1. Introduction
Dispersion and polar interactions are the two important types of interactions between particles. The determination of these interactions is very used in the different domains of colloidal science, surface physics, adsorption, adhesion, adsorption, surface and interface. The dispersive interactions were studied and well-developed by Van der Waals. The corresponding forces, called Van der Waals forces, results from the temporary fluctuations in the charge distribution of the atoms or molecules; whereas, the polar forces or interactions include Coulomb interactions between permanent dipoles and between permanent and induced dipoles. The total interaction energy is the sum of the dispersive and polar interaction energies. The separation of these two types of energy is crucial to understand the behavior of molecules and therefore to predict the various surface physicochemical properties of materials and nanomaterials.
Since 1982, many scientists proposed several methods to separate the dispersive (or London) and polar (or specific) interactions between a solid substrate and a polar molecule. The first attempt for the separation of the two above contributions was proposed by Saint-Flour and Papirer [1-3] when studying untreated and silane-treated glass fibers by using inverse gas chromatography (IGC) and choosing a series of polar and non-polar adsorbates to quantify the dispersive and polar free energies. The authors adopted the concept of the vapor pressure
of the adsorbates to determine the specific free energy of adsorption
of polar molecules on glass fibers as a function of the absolute temperature
T by plotting the variations of
versus the logarithm of the vapor pressure
of probe, where
is the net retention volume and
R the ideal gas constant. Saint-Flour and Papirer [
3] determined the specific enthalpy
and entropy
of polar molecules adsorbed on the glass fibers and deduced their Lewis acid-base constants. Later, Schultz et al. [
4] tried to separate the two dispersive and specific interactions of carbon fibers by using the concept of the dispersive component
of the surface energy of the organic liquids by drawing
of as a function of
of n-alkanes and polar molecules adsorbed on the solid, where
a is the surface area of adsorbed molecule and
the Avogadro’s number. This method allowed to obtain the specific free energy and the dispersive component
of the surface energy of carbon fibers. In 1991, Donnet et al. [
5]. used the deformation polarizability
of solvents and obtained the specific free energy
of polar solvents adsorbed on natural graphite powders by representing the variations of as a function of
, where
is the electronic frequency of the probe and
h the Planck’s constant. With the difficulties and issues encountered with the previous methods, Brendlé and Papirer [
6,
7] used the topological index
, derived from the well-known Wiener index to obtain more accurate results. Other methods were also used in literature such as that the boiling point
[
8] and the standard enthalpy of vaporization
[
9]. In all the above methods, one obtained an excellent linearity of
of n-alkanes as a function of the chosen intrinsic thermodynamic parameter (
,
,
,
or
). The specific free potential
of polar molecule is then directly obtained by the distance the point representing the polar molecule to its hypothetic point located on the n-alkane straight-line. The specific enthalpy and entropy of adsorbed polar solvents as well as the Lewis acid base constants can easily deduced by thermodynamic considerations. The serious problem encountered in these different chromatographic methods that the obtained
One proved in several previous studies the non-validity of the method used by Schultz et al. due to the variations of the surface area a and of solvents as a function of the temperature [10-14]. The values of the surface area of organic molecules versus the temperature obtained on a certain solid material [10-14], cannot be always transferred to another solid, because of the different behaviors existing between the various solid surfaces and the adsorbed moleules.
The used chromatographic methods, even if they satisfied linear relations for n-alkanes adsorbed on solid surfaces, cannot be necessarily considered as accurate if they are not theoretically well-founded. One proved in previous paper [
11,
12] that the linearity of
of n-alkanes is satisfied for more than twenty intrinsic thermodynamic parameters and one concluded on the necessity to find new methods that are theoretically valid.
Given the disparity of the results obtained from the application of the various methods, one privileged, in this paper, the method based on the equation of the London dispersive interaction [
15] between the solvents and the solid materials. By using the London equation (15], one proposed in this study to determine the dispersive free energy
, the specific free energy
, the Lewis acid-base constants and the polar acidic and basic surface energy of several solid materials such as silica (SiO
2), alumina (Al
2O
3), magnesium oxide (MgO), zinc oxide (ZnO), Monogal-Zn, titanium dioxide (TiO
2) and carbon fibers.
2. Methods and models
Inverse gas chromatography (IGC) technique [16-24] was used in this study to characterize the surface properties of the above solid surfaces. IGC allowed us to obtain the net retention time and therefore the net retention volume of the various solvents adsorbed on the different solid materials. This allowed to obtain the free energy of adsorption
of the adsorbed molecules by using the following fundamental equation of IGC:
where
is a constant depending o
the temperature a
d the parameters of interaction between the solid and the solvent.
The total free energy of adsorption
is composed by the two dispersive
and polar
contributions of the total interaction energy:
The free dispersive energy between two non-identical materials was given by London [
15]:
where
and
are the respective deformation polarizabilities of molecules 1 and 2 separated by a distance
,
and
the ionization energies of molecules 1 and 2,
and
their characteristic electronic frequencies and
the permittivity of vacuum.
By denoting S the solid molecule 1 and X the probe molecule 2 and combining the previous equations (1-3), one obtained equation (4):
The thermodynamic parameter
chosen as new indicator variable in this original contribution is given by relation (5):
