Submitted:
05 January 2024
Posted:
05 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics and consent
2.2. Participants
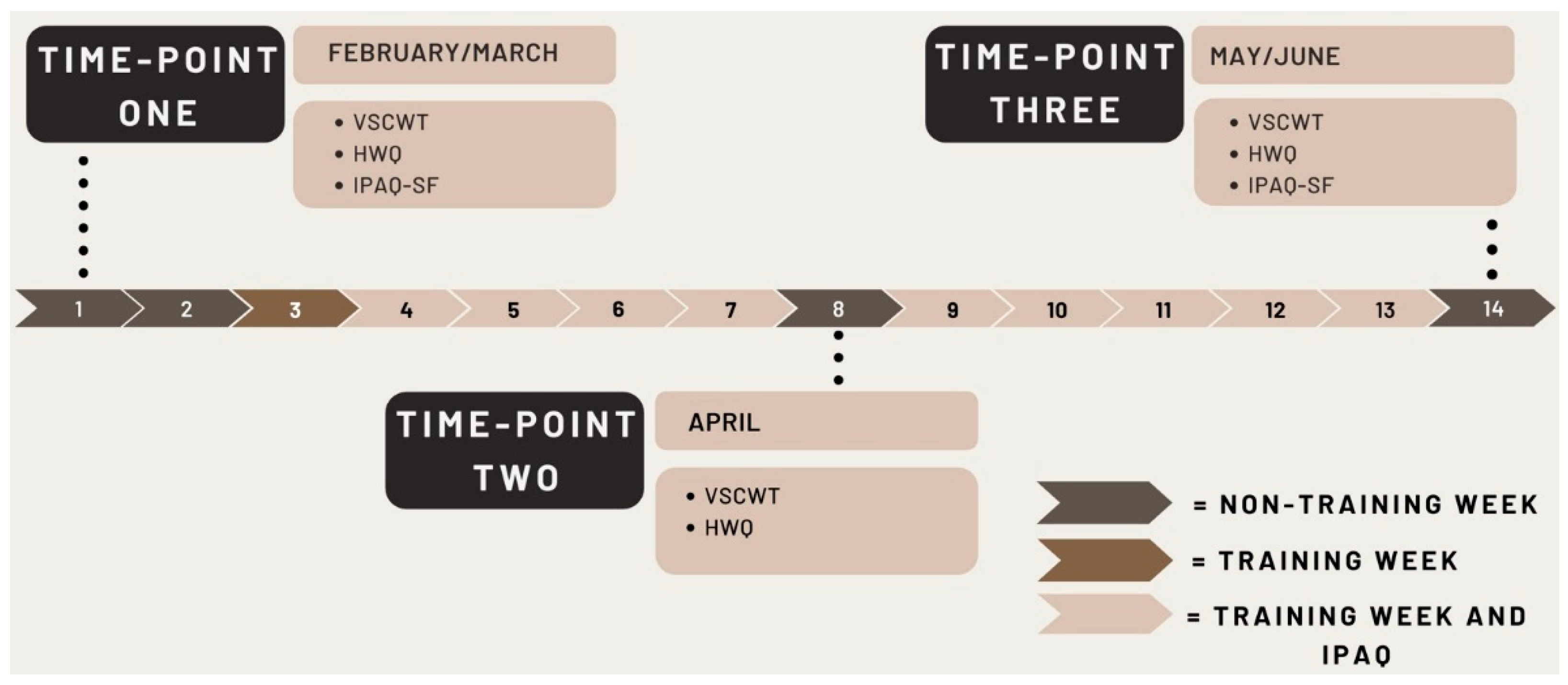
2.3. Study Design
2.4. International Physical Activity Questionnaire – Short Form
2.5. Health and Work Questionnaire
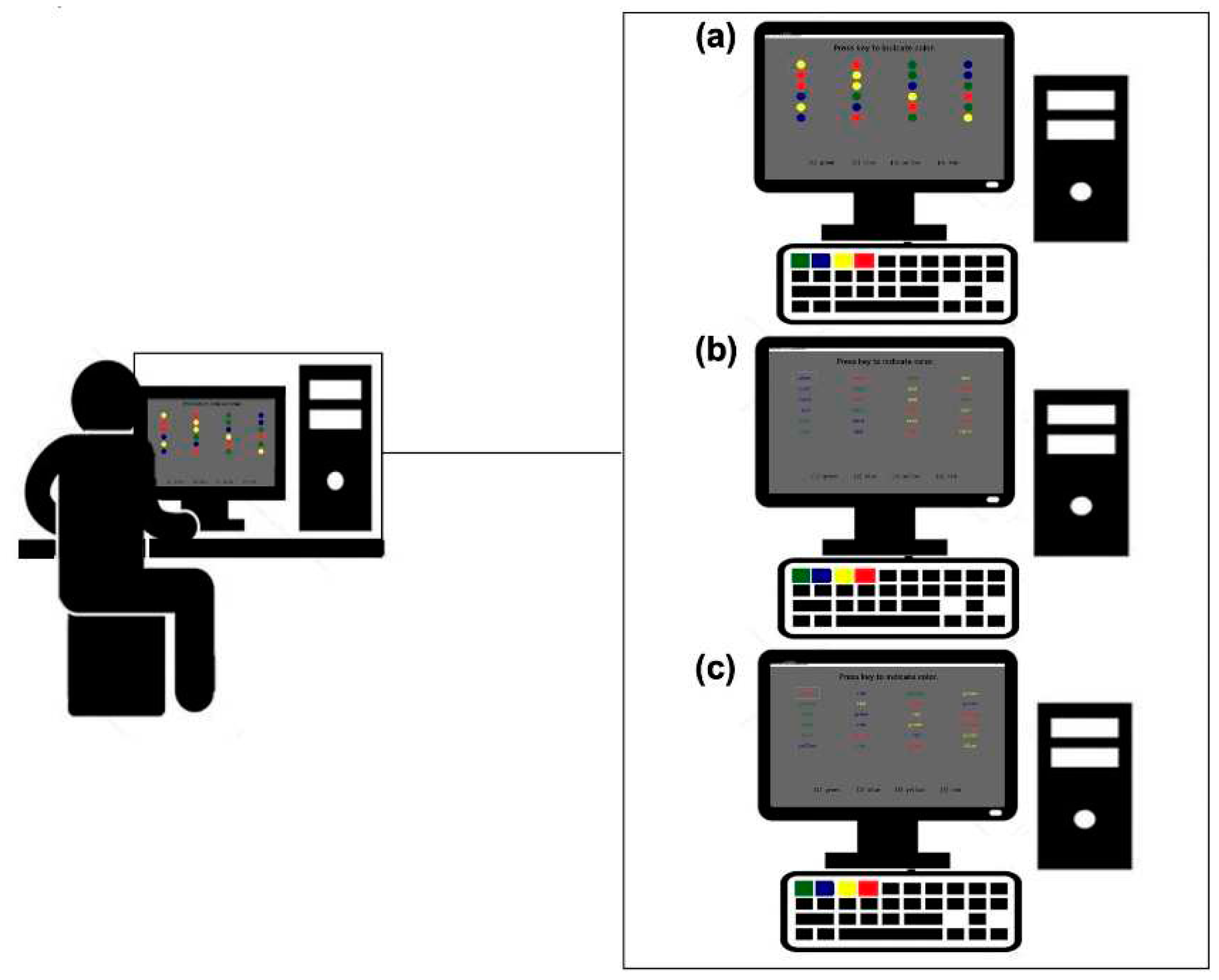
2.6. Victoria Stroop Colour and Word Test
2.7. Confounding factors
2.8. Statistical analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant characteristics
3.2. Confounding factors
3.3. International Physical Activity Questionnaire – Short Form
3.4. Health and Work Questionaire
3.5. Victoria Stroop Colour and Word Test
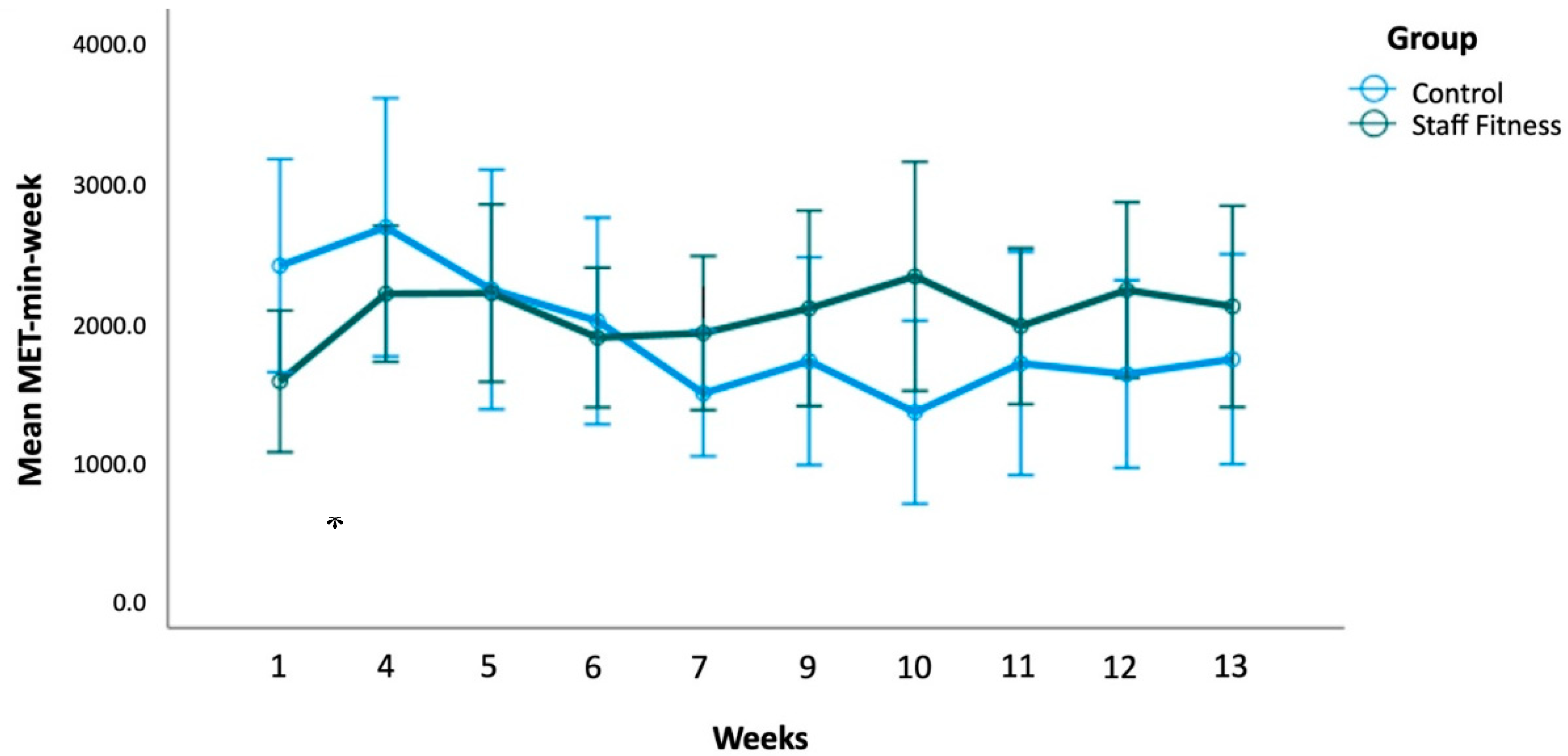
3.6. Longitudinal changes over time
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Australian Institute of Health and Welfare (AIHW). Australian Burden of Disease Study 2022. BOD 37; Australian Government; Canberra, AUS, 2022; 12.
- Australian Institute of Health and Welfare (AIHW). Overweight and Obesity. Available online: https://www.aihw.gov.au/reports/overweight-obesity/overweight-and-obesity/contents/overweight-and-obesity (accessed on 19 March 2023).
- Australian Institute of Health and Welfare (AIHW). Physical Activity. Available online: https://www.aihw.gov.au/reports/physical-activity/physical-activity (accessed on 19 March 2023).
- Dabkowski, E.; Porter, J.E.; Barbagallo, M.; Prokopiv, V.; Snell, C.; Missen, K. A Systematic Literature Review of Workplace Physical Activity Programs: An Exploration of Barriers and Enabling Factors. Cogent Psychol 2023, 10, 2186327: 1- 2186327: 21. [CrossRef]
- Toyoshima, K.; Ichiki, M.; Inoue, T.; Shimura, A.; Masuya, J.; Fujimura, Y.; Higashi, S.; Kusumi, I. Subjective Cognitive Impairment and Presenteeism Mediate the Associations of Rumination with Subjective Well-Being and Ill-Being in Japanese Adult Workers From the Community. Biopsychosoc Med 2021, 15, 15: 1-15: 10. [CrossRef]
- Nye, C.D.; Ma, J.; Wee, S. Cognitive Ability and Job Performance: Meta-Analytic Evidence for the Validity of Narrow Cognitive Abilities. J Bus Psychol 2022, 37, 1119-1139. [CrossRef]
- Toh, W.X.; Yang, H.; Hartanto, A. Executive function and Subjective Well-Being in Middle and Late Adulthood. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci 2020, 75, 69-77. [CrossRef]
