Submitted:
29 December 2023
Posted:
03 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
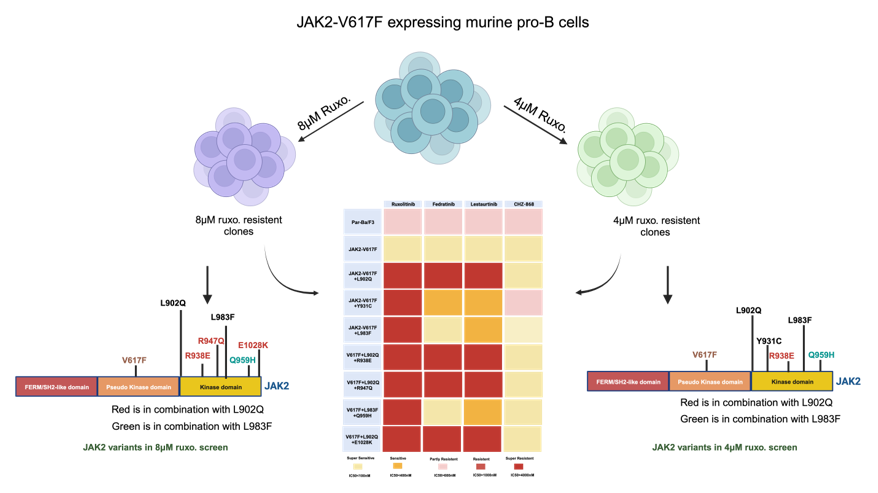
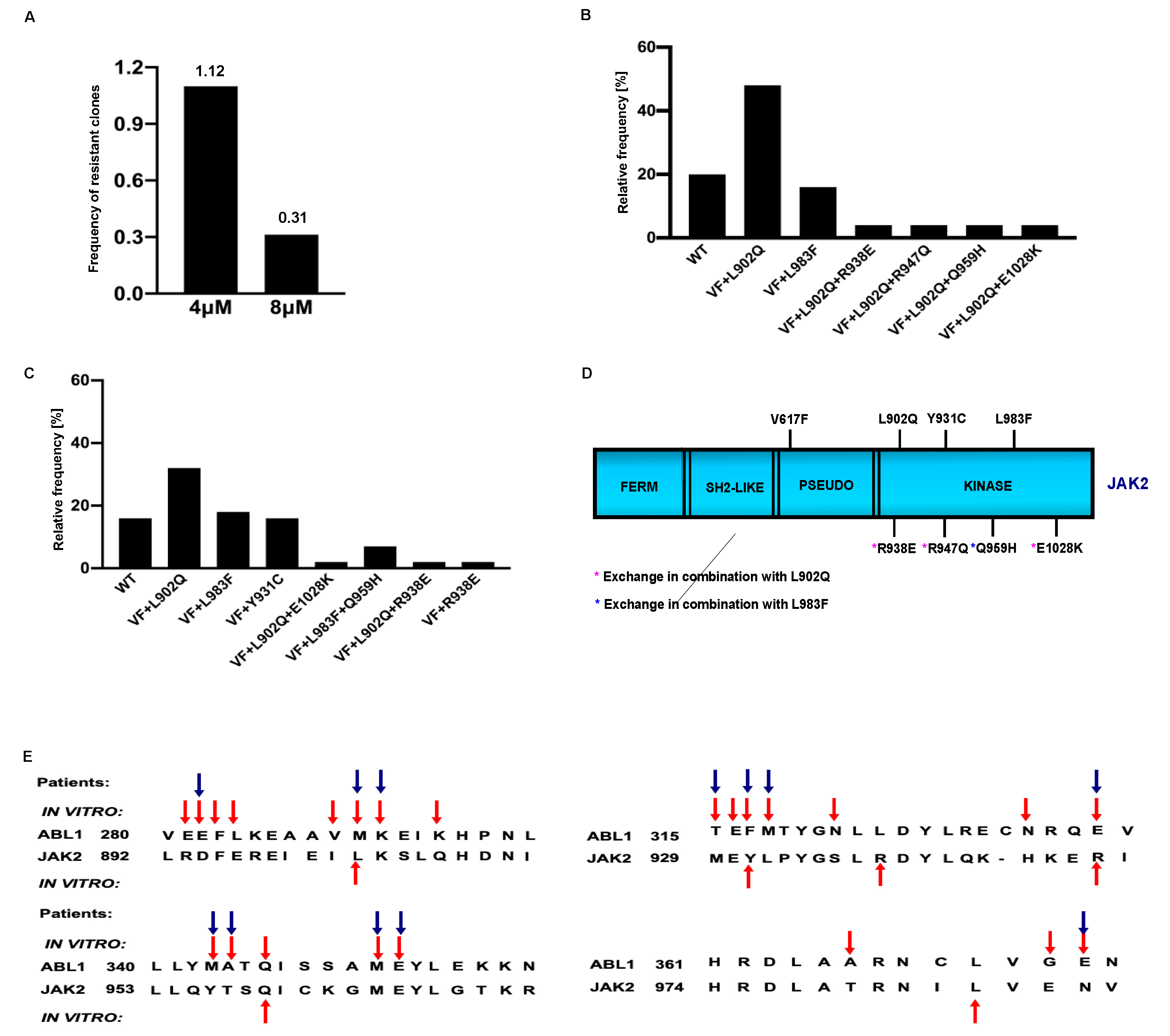
2.1. Frequency of drug resistant clones are decreased after increasing the ruxolitinib concentration
2.1.1. L902Q, Y931C, L983F are the most frequent exchanges identified in ruxolitinib screen performed at 4 μM and 8 μM concentrations
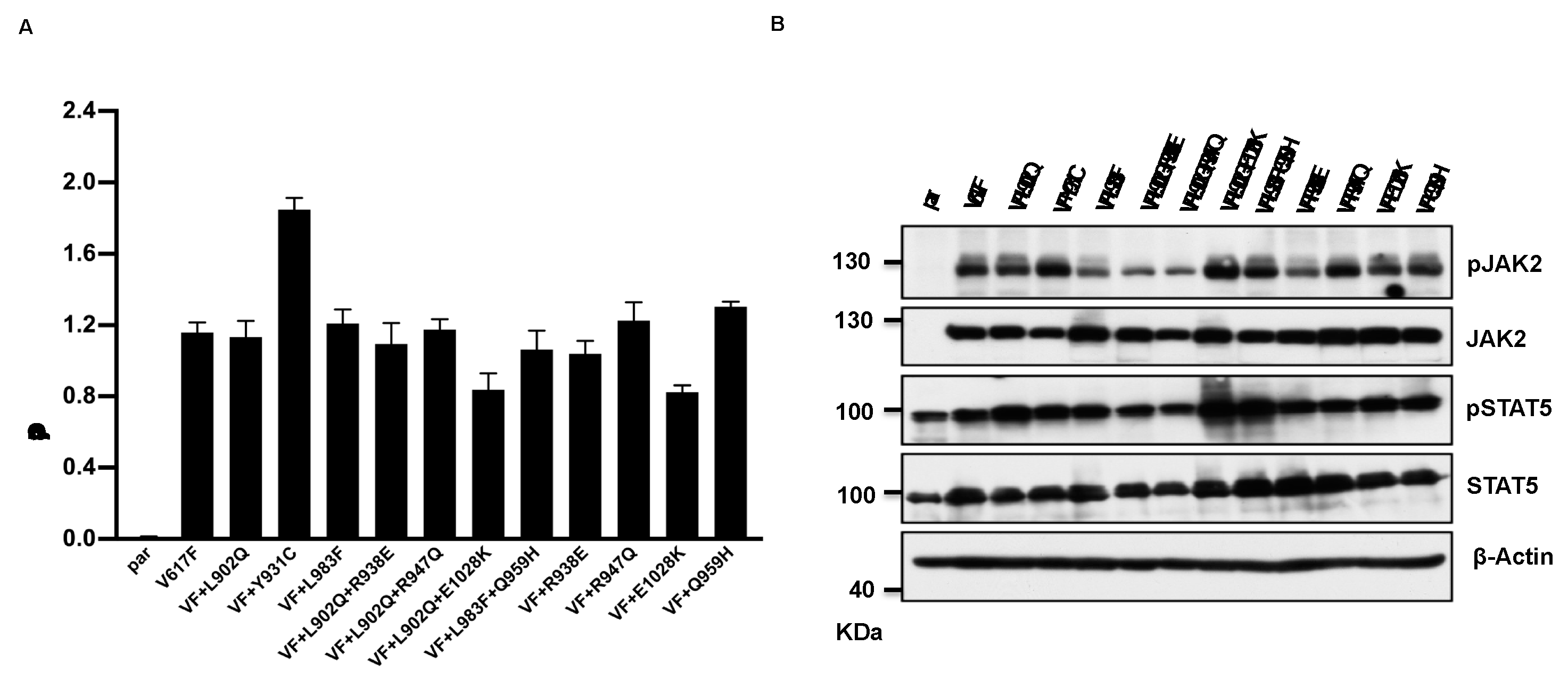
2.2. Drug resistant mutations identified in the cell-based screen transform the Ba/F3 cell and showed constitutive JAK2-STAT5 activation
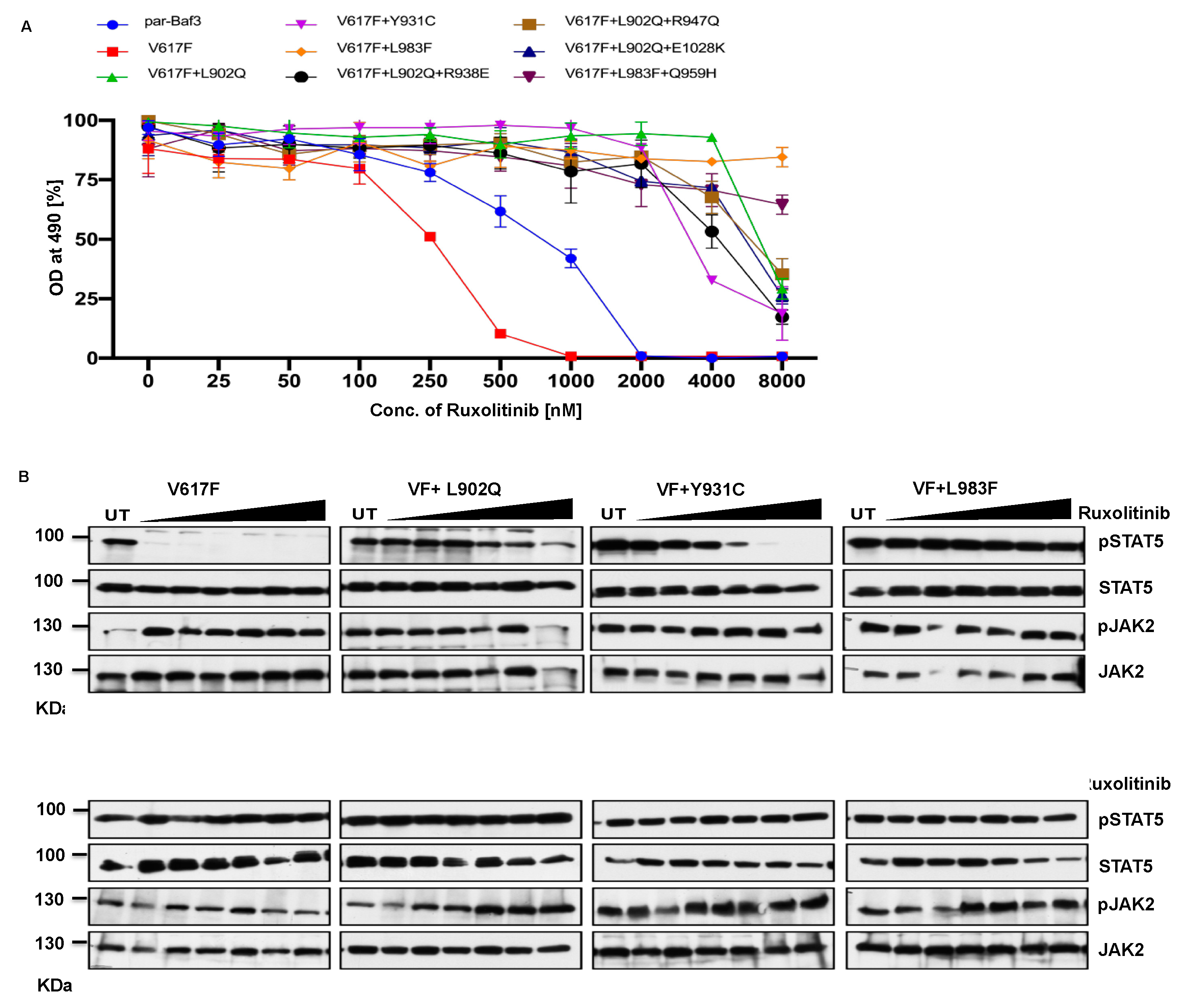
2.3. Kinase domain mutations confers the ruxolitinib resistance and showed persistent activation of STAT5 at higher concentration of drug
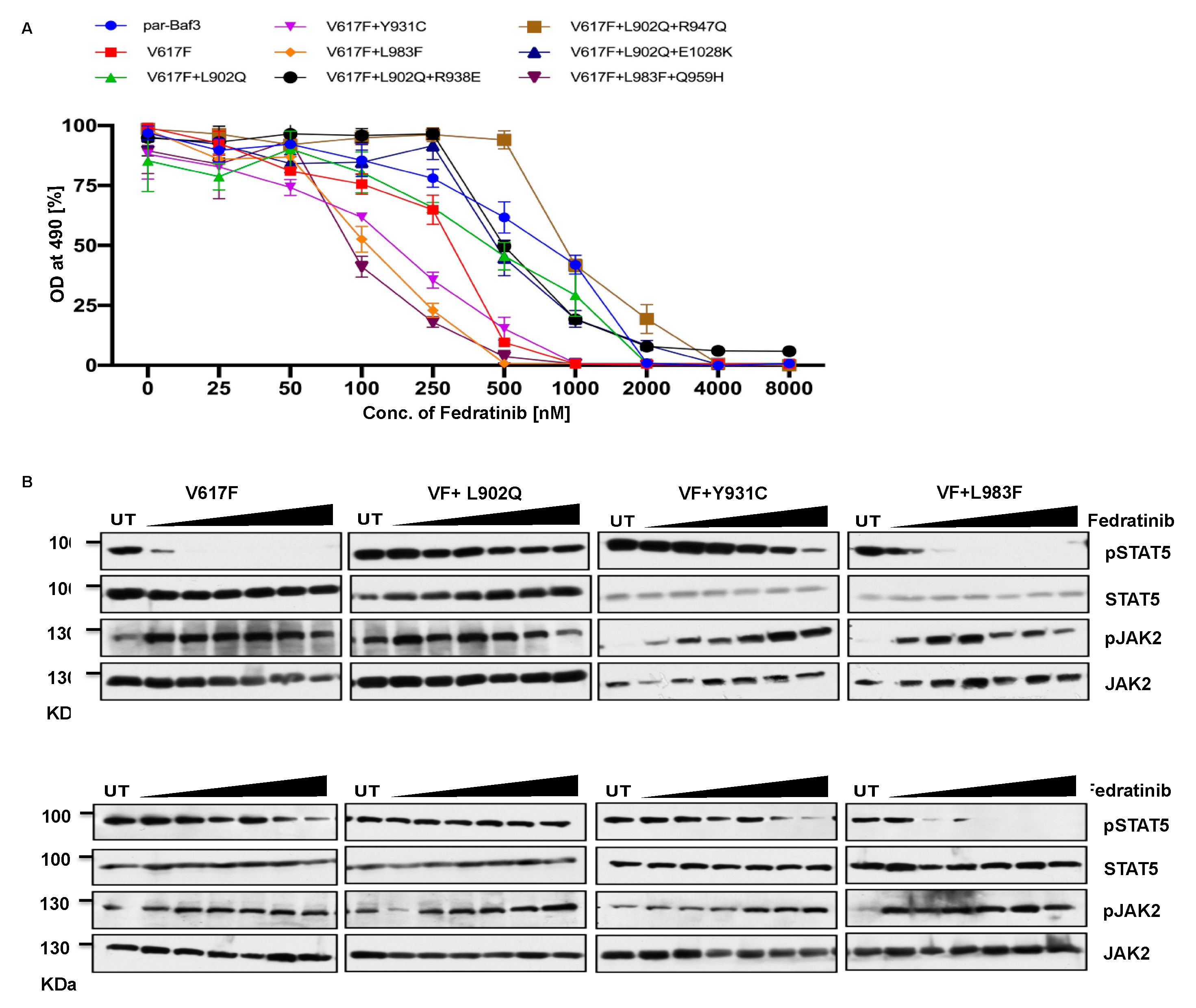
2.4. Ruxolitinib resistant JAK2-L983F is sensitive towards fedratinib
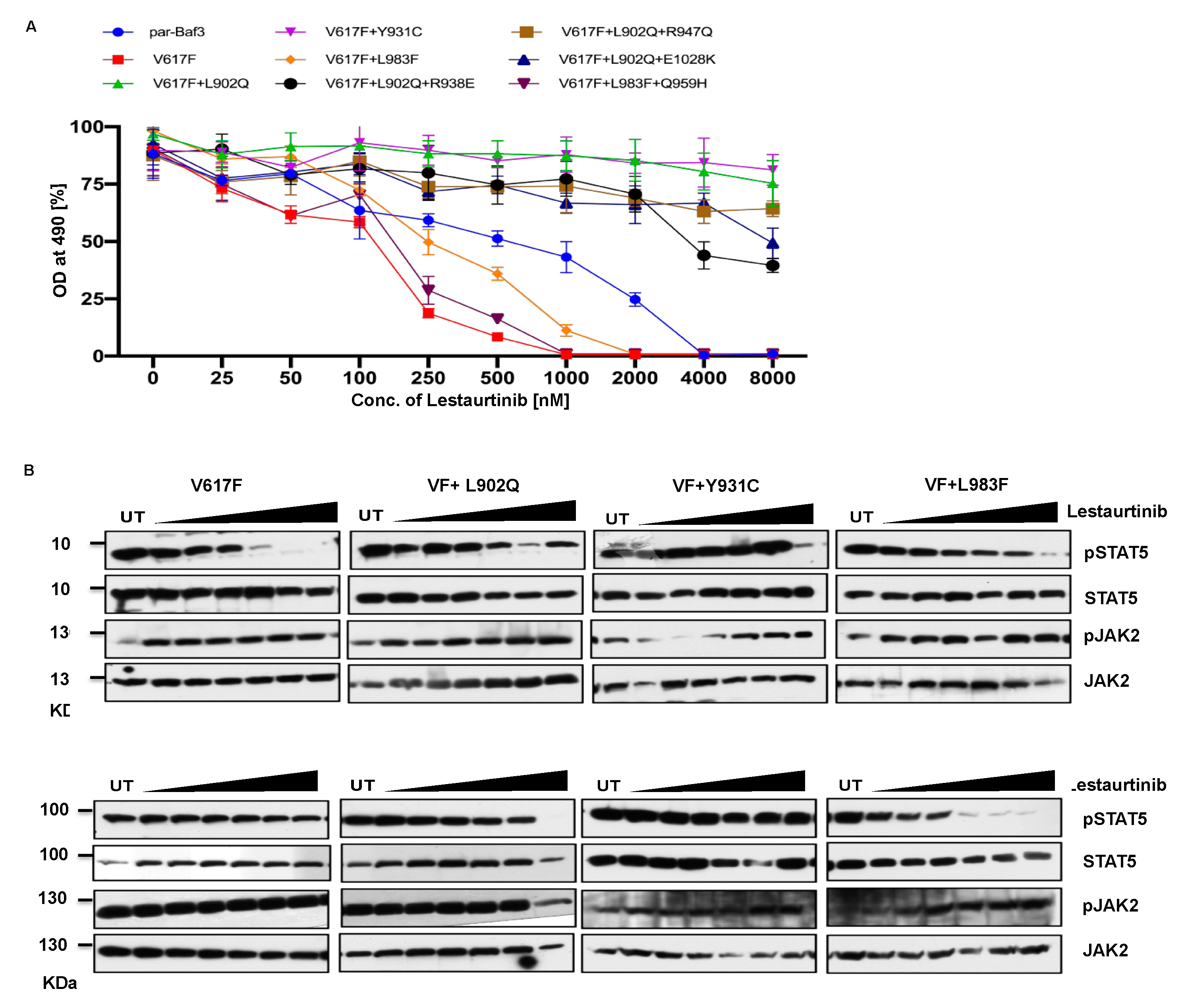
2.5. Lestauritinib is not potent against the ruxolitinib resistant variants and did not change the IC50 value
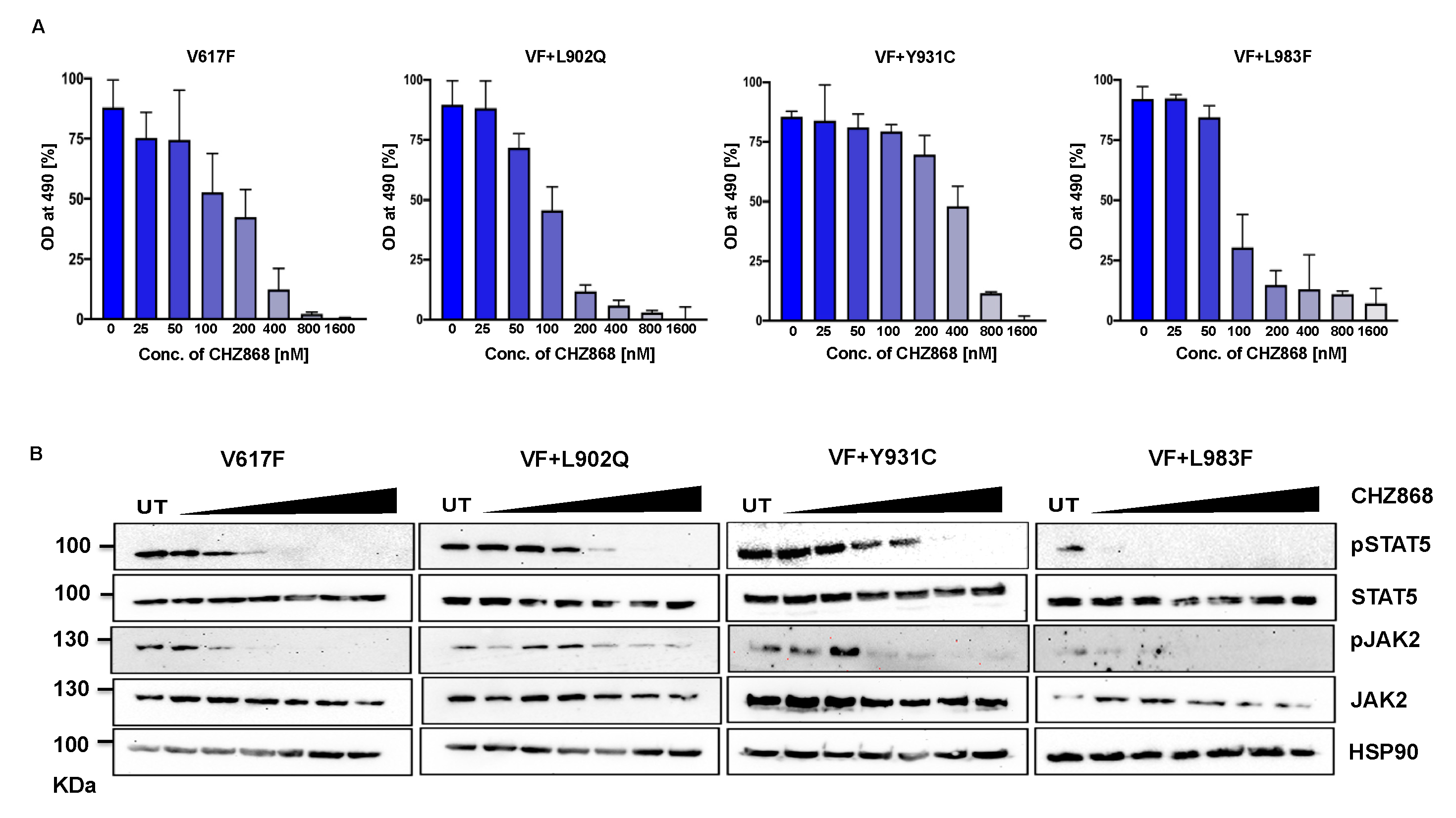
2.6. Type II JAK2 inhibitor CHZ 868 is potent towards the ruxolitinib variants
2.6.1. JAK1-L1010F exchange (L983F homologous JAK2) drives strong ruxolitinib resistance
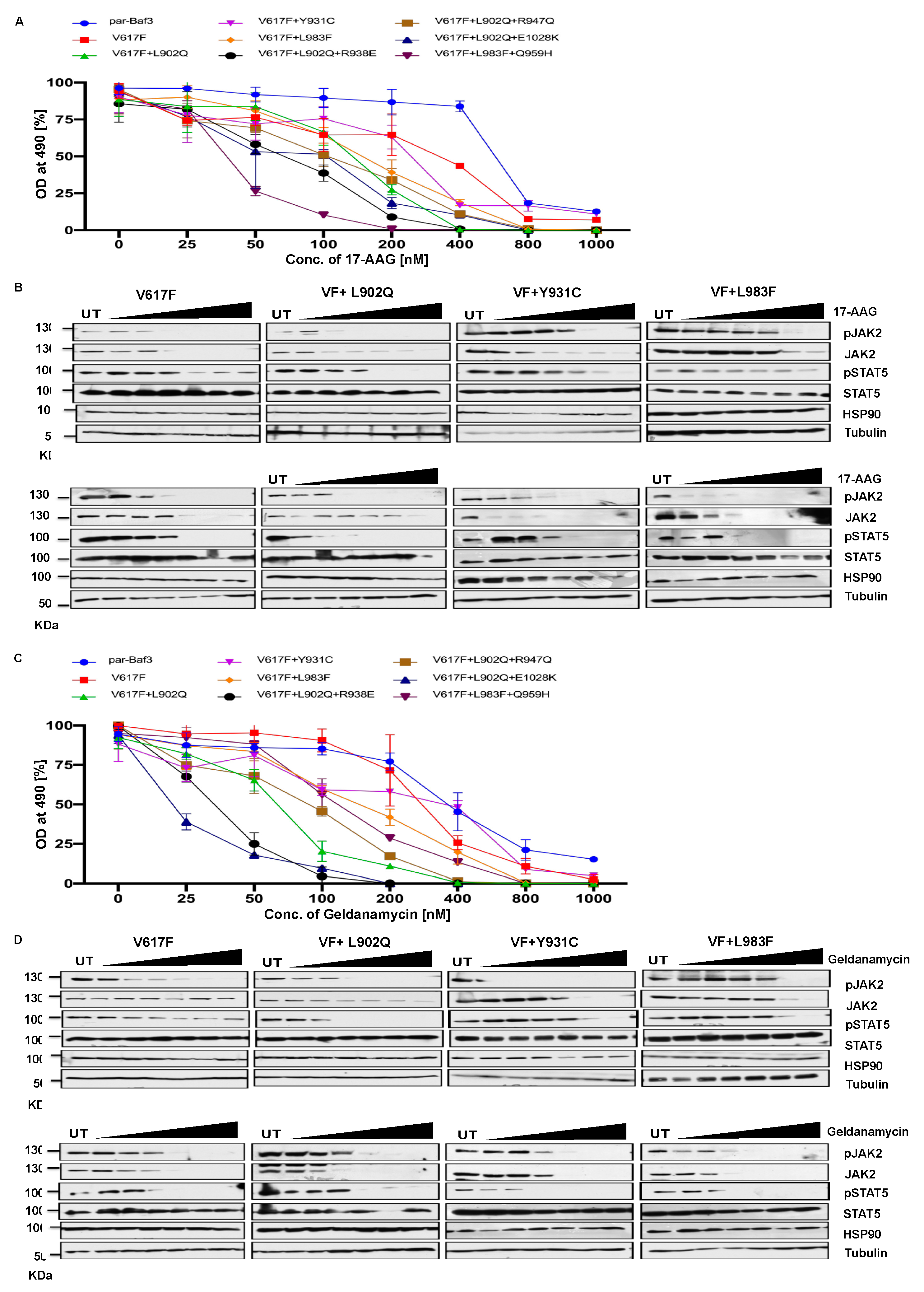
2.7. HSP 90 inhibitors are effective therapeutic agents against the ruxolitinib resistant variants
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Inhibitors
4.2. Cell culture and DNA constructs
4.3. Generation of drug-resistant variants
4.4. Proliferation assay
4.5. Western blot
4.6. Protein and Ligand Preparation
4.7. Molecular Docking Simulation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Neubauer H, Cumano A, Müller M, Wu H, Huffstadt U & Pfeffer K (1998) Jak2 deficiency defines an essential developmental checkpoint in definitive hematopoiesis. Cell 93, 397-409. [CrossRef]
- Parganas E, Wang D, Stravopodis D, Topham DJ, Marine JC, Teglund S, Vanin EF, Bodner S, Colamonici OR, van Deursen JM, Grosveld G & Ihle JN (1998) Jak2 is essential for signaling through a variety of cytokine receptors. Cell 93, 385-395. [CrossRef]
- Baxter EJ, Scott LM, Campbell PJ, East C, Fourouclas N, Swanton S, Vassiliou GS, Bench AJ, Boyd EM, Curtin N, Scott MA, Erber WN & Green AR (2005) Acquired mutation of the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in human myeloproliferative disorders. Lancet 365, 1054-1061. [CrossRef]
- James C, Ugo V, Le Couédic JP, Staerk J, Delhommeau F, Lacout C, Garçon L, Raslova H, Berger R, Bennaceur-Griscelli A, Villeval JL, Constantinescu SN, Casadevall N & Vainchenker W (2005) A unique clonal JAK2 mutation leading to constitutive signalling causes polycythaemia vera. Nature 434, 1144-1148. [CrossRef]
- Kralovics R, Passamonti F, Buser AS, Teo SS, Tiedt R, Passweg JR, Tichelli A, Cazzola M & Skoda RC (2005) A gain-of-function mutation of JAK2 in myeloproliferative disorders. N Engl J Med 352, 1779-1790. [CrossRef]
- Levine RL, Wadleigh M, Cools J, Ebert BL, Wernig G, Huntly BJ, Boggon TJ, Wlodarska I, Clark JJ, Moore S, Adelsperger J, Koo S, Lee JC, Gabriel S, Mercher T, D’Andrea A, Fröhling S, Döhner K, Marynen P, Vandenberghe P, Mesa RA, Tefferi A, Griffin JD, Eck MJ, Sellers WR, Meyerson M, Golub TR, Lee SJ & Gilliland DG (2005) Activating mutation in the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia, and myeloid metaplasia with myelofibrosis. Cancer Cell 7, 387-397. [CrossRef]
- Levine RL, Loriaux M, Huntly BJ, Loh ML, Beran M, Stoffregen E, Berger R, Clark JJ, Willis SG, Nguyen KT, Flores NJ, Estey E, Gattermann N, Armstrong S, Look AT, Griffin JD, Bernard OA, Heinrich MC, Gilliland DG, Druker B & Deininger MW (2005) The JAK2V617F activating mutation occurs in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia and acute myeloid leukemia, but not in acute lymphoblastic leukemia or chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 106, 3377-3379. [CrossRef]
- Steensma DP, Dewald GW, Lasho TL, Powell HL, McClure RF, Levine RL, Gilliland DG & Tefferi A (2005) The JAK2 V617F activating tyrosine kinase mutation is an infrequent event in both "atypical" myeloproliferative disorders and myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 106, 1207-1209. [CrossRef]
- Scott LM, Tong W, Levine RL, Scott MA, Beer PA, Stratton MR, Futreal PA, Erber WN, McMullin MF, Harrison CN, Warren AJ, Gilliland DG, Lodish HF & Green AR (2007) JAK2 exon 12 mutations in polycythemia vera and idiopathic erythrocytosis. N Engl J Med 356, 459-468. [CrossRef]
- Grunebach F, Bross-Bach U, Kanz L & Brossart P (2006) Detection of a new JAK2 D620E mutation in addition to V617F in a patient with polycythemia vera. Leukemia 20, 2210-2211. [CrossRef]
- Schnittger S, Bacher U, Kern W, Schröder M, Haferlach T & Schoch C (2006) Report on two novel nucleotide exchanges in the JAK2 pseudokinase domain: D620E and E627E. Leukemia 20, 2195-2197. [CrossRef]
- Kratz CP, Böll S, Kontny U, Schrappe M, Niemeyer CM & Stanulla M (2006) Mutational screen reveals a novel JAK2 mutation, L611S, in a child with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 20, 381-383. [CrossRef]
- Malinge S, Ben-Abdelali R, Settegrana C, Radford-Weiss I, Debre M, Beldjord K, Macintyre EA, Villeval JL, Vainchenker W, Berger R, Bernard OA, Delabesse E & Penard-Lacronique V (2007) Novel activating JAK2 mutation in a patient with Down syndrome and B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 109, 2202-2204. [CrossRef]
- Lacronique V, Boureux A, Valle VD, Poirel H, Quang CT, Mauchauffé M, Berthou C, Lessard M, Berger R, Ghysdael J & Bernard OA (1997) A TEL-JAK2 fusion protein with constitutive kinase activity in human leukemia. Science 278, 1309-1312. [CrossRef]
- Najfeld V, Cozza A, Berkofsy-Fessler W, Prchal J & Scalise A (2007) Numerical gain and structural rearrangements of JAK2, identified by FISH, characterize both JAK2617V>F-positive and -negative patients with Ph-negative MPD, myelodysplasia, and B-lymphoid neoplasms. Exp Hematol 35, 1668-1676. [CrossRef]
- Marotta LL, Almendro V, Marusyk A, Shipitsin M, Schemme J, Walker SR, Bloushtain-Qimron N, Kim JJ, Choudhury SA, Maruyama R, Wu Z, Gönen M, Mulvey LA, Bessarabova MO, Huh SJ, Silver SJ, Kim SY, Park SY, Lee HE, Anderson KS, Richardson AL, Nikolskaya T, Nikolsky Y, Liu XS, Root DE, Hahn WC, Frank DA & Polyak K (2011) The JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway is required for growth of CD44⁺CD24⁻ stem cell-like breast cancer cells in human tumors. J Clin Invest 121, 2723-2735. [CrossRef]
- Sonbol MB, Firwana B, Zarzour A, Morad M, Rana V & Tiu RV (2013) Comprehensive review of JAK inhibitors in myeloproliferative neoplasms. Ther Adv Hematol 4, 15-35. [CrossRef]
- Pardanani A, Tefferi A, Jamieson C, Gabrail NY, Lebedinsky C, Gao G, Liu F, Xu C, Cao H & Talpaz M (2015) A phase 2 randomized dose-ranging study of the JAK2-selective inhibitor fedratinib (SAR302503) in patients with myelofibrosis. Blood Cancer J 5, e335. [CrossRef]
- Verstovsek S, Kantarjian H, Mesa RA, Pardanani AD, Cortes-Franco J, Thomas DA, Estrov Z, Fridman JS, Bradley EC, Erickson-Viitanen S, Vaddi K, Levy R & Tefferi A (2010) Safety and efficacy of INCB018424, a JAK1 and JAK2 inhibitor, in myelofibrosis. N Engl J Med 363, 1117-1127. [CrossRef]
- Bose P & Verstovsek S (2020) JAK Inhibition for the Treatment of Myelofibrosis: Limitations and Future Perspectives. Hemasphere 4, e424. [CrossRef]
- Kvasnicka HM, Thiele J, Bueso-Ramos CE, Sun W, Cortes J, Kantarjian HM & Verstovsek S (2018) Long-term effects of ruxolitinib versus best available therapy on bone marrow fibrosis in patients with myelofibrosis. J Hematol Oncol 11, 42. [CrossRef]
- Verstovsek S, Gotlib J, Mesa RA, Vannucchi AM, Kiladjian JJ, Cervantes F, Harrison CN, Paquette R, Sun W, Naim A, Langmuir P, Dong T, Gopalakrishna P & Gupta V (2017) Long-term survival in patients treated with ruxolitinib for myelofibrosis: COMFORT-I and -II pooled analyses. J Hematol Oncol 10, 156. [CrossRef]
- Verstovsek S, Mesa RA, Gotlib J, Gupta V, DiPersio JF, Catalano JV, Deininger MW, Miller CB, Silver RT, Talpaz M, Winton EF, Harvey JH, Jr., Arcasoy MO, Hexner EO, Lyons RM, Paquette R, Raza A, Jones M, Kornacki D, Sun K & Kantarjian H (2017) Long-term treatment with ruxolitinib for patients with myelofibrosis: 5-year update from the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 COMFORT-I trial. J Hematol Oncol 10, 55. [CrossRef]
- Pandey G, Kuykendall AT & Reuther GW (2022) JAK2 inhibitor persistence in MPN: uncovering a central role of ERK activation. Blood Cancer J 12, 13. [CrossRef]
- Santos FP, Kantarjian HM, Jain N, Manshouri T, Thomas DA, Garcia-Manero G, Kennedy D, Estrov Z, Cortes J & Verstovsek S (2010) Phase 2 study of CEP-701, an orally available JAK2 inhibitor, in patients with primary or post-polycythemia vera/essential thrombocythemia myelofibrosis. Blood 115, 1131-1136. [CrossRef]
- Gorre ME, Mohammed M, Ellwood K, Hsu N, Paquette R, Rao PN & Sawyers CL (2001) Clinical resistance to STI-571 cancer therapy caused by BCR-ABL gene mutation or amplification. Science 293, 876-880. [CrossRef]
- Pao W, Miller VA, Politi KA, Riely GJ, Somwar R, Zakowski MF, Kris MG & Varmus H (2005) Acquired resistance of lung adenocarcinomas to gefitinib or erlotinib is associated with a second mutation in the EGFR kinase domain. PLoS Med 2, e73. [CrossRef]
- Tamborini E, Bonadiman L, Greco A, Albertini V, Negri T, Gronchi A, Bertulli R, Colecchia M, Casali PG, Pierotti MA & Pilotti S (2004) A new mutation in the KIT ATP pocket causes acquired resistance to imatinib in a gastrointestinal stromal tumor patient. Gastroenterology 127, 294-299. [CrossRef]
- Azam M, Latek RR & Daley GQ (2003) Mechanisms of autoinhibition and STI-571/imatinib resistance revealed by mutagenesis of BCR-ABL. Cell 112, 831-843. [CrossRef]
- Lee TS, Potts SJ & Albitar M (2009) Basis for resistance to imatinib in 16 BCR-ABL mutants as determined using molecular dynamics. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov 4, 164-173. [CrossRef]
- von Bubnoff N, Schneller F, Peschel C & Duyster J (2002) BCR-ABL gene mutations in relation to clinical resistance of Philadelphia-chromosome-positive leukaemia to STI571: a prospective study. Lancet 359, 487-491. [CrossRef]
- Weigert O, Lane AA, Bird L, Kopp N, Chapuy B, van Bodegom D, Toms AV, Marubayashi S, Christie AL, McKeown M, Paranal RM, Bradner JE, Yoda A, Gaul C, Vangrevelinghe E, Romanet V, Murakami M, Tiedt R, Ebel N, Evrot E, De Pover A, Regnier CH, Erdmann D, Hofmann F, Eck MJ, Sallan SE, Levine RL, Kung AL, Baffert F, Radimerski T & Weinstock DM (2012) Genetic resistance to JAK2 enzymatic inhibitors is overcome by HSP90 inhibition. J Exp Med 209, 259-273. [CrossRef]
- Griswold IJ, MacPartlin M, Bumm T, Goss VL, O’Hare T, Lee KA, Corbin AS, Stoffregen EP, Smith C, Johnson K, Moseson EM, Wood LJ, Polakiewicz RD, Druker BJ & Deininger MW (2006) Kinase domain mutants of Bcr-Abl exhibit altered transformation potency, kinase activity, and substrate utilization, irrespective of sensitivity to imatinib. Mol Cell Biol 26, 6082-6093. [CrossRef]
- Gorantla SP, Dechow TN, Grundler R, Illert AL, Zum Buschenfelde CM, Kremer M, Peschel C & Duyster J (2010) Oncogenic JAK2V617F requires an intact SH2-like domain for constitutive activation and induction of a myeloproliferative disease in mice. Blood 116, 4600-4611. [CrossRef]
- Andraos R, Qian Z, Bonenfant D, Rubert J, Vangrevelinghe E, Scheufler C, Marque F, Régnier CH, De Pover A, Ryckelynck H, Bhagwat N, Koppikar P, Goel A, Wyder L, Tavares G, Baffert F, Pissot-Soldermann C, Manley PW, Gaul C, Voshol H, Levine RL, Sellers WR, Hofmann F & Radimerski T (2012) Modulation of activation-loop phosphorylation by JAK inhibitors is binding mode dependent. Cancer Discov 2, 512-523. [CrossRef]
- Kesarwani M, Huber E, Kincaid Z, Evelyn CR, Biesiada J, Rance M, Thapa MB, Shah NP, Meller J, Zheng Y & Azam M (2015) Targeting substrate-site in Jak2 kinase prevents emergence of genetic resistance. Sci Rep 5, 14538. [CrossRef]
- Meyer SC, Keller MD, Chiu S, Koppikar P, Guryanova OA, Rapaport F, Xu K, Manova K, Pankov D, O’Reilly RJ, Kleppe M, McKenney AS, Shih AH, Shank K, Ahn J, Papalexi E, Spitzer B, Socci N, Viale A, Mandon E, Ebel N, Andraos R, Rubert J, Dammassa E, Romanet V, Dolemeyer A, Zender M, Heinlein M, Rampal R, Weinberg RS, Hoffman R, Sellers WR, Hofmann F, Murakami M, Baffert F, Gaul C, Radimerski T & Levine RL (2015) CHZ868, a Type II JAK2 Inhibitor, Reverses Type I JAK Inhibitor Persistence and Demonstrates Efficacy in Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Cancer Cell 28, 15-28. [CrossRef]
- Wu SC, Li LS, Kopp N, Montero J, Chapuy B, Yoda A, Christie AL, Liu H, Christodoulou A, van Bodegom D, van der Zwet J, Layer JV, Tivey T, Lane AA, Ryan JA, Ng SY, DeAngelo DJ, Stone RM, Steensma D, Wadleigh M, Harris M, Mandon E, Ebel N, Andraos R, Romanet V, Dolemeyer A, Sterker D, Zender M, Rodig SJ, Murakami M, Hofmann F, Kuo F, Eck MJ, Silverman LB, Sallan SE, Letai A, Baffert F, Vangrevelinghe E, Radimerski T, Gaul C & Weinstock DM (2015) Activity of the Type II JAK2 Inhibitor CHZ868 in B Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancer Cell 28, 29-41. [CrossRef]
- Marubayashi S, Koppikar P, Taldone T, Abdel-Wahab O, West N, Bhagwat N, Caldas-Lopes E, Ross KN, Gönen M, Gozman A, Ahn JH, Rodina A, Ouerfelli O, Yang G, Hedvat C, Bradner JE, Chiosis G & Levine RL (2010) HSP90 is a therapeutic target in JAK2-dependent myeloproliferative neoplasms in mice and humans. J Clin Invest 120, 3578-3593. [CrossRef]
- Wardrop D & Steensma DP (2009) Is refractory anaemia with ring sideroblasts and thrombocytosis (RARS-T) a necessary or useful diagnostic category? Br J Haematol 144, 809-817. [CrossRef]
- Apperley JF (2007) Part I: mechanisms of resistance to imatinib in chronic myeloid leukaemia. Lancet Oncol 8, 1018-1029. [CrossRef]
- Downes CEJ, McClure BJ, Bruning JB, Page E, Breen J, Rehn J, Yeung DT & White DL (2021) Acquired JAK2 mutations confer resistance to JAK inhibitors in cell models of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. NPJ Precis Oncol 5, 75. [CrossRef]
- Deshpande A, Reddy MM, Schade GO, Ray A, Chowdary TK, Griffin JD & Sattler M (2012) Kinase domain mutations confer resistance to novel inhibitors targeting JAK2V617F in myeloproliferative neoplasms. Leukemia 26, 708-715. [CrossRef]
- Furitsu T, Tsujimura T, Tono T, Ikeda H, Kitayama H, Koshimizu U, Sugahara H, Butterfield JH, Ashman LK, Kanayama Y & et al. (1993) Identification of mutations in the coding sequence of the proto-oncogene c-kit in a human mast cell leukemia cell line causing ligand-independent activation of c-kit product. J Clin Invest 92, 1736-1744. [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto Y, Kiyoi H, Nakano Y, Suzuki R, Kodera Y, Miyawaki S, Asou N, Kuriyama K, Yagasaki F, Shimazaki C, Akiyama H, Saito K, Nishimura M, Motoji T, Shinagawa K, Takeshita A, Saito H, Ueda R, Ohno R & Naoe T (2001) Activating mutation of D835 within the activation loop of FLT3 in human hematologic malignancies. Blood 97, 2434-2439. [CrossRef]
- Hornakova T, Springuel L, Devreux J, Dusa A, Constantinescu SN, Knoops L & Renauld JC (2011) Oncogenic JAK1 and JAK2-activating mutations resistant to ATP-competitive inhibitors. Haematologica 96, 845-853. [CrossRef]
- Marit MR, Chohan M, Matthew N, Huang K, Kuntz DA, Rose DR & Barber DL (2012) Random mutagenesis reveals residues of JAK2 critical in evading inhibition by a tyrosine kinase inhibitor. PLoS One 7, e43437. [CrossRef]
- Koppikar P, Bhagwat N, Kilpivaara O, Manshouri T, Adli M, Hricik T, Liu F, Saunders LM, Mullally A, Abdel-Wahab O, Leung L, Weinstein A, Marubayashi S, Goel A, Gönen M, Estrov Z, Ebert BL, Chiosis G, Nimer SD, Bernstein BE, Verstovsek S & Levine RL (2012) Heterodimeric JAK-STAT activation as a mechanism of persistence to JAK2 inhibitor therapy. Nature 489, 155-159. [CrossRef]
- Gorantla SP, Mueller TA, Albers-Leischner C, Rudelius M, von Bubnoff N & Duyster J (2023) A newly identified 45-kDa JAK2 variant with an altered kinase domain structure represents a novel mode of JAK2 kinase inhibitor resistance. Mol Oncol. [CrossRef]
- Rummelt C, Gorantla SP, Meggendorfer M, Charlet A, Endres C, Dohner K, Heidel FH, Fischer T, Haferlach T, Duyster J & von Bubnoff N (2021) Activating JAK-mutations confer resistance to FLT3 kinase inhibitors in FLT3-ITD positive AML in vitro and in vivo. Leukemia 35, 2017-2029. [CrossRef]
- Bercovich D, Ganmore I, Scott LM, Wainreb G, Birger Y, Elimelech A, Shochat C, Cazzaniga G, Biondi A, Basso G, Cario G, Schrappe M, Stanulla M, Strehl S, Haas OA, Mann G, Binder V, Borkhardt A, Kempski H, Trka J, Bielorei B, Avigad S, Stark B, Smith O, Dastugue N, Bourquin JP, Tal NB, Green AR & Izraeli S (2008) Mutations of JAK2 in acute lymphoblastic leukaemias associated with Down’s syndrome. Lancet 372, 1484-1492. [CrossRef]
- Mullighan CG, Zhang J, Harvey RC, Collins-Underwood JR, