1. Introduction
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is one of the leading causes of liver cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, and mortality worldwide [
1,
2,
3]. Most of the people affected by hepatitis C do not exhibit any symptoms: many of them are unaware of being infected with hepatitis C until liver damage emerges, years or even decades after the virus infection [
4,
5]. The infection can manifest in both acute and chronic phases (85% of cases). The acute phase can present widely differing symptoms due to the interaction of the immune system with the virus and the antigen exposure. About 15% to 25% of individuals with an acute HCV infection typically undergo spontaneous clearance within 6 months, marked by undetectable serum HCV RNA and normalization of ALT levels. Conversely, approximately 75% to 85% of these individuals progress to chronic HCV infection, distinguished by the persistence of HCV RNA in the blood for more than 6 months following the onset of the acute infection [
6]. Lastly, it can lead to fulminant hepatic failure; however, in most cases, it results in undiagnosed infections initially, characterized by subclinical and flu-like symptoms, but diagnosed only in late stages [
7]. The delayed diagnosis leads to the chronicization of this pathology, which tends to re-emerge (usually after the age of 50), progressing to hepatic cirrhosis (80%) and, in the worst cases, hepatocellular carcinomas [
8].
Globally, 71 million people have a chronic HCV infection, and 1.75 million new infections occur each year. However, in low- and middle-income countries and high-income settings, respectively, only 20% and <1% of patients received a diagnosis and treatment [
9].
Hepatitis C prevalence is now estimated to be 2.8% worldwide, with significant regional and demographic variations [
10]. Egypt is thought to have the greatest global prevalence of HCV, at about 12%, whereas Iran has the lowest prevalence, at 0.30% [
10]. In the Italian population, HCV prevalence increased in generations born before the 1950s due to the post-war HCV epidemic. However, over the last forty years, improvements in hygienic conditions, including using disposable sanitary materials, blood transfusion control, and population awareness through anti-HCV screening surveillance programs and educational initiatives, have led to a significant decrease in HCV rates. Furthermore, since 2019 Italy has adhered to the Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) elimination project by 2030, following the WHO recommendation [
10,
11], even if approximately 2 million subjects are still tested reactive for the HCV, i.e., carriers of anti-HCV antibodies, of which 250 thousand subjects with chronic hepatitis are under antiviral treatment [
12,
13].
The majority of prior research has been on HCV screening methods for groups who are at high risk, such as alcoholics, drug users, men who have sex with other males [
14], and HIV-positive patients or hepatitis B virus (HBV) whereas very few studies have focused on screening methods for broader populations. Several studies have shown that chronic alcohol use is one of the most important external risk factors for the progression of chronic hepatitis C to cirrhosis and Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) [
15,
16,
17]. Chronic HCV infection can lead in 10 up to 20 years to liver cirrhosis in 10-20% of individuals [
18].
The World Health Organization (WHO) has created evidence-based recommendations that concentrate on who should be tested for chronic hepatitis C infection and how to conduct the test [
19]: the serological assays approach and the right period to be tested.
Firstly, the diagnosis and monitoring of HCV infection are based on 2 types of tests: a
serological test that detects HCV antigen-specific antibodies and tests that detect
viral RNA or HCV core antigens [
20]. Then, it is crucial to clarify that the detection of the Anti-HCV antibodies through serum analysis should be conducted within a specific timeframe. Performing the antibody detection test beyond six months after the presumed infection may yield a false-negative result [
21]. However, serological tests make no distinction between active infections and resolved ones. In addition, false-negative results are frequent due to a long window period, the period from initial infection to
seroconversion, which lasts between 45 and 68 days. False-positive results from serological tests may occur due to interfering factors, including high
gamma globulin levels,
nephritic syndrome, pregnancy, autoimmune diseases, or viral or parasitic infections [
22]. Through rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) or laboratory-based serum samples, such as enzyme immunoassays (EIAs), electrochemiluminescence immunoassays (ECLs), and chemiluminescence immunoassays (CLIAs), the current diagnostic algorithm prioritizes the detection of HCV antibodies as evidence of past or current HCV infection. To determine whether there is an HCV infection with viremia, further testing for HCV RNA or HCV core antigen is necessary. In order to reduce the need for additional tests and reduce the likelihood of reporting false-positive findings, the ideal S/CO ratio in a variety of laboratory-based serological assays has been studied in the past [
23,
24]. However, the results were not consistent [
24,
25]. The rate of HCV eradication could only be significantly accelerated by widespread population screening.
