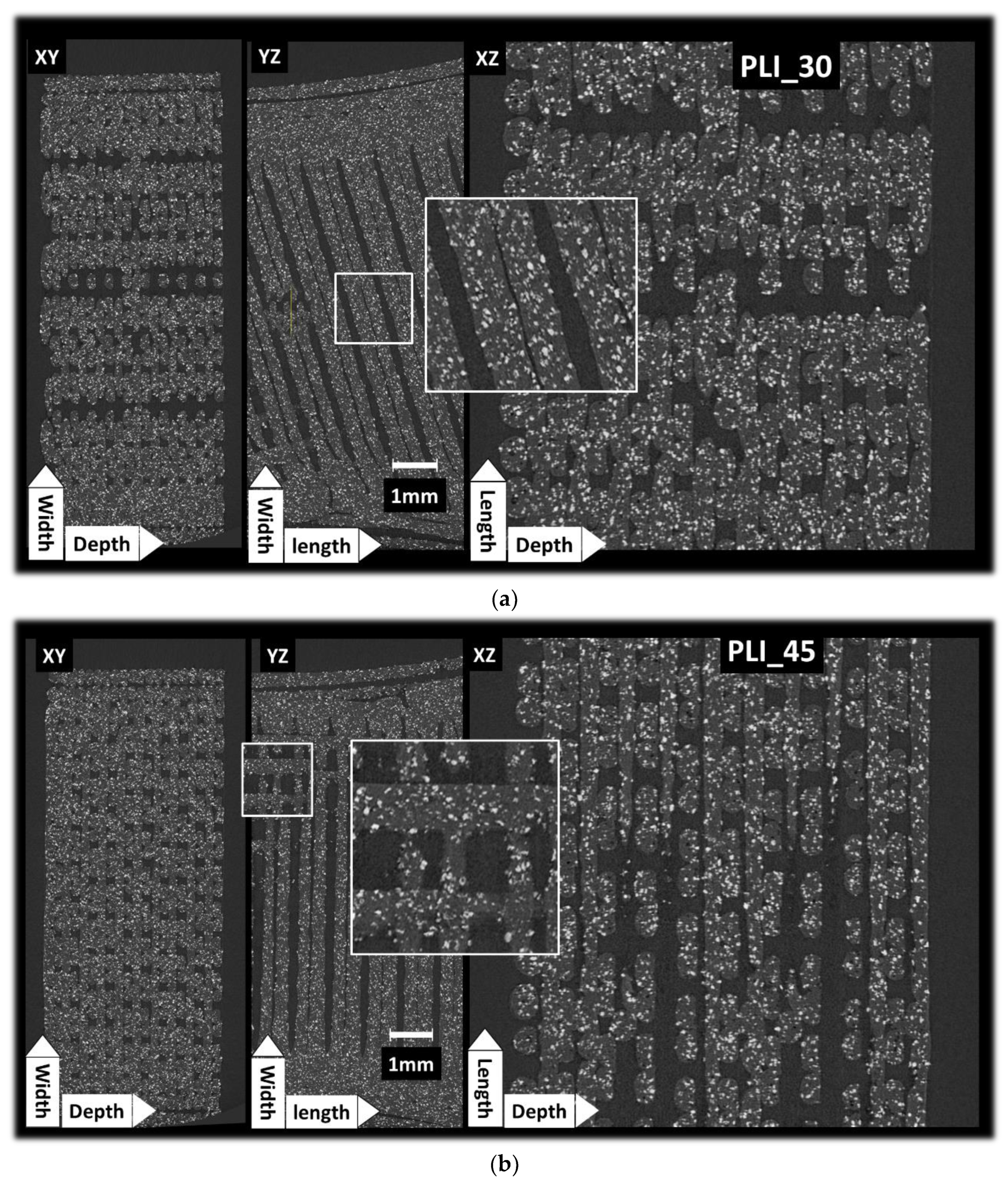
Figure 5 presents cross-sectional views for the remaining conditions, specifically when θ = 30° and θ = 45°. A notable characteristic emerges from the analysis of all samples, including those with different printing angles. This distinctive feature is emphasized in
Figure 5a as the asymmetric discontinuity within the raster generated during the printing process. The asymmetry is attributed to the overestimation of the offset along the length of the specimen when the nozzle travels between two adjacent filaments. It has a direct effect on the porosity morphology and extent.
The microstructural analysis results for θ = 45° are depicted in
Figure 5b. This figure highlights a unique filament arrangement where half of the filaments within the core are fully aligned with the loading direction. No distinct orientation of iron particles can be observed for both cases. Only small clustering can be observed, which does not alter the homogeneity of the iron particle spatial distribution.
Additional analysis is performed to assess the anisotropic spatial distribution of the PLI phases, encompassing iron and process-generated porosity. Axial porosity profiles are investigated for all the examined printing angles. These profiles involve counting the black voxels associated with the porosity phase in a specific direction, normalized with respect to the length, depth, or width, depending on the orientation of the sample. For example, the porosity profile along the depth direction is obtained as follows:
where
represents the porosity level in the Y-direction at the j
th position, specifically along the depth or construction direction (
,
) being the total number of voxels in the X- and Z-directions, corresponding to the height of the specimen).
denotes the grey level associated with the voxel at coordinates i, j, k. For each voxel, the grey level is either 255, corresponding to the solid phase, including the PLA matrix and iron particles, or 0, representing porosity.