Indeed, the London dispersion interactions strongly depend on the deformation polarizability of the organic molecules and on the ionization energies of the solid and the solvents, because the approximation is not always valid and it depends on the product of the ionization energies . To avoid any source of errors on the determination of the London dispersive and polar energies, one privileged to use the true values of the ionization energies and not the approximation of the geometric mean.
Now, by drawing the variations of
of n-alkanes adsorbed on the solid material as a function of
at a fixed temperature
T, one obtained the linear equation given by (6):
where
is the slope of the n-alkanes straight line given by (7):
In the case of adsorbed polar organic molecule such as toulene, the distance between its representative point given by
and the straight-line of n-alkanes shown on
Figure 1, allowed to obtain the polar free energy
(London dispersion interaction).
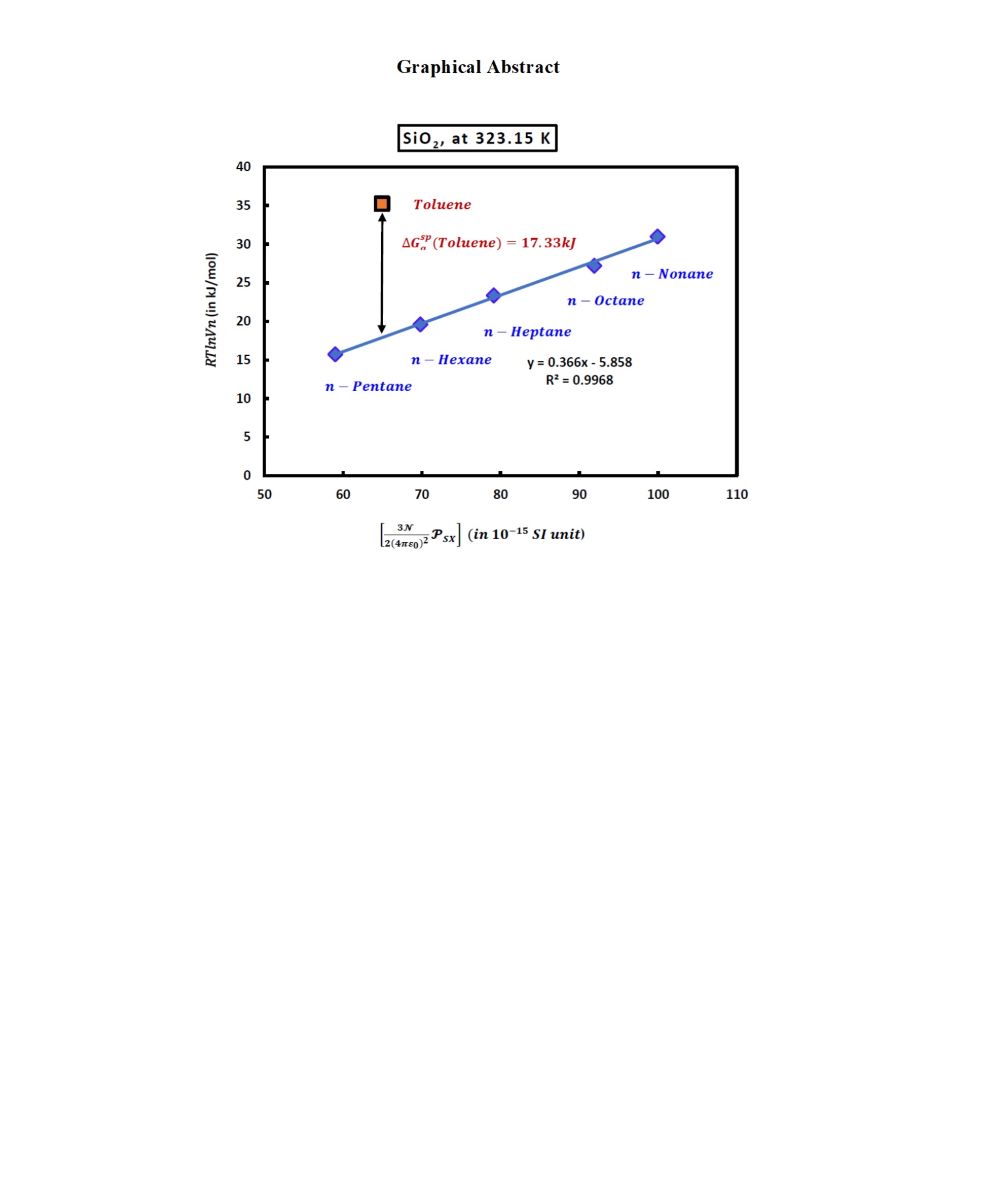
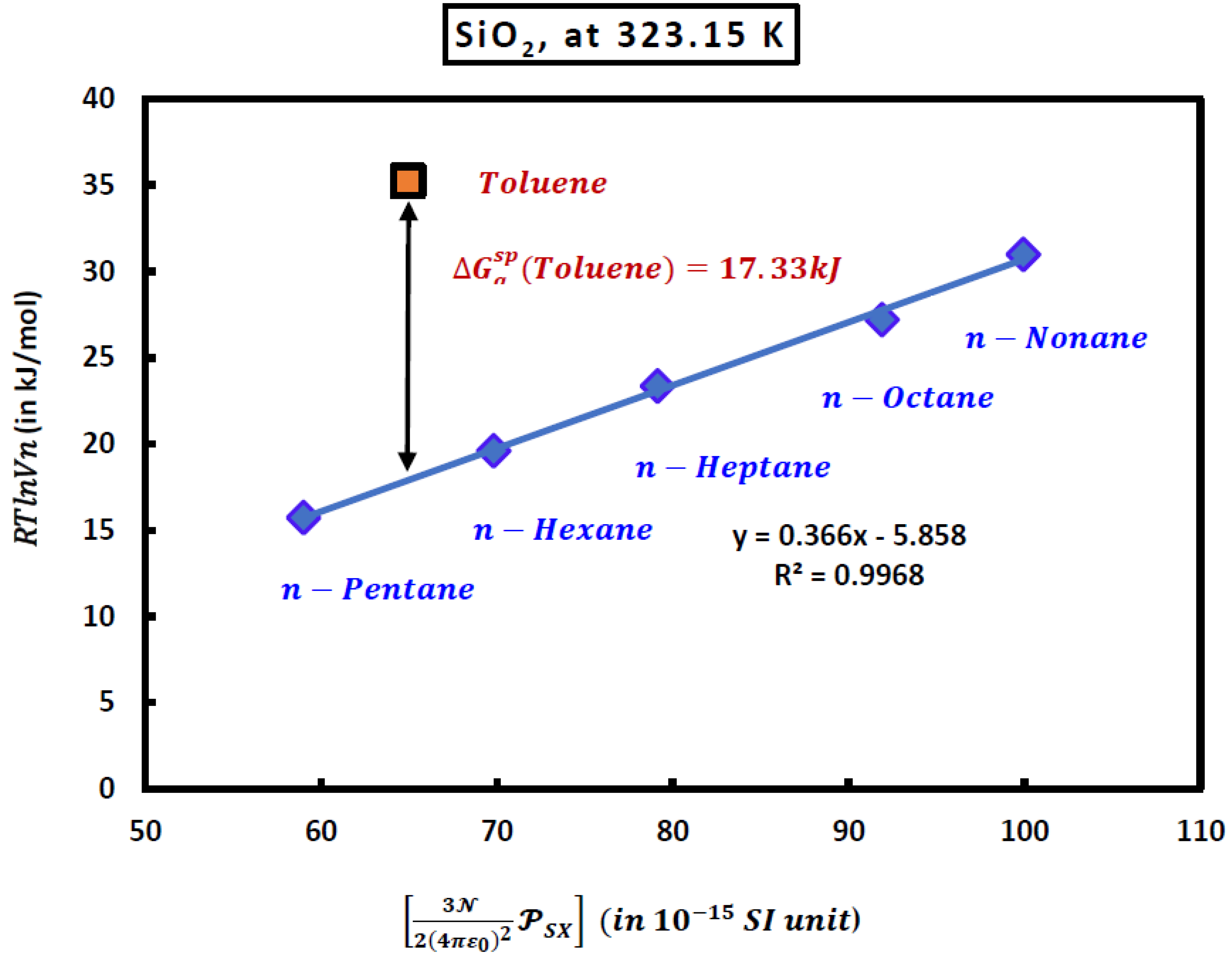
The numerical value of the London dispersion interaction of toluene (in kJ/mol) adsorbed on silica particles is given by the following equation
Experimental results gave at 323.15K:
And one obtained at this temperature the value of the specific free energy of toluene from (8):
By varying the temperature, the calculations allowed to determine the variations of
of polar probes as a function of the temperature and obtain the specific enthalpy
and entropy
of the various polar probes adsorbed on the solid surfaces from equation (11):
And then to deduce the Lewis’s acid base constants
KA and
KD by equation (12):
where
AN and
DN are respectively the electron donor and acceptor numbers of the polar molecule. These numbers were calculated by Gutmann [
25] and corrected by Fowkes [
26].
By using the representation
and equation (13):
The slope of the straight-line gave the acidic constant , whereas, the basic constant is obtained by the ordinate at origin of the straight-line given by equation (13).
However, in many cases, one proved that equation (13) is not verified and one previously proposed another relation taking into account the amphoteric effect of the solid material [
27].
where
is the coupling constant representing the amphoteric character of material.
Equation (14) can be written as:
By considering a polar molecule symbolized by
and putting:
One can write the general equation (17) representing any polar molecule
in interaction with solid surfaces:
where
,
and
are experimentally well-known, whereas,
,
and
are the unkown quantities of the problem (17).
For n polar molecules (), the solution of the linear system (17) can be obtained by the least squares method by finding the vector that minimizes the sum of the squares of the residuals.
In this case, The system of equations (17) will be transformed to a linear system represented by the following equations:
Equations (18) can be represented by the following matrix system
Symbolized by the matrix equation:
The matrix equation is inversible because the matrix
is symmetric and then there is a unique solution
given by the formal equation (21):
Our method was used in all solid materials that did not satisfy the classic equation (13).
In this study, one also determined the Lewis entropic acidic
and basic
parameters to obtain the Lewis entropic acid base character of the solid materials. The equations (22) and (23) were given by analogy that of the Lewis enthalpic acid-base constants
and
:
or
4. Results
4.1. New approach for the calculation of the deformation polarizability and the indicator parameter
Our new approach previously presented allowed us to obtain all necessary parameters of organic solvents and solid substrates by using their values taken from the Handbook of Physics and Chemistry [
28]. The obtained results are presented below on
Table 1,
Table 2,
Table 3,
Table 4,
Table 5,
Table 6,
Table 7 and
Table 8.
In this new approach, one gave more precise values of the parameters of molecules such as the deformation polarizability and the harmonic mean of the ionization energies of solids and organic solvents in contrary of those proposed by Donnet et al. [
5] that only took the characteristic electronic frequencies of the probes independently of those of the solid. Indeed,
Table 2 to 8 clearly showed that the harmonic mean of the ionization energies of the solvents varied as a function of the used solid material.
To show the difference between our values and those of Donnet et al. [
5], one presented on
Table 9 the values of the deformation polarizability of some polar molecules and two n-alkanes.
Table 9 showed that the values relative to some solvents such as n-decane, dichloromethane and methanol and those of solid particles are not given by Donnet et al. The relative error reaches 10% that can have negative effect on the determination of the specific free energy.
Now, if one adds the error committed by Donnet et al. [
5] when neglecting the variations of the harmonic mean of ionization energies
for the various polar molecules that vary from 20% to 70%. Indeed, this parameter varies from a solid surface to another solid material. The variation in the value of
of organic molecules between two solids can reach 70% in certain cases such as ZnO and TiO
2 (
Table 4 and
Table 7).
4.2. London dispersive surface energy of solid particles by using thermal model
The thermal model [10-14] was used to determine the London dispersive surface energy
of the various solid materials used in this study. This model took into consideration the effect of the temperature on the surface area of organic molecules. The obtained results are presented on
Table 10 at several temperatures.
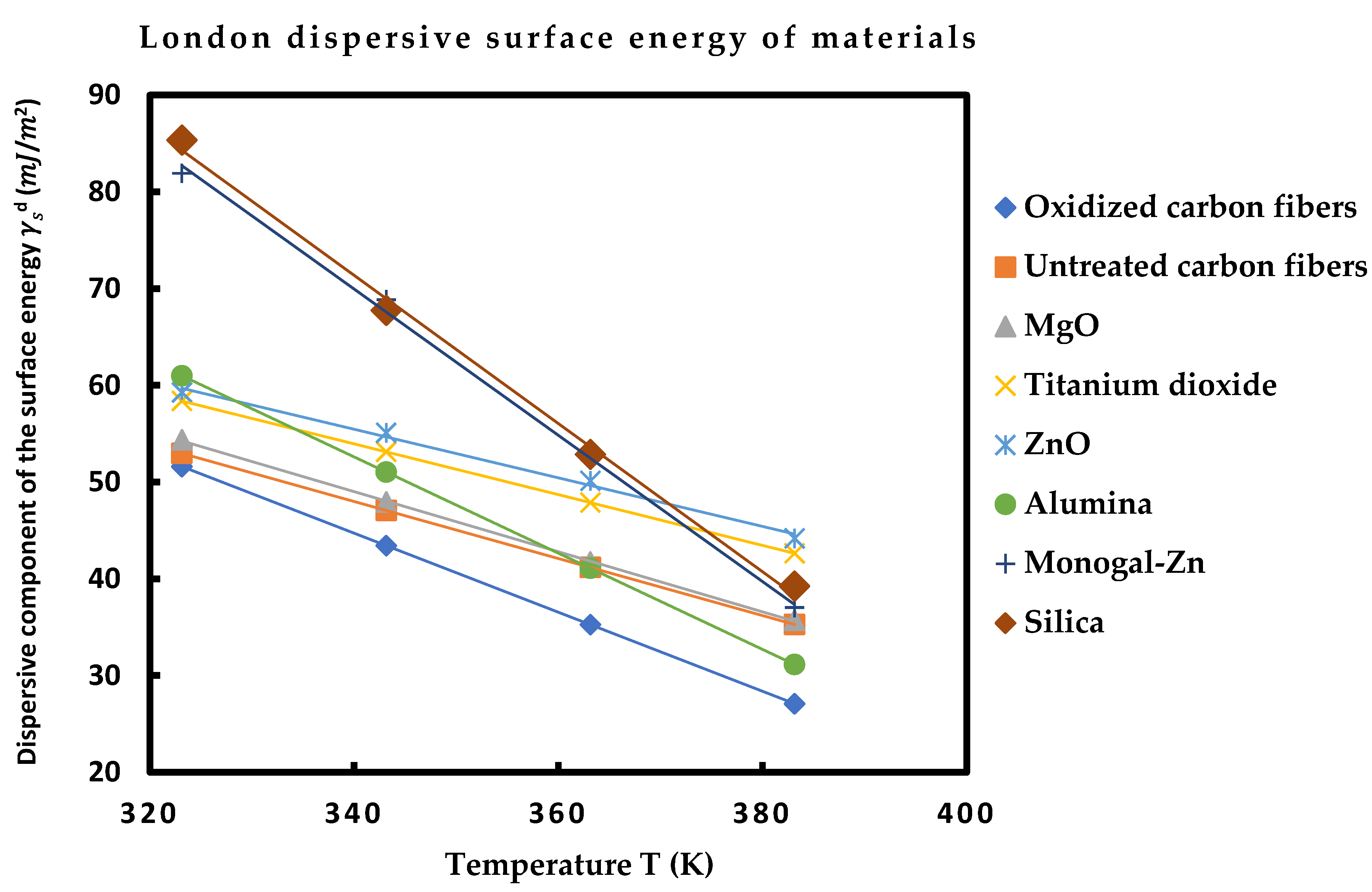
Table 10 showed that the various solid surfaces can be classified with increasing order of their London dispersive surface energy as following:
Oxidized carbon fibers < Untreated carbon fibers < MgO < ZnO < Al2O3 < Monogal-Zn < SiO2
The highest London dispersive surface energy was obtained by the silica particles. One also observed that the dispersive surface energy of the two carbon fibers are very close, and silica and monogal surfaces exhibited close values of
. Furthermore, the linearity of
was assured for all materials with an excellent linear regression coefficients approaching 1.000 (
Figure 2).
