Submitted:
02 January 2024
Posted:
04 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
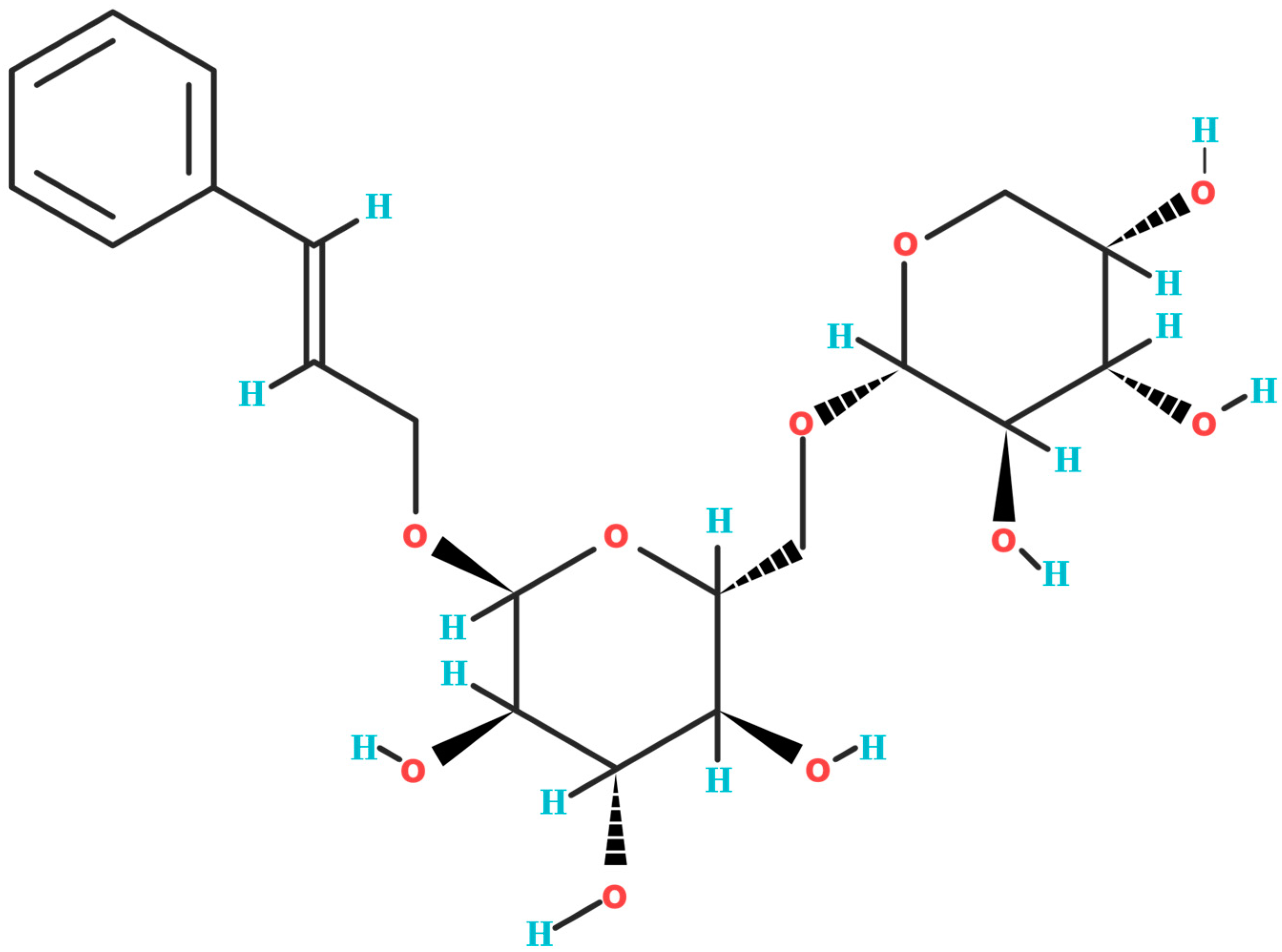
2. Biochemical Structure of Rosavin
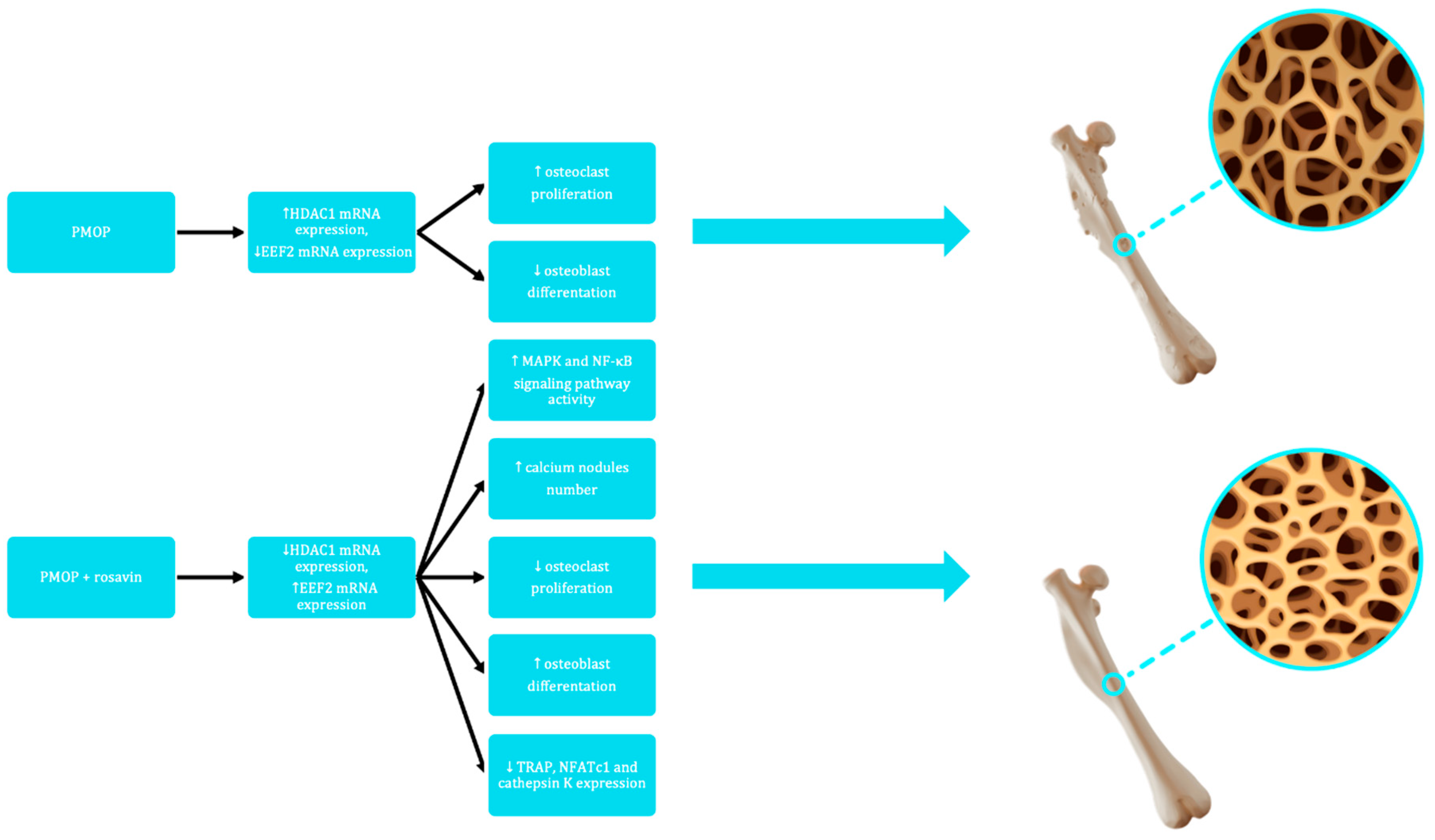
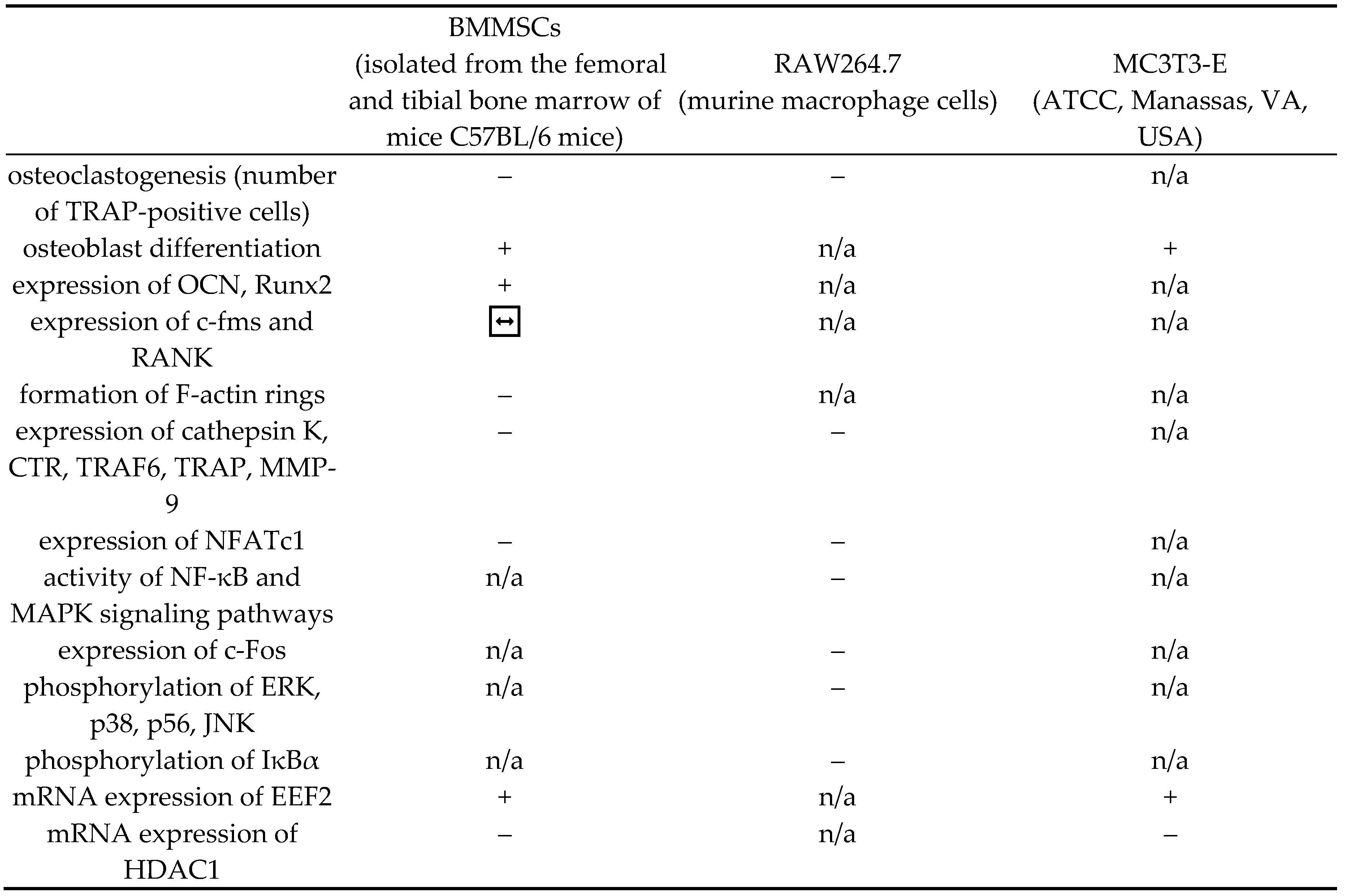
3. Impact of Rosavin on Bone Tissue Metabolism
4. Discussion
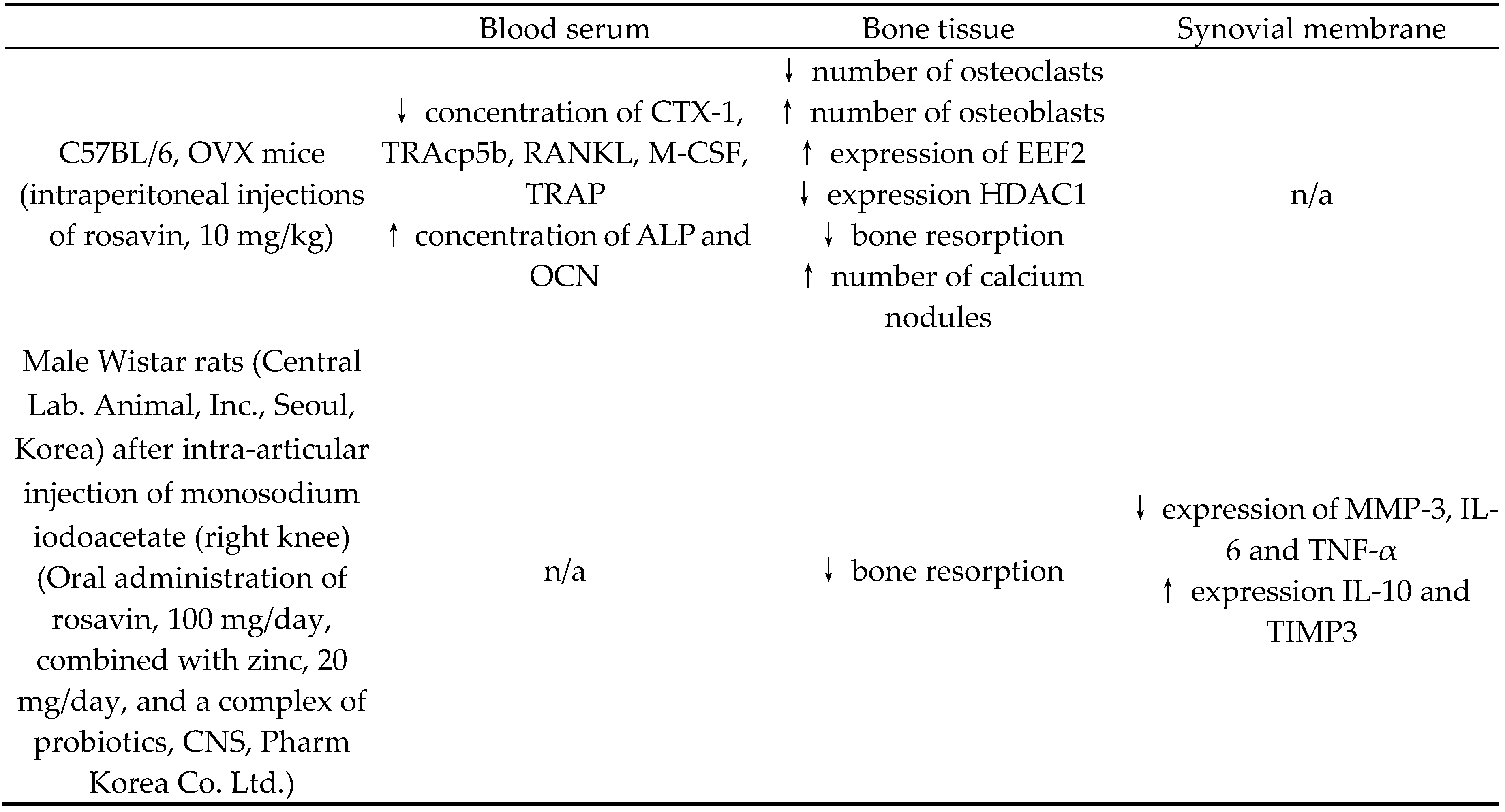
| Blood serum | Bone tissue | Synovial membrane | |
| C57BL/6, OVX mice(intraperitoneal injections of rosavin, 10 mg/kg) | ↓ concentration of CTX-1, TRAcp5b, RANKL, M-CSF, TRAP↑ concentration of ALP and OCN | ↓ number of osteoclasts↑ number of osteoblasts↑ expression of EEF2↓ expression HDAC1↓ bone resorption↑ number of calcium nodules | n/a |
| Male Wistar rats (Central Lab. Animal, Inc., Seoul, Korea) after intra-articular injection of monosodium iodoacetate (right knee)(Oral administration of rosavin, 100 mg/day, combined with zinc, 20 mg/day, and a complex of probiotics, CNS, Pharm Korea Co. Ltd.) | n/a | ↓ bone resorption | ↓ expression of MMP-3, IL-6 and TNF-α↑ expression IL-10 and TIMP3 |