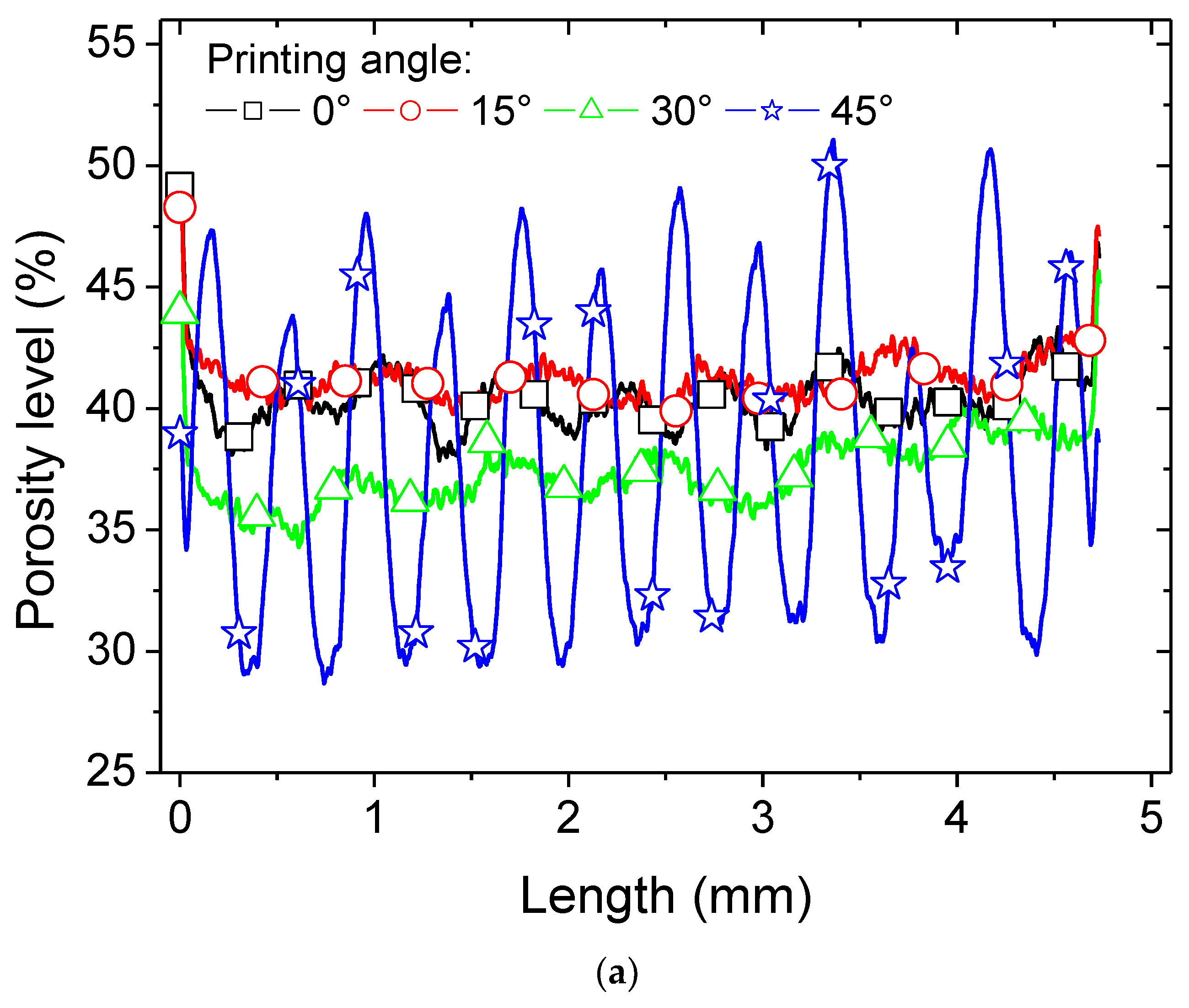
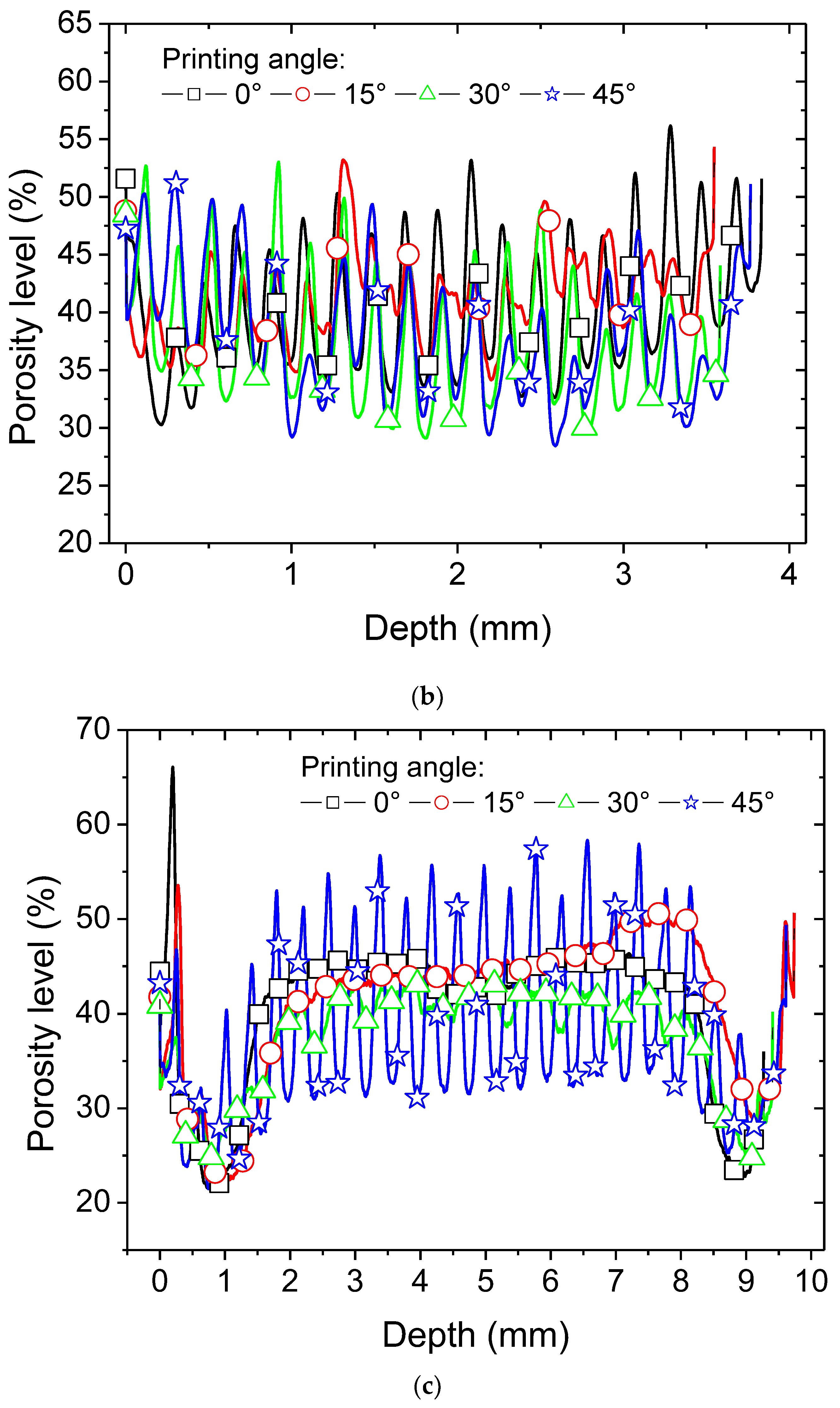
Figure 6 provides more detailed quantitative insights into the porosity distribution through axial porosity profiles. In
Figure 6a, the results of the porosity profiles along the length direction are illustrated. The overall porosity content remains consistent at 39%, regardless of the printing angle. However, when determined through weight and volume measurements, this value is approximately 30%. The average density of the 3D-printed PLI is consistently 1.3 ± 0.22 g/cm
3, irrespective of the printing angle. Given the as-received PLI density of 1.85 g/cm
3, the relative density of the printed samples is approximately 0.70.