The low diagnosis rate of this infection is mainly due to the lack of national policies and/or guidelines for the diagnosis of the infection, expensive and complex diagnostic assays as well as poor acknowledgment in the population and still prejudice for these types of infections.
The early identification of individuals with chronic HCV infection is crucial and enables rapid initiation of necessary treatments, which could help prevent or delay the progression of liver diseases. Early intervention increases the probability of achieving a sustained viral response (SVR), indicating successful treatment in eliminating the virus from the body. Likewise, this contributes to reducing the mortality rate associated with HCV-related liver pathologies. Therefore, since an early and prompt diagnosis of HCV infection is needed to the prevention, care, and treatment of the patients, the role of the laboratory is extremely important. For these reasons, our study aimed to validate and assess a laboratory algorithm for the screening of HCV antibodies. In particular, the purpose is to investigate the reliability of 2 commercially available anti-HCV antibody kits used in routine laboratory testing in Italy, the electrochemiluminescence immunoassay (ECL) (Cobas e 801® Elecsys Anti-HCVII, Roche) and the chemiluminescence immunoassay (CLIA) (Liaison XL® Murex HCV Ab, Diasorin), in comparison with the Recombinant Immunoblot Assay (RIBA), nowadays the gold standard for the HCV screening. The approach with the two assays should avoid the confirmation test with the Western blot, reducing time and cost and limiting the operator-dependent work, using just automatized systems.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study design
A total of 17,926 serum samples were collected from subjects who adhered to anti-HCV screening from Jan 20121 to July 2022. Among them, 6,453 (36%) were males with a mean age of 54.5 + 18 years, and 11,473 (64%) were females with a mean age of 44 + 16 years. All serum samples were analyzed for anti-HCV screening at Cerba Healthcare Italia in Italy.
The first anti-HCV testing was using electrochemiluminescence (ECL) immunoassay systems within four hours after collection.
Each anti-HCV-reactive serum sample was divided into 2 aliquots (each 500 μl) to retest them using the second serological assay (MUREX HCV Ab,) a chemiluminescence (CLIA) and at the end the recombinant immunoblot assay (RIBA), to confirm the results obtained, following the national guidelines (ISTISAN 06/47). To minimize variations related to time or storage, the different tests were performed on the same samples’ aliquot upon 1-2 hours maximum from the first test. The other was stored at − 80 ℃ for RIBA, which was performed as supplemental tests to confirm anti-HCV positivity within 7 days, following the stability ranges, defined by the recommendations of the manufacturers.
The negative cases by CLIA assay and the indeterminate cases by RIBA were also tested with a Nucleic Acid Test (NAT), to determine the results in the discrepancies.
All experimental procedures were conducted according to the Declaration of Helsinki.
2.2. ECL immunoassay for anti-HCV
An ECL immunoassay was applied for anti-HCV testing using the Elecsys anti-HCV II assay on the Cobas 801 analyser (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany). The kit was a third-generation test using peptides and recombinant antigens representing the core, NS3, and NS4 to capture the corresponding antibodies.
The results were expressed as signal-to-cutoff (S/CO) ratios: S/CO < 1.0 indicated anti-HCV nonreactivity, and S/CO ≥ 1.0 indicated anti-HCV reactivity. All S/CO ≥ 1.0 sera were retested in duplicate according to the manufacturer’s instructions. If either of the two results remained S/CO ≥ 1.0, then the subject was considered anti-HCV reactive. The anti-HCV reactive sera were retested using a CLIA anti-HCV reagent kit. The sensitivity and the specificity are respectively of 100% and 99.96% in a European cohort, as declared by the manufacturer. Quality control was performed before any analytical investigation.