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, S.; Feng, Y.; Zheng, L.; He, P.; Tan, J.; Cai, J.; Wu, M.; Ye, X. Rosavin: Research Advances in Extraction and Synthesis, Pharmacological Activities and Therapeutic Effects on Diseases of the Characteristic Active Ingredients of Rhodiola rosea L. Molecules 2023, 28, 7412. [CrossRef]
- Tinsley, G. M., Jagim, A. R., Potter, G. D. M., Garner, D., & Galpin, A. J. (2023). Rhodiola rosea as an adaptogen to enhance exercise performance: a review of the literature. The British journal of nutrition, 1–13. Advance online publication. [CrossRef]
- Ivanova Stojcheva, E.; Quintela, J.C. The Effectiveness of Rhodiola rosea L. Preparations in Alleviating Various Aspects of Life-Stress Symptoms and Stress-Induced Conditions—Encouraging Clinical Evidence. Molecules 2022, 27, 3902. 2022; 27, 3902. [CrossRef]
- Rhodiola rosea: A possible plant adaptogen. Altern. Med. Rev. 2001, 6, 293–302.
- European Medicines Agency; Committee on Herbal Medicinal Products (HMPC). Assessment Report on Rhodiola rosea L., Rhizoma Et Radix; Document Reference. EMA/HMPC/232100/2011; European Medicines Agency: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011.
- Khanna, K., Mishra, K. P., Ganju, L., & Singh, S. B. (2017). Golden root: A wholesome treat of immunity. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie, 87, 496–502. [CrossRef]
