1. Introduction
Inflammation assumes a pivotal role in rectifying imbalances within the body's homeostasis and is crucial for the repair, remodeling, and renewal of various tissues under diverse and adverse conditions [
1]. Functioning as the primary line of defense, inflammation safeguards the host from infections induced by a spectrum of pathogens, including bacteria, fungi, parasites, and virus [
2]. Additionally, others stimuli, such as cellular damage, chemical agents, physical injuries, burns, radiation, freezing, ischemia, and reperfusion, can incite inflammatory responses [
3].
Classically, the treatment of inflammation entails the administration of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or glucocorticoids [
4,
5]. Both exhibit varying degrees of effectiveness in alleviating inflammation and they use are accompanied by a spectrum of adverse effects such as, atherosclerosis, cardiac alterations, gastrointestinal disorders, hypertension, renal toxicity, type 2 diabetes, visceral obesity, and others [
5,
6].
Therefore, the development of new substances exhibiting anti-inflammatory properties holds significant importance in the clinical use, with the goal of securing alternative treatments characterized by efficacy and diminished adverse effects. An attractive strategy in this search for new drugs involves the exploration of molecules with anti-inflammatory potential derived from medicinal plants, given the vast and yet undiscovered diversity of bioactive compounds within the Plant Kingdom [
7,
8]. Natural products stand out as a noteworthy reservoir for therapeutic interventions against various diseases, with the anti-inflammatory effects of traditional herbal medicines, crude plant extracts, natural compounds, and their derivatives having already demonstrated significant promise [
7,
9].
In this context,
Solidago chilensis Meyen (Asteraceae) emerges as a highly promising reservoir for the discovery of anti-inflammatory agents. This plant species, with a historical use spanning over 700 years in South American folk medicine, has been recognized for its diverse therapeutic attributes, including anticancer, antidepressant, diuretic, gastroprotective, burn treatment, and anti-inflammatory activities [
10,
11,
12,
13].
Phytochemical analyses of
S. chilensis have revealed a spectrum of chemical compounds, including flavonoids such as quercitrin, quercetin, and rutin, as well as diterpenes such as deoxysolidagenone, solidagolactol, and solidagenone [
14]. Notably, the relatively underexplored compound solidagenone, isolated from the rhizomes, leaves, and inflorescences of
S. chilensis, exhibits promise biological activities [
13,
15,
16,
17]. Solidagenone has demonstrated gastroprotective activity in a murine model of gastric injury induced by hydrochloric acid [
15], attenuated skin inflammation in experimental models [
16], exhibited antidepressant-like effects in mice [
13], and a protective effect in a model of airway inflammation induced by ovalbumin [
17]. Consequently, solidagenone holds considerable potential for further investigations into its anti-inflammatory activity. The present study is designed to assess the anti-inflammatory properties of solidagenone in acute experimental models of inflammation and its mechanism of action.
2. Results and Discussion
Firstly, the toxicity effects of a single dose of solidagenone was investigated. Administration of 30, 60 or 90 mg/Kg of solidagenone did not result in mortality or elicit any discernible signs of toxicity in the animals (