2.3. CLIA immunoassay for anti-HCV
An indirect CLIA immunoassay was applied for anti-HCV testing using LIAISON XL Murex HCV Ab (DiaSorin SpA, Saluggia, Italy), based on two recombinant antigens (core and NS4) specific for HCV, that are used for coating magnetic particles (solid phase), while a third ready to use aqueous HCV antigen (biotinylated NS3). The samples were analyxed on Liaison XL (DiaSorin SpA, Saluggia, Italy).
The results were expressed as signal-to-cutoff (S/CO) ratios: S/CO ≥ 1.0 indicated anti-HCV reactivity, samples with S/CO values ≥ 0.80 and < 1.00 were considered equivocal, and S/CO < 1.0 anti-HCV nonreactivity, according to the manufacturer’s instructions. If either of the two results remained S/CO ≥ 1.0, then the subject was considered anti-HCV reactive. The sensitivity and the specificity are respectively of 100% and 99.5% in hospitalized population, as declared by the manufacturer. Quality control was performed before any analytical investigation.
2.4. Recombinant immunoblot assay for anti-HCV
Specimens with reactive anti-HCV results were further tested with RIBAs to confirm anti-HCV positivity using a recombinant immunoblot kit for antibodies against the hepatitis C virus (INNO-LIA HCV Score, Beijing Wantai Biopharm, Beijing, China). The nitrocellulose strips contained seven bands for the core, NS3, NS4-1, NS4-2, and NS5 antigens as well as control A and control B. The result was defined as negative, ±, 1 +, or 2 + by comparing the colour of the antigen band with control A. Anti-HCV positivity was defined as the presence of at least two antigens with greater than or equal to 1 + (≥ 1 +) reactivity. An indeterminate result was defined by only one band scoring ≥ 1+. Anti-HCV negativity was defined by the absence of antigens scoring ≥ 1 +. The tests were performed according to the manufacturer’s instructions by expert technicians.
2.5. Statistical analisys
Statistical analysis was performed with MedCalc Software Ver.18.2.18 (MedCalc Software Ltd, Ostend, Belgium).
The data are expressed in Positive Predictive Value (PPV) and Negative Predictive Value (NPV). The statistical significance level established for all tests performed gave a p-value of (p) < 0.05. The frequency data were analyzed using the two-way chi-square (χ2) test analyzing the relationship between two classification factors (reactive vs non-reactive for both the assay). The χ2 test was calculated and, where possible, was applied the Cochran-Armitage test for trend.
The Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curves were calculated for the two assays, categorized by RIBA results, from which the reactivity cut-offs were extrapolated. The ROC curve is an analytical method that represent graphically the performance of a binary diagnostic classification method, interpretating the data from a dichotomous (0-1) form to assess the presence or the absence of the sepsis [
26].
For each ROC curve generated (reported as area under the curve, AUC), a confidence interval (CI) was assumed by 95%. The cut-off was determined by calculating the Youden Index, a summary measure of the effectiveness of the ROC curve.
The Shapiro-Wilk test was used to verify the data distribution and it is applied to a sample with a null hypothesis that the sample has been generated from a normal distribution. If the data showed a non-Gaussian trend, the test of Mann-Whitney was used, being the non-parametric alternative test to the independent sample t-test. The differences of the data collected between the various groups, were represented using median and 1st and 3rd interquartile (InterQuartile Range, IQR).
4. Discussion
The global initiative to eradicate Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) infection has led to the implementation of screening strategies aimed at identifying and managing infected individuals. In our study, we adopted a comprehensive approach involving an ECL screening for HCV followed by a second screening method a CLIA assay, aligning with similar strategies employed for other viruses. Actually, in recent years for the prevention and diagnosis of HIV infection, as indication of non-profit organizations, such as ANLAIDS in Italy [
27,
28]. In the event of a positive result, the test is repeated using a first-level screening test, and if confirmed, further testing for HIV RNA is conducted [
29].