- Bernatoniene, J.; Jakstas, V.; Kopustinskiene, D.M. Phenolic Compounds of Rhodiola rosea L. as the Potential Alternative Therapy in the Treatment of Chronic Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12293. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y., Pham, V., Bui, M., Song, L., Wu, C., Walia, A., Uchio, E., Smith-Liu, F., & Zi, X. (2017). Rhodiola rosea L.: an herb with anti-stress, anti-aging, and immunostimulating properties for cancer chemoprevention. Current pharmacology reports, 3(6), 384–395. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X., Xie, L., Long, J., Xie, Q., Zheng, Y., Liu, K., & Li, X. (2021). Salidroside: A review of its recent advances in synthetic pathways and pharmacological properties. Chemico-biological interactions, 339, 109268. [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y., Zhao, Y., Zheng, C., Meng, Y., & Yang, Y. (2010). Synthesis, biological activity of salidroside and its analogues. Chemical & pharmaceutical bulletin, 58(12), 1627–1629. [CrossRef]
- Huang, M., Sui, R., Zhang, L., Zhu, Y., Yuan, X., Jiang, H., & Mao, X. (2023). Rosavin thwarts amyloid-β-induced macromolecular damages and neurotoxicity, exhibiting anti-Alzheimer's disease activity in Wister rat model. Inflammopharmacology, 10.1007/s10787-023-01320-y. Advance online publication. [CrossRef]
- Zou, H., Li, L., Yang, Z., Tang, L., & Wang, C. (2023). Rosavin protects the blood-brain barrier against ischemia/reperfusion-induced cerebral injury by regulating MAPK-mediated MMPs pathway. Clinical and experimental pharmacology & physiology, 50(8), 664–676. [CrossRef]
- Gao, T., Li, J., Shi, L., & Hu, B. (2023). Rosavin inhibits neutrophil extracellular traps formation to ameliorate sepsis-induced lung injury by regulating the MAPK pathway. Allergologia et immunopathologia, 51(4), 46–54. [CrossRef]
- Liu, R., Jiang, C., Zhao, Z., Lv, Y., & Wang, G. (2023). Rosavin exerts an antitumor role and inactivates the MAPK/ERK pathway in small-cell lung carcinoma in vitro. Acta pharmaceutica (Zagreb, Croatia), 73(2), 269–280. [CrossRef]
- Albadawy, R., Hasanin, A. H., Agwa, S. H. A., Hamady, S., Aboul-Ela, Y. M., Raafat, M. H., Kamar, S. S., Othman, M., Yahia, Y. A., & Matboli, M. (2022). Rosavin Ameliorates Hepatic Inflammation and Fibrosis in the NASH Rat Model via Targeting Hepatic Cell Death. International journal of molecular sciences, 23(17), 10148. 17. [CrossRef]
