1. Introduction
Diabetes mellitus is reported as one of the most serious chronic diseases in the world due to its widespread nature, the economic and social effects it brings, and the significant negative impact on the quality of life of affected patients[
1]. Diabetes mellitus is already one of the major health problems, and according to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) in 2021, almost more than half a billion individuals (537 million) had diabetes and this number is expected to reach 643 million in 2030 and 783 million in 2045 [
2], 90% of diabetes cases are diabetes mellitus type 2 which is alarming to the world[
2,
3,
4]. According to the IDF, the incidence of type 2 diabetes is decreasing or stable in developed countries [
2], while in developing countries a rapid increase in cases of type 2 diabetes has been observed [
5] and more and more effective management is being sought for this disease as the goal of United Nations (UN) is to reduce premature death from no communicable diseases, included diabetes, by 30% by 2030 the prevalence of diabetes by 25% and 33% respectively [
6]. Glucose control forms the foundation of type 2 diabetes treatment [
7]. Managing type 2 diabetes involves implementing programs that include lifestyle modification, the judicious use of oral antihyperglycemic medications, and initiation of insulin when necessary [
8,
9,
10]. Type 2 diabetic patients should receive professional guidance to enhance self-care behaviours, ultimately leading to improved glycemic control [
11]. The four optimal times for providing and adjusting diabetes self-management education and support are: at the time of diagnosis, annually or when objectives are not met, upon the emergence of factors influencing complications, and during significant life care transitions [
12].
The utilization of diabetes self-management education contributes to enhance health outcomes, the quality of care, and the overall quality of life for diabetic patients, ultimately leading to reduced expenses [
12,
13]. This approach has proven effective in the treatment of type 2 diabetic patients, bringing about positive changes in lifestyle and self-care management [
14]. According to the American Diabetes Association (ADA), individuals diagnosed with diabetes should receive comprehensive information and guidance at the time of diagnoses, with ongoing education and support provided thereafter. [
12]. The moment of diagnosis serves as a critical juncture when patients actively seek information about their new health situation and must adapt to new health behaviours [
15]. Despite its benefits, studies indicate a low uptake of diabetes self-management education among diabetic patients [
15,
16,
17]. Implementing lifestyle interventions in newly diabetic patients with T2DM leads to improvements in cardio metabolic parameters offering long-term benefits for health and well-being [
18].
This systematic review aimed to examine the effectiveness of diabetes self-management education used for patients with newly diagnosed T2DM. Also, this study will focus attention on the types of interventions, their duration, the factors affecting the success of this programs used and the resources used to determine the elements that have the potential to be used in the education of newly diagnosed patients with Type 2 Diabetes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study design:
This is a systematic review study.
2.2. Search methods:
A literature search was conducted using the electronic databases of Pub MED, Walter Kluwer, Cochrane Library, Scopus, Elsevier, JSTORE. This search was conducted for 4 months starting from August to November 2022, based on the following sets of keywords: “Newly diagnosed patients with T2DM”, “Diabetes self-management education program evaluation”, “Diabetes self-management program effectiveness”, “Diabetes self-care education”, “Lifestyle intervention”. The study was reported according to PRISMA statement [
19].
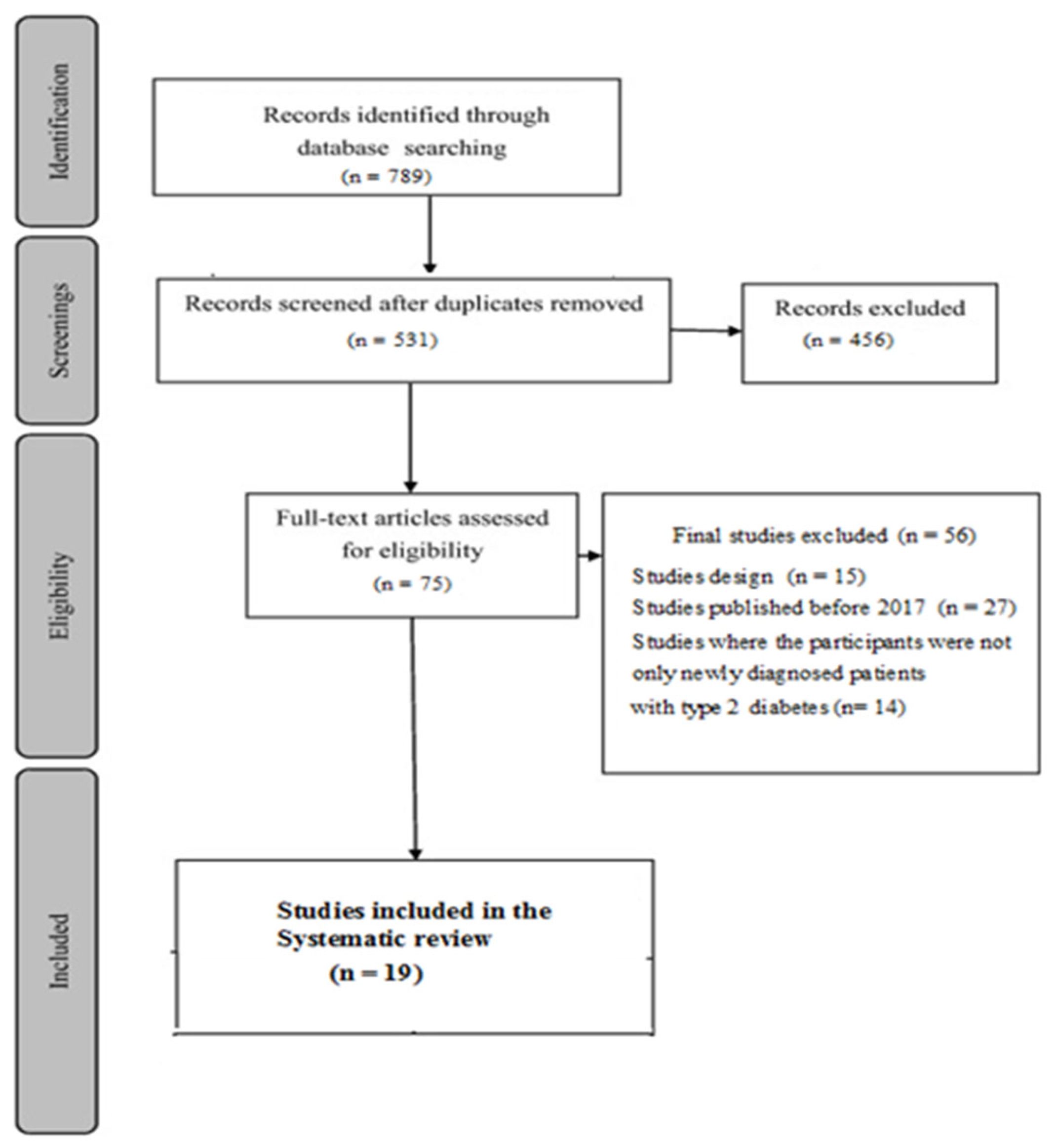
An advanced electronic search was performed where filters were applied to include only those articles that evaluated the use of health education and educational intervention in diabetic patients with type 2 diabetes. These searches were limited to the period 2017 - 2022. The reference list of relevant publications was hand searched to find the relevant articles, based on inclusion and exclusion criteria presented in
Table 1. Full-text articles were further screened (
Figure 1). A second reviewer then independently assessed the selected articles for final eligibility, and everything was discussed within the article's author group.
2.3. Data extraction:
All the data were extracted by a single reviewer. The data included: details of publication (title, authors, journal, year of publication, country of origin), methods (aim of the study, design and duration of the intervention), participants (number of the patients in the intervention group and in the control group, age and gender), intervention (type of intervention, settings, description of the intervention and of the standard care, duration of the intervention, timing, delivery, method of follow-up, providers), outcomes (clinical parameter, psychological, biomedical and behaviours outcomes).
2.4. Synthesis of the results:
A summary of the information from the studies included in this analysis was carried out according to the place of study, population, duration of education, details about the educational interventions such as the method of delivery, the people who carried out the educational interventions, the theoretical materials offered, the frequency and duration of the educational sessions, and a summary of the outcomes of these interventions among diabetic patients. The studies included in this review had different interventions and durations, and for this we have made a narrative summary, presenting the clinical results through mean ± standard deviation.
Risk of Bias:
11 (57.89%) of the included studies had poor quality. This assessment was carried out following the revised Cochrane risk-of-bias tool [
20]. Most of the studies did not non-blinding of participants and personnel because of the nature of educational interventions. (
Table 2 – supplementary material)
3. Results
Nineteen studies met the inclusion criteria established in advance for this review study.
3.1. Characteristics of interventions
Table 3 and
Table 4 outline the key characteristics of the populations included in the 19 studies and the interventions assessed. These studies were conducted in various countries worldwide, including 6 in China [
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26], 4 in India [
27,
28,
29,
30], 2 in Netherlands [
31,
32] and one study each in Spain [
33], Mexico [
34], Italy [
35], USA [
36], United Kingdom [
37], Germany [
38] and Lebanon [
39].
This study encompassed 2512 newly diabetic patients with the sample size ranging from 17 to 358 patients. The mean age range of participants was 25 to 74 years, with 75% of the studies involving a population over 50 years old. The mean duration of diabetes ranged from 3 months to 5 years. (
Table 3)
While analysing the studies, various interventions were identified, each characterized by distinct features, durations, and assessment methods. All studies aimed to assess the impact of educational interventions on type 2 diabetic patients, with intervention duration ranging from 6 weeks to 30 months. Of the 19 studies, 16 evaluated health education interventions by comparing them with a control group, while 3 assessed educational programs or interventions without a control group. Among these studies, 9 were randomized controlled trials (RCTs) [
21,
25,
27,
28,
30,
31,
32,
37]; one was an experimental study [
22], 4 were intervention study [
23,
35,
36,
38]; 2 were program evaluation studies [
34,
39]; 2 were prospective studies [33, 26]; and one study was a non-randomized controlled study [
24].
The interventions assessed in these studies include a multi-intervention program (73.68%) [
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28,
31,
32,
33,
34,
36,
37]; physical activity intervention (10.5%) [
29,
30]; nutrition intervention (10.5%) [
38,
39] and a single study that evaluated psychological interventions [
35]. Educational interventions were conducted in groups of participants in 47.36% of the studies, individual interventions in 47.36% and a combination of individual and group interventions is only one study. (
Table 4)
In terms of intervention methods, 26.3% of the studies utilized telephone applications, and in one study were conducted using text messages directed to the participants. The majority, 68.4% of the studies, implemented interventions face to face. Educational interventions for newly diabetic patients with T2DM were administered by various healthcare professionals, including physicians, nurses, dieticians, pharmacists, and diabetes educators. In 21% of the studies [
21,
24,
33,
34] educational interventions were delivered by a team consisting of more than one member, with nurses being part of the intervention team. Nurses specifically implemented educational interventions in 26.3% of studies [
22,
23,
25,
31,
32]. (
Table 4 – supplementary materials)
The evaluation included five programs were evaluated as: AADE 7 Self – Care Behaviours program [
21]; PAET-Debut DM2 program [
33], Omaha System-based integrated nursing management model [
24], CAIPadi model [
34], Nurse-led integrative medicine-based structured education program - multi intervention program [
25]. (
Table 4 – supplementary material).
Biomedical outcomes were reported in 16 studies, psychosocial outcomes in 12 studies, and behavioral outcomes in 10 studies. Six studies included elements in all outcome categories [
25,
27,
31,
33,
34,
36].
3.2. Impact of educational intervention on biomedical results
3.2.1. The impact of educational intervention on HbA1c levels (Table 5)
The effect of educational interventions on HbA1c levels was evaluated in 12 studies (60%) [
21,
22,
25,
26,
27,
29,
31,
33,
34,
35,
36,
39]. The comparison of the results between the intervention group and the control group is presented in 9 studies, where we evaluated the absolute effect. Improvement in HbA1c values was significant in the intervention group in 10 (83.3%) studies and in the control group in 3 studies. Six studies showed significant differences in the effect on HbA1c values between the two study groups (IG and CG). Notably, in a study conducted in the Netherlands, there were no evident change in HbA1c levels after the intervention; in fact, there was a very slight increase (0,1%) in HBa1cvalues [
31]. The mean difference in the intervention group was 1.18% while in the control group, it was 0.277%. The absolute effect of educational intervention on HbA1c was −0.64±0.008.
Table 5.
The effect of educational intervention on HbA1c.
Table 5.
The effect of educational intervention on HbA1c.
| Studies general information |
Baseline |
Post intervention |
Change |
Absolute effect |
| IG |
CG |
IG |
CG |
IG |
CG |
| [21] |
8.44±2.28 |
8.95±2.34 |
6.92±1.27* |
7.82±12.98*#
|
-1.52$
|
-1.13 |
-0.39 |
| [22] |
7.20(6.40, 9.10) |
7.90(6.80, 10.30) |
6.20(5.80, 6.60)* |
6.70(6.40, 7.30)* |
-1** |
-1.2 |
+0.2 |
| [33] |
7.2(6.6-9.2) |
6.7(6.4-7.5) |
6.2(5.8-6.7)* |
6.4(5.8-6.8) |
-1$
|
-0.3 |
-0.7 |
| [34] |
7.77±2.22 |
No control group |
7.16±1.62 |
No control group |
-0.61*#
|
- |
-0.61 |
| [27] |
9.5±2.1 |
9.5±2.0 |
7.4±1.5* |
9.5±2.1 |
-2.1** |
0 |
-2.1 |
| [29] |
5.95±0.47 |
5.95±0.47 |
5.14±0.36* |
5.85±0.37* |
-0.81** |
-0.1 |
-0.71 |
| [25] |
6.66±1.09 |
6.86±1.34 |
5.85±0.37* |
6.97±1.18 |
-0.81** |
+0.11 |
-0.70 |
| [35] |
7.85±1.19 |
7.32±1.23 |
6.66±0.84* |
6.95±1.31 |
-1.19** |
-0.37 |
-0.82 |
| [31] |
6.5(6.2-7.0) |
6.6(6.3-7.1) |
6.6(6.3-7.1) |
6.7(6.3-7.1) |
+0.1*#
|
+0.1 |
0 |
| [36] |
8.0(1.6) |
- |
6.2(1.1)* |
- |
-1.8*#
|
- |
-1.6±0.5 |
| [26] |
9.82±2.47 |
9.05±2.32 |
6.76±0.50* |
7.25±0.98* |
-3.03** |
-1.8 |
-1.23 |
| [39] |
9.1±2.3 |
- |
7.4±1.3* |
- |
-1.7±2.5* |
- |
-1.7±1 |
| Mean ±SD |
|
|
|
|
-1.18±0.21 |
-0.277±0.13 |
0.64±0.08 |
3.2.2. The impact of educational intervention on FBG and PBG values (Table 6)
Seven studies (35%) assessed the impact of educational interventions on FBG levels [
22,
23,
24,
27,
31,
37]. In one study, a very slight increase in FBG values was observed in both the intervention group and in the control group [
31]. Significant changes in FBG values within the intervention group were reported in four studies [
22,
23,
24,
27], while this difference was significant in the control group in one of these studies [
27]. Notably, significantly different effect between intervention group and control group were observed in three studies [
23,
24,
27].
Four studies (20%) investigated the impact of educational interventions on PBG levels [
22,
23,
24,
27]. All these studies demonstrated a significant difference between pre and post-intervention levels in the intervention group with significant differences observed between the intervention group and control group in only two studies [
23,
24]. Collectively, the mean change (improvement) for FBG after the intervention was 0.32% and for PBG 1.59%. The absolute effect of educational intervention on FBG was −0.32±1.16 and on PBG was −1.598±0.23.
Table 6.
The effect of educational intervention on FBG and PGB.
Table 6.