4.3. Polar surface interactions between solid materials and organic molecules
By using our new method and new findings presented in section 3, one determined the values of the polar free surface energy (
) of the various polar solvents adsorbed on the various solid particles as a function of the temperature
T. The results were given on
Table 11.
Table 11 clearly showed the amphoteric behavior of the various solid surfaces with different acid-base interactions depending on the number of the surface group sites present on the solid particles.
Table 11 led to classify the polar solvents, for each solid surface in increasing order of the polar free surface energy of interaction.
In the case of silica particles, one obtained the following order:
Ethyl Acetate < CCl4 < Acetone < Nitromethane< Toluene < CHCl3 < CH2Cl2 < Diethyl ether < THF
Proving a strong interaction with the acidic organic molecules and lower for the basic solvents and therefore concluding to more basic behavior.
In this case of MgO, the obtained order was:
CH2Cl2 < CHCl3< Ethyl acetate < Diethyl ether < Acetone < Tetrahydrofuran
That showed a behvior rather amphoteric.
For ZnO, one also observed a strong amphoteric character:
Benzene < CHCl3 < CH2Cl2 < Ethyl acetate < Diethyl ether < Tetrahydrofuran
The amphoteric character was proved for monogal-Zn particles:
CH2Cl2 < Ethyl acetate < CHCl3< Diethyl ether < Acetone < Tetrahydrofuran
For alumina, one obtained the following order:
CCl4 < CH2Cl2 < Ethyl acetate < Diethyl ether < CHCl3 < Toluene < Tetrahydrofuran
In case of TiO2:
CH2Cl2 < CHCl3< Ethyl acetate < Acetonitrile < Benzene < Acetone < THF < nitromethane
For untreated carbon fibers:
CCl4 < Diethyl ether < CH2Cl2 < Benzene < Ethyl acetate < Tetrahydrofuran
and the oxidized carbon fibers presented an amphoteric character:
CCl4 < Diethyl ether < Benzene < CH2Cl2 < CHCl3 < Benzene < Ethyl acetate < THF< Acetone
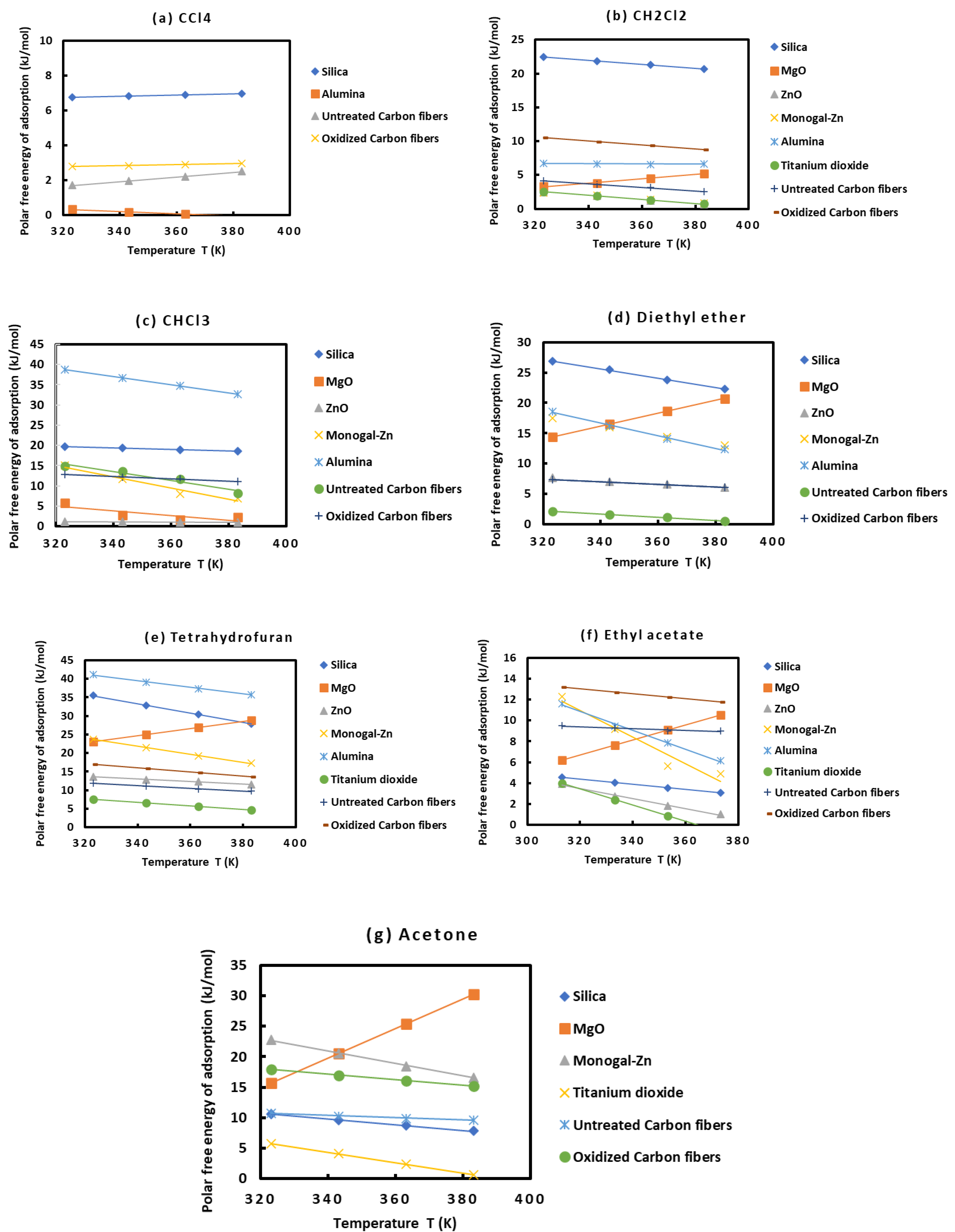
In order to compare the behavior of the various solids as a function of the different polar solvents, one plotted on Figures 3 the variations of () of the various polar molecules as a function of the temperature.
The results on Figures 3 showed different behaviors of the various solid surfaces in interaction with the polar molecules. One gave the classification of these solid materials in increasing order of their polar free energies with the different polar solvents:
o with CCl4: alumina < untreated carbon fibers < oxidized carbon fibers < silica
o with CH2Cl2, Monogal-Zn < ZnO < TiO2 < MgO < untreated carbon fibers < alumina < oxidized carbon fibers < silica
o with CHCl3, ZnO < MgO < oxidized carbon fibers < untreated carbon fibers < Monogal-Zn < silica < alumina
o with diethyl ether, untreated carbon fibers < oxidized carbon fibers < ZnO < MgO < Monogal-Zn < alumina < silica
o with tetrahydrofuran, TiO2 < untreated carbon fibers < ZnO < oxidized carbon fibers < MgO < Monogal-Zn < silica < alumina
o with ethyl acetate, TiO2 < ZnO < silica < MgO < untreated carbon fibers < alumina < monogal-Zn < oxidized carbon fibers
o with acetone, TiO2 < silica < untreated carbon fibers < MgO < oxidized carbon fibers
These results proved that alumina, silica and oxidized carbon fibers exhibited stronger interactions with the acidic and basic molecules then showing their higher amphoteric character than the other solid substrates.
4.4. Lewis’s ethalpic and entropic acid base parameters
By using the results of
given on
Table 11 and Figures 3, one determined from equation (11), the different values of the polar enthalpy (
and entropy (
of adsorption of the various polar molecules on the solid surfaces. The results were presented on
Table 12.
Table 12 also showed a difference in the behavior of the various solid surfaces in interaction with acidic, basic and amphoteric polar solvents. In order to qunatify the acid-base constants of the solid materials, one used equations (13) and (23). The obtained values of Lewis enthalpic acid base constants
and
and Lewis entropic acid base constants
and
of the different solid particles were presented on
Table 13. The comparison of the acid-base behavior of the different solid materials allowed to classify them in decreasing order of acidity and basicity.