- Marin-Farrona, M.; Wipfli, B.; Thosar, S.S.; Colino, E.; Garcia-Unanue, J.; Gallardo, L.; Felipe, J.L.; López-Fernández, J. Effectiveness of worksite wellness programs based on physical activity to improve workers’ health and productivity: a systematic review. Systematic Reviews 2023, 12, 87: 1-87: 13. [CrossRef]
- Grimani, A.; Aboagye, E.; Kwak, L. The Effectiveness of Workplace Nutrition and Physical Activity Interventions in Improving Productivity, Work Performance and Workability: A Systematic Review. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 1676: 1-1676: 12. [CrossRef]
- Hervieux, V.; Biron, C.; Dima, J. Investigating Associations Between Physical Activity and Presenteeism – A Scoping Review. Am J Health Promot 2023, 0, e04074015: e1-e04074015: 15. [CrossRef]
- Gil-Beltrán, E.; Llorens, S.; Salanova, M. Employees’ Physical Exercise, Resources, Engagement, and Performance: A Cross-Sectional Study from HERO Model. J work org sych 2020, 36, 39-47. [CrossRef]
- Naczenski, L.M.; De Vries, J.D.; Van Hooff, M.L.M.; Kompier, M.A.J. Systematic Review of the Association Between Physical Activity and Burnout. J Occup Health 2017, 59, 477-494. [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, M.T.; Blangsted, A.K.; Andersen, L.L.; Jørgensen, M.B.; Hansen, E.A.; Sjøgaard, G. The Effect of Worksite Physical Activity Intervention on Physical Capacity, Health, and Productivity: A 1-Year Randomized Controlled Trial. J Occup Environ Med 2009, 51, 759-770. [CrossRef]
- Martland, R.; Gaughran, F.; Stubbs, B.; Onwumere, J. Perspectives on Implementing Exercise Bikes for Use by Inpatient Mental Health Staff in the Workplace: A Qualitative Study Investigating Staff Attitudes. J Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs 2023, 30, 1027-1039. [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J.R.; Gordon, B.A.; Lythgo, N.; Bird, S.R.; Benson, A.C. Exercise at an Onsite Facility With or Without Direct Exercise Supervision Improves Health-Related Physical Fitness and Exercise Participation: An 8-Week Randomised Controlled Trial With 15-Month Follow-Up. Health Promot J Austr 2018, 29, 84-92. [CrossRef]