It’s worth noting a significant difference between density-based and X-ray microtomography-based measurements of porosity. Despite this contrast, both methods exhibit similar trends with an increase in the printing angle.
In the case of density-based measurement, the following linear correlation is obtained:
For microtomography-based measurement, the linear approximation of porosity content with respect to the printing angle is expressed as:
This discrepancy can be attributed to two main reasons:
A slight overlap between the grey levels, particularly around the void contours, due to the solid phase and voids, influencing the outcome of image processing.
Density measurements are conducted on the entire sample, while image processing is performed on the central part of the sample.
The markedly uneven profiles along the length of the sample reveal a periodicity in the positions of porosity, consistent with a grid-like porous structure (as depicted in
Figure 6a). Although the 45° printing angle yields the lowest average porosity level (as indicated in
Table 1), it also exhibits the highest variation in axial porosity levels along the length. The peak values reach levels close to 51%, while the lowest values are as low as 30%. The 30° printing condition also displays significant variation, followed by the remaining printing angles in a descending order. At this juncture, it can be inferred that the larger the printing angle, the greater the perturbation in the porosity profile. This variability can have a notable impact on stress localisation, particularly with a substantial modulation of the porosity level across a short length, as small as 200 µm.
Throughout the depth, significant peaks are not evident for the 45° printing angle (
Figure 6b). All samples demonstrate a consistent variation in porosity levels, ranging from 30% to 55%. This serves as evidence for the uniformity of the printing process across the specimen’s depth, regardless of the printing angle.
Porosity profiles along the width of the specimen (
Figure 6c) reveal the existence of interfilament porosity within the external frame, as illustrated in
Figure 4a. The porosity level peaks at values as high as 65%. In proximity to the specimen’s edges at 1 mm and 9 mm, low porosity levels indicate connectivity between the raster and the frame. In the core of the specimens, the sequencing results in a periodic filament arrangement, where the spaces between adjacent filaments contribute to the observed porosity trend between 2 and 8 mm. It’s worth noting that the porous structure appears notably jagged for a printing angle of 45°, while for the remaining conditions, the porosity level trend seems more stable.
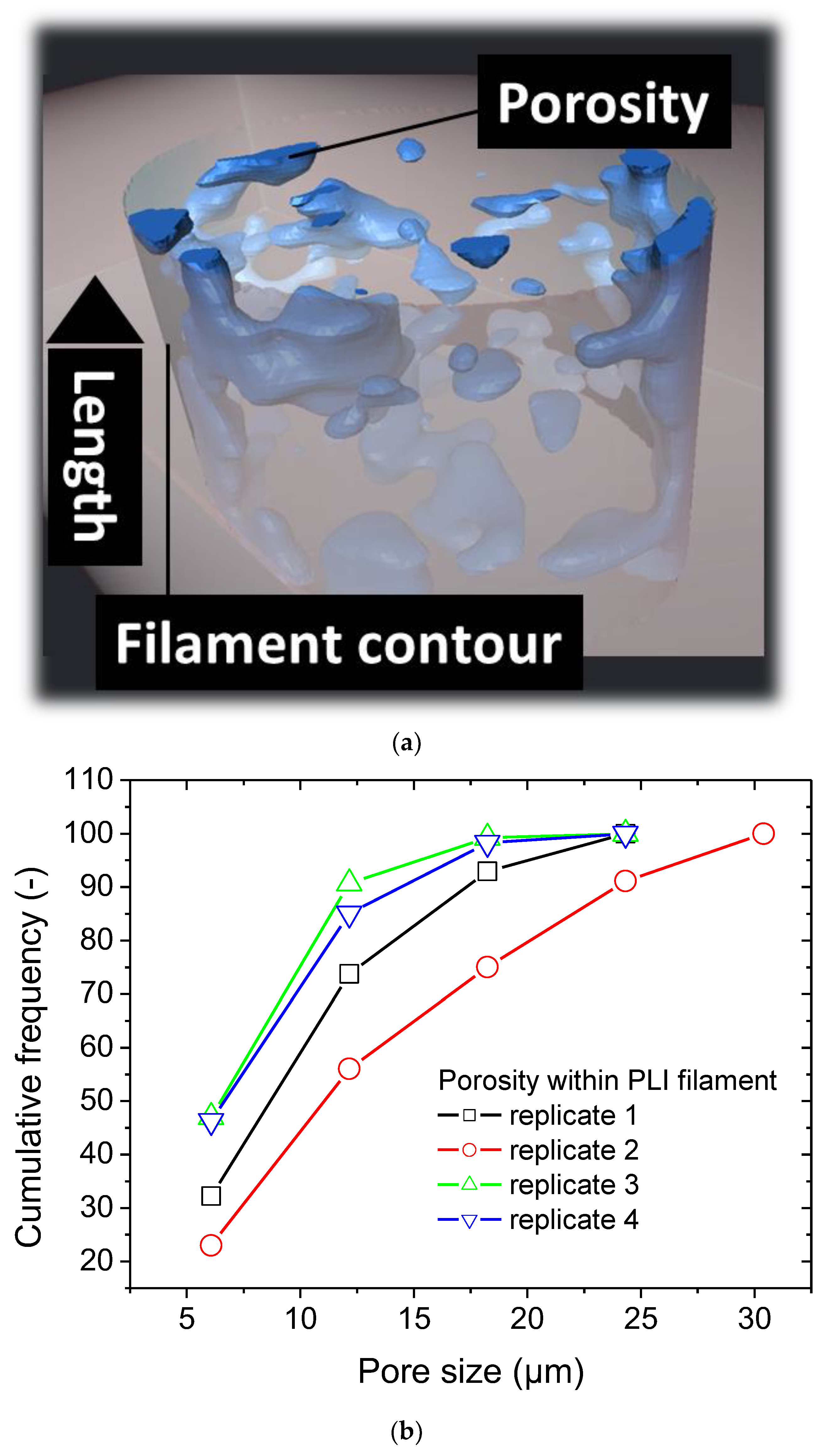
Figure 7 shows closer view on the main features within the PLI filament.