For the acidity, one obtained the following classification:
Silica > alumina > Monogal-Zn > TiO2 > ZnO > oxidized carbon fibers > untreated carbon fibers > MgO
Whereas, the comparison between their basicity led to give the following order:
Oxidized carbon fibers > alumina > untreated carbon fibers > ZnO > Monogal-Zn > Silica > MgO > TiO2
By comparing the various solids in decreasing order of their ratio /, on found the following classification:
Oxidized carbon fibers > untreated carbon fibers > MgO > ZnO > TiO2 > alumina > Monogal-Zn > Silica
The last classification seems to be very interesting, because the oxidization of carbon fibers will increase the polar surface groups and therefore their basicity, in contrary to the behavior of silica that exhibits higher acidity than the other solid surfaces.
However, when we observed the linear regression coeffcients given on
Table 13, one found that the liearity of equations (13) and (23) are not satisfied for most of the solid surfaces. In such case, a correction has to be executed. To do that, one used equation (17) and resolved the linear system with three unkown numbers. The solution was perofrmed for all solids except for titanium dioxide that presented an excellent linear regression coefficient. The more results were given on
Table 14.
Table 14 gave the corrected values of the acid-base constants with an additional constant called coupling constant reflecting the amphoteric character of materials.
One obsrved that the classification of acidity of different solid materials was conserved after correction, however it was changed for the basicity. One found the following classification of solid surfaces in decreasing basicity:
Oxidized carbon fibers > silica > monogal-Zn > untreated carbon fibers > alumina > ZnO > TiO2 > MgO
It was proved that the oxidized carbon fibers exhibited the strongest basicity, whereas, silica had the highest acidity. It was also showed the MgO presented more neutral surface with small basic tendency.
4.5. Consequences of the application of the new method
The first scientific result of the application of the new parameter
relative to the interaction between solids and organic molecule was the separation between the London dispersive energy and the polar free energy of the adsorption of polar organic molecules and solid surfaces. It is the first time that we were able to calculate exactly the two contributions of the free surface energy of interaction. Equation (6) was perfectly applied for all solids and solvents with an excellent linear regression coefficient approaching 1.000 and the determination of the slope
of the straight line given by equation (6) in the case of n-alkanes adsorbed on solid surfaces conducted to calcule the London dipersive energy of interaction not only for n-alkanes, but also for polar organic solvents by using the following relation
With this new approach, one characterized all studied solids by giving on Tables S1 to S16, the two London dispersive and polar free energies of interaction between solids and organic molecules. This also allowed to obtain the total free surface energy of adsorption without calculating the surface specific area of the considered solid materials.
The second consequence was to clearly verify the insufficiency of the approach proposed by Donnet et al. [
5]. Indeed, if we applied their method on silica particles, one obtained the values of (
) of polar solvents adsorbed on silica surfaces. These results compared to our new findings were presented on
Table 15.
The results on
Table 15 clearly showed a large difference between the values obtained by the two above methods. The calculation of the ratios
,
and
given on
Table 16 showed a surestimation of the values of
obtained by Donnet et al. method varying from 1.3 to 7.7 times the values obtained by our new method. Whereas, in the calculation of the specific entropy and enthalpy,
Table 16 showed ratios varying from 3.1 to 23.7 strongly depending on the adsorbed polar molecule. However, one globaly found a ratio approaching 2 for most of polar molecules.
These large variations of the values obtained by applying Donnet et al. method is certainly due to the fact that this method omitted the variation of the harmonic mean
of the ionization energies of the solid and the adsorbed polar solvent given by relation (25).
Donnet et al. used the concept
or
. The variations of
is not identical to those of
of the interaction solid-polar molecule as it was shown by
Table 17.
It was observed on
Table 17 that the harmonic mean
strongly depend on the interaction between the solid and the polar solvent and cannot be considered as constant for all studied materials as was supposed by the method proposed by Donnet et al.
The third consequence of our new approach was the determination of the average separation distance H between the solid particle and the organic moolecule as a function of the temperature when the deformation polarizability of the solid is known. By using equation (7) and the experimental results, one gave on
Table 18 the values of the average separation distance H at different temperatures for the various solid substrates.
Table 18 showed that the average separation distance H is comprised between 4.45 Å and 5.56 Å for the various solid particles. A slight increasing effect of the temperature on the separation distance was observed in all studied solid substrates. Furthermore, one observed that the separation distance between a solid and an organic molecule is an intrinsic parameter of the solid.
Table 18 allowed to classify the various solid materials in increasing order of the separation distance for all temperatures:
Untreated carbon fibers Oxidized carbon fibers > ZnO > alumina > Monogal-Zn > Silica > MgO > TiO2
This classification is very close to that obtained with the basicity of solid materials. It seems that when the basicity or the ratio / decreases, the separation distance slightly increases to reach a maximum value with TiO2 equal to 5.50 Å.
The fourth consequence of this new method was to be able to give with more accuracy the values of the acid-base surface energy of the various solid materials. Indeed, by applying Van Oss et al. relation [
29] that gave the specific enthalpy of adsorption as a function of the Lewis acid surface energy of the solid surface
and the solvent
; and the corresponding Lewis base surface energy (
for the surface and
for the solvent) by equation (26)
By choosing two monopolar solvents such as ethyl acetate (EA) and dichloromethane characterized by:
The Lewis’s acid and base surface energies of a solid surface
and
can be obtained from relations (26) and (27):
The experimental values of free specific energy of ethyl acetate
and dichloromethane
given in
Table 19, one determined the values of the specific acid and base surface energy contributions
,
as well as the acid-base surface energy
given by relation (29):
By using the values given on tables 10 and 19, and relation (29), one presented on
Table 20 the Lewis’s acid and base surface energies of solid particles
,
,
and the total surface energy
of the various solid materials. The total surface energy
of the solid surfaces was obtained by using relation (30):
The values of the dispersive surface energy of the different solid materials were taken from table 10.
The values of the different acid-base surface energies of the various solid substrates given on
Table 20 showed that the oxidized carbon fibers and the silica particles gave the highest values of
,
and
followed by alumina particles and monogal-Zn surfaces, whereas, the oxidized carbon fibers and alumina surfaces gave larger values of
again confirming the highest acid-base properties of these materials. The determination of the ratio
of the solid materials showed that this ratio varies from 12% for ZnO particles to reach 70% for the oxidized carbon fibers and about 50% for silica and alumina surfaces. This clearly proved the strong contribution of acid-base surface energy relative to the corresponding London dispersive energy.
5. Conclusions
A new method of separation of London dispersive and polar surface energy was proposed by using the inverse gas chromatography technique (IGC) at infinite dilution. The parameter of polarizability of organic molecules adsorbed on eight different solid materials was used to propose a new parameter taking into account all terms involved in the expression of London dispersive energy of interaction. The originality of this new method concerned the full determination and use of a new intrinsic thermodynamic parameter reflecting the London dispersive energy of interaction between solid materials and organicmolecules. One calculated the parameter for different materials and organic molecules. Experimental results obtained by IGC allowed to determine the average separation distance solid-organic solvents at different temperatures. The dispersive free energy and the polar energy of n-alkanes and polar probes were determined by this method. The thermal model was used to quantify the London dispersive surface energy of the various solid materials at different temperatures and allowed to determine the different components , and of acid-base surface energies of solid particles as well as their total surface energy . Results showed the highest acid-base surface energy was obtained by the oxidized carbon fibers followed by silica particles and alumina surfaces.
The determination of the polar interaction energy of the different polar molecules adsorbed on the solid materials allowed to obtain the polar enthalpy and entropy of interaction and therefore the enthalpic and entropic Lewis’s acid-base constants. The results showed that all studied solid surfaces exhibited amphoteric behavior with stronger Lewis’s basicity. The oxidized and untreated carbon fibers, ZnO and silica particles showed an important basic force, whereas, silica, alumina, monogal-Zn presented the highest Lewis’s acidity.
The application of the classic equation (12) allowing the determination of the acid-base constants showed poor linear regression coefficients. It was corrected by using Hamieh model that added a coupling constant reflecting the amphoteric character of solid materials.
It was proved that the method proposed by Donnet et al. neglected the values of harmonic mean of ionization energies of solids and solvents and this conducted to a surestimation of the specific or polar free energy of interaction reaching in several cases 5 times the corrected value. By taking into account the different values of harmonic mean and the deformation polarizability of n-alkanes and polar organic molecules, one obtained more accurate values of the London dispersive energy, the polar energy, the acid-base constants and the acid-base surface energies of the various solids in interaction with several polar molecules.
Figure 1.
Variations of of n-alkanes and toluene adsorbed on the silica particles as a function of at T=323.15K.
Figure 1.
Variations of of n-alkanes and toluene adsorbed on the silica particles as a function of at T=323.15K.
Figure 2.
Dispersive component of the surface energy of solid materials as a function of the temperature T (K).
Figure 2.
Dispersive component of the surface energy of solid materials as a function of the temperature T (K).
Figure 3.
Evolution of the specific free surface energy () of the various solid materials in interactions with the different polar molecules Such as CCl4 (a), CH2Cl2 (b), CHCl3 (c), diethyl ether (d), tetrahydrofuran (e), ethyl acetate (f), and acetone (g) as function of the temperature.
Figure 3.
Evolution of the specific free surface energy () of the various solid materials in interactions with the different polar molecules Such as CCl4 (a), CH2Cl2 (b), CHCl3 (c), diethyl ether (d), tetrahydrofuran (e), ethyl acetate (f), and acetone (g) as function of the temperature.
Table 1.
Values of deformation polarizability (in 10-30 m3) and (in 10-40 C m2/V) and ionization energy (in eV) of the various organic molecules and solid materials.
Table 1.