- Hergenroeder, A.; Quinn, T.D.; Perdomo, S.J.; Kline, C.E.; Gibbs, B.B. Effect of a 6-Month Sedentary Behavior Reduction Intervention on Well-Being and Workplace Health in Desk Workers With Low Back Pain. Work 2022, 71, 1145-1155. [CrossRef]
- Chau, J.Y.; Sukala, W.; Fedel, K.; Do, A.; Engelen, L.; Kingham, M.; Sainsbury, A.; Bauman, A.E. More Standing and Just As Productive: Effects of a Sit-Stand Desk Intervention on Call Center Workers’ Sitting, Standing, and Productivity at Work in the Opt to Stand Pilot Study. Prev Med Rep 2016, 3, 68-74. [CrossRef]
- Niven, A.; Ryde, G.C.; Wilkinson, G.; Greenwood, C.; Gorely, T. The Effectiveness of an Annual Nationally Delivered Workplace Step Count Challenge on Changing Step Counts: Findings from Four Years of Delivery. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2021, 18, 5140: 1-5140: 11. [CrossRef]
- Ryde, G.C.; Tomaz, S.A.; Sandison, K.; Greenwood, C.; Kelly, P. Measuring Productivity, Perceived Stress and Work Engagement of a Nationally Delivered Workplace Step Count Challenge. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022, 19, 1843: 1-1843: 14. [CrossRef]
- Lock, M.; Post, D.; Dollman, J.; Parfitt, G. Efficacy of Theory-Informed Workplace Physical Activity Interventions: A Systematic Literature Review With Meta-Analyses. Health Psychol Rev 2021, 15, 483-507. [CrossRef]
- Murphy, B.; Parekh, N.; Vieira, D.L.; O’Connor, J.A. A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials Examining Workplace Wellness Interventions. Nutrition and Health 2022, 28, 111-122. [CrossRef]
- Sköld, M.B.; Bayattork, M.; Andersen, L.L.; Schlünssen, V. Psychosocial Effects of Workplace Exercise – A Systematic Review. Scand J Work Environ Health 2019, 45, 533-545. [CrossRef]
- Guiney, H.; Lucas, S.J.; Cotter, J.D.; Machado, L. Evidence Cerebral Blood-Flow Regulation Mediates Exercise-Cognition Links in Healthy Young Adults. Neuropsychology 2015, 29, 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Haverkamp, B.F.; Wiersma, R.; Vertessen, K.; van Ewijk, H.; Oosterlaan, J.; Hartman, E. Effects of Physical Activity Interventions on Cognitive Outcomes and Academic Performance in Adolescents and Young Adults: A Meta-Analysis J Sports Sci 2020, 38, 2637-2660. [CrossRef]
