1. Introduction
Chemical and isotopic composition of light hydrocarbons have long been used to study the origins, generation, accumulation and degradation process of hydrocarbons in the past decades (Schoell, 1980; Rooney et al., 1995; Tang et al., 2000; Galimov, 2006; Liu et al., 2013; Zhao et al., 2019, 2020, 2021; Pei at al., 2023). However, with the large-scale exploration & development and intensive isotopic geochemistry study of natural gas resources in high evolution strata of superimposed basin, it is increasingly difficult to clearly identify the origin and evolutionary process of hydrocarbons by chemical and isotopic characteristics of alkanes. This is because there are many factors and geochemical processes responsible for chemical and isotopic compositions of hydrocarbons in geological conditions, such as the inheritance of isotopic signatures from precursor organics, kinetic isotope fractionations, equilibrium isotope fractionations and the mixing of hydrocarbons from different origins/maturities. Combined, these factors can readily lead to overlapping of bulk isotopic signatures of hydrocarbons of different origins and history, obscuring their origins and evolutionary processes. The mechanism responsible for the evolution of isotopic composition of alkanes, for example, the cause for the reversed alkane δ13C values in many natural gas plays, is still controversial and remains an open question(Hunt et al. , 2012; Tilley et al., 2011; Dai et al., 2016;Shen et al., 2022).
The problems in the application of traditional natural gas isotope geochemistry can be attributed to the following two aspects: a) For current isotope analysis technology of monomer hydrocarbon, the isotopic information of the internal functional groups of the monomer hydrocarbon disappears in the process of oxidizing the target component to CO2 or reducing it to H2, accordingly, the intra-molecular isotope distribution information which can disclose the formation and evolution process of natural gas is not fully obtained (Zhao et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2019;Wen et al., 2023 ); b) The dynamic evolution laws of isotope composition of monomer hydrocarbon and corresponding mechanism during the formation and evolution process of natural gas are still in disputes(XiaXinyu and Tang Yongchun, 2012; Dai et al., 2016; Wang et al., 2015; Zhao et al., 2019). Efforts to explore the intra-molecular isotope distribution of hydrocarbons, including position-specific isotope and clumped isotope, have been made in the past decades (Stolper et al., 2014;Gilbert et al., 2016; Piasecki et al., 2016; Liu et al., 2019; Zhao et al., 2020). These isotopic information with higher dimensions are expected to provide unique constrains on their formation and migration-degradation processes, however, the theoretical studies and applications of intra-molecular isotope distribution are still in its infancy, and can't be widely used to date. Traditional monomer hydrocarbon isotope is still the main research method of natural gas isotope geochemistry, accordingly, research on the dynamic evolution of chemical and isotopic composition of alkanes still needs to be strengthened, especially the dynamic evolution during hydrocarbon generation process.
Efforts to study the dynamic evolution of chemical and isotopic composition of alkanes (especially C1-3) during hydrocarbon generation process have been made in the past decades. Many empirical models have been put forward to study the compositional and isotopic variation of natural gas(Stahl et al.,1975; Schoell, 1980;Prinzhofer et al.,1995; Liu et al.,1999). However, these empirical models are developed based on statistic analysis of massive data, the mechanisms responsible for the compositional and isotopic variation of alkanes were not fully understood. Rayleigh model is the first semi-quantitative model to study the compositional and isotopic variation of alkanes (Clayton, 1991; Berner et al., 1992; Lorant etal., 1998). But Rayleigh model can not exactly study the compositional and isotopic variation of alkanes either, the obvious defects of Rayleigh model are as follows (Tang et al., 2000): one is the assumption that methane and the higher hydrocarbons can be modeled using a single extent of reaction parameter; the other is the assumption that the fractionation factor of each first-order reaction is constant. Hydrocarbon generation kinetic model based on various pyrolysis experiments are widely be applied to quantitative study the yield evolution of methane and total gaseous hydrocarbon (C1-C5) ,while carbon isotope kinetic model based on various pyrolysis experiments are widely be applied to quantitative study the isotopic evolution of methane during the hydrocarbon generation process(Tang et al.,2000, 2005;Wang et al. 2006; Tian et al . 2007; Pan et al., 2010; Jia et al., 2014; Liu et al.,2016).Whereas, hydrocarbon generation kinetic model and carbon isotope kinetic model are only applicable to the first order reaction in the hydrocarbon generation process. The yield of total gaseous hydrocarbon (C1-5) can also reach a plateau in hydrocarbon generation simulation experiments, so C1-5 can be considered as a whole to calculate its yield evolution using hydrocarbon generation simulation data. However, the yield of individual heavy hydrocarbon components initially increase and then decrease after reaching maximum yield in the hydrocarbon generation simulation experiments, indicating that the heavy hydrocarbon components have undergone pyrolysis. In addition, the heavy hydrocarbon components may involve Fischer-Tropsch reaction in the high evolution stage, so individual heavy hydrocarbon components cannot be regarded as a first-order reaction and are not suitable for hydrocarbon generation kinetic model and carbon isotope kinetic model. Tang et al.(2000) predicted the evolution of cumulative yield of methane, instantaneous yield of methane, instantaneous δ13C1 and cumulative δ13C1 by hydrocarbon generation kinetic model and carbon isotope kinetic model based on the pyrolysis of n-octadecan. Shuai et al.(2005,2006) carried out the hydrocarbon generation kinetic and carbon isotope kinetic study of ethane by dividing the evolution process of ethane into two stages: the generation dominated stage and the cracking dominated stage. However, each stage simultaneously involves the generation and cracking of ethane, and there may be ethane generated by the Fischer Tropsch reaction in the cracking dominated stage. To sum up, there is no valid model to quantitatively study the chemical and isotopic variation of C1-3 during the hydrocarbon generation process to date, making it very difficult to identify the origin, source and resources of natural gas by chemical and isotopic data.
To address this limitation, a quantitative model was built to illustrate the chemical and isotopic variation of C1-3 during the process of hydrocarbon generation.
The objective of this work is multifold:
(1) Summarize the universal evolution laws of chemical and isotopic composition of C1-3 in hydrocarbon generation process on the basis of fitting systematic data obtained from published papers for pyrolysis of various hydrocarbon sources.
(2)Introduce the theoretical approach and detailed steps to built the dynamic model of chemical and isotopic evolution of C1-3 during the hydrocarbon generation process.
(3)Illustrate the application of the dynamic model on the pyrolysis experiment of the Ordovician Pingliang Shale from Ordos Basin, China (Jia et al., 2014) to study its chemical and isotopic evolution of C1-3 during the hydrocarbon generation process.
