1. Introduction
Over the past 5 years, many novel Flaviviridae viruses possessing atypical genome structures have been discovered using high-throughput sequencing, which has challenged traditional principles of virus classification [
1]. The Flaviviridae family comprises epidemiologically significant orthoflaviviruses, such as West Nile virus, Zika virus, Dengue virus, Yellow fever virus, tick-borne encephalitis, etc. Jingmenviruses (JMVs) are novel RNA viruses that were first discovered in
Rhipicephalus microplus ticks from the Jingmen region of Hubei Province in China in 2014 [
2]. According to the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV), the JMV group is considered as unclassified viruses of the Flaviviridae family and currently includes Jingmen tick virus (JMTV), Mogiana tick virus (MGTV), Kindia tick virus (KITV), Alongshan virus (ALSV), Yanggou tick virus (YGTV), Takachi virus (TAKV), Harz mountain virus (HMV), Sichuan tick virus (SCTV), SCWL tick virus (SCWLTV), etc. The genetic material of these viruses has been found not only in ticks but also in mosquitoes, cattle, bats, rodents, and humans [
3,
4,
5,
6]. To date, JMVs have been discovered in Asia, Europe, Central and South America, and Africa. Recently, the discovery of JMVs in Russia and their possible pathogenicity for humans have been first reported [
7,
8,
9].
JMVs are fundamentally different from “classical” orthoflaviviruses by a segmented single-stranded RNA positive-sense genome. The genome consists of 4 (5) segments; each segment comprises one or more open reading frames (ORFs) and characteristic 5’ and 3’ untranslated regions (5’ and 3’ UTRs) and is presumably packaged into a separate viral particle [
4,
10]. The proteins encoded by segments 1 and 3 are genetically and functionally related to nonstructural NS3 and NS5 proteins of classical orthoflaviviruses from the Flaviviridae family. The RNA-dependent RNA polymerase gene was shown to be integrated into the genome of
Ixodes ricinus ticks. Other two segments, encoding structural VP1–VP3 proteins, are of unknown origin [
11]. Very little information is currently available on the secondary structure of the JMV 5’ and 3’ UTRs that function as cis-acting elements during viral genome replication and translation [
6,
12].
Kindia tick virus (KITV) is a novel unclassified tick-borne flavi-like virus from the JMV group of the Flaviviridae family. It was first discovered in ixodid ticks
Rhipicephalus geigyi collected from cattle around the city of Kindia, Republic of Guinea, in 2017 [
13]. Then, KITV genetic material was found in six more
Rhipicephalus geigyi ticks from the 2021 collection [
14]. KITV has a genome structure typical of that in JMVs; NS3 and NS5 proteins are structurally and functionally similar to those in orthoflaviviruses, which confirms their possible evolutionary relationship and taxonomic unity; structural VP1–VP3 proteins of KITV have no analogues among known viral proteins [
15]. In this study, the secondary structure of the KITV RNA 5’ and 3’UTRs was for the first time modeled and analyzed, regulatory elements in the KITV 5’ and 3’ UTRs characteristic of orthoflaviviruses were discovered, and conserved motifs were identified in JMVs, including KITV.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tick collection
The collection of ixodid ticks was formed in 2018 from freshly slaughtered cattle in a slaughterhouse of Kindia, the Republic of Guinea. Sampled ticks were classified to species based on their morphological characteristics. Next, they were homogenized and stored at –80 ℃ until analyses [
16].
2.2. Whole-genome sequencing
Total RNA was isolated from tick (
Rhipicephalus spp.) homogenates using phenol–chloroform extraction and an ExtractRNA reagent (Evrogen, Russia). Reverse transcription was performed using a MMLV RT kit (Evrogen, Russia). Screening for genetic material of segmented flavi-like viruses was carried out by PCR using JMV_f – TGGACCAGGGCMGTIGGRGAGTA and JMV_r – GAAAACCTGRTAGTYIGGGTCGCA oligonucleotides [
2]. Kindia tick virus cDNA fragments were amplified using a Q5 High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase kit (NEB, UK) and original oligonucleotides calculated by the authors. The data are shown in
Table S1. Amplicons were analyzed by electrophoresis in 2% agarose gel and purified using a Cleanup Standard kit (Evrogen, Russia). The sequencing reaction was performed using a BigDye Terminator v3.1 kit (Thermo FS, USA). After the sequencing reaction, fragments were purified by direct reprecipitation with ethanol. Whole-genome sequencing was performed on an ABI 3500/3500xl device (Applied Biosystems, USA). Whole-genome sequence assembly and sequence chromatogram processing were performed using Lasergene 10 SeqMan (DNASTAR, USA) and UGENE (UNIPRO, Russia) software. Search for open reading frames and translation into amino acid sequences were performed using Vector NTI (Invitrogen, USA). All whole-genome sequences were deposited to the GenBank database under accession numbers MW341206–MW341213.
2.3. Analysis of whole-genome sequencing
All deposited whole-genome sequences of segmented flavi-like viruses were downloaded from the GenBank database: Kindia tick virus, JMTV, MGTV, ALSV, YGTV, TAKV, HMV, SCTV, and SCWLTV. A total of 541 whole-genome sequences were downloaded: 128 sequences for segment 1, 124 for segment 2, 144 for segment 3, and 145 for segment 4. Multiple alignment of whole-genome sequences and 5’–3’ UTRs was carried out in MEGA X (PSU, USA) using ClustalW. The number of selected objects of the segment 1 5’ and 3’ UTRs was as follows: 79 for JMTV, 5 for TAKV, 6 for YGTV, 10 for ALSV, 7 for HMV, 3 for MGTV, 18 for KITV. The number of selected objects of the segment 2 5’ and 3’ UTRs was as follows: 82 for JMTV, 3 for YGTV, 9 for ALSV, 5 for HMV, 3 for MGTV, 18 for KITV, 3 for SCTV, and 1 for SCWLTV. The number of selected objects of the segment 3 5’ and 3’ UTRs was as follows: 101 for JMTV, 3 for YGTV, 8 for ALSV, 7 for HMV, 3 for MGTV, 18 for KITV, 3 for SCTV, and 1 for SCWLTV. The number of selected objects of the segment 4 5’ and 3’ UTRs was as follows: 102 for JMTV, 3 for YGTV, 8 for ALSV, 7 for HMV, 3 for MGTV, 18 for KITV, 3 for STCV, and 1 for SCWLTV.
For construction of a phylogenetic tree, complete nucleotide sequences of the segment 1 open reading frame from seventeen representative isolates of segmented flavi-like viruses were aligned and analyzed by the maximum likelihood method with 1,000 bootstrap replicates using the MEGA X molecular evolutionary genetic analysis software (PSU, USA). The tree optimization algorithm and distance correction (G+R+I) were selected using the JMODELTEST software (University of Vigo, Spain). Isolates in the phylogenetic tree were labeled by a GenBank number followed by the isolate name and country, origin, and year of isolation.
2.4. 5’ UTR – 3’ UTR sequences and structures
The primary criterion for selection of untranslated regions was their size. Isolates lacking an untranslated region or shorter than 35 nucleotides, which indicated their undersequencing, were excluded from the sample.
Novel unresolved 5’–3’ UTR motifs (recurring, fixed-length patterns) was searched using a software package provided by the MEME Suite web server (
https://meme-suite.org/meme). Prediction of 5’–3’ UTR structures and sequence alignment were performed using the LocARNA tool (
http://www.uni-freiburg.de). The resulting structural alignments were visualized as RNA secondary structures with RNAplot from the ViennaRNA package using the “most informative sequence” and “annotate covariance of base pairs” modes and the RNApuzzler plotting layout algorithm.
Secondary structures of the KITV RNA 5’ and 3’ UTRs of segments 1 and 2 were predicted using three independent tools: ViennaRNA Fold (
http://rna.tbi.univie.ac.at), UNA MFOLD 3.6 (
http://www.unafold.org/mfold), and RNAstructure (
https://rna.urmc.rochester.edu) [
17,
18,
19]. Simulation was performed at a folding temperature of 37 °C and ionic conditions of 1M NaCl without divalent ions. The parameters “maximal distance between paired bases” (MDBPB) and “percent suboptimality” (%S) were selected manually. An MDBPB of 60 to 100 and a %S of up to 50% were established. The upper bound on the number of computed folds and the upper bound on the total number of single-stranded bases that are allowed in a bulge or interior loop were set to 25. Other parameters were set as default, and the initial free energy ∆G was set to be the minimum value. For detailed analysis, secondary structures were linearized in the VARNA 3.9 software (
http://varna.lri.fr) and redrawn using graphic editors [
20].