Values of deformation polarizability (in 10-30 m3) and (in 10-40 C m2/V) and ionization energy (in eV) of the various organic molecules and solid materials.
| Molecule |
(eV) |
(in 10-30 m3) |
(in 10-40 C m2/V) |
| n-pentane |
10.28 |
9.99 |
11.12 |
| n-hexane |
10.13 |
11.90 |
13.24 |
| n-heptane |
9.93 |
13.61 |
15.14 |
| n-octane |
9.80 |
15.90 |
17.69 |
| n-nonane |
9.71 |
17.36 |
19.32 |
| n-decane |
9.65 |
19.10 |
21.25 |
| CCl4
|
11.47 |
10.85 |
12.07 |
| Nitromethane |
11.08 |
7.37 |
8.20 |
| CH2Cl2
|
11.32 |
7.21 |
8.02 |
| CHCl3 |
11.37 |
8.87 |
9.86 |
| Diethyl ether |
9.51 |
9.47 |
10.54 |
| Tetrahydrofuran |
9.38 |
8.22 |
9.15 |
| Ethyl acetate |
10.01 |
9.16 |
10.19 |
| Acetone |
9.70 |
6.37 |
7.09 |
| Acetonitrile |
12.20 |
4.44 |
4.94 |
| Toluene |
8.83 |
11.80 |
13.13 |
| Benzene |
9.24 |
10.35 |
11.52 |
| Methanol |
10.85 |
3.28 |
3.65 |
| SiO2
|
8.15 |
5.42 |
6.04 |
| MgO |
7.65 |
5.47 |
6.09 |
| ZnO |
4.35 |
5.27 |
5.86 |
| Zn |
9.39 |
5.82 |
6.47 |
| Al2O3
|
5.99 |
5.36 |
5.96 |
| TiO2
|
9.50 |
7.12 |
7.92 |
| Carbon |
11.26 |
1.76 |
1.96 |
Table 2.
Values of the harmonic mean of the ionization energies of SiO2 particles and organic solvents (in 10-19 J) and the parameter (in 10-15 SI unit) for the various organic molecules.
Table 2.
Values of the harmonic mean of the ionization energies of SiO2 particles and organic solvents (in 10-19 J) and the parameter (in 10-15 SI unit) for the various organic molecules.
| Molecule |
(in 10-19J) |
(in 10-15 SI) |
| n-pentane |
7.274 |
58.992 |
| n-hexane |
7.226 |
69.814 |
| n-heptane |
7.162 |
79.135 |
| n-octane |
7.119 |
91.901 |
| n-nonane |
7.089 |
99.919 |
| n-decane |
7.069 |
109.623 |
| CCl4
|
7.623 |
67.151 |
| Nitromethane |
7.513 |
44.956 |
| CH2Cl2
|
7.582 |
44.379 |
| CHCl3 |
7.596 |
54.666 |
| Diethyl ether |
7.022 |
53.988 |
| Tetrahydrofuran |
6.977 |
46.564 |
| Ethyl acetate |
7.188 |
53.453 |
| Acetone |
7.087 |
36.652 |
| Acetonitrile |
7.818 |
28.180 |
| Toluene |
6.780 |
64.955 |
| Benzene |
6.930 |
58.231 |
| Methanol |
7.447 |
19.829 |
Table 3.
Values of the harmonic mean of the ionization energies of MgO particles and organic solvents (in 10-19 J) and the parameter (in 10-15 SI unit) for the various organic molecules.
Table 3.
Values of the harmonic mean of the ionization energies of MgO particles and organic solvents (in 10-19 J) and the parameter (in 10-15 SI unit) for the various organic molecules.
| Molecule |
(in 10-19J) |
(in 10-15 SI) |
| n-pentane |
7.018 |
56.917 |
| n-hexane |
6.974 |
67.374 |
| n-heptane |
6.914 |
76.393 |
| n-octane |
6.874 |
88.735 |
| n-nonane |
6.846 |
96.490 |
| n-decane |
6.828 |
105.872 |
| CCl4
|
7.343 |
64.680 |
| Nitromethane |
7.241 |
43.325 |
| CH2Cl2
|
7.304 |
42.754 |
| CHCl3 |
7.317 |
52.662 |
| Diethyl ether |
6.783 |
52.153 |
| Tetrahydrofuran |
6.742 |
44.991 |
| Ethyl acetate |
6.938 |
51.595 |
| Acetone |
6.844 |
35.395 |
| Acetonitrile |
7.523 |
27.117 |
| Toluene |
6.557 |
62.820 |
| Benzene |
6.697 |
56.277 |
| Methanol |
7.179 |
19.116 |
Table 4.
Values of the harmonic mean of the ionization energies of ZnO particles and organic solvents (in 10-19 J) and the parameter (in 10-15 SI unit) for the various organic molecules.
Table 4.
Values of the harmonic mean of the ionization energies of ZnO particles and organic solvents (in 10-19 J) and the parameter (in 10-15 SI unit) for the various organic molecules.
| Molecule |
(in 10-19J) |
(in 10-15 SI) |
| n-pentane |
4.891 |
39.665 |
| n-hexane |
4.869 |
47.041 |
| n-heptane |
4.840 |
53.478 |
| n-octane |
4.820 |
62.224 |
| n-nonane |
4.807 |
67.745 |
| n-decane |
4.797 |
74.392 |
| CCl4
|
5.046 |
44.451 |
| Nitromethane |
4.998 |
29.904 |
| CH2Cl2
|
5.028 |
29.431 |
| CHCl3 |
5.034 |
36.231 |
| Diethyl ether |
4.776 |
36.716 |
| Tetrahydrofuran |
4.755 |
31.732 |
| Ethyl acetate |
4.852 |
36.080 |
| Acetone |
4.806 |
24.852 |
| Acetonitrile |
5.131 |
18.494 |
| Toluene |
4.662 |
44.666 |
| Benzene |
4.733 |
39.769 |
| Methanol |
4.968 |
13.230 |
Table 5.
Values of the harmonic mean of the ionization energies of Monogal-Zn and organic solvents (in 10-19 J) and the parameter (in 10-15 SI unit) for the various organic molecules.
Table 5.
Values of the harmonic mean of the ionization energies of Monogal-Zn and organic solvents (in 10-19 J) and the parameter (in 10-15 SI unit) for the various organic molecules.
| Molecule |
(in 10-19J) |
(in 10-15 SI) |
| n-pentane |
7.852 |
63.683 |
| n-hexane |
7.797 |
75.326 |
| n-heptane |
7.722 |
85.324 |
| n-octane |
7.672 |
99.042 |
| n-nonane |
7.638 |
107.648 |
| n-decane |
7.615 |
118.076 |
| CCl4
|
8.261 |
72.769 |
| Nitromethane |
8.132 |
48.658 |
| CH2Cl2
|
8.212 |
48.070 |
| CHCl3 |
8.228 |
59.222 |
| Diethyl ether |
7.560 |
58.122 |
| Tetrahydrofuran |
7.508 |
50.105 |
| Ethyl acetate |
7.752 |
57.650 |
| Acetone |
7.635 |
39.486 |
| Acetonitrile |
8.490 |
30.603 |
| Toluene |
7.280 |
69.743 |
| Benzene |
7.453 |
62.627 |
| Methanol |
8.054 |
21.447 |
Table 6.
Values of the harmonic mean of the ionization energies of and organic solvents (in 10-19 J) and the parameter (in 10-15 SI unit) for the various organic molecules.
Table 6.
Values of the harmonic mean of the ionization energies of and organic solvents (in 10-19 J) and the parameter (in 10-15 SI unit) for the various organic molecules.
| Molecule |
(in 10-19J) |
(in 10-15 SI) |
| n-pentane |
6.056 |
49.114 |
| n-hexane |
6.023 |
58.186 |
| n-heptane |
5.978 |
66.053 |
| n-octane |
5.948 |
76.784 |
| n-nonane |
5.927 |
83.541 |
| n-decane |
5.913 |
91.697 |
| CCl4
|
6.296 |
55.460 |
| Nitromethane |
6.221 |
37.222 |
| CH2Cl2
|
6.268 |
36.687 |
| CHCl3 |
6.277 |
45.177 |
| Diethyl ether |
5.880 |
45.209 |
| Tetrahydrofuran |
5.849 |
39.033 |
| Ethyl acetate |
5.996 |
44.590 |
| Acetone |
5.926 |
30.646 |
| Acetonitrile |
6.428 |
23.171 |
| Toluene |
5.710 |
54.699 |
| Benzene |
5.816 |
48.867 |
| Methanol |
6.175 |
16.443 |
Table 7.
Values of the harmonic mean of the ionization energies of (in 10-15 SI unit) for the various organic molecules.
Table 7.
Values of the harmonic mean of the ionization energies of (in 10-15 SI unit) for the various organic molecules.
| Molecule |
(in 10-19J) |
(in 10-15 SI) |
| n-pentane |
7.900 |
64.071 |
| n-hexane |
7.844 |
75.781 |
| n-heptane |
7.768 |
85.834 |
| n-octane |
7.718 |
99.631 |
| n-nonane |
7.683 |
108.285 |
| n-decane |
7.660 |
118.773 |
| CCl4
|
8.314 |
73.236 |
| Nitromethane |
8.183 |
48.965 |
| CH2Cl2
|
8.264 |
48.376 |
| CHCl3 |
8.281 |
59.600 |
| Diethyl ether |
7.604 |
58.462 |
| Tetrahydrofuran |
7.552 |
50.396 |
| Ethyl acetate |
7.799 |
57.996 |
| Acetone |
7.680 |
39.719 |
| Acetonitrile |
8.546 |
30.804 |
| Toluene |
7.321 |
70.137 |
| Benzene |
7.496 |
62.988 |
| Methanol |
8.104 |
21.581 |
Table 8.
Values of the harmonic mean of the ionization energies of carbon fibers and organic solvents (in 10-19 J) and the parameter (in 10-15 SI unit) for the various organic molecules.
Table 8.