The diagnostics and the clinical laboratories play an essential role in the identification of the HCV reactive cases, in the reduction of the HCV infection rate and hepatitis-related mortality [
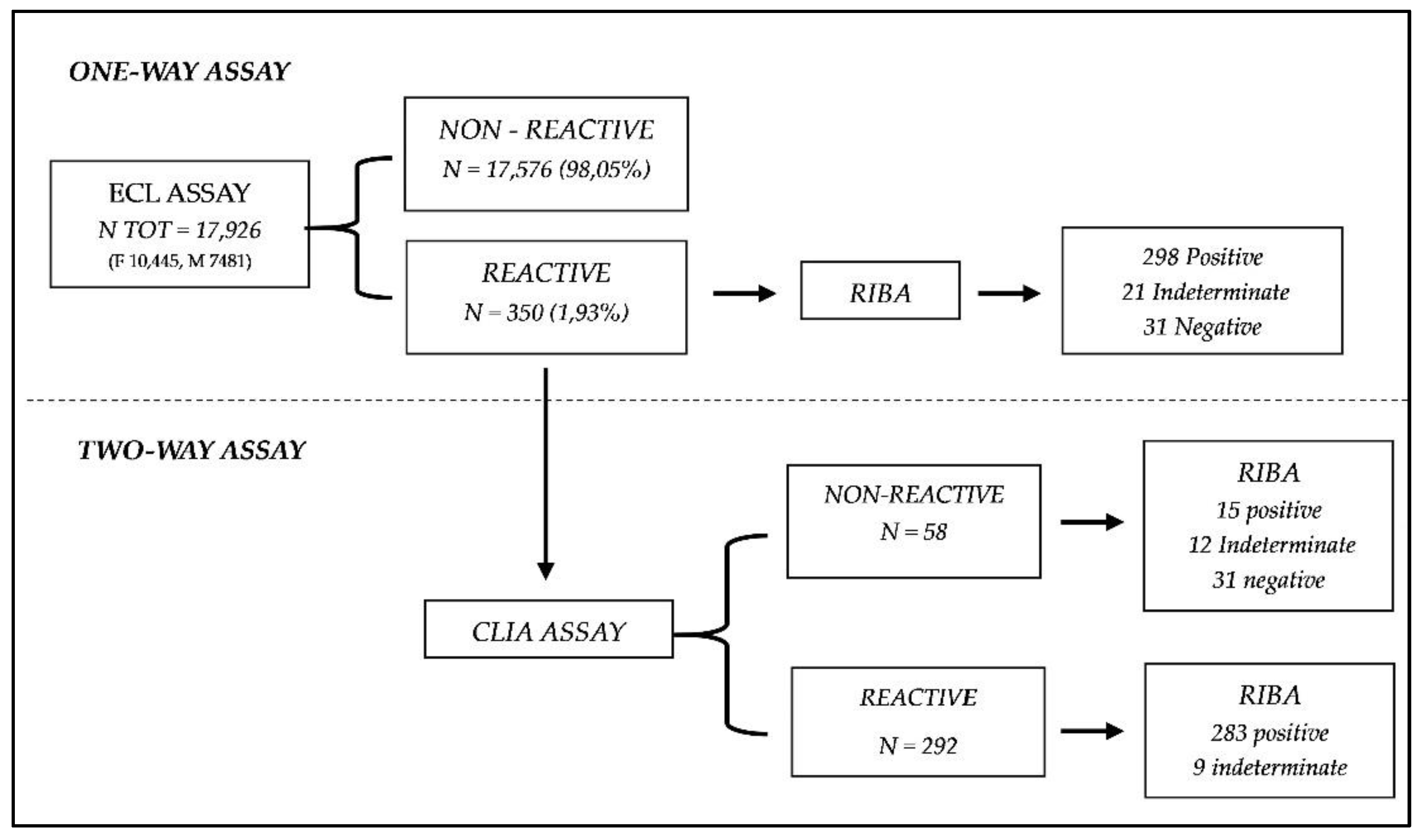
30]. In this context of the global for the eradication of HCV infection, a cohort of 17,926 patients underwent testing from January 2021 to July 2022 using ECL screening for HCV. Of these, 350 patients tested positive and were subsequently retested using a second screening test (CLIA assay).