- Park, J. S., Choi, J., Kwon, J. Y., Jung, K. A., Yang, C. W., Park, S. H., & Cho, M. L. (2018). A probiotic complex, rosavin, zinc, and prebiotics ameliorate intestinal inflammation in an acute colitis mouse model. Journal of translational medicine, 16(1), 37. 1. [CrossRef]
- Williams, S. A., Daigle, S. G., Weiss, R., Wang, Y., Arora, T., & Curtis, J. R. (2021). Economic Burden of Osteoporosis-Related Fractures in the US Medicare Population. The Annals of pharmacotherapy, 55(7), 821–829. [CrossRef]
- Si, L., Winzenberg, T. M., Jiang, Q., Chen, M., & Palmer, A. J. (2015). Projection of osteoporosis-related fractures and costs in China: 2010-2050. Osteoporosis international : a journal established as result of cooperation between the European Foundation for Osteoporosis and the National Osteoporosis Foundation of the USA, 26(7), 1929–1937. [CrossRef]
- Hernlund, E., Svedbom, A., Ivergård, M., Compston, J., Cooper, C., Stenmark, J., McCloskey, E. V., Jönsson, B., & Kanis, J. A. (2013). Osteoporosis in the European Union: medical management, epidemiology and economic burden. A report prepared in collaboration with the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF) and the European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industry Associations (EFPIA). Archives of osteoporosis, 8(1), 136. [CrossRef]
- Lajas, C., Abasolo, L., Bellajdel, B., Hernández-García, C., Carmona, L., Vargas, E., Lázaro, P., & Jover, J. A. (2003). Costs and predictors of costs in rheumatoid arthritis: a prevalence-based study. Arthritis and rheumatism, 49(1), 64–70. [CrossRef]
- Dong, N. Q., & Lin, H. X. (2021). Contribution of phenylpropanoid metabolism to plant development and plant-environment interactions. Journal of integrative plant biology, 63(1), 180–209. [CrossRef]
- Masi, F., Chianese, G., Hofstetter, R. K., Cavallaro, A. L., Riva, A., Werz, O., & Taglialatela-Scafati, O. (2023). Phytochemical profile and anti-inflammatory activity of a commercially available Rhodiola rosea root extract. Fitoterapia, 166, 105439. [CrossRef]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (2023). PubChem Compound Summary for CID 9823887, Rosavin. Retrieved , 2023 from https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Rosavin. 15 December.