3. Results
3.1. Phylogenetic tree and substitution rate
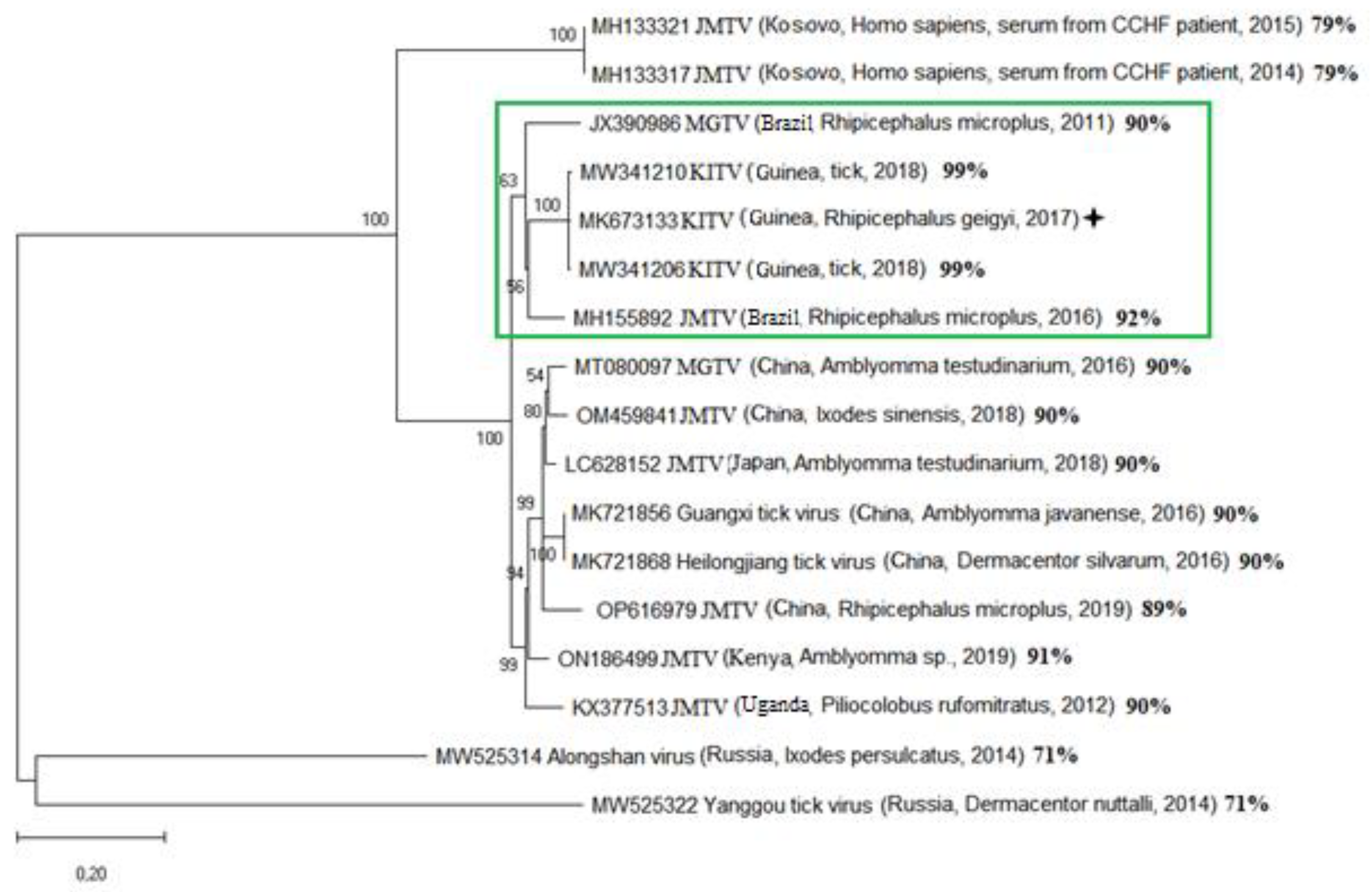
In this study, we obtained whole-genome sequences of two new Kindia tick virus (KITV) isolates, KITV/2018/1 and KITV/2018/2, from homogenates of Rhipicephalus spp ticks collected from cattle in Kindia, Republic of Guinea, in 2018. The total genome length for all segments amounted to ~11,100 b.p.: KITV/2018/1 – 11,173 b.p. and KITV/2018/2 – 11,129 b.p., which is consistent with the genome size of classical orthoflaviviruses.
Phylogenetic analysis of the segment 1 open reading frame encoding RNA-dependent RNA polymerase allowed KITV to be taxonomically classified as a flavi-like virus of the JMV group of the Flaviviridae family. The result of the phylogenetic analysis is shown in
Figure 1. KITV/2018/1 and KITV/2018/2 isolates and a previously discovered KITV/2017/1 isolate form a separate genogroup (MK673133–MK673136). The homology level between KITV/2018/1 and KITV/2018/2 isolates and the KITV/2017/1 isolate were 96–99% for nucleotide sequences (different segments) and 97–99% for amino acid sequences. In this case, amino acid substitutions were found in all viral proteins: VP1 (9 substitutions and 11 substitutions), VP2 (1 and 1), VP3 (4 and 6), NS3 (7 and 9), and NS5 (3 and 11). There were also amino acid differences between KITV/2018/1 and KITV/2018/2 isolates in VP1 (2), VP3 (2), NS3 (4), and NS5 (5) proteins The data are shown in
Table S2. JMTV_1 (MH155892), MGTV/V4/11 (JX390986), and MGTV Yunnan2016 (MT080097) isolates are most closely related to KITV. The level of amino acid sequence homology between KITV/2018/1 and KITV/2018/2 isolates and Brazilian JMTV_1 and MGTV/V4/11 isolates and the Chinese MGTV Yunnan2016 isolate was 91–95% and 83–89%, respectively.
3.2. KITV 5’ and 3’ UTR sequences
Multiple alignment of KITV and MGTV 5’ and 3’ UTRs revealed that lengths of the 5’ and 3’ UTRs varied significantly due to various insertions, deletions, and nucleotide substitutions. The data are shown in
Table 1. KITV is characterized by a short 5’ UTR (91–154 b.p.) and a longer 3’ UTR (up to 387 b.p.), which is consistent with the length of untranslated regions in Zika virus and tick-borne encephalitis virus. The data are shown in
Table 1. The 3’ UTR of KITV and MGTV contains a ~20 b.p. polyA tail, which is not typical of viruses of the Flaviviridae family. Moreover, the 3’ UTR of all KITV segments was found to harbor multiple UAG sites (2 to 6) for interaction with the RNA-binding protein Musashi-1 (MSI1) associated with Zika virus neurotropism. The data are shown in
Table S3.