The effect of educational intervention on FBG and PGB.
| Studies general information |
Baseline |
Post intervention |
Change |
Absolute effect |
| IG |
CG |
IG |
CG |
IG |
CG |
| Effect of educational intervention on FBG |
| [22] |
8.00 |
8.00 |
6.78* |
7.70* |
-1.22$
|
-0.3 |
-0.92 |
| [23] |
8.43±1.25 |
8.51±1.17 |
7.03±1.01* |
7.68±1.12 |
-1.4** |
-0.83 |
-0.57 |
| [24] |
9.964±2.707 |
10.490±2.781 |
7.792±0.925* |
9.042±1.561 |
-2.172** |
-1.448 |
-0.72 |
| [27] |
10.9±3.6 |
11.5±3.9 |
7.5±2.3* |
8.4±2.8* |
-3.4** |
-3.1 |
-0.3 |
| [31] |
7.4 |
7.3 |
7.9 |
7.5 |
+0.5**#
|
+0.2**#
|
+0.3 |
| [37] |
5.75 ± 1.01 |
6.55±1.76 |
5.66 ± 1.20 |
6.73 ± 2.66 |
-0.09**#
|
+0.18 |
0.27 |
| Mean ±SD |
|
|
|
|
-1.656±2.11 |
-2.839±2.31 |
-0.32±1.16 |
| Effect of educational intervention on PBG |
| [22] |
13.29 |
12.67 |
7.90* |
10.58* |
-5.39$
|
-2.09 |
-3.3 |
| [23] |
11.21±1.65 |
11.34±1.73 |
9.52±1.05* |
10.43±1.24 |
-1.69** |
-0.91 |
-0.78 |
| [24] |
14.612±4.685 |
14.692±4.400 |
9.980±1.446* |
12.275±2.120 |
-4.632** |
-2.417 |
-2.215 |
| [27] |
17.1±4.6 |
17.2±4.9 |
12.5±3.3* |
12.7±3.6* |
-4.6**#
|
-4.5 |
-0.1 |
| Mean ±SD |
|
|
|
|
-4.078±2.35 |
-2.479±2.41 |
-1.598±0.23 |
3.2.3. The impact of educational intervention on lipid profile
Five studies have examined the impact of educational interventions on the lipid profile (total cholesterol (T-Chol), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDLC), and triglyceride (TG) [
22,
31,
33,
38,
39]. These studies utilized different units of measurement to assess lipid levels, making it impossible to statistically evaluate the Mean ±SD.
Significant differences in T-Chol between pre- and post-intervention in the intervention group were observed in two studies [
33,
38], and for LDL-C in two studies [
31,
39]. Changes in HDL-C and Triglyceride levels were not statistically significant.
3.2.4. The impact of educational intervention on Anthropometric parameters (Table 7 - supplementary material)
The impact of educational interventions on the body weight of newly diabetic patients with T2DM has been assessed in 5 studies [
21,
30,
31,
37,
38] and on BMI in 11 studies [
21,
22,
26,
30,
31,
33,
34,
36,
37,
38,
39].
Decreases in body weight were observed in 4 studies, but only in one of them reported a significant change in body weight [
21]. The absolute effect of education intervention, among study with 2 groups (intervention and control group), on weight is 2.94%.
Out of the 11 studies evaluating the effect of educational interventions on the BMI of diabetic patients, 5 studies did not compare the results with a control group [
33,
34,
36,
38,
39]. BMI decreased in both groups without a significant intervention effect except for one study where the effect size was insignificant or small [
37]. The absolute effect of education intervention, among studies with two groups (intervention group and control group) on BMI was 0.39%.
3.2.5. The impact of educational intervention on Blood Pressure (Table 8 – supplementary material)
Eight studies [
21,
22,
30,
31,
33,
34,
37,
39], have assessed the impact of educational interventions on the arterial pressure among newly diagnosed patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus(T2DM) and six of them compared the arterial pressure values between the two study groups (intervention group and control group) [
21,
22,
30,
31,
37]. Only one study reported a statistically significant difference in systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) [
39].
The mean change in SBP and DBP of the intervention group was −2.3±6.5 mmHg and -0.87±4.5mmHg, respectively. The absolute effect of educational intervention on SBP was −0.34±7.9 mmHg and on DBP was −0.36±5.5 mmHg.
3.3. The impact of educational intervention on emotional and social results
Improving knowledge, illness perception, anxiety and depression, diabetes distress, empowerment, diabetes self-efficacy, diabetes self-management and quality of life among newly diabetic patients with T2DM are used to evaluate emotional and social results.
Five studies evaluated the impact of educational interventions on the knowledge of diabetic patients, using different assessment tools [
21,
24,
28,
34,
36]. In all these studies, a significant improvement in knowledge was observed at the end of the interventions, with a significant difference in knowledge between the intervention group (IG) and control group (CG) observed in three studies [
21,
24,
28].
Illness perception was assessed in one study [
32] which used the “Illness Perceptions Questionnaire (IPQ-R)” as an evaluation tool. Immediately after the education program, the intervention group showed a significantly higher belief in having diabetes than the control group.
Anxiety and depression levels were evaluated in three studies
, [
22,
34] for anxiety and [
22,
34,
36] for depression. All these studies have shown that educational interventions had a positive impact on reducing anxiety, depression or their symptoms in diabetic patients.
Two studies showed significant improvements in diabetes distress as a result of educational interventions [
34,
36]
, while another study did not show any improvement in this aspect [
32].
Diabetic patients empowerment was assessed in three studies using different assessment methods such as The Diabetes Empowerment Scale Short Form [DESSF] [
34], Diabetes Empowerment Scale (DES) [
32,
36]. All three of these studies reported significant improvements in the intervention groups.
Quality of life was evaluated in six studies [
23,
24,
27,
31,
33,
34], with two of them lacking data comparison between the intervention group and control group. The instruments used to evaluate interventions in the quality of life were SF-36, EuroQol-5d, Diabetes specificity quality of life scale (DSQL), Diabetes Quality of Life Measure [DQoL]), Diabetes-Dependent Quality-of-Life (ADDQoL). In four studies [
23,
24,
33,
34], significant improvements were observed in the quality of life of newly diagnosed patients with GT2DM, while in the other two studies, patients presented negative effects that did not change over time [
27,
31].
3.4. The impact of educational intervention on behavioral results
The studies included in this analysis employed diverse assessment methods.
Three studies assessed changes in tobacco use. In one study, there was a moderate but significant reduction in smoking and the alcohol consumption [
33]. In two other studies, a moderate reduction in tobacco use was observed, although not statistically significant [
25,
32].
Eight studies reported on physical activity, assessed in six studies through standardized questionnaires [
25,
27,
30,
31,
32,
34]
, the use of a mobile application [
37] or through subjective measures [
39]. Hernandez et al reported improvement in physical activity [
34]
, while in other studies these changes were not significant between intervention group and control group.
Changes in dietary behavior were reported in five studies. In four of them, the impact of educational interventions was evaluated through the use of validated questionnaires [
25,
31,
32,
33] and self-reporting of patients regarding the use of high and low-carbohydrate food [
36]. Initially, changes in these studies were not significant in 2 of them [
31,
33]. Participants in the intervention group exhibited significantly better self-management behaviors related to the intake of fruits and vegetables at both the immediate post-intervention and the 12th-week follow-ups (β = 1.02,
p = 0.011 and β = 0.98,
p = 0.016, respectively) [
31]. Meanwhile, in another study, although immediately after the program used [
32], the results showed an increase in the consumption of fruits and vegetables, these effects were no longer present 6 months after the interventions. Oser TK et al reported satisfactory results in terms of reducing the consumption of High-carbohydrate foods even 3 months after the interventions [
36].
The approach of newly diabetic patients with T2DM to self-care activities has been evaluated in five studies, all of which presented a positive impact of educational interventions, thereby increasing patients` awareness [
25,
31,
32,
33,
34].
3.5. Factors affecting glucose control among newly diabetic patients with T2DM (Table 9-13 – supplementary material)
Factors influencing glucose control among newly diagnosed patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus are crucial for understanding glycemic management.
One parameter indicating glycemic control in diabetic patients is the HbA1c level. Therefore, in this review, we have examined some of the factors that impact the enhancement of HbA1c levels in newly diagnosed patients with T2DM.
Educational interventions demonstrate visible effects in reducing HbA1c level, particularly in cases with a smaller number of patients attending educational sessions and interventions lasting 12 months [
33,
35,
39]. Additionally, a combination of face to face and online educational methods [
21,
27,
39] has proven effective.
Concerning the personnel involved in the educational interventions, cases with only one type of professional yielded more satisfactory results (absolute effect on the level of HbA1c was -0.87±0.67). When interventions were conducted by nurses, the absolute effect was -0.50± 0.15. Conversely, when interventions were carried out by a team, the absolute effect was 0.56±0.78.
Individual interventions emerged as the most efficient in 55% of the studies assessing HbA1c levels. These individual interventions demonstrated a notable improvement in the HbA1 level by 1.12% [
21,
26,
27,
29,
34,
39]
, while group-based education resulted in a less pronounced effect of 0.50%.
4. Discussion
This study aimed to assess the effectiveness of educational interventions concerning biomedical parameters, emotional and social effects, and behavioral changes among newly diabetic patients with T2DM.
According to the American Diabetes Association (ADA), educational interventions can lead to a 1% improvement in HbA1c levels among diabetic patients [
16]. Our study reported an effect size on glycemic control of 0.64%, slightly lower than another review study (1.05%) [
40] but somewhat higher than in two other review studies [
41,
42] (0.21% and 0.44% respectively).
The effectiveness of educational interventions in improving glycemic control appears to depend significantly on the characteristic of the patients, their willingness to adopt lifestyle changes, and the socioeconomic development of the countries where the studies were conducted.
Regarding clinical parameters, changes in fasting blood glucose (FBG) were 0.32, and postprandial blood glucose (PBG) changes were 1.59 in the four studies that assessed it. However, findings related to lipid profile changes were inconclusive due to variations in measurement units.
Anthropometric parameters, specifically body mass index (BMI), showed a difference of 0.87% in 11 studies, with a 0.39 difference in the intervention group. Changes in arterial pressure were not statistically significant.
In terms of emotional and social results, six studies assessed knowledge levels in diabetic patients, showing significant improvements in intervention groups. Similar results were found in a previous study [
41]. Additionally, 50% of studies focused on emotional and social aspect, with evident changes in anxiety, illness perception, empowerment, depression, diabetes distress, diabetes self-efficacy, and quality of life.
Behavioral results indicated positive changes, including reduced tobacco and alcohol use. Physical activity and adherence to healthy diets were evaluated in eight and five studies, respectively. Some studies reported significant changes immediately after intervention, but the effects were not sustained over time A result similar to our study was presented by Tanaka et al [
41].
Newly diabetic patients with T2DM are more likely to engage in positive behavioral change [
43].