Table 1). Furthermore, no significant variance in body weight was noted among animals treated with different doses of solidagenone when compared to mice treated only with vehicle solution (
Table 2).
Toxicological investigations of bioactive compounds derived from medicinal plants are essential to ensure the safety of using herbs in the treatment of a series of diseases [
18]. Therefore, it is relevant to analyze the acute toxicity generated by treatment with solidagenone in mice. Here we verified that the compound did not present toxicity at any of the administered doses used (30, 60, and 90 mg/Kg). These findings are consistent with the literature, considering that Rodriguez and collaborators [
19], used a similar methodology used in this study and verified that solidagenone, intraperitoneally injected, did not show any observable symptoms of toxicity or mortality in Swiss mice treated with doses ranging from 100 to 600 mg/Kg.
A crucial index for evaluating the physiological or pathological state of mice subjected to experimental tests is body weight. Alterations in body weight often correlate with significant physiological changes, warranting a thorough analysis of this parameter [
20]. In our study, we found that treatment with solidagenone did not induce significant changes in the weight of the animals.
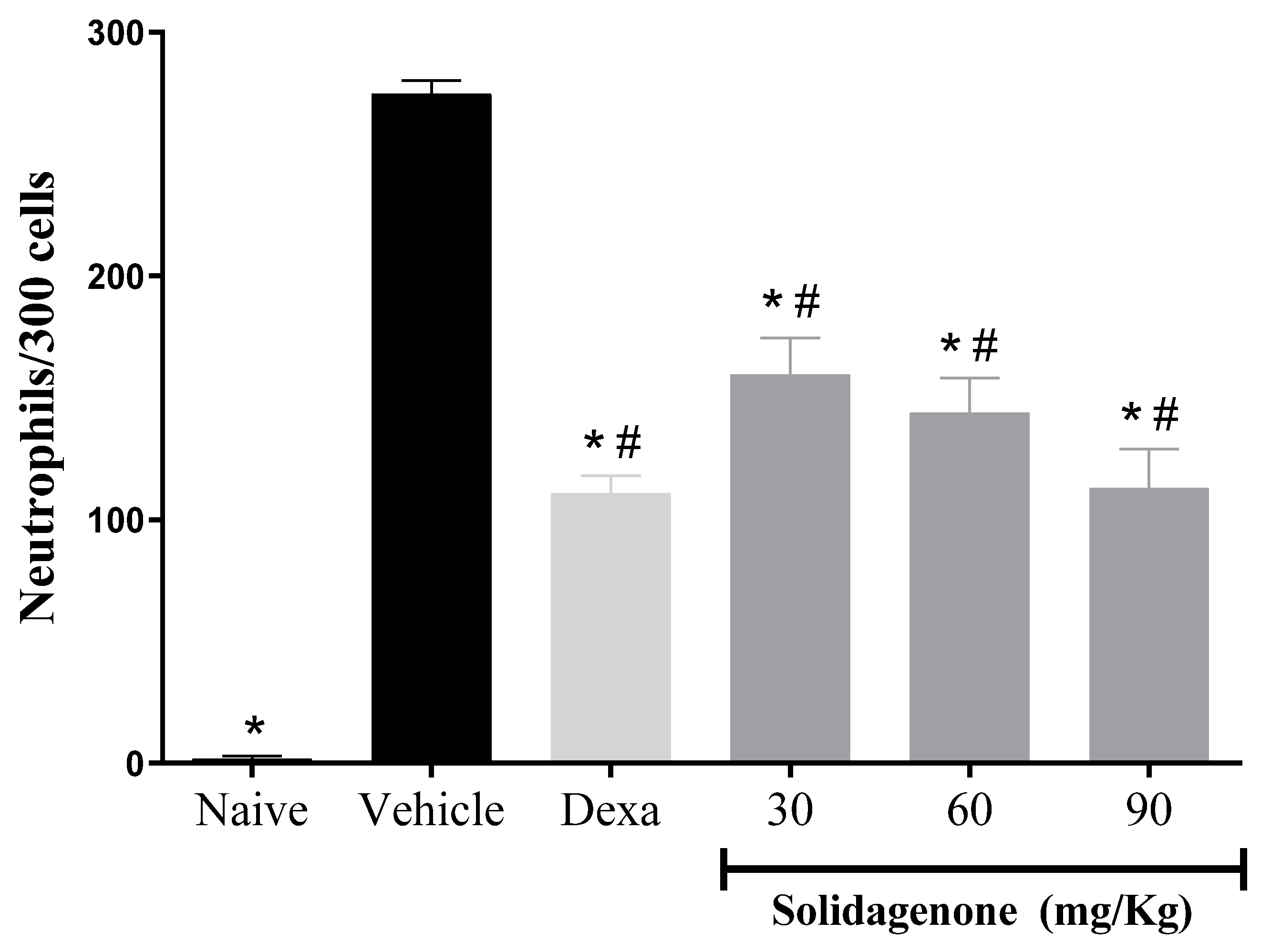
Next, we assessed the anti-inflammatory activity of solidagenone, firstly, in a mouse model of acute peritonitis induced by carrageenan. As revealed in
Figure 1, mice subjected to carrageenan stimulation and treated with a vehicle solution exhibited a mean of 274.8 neutrophils in 300 counted cells, a significative increase (
p < 0.05) compare to naïve group which presented a mean of 1.8 neutrophils in 300 counted cells. In comparison to the vehicle-treated group, pre-treatment with solidagenone at doses of 30, 60, and 90 mg/kg resulted in a statistically significant reduction (
p < 0.05) in neutrophil migration by 58.9%, 47.6%, and 41.9%, respectively. Under the same conditions, the administration of dexamethasone, at a dose of 30 mg/kg, also promoted a significative reduction (
p < 0.05) of 59.6% in neutrophil migration (
Figure 1). In agreement with these data, Liz and colleagues [
21] demonstrated that an aqueous rhizome extract of
S. chilensis and its two derived fractions promoted inhibition of leukocytes migration, particularly affecting neutrophil migration, and exudation in a mouse model of air pouch using carrageenan. Moreover, these effects were accompanied by a reduction of IL-1β, TNFα, and nitric oxide production, as well as a decrease in myeloperoxidase and adenosine deaminase activity [
21]. Similar results, using a model of pleurisy induced by carrageenan, were found with extracts from leaves or inflorescences of
S. chilensis [
22].
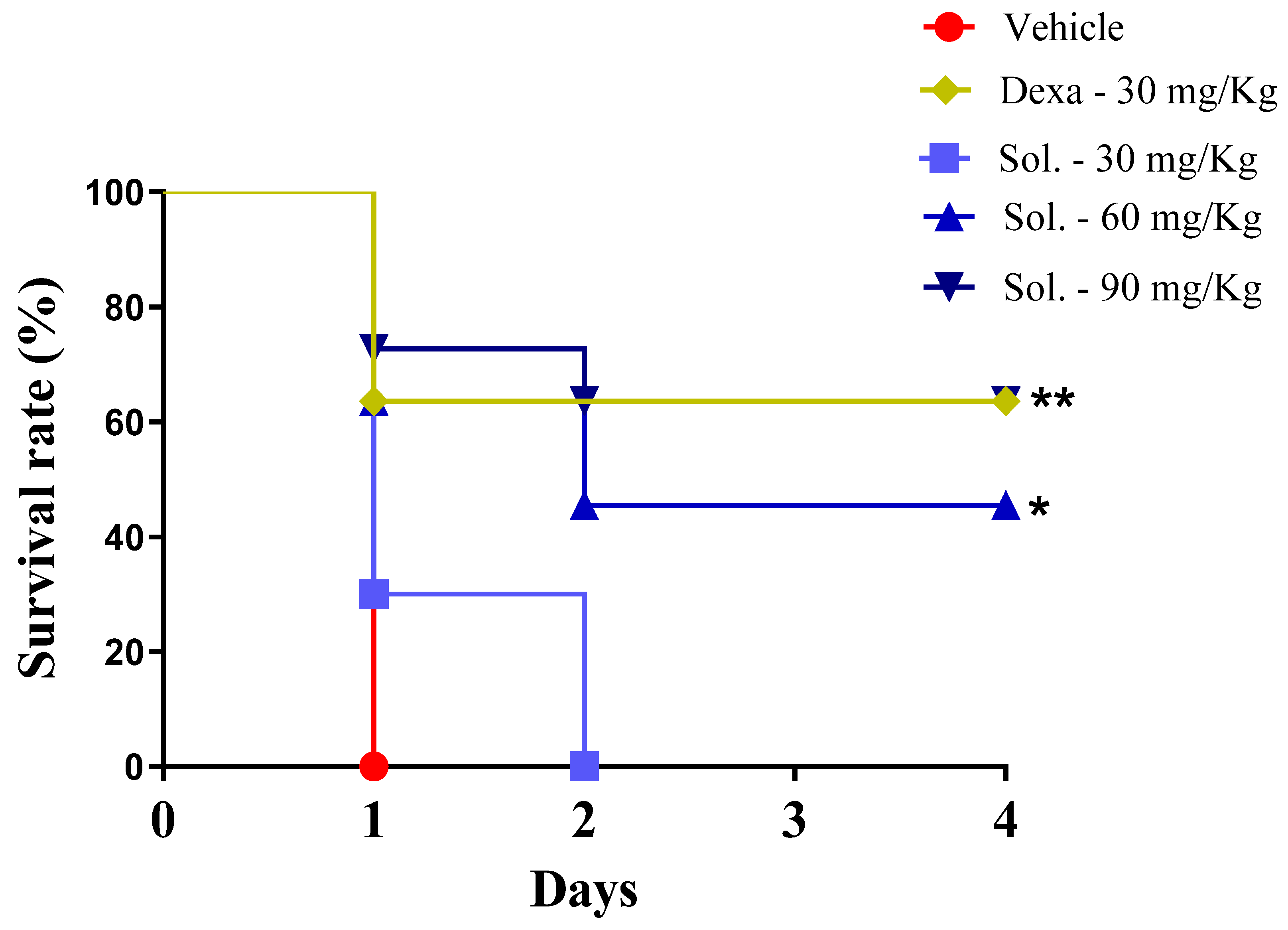
Next, the anti-inflammatory effect of solidagenone was further investigated in a mouse model of endotoxic shock. As revealed in
Figure 2, in comparison with the vehicle group, the animals treated with solidagenone at 60 and 90 mg/Kg exhibited an increased survival rate of 45.5 and 63.3% respectively, which was significant (
p < 0.05). Under the same conditions, dexamethasone, administered at a dose of 30 mg/kg, also promoted a significant increase (
p < 0.05) in survival rate of 63.3%.
As expected, LPS administration induced a leukopenia and thrombocytopenia in the animals (
Table 3). Interestingly, treatment with solidagenone also conferred a significant (
p < 0,05) protective effect against these hematological disorders, commonly observed in sepsis conditions. Dexamethasone, while promoting a more pronounced leukocyte recovery, did not afford protection against thrombocytopenia (
Table 3).
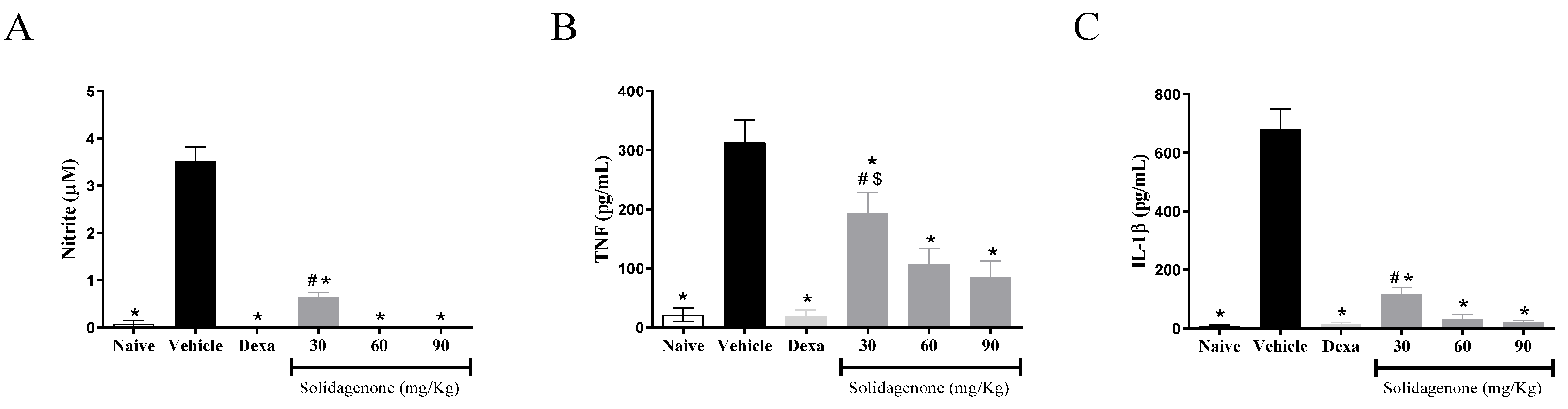
For better understanding the anti-inflammatory effect of solidagenone, we measured the amount of nitric oxide and cytokines in the supernatant of resident macrophages from animals previously treated with solidagenone and stimulated
in vitro with LPS plus IFNγ. As revealed in
Figure 3, treatment with all the doses of solidagenone promoted a significative reduction in nitric oxide (
Figure 3A), TNF-α (
Figure 3B), and IL-1β (
Figure 3C) relative to the LPS-stimulated vehicle-treated cultures. In a similar way, dexamethasone, administered at a dose of 30 mg/kg, also promoted a significative (
p < 0.05) reduction of all the pro-inflammatory molecules evaluated (
Figure 3). In agreement with these data, solidagenone also reduced NO, IL-1β, and TNFα production and gene expression of several inflammatory mediators (
NOS2,
IL1β,
TNFα, and
Cox2) in peritoneal macrophages stimulated
in vitro with LPS plus IFNγ [
17]. Moreover, the anti-inflammatory activity of solidagenone was also associated with nitric oxide, IL-6, and TNFα reduction in croton-oil-, arachidonic acid-, and phenol-induced ear oedema mouse models [
16].
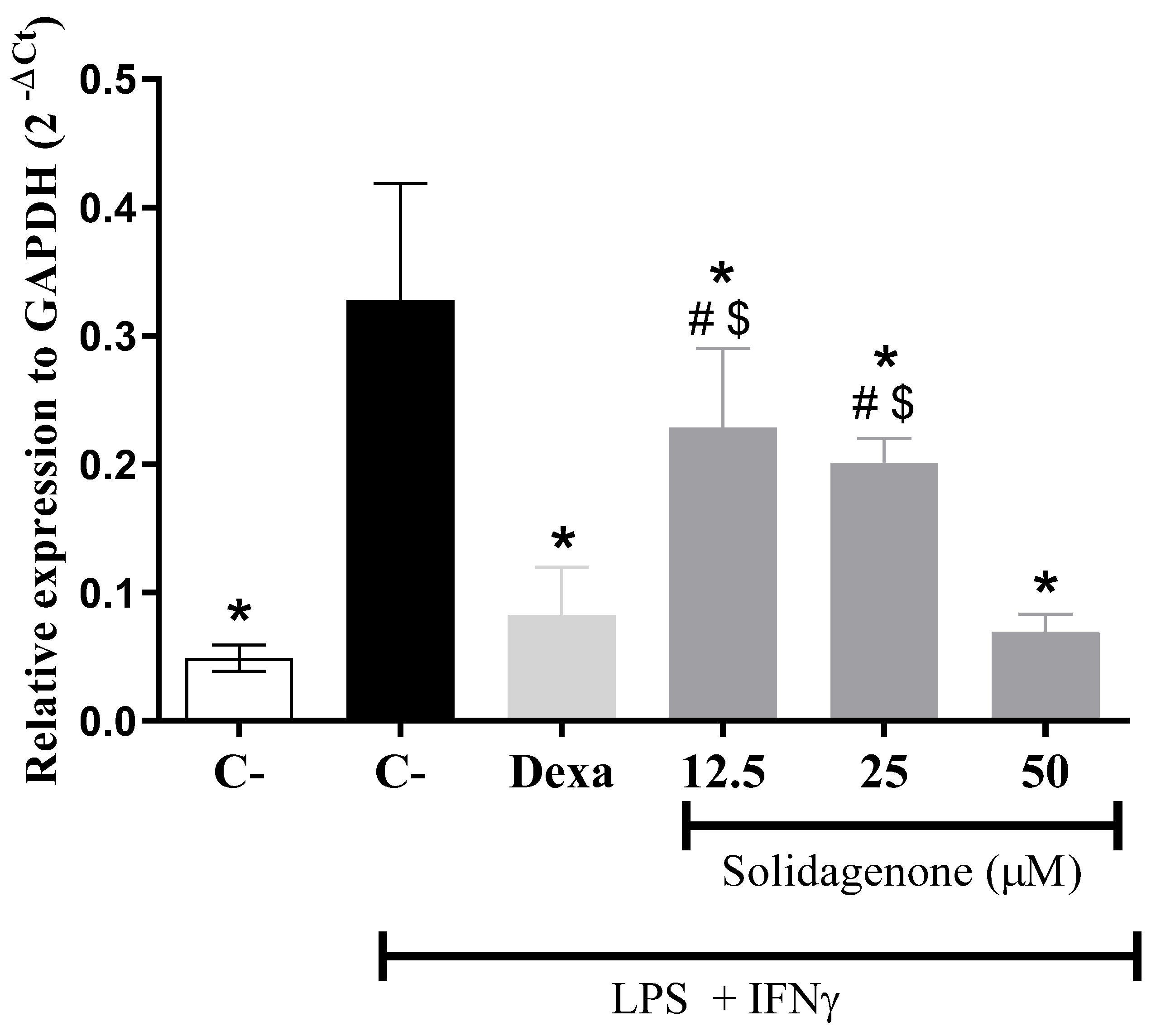
It is well-established that LPS induces Toll-like receptor-4 (TLR4) activation, triggering intracellular signaling pathways, including NF-ƙB activation, a pivotal transcription factor that modulates diverse pro-inflammatory genes such as IL-1β, NOS2, and TNF-α [
23,
24]. Notably, as revealed in
Figure 4, treatment of activated macrophages
in vitro with different concentrations of solidagenone resulted in a significant (p < 0.05) reduction in the gene expression of NF-ƙB. Similar results were obtained with the treatment with dexamethasone.
To understand the interaction between solidagenone and NF-κB, we investigate how solidagenone may interact with p65 subunit of NF-κB transcription factor and IκB kinase enzyme (IKK), through docking simulations. Both molecules are critical to preventing the displacement of NF-κB into the nucleus and consequently its activation [
25,
26].
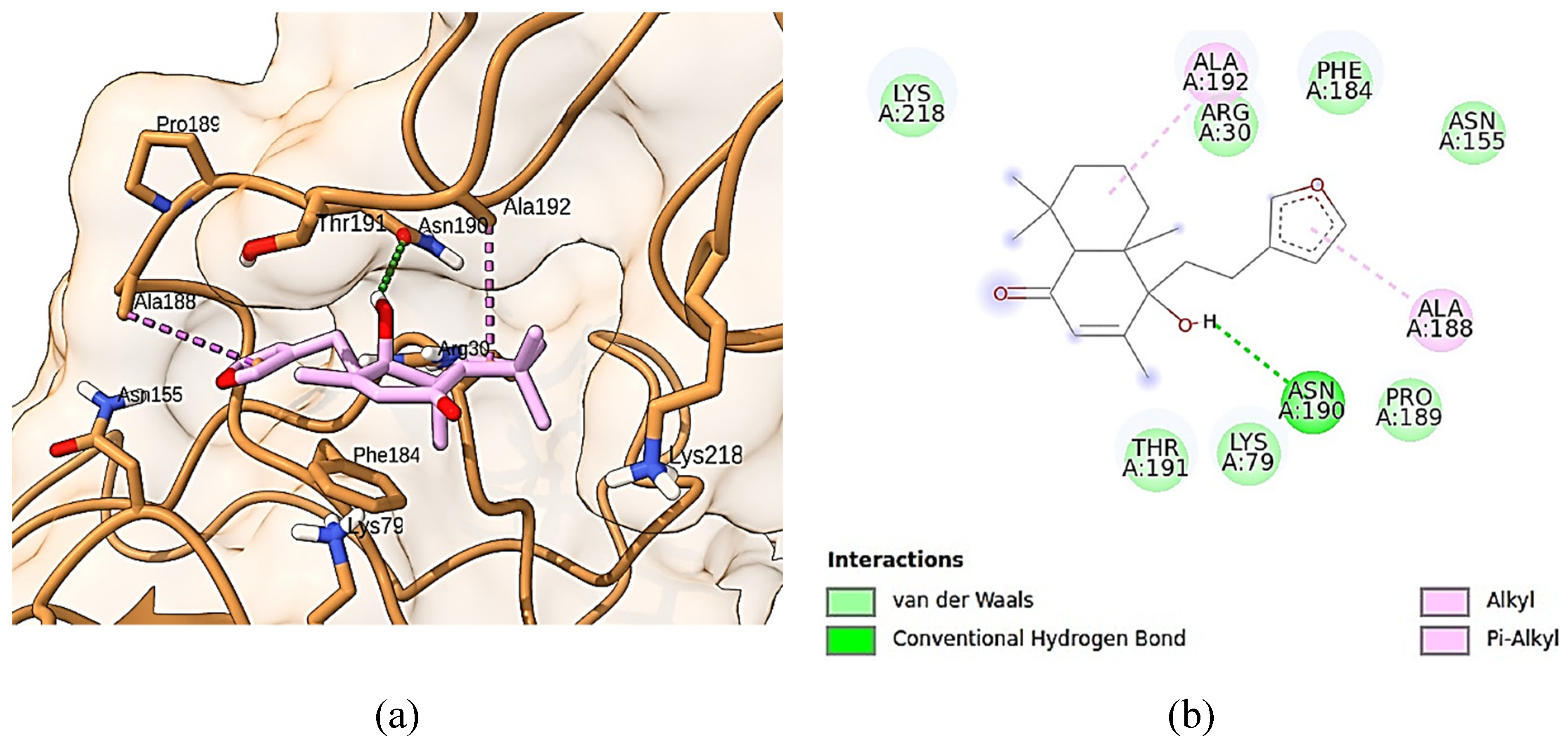
Figure 5 shows solidagenone docked into the binding site of p65 subunit of NF-κB. As can be seen, solidagenone docks to NF-Κb system due seven van der Waals interactions (Lys-218, Arg-30, Phe-184, Asn-155, Pro189, Lys-79, and Thr-191), one alkyl interaction (Ala-192), one Pi-alkyl interaction (Ala-188), and one hydrogen bond interaction (Asn-190). The calculated docking energy was equal to -6.4 kcal/mol. Some other images regarding solidagenone-p65 subunit of NF-κB are shown in
Supplementary material (Figure S1).
Regarding the IKK system, it is important to mention that it is organized in two chains (A and B), comprising four domains each: C-terminal dimerization domain (SDD), C-terminal kinase domain (KDC), N-terminal kinase domain (KDN), and ubiquitin-like domain (ULD) (
Suplementary material, Figure S2). Since, according to Liu and coworkers [
27], chain B is the one in the active conformation, this was the chosen chain used as the protein target for docking solidagenone.