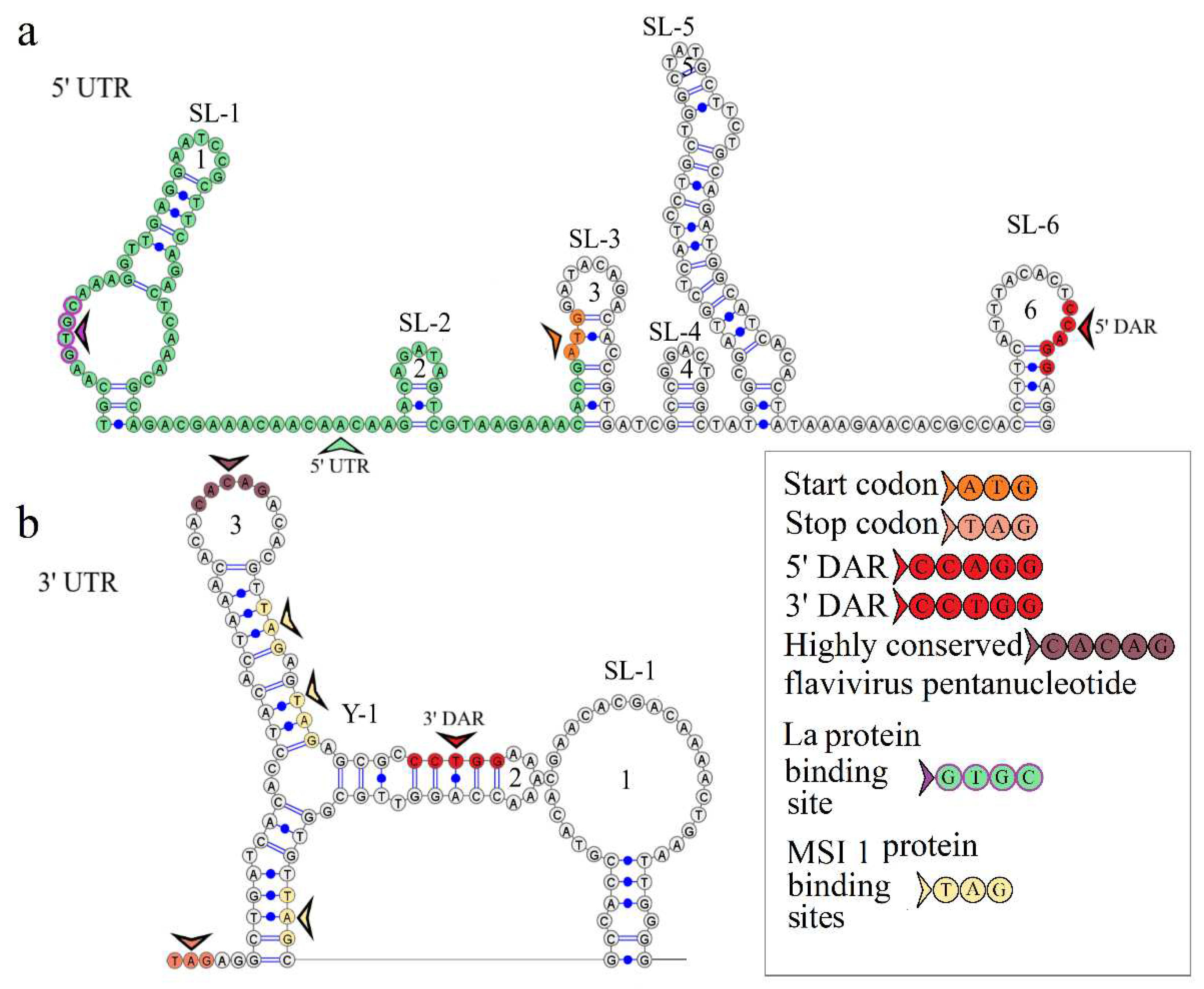
3.3. KITV segment 1 5’ and 3’ UTR structures
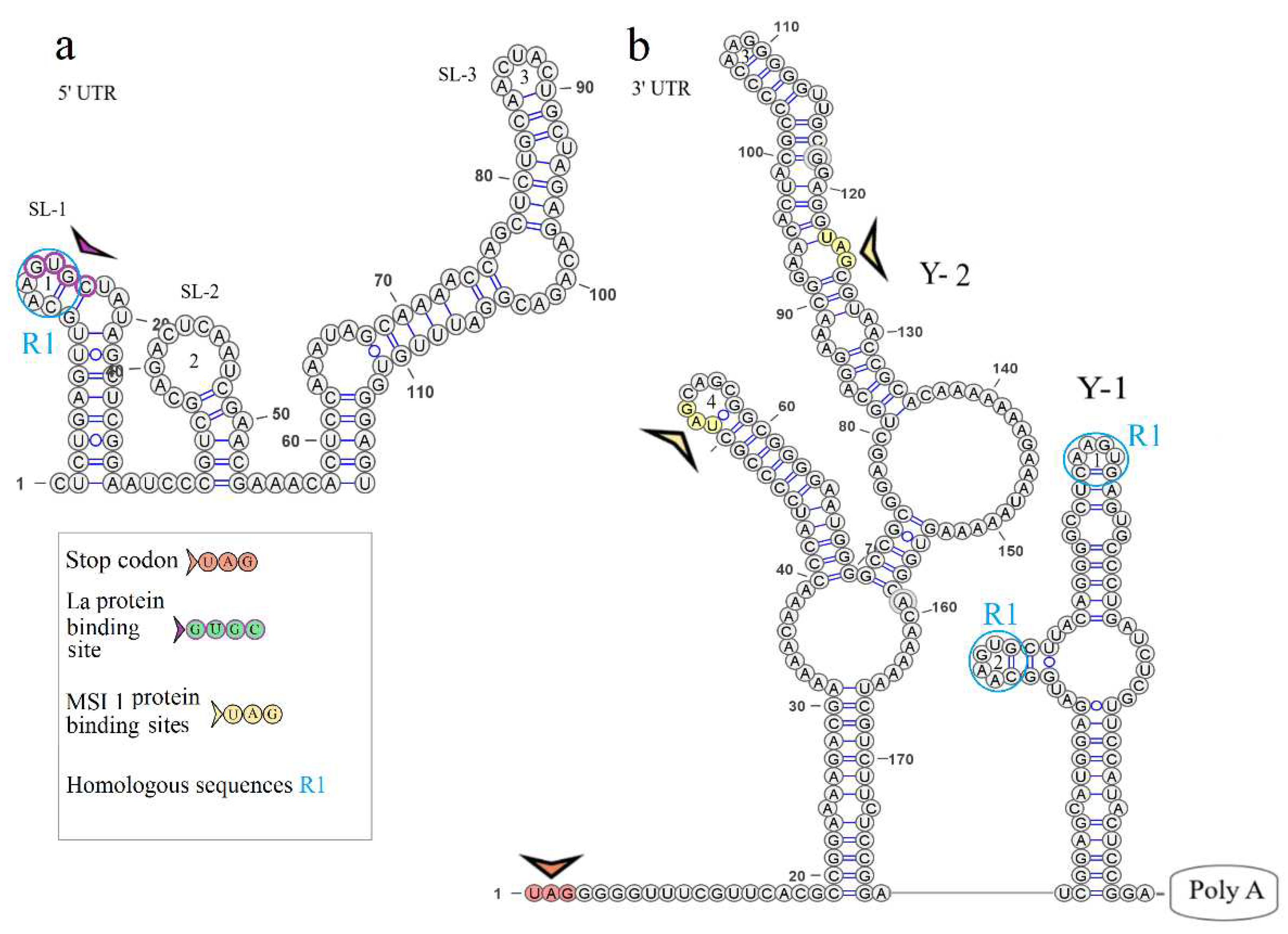
The secondary structure of the segment 1 5’ UTR is represented by two stem loops SL-1 and SL-2. The model of secondary structure is shown in
Figure 2a. Hairpin 1 comprises a 5’-GUGC-3’ inverted sequence that is the La autoantigen binding site [
21]. The CCAGG sequence is located 111 nucleotides downstream of the AUG start codon. In orthoflaviviruses, this sequence is called 5’ DAR. In the 3’ UTR, the complementary 5’-CCUGG-3’ sequence (3’ DAR) was found 50 nucleotides downstream of the stop codon. The 5’ DAR–3’ DAR regions are involved in flavivirus genome cyclization [
22]. A distant location of the KITV 5’ DAR results in the emergence of three stem loops (SL-3, SL-4, SL-5) and a Y-structure. The 3’ UTR topology is conserved among the JMV isolates examined. It is represented by the Y-1 structure and SL-1 in all KITV isolates and the MGTV/V4/11 isolate. The model of secondary structure is shown in
Figure 2b. A difference was found in the MGTV Yunnan2016 isolate in which this region was represented by two Y-structures. A highly conserved orthoflaviviral 5’-CACAG-3’ pentanucleotide was found in hairpin 3 of the Y-1 structure.