Factors influencing the effectiveness of educational interventions include the number of patients involved, with smaller groups showing better improvement in HbA1c levels. [
40]. The duration of training is crucial, with ADA recommending 6-12 months [
44]. Our study found that we had significant improvement in HbA1c levels in those studies where patient education follows up for 12 months.
Education and support of newly diabetic patients with T2DM can be provided in patient groups or individually. If we were to see the results of our study, we have a better improvement of HbA1c levels in those studies where educational interventions were offered individually to diabetic patients, while in other studies it was evidenced that individual and group interventions have demonstrated positive clinical results [
45]. Combining online and face to face education, as well as individual approaches, yielded better results. Studies with support strategies demonstrated enhanced patient involvement in self-care activities. While the use of the face to face method, has given more efficiency in the education of diabetic patients by pharmacists [
45].
The support of a health care team is crucial for diabetes management [
46]. Our study found that we had more significant improvement in HbA1c levels in those studies where educational interventions were provided by one kind of specialist. This result is consistent with a study which showed that the individual-based education can archive greater glycemic improvement that team-based education [
40].
If we were to evaluate the 19 studies and the results achieved, we see that we have better results in those studies where the education of the patients is accompanied by a supporting strategy, which help the greater involvement of diabetic patients in self-care activities.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, effective education and support for newly diagnosed patient s with type 2 diabetes mellitus should incorporate individualized approaches, extended duration, and supportive strategies to enhance outcomes in glycemic control and overall patient well-being. Education and support provided to newly diagnosed patients T2DM play a crucial role in improving biomedical, emotional and social results and behavioral aspects, thereby contributing to the prevention of early complication.
Informing and supporting recently diagnosed patients, not only increases their knowledge but also promotes positive behavioral changes, ultimately enhancing their quality of life and self-management of the condition.
Health literacy, delivered by healthcare professionals through various channels such as online platforms, face to face interaction, and
supplementary materials like videos and materials in paper, has demonstrated the potential to significantly improve glycemic control. This comprehensive approach fosters a patient-centered strategy, empowering individuals to actively participate in their health management and reducing the risk of complications associated with T2DM
6. Implications of health care personnel and patients:
The increasing prevalence of type 2 diabetes poses a critical challenge in healthcare, necessitating a comprehensive approach to education. The first crucial step in empowering newly diagnosed T2DM is providing a nuanced understanding of type 2 diabetes. By unraveling its intricacies, healthcare professionals can facilitate informed decision-making and instill healthy behaviors.
Comprehensive education becomes the cornerstone of diabetes management, covering key aspects such as dietary adjustments, regular exercise, medication adherence and blood glucose monitoring. This holistic approach equips patients with the tools necessary for successful self-management.
Healthcare providers, including physicians, nurses, dietitians or diabetes educators, collaborate to form a dedicated network for patient education. Their role extends beyond prescribing medications, involving the delivery of tailored information that addresses individual needs and challenges. Healthcare professionals must navigate the delicate terrain of addressing mental health, providing emotional support.
The healthcare system faces challenges such as limited resources and time constraints. Overcoming these obstacles requires innovative solution and interdisciplinary collaboration to prioritize and maintain diabetes education.
In the digital age, technology becomes a powerful ally in diabetes education. Mobile application, wearable devices and telehealth services, enhance communication between healthcare providers and patients.
The symbiotic relationship between health care personnel and patients is identified as a crucial for successful management. Fostering a culture of continues education and personalized care paves the way for empowered individuals who not only effectively manage their conditions but also thrive in their pursuit of holistic health and wellness.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.K. and L.R.; methodology, E.K and A.S.; validation, L.R. and A.S.; formal analysis, E.K.; investigation, E,K and A.S.; resources, E.K.; data curation, E.K.; writing—original draft preparation, E.K and L.R.; writing—review and editing, E.K and L.R.; visualization, E.K.; supervision, L.R and A.S.; project administration, E.K and L.R.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- J. A. da Silva, E. C. F. de Souza, A. G. Echazú Böschemeier, C. C. M. da Costa, H. S. Bezerra, and E. E. L. C. Feitosa, ‘Diagnosis of diabetes mellitus and living with a chronic condition: participatory study’, BMC Public Health, vol. 18, no. 1, p. 699, Jun. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Internationa Diabetes Federation, ‘IDF Atlas 10th Edition’, 10th Edition, 2021. Accessed: Oct. 10, 2022. [Online]. Available: https://diabetesatlas.org/idfawp/rwsource-files/2021/07/IDF_Atlas_10th_Edition_2021.pdf.
- M. K. Ali, J. Pearson-Stuttard, E. Selvin, and E. W. Gregg, ‘Interpreting global trends in type 2 diabetes complications and mortality’, Diabetologia, vol. 65, no. 1, pp. 3–13, Jan. 2022. [CrossRef]
- S. Chatterjee, K. Khunti, and M. J. Davies, ‘Type 2 diabetes’, Lancet, vol. 389, no. 10085, pp. 2239–2251, Jun. 2017. [CrossRef]
- A. Misra et al., ‘Diabetes in developing countries’, J Diabetes, vol. 11, no. 7, pp. 522–539, Jul. 2019. [CrossRef]
- WHO, ‘Global Report on Diabetes; World Health Organization’, Geneva, 2016. [Online]. Available: iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/204871/9789241565257_eng.pdf?sequence=1.