Figure 7a shows the porosity morphology and spatial distribution within the filament. There is no direct relationship between the laying down process and the pore morphology. The elliptical shape of the PLI extruded filament is due to the difference between the layer height (0.2 mm) and the nozzle diameter (0.4 mm). The shape factor representing the ratio between the semi-lengths is 0.65 ± 0.06. The porosity content within the filament exhibits a low discrepancy as well with an average value close to 24 ± 4%. Based on the assessment of size distribution depicted in
Figure 7b, the pores exhibit a monomodal distribution, with an average size of 12.00 ± 2.54 µm. The entire range of distribution is confined within 5 to 30 µm. Additionally, the 3D labelling-derived pore connectivity reveals a nearly equal ratio, approximately 95 ± 2%.
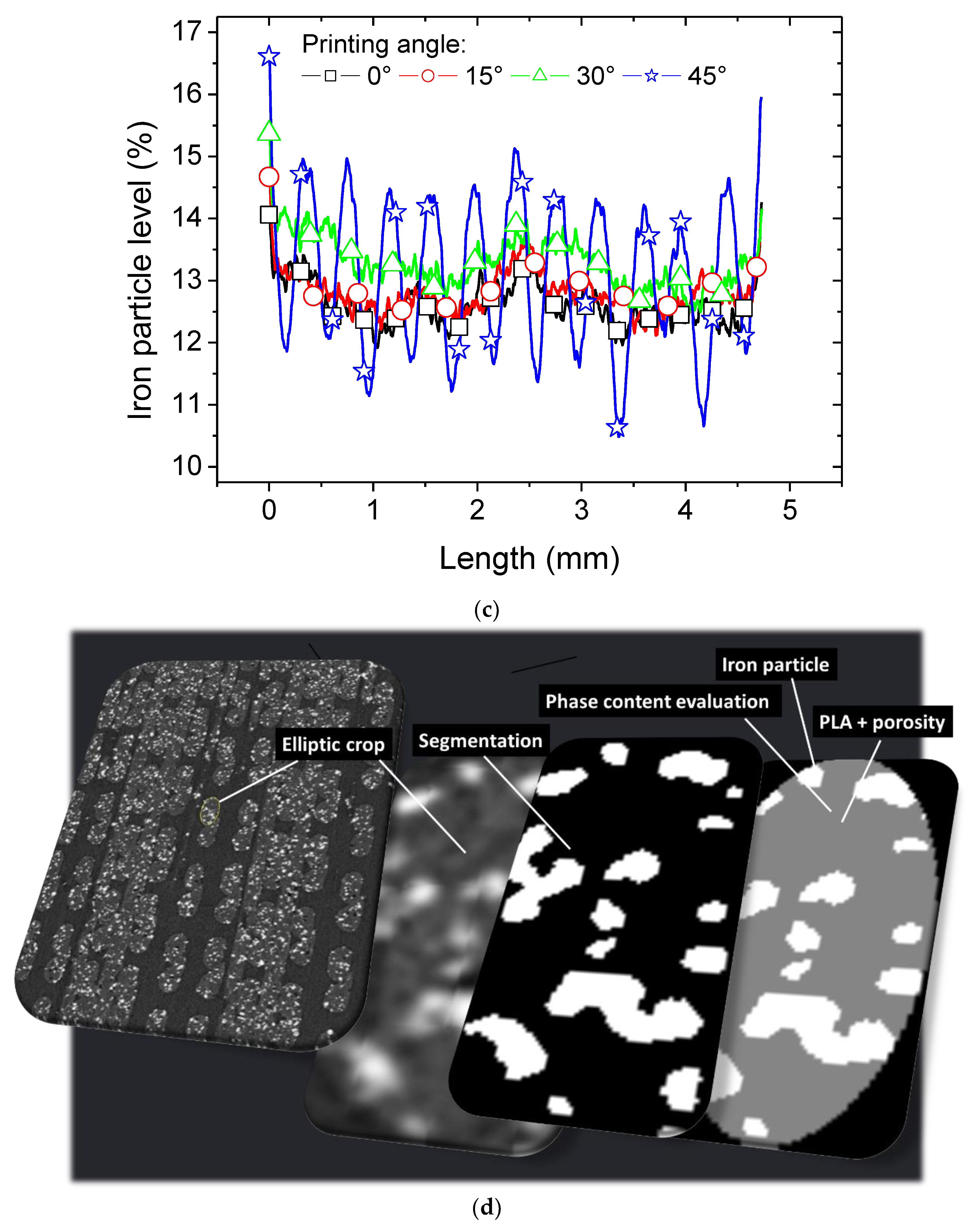
Analysis of the iron particle content is performed by imposing a threshold of 107 to all grey level images, and achieving binary images. The axial profiles of iron particle content can be retrieved as follows
where
represents the iron particle content in the Y-direction at the j
th position, specifically along the depth or construction direction (
,
) being the total number of voxels in the X- and Z-directions, corresponding to the height of the specimen).
denotes the grey level associated with the voxel at coordinates i, j, k. For each voxel, the grey level is either 255, corresponding to the iron phase, or 0 including the PLA matrix and porosity.
Figure 7c shows the axial profiles along sample length of iron particle content for all printing conditions. The axial profiles exhibit the same trend as the porosity level shown in
Figure 6a. The sample exhibits an uneven iron content profile along its length, indicating a periodicity in the positions of iron particles that corresponds to filament arrangement within the raster. The average iron particle content does not depend on the printing angle. Its average value is 13.0 ± 0.3. Despite the 45° printing angle resulting in the same iron particle content, it also shows the highest variation in axial iron content levels. The iron content ranges from a peak of close to 16.5% to a minimum of 10.5%. The 30° printing condition also demonstrates high variation in iron content along the length, but the extent is much lower compared to 45°. This suggests that larger printing angles lead to greater perturbations in filament arrangement, which in turn tunes significantly the iron content.