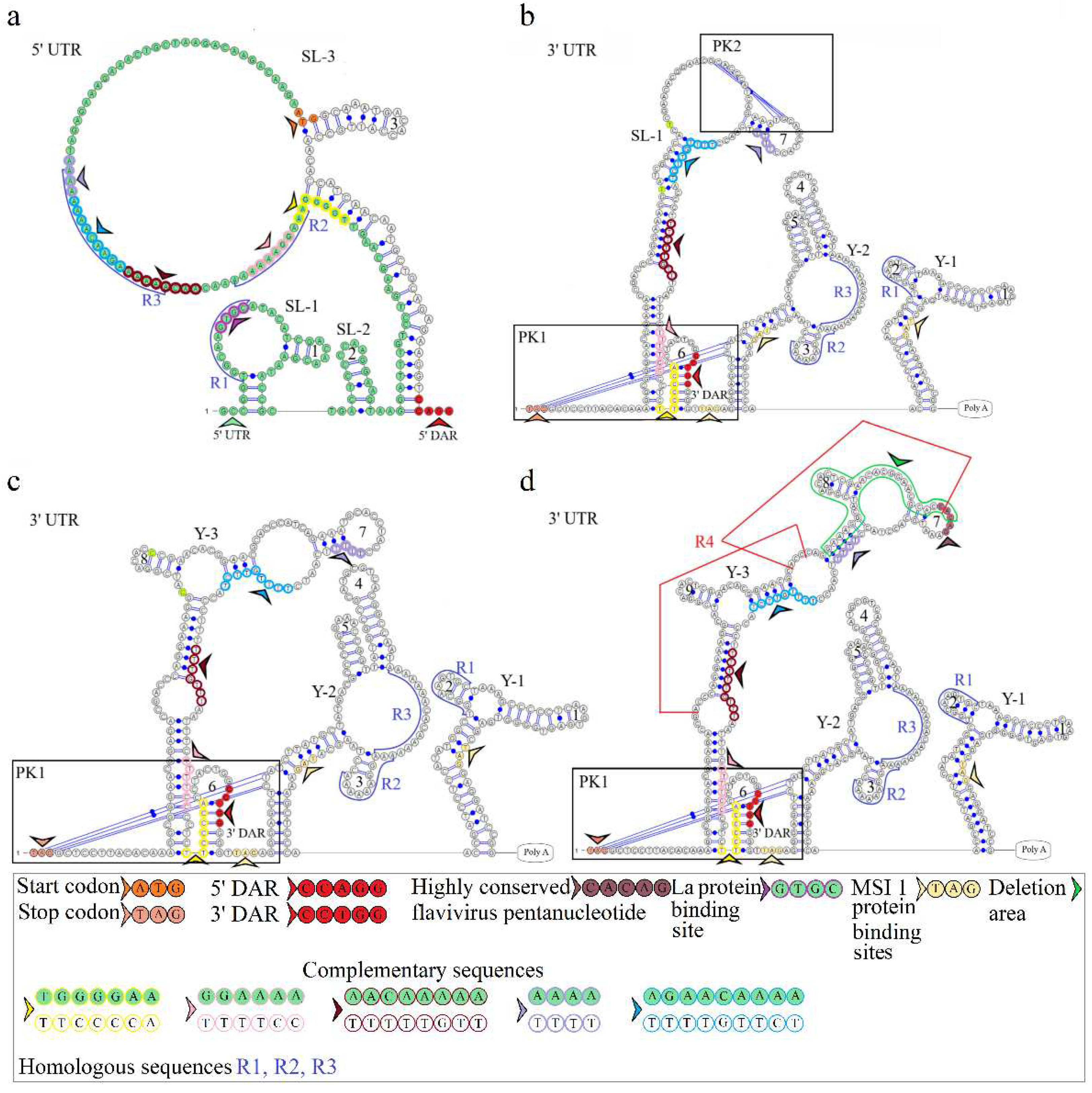
3.4. KITV segment 2 5’ and 3’ UTR structures
The secondary structure of the segment 2 5’ UTR is represented by SL-1 and SL-2. The model of secondary structure is shown in
Figure 3a. This segment comprises a La binding region at position 12 and downstream regions 5’ DAR – 3’ DAR. The 5’ DAR is located 50 nucleotides downstream of AUG, which results in SL-4 and an extended free end. The AUG start codon occurs in SL-4, and the 5’ DAR is located in the free end. Similarly, the 3’ UTR comprises the 3’ DAR at position 2608 of the SL-6 nucleotide structure.
The secondary structure of the segment 2 3’ UTR is represented by Y-1 and Y-2 structures in the MGTV Yunnan2016 isolate, Y-1, Y-2, and Y-3 structures in KITV/2017/1 and KITV/2018/2 isolates, and SL-1, Y-1, and Y-2 structures in KITV/2018/1. Models of secondary structure are shown in Figures 3b-3d. The Y-1 and Y-2 structures are conservative, and the Y-3 structure is variable. C47->U47 and C57->U57 substitutions in the 3’ UTR of KITV/2018/1 cause the replacement of Y-3 by SL-1. There is a modification in the Y-3 structure of KITV/2018/1 and KITV/2018/2 isolates compared with KITV/2017/1. In addition, the orthoflaviviral 5’-CACAG-3ʹ pentanucleotide was found to occur in hairpin 7 of KITV/2017/1 and be absent in KITV/2018/1 and KITV/2018/2 due to a deletion in this region.
Four complementary and three homologous sequences (R1, R2, R3) were identified in the 5’ and 3’ UTRs. The discovered sequences are shown in
Figure 3. The R1 sequence 5’-UGGCAAGUGC-3’ (10 b.p.) was found at nucleotide positions 6–15 in the 5ʹ UTR and positions 2749–2758 (2712–2721) in the 3’ UTR; the R2 sequence 5’-AAAGGAAAAAA-3ʹ (11 b.p.) was found at positions 82–92 and 2699–2709 (2662–2669), respectively; the R3 sequence 5’-AAAAAAGAACAAAAAAA-3’ (17 b.p.) was found at positions 101–117 and 2566–2576 in KITV/2017/1 and KITV/2018/1 with 88% homology, an A-to-U nucleotide substitution occurs in KITV/2018/2, which reduces homology to 82%. Moreover, there are two 40-nucleotide extended sequences in the 3’ UTR, which form the R4 repeat (positions 2450–2489 and 2487–2526). R4 is found only in KITV/2017/1 and leads to a modification of the Y-3 structure and the emergence of the orthoflaviviral 5’-CACAG-3’ pentanucleotide. In KITV/2018/1 and KITV/2018/2 isolates, there is a 35-nucleotide deletion in the second R4 repeat region. This region in KITV/2017/1 involves hairpins 7 and 8 in Y-3 and causes the disappearance of 5’-CACAG-3’. The discovered region is shown in Figures 3b-3d.
Two pseudoknots, PK1 and PK2, were found in the KITV segment 2 3’ UTR. PK1 is present in all KITV isolates and occurs at positions 2416 (UAG) and 2630 (AUC) in KITV/2017/1 and in 2414 (UAG) and 2593 (AUC) in KITV/2018/1 and KITV/2018/2. The discovered regions are shown in Figures 3b-3d. PK2 is found only in the KITV/2018/1 isolate, occurs in positions 2483 (GCA) and 2497 (UGC), and stabilizes the SL-1 structure. The discovered region is shown in
Figure 3b.
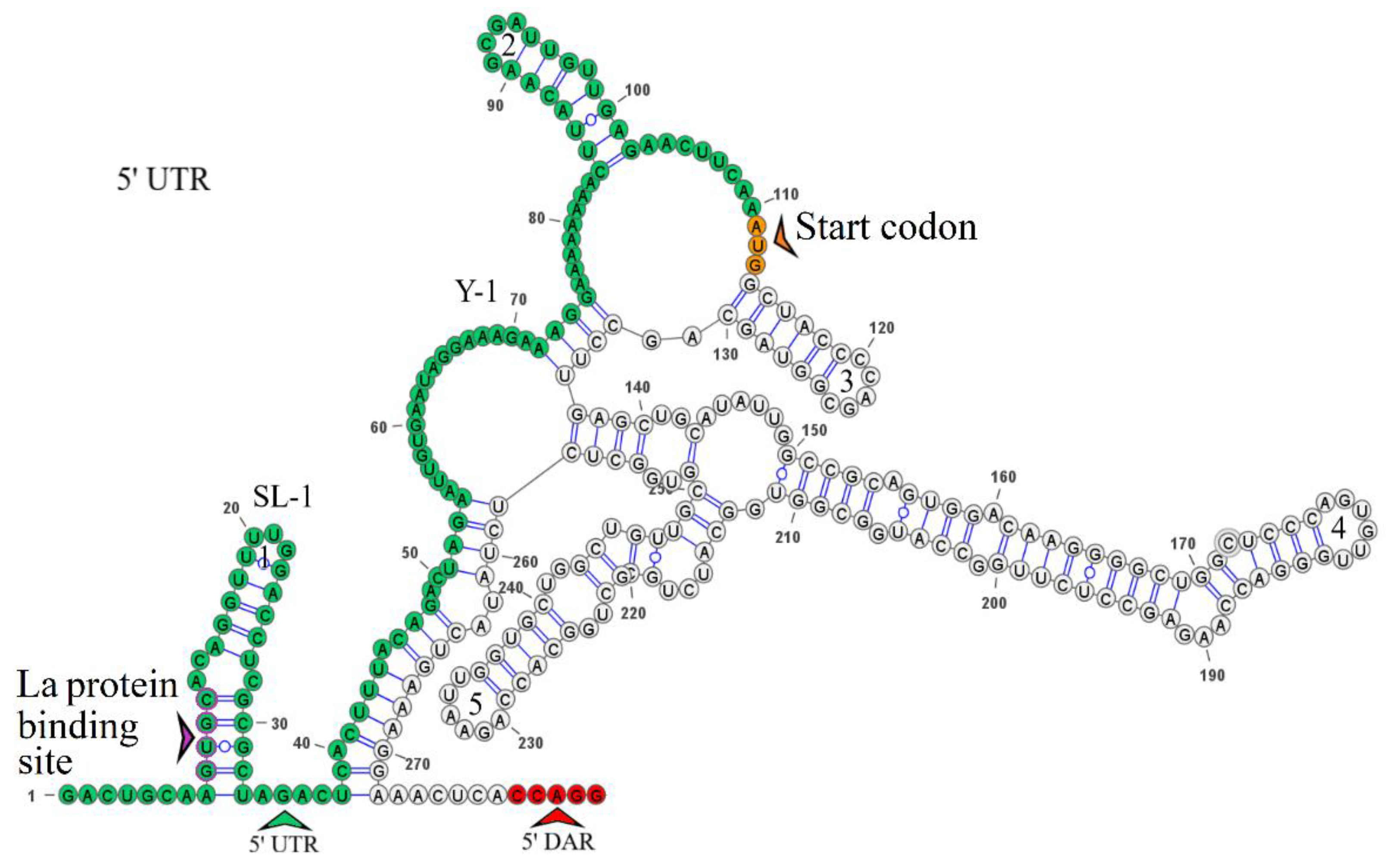
3.5. KITV segment 3 5’ and 3’ UTR structures
The secondary structure of the segment 3 5’ UTR is represented by one stem loop and one Y-structure. The model of secondary structure is shown in
Figure 4. Hairpin 1 contains an inverted sequence of the La autoantigen binding site. The 5’-CCAGG-3’ sequence occurs 165 nucleotides downstream of the AUG start codon. No complementary 5’-CCTGG-3’ sequence (3’ DAR) was found in the 3’ UTR. The distant location of the 5’ DAR in KITV modifies the Y-structure by the emergence of four hairpins in it. The 5’-CACAG-3’ pentanucleotide was not found in the 3’ UTR, which may be due to undersequencing of this region. However, a similar sequence was found in the 5’ UTR of KITV/2018/1 and KITV/2018/2 isolates (coordinates 12–16); in the KITV/2017/1 isolate, there was a substitution at position 14, leading to the disappearance of this pentanucleotide. The data are shown in
Table S4.