2. Theoretical Approach
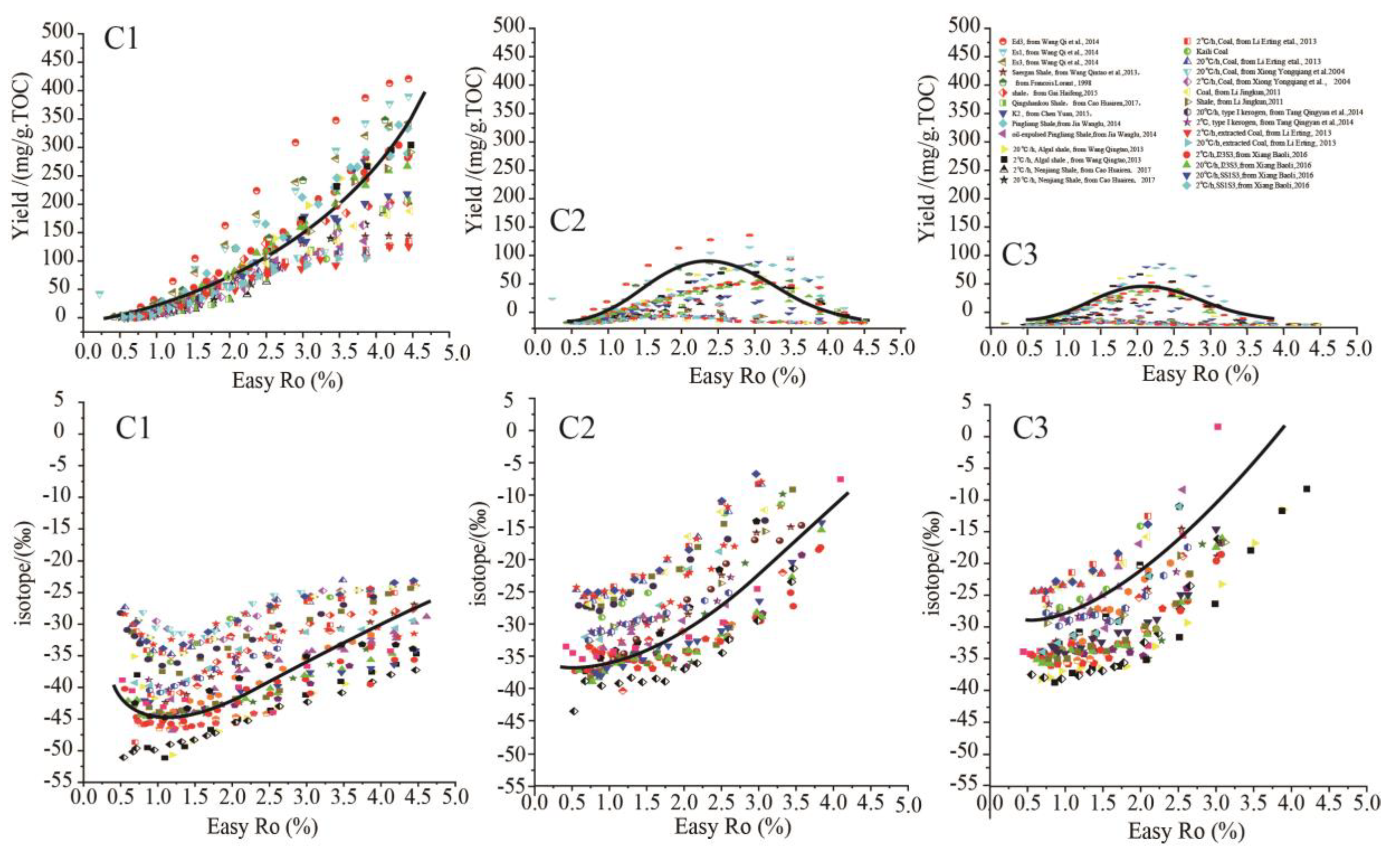
2.1. The Universal Chemical and Isotopic Evolution Laws of C1-3in Hydrocarbon Generation Simulation Experiments
The universal evolution laws of hydrocarbon composition and isotope were summarized by data fitting of massive hydrocarbon generation simulation experiments involving various hydrocarbon sources obtained from available literature, including type I kerogen/source rock, type II kerogen/source rock, type III kerogen/source rock, crude oil, asphalt, etc (Lorant et al.,1998; Xiong et al.,2002,2004; Hill et al.,2003; Gong et al.,2004; Shuai et al.,2005; Wang et al.,2006; Yin etal.,2010; Li et al.,2011; Liu et al.,2012; Pan et al., 2012; Tian et al., 2012; Li et al.,2013;Tang et al.,2013, 2014;Cao et al.,2017;Wang et al.,2013;Gao et al., 2014; Jia et al., 2014;Wang et al., 2014; Chen,2015;Gai et al., 2015; Xiang et al., 2016; Shao et al., 2018)(
Figure 1). For the yields evolution laws of C
1-3, C
1 yields increase continuously with rising maturity; while C
2 and C
3 yields initially increase and then decrease with increasing thermal maturity, reaching maximum yields at certain intermediate maturity. As regards the evolution laws of δ
13C
1-3, δ
13C
1 present obvious isotope rollover , initially shifting negatively and then shifting positively with increasing maturity; while δ
13C
2 and δ
13C
3 in certain simulation experiments also present isotope rollover with increasing maturity, but the variation amplitude is much lower than that of δ
13C
1.Overall, the δ
13C
2 and δ
13C
3 generally shift positively with increasing maturity(
Figure 1).
Since the samples adopted in the hydrocarbon generation simulation experiments are of different organic matter type and different maturity, the yields and isotope compositions of C1-3 may vary greatly from each other, however, the yields and isotope compositions of C1-3 present universal variation trends. Although these universal laws are empirical models summarized from massive data statistics (only the variation of C1 yields and δ13C1values are verified by hydrocarbon generation kinetics and isotope kinetics), massive hydrocarbon generation simulation data of various hydrocarbon sources all comply with these universal laws, convincing us that these universal laws are applicable to hydrocarbon generation process of various organic matter.
2.2. The Calculation of the Isotopic Composition of Mixed Natural Gas from Different Maturities (δ13Cmixed)
The carbon isotope of mixed natural gas at different maturities can be formulated by equation (1) and equation (2) according to the definition of natural gas isotope.
where R denotes the isotope ratio of
13C/
12C of PDB standard.
A, B represent different natural gas end member; X,Y represent the proportion of A,B in mixed natural gas, respectively; n
i represents the concentration of alkane component i in natural gas; δ
13C
i represents the carbon isotope of component i;Δ=δ
13C/1000+1;R represents the
13C/
12C ratio of PDB standard. However, too many parameters in equation (2) make it too complex to calculateδ
13C
mixed.
Xia et al.(1998) put forward a simplified formula to studied the influence of mixture on natural gas isotope(equation(3)).Although the simplified formula proposed by Xia et al.(1998) has been widely applied to the isotopic study of natural gas, some researchers are still skeptical of this formula and insist that it is only applicable to limited proportions of end members and may lead to obvious mistakes beyond limited proportions.Comparative study of the definition formula of mixed natural gas (equation (2)) and the simplified formula (equation (3)) were conducted under different proportions (A:B=1:9999-9999:1) to verify the validity of the simplified formula. To strengthen reliability and persuasion, the scope between δ
13C
iA and δ
13C
iB should cover the variation range of δ
13C
i in geological and experimental conditions, in addition, the difference of δ
13C
iA and δ
13C
iB should be big enough. Accordingly, we assignδ
13C
iA andδ
13C
iB to be -10‰ and -50‰, respectively. As shown in
Table 1, the δ
13C
mixed values calculated according to simplified formula are very close with those calculated according to the definition formula under obviously different proportions, with only minor difference on the
fifth significant digit To date, the precision of one digit after decimal point for δ
13C is sufficient to meet the requirement of isotope study of natural gas. So the simplified formula of δ
13C
mixed can be widely applied to the isotopic study of natural gas under diverse proportions of different end member.
2.3. Dynamic Modeling of Chemical and Isotopic Variation of C1-3 during hydrocarbon Generation Process
2.3.1. Nomenclature
Cumulative yield: The total yield of certain alkane gas in certain maturity interval or geological period;
Instantaneous yield: The yield of certain alkane gas at certain single maturity point or single point of geological time;
Cumulative Isotope: The isotopic composition of alkane generated in certain maturity interval or geological period;
Instantaneous Isotope: The isotopic composition of alkane generated at certain single maturity point or single point of geological time;
Supposing the cumulative isotope function of X(maturity) is A(X); the cumulative yield function of X(maturity) is B(X); the instantaneous isotope function of X(maturity) is C(X); the instantaneous yield function of X(maturity) is D(x).