Values of the harmonic mean of the ionization energies of carbon fibers and organic solvents (in 10-19 J) and the parameter (in 10-15 SI unit) for the various organic molecules.
| Molecule |
(in 10-19J) |
(in 10-15 SI) |
| n-pentane |
8.598 |
69.736 |
| n-hexane |
8.532 |
82.430 |
| n-heptane |
8.443 |
93.286 |
| n-octane |
8.384 |
108.220 |
| n-nonane |
8.342 |
117.574 |
| n-decane |
8.314 |
128.928 |
| CCl4
|
9.091 |
80.082 |
| Nitromethane |
8.935 |
53.465 |
| CH2Cl2
|
9.032 |
52.869 |
| CHCl3 |
9.052 |
65.147 |
| Diethyl ether |
8.249 |
63.421 |
| Tetrahydrofuran |
8.188 |
54.640 |
| Ethyl acetate |
8.479 |
63.053 |
| Acetone |
8.339 |
43.125 |
| Acetonitrile |
9.369 |
33.772 |
| Toluene |
7.917 |
75.847 |
| Benzene |
8.122 |
68.249 |
| Methanol |
8.841 |
23.543 |
Table 9.
Values of deformation polarizability (in 10-40 C m2/V) compared to those proposed by Donnet et al. of the various organic molecules, with the calculated relative error.
Table 9.
Values of deformation polarizability (in 10-40 C m2/V) compared to those proposed by Donnet et al. of the various organic molecules, with the calculated relative error.
| Molecule |
(in 10-40 C m2/V)
(Donnet values) |
(in 10-40 C m2/V)
(Our values) |
Relative error (in %) |
| n-nonane |
19.75 |
19.32 |
2.2 |
| n-decane |
- |
21.25 |
- |
| CCl4
|
11.68 |
12.07 |
3.2 |
| CH2Cl2
|
- |
8.02 |
- |
| CHCl3 |
10.57 |
9.86 |
7.2 |
| Diethyl ether |
9.71 |
10.54 |
8.0 |
| Tetrahydrofuran |
8.77 |
9.15 |
4.2 |
| Ethyl acetate |
10.79 |
10.19 |
5.9 |
| Acetone |
7.12 |
7.09 |
0.4 |
| Acetonitrile |
5.43 |
4.94 |
10.0 |
| Toluene |
13.68 |
13.13 |
4.2 |
| Benzene |
11.95 |
11.52 |
3.7 |
| Methanol |
- |
3.65 |
- |
| SiO2
|
- |
6.04 |
- |
| MgO |
- |
6.09 |
- |
| ZnO |
- |
5.86 |
- |
| Zn |
- |
6.47 |
- |
| Al2O3
|
- |
5.96 |
- |
| TiO2
|
- |
7.92 |
- |
| Carbon |
- |
1.96 |
- |
Table 10.
Values of the London dispersive surface energy (in mJ/m2) of the various solid materials
Table 10.
Values of the London dispersive surface energy (in mJ/m2) of the various solid materials
| Temperature T(K) |
323.15 |
343.15 |
363.15 |
383.15 |
Equation of
|
| Oxidized carbon fibers |
51.59 |
43.42 |
35.25 |
27.08 |
= -0.408 T + 183.6 |
| Untreated carbon fibers |
52.96 |
47.06 |
41.16 |
35.27 |
= -0.295 T + 148.2 |
| MgO |
54.35 |
47.92 |
41.71 |
35.71 |
= -0.311 T + 154.6 |
| MgO |
58.37 |
53.12 |
47.87 |
42.62 |
= -0.262 T + 143.2 |
| ZnO |
59.25 |
55.07 |
50.12 |
44.16 |
= -0.251 T + 140.8 |
| Al2O3
|
60.98 |
51.03 |
41.08 |
31.13 |
= -0.497 T + 221.7 |
| Monogal-Zn |
81.90 |
68.84 |
52.26 |
37.03 |
= -0.756 T + 327.0 |
| SiO2
|
85.34 |
67.75 |
52.86 |
39.23 |
= -0.766 T + 331.8 |
Table 11.
Values of () (in kJ/mol) of the various polar molecules adsorbed on the different used solid materials
Table 11.
Values of () (in kJ/mol) of the various polar molecules adsorbed on the different used solid materials
| Silica |
|---|
| T(K) |
323.15 |
343.15 |
363.15 |
383.15 |
| CCl4
|
6.752 |
6.810 |
6.881 |
6.968 |
| Nitromethane |
13.573 |
12.367 |
11.273 |
10.191 |
| CH2Cl2
|
22.490 |
21.846 |
21.269 |
20.716 |
| CHCl3
|
19.752 |
19.304 |
18.925 |
18.546 |
| Diethyl ether |
26.838 |
25.462 |
23.802 |
22.314 |
| THF |
35.506 |
32.787 |
30.435 |
27.908 |
| Ethyl Acetate |
4.566 |
4.015 |
3.530 |
3.079 |
| Acetone |
10.612 |
9.608 |
8.703 |
7.816 |
| Acetonitrile |
16.734 |
15.304 |
14.016 |
12.738 |
| Toluene |
17.330 |
16.724 |
16.168 |
15.598 |
| Benzene |
5.640 |
5.170 |
4.745 |
4.328 |
| MgO |
| T(K) |
323.1500 |
343.1500 |
363.1500 |
383.15 |
| CH2Cl2
|
3.3120 |
3.7860 |
4.5320 |
5.211 |
| CHCl3
|
5.833 |
2.693 |
1.560 |
2.176 |
| Diethyl ether |
14.415 |
16.559 |
18.671 |
20.721 |
| THF |
23.053 |
25.004 |
26.928 |
28.797 |
| Acetone |
15.723 |
20.520 |
25.354 |
30.243 |
| Ethyl acetate |
6.224 |
7.620 |
9.112 |
10.523 |
| ZnO |
| T(K) |
323.15 |
343.15 |
363.15 |
383.15 |
| CH2Cl2
|
2.4490 |
1.9151 |
1.2231 |
0.6320 |
| CHCl3
|
1.1506 |
1.0611 |
0.9988 |
0.9325 |
| Diethyl ether |
7.7211 |
7.0452 |
6.5940 |
6.0373 |
| THF |
13.5961 |
12.9006 |
12.2948 |
11.5175 |
| Ethyl acetate |
3.9554 |
2.7149 |
1.8004 |
1.0420 |
| Benzene |
0.8696 |
0.6900 |
0.5367 |
0.3535 |
| Monogal-Zn |
| T(K) |
323.15 |
343.15 |
363.15 |
383.15 |
| CH2Cl2
|
2.354 |
1.965 |
1.426 |
0.854 |
| CHCl3
|
15.001 |
11.698 |
7.938 |
6.927 |
| Diethyl ether |
17.481 |
15.950 |
14.408 |
12.982 |
| THF |
23.786 |
21.503 |
19.298 |
17.285 |
| Acetone |
22.779 |
20.603 |
18.500 |
16.582 |
| Ethyl acetate |
12.287 |
9.154 |
5.642 |
4.895 |
| Alumina |
| T(K) |
323.15 |
343.15 |
363.15 |
383.15 |
| CCl4
|
0.334 |
0.163 |
0.084 |
- |
| CH2Cl2
|
6.751 |
6.654 |
6.575 |
6.648 |
| CHCl3
|
38.808 |
36.648 |
34.670 |
32.613 |
| Ether |
18.559 |
16.226 |
14.028 |
12.322 |
| THF |
41.085 |
39.144 |
37.268 |
35.790 |
| Ethyl acetate |
11.624 |
9.452 |
7.875 |
6.125 |
| Toluene |
40.532 |
38.377 |
36.371 |
34.878 |
| TiO2 |
| T(K) |
313.15 |
333.15 |
353.15 |
373.15 |
| CH2Cl2
|
2.546 |
1.924 |
1.254 |
0.723 |
| CHCl3
|
3.146 |
2.019 |
0.893 |
- |
| THF |
7.620 |
6.620 |
5.620 |
4.620 |
| Ethyl Acetate |
3.979 |
2.417 |
0.857 |
- |
| Acetone |
5.776 |
4.068 |
2.362 |
0.651 |
| Benzene |
5.564 |
4.199 |
2.834 |
1.463 |
| Nitromethane |
10.394 |
9.024 |
7.657 |
6.283 |
| Acetonitrile |
4.615 |
2.524 |
0.433 |
-1.661 |
| Untreated Carbon fibers |
| T(K) |
323.15 |
343.15 |
363.15 |
383.15 |
| CCl4
|
1.723 |
1.956 |
2.203 |
2.518 |
| CH2Cl2
|
4.096 |
3.645 |
3.129 |
2.548 |
| CHCl3
|
14.829 |
13.537 |
11.761 |
8.193 |
| Ether |
2.112 |
1.633 |
1.131 |
0.546 |
| THF |
11.852 |
11.079 |
10.310 |
9.748 |
| C6H6 |
8.577 |
8.315 |
8.055 |
8.011 |
| Ethyl acetate |
9.500 |
9.251 |
9.019 |
8.975 |
| Acetone |
10.723 |
10.282 |
9.865 |
9.647 |
| Oxidized Carbon fibers |
| T(K) |
323.15 |
343.15 |
363.15 |
383.15 |
| CCl4
|
2.785 |
2.843 |
2.911 |
2.974 |
| CH2Cl2
|
10.546 |
9.952 |
9.379 |
8.800 |
| CHCl3
|
12.788 |
12.228 |
11.685 |
11.134 |
| Ether |
7.399 |
6.965 |
6.548 |
6.124 |
| THF |
17.020 |
15.878 |
14.753 |
13.623 |
| C6H6 |
10.429 |
9.943 |
9.473 |
8.995 |
| Ethyl acetate |
13.212 |
12.718 |
12.242 |
11.758 |
| Acetone |
17.928 |
16.999 |
16.094 |
15.183 |
Table 12.
Values of polar enthalpy () and entropy () of the various polar solvents adsorbed on the various solid surfaces by using our new method.
Table 12.