The iron volume content retrieved from the segmentation process is an effective content as the 3D printed PLI is an airy structure. In order to have a precise value of the iron content within the PLI filament itself, further processing is undertaken based on elliptic crops that are performed on the filaments. The elliptical cropping is selected based on the result of the laying down of the filaments as shown in
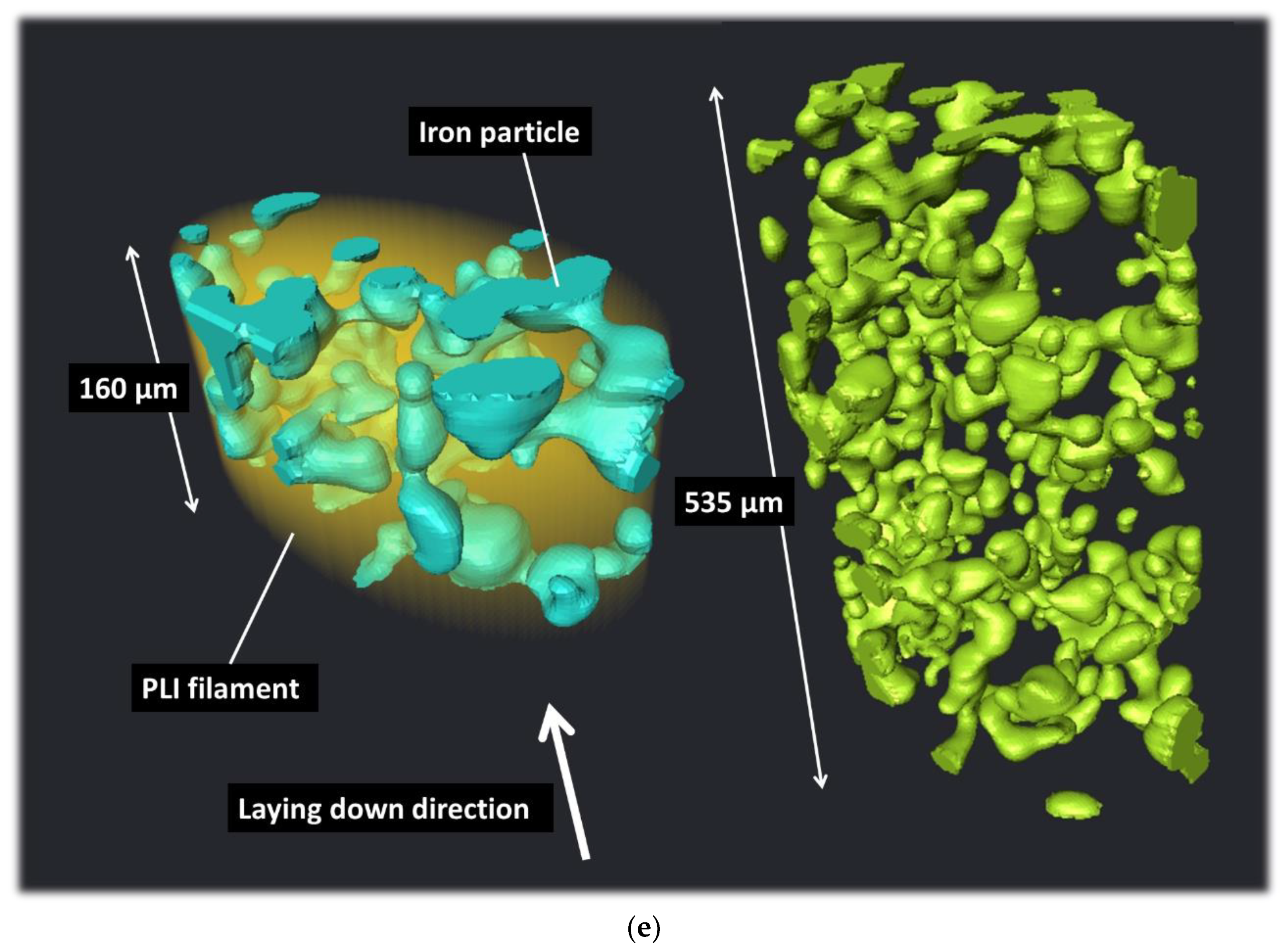
Figure 5c. Based on the quantitative analysis of the volume content of iron particle content, this content is stable irrespective of the printing condition around 18.5 ± 2.2 %.
Figure 5e shows that such a content of iron particles allows a connectivity of about 22 ± 2.3 %. This small connectivity is mostly due to the globular morphology of iron particles as shown in
Figure 7e.