The study's findings confirmed the appropriateness of the dual testing approach: the use of just one screening method achieved a sensibility and specificity of 93. 62% and 96.77%, data confirmed also by other precedent studies [
31,
32]; meanwhile the use of two screening method improved the sensitivity to 99.66% and specificity to 100%, as showed in
Figure 2. This high level of accuracy underscores the effectiveness of utilizing two different screening methods to ensure reliable results. Despite the overall success of the dual testing approach, a slight overestimation was observed in the screening methods, particularly in +3.18% (292 out of 283) of cases, that the RIBA detected as negatives. Nevertheless, the percentages of false positive in
Table 1 after the two-method testing were significantly decrease (PPV: one assay 90.60 vs two assay 95.00), suggesting the excellent performance of the strategy. As well as the PPV, the χ
2 analysis in
Table 1 proved that the dual approach could manage better the discrimination of positive and negative results in the population studied (χ
2 test: one assay 34.51, p<0.001 vs two assay 7.59, p<0.01).
These last results overturn the data previously evaluated in another work [
33], which showed no significant ability to discriminate false positives rate between one assay and two assays. Probably, the discordant findings are related to the different methods used, our study utilized CLIA instead of Chemiluminescence Microparticle Immunoassay (CMIA), and the different order to test. Our approach was to use a more stringent second test with higher sensitivity and specificity, declared by the manufacturers in order to give a faster, but accurate, response and minimalize the laboratory’s costs.
Although, the world has focused the attention mostly on the detection and the treatment of the HCV infection [
10], less effort and investment has been made to ensure accurate and affordable diagnostic tools. Ironically, in many settings, the prohibitive costs of HCV diagnostics often exceed the cost of curative therapy [
34]. The dual approach investigated in our study could minimize the cost and the Turn Around Time (TAT), improving the laboratory routine to rapid, easy, and economical HCV diagnostics. The use of two assay could reduce the need of a confirmatory test, like the RIBA, that, despite it is still the method of choice for serological assays due to the higher PPV, the higher cost and increased likelihood of indeterminate results underscore some limitations. Specifically, the combined reactivity results for both of these two tests proved a clear ability to identify all the positive samples. On the other hand, a notable diagnostic limitation is observed in the discordant cases, i.e., the samples that resulted reactive for ECL assay, but non-reactive for CLIA assay (N= 58,
Figure 1). In these discordant cases, several outcomes were observed after the RIBA execution: 15 positive, 21 indeterminate, 31 negative. This diversity of results limits the full feasibility of the diagnostic approach hypothesized, as for all those samples with different results between the two assays, a second-level analysis with RIBA or directly a molecular NAT analysis must still be carried out. Anyhow, the initial hypothesis of employing two primary level tests for analyzing serological samples for HCV is still satisfied aiming to minimize the use of RIBA in the clinical laboratory. Cases resulting reactivity for both methods conclusively affirm the positivity of the respective samples. This certainty supports the reduction or potentially substitution of RIBA in the diagnostic laboratory workflow. By adopting this approach and carrying out the RIBA only for the few discordant cases (58 out of 350), laboratory costs and times could be significantly lowered. This optimized approach allows for the streamlining of HCV screening while saving the capability to identify all infected individuals. The data observed highlighted the effectiveness of the combined tests in confirming true positives (PPV: 95%). Even though, it is necessary to remember that the discordant results underlined the necessity of still use the confirmatory tests. Continuous investigation and validation of the diagnostic pathway are essential for ensuring the reliability and accuracy of HCV screening protocols.