Values of polar enthalpy () and entropy () of the various polar solvents adsorbed on the various solid surfaces by using our new method.
| Silica |
|---|
| Polar solvent |
() |
() |
| CCl4
|
-4.6 |
5.2514 |
| Nitromethane |
52.8 |
30.543 |
| CH2Cl2
|
27.7 |
31.377 |
| CHCl3
|
18.8 |
25.788 |
| Diethyl ether |
77.4 |
51.914 |
| THF |
123.5 |
75.304 |
| Ethyl acetate |
23 |
11.944 |
| Acetone |
43.6 |
24.624 |
| Acetonitrile |
62.2 |
36.719 |
| Toluene |
27.1 |
26.027 |
| Benzene |
20.4 |
12.173 |
| MgO |
| CH2Cl2
|
32.2 |
7.1665 |
| CHCl3
|
-60.5 |
-24.435 |
| Diethyl ether |
105.1 |
19.543 |
| Ethyl acetate |
71.9 |
17.038 |
| THF |
95.8 |
7.8791 |
| Acetone |
242 |
62.489 |
| Acetonitrile |
81.6 |
2.0138 |
| Toluene |
-13.8 |
15.211 |
| ZnO |
| CH2Cl2
|
20.9 |
8.9949 |
| CHCl3
|
-11.4 |
1.0743 |
| Diethyl ether |
18.5 |
18.218 |
| THF |
23.8 |
26.647 |
| Ethyl acetate |
38.2 |
17.176 |
| Benzene |
-1.0 |
6.7082 |
| Monogal |
| CH2Cl2
|
25.2 |
10.547 |
| CHCl3
|
139.9 |
59.803 |
| Diethyl ether |
75.2 |
41.760 |
| THF |
108.5 |
58.796 |
| Ethyl acetate |
44.2 |
21.674 |
| Acetone |
103.5 |
56.155 |
| Acetonitrile |
110.8 |
54.921 |
| Toluene |
99.9 |
54.474 |
| Alumina |
| CCl4
|
6.2 |
2.314 |
| CH2Cl2
|
1.9 |
7.3421 |
| CHCl3
|
102.8 |
71.989 |
| Diethyl ether |
104.6 |
52.207 |
| THF |
88.8 |
69.683 |
| Ethyl acetate |
90.4 |
40.683 |
| Toluene |
94.9 |
71.036 |
| Titanium dioxide |
| CH2Cl2
|
30.7 |
12.146 |
| CHCl3
|
56.4 |
20.818 |
| THF |
10.0 |
23.277 |
| Ethyl Acetate |
78.1 |
28.448 |
| Acetone |
85.4 |
32.518 |
| Benzene |
68.3 |
26.965 |
| Nitromethane |
68.5 |
31.846 |
| Acetonitrile |
104.6 |
37.370 |
| Untreated carbon fibers |
| CCl4
|
-13.2 |
-2.4181 |
| CH2Cl2
|
25.8 |
12.209 |
| CHCl3
|
108.4 |
49.284 |
| Benzene |
9.8 |
11.602 |
| Diethyl ether |
26 |
10.275 |
| THF |
35.4 |
22.895 |
| Ethyl acetate |
9 |
12.289 |
| Acetone |
18.2 |
16.380 |
| Oxidized carbon fibers |
| CCl4
|
3.2 |
1.7876 |
| CH2Cl2
|
29.1 |
19.639 |
| CHCl3
|
27.5 |
21.406 |
| Benzene |
23.9 |
17.897 |
| Diethyl ether |
21.2 |
14.038 |
| THF |
56.6 |
34.733 |
| Ethyl acetate |
24.2 |
20.782 |
| Acetone |
45.7 |
32.230 |
Table 13.
Values of the enthalpic acid base constants and (unitless) and the entropic acid base constants and (unitless) of the various solid surfaces and the corresponding acid base ratios.
Table 13.
Values of the enthalpic acid base constants and (unitless) and the entropic acid base constants and (unitless) of the various solid surfaces and the corresponding acid base ratios.
| Solid surfaces |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Silica |
0.73 |
1.45 |
2.0 |
0.6509 |
1.23 |
1.45 |
1.2 |
0.651 |
| MgO |
0.08 |
1.13 |
14.0 |
0.1722 |
1.16 |
0.57 |
0.5 |
0.8126 |
| ZnO |
0.22 |
1.63 |
7.4 |
0.422 |
0.29 |
0.08 |
0.3 |
0.8761 |
| Monogal-Zn |
0.59 |
1.49 |
2.5 |
0.7296 |
1.07 |
3.08 |
2.9 |
0.7295 |
| Alumina |
0.71 |
2.21 |
3.1 |
0.7301 |
0.92 |
4.21 |
4.6 |
0.7739 |
| Titanium dioxide |
0.25 |
0.87 |
3.5 |
0.9874 |
0.86 |
1.80 |
2.1 |
0.9804 |
| Untreated Carbon fibers |
0.13 |
2.19 |
16.8 |
0.0799 |
0.30 |
1.56 |
5.2 |
0.3195 |
| Oxidized Carbon fibers |
0.20 |
3.41 |
17.4 |
0.0779 |
0.37 |
4.32 |
11.6 |
0.141 |
Table 14.
Corrected values of Lewis’s acid-base constants , and of the various solid surfaces and the corresponding acid base ratios.
Table 14.
Corrected values of Lewis’s acid-base constants , and of the various solid surfaces and the corresponding acid base ratios.
| Solid surfaces |
|
|
|
|
| Silica |
1.105 |
3.572 |
0.186 |
3.23 |
| MgO |
0.005 |
0.336 |
-0.045 |
71.66 |
| ZnO |
0.401 |
2.418 |
0.089 |
6.03 |
| Monogal-Zn |
0.782 |
3.477 |
0.113 |
4.45 |
| Alumina |
0.988 |
3.291 |
0.136 |
3.33 |
| Untreated Carbon fibers |
0.359 |
3.339 |
0.110 |
9.29 |
| Oxidized Carbon fibers |
0.529 |
5.085 |
0.161 |
9.61 |
Table 15.
Values of (), () and () of polar molecules adsorbed on silica surfaces by comparing Donnet et al.’s method and our new method .
Table 15.
Values of (), () and () of polar molecules adsorbed on silica surfaces by comparing Donnet et al.’s method and our new method .
| Results by using Donnet et al.’s method |
|---|
| T(K) |
323.15 |
343.15 |
363.15 |
383.15 |
403.15 |
() |
() |
| CCl4 |
34.616 |
31.401 |
28.904 |
26.818 |
24.489 |
124.2 |
74.643 |
| Nitromethane |
34.014 |
30.151 |
27.038 |
24.328 |
21.424 |
155 |
83.687 |
| CH2Cl2 |
53.122 |
48.974 |
45.622 |
42.692 |
39.626 |
166.4 |
106.43 |
| CHCl3 |
48.598 |
44.795 |
41.775 |
39.150 |
36.312 |
151.1 |
96.995 |
| Diethyl ether |
53.703 |
49.136 |
44.982 |
41.394 |
37.319 |
202.5 |
118.86 |
| THF |
57.922 |
52.382 |
47.865 |
43.564 |
39.053 |
232.8 |
132.69 |
| Ethyl Acetate |
33.315 |
29.418 |
26.298 |
23.608 |
20.724 |
155 |
82.944 |
| Acetone |
25.935 |
22.701 |
20.154 |
18.016 |
15.527 |
127.5 |
66.771 |
| Acetonitrile |
25.145 |
22.059 |
19.641 |
17.621 |
15.228 |
121.4 |
64.011 |
| Toluene |
55.833 |
51.069 |
47.157 |
43.631 |
40.161 |
193.9 |
117.99 |
| Benzene |
38.564 |
34.399 |
31.032 |
28.069 |
25.006 |
167.2 |
92.143 |
| Results by using our new method |
| T(K) |
323.15 |
343.15 |
363.15 |
383.15 |
403.15 |
() |
() |
| CCl4 |
6.752 |
6.810 |
6.881 |
6.968 |
7.129 |
5.2514 |
6.752 |
| Nitromethane |
13.573 |
12.367 |
11.273 |
10.191 |
9.378 |
30.543 |
13.573 |
| CH2Cl2 |
22.490 |
21.846 |
21.269 |
20.716 |
20.287 |
31.377 |
22.490 |
| CHCl3 |
19.752 |
19.304 |
18.925 |
18.546 |
18.250 |
25.788 |
19.752 |
| Diethyl ether |
26.838 |
25.462 |
23.802 |
22.314 |
20.676 |
51.914 |
26.838 |
| THF |
35.506 |
32.787 |
30.435 |
27.908 |
25.593 |
75.304 |
35.506 |
| Ethyl Acetate |
4.566 |
4.015 |
3.530 |
3.079 |
2.732 |
11.944 |
4.566 |
| Acetone |
10.612 |
9.608 |
8.703 |
7.816 |
7.144 |
24.624 |
10.612 |
| Acetonitrile |
16.734 |
15.304 |
14.016 |
12.738 |
11.793 |
36.719 |
16.734 |
| Toluene |
17.330 |
16.724 |
16.168 |
15.598 |
15.187 |
26.027 |
17.330 |
| Benzene |
5.640 |
5.170 |
4.745 |
4.328 |
4.026 |
12.173 |
5.640 |
Table 16.
Values of the ratios at different temperatures, and and of the various polar organic molecules
Table 16.