3.2. Mechanical Results
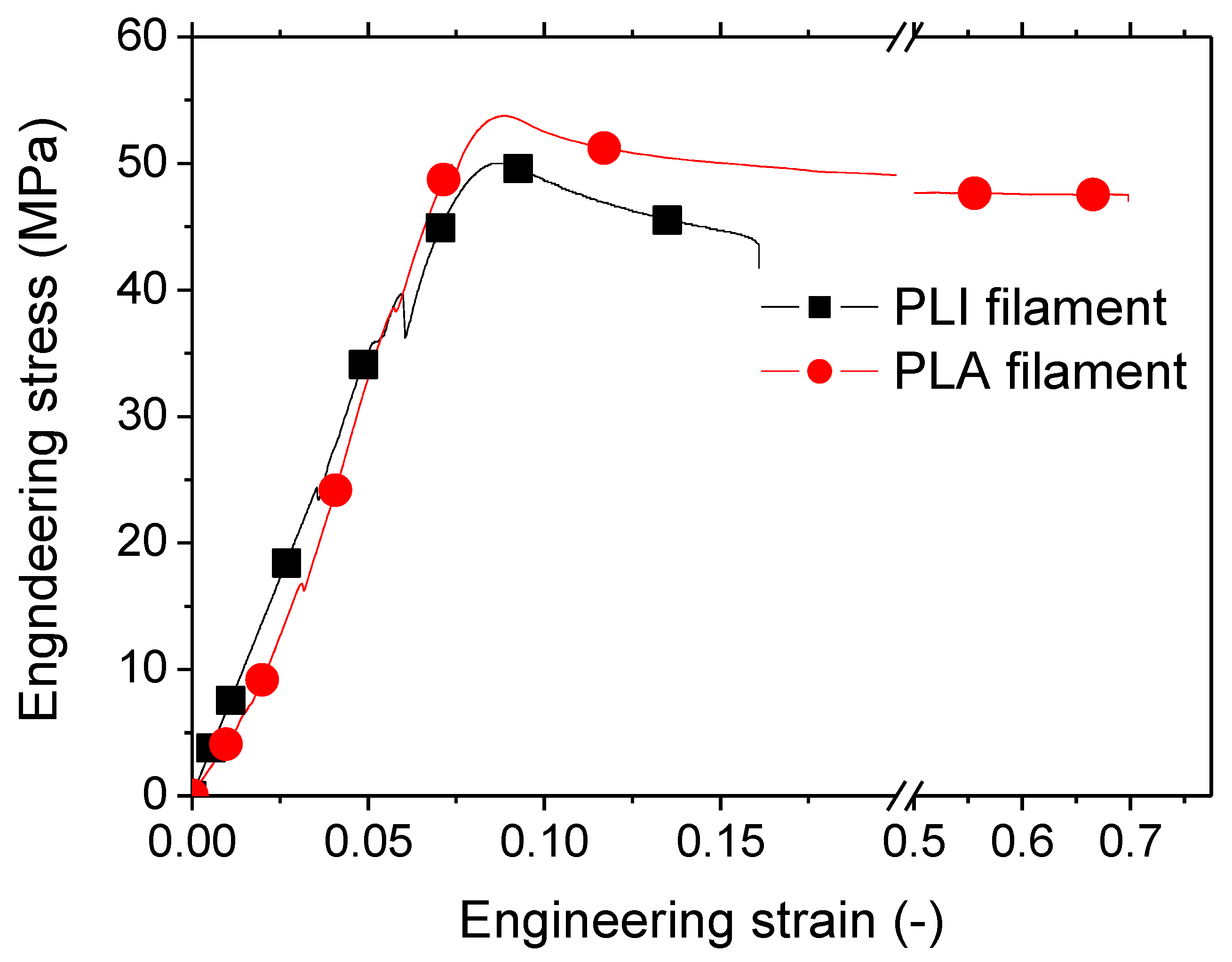
Figure 8 illustrates the tensile response of the as-received PLI filament, with a comparison to the typical tensile response of PLA. The trend captured for as received PLI filament is typical of all replicates, as suggested by the good repeatability in the tensile behaviour (refer to
Table 1 for achieved standard deviation).
The PLI filament displays an elastic-plastic behaviour, characterized by a phenomenon of contraction or constriction before rupture. This constriction is due to the behaviour of PLA matrix. The tensile response of PLI reveals abrupt drops in tensile force, possibly attributed to interfacial effects, considering the significant dispersion of iron particles and the presence of porosities within the filaments acting as stress concentrators. These two factors combined may induce micro-cracking or diffuse damage, resulting in sudden changes in force magnitude.
Similar occurrences of local damage have been observed in other types of PLA composites used as feedstock materials in Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF), such as PLA-wood, PLA-hemp, and PLA-flax fibres [
28,
29,
30]. Comparing the performance of PLI to PLA in
Figure 8, it is evident that the reinforcement expected from iron particles is not observed due to the lack of mechanical transfer, manifested by the abrupt changes in PLI reaction force during tensile loading.
The stiffness reduction is substantial at 39% when iron particles are added to the PLA filament formulation, assuming no significant differences in the grades of PLA in both filaments. On average, variations in elongation at break and tensile strength of the as-received PLI compared to PLA as-received filament are -6% and -71%, respectively. The notable reduction in elongation at break can be explained by the percolation of iron particles promoting interfacial damage, leading to a reduction in ultimate properties. However, the impact on tensile strength appears to be minor in the presence of iron particles.