2.3.2. Calculations
According to the simplified formula ofδ
13C
mixed (formula(3)), we can infer that A(X), B(X), C(X), D(x) comply with the formula (4) in the maturity interval of (X
0-X) based on the theory of integration and differentiation.
From equation (4), we have
Derivatives were taken on both sides of formula (5), we have
The cumulative isotope function (A(X)) and cumulative yield function (B(X)) can be obtained by data fitting of the yield and isotope data from pyrolysis experiments using Origin software. The conventional viewpoints insist that the yield and isotope of alkanes collected at certain temperature/maturity point in open pyrolysis experiments can represent the instantaneous yield and instantaneous isotope, respectively. However, the alkanes collected at certain temperature/maturity in open pyrolysis experiments are actually the cumulative pyrolysis product during the maturity interval of two sampling points (except using on-line pyrolysis -GC- IRMS method). Although alkanes collected at certain maturity in open pyrolysis experiments can reflect the variation trend of instantaneous yield and instantaneous isotope when the sampling interval is very small, they cannot accurately represent the instantaneous yield and instantaneous isotope. In this study, the instantaneous yield function (D(x)) can be obtained by taking derivative of cumulative yield function (B(X)), and the instantaneous isotope function (C(x)) can be calculated by formula(6). The calculation and plotting of formula(6) were conducted by Maple software.
It has been documented that the hydrocarbon generation history (including heating rate (subsidence rate), geothermal gradient, primary/secondary hydrocarbon generation) also impose significant influence on the component and isotopic characteristics of hydrocarbon(Tang et al., 2000; Qin et al., 2000; Jin et al., 2008). But for simplicity, it is assumed in this study that the hydrocarbon generation history does not influence the instantaneous yield and isotope characteristics of hydrocarbon at each maturity. The above-mentioned cumulative yield function (B(X)) and cumulative isotope function (A(X)) are obtained based on the fact that all pyrolysis products are preserved in confined pyrolysis system. For natural gas systems which experienced hydrocarbon expulsion, the calculation of cumulative isotope (A(X)) must take consideration of the expulsion ratio on the basis of formula (4), which are discussed elsewhere (Zhao et al., in prep).
3. Results and Discussion
The quantitative model was applied on the anhydrous confined pyrolysis data of the kerogen extracted from the Ordovician Pingliang Shale from Ordos Basin, China (Jia et al., 2014) to study its chemical and isotopic evolution of C1-C3 during the hydrocarbon generation process. The detailed information of Ordovician Pingliang Shale are as follows: marine shale, type II kerogen, TOC 18.1%, vitrinite reflectance (RO) 0.7%. The δ13C of the isolated kerogen is 30.1‰. The detailed procedures of anhydrous confined pyrolysis experiment are as follows: the kerogen samples were introduced into gold tubes and were sealed under argon; the tubes containing fresh kerogen were loaded into the stainless vessel; pyrolysis was performed under a constant pressure of 50 MPa, and the pyrolysis temperatures ranged from 250–600℃ at heating rates of 2 ℃/h(Liu and Tang (1998)).The simulation temperatures was converted to “Easy Ro” to represent the evolutionary maturity of Pingliang Shale (Sweeney and Burnham,1990).
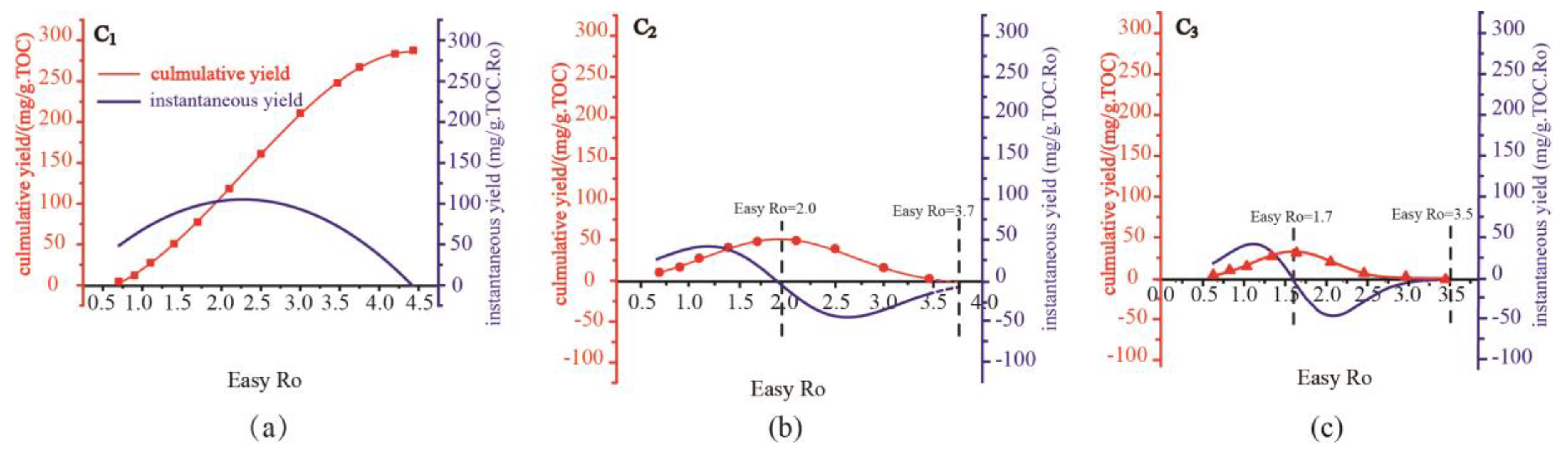
The cumulative isotope function (A(X)) and cumulative yield function (B(X)) of kerogen from Pingliang Shale are obtained by data fitting of confined pyrolysis experiments (
Figure 2 and
Figure 3). The instantaneous yield function (D(x)) can be obtained by taking derivative of cumulative yield function (B(X)), and the instantaneous isotope function (C(x)) can be calculated by formula (6) (
Figure 2 and
Figure 3). The unit of instantaneous yield function [mg/(g.TOC.Ro)] is different with the unit of cumulative yield function[mg/(g.TOC)],so the charts of instantaneous and cumulative yield were plotted using Dual-axis method, and there are no direct comparability between the value of instantaneous yield and cumulative yield.
3.1. Dynamic Chemical Evolution of C1-3 During hydrocarbon Generation Process
3.1.1. Dynamic Evolution of C1 Yield During Hydrocarbon Generation Process
The cumulative yield of C1 originated from the pyrolysis of Pingliang Shale
increase continuously with rising maturity and reach a plateau at the end of methane generation process , which is consistent with that the instantaneous yield of C1 always keep positive during the methane generation process. The cumulative yield of C1 increase quite mildly at two end of the curve and increase quite sharply in the middle of the curve, which is consistent with that the instantaneous yield of C1 initially increase and then decrease with raising maturity, reaching maximum instantaneous yield at certain intermediate maturity(Easy Ro approx=2.4%).