- R. Rodriguez-Gutierrez et al., ‘Shared decision making in endocrinology: present and future directions’, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, vol. 4, no. 8, pp. 706–716, Aug. 2016. [CrossRef]
- K. Masuo, ‘Lifestyle Modification Is the First Line Treatment for Type 2 Diabetes’, in Type 2 Diabetes, K. Masuo, Ed., InTech, 2013. [CrossRef]
- A. Y. Y. Cheng and I. G. Fantus, ‘Oral antihyperglycemic therapy for type 2 diabetes mellitus’, CMAJ, vol. 172, no. 2, pp. 213–226, Jan. 2005. [CrossRef]
- M. Hanefeld, H. Fleischmann, T. Siegmund, and J. Seufert, ‘Rationale for Timely Insulin Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes Within the Framework of Individualised Treatment: 2020 Update’, Diabetes Ther, vol. 11, no. 8, pp. 1645–1666, Aug. 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. D. Adu, U. H. Malabu, A. E. O. Malau-Aduli, and B. S. Malau-Aduli, ‘Enablers and barriers to effective diabetes self-management: A multi-national investigation’, PLoS One, vol. 14, no. 6, p. e0217771, 2019. [CrossRef]
- M. A. Powers et al., ‘Diabetes Self-management Education and Support in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes: A Consensus Report of the American Diabetes Association, the Association of Diabetes Care & Education Specialists, the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, the American Academy of Family Physicians, the American Academy of PAs, the American Association of Nurse Practitioners, and the American Pharmacists Association’, Diabetes Care, vol. 43, no. 7, pp. 1636–1649, Jul. 2020. [CrossRef]
- K. D. Brunisholz et al., ‘Diabetes self-management education improves quality of care and clinical outcomes determined by a diabetes bundle measure’, J Multidiscip Healthc, vol. 7, pp. 533–542, 2014. [CrossRef]
- U. Ernawati, T. A. Wihastuti, and Y. W. Utami, ‘Effectiveness of diabetes self-management education (DSME) in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients: Systematic literature review’, J Public Health Res, vol. 10, no. 2, p. 2240, Apr. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Y. Yoshida et al., ‘Patient-specific factors associated with use of diabetes self-management education and support programs in Louisiana’, BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care, vol. 9, no. Suppl 1, p. e002136, Dec. 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. A. Powers et al., ‘Diabetes Self-management Education and Support in Type 2 Diabetes: A Joint Position Statement of the American Diabetes Association, the American Association of Diabetes Educators, and the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics’, Clin Diabetes, vol. 34, no. 2, pp. 70–80, Apr. 2016. [CrossRef]
- A. L. Nguyen, E. Sepulveda, and M. Angulo, ‘It Feels Good to Know That Someone Cares’, Hisp Health Care Int, vol. 15, no. 2, pp. 52–57, Jun. 2017. [CrossRef]
- S. Taheri et al., ‘Effect of intensive lifestyle intervention on bodyweight and glycaemia in early type 2 diabetes (DIADEM-I): an open-label, parallel-group, randomised controlled trial’, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, vol. 8, no. 6, pp. 477–489, Jun. 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. J. Page et al., ‘The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews’, BMJ, p. n71, Mar. 2021. [CrossRef]
- J. P. T. Higgins et al., ‘The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials’, BMJ, vol. 343, no. oct18 2, pp. d5928–d5928, Oct. 2011. [CrossRef]
- D. Y. Chao, T. M. Lin, and W.-Y. Ma, ‘Enhanced Self-Efficacy and Behavioral Changes Among Patients With Diabetes: Cloud-Based Mobile Health Platform and Mobile App Service’, JMIR Diabetes, vol. 4, no. 2, p. e11017, May 2019. [CrossRef]
- S. Chai et al., ‘The effect of diabetes self-management education on psychological status and blood glucose in newly diagnosed patients with diabetes type 2’, Patient Educ Couns, vol. 101, no. 8, pp. 1427–1432, Aug. 2018. [CrossRef]
- X.-J. Jiang, ‘Influence of Orem’s self-care theory based “one-to-one” health education on self-management ability and quality of life in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes’, WCJD, vol. 26, no. 4, p. 282, 2018. [CrossRef]
- L. Wei, J. Wang, Z. Li, Y. Zhang, and Y. Gao, ‘Design and implementation of an Omaha System-based integrated nursing management model for patients with newly-diagnosed diabetes’, Prim Care Diabetes, vol. 13, no. 2, pp. 142–149, Apr. 2019. [CrossRef]
- X. Yu et al., ‘The effects of a nurse-led integrative medicine-based structured education program on self-management behaviors among individuals with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial’, BMC Nurs, vol. 21, no. 1, p. 217, Aug. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Y. Hao and H. Xu, ‘A Prospective Cohort Study on the Management of Young Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Using Mobile Medical Applications’, Diabetes Ther, vol. 9, no. 5, pp. 2099–2106, Oct. 2018. [CrossRef]
- R. Vinitha et al., ‘Effectiveness of mobile phone text messaging in improving glycaemic control among persons with newly detected type 2 diabetes’, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, vol. 158, p. 107919, Dec. 2019. [CrossRef]
- V. S. Parmar, S. V. Patel, and C. C. Iyer, ‘Effect of Counseling on Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients Visiting a Tertiary Care Hospital: A Randomized Control Trial’, Indian J Community Med, vol. 43, no. 3, pp. 244–245, 2018. [CrossRef]