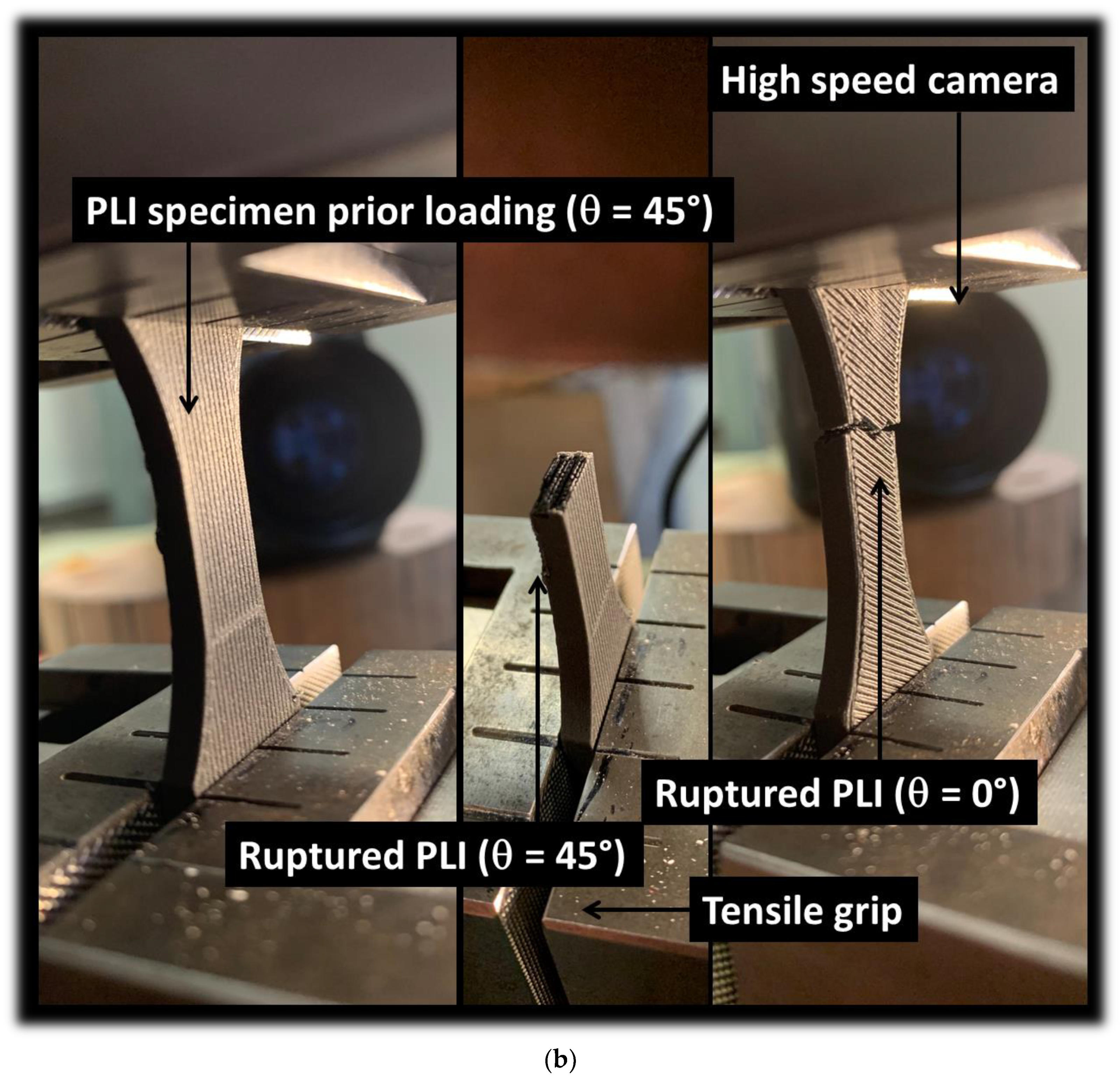
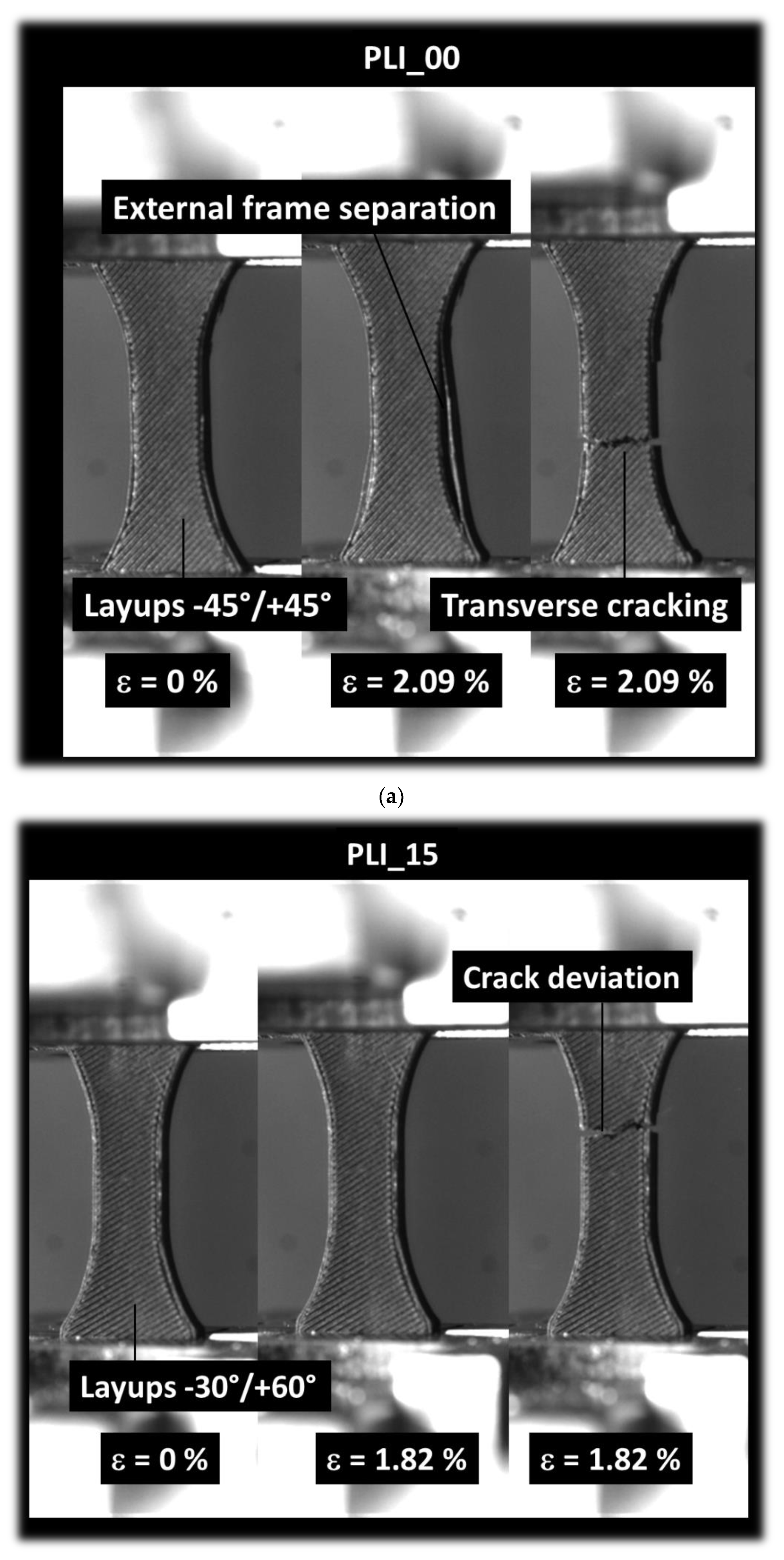
Figure 9 illustrates the fracture characteristics of PLI material printed throughout the sample thickness with a printing angle set at 0°. This orientation aligns with a building direction parallel to the sample thickness (horizontal orientation). The image captures the limited extension of the sample before rupture, revealing an overall quasi-brittle behaviour. The cracking process is notably swift, and the accumulation of damage is scarcely discernible.
Within the construction plane defined by the sample width and length, the impact of filament layup becomes evident. In the case of the 0° printing angle (
Figure 9a), distinct crack deviation toward -45° is observable, due to a significant shearing. However, the inherent brittleness of the specimen constrains substantial deviation, emphasizing a predominant opening mode. Additionally, besides the cracking behaviour, frame desoldering is noted, stemming from the uniaxial deformation of the filaments composing the external frame—specifically those oriented in the loading direction. The remaining filaments within the raster experience a combination of uniaxial and shearing forces.
When a printing angle of 15° is employed, a comparable cracking behaviour is noted, with the crack deviation now following a lower angle of -30° or 60° (
Figure 9b). This alteration in crack deviation aligns with the initial filament orientation within the layup, as depicted in
Figure 9b. It’s worth noting that a reduced degree of stretching is observed in this scenario when compared to the printing angle of 0°.