- Gallardo-Gómez, D.; del Pozo-Cruz, J.; Noetel, M.; Álvarez-Barbosa, F.; Alfonso-Rosa, R.M.; del Pozo Cruz, B. Optimal Dose and Type of Exercise to Improve Cognitive Function in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Bayesian Model-Based Network Meta-Analysis of RCTs. Ageing Res Rev 2022, 76, 101591: 1-101591: 11. [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Ye, M.; Wang, L.; Zheng, G. Effects of Physical Exercise on Executive Function in Cognitively Healthy Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials: Physical Exercise for Executive Function Int J Nurs Stud 2021, 114, 103810: 1-103810. [CrossRef]
- Basso, J.C.; Suzuki, W.A. The Effects of Acute Exercise on Mood, Cognition, Neurophysiology, and Neurochemical Pathways: A Review. Brain Plast 2017, 2, 127-152. [CrossRef]
- Wilke, J.; Giesche, F.; Klier, K.; Vogt, L.; Herrmann, E.; Banzer, W. Acute Effects of Resistance Exercise on Cognitive Function in Healthy Adults: A Systematic Review with Multilevel Meta-Analysis. Sports Med 2019, 49, 905-916. [CrossRef]
- Stoner, L.; Willey, Q.; Evans, W.S.; Burnet, K.; Credeur, D.P.; Fryer, S.; Hanson, E.D. Effects of Acute Prolonged Sitting on Cerebral Perfusion and Executive Function in Young Adults: A Randomized Cross-Over Trial. Psychophysiology 2019, 56, e13457: e1- e13457: 29. [CrossRef]
- Heijnen, S.; Hommel, B.; Kibele, A.; Colzato, L.S. Neuromodulation of Aerobic Exercise-A Review. Front Psychol 2016, 6, 1890: 1-1890: 6. [CrossRef]
- Herold, F.; Törpel, A.; Schega, L.; Müller, N.G. Functional and/or Structural Brain Changes in Response to Resistance Exercises and Resistance Training Lead to Cognitive Improvements – A Systematic Review. Eur Rev Aging Phys Act 2019, 16, 10: 1-10: 33. [CrossRef]
- Landrigan, J.-F.; Bell, T.; Crowe, M.; Clay, O.J.; Mirman, D. Lifting Cognition: A Meta-Analysis of Effects of Resistance Exercise on Cognition. Psychol Res 2020, 84, 1167-1183. [CrossRef]
- Chow, Z.-S.; Moreland, A.T.; Macpherson, H.; Teo, W.-P. The Central Mechanisms of Resistance Training and Its Effects on Cognitive Function. Sports Med 2021, 51, 2483-2506. [CrossRef]
- Wechsler, D. Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale. Administration and Scoring Manual, 3rd ed.; The Psychological Corporation, Harcourt Brace: San Antonio, TX, USA, 1997; ISBN: 0158981030.