- Zhang, W. , Zhang, W., Huo, L., Chai, Y., Liu, Z., Ren, Z., & Yu, C. (2021). Rosavin suppresses osteoclastogenesis in vivo and in vitro by blocking the nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways. Annals of translational medicine, 9(5), 383. [CrossRef]
- Komori, T. (2010). Regulation of osteoblast differentiation by Runx2. Advances in experimental medicine and biology, 658, 43–49. [CrossRef]
- da Silva Sasso, G. R. , Florencio-Silva, R., de Pizzol-Júnior, J. P., Gil, C. D., Simões, M. J., Sasso-Cerri, E., & Cerri, P. S. (2023). Additional Insights Into the Role of Osteocalcin in Osteoblast Differentiation and in the Early Steps of Developing Alveolar Process of Rat Molars. The journal of histochemistry and cytochemistry : official journal of the Histochemistry Society, 71(12), 689–708. [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, T., Kinbara, M., Maeda, T., Yoshizawa, M., Kokabu, S., & Takano Yamamoto, T. (2017). Regulation of osteoclast differentiation and actin ring formation by the cytolinker protein plectin. Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 489(4), 472–476. 4. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q. , Wang, X., Liu, Y., He, A., & Jia, R. (2010). NFATc1: functions in osteoclasts. The international journal of biochemistry & cell biology, 42(5), 576–579. [CrossRef]
- Takayanagi, H. (2007). The role of NFAT in osteoclast formation. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1116, 227–237. [CrossRef]
- Omata, Y. , Tachibana, H., Aizaki, Y., Mimura, T., & Sato, K. (2023). Essentiality of Nfatc1 short isoform in osteoclast differentiation and its self-regulation. Scientific reports, 13(1), 18797. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J. H., Kim, K., Youn, B. U., Jin, H. M., Kim, J. Y., Moon, J. B., Ko, A., Seo, S. B., Lee, K. Y., & Kim, N. (2011). RANKL induces NFATc1 acetylation and stability via histone acetyltransferases during osteoclast differentiation. The Biochemical journal, 436(2), 253–262. 2. [CrossRef]
- McClung, M. (2007). Role of RANKL inhibition in osteoporosis. Arthritis research & therapy, 9 Suppl 1(Suppl 1), S3. [CrossRef]
- Ko, Y. , Lee, G., Kim, B., Park, M., Jang, Y., & Lim, W. (2020). Modification of the RANKL-RANK-binding site for the immunotherapeutic treatment of osteoporosis. Osteoporosis international : a journal established as result of cooperation between the European Foundation for Osteoporosis and the National Osteoporosis Foundation of the USA, 31(5), 983–993. [CrossRef]
- Chang, J. , Wang, Z., Tang, E., Fan, Z., McCauley, L., Franceschi, R., Guan, K., Krebsbach, P. H., & Wang, C. Y. (2009). Inhibition of osteoblastic bone formation by nuclear factor-kappaB. Nature medicine, 15(6), 682–689. [CrossRef]
- Boyce, B. F. , Li, J., Yao, Z., & Xing, L. (2023). Nuclear Factor-Kappa B Regulation of Osteoclastogenesis and Osteoblastogenesis. Endocrinology and metabolism (Seoul, Korea), 38(5), 504–521. [CrossRef]
- Cong, Q. , Jia, H., Li, P., Qiu, S., Yeh, J., Wang, Y., Zhang, Z. L., Ao, J., Li, B., & Liu, H. (2017). p38α MAPK regulates proliferation and differentiation of osteoclast progenitors and bone remodeling in an aging-dependent manner. Scientific reports, 7, 45964. [CrossRef]
- Yousefzadeh, N. , Kashfi, K., Jeddi, S., & Ghasemi, A. (2020). Ovariectomized rat model of osteoporosis: a practical guide. EXCLI journal, 19, 89–107. [CrossRef]
- van Straalen, J. P. , Sanders, E., Prummel, M. F., & Sanders, G. T. (1991). Bone-alkaline phosphatase as indicator of bone formation. Clinica chimica acta; international journal of clinical chemistry, 201(1-2), 27–33. [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, A., Dohi, Y., Akahane, M., Ohgushi, H., Nakajima, H., Funaoka, H., & Takakura, Y. (2009). Osteocalcin secretion as an early marker of in vitro osteogenic differentiation of rat mesenchymal stem cells. Tissue engineering. Part C, Methods, 15(2), 169–180. 2. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W. , Yu, L., Wang, F., Chen, M., & Li, H. (2023). Rosavin regulates bone homeostasis through HDAC1-induced epigenetic regulation of EEF2. Chemico-biological interactions, 384, 110696. [CrossRef]