Methane is widespread in various stages of hydrocarbon generation evolution of Pingliang Shale:immature stage, low mature stage, mature stage, high mature stage and over mature stage. At immature-low mature stage and mature stage, liquid hydrocarbons dominate the hydrocarbon generation product of sapropelic Pingliang Shale, the gaseous hydrocarbons originated mainly from the degradation of aliphatic side chain only account for very low proportion of the total hydrocarbons, so the instantaneous and cumulative yield of C1 is quite low at the beginning of hydrocarbon generation process. At high mature stage, liquid hydrocarbons start to be extensively cracked, crude oil cracking gas become the dominate origin of gaseous hydrocarbon, while the proportion of kerogen cracking gas decrease quickly. Since the hydrocarbon-generating intensity of crude oil cracking is 3~4 times of that of kerogen cracking(Zhao et al., 2005; Li et al., 2018), the instantaneous yield of C1 increase sharply and reach maximum at Easy Ro approx. 2.4% in this period. At over mature stage, liquid hydrocarbons are mostly cracked and the gas generation potential of kerogen is also nearly exhausted, so the instantaneous yield of C1 decrease sharply at the end of over mature stage(Li et al., 2018). At Easy Ro approx. 4.5%, the cumulative yield of C1 reach plateau and meantime the instantaneous yield of C1 approach zero, implying that the hydrocarbon generation potential of Pingliang Shale is already exhausted at Easy Ro approx. 4.5%. However, the instantaneous yield of C1 has never become negative during the whole hydrocarbon generation evolution stage, indicating that there exist no cracking of methane. Previous researches on the calculation of reaction activation energy and pyrolysis experiments of methane have also prove that methane is so thermodynamically stable that it can hardly be pyrolyzed under geological conditions and hydrocarbon generation simulation experiments(Ni et al., 1995; Zhang et al.,2012; Li et al., 2018). Previous calculations have shown that the activation energy required for methane cracking is 441kJ/mol,higher than that of ethane and propane(Ni et al., 1995; Zhang et al.,2012). Moreover, it has been verified by extensive pyrolysis experiments of methane that the threshold temperature of methane pyrolysis is 1100 °C at atmospheric pressure(equivalent Ro approx=5.0%) (Li et al., 2018). While the maximum temperature of the pyrolysis experiment of Pingliang shale is 600 °C, far lower than the threshold temperature of methane pyrolysis. It follows that the instantaneous yield of C1 is hopeful to predict the maturity deadline of hydrocarbon generation, which has practical significance to define the upper limit of natural gas exploration.
3.1.2. Dynamic Evolution of C2-3 Yield During Hydrocarbon Generation Process
The variation trends of cumulative yields C
2 and C
3 are identical, the cumulative yields initially increase and then decrease with increasing thermal maturity, reaching maximum yields at certain intermediate maturity.C
2 and C
3 reach maximum cumulative yield at Easy Ro appr.2.0 and 1.7, respectively (
Figure 2). At the same time, the instantaneous yield of C
2 and C
3 shift from positive values to negative values also at Easy Ro 2.0 and 1.7, respectively, which indicate the cracking threshold maturity of C
2 and C
3. Actually, there are both generation and cracking of C
2 and C
3 before and after the threshold maturity, C
2 and C
3 just shift from generation-dominated stage to cracking-dominated stage at Easy Ro 2.0 and 1.7, respectively. For simplicity, it is assumed in this study that there is only generation of C
2 and C
3 before the threshold maturity(Easy Ro 2.0% and 1.7%, respectively), and there is only cracking of C
2 and C
3 after the threshold maturity.
Propane starts cracking at Easy Ro 1.7% and ends cracking at Easy Ro 3.5%, while ethane starts cracking at Easy Ro 2.0% and ends cracking at Easy Ro 3.7%. Previous studies have shown that the activation energy required for ethane cracking is higher than that of propane (Li et al., 2018), therefore the later cracking of ethane can probably be attributed to its higher molecular stability.The variation trends of instantaneous yield of C2 and C3 are also identical. During the generation stage(instantaneous yield>0),the instantaneous yield initially increase and then decrease with raising maturity, reaching maximum instantaneous yield at certain intermediate maturity. The increase of instantaneous yield of C2 and C3 at the early generation stage mainly be