3.6. KITV segment 4 5’ and 3’ UTR structures
The secondary structure of the segment 4 5’ UTR is represented by SL-1, SL-2, and SL-3, and that of the segment 4 3’ UTR is represented by two Y-structures. Models of secondary structure are shown in
Figure 5. The 5’ UTR SL-1 structure comprises a La binding region and the 5’-UGGCAAGUGC-3’ R1 sequence previously found in the KITV segment 2 5’ and 3’ UTRs. The same R1 sequence is present in the second hairpin of the 3’ UTR Y-1 structure. No other regulatory elements were found.
3.7. Conserved regions of KITV 5’ and 3’ UTRs
Based on the primary selection criteria, segment 1 5’ UTRs of 25 JMTV and 2 ALSV isolates, segment 2 5’ UTRs of 1 JMTV and 2 ALSV isolates, segment 3 5’ UTRs of 27 JMTV isolates, segment 4 5’ UTRs of 31 JMTV isolates, and segment 4 3’ UTRs of 3 JMTV isolates were excluded from further analysis. The segment 4 3’ UTRs of 6 JMTV isolates were also excluded because an untranslated region was not identified due to a mutation in the VP3 protein.
3.7.1. Segment 1 5’ UTR
Six conserved motifs were found in the segment 1 5’ UTR. The discovered motifs are shown in
Figure 6a. All analyzed KITV isolates were characterized by the presence of motifs 1, 2, and 4. The highly conserved 5’-CAAGUG-3’ sequence was present in motif 2 of KITV. No motifs characteristic of KITV were found in TAKV (100%). In YGTV, there were motifs 2 and 4 in four isolates (66.67%), and motif 4 alone in two isolates (33.33%). In ALSV, motif 2 alone was found in five isolates (62.5%), and no motifs characteristic of KITV were found in the other isolates (37.5%). In HMV, only motif 2 was found in all isolates (100%). In JMTV, there were motifs 1, 2, and 4 in 32 isolates (59.26%), motifs 1 and 4 in 13 isolates (24.07%), motifs 2 and 1 in five isolates (9.26%), motif 1 alone in two isolates (3.70%), and two isolates (3.70%) lacked any motifs. In MGTV, motifs 1, 2, and 4 were found in all isolates (100%). The data are shown in
Table S5. On the basis of multiple alignment and the lack of motif 2, we identified additional 22 JMTV isolates, 2 Yanggou tick virus isolates, and 3 ALSV isolates, which were undersequenced.
3.7.2. Segment 1 3’ UTR
Four conserved motifs were found in the segment 1 3’ UTR The discovered motifs are shown in
Figure 7a. All analyzed KITV isolates were characterized by motifs 1 and 3. The highly conserved 5’-CAAGUG-3’ sequence was found in motif 4 that is absent in KITV. Motifs 1 and 3 were detected in all MGTV isolates (100%). Only motif 1 was found in all TAKV, YGTV, ALSV, and HMV isolates (100%). In JMV, motifs 1 and 3 were detected in 75 isolates (94.9%), and motif 1 alone was present in four isolates (5.1%). The data are shown in
Table S6. On the basis of multiple nucleotide sequence alignment and the lack of motif 4, 36 JMV isolates, 2 YGTV isolates, 7 ALSV isolates, 2 MGTV isolates, and 18 KITV isolates were considered to be presumably undersequenced. Probably, the final secondary structure of this region for the fully sequenced KITV 3’ UTR should be represented not by a stem loop and a Y-structure but by two Y-structures, like in JMTV.
3.7.3. Segment 2 5’ UTR
Four conserved motifs were found in the segment 2 5’ UTR. The discovered motifs are shown in
Figure 6b. The highly conserved 5’-CAAGUG-3’ sequence was present in motif 3 of KITV. In isolates KITV/2018/1 and KITV/2018/2, motifs 1, 2, and 3 (11.11%) were found; in isolate KITV/2017/1, in addition to motifs 1, 2, and 3, motif 4 was found (5.56%). Motif 4 arises from the insertion of two adenines at positions 87 and 88 in KITV/2017/1. In KITV isolates (GenBank ID: OP612414.1–OP612428.1), only motifs 1 and 2 (83.33%) were detected. The results of multiple alignment of the 5’ UTRs indicate that they are undersequenced. The lack of the 5’-GCCGGUGGCAAGUGCAUACAUCGACAACGAAU-3’ region at the beginning of the nucleotide sequence leads to the disappearance of motif 3 that involves the highly conserved 5’-CAAGUG-3’ sequence characteristic of fully sequenced isolates of KITV and other closely related viruses. Motifs 1, 2, and 3 were present in SCWL. In SCTV, there motifs 1, 2, and 3 in two isolates (66.67%), and motifs 1 and 2 in one isolate (33.33%). In MGTV, motifs 1, 2, 3, and 4 were found in one isolate (33.33%). No motifs characteristic of KITV were identified in the other MGTV isolates (66.67%). In ALSV, motif 4 was found in only one isolate (14.29%), and no motifs characteristic of KITV were found in the other isolates (85.71%). No motifs were found in all YGTV isolates (100%). Only motif 4 was identified in all HMV isolates (100%). In JMTV, there were motifs 1, 2, 3, and 4 in 35 isolates (43.21%), motifs 2 and 4 in 30 isolates (37.04%), motifs 1, 2, and 4 in 14 isolates (17.28%), no motifs were found in one isolate (1.23%), and motifs 1, 2, and 3 were identified in one isolate (1.23%). The data are shown in
Table S7. On the basis of multiple alignment and the lack of motif 3, we identified another 44 JMTV isolates, 1 SCTV isolate, 2 MGTV isolates, 6 ALSV isolates, and 2 YGTV isolates, which were presumably undersequenced.