- Wechsler, D. Wechsler Memory Scale. Administrationand Scoring Manual, 3rd ed.; The Psychological Corporation, Harcourt Brace: San Antonio, TX, USA, 1997.
- Norton, K. New Australian Standard for Adult Pre-Exercise Screening. Sport health 2012, 30, 12-16. https://search.informit.org/doi/10.3316/informit.808362433833839.
- Exercise and Sports Science Australia (ESSA). Accredited Exercise Scientist Professional Standards for Accreditation; Queensland, AUS, 2020.
- Qualtrics, 18.9; Qualtrics: Utah, USA, 2005.
- Craig, C.L.; Marshall, A.L.; Sjöström, M.; Bauman, A.E.; Booth, M.L.; Ainsworth, B.E.; Pratt, M.; Ekelund, U.; Yngve, A.; Sallis, J.F.; et al. International Physical Activity Questionnaire: 12-Country Reliability and Validity. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2003, 35, 1381-1395. [CrossRef]
- Shikiar, R.; Halpern, M.T.; Rentz, A.M.; Khan, Z.M. Development of the Health and Work Questionnaire (HWQ): An Instrument for Assessing Workplace Productivity in Relation to Worker Health. Work 2004, 22, 219-229. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15156087/.
- Scarpina, F.; Tagini, S. The Stroop Color and Word Test. Front Psychol 2017, 8, 557: 1-557: 8, doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00557.Golden, C.J. Stroop Color and Word Test: A Manual for Clinical and Experimental Uses; Stoelting Co.: Chicago, IL, USA, 1978. [CrossRef]
- Golden, C.J. Stroop Color and Word Test: A Manual for Clinical and Experimental Uses; Stoelting Co.: Chicago, IL, USA, 1978.43.
- Strauss, E.; Sherman, E.M.S.; Spreen, O. A Compendium of Neuropsychological Tests: Administration, Norms, and Commentary, 3rd ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2006. ISBN: 0195159578.
- Klein, M.; Ponds, R.W.H.M.; Houx, P.J.; Jolles, J. Effect of Test Duration on Age-Related Differences in Stroop Interference. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 1997, 19, 77-82. [CrossRef]
- The Psychology Experiment Building Language (PEBL), 2.1; Mueller, S.T: Michigan, USA, 2013.
- Mueller, S.T.; Piper, B.J. The Psychology Experiment Building Language (PEBL) and PEBL Test Battery. Journal of Neuroscience Methods 2014, 222, 250-259. [CrossRef]
- Microsoft Windows 10, 22H2; Microsoft: Washington, USA, 2015.