Values of the ratios at different temperatures, and and of the various polar organic molecules
| T(K) |
323.15 |
343.15 |
363.15 |
383.15 |
403.15 |
() |
() |
| CCl4 |
5.1 |
4.6 |
4.2 |
3.8 |
3.4 |
23.7 |
11.1 |
| Nitromethane |
2.5 |
2.4 |
2.4 |
2.4 |
2.3 |
5.1 |
6.2 |
| CH2Cl2 |
2.4 |
2.2 |
2.1 |
2.1 |
2.0 |
5.3 |
4.7 |
| CHCl3 |
2.5 |
2.3 |
2.2 |
2.1 |
2.0 |
5.9 |
4.9 |
| Diethyl ether |
2.0 |
1.9 |
1.9 |
1.9 |
1.8 |
3.9 |
4.4 |
| THF |
1.6 |
1.6 |
1.6 |
1.6 |
1.5 |
3.1 |
3.7 |
| Ethyl Acetate |
7.3 |
7.3 |
7.5 |
7.7 |
7.6 |
13.0 |
18.2 |
| Acetone |
2.4 |
2.4 |
2.3 |
2.3 |
2.2 |
5.2 |
6.3 |
| Acetonitrile |
1.5 |
1.4 |
1.4 |
1.4 |
1.3 |
3.3 |
3.8 |
| Toluene |
3.2 |
3.1 |
2.9 |
2.8 |
2.6 |
7.4 |
6.8 |
| Benzene |
6.8 |
6.7 |
6.5 |
6.5 |
6.2 |
13.7 |
16.3 |
Table 17.
Harmonic mean (in 10-19J) values of the ionization energies of the various materials and the adsorbed polar solvents found in our new approach, and values of (in 10-10J1/2) used by Donnet et al. method.
Table 17.
Harmonic mean (in 10-19J) values of the ionization energies of the various materials and the adsorbed polar solvents found in our new approach, and values of (in 10-10J1/2) used by Donnet et al. method.
| Molecule |
(in 10-19J) |
(in 10-19J) |
(in 10-19J) |
(in 10-19J) |
(in 10-19J) |
(in 10-19J) |
(in 10-19J) |
(in 10-10J1/2) |
| n-pentane |
7.27 |
7.02 |
4.89 |
7.85 |
6.06 |
7.90 |
8.60 |
12.83 |
| n-hexane |
7.23 |
6.97 |
4.87 |
7.80 |
6.02 |
7.84 |
8.53 |
12.73 |
| n-heptane |
7.16 |
6.91 |
4.84 |
7.72 |
5.98 |
7.77 |
8.44 |
12.61 |
| n-octane |
7.12 |
6.87 |
4.82 |
7.67 |
5.95 |
7.72 |
8.38 |
12.52 |
| n-nonane |
7.09 |
6.85 |
4.81 |
7.64 |
5.93 |
7.68 |
8.34 |
12.46 |
| n-decane |
7.07 |
6.83 |
4.80 |
7.62 |
5.91 |
7.66 |
8.31 |
12.43 |
| CCl4
|
7.62 |
7.34 |
5.05 |
8.26 |
6.30 |
8.31 |
9.09 |
13.55 |
| Nitromethane |
7.51 |
7.24 |
5.00 |
8.13 |
6.22 |
8.18 |
8.94 |
13.32 |
| CH2Cl2
|
7.58 |
7.30 |
5.03 |
8.21 |
6.27 |
8.26 |
9.03 |
13.46 |
| CHCl3 |
7.60 |
7.32 |
5.03 |
8.23 |
6.28 |
8.28 |
9.05 |
13.49 |
| Diethyl ether |
7.02 |
6.78 |
4.78 |
7.56 |
5.88 |
7.60 |
8.25 |
12.34 |
| Tetrahydrofuran |
6.98 |
6.74 |
4.76 |
7.51 |
5.85 |
7.55 |
8.19 |
12.25 |
| Ethyl acetate |
7.19 |
6.94 |
4.85 |
7.75 |
6.00 |
7.80 |
8.48 |
12.66 |
| Acetone |
7.09 |
6.84 |
4.81 |
7.64 |
5.93 |
7.68 |
8.34 |
12.46 |
| Acetonitrile |
7.82 |
7.52 |
5.13 |
8.49 |
6.43 |
8.55 |
8.60 |
13.97 |
| Toluene |
6.78 |
6.56 |
4.66 |
7.28 |
5.71 |
7.32 |
8.53 |
11.89 |
| Benzene |
6.93 |
7.02 |
4.73 |
7.45 |
5.82 |
7.50 |
8.44 |
12.16 |
| Methanol |
7.45 |
6.97 |
4.97 |
8.05 |
6.18 |
8.10 |
8.38 |
13.18 |
Table 18.
Values of the average separation distance H (in Å) btween the various solid substrates and the organic molecules at different temperatures.
Table 18.
Values of the average separation distance H (in Å) btween the various solid substrates and the organic molecules at different temperatures.
| T(K) |
323.15 |
343.15 |
363.15 |
383.15 |
| SiO2 |
5.05 |
5.12 |
5.19 |
5.27 |
| MgO |
5.23 |
5.27 |
5.31 |
5.35 |
| ZnO |
4.87 |
4.88 |
4.89 |
4.90 |
| Monogal |
5.18 |
5.24 |
5.33 |
5.44 |
| Al2O3 |
5.03 |
5.08 |
5.13 |
5.16 |
| TiO2 |
5.51 |
5.53 |
5.54 |
5.56 |
| Untreated carbon fibers |
4.45 |
4.48 |
4.50 |
4.52 |
| Oxidized carbon fibers |
4.49 |
4.54 |
4.59 |
4.64 |
Table 19.
Values of () of the dichloromethane and the ethyl acetate adsorbed on the different solid materials at various temperatures.
Table 19.
Values of () of the dichloromethane and the ethyl acetate adsorbed on the different solid materials at various temperatures.
| () of dichloromethane |
| T(K) |
323.15 |
343.15 |
363.15 |
383.15 |
| SiO2 |
22.49 |
21.846 |
21.269 |
20.716 |
| MgO |
3.312 |
3.786 |
4.532 |
5.211 |
| ZnO |
2.449 |
1.9151 |
1.2231 |
0.632 |
| Monogal |
2.354 |
1.965 |
1.426 |
0.854 |
| Al2O3 |
6.751 |
6.654 |
6.575 |
6.648 |
| TiO2 |
2.546 |
1.924 |
1.254 |
0.723 |
| Untreated carbon fibers |
4.096 |
3.645 |
3.129 |
2.548 |
| Oxidized carbon fibers |
10.546 |
9.952 |
9.379 |
8.8 |
| () of ethyl acetate |
| T(K) |
323.15 |
343.15 |
363.15 |
383.15 |
| SiO2 |
4.566 |
4.015 |
3.53 |
3.079 |
| MgO |
6.224 |
7.62 |
9.112 |
10.523 |
| ZnO |
3.9554 |
2.7149 |
1.8004 |
1.042 |
| Monogal |
12.287 |
9.154 |
5.642 |
4.895 |
| Al2O3 |
11.624 |
9.452 |
7.875 |
6.125 |
| TiO2 |
3.979 |
2.417 |
0.857 |
- |
| Untreated carbon fibers |
9.500 |
9.251 |
9.019 |
8.975 |
| Oxidized carbon fibers |
13.212 |
12.718 |
12.242 |
11.758 |
Table 20.
Values of the specific acid and base surface energy contributions , , and (in mJ/m2) of the different solid surfaces.
Table 20.
Values of the specific acid and base surface energy contributions , , and (in mJ/m2) of the different solid surfaces.
| Values of (in mJ/m2) |
| T(K) |
323.15 |
343.15 |
363.15 |
383.15 |
| SiO2
|
8.11 |
6.15 |
4.66 |
3.47 |
| MgO |
15.07 |
22.14 |
31.03 |
40.57 |
| ZnO |
6.08 |
2.81 |
1.21 |
0.40 |
| Monogal |
58.72 |
31.95 |
11.90 |
8.78 |
| Al2O3
|
52.55 |
34.06 |
23.18 |
13.75 |
| TiO2
|
6.16 |
2.23 |
0.27 |
0.03 |
| Untreated carbon fibers |
33.54 |
31.08 |
28.63 |
26.18 |
| Oxidized carbon fibers |
64.04 |
57.33 |
50.62 |
43.91 |
| Values of (in mJ/m2) |
| T(K) |
323.15 |
343.15 |
363.15 |
383.15 |
| SiO2
|
275.18 |
254.53 |
236.49 |
219.94 |
| MgO |
5.97 |
7.64 |
10.74 |
13.92 |
| ZnO |
3.26 |
1.96 |
0.78 |
0.20 |
| Monogal |
3.01 |
2.06 |
1.06 |
0.37 |
| Al2O3
|
24.80 |
23.61 |
22.60 |
22.65 |
| TiO2
|
3.53 |
1.97 |
0.82 |
0.27 |
| Untreated carbon fibers |
8.01 |
5.99 |
3.98 |
1.96 |
| Oxidized carbon fibers |
55.89 |
48.21 |
40.53 |
32.85 |
| Values of (in mJ/m2) |
| T(K) |
323.15 |
343.15 |
363.15 |
383.15 |
| SiO2
|
94.46 |
79.11 |
66.37 |
55.27 |
| MgO |
18.96 |
26.02 |
36.51 |
47.52 |
| ZnO |
8.91 |
4.69 |
1.95 |
0.57 |
| Monogal |
26.61 |
16.22 |
7.11 |
3.62 |
| Al2O3
|
65.95 |
56.00 |
46.05 |
36.11 |
| TiO2
|
9.32 |
4.19 |
0.95 |
0.17 |
| Untreated carbon fibers |
32.75 |
27.04 |
21.32 |
15.61 |
| Oxidized carbon fibers |
119.64 |
105.11 |
90.58 |
76.04 |
| Values of (in mJ/m2) |
| T(K) |
323.15 |
343.15 |
363.15 |
383.15 |
| SiO2
|
179.80 |
146.86 |
119.23 |
94.50 |
| MgO |
76.31 |
77.15 |
81.42 |
86.23 |
| ZnO |
71.12 |
61.88 |
54.11 |
47.71 |
| Monogal |
116.87 |
91.36 |
67.14 |
48.53 |
| Al2O3
|
128.31 |
106.07 |
86.64 |
67.71 |
| TiO2
|
70.06 |
60.18 |
51.74 |
45.15 |
| Untreated carbon fibers |
85.71 |
74.10 |
62.49 |
50.87 |
| Oxidized carbon fibers |
171.23 |
148.53 |
125.83 |
103.13 |