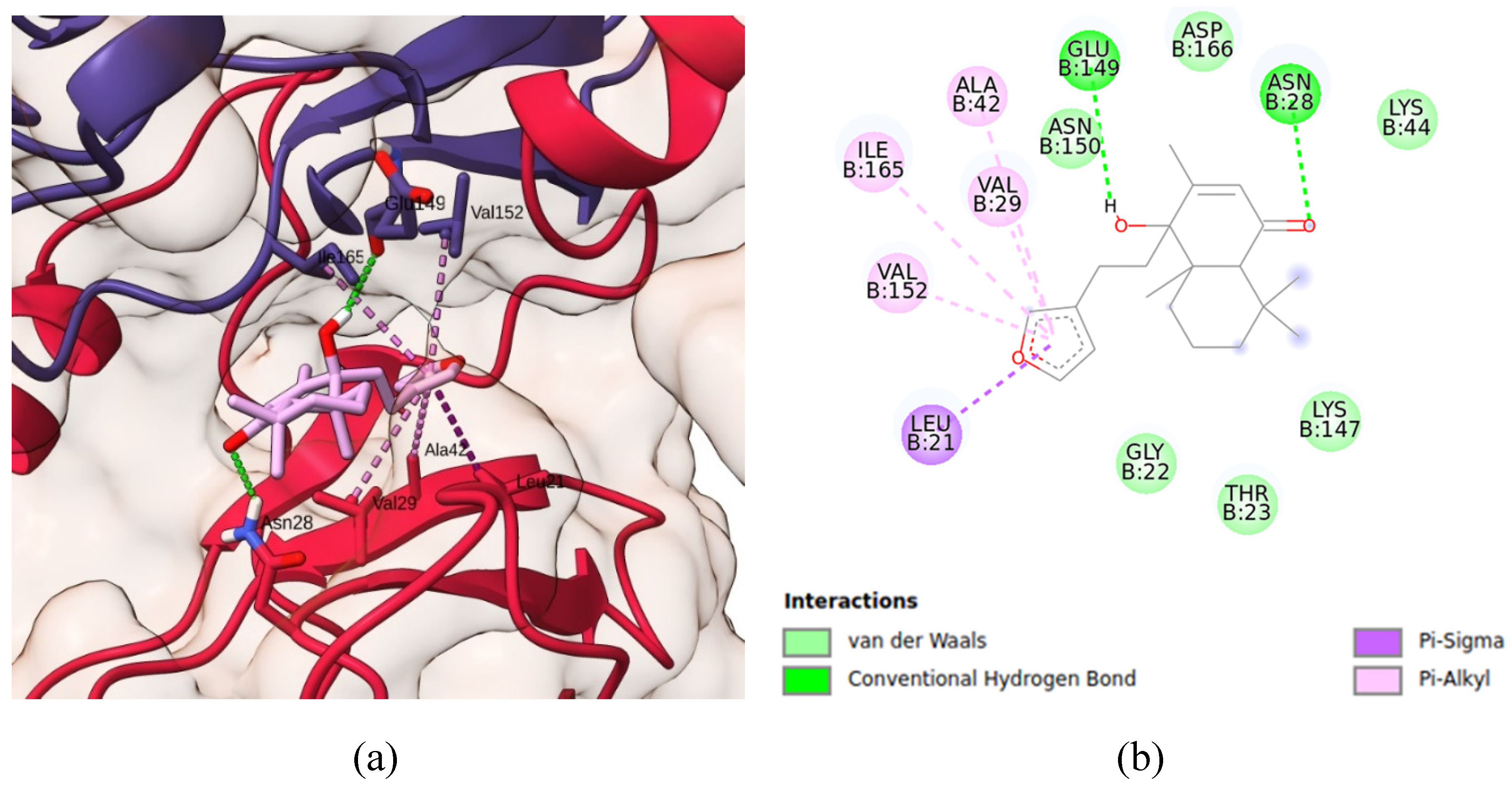
Figure 6 shows detains of simulated IKK-solidagenone complex. Solidagenone docks to IKK system due six van der Waals interactions (Lys-44, Asp-166, Lys-147, Thr-23, Gly-22, and Asn-150), one Pi-Sigma interaction (Leu-2), four Pi-alkyl interactions (Ala-42, Va-l29, Ile-165, and Val-152), and two hydrogen bond interactions (Asn-28 and Glu-149). The calculated docking energy was equal to -7.8 kcal/mol. Consequently, the solidagenone-IKK interaction is more stable than the solidagenone-NF-κB interaction.
Figure S3 shows some images regarding solidagenone-IKK interaction.