- Lim, L.W.; Aquili, L. GABA Supplementation Negatively Affects Cognitive Flexibility Independent of Tyrosine. J Clin Med 2021, 10, 2028: 1-2028: 10. [CrossRef]
- Pilli, R.; Mur, N.; Pingali, U.R.; Shobha, J.C.; Reddy, A.P. A Computerized Stroop Test for the Evaluation of Psychotropic Drugs in Healthy Participants. Indian J Psychol Med 2013, 35, 180-189. [CrossRef]
- Ferris, L.T.; Williams, J.S.; Shen, C.-L. The Effect of Acute Exercise on Serum Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Levels and Cognitive Function. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2007, 39, 728-734. [CrossRef]
- Coetsee, C.; Terblanche, E. The Effect of Three Different Exercise Training Modalities on Cognitive and Physical Function in a Healthy Older Population. Eur Rev Aging Phys Act 2017, 14, 13: 1-13: 10. [CrossRef]
- da Silva, D.N.F.B.; Faro, H.K.C.; Tavares, M.P.M.; do Nascimento Neto, L.I.; Agrícola, P.M.D.; da Silva Machado, D.G. Influence of Workplace Exercise on Workers’ Cognitive Performance. Rev Bras Med Trab 2021, 19, 157-164. [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.-H. Review of the Psychometric Evidence of the Perceived Stress Scale. Asian Nurs Res 2012, 6, 121-127. [CrossRef]
- Microsoft Excel, 16.77.1; Microsoft Office: Washington, USA, 1985.
- IBM SPSS, 28.0.1.0; IBM Corp: New York, USA 1968.
- Hedges, L.V.; Olkin, I. Statistical Methods for Meta-Analysis, 1st ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1985. ISBN: 0080570658.
- Morris, S.B. Estimating Effect Sizes From Pretest-Posttest-Control Group Designs. Organ Res Methods 2008, 11, 364-386. [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, L.; Hasni, A.; Shinohara, M.; Duarte, A. A Single Bout of Resistance Exercise Can Enhance Episodic Memory Performance. Acta Psychologica 2014, 153, 13-19. [CrossRef]
- Ekelund, U.; Tarp, J.; Steene-Johannessen, J.; Hansen, B.H.; Jefferis, B.; Fagerland, M.W.; Whincup, P.; Diaz, K.M.; Hooker, S.P.; Chernofsky, A.; et al. Dose-Response Associations Between Accelerometry Measured Physical Activity and Sedentary Time and All Cause Mortality: Systematic Review and Harmonised Meta-Analysis. BMJ 2019, 366, 4570: 1-4570: 10. [CrossRef]
- Gill, D.L.; Hammond, C.C.; Reifsteck, E.J.; Jehu, C.M.; Williams, R.A.; Adams, M.M.; Lange, E.H.; Becofsky, K.; Rodriguez, E.; Shang, Y.T. Physical Activity and Quality of Life. J Prev Med Public Health 2013, 46, 28-34. [CrossRef]
- Justesen, J.B.; Søgaard, K.; Dalager, T.; Christensen, J.R.; Sjøgaard, G. The Effect of Intelligent Physical Exercise Training on Sickness Presenteeism and Absenteeism Among Office Workers. J Occup Environ Med 2017, 59, 942-948. [CrossRef]
- Eather, N.; Babic, M.; Riley, N.; Harris, N.; Jung, M.; Jeffs, M.; Barclay, B.; Lubans, D.R. Integrating High-Intensity Interval Training Into the Workplace: The Work-HIIT Pilot RCT. Scand J Med Sci Sports 2020, 30, 2445-2455. [CrossRef]
- Michishita, R.; Jiang, Y.; Ariyoshi, D.; Yoshida, M.; Moriyama, H.; Obata, Y.; Nagata, M.; Nagata, T.; Mori, K.; Yamato, H. The Introduction of an Active Rest Program by Workplace Units Improved the Workplace Vigor and Presenteeism Among Workers: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J Occup Environ Med 2017, 59, 1140-1147. [CrossRef]
- Dalager, T.; Justesen, J.B.; Murray, M.; Boyle, E.; Sjøgaard, G. Implementing Intelligent Physical Exercise Training at the Workplace: Health Effects Among Office Workers—A Randomized Controlled Trial. Eur J Appl Physiol 2016, 116, 1433-1442. [CrossRef]