attributed to that C2 and C3 originated from kerogen cracking and crude oil cracking begin to be extensively generated at mature stage and high mature stage. While the decrease of instantaneous yield of C2 and C3 at the late generation stage can mainly be attributed to that kerogen cracking and crude oil cracking are more inclined to generate C1 rather than C2 and C3 at high mature stage. During the consumption stage(instantaneous yield<0), the instantaneous consumption rate initially increase and then decrease with raising maturity, reaching maximum instantaneous consumption rate at certain intermediate maturity. The increase of instantaneous consumption rate at the early consumption stage is owning to the initiation of extensive cracking of C2 and C3 at high mature stage and over mature stage. While the decrease of instantaneous consumption rate at the late consumption stage is owning to that the cumulative yields C2 and C3are mostly cracked and cracking potential of C2 and C3 is nearly exhausted.
3.2. Dynamic isotopic Evolution of δ13C1-3 During hydrocarbon Generation Process
3.2.1. Dynamic Isotopic Evolution of δ13C1 During Hydrocarbon Generation Process.
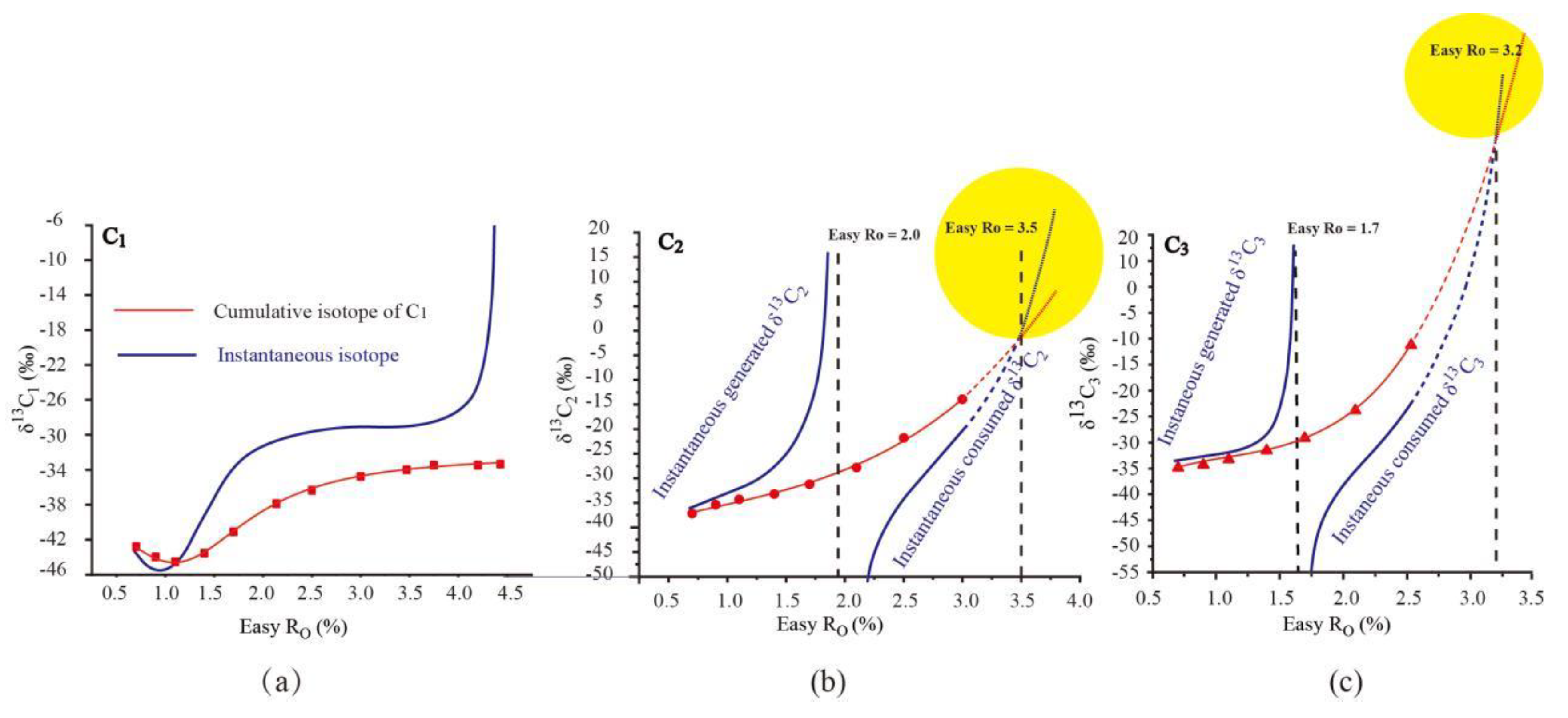
The cumulative and instantaneous δ
13C
1 from the pyrolysis of Pingliang Shale all present identical variation pattern: shift negatively at the early hydrocarbon generation stage, and then shift positively until the end of methane generation. The variation trend of cumulative δ
13C
1 depends on the relative isotopic composition values between cumulativeδ
13C
1 and instantaneous δ
13C
1: when instantaneousδ
13C
1is lighter than cumulativeδ
13C
1(Easy Ro< 1.1%), the cumulative δ
13C
1 shift negatively; when instantaneous δ
13C
1 is heavier than cumulativeδ
13C
1 (Easy Ro> 1.1%), the cumulative δ
13C
1 shift positively. The rollover of cumulative and instantaneous δ
13C
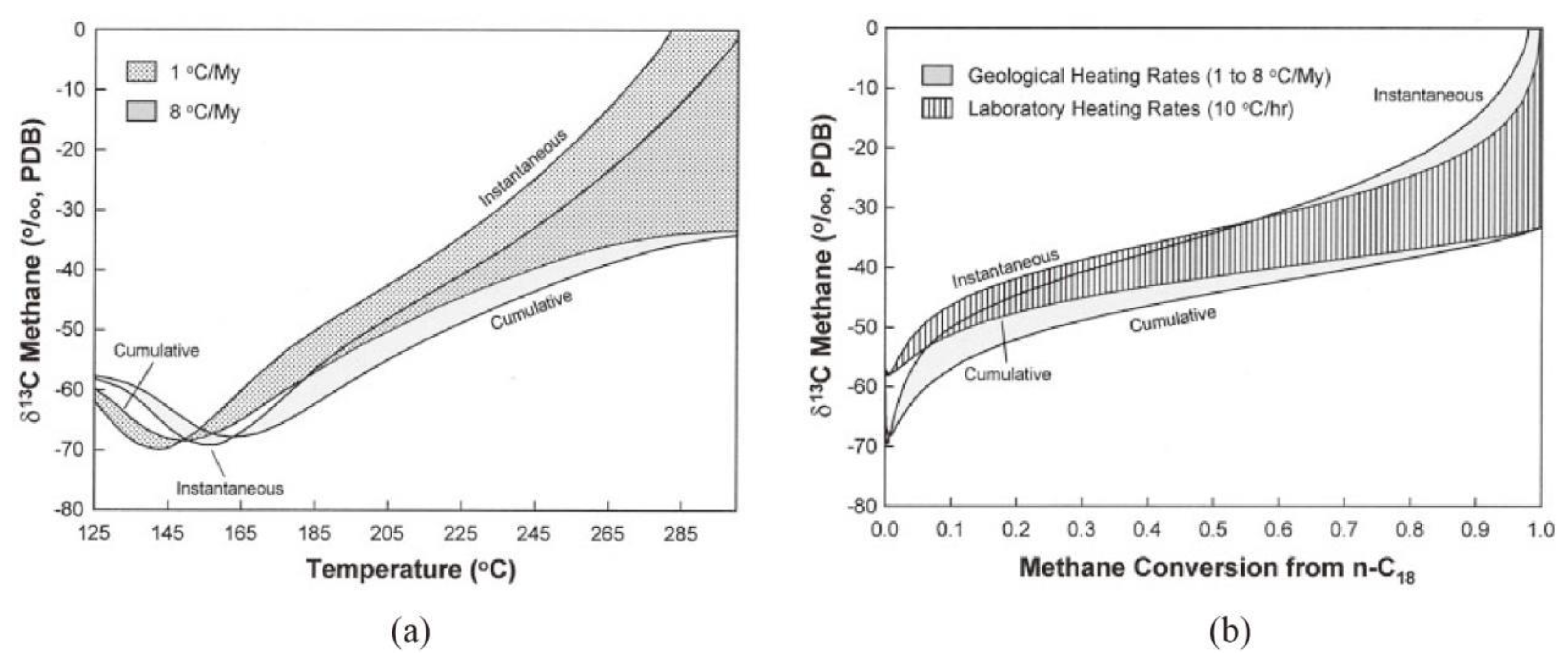
1have already be verified by the study of Tang et al. (2000) using carbon isotope kinetic model(
Figure 4. a). Moreover, the rollover of cumulative δ
13C
1 from the pyrolysis of Pingliang Shale were also observed in many pyrolysis experiments (
Figure 1) (Lorant, 1998;Wang et al.,2013;Tang et al.,2013;Jia et al.,2014;Chen,2015;Li et al.,2013; Tian et al., 2012).
The mechanism responsible for the isotope rollover of δ13C1include:(a) There are two or more precursors for methane generation with different isotopic compositions, the mixing of methane originated from different precursors lead to the isotope rollover of C1(Tang et al., 2000).. Heteroatoms such as O and S are widely present in organic matter, and alkyl carbons connected to these heteroatoms are more isotopically heavier. Due to the instability of the C-O or C-S bonds, these isotopically heavier alkyl groups were preferentially decomposed to form isotopically heavier methane. When the alkyl carbons connected to heteroatoms were almost cracked, the isotopically lighter methane originated from the cracking of more tightly bound C-C bonds was extensively generated. The initial trend of decreasing δ13C1 values can be explained by the mixing of isotopically lighter methane. For alkyl groups connected with C-C bond, 12C enriched alkyl groups were preferentially decomposed to form isotopically lighter methane. With increasing evolution degree, 13C enriched alkyl groups were gradually decomposed to form isotopically heavier methane , resulting in the increase of δ13C1. However, the rollover of δ13C1were also observed in many pyrolysis experiments of pure n-alkanes which are free of heteroatoms, indicating that this theory cannot cover all the δ13C1rollover occurrences.(b)There are two sets of methane precursors with significantly different activation energy in hydrocarbon source, and precursor with lower activation energy typically has higher isotope fractionation factor and tends to generate isotopically lighter methane, while precursor with higher activation energy typically has lower isotope fractionation factor and tends to generate isotopically heavier methane(Tang et al., 2000). Since precursor with lower activation energy was preferentially decomposed to form isotopically heavier methane, the variation trends of δ13C1initially decrease with the mixing of isotopically lighter methane originated from the decomposition of precursor with higher activation. When precursor with lower activation was almost decomposed, precursor with higher activation were gradually decomposed to form isotopically heavier methane, leading to the increase of δ13C1 (Zhao, 2019).