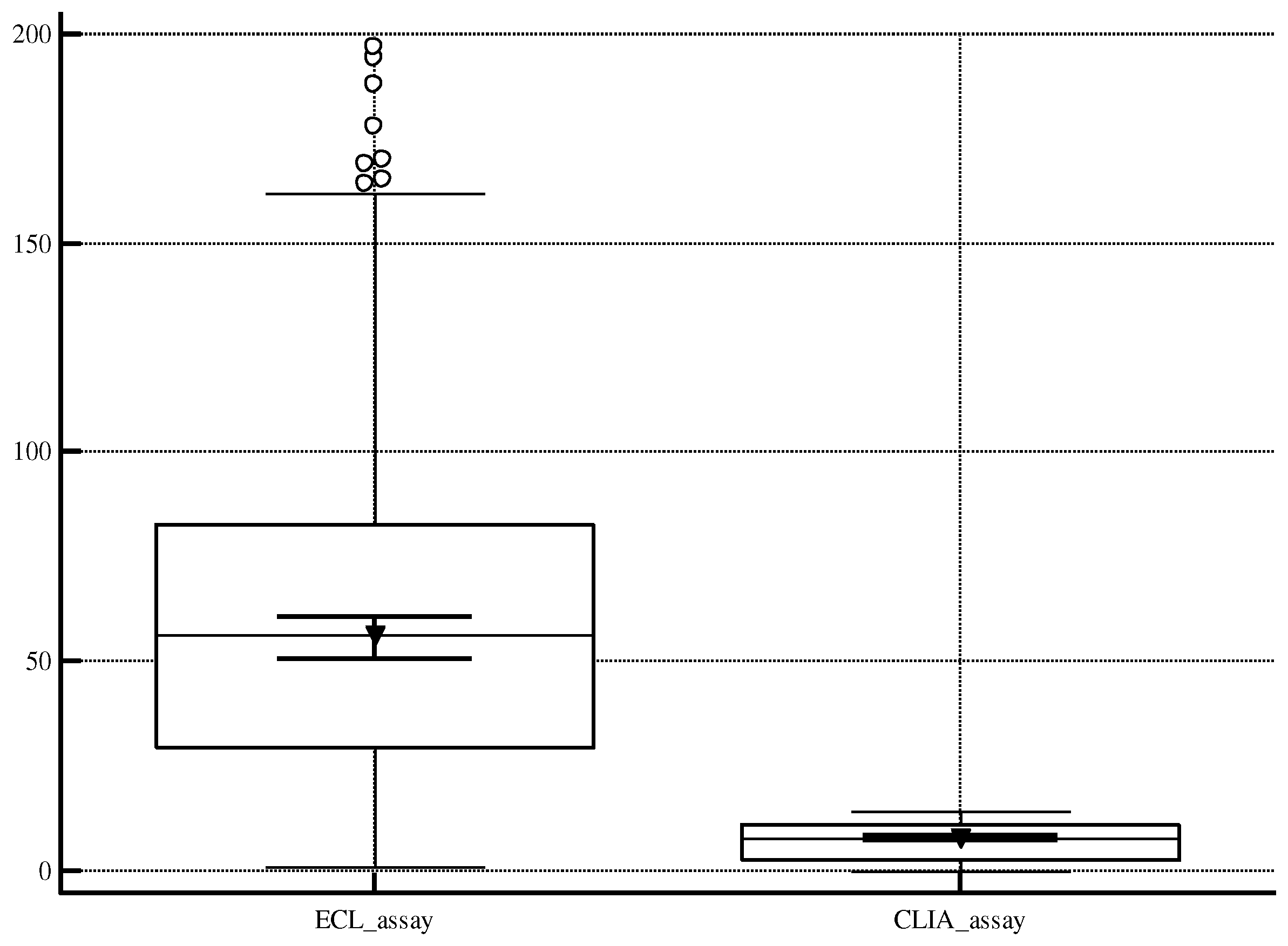
Moreover, it is important to recognize the limitations associated with the screening tests utilized in the study, variables such as cross-reactivity, time testing, or different antigens detected, that could influence some results. In
Figure 3, we would represent the huge difference between the medians of the results for the two methods (ECL: 56.70 S/CO; CLIA: 7.80 S/CO), due to detection of distinct antigens (ECL: core, NS3, and NS4; CLIA: core and NS4), which could cause potential challenges in reporting. Consequently, the application of this dual testing strategy in routine laboratory may lead to the release of results only in a qualitative information. Another limit is the lack of information about the anamnesis for the HCV reactive patients and a stratification of the population.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.E. and S.S.; methodology, C.T. and C.T.E.; validation, V.M., F.B. and E.Z.; formal analysis, and investigation, C.T., C.T.E., S.S., Z.E., C.L., P.I., T.F.; data curation, B.F., P.M. and T.F; writing—original draft preparation, B.F., P.I., and T.F; writing—review and editing, B.F., Z.E., S.S., P.I., and T.F.; visualization and supervision, V.M., Z.E., C.L. and B.F; project administration, B.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.