- Shakespear, M. R., Halili, M. A., Irvine, K. M., Fairlie, D. P., & Sweet, M. J. (2011). Histone deacetylases as regulators of inflammation and immunity. Trends in immunology, 32(7), 335–343. 7. [CrossRef]
- Cantley, M. D. , Zannettino, A. C. W., Bartold, P. M., Fairlie, D. P., & Haynes, D. R. (2017). Histone deacetylases (HDAC) in physiological and pathological bone remodelling. Bone, 95, 162–174. [CrossRef]
- Parveen, R., Harihar, D., & Chatterji, B. P. (2023). Recent histone deacetylase inhibitors in cancer therapy. Cancer, 129(21), 3372–3380. 21. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. , Wang, J., Wu, X., Simon, N., Svensson, C. I., Yuan, J., Hart, D. A., Ahmed, A. S., & Ackermann, P. W. (2023). eEF2 improves dense connective tissue repair and healing outcome by regulating cellular death, autophagy, apoptosis, proliferation and migration. Cellular and molecular life sciences : CMLS, 80(5), 128. [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J. Y., Lee, S. H., Jhun, J., Choi, J., Jung, K., Cho, K. H., Kim, S. J., Yang, C. W., Park, S. H., & Cho, M. L. (2018). The Combination of Probiotic Complex, Rosavin, and Zinc Improves Pain and Cartilage Destruction in an Osteoarthritis Rat Model. Journal of medicinal food, 21(4), 364–371. 4. [CrossRef]
- Im, G. I., & Kim, M. K. (2014). The relationship between osteoarthritis and osteoporosis. Journal of bone and mineral metabolism, 32(2), 101–109. 2. [CrossRef]
- Kaspiris, A. , Hadjimichael, A. C., Lianou, I., Iliopoulos, I. D., Ntourantonis, D., Melissaridou, D., Savvidou, O. D., Papadimitriou, E., & Chronopoulos, E. (2023). Subchondral Bone Cyst Development in Osteoarthritis: From Pathophysiology to Bone Microarchitecture Changes and Clinical Implementations. Journal of clinical medicine, 12(3), 815. [CrossRef]
- McLean R., R. (2009). Proinflammatory cytokines and osteoporosis. Current osteoporosis reports, 7(4), 134–139. [CrossRef]
- Jehan, F. , Zarka, M., de la Houssaye, G., Veziers, J., Ostertag, A., Cohen-Solal, M., & Geoffroy, V. (2022). New insights into the role of matrix metalloproteinase 3 (MMP3) in bone. FASEB bioAdvances, 4(8), 524–538. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q. , Chen, B., Yan, F., Guo, J., Zhu, X., Ma, S., & Yang, W. (2014). Interleukin-10 inhibits bone resorption: a potential therapeutic strategy in periodontitis and other bone loss diseases. BioMed research international, 2014, 284836. [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y. , Winkler, I. G., Barbier, V., Sims, N. A., Hendy, J., & Lévesque, J. P. (2010). Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-3 (TIMP-3) regulates hematopoiesis and bone formation in vivo. PloS one, 5(9), e13086. [CrossRef]
- Eek, D. , Krohe, M., Mazar, I., Horsfield, A., Pompilus, F., Friebe, R., & Shields, A. L. (2016). Patient-reported preferences for oral versus intravenous administration for the treatment of cancer: a review of the literature. Patient preference and adherence, 10, 1609–1621. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. K. , Yang, L., Meng, G. L., Yuan, Z., Fan, J., Li, D., Chen, J. Z., Shi, T. Y., Hu, H. M., Wei, B. Y., Luo, Z. J., & Liu, J. (2013). Protection by salidroside against bone loss via inhibition of oxidative stress and bone-resorbing mediators. PloS one, 8(2), e57251. [CrossRef]
- Fu, S. , Yan, M., Fan, Q., & Xu, J. (2022). Salidroside promotes osteoblast proliferation and differentiation via the activation of AMPK to inhibit bone resorption of knee osteoarthritis mice. Tissue & cell, 79, 101917. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H. , Qi, S., & Chen, C. (2018). Salidroside Improves Bone Histomorphology and Prevents Bone Loss in Ovariectomized Diabetic Rats by Upregulating the OPG/RANKL Ratio. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland), 23(9), 2398. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