A sudden and sharp increase of instantaneousδ
13C
1 was observed at the end of methane generation stage, but the cumulative δ
13C
1 shows only very gentle increase at this stage. The sharply increasing instantaneous δ
13C
1 was also observed when the methane conversion rate approaching 1.0 in the study of Tang et al.(2000) (
Figure 4. b).In addition, Liu and Xu(1999) also documented the sudden and sharp increase of δ
13C
1in 106 coal-type gas samples from 10 basins of China at high mature and over mature stages, and a two-stage model of carbon isotopic fractionation was built to explain the fractionation mechanism of δ
13C
1. As mentioned in 3.1.1, methane is mainly generated from the cracking of kerogen and the instantaneous yield is very limited at the end of methane generation stage, moreover there exists no cracking of methane in this period. Accordingly, the sudden and sharp increase of instantaneous δ
13C
1 may be attributed to the sudden transform of precursor with higher activation energy and lower isotope fractionation factor. Since previous normal methane precursors have been mostly cracked at the end of methane generation stage, the continuously advancing evolutionary process may suddenly result in the cracking of unconventional precursor with higher activation energy, and lead to sudden and sharp increase of instantaneous δ
13C
1. As the instantaneous C
1 yield is very limited in this period, the sharp increase of instantaneous δ
13C
1did not lead to the obvious increase of cumulative δ
13C
1.
3.2.2. Dynamic Isotopic Evolution of δ13C2-3 During hydrocarbon Generation Process
The cumulative δ13C2/δ13C3 and instantaneous δ13C2/δ13C3from the pyrolysis of Pingliang Shale all present identical variation pattern: the cumulative δ13C2/δ13C3
increase continuously with increasing maturity while the instantaneous δ
13C
2/δ
13C
3 present two-stage pattern(
Figure 3). The instantaneous δ
13C
2/δ
13C
3 in the generation stage(instantaneous yield>0) mainly represents the isotope of instantaneously generated C
2/C
3 ,while the instantaneous δ
13C
2/δ
13C
3 in the consumption stage(instantaneous yield<0) mainly represents the isotope of instantaneously cracked C
2/C
3. The instantaneous generated δ
13C
2/δ
13C
3 increase with raising maturity until the end of C
2/C
3 generation, which is result from the preferential generation of
12C enriched C
2/C
3. While the instantaneous consumed δ
13C
2/δ
13C
3 increase with raising maturity until the exhaustion of C
2/C
3 , which can all be attributed to the preferential decomposition of
12C enriched C
2/C
3. Similar with the variation trend of instantaneous δ
13C
1 at the end of methane generation stage, the instantaneous generated δ
13C
2/δ
13C
3 also present sudden and sharp increase at the end of C
2/C
3generation stage, which may also be attributed to the cracking of unconventional precursor with higher activation energy.
The variation trend of cumulativeδ
13C
2/δ
13C
3was controlled by the relative isotopic composition values between cumulativeδ
13C
2/δ
13C
3 and instantaneous generated δ
13C
2/δ
13C
3 in the generation stage as well as the relative isotopic composition values between cumulativeδ
13C
2/δ
13C
3 and instantaneous consumed δ
13C
2/δ
13C
3in the consumption stage
. In the generation stage, the instantaneous generated δ
13C
2/δ
13C
3 is heavier than corresponding cumulativeδ
13C
2/δ
13C
3, accordingly, the cumulative δ
13C
2/δ
13C
3increase continuously with raising maturity. In the consumption stage, the instantaneous consumed δ
13C
2/δ
13C
3is lighter than corresponding cumulativeδ
13C
2/δ
13C
3, accordingly, the cumulativeδ
13C
2/δ
13C
3 still increase continuously with raising maturity. As common acknowledged, the bond energy of
12C-
12C is lighter than that of
12C-
13C and
12C-
13C, so
12C enriched C
2/C
3 should be preferential decomposed during the consumption stage. As a result, the δ
13C of residual δ
13C
2/δ
13C
3 (cumulative δ
13C
2/δ
13C
3) should be heavier than instantaneous consumed δ
13C
2/δ
13C
3 during the consumption stage. This is the case observed in most of the consumption stage of C
2/ C
3, but at the end of consumption stage, the instantaneous consumed δ
13C
2/δ
13C
3 reversed to be more positive than cumulative δ
13C
2/δ
13C
3(yellow labelled area in
Figure 3.(b),(c)), which is unreasonable according to the bond energy theory. The reversal of instantaneous consumed δ
13C
2/δ
13C
3 and cumulative δ
13C
2/δ
13C
3 happened when the cumulative C
2/C
3 have almost been decomposed (Easy Ro above 3.5% C
2 and 3.2% for C
3,correspondingly).As shown in
Figure 3, the reversal of instantaneous consumed
13C
2/δ
13C
3 and cumulative δ
13C
2/δ
13C
3 can mainly be ascribed to the sudden and sharp increase of instantaneous consumed
13C
2/δ
13C
3, which is similar with the sudden and sharp increase of instantaneous generated δ
13C
1. Accordingly, it can be speculated that the sudden and sharp increase of instantaneous consumed
13C
2/δ
13C
3 may also be attributed to the sudden transform of an unconventional precursor, e.g. propane analogues with unconventionally heavier intra-molecular isotope distribution and higher activation energy, when common precursors have been mostly cracked .
4. Conclusions
Based on systematic data obtained from published papers for pyrolysis of various hydrocarbon sources, the empirical evolution framework of chemical and isotopic composition of C1-3 generated from various organic matter was built., which laid overall foundation for the dynamic evolution model of chemical and isotopic composition of C1-3 in this study.
Based on the calculation of the isotopic composition of mixed natural gas at different maturities (δ13Cmixed), the quantitative relationship between cumulative isotopic composition(A(X)), cumulative yield(B(X)), instantaneous isotope(C(X)),and instantaneous yield(D(x)) were accomplished according to integration theory, which is the core of dynamic model. Moreover, the dynamic model was applied on the pyrolysis data of Pingliang Shale, and the cumulative yield ,instantaneous yield, cumulative isotope and instantaneous isotope were illustrated to study its chemical and isotopic evolution of C1-3 during the hydrocarbon generation process
The geological significances of the dynamic model are as follows:
(1) Quantified the yield and proportion of methane, ethane and propane during the hydrocarbon generation process by the parameters of cumulative yield of C1-3 and instantaneous yield of C1-3, provided a basis for evaluation of natural gas resources from hydrocarbon source rock of different maturity, especially the evaluation of high mature source rock.
(2) Clarified the cracking maturity of ethane and propane, and proposes that there exists no cracking of methane below the Easy Ro of 4.5%, which may be helpful for natural gas exploration of deep formations.
(3) Quantified the evolution of δ13C1, δ13C2 and δ13C3 respectively during hydrocarbon generation processby the parameters of cumulative 13C1-3 and instantaneous 3C1-3, improved the accuracy to identify the origin and evolutionary process of hydrocarbons by chemical and isotopic data, and made it possible to study the dynamic evolution of isotope series of C1-3 (including reversed alkane series) .
The empirical evolution framework of chemical and isotopic composition of C1-3, which was built on the basis of data fitting of systematic pyrolysis experiments of different hydrocarbon source, laid a factual basis for the dynamic model in this study . However, the theoretical basis is still weak, accordingly, the mechanism responsible for the evolution trends of cumulative yield ,instantaneous yield, cumulative isotope and instantaneous isotope still needs to be systematically and deeply studied.