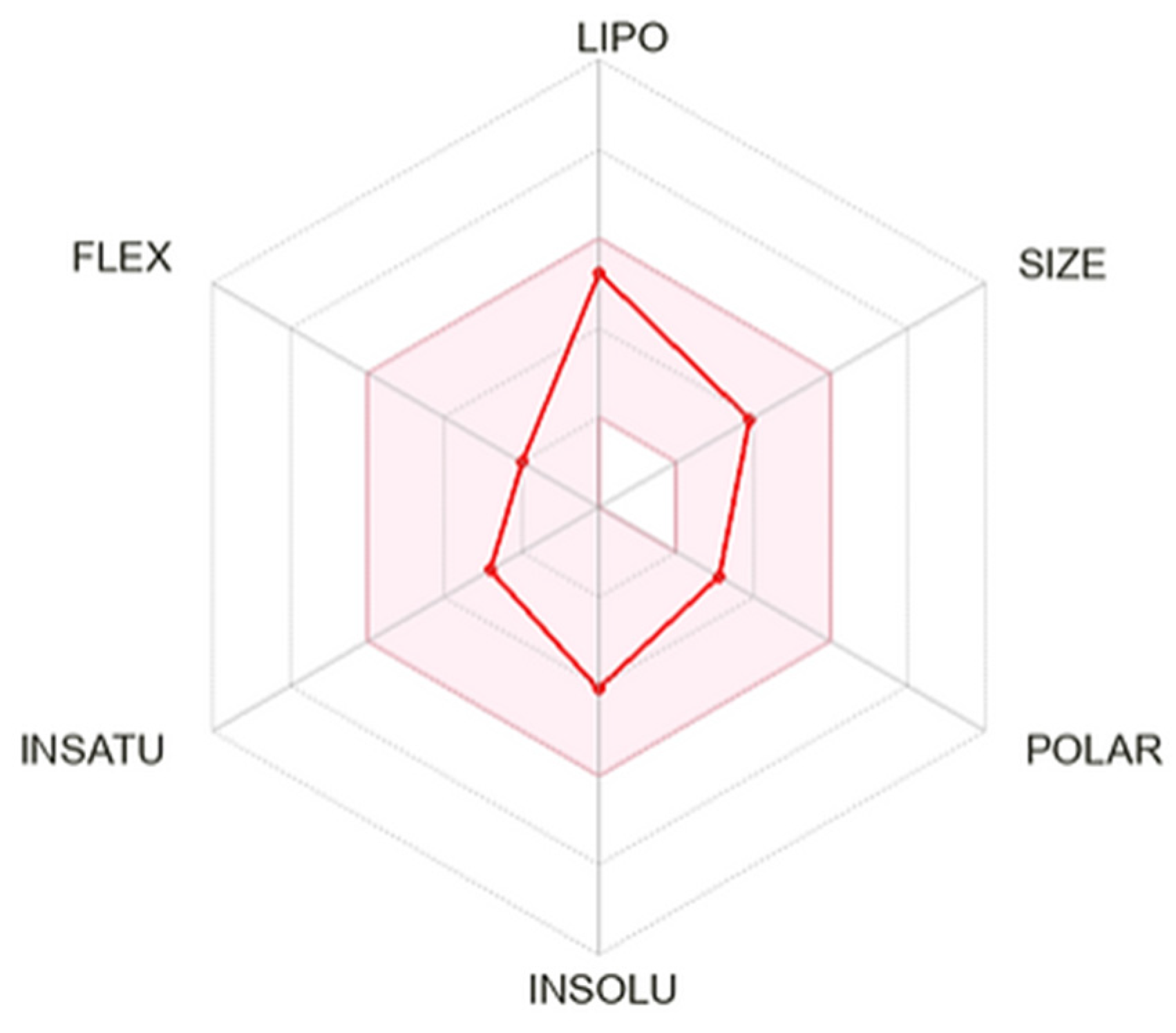
In silico ADME profile of solidagenone is shown summarized in
Figure 7 and
Table S1. The
Bioavailability Radar (
Figure 7) bears six axes for six relevant properties for oral bioavailability. Each property is determine by a descriptor and a range of optimal values is depicted as a pink area. For saturation, the ratio of sp
3 hybridized carbons over the total carbon count of the molecule (Fraction Csp3) should be at least 0.25. For size, the molecular weight should be between 150 and 500 g/mol. For polarity, the TPSA should be between 20 and 130 Å. For solubility, log
S should not exceed 6. For lipophilicity, XLOGP3 should be in the range from − 0.7 to + 6.0. For flexibility, the molecule should not have more than 9 rotatable bonds. In this context, solidagenone ca be estimated as drug-like, since the red line is fully included in the pink area.
Table S1 shows computed parameters for solidagenone, grouped in different sections (physicalchemical properties, lipofilicity, water solubility, pharmacokinetics, druglikeness, and medicinal chemistry).
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Drugs
Solidagenone was obtained from Solidago chilensis inflorescences at Pharmaceutical Technology Institute (FarManguinhos, Oswaldo Cruz Foundation, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil) as previously described [
16,
28]. Dexamethasone (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) was used as positive control in anti-inflammatory experiments. All compounds were solubilized in Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO; PanReac, Barcelona, Spain) and diluted in culture medium for use in in vitro assays or saline for in vivo assays. The final concentration of DMSO wdid not extrapolate 0.1% in all in vitro assays or 10% in all in vivo analysis.
3.2. Animals
BALB/c mice (4 to 8 weeks old) were bred and housed at the Gonçalo Moniz Institute (Oswaldo Cruz Foundation, Bahia, Brazil) in sterilized cages, under controlled environmental conditions, and provided with a balanced rodent diet and water ad libitum. All animal experiments and procedures were conducted in accordance with the institution’s committee on the ethical handling of laboratory animals and were approved under the number L-IGM-29/2009.
3.3. Acute toxicity in mice
BALB/c mice (male; 6-8 weeks of age; n=6/ group) were divided into four experimental groups and treated orally with a single dose of with different doses of solidagenone (30, 60, and 90 mg/kg) or vehicle (saline solution with 10% DMSO). Following the completion of the treatment, the mice were monitored for general toxicity signs over a 15-day period. This involved the observation of morphological and behavioral changes. Additionally, the body mass of the animals was measured on days 0, 7, and 14.
3.4. Induction of acute peritonitis in mice
BALB/c mice (males; 6-8 weeks old) were divided into six experimental groups (n = 6) and treated orally with different doses of solidagenone (30, 60, and 90 mg/kg), dexamethasone (30 mg/kg) or vehicle (saline solution with 10% DMSO) 24 and 1 hour before the challenge. Subsequently, animals were challenged through an intraperitoneal injection of 250 μL of carrageenan (Sigma-Aldrich; 1 mg/mL; 250 μL). After 4 h, mice were euthanized and peritoneal exudates were harvested by peritoneal lavage using saline solution. Cells were centrifuged at x400 g for 10 min, at 4º C. Cytospin preparations were stained with rapid panoptic and a differential count of 300 cells was performed by a blinded investigator.
3.5. LPS-induced endotoxin shock
BALB/c mice (male;4-5 weeks of age;) were randomized into five experimental groups (n=11/ group) and treated orally with different doses of solidagenone (30, 60, and 90 mg/kg), dexamethasone (30 mg/kg) or vehicle (saline solution with 10% DMSO) 24 and 3 hour before the challenge. Subsequently, animals received a lethl dose of LPS (600 µg; from serotype 0111:B4 Escherichia coli, Sigma-Aldrich) in saline, by intraperitoneally route. The animals were monitored for 4 days to observe survival. In addition, a second set of experiments was performed and heparinized blood samples were collected after 6 h after challenge with LPS (600 µg) and to analyses leukocytes and thrombocytes using the Hematology Analyzer PE 7010VET (Shenzhen Prokan Eletronics Inc.).
3.6. Cytokine and nitric oxide production by resident macrophages
To evaluate nitric oxide and cytokines production by resident macrophages, groups of male BALB/c mice were orally treated with solidagenone, dexamethasone or vehicle in the doses described above. After 90 min, the mice were subjected to euthanasia for macrophage collection by means of peritoneal wash using cold Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM; Life Technologies, GIBCO-BRL, Gaithersburg, MD). Cells were washed twice with DMEM, resuspended in DMEM supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS; GIBCO) and 50 μg/mL of gentamycin (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA), and plated in 96-well plates at a cell density of 2 × 105 cells/well. After 2 hours of incubation at 37°C, the plate was washed with saline solution and new medium was added to remove non-adherent cells. Cells were then activated or not with LPS (500 ng/mL) ) and IFNγ (5 ng/mL), and further incubated at 37° C and 5% CO2. Cell-free supernatants were collected at two different times after incubation for quantification of TNFα (4 hours) and for quantification of nitric oxide and IL-1β (24 hours) and kept at -80 °C until use.