- H. Kour, V. Kothiwale, and S. Goudar, ‘Impact of structured exercise therapy on impaired cognitive function among young adults diagnosed newly with type 2 diabetes mellitus – A randomized controlled trial’, Medical Journal of Dr. D.Y. Patil Vidyapeeth, vol. 13, p. 341, Jan. 2020. [CrossRef]
- L. Patnaik, S. K. Panigrahi, A. K. Sahoo, D. Mishra, A. K. Muduli, and S. Beura, ‘Effectiveness of Mobile Application for Promotion of Physical Activity Among Newly Diagnosed Patients of Type II Diabetes - A Randomized Controlled Trial’, Int J Prev Med, vol. 13, p. 54, 2022. [CrossRef]
- R. C. Vos, L. van Heusden, N. W. D. Eikelenboom, and G. E. H. M. Rutten, ‘Theory-based diabetes self-management education with pre-selection of participants: a randomized controlled trial with 2.5 years’ follow-up (ELDES Study)’, Diabet Med, vol. 36, no. 7, pp. 827–835, Jul. 2019. [CrossRef]
- A. L. van Puffelen, M. Rijken, M. J. W. M. Heijmans, G. Nijpels, F. G. Schellevis, and Diacourse study group, ‘Effectiveness of a self-management support program for type 2 diabetes patients in the first years of illness: Results from a randomized controlled trial’, PLoS One, vol. 14, no. 6, p. e0218242, 2019. [CrossRef]
- C. Colungo et al., ‘Health care and therapeutic education program for newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: A new approach in primary care’, Endocrinol Diabetes Nutr (Engl Ed), vol. 65, no. 9, pp. 486–499, Nov. 2018. [CrossRef]
- S. Hernández-Jiménez, A. C. García-Ulloa, O. Y. Bello-Chavolla, C. A. Aguilar-Salinas, D. Kershenobich-Stalnikowitz, and Group of Study CAIPaDi, ‘Long-term effectiveness of a type 2 diabetes comprehensive care program. The CAIPaDi model’, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, vol. 151, pp. 128–137, May 2019. [CrossRef]
- E. Brusadelli, A. Tomasich, S. Bruno, A. Romanazzi, R. Dagani, and P. Porcelli, ‘Effects of Psychological Intervention in Glycemic Control of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes in Integrated Primary Care Setting’, Psychother Psychosom, vol. 87, no. 2, pp. 124–125, 2018. [CrossRef]
- T. K. Oser, M. Cucuzzella, M. Stasinopoulos, M. Moncrief, A. McCall, and D. J. Cox, ‘An Innovative, Paradigm-Shifting Lifestyle Intervention to Reduce Glucose Excursions With the Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring to Educate, Motivate, and Activate Adults With Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes: Pilot Feasibility Study’, JMIR Diabetes, vol. 7, no. 1, p. e34465, Feb. 2022. [CrossRef]
- D. P. Bailey, L. H. Mugridge, F. Dong, X. Zhang, and A. M. Chater, ‘Randomised Controlled Feasibility Study of the MyHealthAvatar-Diabetes Smartphone App for Reducing Prolonged Sitting Time in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus’, Int J Environ Res Public Health, vol. 17, no. 12, p. 4414, Jun. 2020. [CrossRef]
- O. P. Zaharia et al., ‘Improving insulin sensitivity, liver steatosis and fibrosis in type 2 diabetes by a food-based digital education-assisted lifestyle intervention program: a feasibility study’, Eur J Nutr, vol. 60, no. 7, pp. 3811–3818, Oct. 2021. [CrossRef]
- N. Yahia, M. Khoury, T. Salloum, R. Younes, M. Saleh, and E. Myers, ‘Implementing Evidence-Based Nutrition Practice Guidelines for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Lebanon’, Top Clin Nutr, vol. 32, no. 4, pp. 316–329, Oct. 2017. [CrossRef]
- E. M. Mikhael, M. A. Hassali, and S. A. Hussain, ‘Effectiveness of Diabetes Self-Management Educational Programs For Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients In Middle East Countries: A Systematic Review’, Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes, vol. 13, pp. 117–138, 2020. [CrossRef]
- R. Tanaka, T. Shibayama, K. Sugimoto, and K. Hidaka, ‘Diabetes self-management education and support for adults with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials’, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, vol. 169, p. 108480, Nov. 2020. [CrossRef]
- A. Steinsbekk, L. Ø. Rygg, M. Lisulo, M. B. Rise, and A. Fretheim, ‘Group based diabetes self-management education compared to routine treatment for people with type 2 diabetes mellitus. A systematic review with meta-analysis’, BMC Health Serv Res, vol. 12, p. 213, Jul. 2012. [CrossRef]
- M. J. Davies et al., ‘Effectiveness of the diabetes education and self management for ongoing and newly diagnosed (DESMOND) programme for people with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: cluster randomised controlled trial’, BMJ, vol. 336, no. 7642, pp. 491–495, Mar. 2008. [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association, ‘Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2022 Abridged for Primary Care Providers’, Clin Diabetes, vol. 40, no. 1, pp. 10–38, Jan. 2022. [CrossRef]
- T. Katangwe, D. Bhattacharya, and M. J. Twigg, ‘A systematic review exploring characteristics of lifestyle modification interventions in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes for delivery in community pharmacy’, Int J Pharm Pract, vol. 27, no. 1, pp. 3–16, Feb. 2019. [CrossRef]
- B. Chester, W. G. Stanely, and T. Geetha, ‘Quick guide to type 2 diabetes self-management education: creating an interdisciplinary diabetes management team’, Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes, vol. 11, pp. 641–645, 2018. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).