Author Contributions
“Conceptualization, Wenhui Liu. and Heng Zhao.; methodology, Heng Zhao.; software, Heng Zhao.; validation, Yanjie Li..; formal analysis, Heng Zhao.; investigation, Heng Zhao.; data curation, Yanjie Li; writing—original draft preparation, Heng Zhao and Yanjie Li; writing—review and editing, Heng Zhao and Yanjie Li; supervision, Guchun Zhang and Yanjun Wang.; project administration, Guchun Zhang and Yanjun Wang.;. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.”.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(Grant No.42102180) and Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China (Grant No. BK20200171).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Berner U, Faber E, Stahl W. Mathematical simulation of the carbon isotopic fractionation between huminitic coals and related methane. 3: Chemical Geology Isotope Geoscience: 1992,94(4), 1992.
- Cao, H.R. The paleo-environment of source rock formation and geological evaluation of shale oil in the Songliao Basin[D]. 2017, Guangzhou: Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences (In Chinese, with English abstract).
- Chen, Y. .Mechanisms and evaluation of shale gas generation from organic-rich marine shales. 2015, Guangzhou: Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences (In Chinese, with English abstract).
- Clayton Chris. Carbon Isotope Fractionation during Natural Gas Generation from Kerogen.Marine and Petroleum:1991(8): 232 -240.
- Dai J, Zou C, Dong D, et al. Geochemical characteristics of marine and terrestrial shale gas in China. Marine & Petroleum Geology: 2016, 76:444-463.
- Gai, H.F., Xiao, X.M., Cheng, P., Tian, H., Fu, J.M.. Gas generation of shale organic matter with different contents of residual oil based on a pyrolysis experiment. Organic Geochemistry, 2015,78, 69-78.
- Galimov, E.M.. Isotope organic geochemistry. Org. Geochem. 2006,37, 1200–1262. [CrossRef]
- Gao, L. , Schimmelmann, A. , Tang, Y. , Mastalerz, M.Isotope rollover in shale gas observed in laboratory pyrolysis experiments: insight to the role of water in thermogenesis of mature gas.Organic Geochemistry, 2014,68, 95-106.
- Gilbert A, Yamada K, Suda K, et al. Measurement of position-specific 13C isotopic composition of propane at the nanomole level. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta: 2016, 177:205-216.
- Gong, S. ,Peng, P.A.,Lu, Y.H., Xiao,Z.X., Jia, W.L., Wang, Z.Q.,Yu, C.L.,Liu, D.H.,Lu, J.L., Liu, J.Z..The second heating experiment of biodegraded asphalt sand. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2004,49(S):39-47(In Chinese).
- Hill R J, Tang Y, Kaplan I R. Insights into oil cracking based on laboratory experiments. Organic Geochemistry: 2003, 34(12):1651-1672.
- Hunt A G, Darrah T H, Poreda R J. Determining the source and genetic fingerprint of natural gases using noble gas geochemistry: A northern Appalachian Basin case study. AAPG Bulletin:2012, 96(96):1785-1811.
- Jia, W.L. , Wang, Q.L., Liu, J.Z., Peng, P.A., Li, B.H., Lu, J.L.. The effect of oil expulsion or retention on further thermal degradation of kerogen at the high maturity stage: a pyrolysis study of type ii kerogen from pingliang shale, china. Organic Geochemistry, 2014, 71, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q, Wang, X.H, Hu, X.Q, Wang, L, Wang, J, Song, G.Q. Kinetics of primary and secondary generation of coal-derived gases and its applications to genesis of natural gases found in Gubei area, Zhanhua Depression. Geochimica, 2008,37(3):239-244.
- LI, J. , MA, W., WANG, Y.F., et al. Modeling of the whole hydrocarbon-generating process of sapropelic source rock.Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45(3): 445-454.
- Li, E.T. , Pan, C.C , Yu, S. , Jin, X.D. , Liu, J.Z.. Hydrocarbon generation from coal, extracted coal and bitumen rich coal in confined pyrolysis experiments.Organic Geochemistry, 2013,64, 58-75.
- Li, J.K. , Fang, W., Zeng, H.S.,Liu, W., Zou Y.R., LIU J.Z.,Possible origins for inverse stable carbon isotopes of gaseous alkanes from the Xujiaweizi fault depression ACTA PETROLEI SINICA,2011,32(1):54-61(In Chinese, with English abstract).
- Liu, C., Liu, P., McGovern, G.P., Horita, J.. Molecular and intramolecular isotope geochemistry of natural gases from the Woodford Shale, Arkoma Basin, Oklahoma.Geochem. Cosmochim. Acta, 2019, 255, 188–204.
- Liu, J.Z., Tang, Y.C.. Kinetics of early methane generation from Green River shale. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1998, 43, 1908–1912. (In Chinese with English Abstract).
- Liu, Q.Y. , Worden, R.H., Jin, Z.J., Liu, W.H., Li, J., Gao, B., Zhang, D.W., Hu, A.P., Yang,C.. TSR versus non-TSR processes and their impact on gas geochemistry and carbon stable isotopes in Carboniferous, Permian and Lower Triassic marine carbonate gas reservoirs in the Eastern Sichuan Basin, China. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2013 100, 96–115.
- Liu, W. H. , & Xu, Y. C.. A two stage model of carbon isotopic fractionation in coal gas. GEOCHIMICA, 1999,28(4):359-366.
- Liu, W.H. , Wang, J., Tenger,B., Qin, J.Z., Zheng, L.J.. Stable carbon isotopes of gaseous alkanes as genetic indicators inferred from laboratory pyrolysis experiments of various marine hydrocarbon source materials from southern China. Science China-Earth Sciences. 2012,55(6):966-974.
- Lorant, F. , Prinzhofer, A., Behar, F., Huc, A.Carbon isotopic and molecular constraints on the formation and the expulsion of thermogenic hydrocarbon gases. Chemical Geology: 1998,147:249–264.
- NI, L. J. ., ZHANG, L. G.., NI, J. F.., et al. Structural kinetic model of pyrolysis process of paraffins and its simulation. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering (China), 1995, 46(5): 562-570.
- Pan C, Jiang L, Liu J, et al. The effects of calcite and montmorillonite on oil cracking in confined pyrolysis experiments. Organic Geochemistry: 2010, 41(7):611-626.
- Pei, L. X, liu, W. H, Guo, Q,et al. Genetic significance of carbon isotope curve types of methane, ethane, and propane in natural gas.. Organic Geochemistry, 2023, 186:104691.
- Piasecki, A., Sessions, A., Lawson, M., Ferreira, A., Neto, E.S., Eiler, J.M.. Analysisof the site-specific carbon isotope composition of propane by gas source isotope ratiomass spectrometer. Geochem. Cosmochim. Acta, 2016, 188, 58–72.
- Prinzhofer A, Hue A. Genetic and post-genetic molecular and isotopic fractionation in natural gas. 2: Chemical Geology: 1995,126, 1995.
- Qin, Y, Zhang, Y.S, Zhu, Y.M, Fan, B.H, Jiang, B, Li, T.Z. Lagging and reaction kinetic mechanism of hydrocarbonregeneration from organic matters in coals. Earth Science— Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2000,25(3): 278-282.
- Rooney, M.A., Claypool, G.E., Moses Chung, H.. Modeling thermogenic gas generation using carbon isotope ratios of natural gas hydrocarbons. Chem. Geol. 1995,126, 219–232.
- Schoell, M. . The hydrogen and carbon isotopic composition of methane from natural gases of various origins. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 44, 1980,649-661.
- Shao, D.Y. , Ellis, G. S., Li, Y.F., Zhang, T.W.. Experimental investigation of the role of rock fabric in gas generation and expulsion during thermal maturation: anhydrous closed-system pyrolysis of a bitumen-rich Eagle Ford shale. Organic Geochemistry, 2018, 119:22-35.