3.7.4. Segment 2 3’ UTR
Five conserved motifs were found in the segment 2 3’ UTR. The discovered motifs are shown in
Figure 7b. Motifs 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 were characteristic of all analyzed KITV isolates (100%). The highly conserved sequence 5’-CAAGUG-3’ was present in motif 4. In SCTV, there were motifs 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 in one isolate (33.33%), motifs 1, 2, 3, and 5 in one isolate (33.33%), and motifs 1, 2, and 3 in one isolate (33.33%). Motifs 1, 2, and 3 were found in SCWL. In MGTV, motifs 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 were found in one isolate (33.33%), and motifs 1, 2, 3, and 5 were identified in two isolates (66.67%). In ALSV, there was motif 1 in five isolates (55.56%), motifs 1 and 4 in one isolate (11.11%), and no motifs characteristic of KITV in the other isolates (33.33%). In YGTV, motif 4 was found in one isolate (33.33%), and the other isolates (66.67%) lacked motifs characteristic of KITV. All HMV isolates (100%) had motifs 1 and 4. In JMV, there were motifs 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 in 44 isolates (53.66%), motifs 1, 2, 3, and 5 in 2 isolates (2.44%), motifs 1, 2, and 3 in 14 isolates (17.07%), motifs 2 and 3 in 8 isolates (9.76%), motifs 1 and 3 in one isolate (1.22%), and motif 2 in 4 isolates (4.88%), 9 isolates (10.98%) lacked any motifs. The data are shown in
Table S8. On the basis of multiple alignment and the lack of motif 4, we suggested that 37 JMV isolates, 8 ALSV isolates, 2 YGTV isolates, and 2 MGTV isolates were presumably undersequenced.
3.7.5. Segment 3 5’ UTR
Four conserved motifs were found in the segment 3 5’ UTR. The discovered motifs are shown in
Figure 6c. Motifs 1 and 2 were characteristic of all analyzed KITV isolates. Motifs 1 and 2 characteristic of KITV were found in all MGTV, SCWL, and SCTV isolates (100%). No motifs characteristic of KITV were found in all HMV, YGTV, and ALSV isolates. In JMTV, there were motifs 1 and 2 in 42 isolates (56.76%), motif 1 alone in 2 isolates (2.70%), and motif 2 alone in 18 isolates (24.32%). The other JMTV isolates (16.22%) lacked motifs characteristic of KITV. The data are shown in
Table S9. On the basis of multiple alignment and the lack of motif 1, we identified another 27 JMTV isolates. Other motifs were found in HMV and ALSV viruses. Interestingly, motif 4 in these viruses also contains the highly conserved 5’-CAAGUG-3’ nucleotide sequence typical of motif 1.
3.7.6. Segment 3 3’ UTR
Multiple alignment of KITV nucleotide sequences with nucleotide sequences of other closely related viruses revealed undersequening of this region. Further analysis was not performed because similar analysis of the segment 1 3’ UTR did not provide full information about conserved motifs and the secondary structure.
3.7.7. Segment 4 5’ UTR
Five conserved motifs were found in the segment 4 5’ UTR. The discovered motifs are shown in
Figure 6d. All considered KITV isolates were characterized by the presence of motifs 1, 2, and 3. Motif 3 contained the highly conserved 5’-CAAGUG-3’ sequence. Motifs 1, 2, and 3 characteristic of KITV were found in all MGTV, SCWL, and SCTV isolates (100%). In all HMV and ALSV isolates (100%), only motif 3 characteristic of KITV was detected. In YGTV, only one isolate (33.33%) harbored motif 3, whereas two other isolates (66.67%) lacked any motifs characteristic of KITV. In JMTV, there were motifs 1, 2, and 3 in 42 isolates (59.15%), motifs 1 and 2 in 14 isolates (19.72%), motifs 2 and 3 in one isolate (1.41%), motif 1 alone in 2 isolates (2.82%), motif 2 alone in 5 isolates (7.04%), and motif 3 alone in 3 isolates (4.23%), the other isolates (5.63%) lacked any motifs characteristic of KITV. The data are shown in
Table S10. On the basis of multiple alignment and the lack of motif 3, we identified another 24 JMTV and 2 YGTV isolates, which were presumably undersequenced.
3.7.8. Segment 4 3’ UTR
Six conserved motifs characteristic of KITV isolates were found in the JMV segment 4 3’ UTR. The discovered motifs are shown in
Figure 7c. Motif 4 comprised the highly conserved 5’-CAAGUG-3’ sequence. In all MGTV, SCWL, and SCTV isolates (100%), we found motifs 1–6 characteristic of KITV. In all HMV isolates (100%), only motifs 1 and 4 were detected. In seven ALSV isolates (87.5%), motifs 1, 4, and 6 were present; only motifs 4 and 6 were found in one ALSV isolate (12.5%). In all YGTV isolates (100%), only motif 1 typical of KITV was detected. In JMV, all six motifs were present in 51 isolates (53.13%), motifs 1, 2, 3, 5, and 6 were found in 10 isolates (10.42%), motifs 1, 2, 5, and 6 were identified in 24 isolates (25%), motifs 2, 5, and 6 occurred in 3 isolates (3.13%), motifs 1 and 4 were present in only one isolate (1.04%), motif 5 alone was detected in six isolates (6.25%), and the other isolates (1.04%) lacked motifs characteristic of KITV. The data are shown in
Table S11. On the basis of multiple alignment and the lack of motif 4, we suggested that 42 JMV isolates were presumably undersequenced.
4. Discussion
Orthoflaviviruses are important pathogens that cause serious infections in humans, from mild fever to encephalitis and hemorrhagic fever, which often result in death. JMVs are a recently discovered group of viruses of unknown pathogenicity. They have a segmented RNA genome consisting of four segments, two of which are functionally related to non-structural genes of viruses from the Orthoflavivirus genus, suggesting the existence of segmented flavi-like viruses in the Flaviviridae family.
In this study, we performed whole-genome sequencing of two new KITV/2018/1 and KITV/2018/2 isolates from the collection of Rhipicephalus spp. ticks from the city of Kindia, Republic of Guinea. The genomic analysis revealed that KITV isolates clustered together with the JMTV_1 (MH155892) isolate and the MGTV/V4/11 (JX390986) isolate, which were previously detected in
Rhipicephalus microplus ticks from the central-west and southeast regions of Brazil and had 90% and 92% nucleotide sequence identity in the segment 1 ORF [
23]. Interestingly, the KITV isolates from the Republic of Guinea and the JMTV and MGTV isolates from Brazil cluster within a monophyletic clade that is different from isolates identified in Asia, Africa, and Southeast Europe, suggesting that these isolates likely belong to a novel virus species within JMVs.
Comparative analysis of the KITV genome and those of other flaviviruses revealed important structural elements of the 5’ and 3’ UTRs. The 5’ and 3’ UTR of segments 1–3 harbor functional orthoflaviviral 5’ DAR and 3’ DAR regions that are responsible for long-range RNA–RNA interactions during genome cyclization before replication onset [
22,
24]. The distant location of the 5’ DAR in segment 1 of the KITV genome leads to the emergence of SL-3, SL-4, SL-5, and a Y-structure; additionally, SL-4 arises in segment 2, and the Y-1 structure in segment 3 is modified. When describing a genome cyclization model, the region located downstream of the start codon (5’ DAR) forms hairpin structures, thereby facilitating the replication initiation step. These regions, when approach each other, activate viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase [
25]. The 5’ UTR of all segments comprises the 5’-GCAC-3’ sequence that binds the La protein, or its complementary 5’-GUGC-3’ sequence, which may facilitate stabilization of the replication complex [
26]. Mutations in the 5’-GCAC-3’ motif are known to alter the binding affinity of La to the hepatitis C virus IRES and have a profound effect on its translation both in vitro and ex vivo [
27]. A highly conserved orthoflaviviral 5’-CACAG-3’ pentanucleotide was found in hairpin 3 of the Y-1 structure of the segment 1 3’ UTR. This region is conserved in the segment 2 3’ UTR only in the KITV/2017/1 isolate and is located in hairpin 7 of Y-3. In flaviviruses, this pentanucleotide is located in the 3’ LSH (3’ long stable hairpin) that is involved in the initiation of genome replication [
28]. The KITV segment 2 3’ UTR is most heterogeneous. It contains three homologous 5’ UTR sequences R1–R3 and two 40-nucleotide repeats. In KITV/2018/1 and KITV/2018/2 strains, a 35-nucleotide deletion occurs in the second repeat. In the KITV segment 2 3’ UTR, two pseudoknots, PK1 and PK2, were found, which are responsible for stabilizing the secondary structure of this region in orthoflaviviruses [
29]. These results suggest an unusual evolutionary relationship between unsegmented and segmented viruses of the Flaviviridae family.
Furthermore, multiple UAG sites (2 to 6) for interactions with the RNA-binding protein Musashi-1 (MSI1) were found in the 3’ UTR of all KITV RNA segments. The data are shown in
Table S3. In comparison, African Zika virus and European tick-borne encephalitis virus contain 6 MSI1 binding sites. In this case, the saturation coefficient of the 3’ UTR with UAG trinucleotides in Zika virus is 1.09, which indicates a high level of binding sites relative to the 3’ UTR size, whereas this coefficient in tick-borne encephalitis virus is 0.55 [
30]. According to in vivo studies, MSII, through the interaction with the Zika virus RNA 3’ UTR, enhances virus replication, regulates translation, and is involved in Zika virus-induced neurotropism [
31,
32]. Zika virus RNA may compete with endogenous targets for binding of MSI1 in the developing embryonic brain, thereby dysregulating expression of genes essential for neural stem cell development, which suggests the presence of mechanisms of MSI1-mediated congenital neuropathology [
33]. Therefore, many binding sites of the KITV 3’ UTR to MSI1 may indicate a possible neurotropic potential of this virus, which requires further research to clarify the epidemiological significance of this unusual multicomponent flavi-like virus.