- Brox, J.I.; Frøystein, O. Health-Related Quality of Life and Sickness Absence in Community Nursing Home Employees: Randomized Controlled Trial of Physical Exercise. Occup Med 2005, 55, 558-563. [CrossRef]
- Madinabeitia-Cabrera, I.; Alarcón-López, F.; Chirosa-Ríos, L.J.; Pelayo-Tejo, I.; Cárdenas-Vélez, D. The Cognitive Benefits of Basketball Training Compared to a Combined Endurance and Resistance Training Regimen: A Four-Month Intervention Study. Sci Rep 2023, 13, 11132: 1-11132: 11. [CrossRef]
- Fortes, L.d.S.; Costa, M.d.C.; Perrier-Melo, R.J.; Brito-Gomes, J.L.; Nascimento-Júnior, J.R.A.; de Lima-Júnior, D.R.A.A.; Cyrino, E.S. Effect of Volume in Resistance Training on Inhibitory Control in Young Adults: A Randomized and Crossover Investigation. Front Psychol 2018, 9, 2028: 1-2028: 10. [CrossRef]
- Peig-Chiello, P.; Perrig, W.J.; Ehrsam, R.; Staehelin, H.B.; Krings, F. The Effects of Resistance Training on Well-Being and Memory in Elderly Volunteers. Age Ageing 1998, 27, 469-475. [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.H.; Blake, H.; Suggs, L.S. A Systematic Review of Workplace Health Promotion Interventions for Increasing Physical Activity. Br J Health Psychol 2014, 19, 149-180. [CrossRef]
- Alomari, M.A.; Keewan, E.F.; Qhatan, R.; Amer, A.; Khabour, O.F.; Maayah, M.F.; Hurtig-Wennlöf, A. Blood Pressure and Circulatory Relationships with Physical Activity Level in Young Normotensive Individuals: IPAQ Validity and Reliability Considerations. Clin Exp Hypertens 2011, 33, 345-353. [CrossRef]
- Encarnação, S.G.A.d.; Moreira, O.C.; de Castro Pinto, B.W.F.; de Miranda, C.N.; Araújo, D.P.d.S.; Pereira, F.S.T.; Fazolo, S.L.; Carneiro-Júnior, M.A. Physical Activity Levels and Mental Illness Risk in Elderly Women During COVID-19. Motricidade 2022, 18, 225-229. [CrossRef]
- Cooper, K.; Barton, G.C. An Exploration of Physical Activity and Wellbeing in University Employees. Perspect Public Health 2015, 136, 152-160. [CrossRef]
- Thonon, F.; Godon-Rensonnet, A.-S.; Perozziello, A.; Garsi, J.-P.; Dab, W.; Emsalem, P. Return on Investment of Workplace-Based Prevention Interventions: A Systematic Review. Eur J Public Health 2023, 33, 612-618. [CrossRef]
- SantaBarbara, N.J.; Rezai, R.; Soetenga, S.; Terry, E.; Carpenter, C.L.; Comulada, W.S. Exercise Preferences for a Workplace Wellness Program to Reduce Cardiovascular Risk and Increase Work Productivity. J Occup Environ Med 2022, 64, 545-549. [CrossRef]
| Variable | All participants (n = 44) | Staff Fitness (n = 26) | Control (n = 18) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 42.30 ± 11.68 | 43.12 ± 11.83 | 41.11 ± 11.69 |
| Women: Men | 24: 20 | 17: 9 | 7: 11 |
| Occupation | |||
| Casual/sessional academic staff | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| Full-time academic staff | 9 | 2 | 7 |
| Full-time professional staff | 17 | 14 | 3 |
| Part-time academic staff | 11 | 5 | 6 |
| Part-time professional staff | 5 | 4 | 2 |
| Staff Fitness group (26) | Control Group (18) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MET-min-week | N | Mean | SD | N | Mean | SD | Effect Size dCohen resp. gHedges |
| Week 1 | 20 | 1540.93* | 1083.74 | 15 | 2368.80* | 1377.70 | -0.68 |
| Week 4 | 25 | 2167.58 | 1180.41 | 14 | 2643.96 | 1601.89 | -0.36 |