3.7. Real time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR)
Peritoneal exudate macrophages were obtained as previously described [
17]. Then, cells were plated into 24-well plate at 1×10
6 cells/well in DMEM medium supplemented with FBS and gentamicin for 24 h at 37°C and 5% CO
2. Cells were then pretreated or not with solidagenone (50, 25, and 12.5 µM) or dexamethasone (12.5 µM) for 1 h and then stimulated or not with LPS (500 ng/mL) and IFNγ (5 ng/mL) and incubated at 37
oC for 3 h. After treatment, gene expression of NF-ƙb was performed as previously described [
17]. The following primer sequences were used in real-time PCR assays:
NFkb:5´-ATGGCAGACGATGATCCCTAC-3 and 3´-TGTTGACAGTGGTATTTCTGGTG-5.
3.8. Solidagenone structure
For molecular modeling purpose, the solidagenone structure was obtained from PubChem, a public chemical database at the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) of the National Library of Medicine (NLM), an institute within the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) [
29]. That structure was energy-minimized by using quantum mechanical modeling method DFT B3LYP/def2-TZVP, as implemented in Orca 5.0.3 software [
30].
3.9. Crystallographic protein structures
The crystallographic structures of human proteins p65 subunit of NF-κB transcriptor factor, with resolution of 2.70 Å (PDB ID: 1NFI) [
31], and IκB kinase enzyme (IKK), with resolution 2.83 Å (PDB ID: 4KIK) [
27], were both obtained from the Protein Data Bank [
32], and used in the docking simulations with solidagenone. The proteins preparation steps were carried out as follows: (1) non-essential water molecules were removed; (2) polar hydrogens were added to the protein; (3) partial charges were calculated using both Kollman [
33], and Gasteiger’s approaches [
34].
3.10. Molecular docking simulations
Molecular docking simulations were made with the AutoDock Vina 1.1.2 program [
35]. Two molecular graphical programs, UCSF Chimera X [
36] and BIOVIA Discovery Studio 2021 [
37], were used for visualizing ligand-proteins docking interactions in 3D- and 2D-representations, respectively.
3.11. ADME in silico
SwissADME platform [
38] was used for computing physicochemical and pharmacokinetics parameters related to adsorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) properties of solidagenone, as well as its drug-likeness.
3.12. Statistical analyses
Statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism version 8.0 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA). One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Newman-Keuls multiple comparison tests were used for the comparison of groups. Statistical significance was considered when p-values were less than 0.05. The presented data are representative of at least two or three independent experiments.
Author Contributions
I.P.S.: Investigation, conceptualization, formal analysis, writing-original draft, L.P.S.: formal analysis, writing-original draft, D.K.C.S.: methodology, formal analysis, B.P.Z.C.d.R.: methodology, formal analysis, T.B.d.O.: methodology, formal analysis, A.M.K.: methodology, formal analysis, E.d.S.R.: methodology, formal analysis, C.V.C.d.S.: methodology, conceptualization, writing-review and editing, J.F.O.C.: conceptualization, investigation, formal analysis, S.S.V.: conceptualization, writing-review and editing, O.A.S.-F.: conceptualization, resources, writing-review, supervision, and editing, M.B.P.S.: conceptualization, writing—review and editing, supervision, funding acquisition, C.S.M.: conceptualization, formal analysis, writing—review and editing, supervision.
Figure 1.
Effect of solidagenone in a model of acute peritonitis. BALB/c mice (n=6/group) were submitted to a challenge with 1% carrageenan solution after treatment with solidagenone (30, 60, and 90 mg/Kg) or dexamethasone (Dexa; 30 mg/Kg) or vehicle (saline solution with 10% DMSO). Untreated and unchallenged animals consists of naïve group. Values represent the means ± S.D. of six mice/group. *p < 0.05 compared to the vehicle group; #p < 0.05 compared to naïve group.
Figure 1.
Effect of solidagenone in a model of acute peritonitis. BALB/c mice (n=6/group) were submitted to a challenge with 1% carrageenan solution after treatment with solidagenone (30, 60, and 90 mg/Kg) or dexamethasone (Dexa; 30 mg/Kg) or vehicle (saline solution with 10% DMSO). Untreated and unchallenged animals consists of naïve group. Values represent the means ± S.D. of six mice/group. *p < 0.05 compared to the vehicle group; #p < 0.05 compared to naïve group.
Figure 2.
Solidagenone promoted an increase in the survival rate of animals challenged with LPS.. Mice were orally treated with solidagenone at doses of 30 mg/kg (■), 60 mg/Kg (▲) and 90 mg/kg (▼) or dexamethasone at a dose of 30 mg/kg (♦), or vehicle (●). The animals were monitored for 4 days to observe survival. Data from two independent experiments are represented in the graph.. *p < 0.05 compared to the vehicle group. **p < 0.01 compared to the vehicle group. Statistical analysis were performed using Logrank (Mantel Cox).
Figure 2.
Solidagenone promoted an increase in the survival rate of animals challenged with LPS.. Mice were orally treated with solidagenone at doses of 30 mg/kg (■), 60 mg/Kg (▲) and 90 mg/kg (▼) or dexamethasone at a dose of 30 mg/kg (♦), or vehicle (●). The animals were monitored for 4 days to observe survival. Data from two independent experiments are represented in the graph.. *p < 0.05 compared to the vehicle group. **p < 0.01 compared to the vehicle group. Statistical analysis were performed using Logrank (Mantel Cox).
Figure 3.
In vivo treatment with solidagenone reduces nitric oxide and cytokines production in macrophages stimulated with LPS. Resident peritoneal macrophages were collected from animals treated with different doses of solidagenone (30, 60, and 90 mg/Kg) or dexamethasone (Dexa; 30 mg/Kg) or vehicle (saline solution with 10% DMSO). Macrophages were plated in 96-well plates in the absence or presence of LPS plus IFNγ and, cell-free supernatants were collected after 4 or 24 h,. Levels of nitrite (A), TNF-α (B), and IL-1β (C) were obtained throw Griess method and ELISA respectively. Values represent the means ± S.D. of six mice/group. *p < 0.05 compared to the vehicle group; #p < 0.05 compared to naïve group. $p < 0.05 compared to dexamethasone group.
Figure 3.
In vivo treatment with solidagenone reduces nitric oxide and cytokines production in macrophages stimulated with LPS. Resident peritoneal macrophages were collected from animals treated with different doses of solidagenone (30, 60, and 90 mg/Kg) or dexamethasone (Dexa; 30 mg/Kg) or vehicle (saline solution with 10% DMSO). Macrophages were plated in 96-well plates in the absence or presence of LPS plus IFNγ and, cell-free supernatants were collected after 4 or 24 h,. Levels of nitrite (A), TNF-α (B), and IL-1β (C) were obtained throw Griess method and ELISA respectively. Values represent the means ± S.D. of six mice/group. *p < 0.05 compared to the vehicle group; #p < 0.05 compared to naïve group. $p < 0.05 compared to dexamethasone group.
Figure 4.
Solidagenone treatment reduces NF-ƙβ expression levels in peritoneal macrophages. Cells were stimulated or not with LPS + IFN-γ and treated or not with solidagenone or dexamethasone. Analysis of gene expression was made by real-time qRT-PCR. Values represent the means ± S.D. of four determinations obtained in one of two assays performed. *p < 0.05 compared to stimulated and untreated cells; #p < 0.05 compared to unstimulated and untreated cells; $p < 0.05 compared to cells treated with dexamethasone.
Figure 4.
Solidagenone treatment reduces NF-ƙβ expression levels in peritoneal macrophages. Cells were stimulated or not with LPS + IFN-γ and treated or not with solidagenone or dexamethasone. Analysis of gene expression was made by real-time qRT-PCR. Values represent the means ± S.D. of four determinations obtained in one of two assays performed. *p < 0.05 compared to stimulated and untreated cells; #p < 0.05 compared to unstimulated and untreated cells; $p < 0.05 compared to cells treated with dexamethasone.
Figure 5.
Docking analysis of solidagenone into the bind site of p65 subunit of NF-κB transcription factor. (a) x of selected protein (PDB ID: 1NFI) and its interactions with solidagenone. (b) 2D interactions of solidagenone with amino acid residues in the p65 subunit of NF-κB.
Figure 5.
Docking analysis of solidagenone into the bind site of p65 subunit of NF-κB transcription factor. (a) x of selected protein (PDB ID: 1NFI) and its interactions with solidagenone. (b) 2D interactions of solidagenone with amino acid residues in the p65 subunit of NF-κB.
Figure 6.
Docking analysis of solidagenone into IKK domain. (a) Three-dimensional structure of selected protein (PDB ID: 4KIK) and its interaction with solidagenone. (b) 2D interactions of solidagenone with amino acid residues in the IKK domain.
Figure 6.
Docking analysis of solidagenone into IKK domain. (a) Three-dimensional structure of selected protein (PDB ID: 4KIK) and its interaction with solidagenone. (b) 2D interactions of solidagenone with amino acid residues in the IKK domain.
Figure 7.
SwissADME plot of drug-likeness of solidagenone. The pink area represents the optimal range for each property. For saturation (INSATU), the ratio of sp3 hybridized carbons over the total carbon count of the molecule (Fraction Csp3) should be at least 0.25. For size, the molecular weight should be between 150 and 500 g/mol. For polarity (POLAR), the TPSA should be between 20 and 130 Å. For solubility (INSOLU), log S should not exceed 6. For lipophilicity (LIPO), XLOGP3 should be in the range from − 0.7 to + 6.0. For flexibility (FLEX), the molecule should not have more than 9 rotatable bonds.
Figure 7.
SwissADME plot of drug-likeness of solidagenone. The pink area represents the optimal range for each property. For saturation (INSATU), the ratio of sp3 hybridized carbons over the total carbon count of the molecule (Fraction Csp3) should be at least 0.25. For size, the molecular weight should be between 150 and 500 g/mol. For polarity (POLAR), the TPSA should be between 20 and 130 Å. For solubility (INSOLU), log S should not exceed 6. For lipophilicity (LIPO), XLOGP3 should be in the range from − 0.7 to + 6.0. For flexibility (FLEX), the molecule should not have more than 9 rotatable bonds.
Table 1.
Effect of Solidagenone on behavioral and general appearance of male BALB/c mice.
Table 1.
Effect of Solidagenone on behavioral and general appearance of male BALB/c mice.
| Behavior and general appearance |
Observations |
|
| Vehicle |
Solidagenone
(30 mg/Kg) |
Solidagenone
(60 mg/Kg) |
Solidagenone
(90 mg/Kg) |
| Changes in the eyes |
No changes |
No changes |
No changes |
No changes |
| Changes in the fur |
No changes |
No changes |
No changes |
No changes |
| Changes in the skin |
No changes |
No changes |
No changes |
No changes |
| Coma |
Absent |
Absent |
Absent |
Absent |
| Convulsions |
Absent |
Absent |
Absent |
Absent |
| Diarrhea |
Absent |
Absent |
Absent |
Absent |
| Lethargy |
Absent |
Absent |
Absent |
Absent |
| Salivation |
Absent |
Absent |
Absent |
Absent |
| Sleep |
Usual |
Usual |
Usual |
Usual |
| Tremors |
Absent |
Absent |
Absent |
Absent |
Table 2.
Body weight of BALB/c mice treated with the compound solidagenone.
Table 2.
Body weight of BALB/c mice treated with the compound solidagenone.
| Days |
Vehicle |
Solidagenone
(30 mg/Kg) |
Solidagenone
(60 mg/Kg) |
Solidagenone
(90 mg/Kg) |
| 0 |
24.3 (± 0.6) |
24.1 (± 0.3) |
23.8 (± 1.6) |
22.8 (± 0.9) |
| 7 |
24.2 (± 0.3) |
24.7 (± 0.5) |
24.0 (± 1.8) |
22.8 (± 1.2) |
| 14 |
24.4 (± 0.5) |
24.8 (± 0.6) |
24.5 (± 1.5) |
23.0 (± 0.7) |
Table 3.
Solidagenone attenuates leukopenia and thrombocytopenia in mice challenged with a LPS.
Table 3.
Solidagenone attenuates leukopenia and thrombocytopenia in mice challenged with a LPS.
| Group |
Dose (mg/Kg) |
Leukocytes
(103 cells/µL) |
Thrombocytes
(103 mm3) |
| Naive |
- |
3.8 ± 0.9* |
449.8 ± 49.2* |
| Vehicle |
- |
1.7 ± 0.2 |
334.5 ± 36.7 |
| Dexamethasone |
30 |
3.8 ± 0.4* |
337.0 ± 26.8 |
| Solidagenone |
30 |
1.9 ± 0.3 |
365.8 ± 15.2 |
| Solidagenone |
60 |
2.2 ± 0.4 |
399.4 ± 3.4* |
| Solidagenone |
90 |
2.7 ± 0.5* |
403.5 ± 40.4* |