The 5’ UTR and 3’ UTR of segmented flavi-like viruses have been found to consist of patterns of repeating sequences (conserved motifs). The structure and number of conserved motifs are individual for each virus. However, the 5’ UTR and 3’ UTR of all segments contained the 5’-CAAGUG-3’ sequence in at least one conserved motif. These data are consistent with a previously published paper on the search for conserved sequences in the untranslated regions of JMVs [
12]. Analysis of the obtained models revealed that the 5’-CAAGUG-3’ sequence often forms the first hairpin of the 5’ UTR and hairpins of the 3’ UTR Y-1 structure. These regions are shown in
Figures S1–S4 and S5–S7, respectively. KITV is also characterized by the presence of 5’-CAAGUG-3’in hairpin 1 of the 5’ UTR of segments 1, 2, and 4 and in hairpins of the Y-1 structure of the segment 2 and 4 3’ UTR. As reported, JMTV retained the 5’-CAAGUG-3’ sequence in the UTR of all segments during its first isolation, which indicated that all four segments belonged to the same virus [
2]. The conserved location of the 5’-CAAGUG-3’ sequence in the first structures of the untranslated regions may indicate that this region is involved in interactions with viral and/or cellular proteins to regulate the virus life cycle, similar to how it occurs in other viruses of the
Orthoflavivirus genus [
34,
35,
36,
37,
38].
5. Conclusions
In this study, we obtained two complete genome sequences and modeled, for the first time, the 5’ and 3’ UTRs of a novel flavi-like Kindia tick virus with a segmented genome. The regulatory elements identified during analysis of the 5’ and 3’ UTR structures indicate an evolutionary link between JMVs and classical orthoflaviviruses. Further investigation of each individual component of the main 5’ and 3’ UTR elements will promote an understanding of routes for implementation of genetic information in novel multicomponent flavi-like viruses. The results of this study may be helpful in future research aimed at investigating the epidemiology, structural organization, replication, and pathogenesis of these mysterious multicomponent flavi-like viruses of the JMV group.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at:
www.mdpi.com/xxx/s1, Table S1: Oligonucleotides used for KITV PCR; Table S2: Amino acid substitutions between isolates KITV/2018/1, KITV/2018/2 and KITV/2017/1; Table S3: Location of putative UAG binding sites for MSI1 protein in the 3ʹ UTRs of KITV and MGTV; Table S4: Nucleotide substitutions in the 5’ and 3’ UTRs between different KITV isolates; Table S5: Conserved regions in 5ʹ UTR of the KITV Segment 1; Table S6: Conserved regions in 3ʹ UTR of the KITV Segment 1; Table S7: Conserved regions in 5ʹ UTR of the KITV Segment 2; Table S8: Conserved regions in 3ʹ UTR of the KITV Segment 2; Table S9: Conserved regions in 5ʹ UTR of the KITV Segment 3; Table S10: Conserved regions in 5ʹ UTR of the KITV Segment 4; Table S11: Conserved regions in 3ʹ UTR of the KITV Segment 4; Figure S1: Models of secondary structures of the 5’ UTR of the first segment of viruses; Figure S2: Models of secondary structures of the 5’ UTR of the second segment of viruses; Figure S3: Models of secondary structures of the 5’ UTR of the third segment of viruses; Figure S4: Models of secondary structures of the 5’ UTR of the fourth segment of viruses; Figure S5: Models of secondary structures of the 3’ UTR of the first segment of viruses; Figure S6: Models of secondary structures of the 3’ UTR of the second segment of viruses; Figure S7: Models of secondary structures of the 3’ UTR of the fourth segment of viruses; Figure S8: Conservative motifs in the 5ʹ UTR of segment 1 of segmented flavi-like viruses; Figure S9: Conservative motifs in the 5ʹ UTR of segment 2 of segmented flavi-like viruses; Figure S10: Conservative motifs in the 5ʹ UTR of segment 3 of segmented flavi-like viruses; Figure S11: Conservative motifs in the 5ʹ UTR of segment 4 of segmented flavi-like viruses; Figure S12: Conservative motifs in the 3ʹ UTR of segment 1 of segmented flavi-like viruses; Figure S13: Conservative motifs in the 3ʹ UTR of segment 2 of segmented flavi-like viruses; Figure S14: Conservative motifs in the 3ʹ UTR of segment 4 of segmented flavi-like viruses.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization A.V.G.; methodology, A.V.G. and A.A.T.; formal analysis, A.V.G. and D.A.A.; investigation, A.A.T., D.A.A., R.B.B. and A.V.G.; resources, M.Yu.K. and V.A.T.; writing—original draft preparation, A.V.G.; writing—review and editing, A.A.T., D.A.A., R.B.B., M.Yu.K., V.A.T. and A.V.G.; visualization, A.A.T.; supervision, V.A.T. and A.V.G.; funding acquisition, A.V.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Whole-genome sequencing of Kindia tick virus was performed within the framework of the Order of the Government of the Russian Federation of November 14, 2020 No. 2985-r on Russian–Guinean scientific and technical cooperation in the field of epidemiology, prevention, and monitoring of bacterial and viral infections in the Republic of Guinea. Analysis of untranslated regions was supported by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation (agreement No. 075-15-2021-1355 of October 12, 2021) as part of the implementation of certain activities of the Federal Scientific and Technical Program for the Development of Synchrotron and Neutron Research and Research Infrastructure for 2019–2027.
Data Availability Statement
All obtained sequences were deposited in GenBank.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Research Institute of Applied Biology of the Republic of Guinea and Russian Research Anti-Plague Institute “Microbe” for kindly providing access to the collection of ixodid ticks.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhang, X.; Wang, N.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Q. The Discovery of Segmented Flaviviruses: Implications for Viral Emergence. Curr Opin Virol 2020, 40, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.-C.; Shi, M.; Tian, J.-H.; Lin, X.-D.; Gao, D.-Y.; He, J.-R.; Wang, J.-B.; Li, C.-X.; Kang, Y.-J.; Yu, B.; et al. A Tick-Borne Segmented RNA Virus Contains Genome Segments Derived from Unsegmented Viral Ancestors. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2014, 111, 6744–6749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuivanen, S.; Levanov, L.; Kareinen, L.; Sironen, T.; Jääskeläinen, A.J.; Plyusnin, I.; Zakham, F.; Emmerich, P.; Schmidt-Chanasit, J.; Hepojoki, J.; et al. Detection of Novel Tick-Borne Pathogen, Alongshan Virus, in Ixodes Ricinus Ticks, South-Eastern Finland, 2019. Eurosurveillance 2019, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladner, J.T.; Wiley, M.R.; Beitzel, B.; Auguste, A.J.; Dupuis, A.P.; Lindquist, M.E.; Sibley, S.D.; Kota, K.P.; Fetterer, D.; Eastwood, G.; et al. A Multicomponent Animal Virus Isolated from Mosquitoes. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 20, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-D.; Wang, W.; Wang, N.-N.; Qiu, K.; Zhang, X.; Tana, G.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, X.-Q. Prevalence of the Emerging Novel Alongshan Virus Infection in Sheep and Cattle in Inner Mongolia, Northeastern China. Parasit Vectors 2019, 12, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-D.; Wang, B.; Wei, F.; Han, S.-Z.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Z.-T.; Yan, Y.; Lv, X.-L.; Li, L.; Wang, S.-C.; et al. A New Segmented Virus Associated with Human Febrile Illness in China. New England Journal of Medicine 2019, 380, 2116–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, K.; Zhu, W.; Feng, S.; Qi, J.; Niu, G. Jingmen Tick Virus: An Emerging Arbovirus with a Global Threat. mSphere 2023, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kholodilov, I.S.; Belova, O.A.; Morozkin, E.S.; Litov, A.G.; Ivannikova, A.Y.; Makenov, M.T.; Shchetinin, A.M.; Aibulatov, S. V.; Bazarova, G.K.; Bell-Sakyi, L.; et al. Geographical and Tick-Dependent Distribution of Flavi-Like Alongshan and Yanggou Tick Viruses in Russia. Viruses 2021, 13, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ternovoi, V.; Gladysheva, A.; Sementsova, A.; Zaykovskaya, A.; Volynkina, A.; Kotenev, E.; Loktev, V.; Agafonov, A. Detection of the RNA for New Multicomponent Virus in Patients with Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever in Southern Russia. Annals of the Russian academy of medical sciences 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, N.; Liu, H.-B.; Ni, X.-B.; Bell-Sakyi, L.; Zheng, Y.-C.; Song, J.-L.; Li, J.; Jiang, B.-G.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Y.; et al. Emergence of Human Infection with Jingmen Tick Virus in China: A Retrospective Study. EBioMedicine 2019, 43, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhu, K.; Wojdyla, J.A.; Chen, P.; Qin, B.; Li, Z.; Wang, M.; Cui, S. Crystal Structure of the NS3-like Helicase from Alongshan Virus. IUCrJ 2020, 7, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litov, A.G.; Okhezin, E. V.; Kholodilov, I.S.; Belova, O.A.; Karganova, G.G. Conserved Sequences in the 5′ and 3′ Untranslated Regions of Jingmenvirus Group Representatives. Viruses 2023, 15, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ternovoi, V.; Protopopova, E.; Shvalov, A.; Kartashov, M.; Bayandin, R.; Tregubchak, T.; Yakovlev, S.; Nikiforov, K.; Konovalova, S.; Loktev, V.; et al. Complete Coding Genome Sequence for a Novel Multicomponent Kindia Tick Virus Detected from Ticks Collected in Guinea 2020.