Increasing the printing angle further to 30° results in a layup that is closely oriented toward the transverse direction, as illustrated in
Figure 9c. This orientation makes it more favourable for transverse cracks to propagate throughout the external frame. Despite this, a noticeable change in the course of the main crack is observed, allowing the fracture to evolve in a mixed mode with two main crack angles: -15° and 75°.
When the printing angle is set at 45° (
Figure 9d), there is a significant likelihood of witnessing full unstable transverse cracking due to the presence of discontinuities oriented perpendicularly to the loading direction. In this scenario, cracking occurs predominantly under a full opening mode.
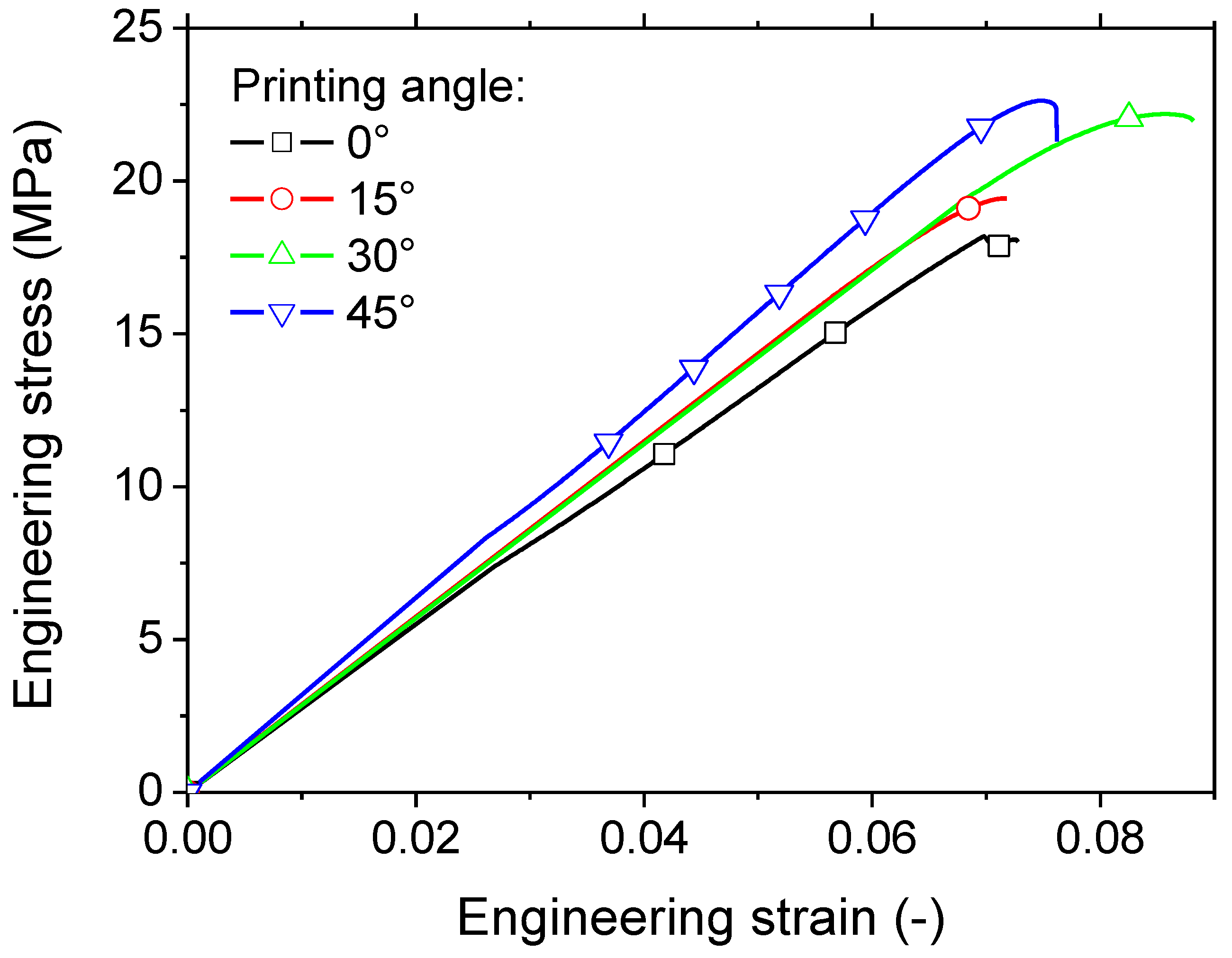
The tensile behaviour of various conditions is further elaborated in
Figure 10 through the examination of engineering stress–engineering strain curves. All tested samples demonstrate elastic characteristics with a modest plastic phase. The extent of plasticity is comparatively restrained when compared to the tensile behaviour of the original PLA or PLI filaments. The elastic-like behaviour can be attributed to the porosity induced during the manufacturing process, as discussed in
Figure 3,
Figure 4 and
Figure 5. The incorporation of iron particles, which exhibit percolation trend, appears to have a detrimental effect on the ductility of the 3D printed PLI.
The 3D printed composite with a printing angle of 45° is identified as the top performer, enhancing both strength and stiffness while minimising the material’s stretching capacity. This can be elucidated by the significant alignment of filaments in the loading direction, as depicted in
Figure 5. A more quantitative evaluation of the impact of the printing angle is summarised in
Table 1. Key engineering parameters, such as Young’s modulus (E
Y), tensile strength (σ
T), and elongation at break (ε
R) are derived from the tensile responses of 3D printed PLI samples.
Stiffness test results unveil a performance decline ranging from -52% for the optimal printing angle ( = 45°) to -61% for the least favourable one ( = 0°). Similar trends are observed for strength, displaying a reduction ranging from approximately -55% to -71% depending on the printing condition. The only engineering parameter that remains relatively unchanged is the elongation at break, experiencing only a 3% decrease for a printing angle of 0°. However, this value notably increases to 52% for the superior condition ( = 45°). The contrast between printing conditions can be interpreted as a trade-off between the enhancement of stiffness and the reduction of elongation at break.
Relative to the decline in mechanical performance compared to filament properties, the density of PLI composites experiences a reduction ranging from 18% to 42%, contingent on the specific printing condition. This decrease is linked to the porosity induced during the manufacturing process.