- Shen, B. J. , He, Z. L., Tao, C., Shen, J. C., Hu, Z. Q., & Li, Z. M., et al.. A mathematical diffusion model of carbon isotopic reversals inside ultra-tight longmaxi shale matrixes. Petroleum Science, 2022, 19(5), 2014-2026.
- Shuai, Y., Y. Zou, and J. Liu. "Carbon Isotope Modeling of Coal-derived Methane and Ethane from the Upper Paleozoic of the Ordos Basin,China." Geological Review (2005), 51(6):665-671.
- Shuai, Y., Y. Zou, and P. Peng. "Kinetic modeling of stable carbon isotope ratios of ethane from coal in confined system and its significance in geological application." Geochimica 35.2(2006):151-156.
- Stahl W J, Carey Jr B B. Source rock identification by isotope analyses of natural gases from fields in the Val Varde Delaware Basins, West Texas. 2: Chemical Geology: 1975,16, 1975.
- Stolper, D. A. , Lawson, M., Davis, C. L., Ferreira, et al. Gas formation. formation temperatures of thermogenic and biogenic methane. Science:2014, 344(6191):1500.
- Sweeney J J, Burnham A K. Evaluation of a simple model of vitrinite reflectance based on chemical kinetics. AAPG Bulletin:1990, 10(10):1559-1570.
- Tang Y, Perry J K, Jenden P D, et al. Mathematical modeling of stable carbon isotope ratios in natural gases. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta:2000, 64(15):2673-2687.
- Tang, Q.Y. , Zhang, M.J., Yu M., Zhang, T.W., Liu J.Z., Zhang, M.C.. Pyrolysis constraints on the generation mechanism of shale gas. Journal Of China Coal Society. 2013,38(5):742-747(In Chinese, with English abstract).
- Tang, Q.Y. , Zhang, M.J., Zhang, T.W., Liu, J.J, Yu, M.. Kinetic pyrolysis simulation of hydrocarbon generation in shale system: A case study on Pearl River Mouth Basin, China, 2014, 43(5): 518–528(In Chinese, with English abstract).
- Tang, Y. C., Huang, Y.S., Ellis, G. S. , Wang, Y., Kralert, P. G., & Gillaizeau, B., Ma, Q. S., Wang, R.H.. A kinetic model for thermally induced hydrogen and carbon isotope fractionation of individual n-alkanes in crude oil. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 2005,69(18), 4505-4520.
- Tian H, Xiao X M, Wilkins R, et al. Gas sources of the YN2 gas pool in the TarimBasin—Evidence from gas generation and methane carbon isotope fractionation kinetics of source rocks and crude oils. Marine & Petroleum Geology: 2007, 24(1):29-41.
- Tian, H. , Xiao, X. , Wilkins, R. W. T. , & Tang, Y. .. An experimental comparison of gas generation from three oil fractions: implications for the chemical and stable carbon isotopic signatures of oil cracking gas. Organic Geochemistry, 2012,46(191), 96–112.
- Tilley B, Mclellan S, Hiebert S, et al. Gas isotope reversals in fractured gas reservoirs of the western Canadian Foothills: Mature shale gases in disguise. AAPG Bull: 2011, 95 (8):1399-1422.
- Wang Y, Zhang S, Wang F, et al. Thermal cracking history by laboratory kinetic simulation of Paleozoic oil in eastern Tarim Basin, NW China, implications for the occurrence of residual oil reservoirs. Organic Geochemistry: 2006, 37(12):1803-1815.
- Wang, Q. , Zou, H.Y., Hao, F., Zhu, Y.M., Zhou, X.H., Wang, Y.B., Tian, J.Q., Liu, J.Z.. Modeling hydrocarbon generation from the Paleogene source rocks in Liaodong Bay, Bohai Sea: A study on gas potential of oil-prone source rocks. Organic Geochemistry, 201476, 204-219.
- Wang, Q.T. , Lu, H., Gao, L.H., Xiong, P., Shen, C.C., Liu, J.Z.,Peng, P.A.Geochemical characterization of thermogenic gas during the simulation experiments of the mature Salgan Shale. 7: OF CHINA COAL SOCIETY, 2013,38(5), 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. P. , Zhao, C. Y., Wang, Z. Y., Wang, H. J., Tian, J., & Zou, Y. R., et al.. Identification of marine natural gases with different origin sources. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2008, 51(1 Supplement), 148-164.
- Wen Y, Zhang L, Li Y.Late Mesozoic elevation history of the north Taihang Mountains, China: Constraints from clumped isotope geochemistry.Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2023.
- Xia, X.Y. , Li C.Y., Zhao L.. Influence of mixture on isotope indices in gas source discrimination. Petroleum exploration and development,,1998,25(3):89-93 (In Chinese, with English abstract).
- Xia, X.Y. ., and Tang,Y. Isotope fractionation of methane during natural gas flow with coupled diffusion and adsorption/desorption. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 83.1,2012:489-503.
- Xiang, B.L. , Li, E.T., Gao, X.W., Wang, M., Wang, Y., Xu, H., Huang, P., Yu, Shuang., Petroleum generation kinetics for Permian lacustrine source rocks in the Junggar Basin, NW China - ScienceDirect. Organic Geochemistry, 98(2016):1-17.
- Liu, J.Z. , Zou, Y.R., Pan, C.C.. Petroleum generation kinetics for Permian lacustrine source rocks in the Junggar Basin, NWChina. Organic Geochemistry, 2016,98:1-17.
- Wang,X.F., Li,X.F., Wang,X.Z., et al.. Carbon isotopic fractionation by desorption of shale gases. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2015, 60: 79-86.
- Xiong, Y.Q. , Geng A.S., Liu J.Z.. Kinetic modeling of carbon isotope fractionation of coal-derived methane. Geochimica, 2004, 33(6):545-550(In Chinese, with English abstract).
- Xiong, Y.Q. , Geng A.S., Liu J.Z., Wang Y.P., LIU D.H., Jia R.F., Shen J.G..Kinetic simulating experiment combined with GC-IRMS analysis: Application to identification of effective source rock. Geochimica, 2002,31(1):21-25(In Chinese, with English abstract).
- Yin, Q,Song, Z.G.,Liu J.Z.,2010.Influences of sulfur on composition of oil cracked gas and carbon isotopes.Oil &Gas Geology.31(3):309-314(In Chinese, with English abstract).
- ZHANG, H.M. , ZHANG, H.W., GU, P.P., et al. Molecular simulation of propane pyrolysis reaction[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica (Petroleum Processing Section), 2012, 28(6): 146-150.
- ZHAO, W.Z. , WANG, Z.Y., ZHANG, S.C., et al.Successive generation of natural gas from organic materials and itssignificance in future exploration. Petroleum Exploration andDevelopment, 2005, 32(2): 1-7.
- Zhao, H. The isotopic evolution of natural gas during accumulation process- a model of differential accumulation and loss of hydrocarbon for isotope reversal. 2019,Lanzhou:Northwest Institute of Eco-Envirenment and Resources, Chinese Academy of Sciences (In Chinese, with English abstract).
- Zhao, H. , Liu, C., Larson, T. E., Mcgovern, G. P., & Horita, J... Bulk and position-specific isotope geochemistry of natural gases from the late cretaceous eagle ford shale, south texas. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020, 122(11), 104659.
- Zhao,H., Luo, H.Y., Zhang, G.C., et al. Study of the Mechanism for Identifying the Shale Gas ‘Sweet Spot’ Using the Reversed δ13C1-3 Series. ActaGeologica Sinica (English Edition), 2021,95(2): 710–712.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).