- Kartashov, M.Yu.; Gladysheva, A. V.; Naidenova, E. V.; Zakharov, K.S.; Shvalov, А.N.; Krivosheina, E.I.; Senichkina, A.M.; Bah, M.B.; Ternovoi, V.A.; Boumbaly, S.; et al. Molecular and Genetic Characteristics of the Multicomponent Flavi-like Kindia Tick Virus (Flaviviridae) Found in Ixodes Ticks on the Territory of the Republic of Guinea. Probl Virol 2023, 67, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladysheva, A.A.; Gladysheva, A. V.; Ternovoi, V.A.; Loktev, V.B. Structural Motifs and Spatial Structures of Helicase (NS3) and RNA-Dependent RNA-Polymerase (NS5) of a Flavi-like Kindia Tick Virus (Unclassified Flaviviridae). Probl Virol 2023, 68, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, A.; Bouattour, A.; Camicas, J.-L.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Horak, I.; Latif, A.; Pegram, R.G.; Preston, P.M. Ticks of Domestic Animals in Africa: A Guide to Identification of Species; Bioscience Reports: Edinburgh, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Bellaousov, S.; Kayedkhordeh, M.; Peterson, R.J.; Mathews, D.H. Accelerated RNA Secondary Structure Design Using Preselected Sequences for Helices and Loops. RNA 2018, 24, 1555–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, R.; Bernhart, S.H.; Höner zu Siederdissen, C.; Tafer, H.; Flamm, C.; Stadler, P.F.; Hofacker, I.L. ViennaRNA Package 2.0. Algorithms for Molecular Biology 2011, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markham, N.R.; Zuker, M. UNAFold. In; 2008; pp. 3–31.
- Darty, K.; Denise, A.; Ponty, Y. VARNA: Interactive Drawing and Editing of the RNA Secondary Structure. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1974–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vashist, S.; Anantpadma, M.; Sharma, H.; Vrati, S. La Protein Binds the Predicted Loop Structures in the 3′ Non-Coding Region of Japanese Encephalitis Virus Genome: Role in Virus Replication. Journal of General Virology 2009, 90, 1343–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friebe, P.; Shi, P.-Y.; Harris, E. The 5′ and 3′ Downstream AUG Region Elements Are Required for Mosquito-Borne Flavivirus RNA Replication. J Virol 2011, 85, 1900–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, W.M. de; Fumagalli, M.J.; Torres Carrasco, A. de O.; Romeiro, M.F.; Modha, S.; Seki, M.C.; Gheller, J.M.; Daffre, S.; Nunes, M.R.T.; Murcia, P.R.; et al. Viral Diversity of Rhipicephalus Microplus Parasitizing Cattle in Southern Brazil. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 16315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khelaifi, F.; Yousri, N.A.; Diboun, I.; Semenova, E.A.; Kostryukova, E.S.; Kulemin, N.A.; Borisov, O. V.; Andryushchenko, L.B.; Larin, A.K.; Generozov, E. V.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study Reveals a Novel Association Between MYBPC3 Gene Polymorphism, Endurance Athlete Status, Aerobic Capacity and Steroid Metabolism. Front Genet 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-D.; Deng, C.-L.; Yuan, Z.-M.; Ye, H.-Q.; Zhang, B. Different Degrees of 5’-to-3’ DAR Interactions Modulate Zika Virus Genome Cyclization and Host-Specific Replication. J Virol 2020, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, G.; Heise, T. Role of the RNA-Binding Protein La in Cancer Pathobiology. RNA Biol 2021, 18, 218–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Ray, U.; Das, S. Human La Protein Interaction with GCAC near the Initiator AUG Enhances Hepatitis C Virus RNA Replication by Promoting Linkage between 5′ and 3′ Untranslated Regions. J Virol 2013, 87, 6713–6726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.-Y.; Liu, S.-Q.; Li, X.-D.; Li, J.-Q.; Zhang, Y.-N.; Deng, C.-L.; Zhang, H.-L.; Li, X.-F.; Fang, C.-X.; Yang, F.-X.; et al. Sequence Duplication in 3′ UTR Modulates Virus Replication and Virulence of Japanese Encephalitis Virus. Emerg Microbes Infect 2022, 11, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slonchak, A.; Parry, R.; Pullinger, B.; Sng, J.D.J.; Wang, X.; Buck, T.F.; Torres, F.J.; Harrison, J.J.; Colmant, A.M.G.; Hobson-Peters, J.; et al. Structural Analysis of 3’UTRs in Insect Flaviviruses Reveals Novel Determinants of SfRNA Biogenesis and Provides New Insights into Flavivirus Evolution. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A. de B.; Wolfinger, M.T. Musashi Binding Elements in Zika and Related Flavivirus 3′UTRs: A Comparative Study in Silico. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 6911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavali, P.L.; Stojic, L.; Meredith, L.W.; Joseph, N.; Nahorski, M.S.; Sanford, T.J.; Sweeney, T.R.; Krishna, B.A.; Hosmillo, M.; Firth, A.E.; et al. Neurodevelopmental Protein Musashi-1 Interacts with the Zika Genome and Promotes Viral Replication. Science (1979) 2017, 357, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darai, N.; Mahalapbutr, P.; Wolschann, P.; Lee, V.S.; Wolfinger, M.T.; Rungrotmongkol, T. Theoretical Studies on RNA Recognition by Musashi 1 RNA-Binding Protein. Sci Rep 2022, 12, 12137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klase, Z.A.; Khakhina, S.; Schneider, A.D.B.; Callahan, M. V.; Glasspool-Malone, J.; Malone, R. Zika Fetal Neuropathogenesis: Etiology of a Viral Syndrome. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2016, 10, e0004877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upstone, L.; Colley, R.; Harris, M.; Goonawardane, N. Functional Characterization of 5′ Untranslated Region (UTR) Secondary RNA Structures in the Replication of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus in Mammalian Cells. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2023, 17, e0011098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berzal-Herranz, A.; Berzal-Herranz, B.; Ramos-Lorente, S.E.; Romero-López, C. The Genomic 3′ UTR of Flaviviruses Is a Translation Initiation Enhancer. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23, 8604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avila-Bonilla, R.G.; Salas-Benito, J.S. Interactions of Host MiRNAs in the Flavivirus 3´UTR Genome: From Bioinformatics Predictions to Practical Approaches. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ternovoi, V.A.; Gladysheva, A. V.; Ponomareva, E.P.; Mikryukova, T.P.; Protopopova, E. V.; Shvalov, A.N.; Konovalova, S.N.; Chausov, E. V.; Loktev, V.B. Variability in the 3′ Untranslated Regions of the Genomes of the Different Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus Subtypes. Virus Genes 2019, 55, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafalsky, V.; Averyanov, A.; Bart, B.; Minina, E.; Putilovskiy, M.; Andrianova, E.; Epstein, O. Efficacy and Safety of Ergoferon versus Oseltamivir in Adult Outpatients with Seasonal Influenza Virus Infection: A Multicenter, Open-Label, Randomized Trial. International Journal of Infectious Diseases 2016, 51, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).