| Week 5 | 22 | 2173.02 | 1433.30 | 13 | 2198.46 | 1418.88 | -0.02 |
| Week 6 | 20 | 1854.40 | 1069.78 | 15 | 1973.90 | 1335.54 | -0.10 |
| Week 7 | 20 | 1886.63 | 1177.34 | 15 | 1455.12 | 814.72 | 0.42 |
| Week 9 | 19 | 2063.50 | 1452.80 | 11 | 1686.00 | 1107.13 | 0.28 |
| Week 10 | 17 | 2292.82 | 1594.43 | 13 | 1319.27 | 1084.48 | 0.70 |
| Week 11 | 15 | 1936.60 | 1010.11 | 14 | 1668.89 | 1384.36 | 0.22 |
| Week 12 | 23 | 2194.83 | 1454.72 | 12 | 1592.50 | 1057.62 | 0.45 |
| Week 13 | 17 | 2077.32 | 1401.48 | 15 | 1699.50 | 1359.31 | 0.27 |
| Staff Fitness Group (26) | Control Group (18) | Effect size dppc2 sensu Morris (2008) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subscale | Start (25) | Mid-point (21) | End (20) | Start (15) | Mid-point (15) | End (11) | Start-end | Start-middle | Middle-end |
| Productivity | 7.33 ± 0.97 | 7.09 ± 1.09 | 7.10 ± 0.92 | 7.28 ± 1.10 | 6.85 ± 1.21 | 6.97 ± 0.84 | 0.08 | 0.18 | -0.09 |
| Supervisor perceived | 7.68 ± 1.44 | 7.32 ± 1.45 | 7.38 ± 1.41 | 7.84 ± 1.05 | 7.21 ± 1.54 | 7.58 ± 1.22 | -0.03 | 0.20 | -0.20 |
| Self-rated | 7.12 ± 0.85 | 6.95 ± 0.94 | 6.93 ± 0.71 | 6.93 ± 1.29 | 6.76 ± 1.08 | 6.62 ± 0.76 | 0.11 | 0.00 | 0.12 |
| Concentration/Focus | 6.68 ± 1.88 | 6.82 ± 1.75 | 6.92 ± 1.71 | 7.31 ± 2.37 | 6.28 ± 2.23a | 6.61 ± 1.76 | 0.44 | 0.55 | -0.12 |
| Impatience/Irritability | 7.63 ± 1.94 | 8.03 ± 1.51 | 7.98 ± 1.66 | 7.93 ± 1.64 | 7.91 ± 1.77 | 8.58 ± 1.29 | -0.16 | 0.22 | -0.43 |
| Work satisfaction | 6.89 ± 1.67 | 6.73 ± 1.89 | 6.88 ± 1.53 | 6.88 ± 1.34 | 6.22 ± 1.73 | 6.57 ± 1.53 | 0.19 | 0.32 | -0.11 |
| Non-work satisfaction | 7.32 ± 1.53 | 7.71 ± 1.35 | 7.43 ± 1.43 | 7.36 ± 2.09 | 7.44 ± 1.90 | 8.00 ± 1.24 | -0.30 | 0.17 | -0.51 |
| Supervisor relationships | 7.46 ± 2.52 | 6.98 ± 2.91 | 7.67 ± 1.92 | 8.30 ± 1.72 | 7.63 ± 2.33 | 7.45 ± 2.14 | 0.46 | 0.08 | 0.32 |
| Total HWQ score | 7.18 ± 1.17 | 7.18 ± 0.97 | 7.14 ± 0.88 | 7.32 ± 1.21 | 6.89 ± 1.18 | 7.18 ± 0.89 | 0.08 | 0.36 | -0.30 |
| Variable | Staff Fitness group (26) | Control Group (18) | Effect size dppc2 sensu Morris (2008) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Start (25) | Mid-point (25) | End (24) | Start (17) | Mid-point (16) | End (16) | Start-end | Start-middle | Middle-end | |
| Dot (seconds) | 19.93 ± 5.43 | 19.26 ± 3.96 | 18.77 ± 4.63 b | 19.51 ± 4.53 | 22.28 ± 10.04 | 19.78 ± 4.15 | -0.28 | -0.66 | 0.28 |
| Accuracy (%) | 98.50 ± 1.64 | 98.50 ± 3.15 | 97.92 ± 4.08 | 99.26 ± 1.64 | 97.40 ± 3.36 a | 97.92 ± 3.40 | 0.46 | 1.11 | -0.33 |
| Word (seconds) | 20.26 ± 4.47 | 19.64 ± 4.29 | 19.20 ± 4.18 b | 21.42 ± 5.25 | 20.69 ± 3.35 | 20.16 ± 4.14 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| Accuracy (%) | 99.00 ± 2.53 | 98.67 ± 2.88 | 98.96 ± 2.22 | 98.53 ± 2.53 | 97.92 ± 3.40 | 97.66 ± 4.56 | 0.32 | 0.11 | 0.16 |
| Colour (seconds) | 24.76 ± 11.96 | 23.02 ± 8.41 | 23.43 ± 8.96 | 23.58 ± 6.33 | 23.07 ± 5.36 | 22.63 ± 5.17 | -0.04 | -0.12 | 0.11 |
| Accuracy (%) | 97.33 ± 5.63 | 98.00 ± 5.12 | 96.70 ± 5.35 | 98.77 ± 2.45 | 98.44 ± 2.58 | 98.18 ± 3.72 | -0.01 | 0.21 | -0.24 |
| Colour/Dot | 1.23 ± 0.27 | 1.18 ± 0.24 | 1.24 ± 0.22 | 1.21 ± 0.13 | 1.10 ± 0.22 | 1.16 ± 0.16 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.00 |
| Word/Dot | 1.03 ± 0.11* | 1.02 ± 0.12 | 1.04 ± 0.11 | 1.10 ± 0.11* | 0.99 ± 0.18 a | 1.03 ± 0.14 | 0.71 | 0.89 | -0.13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





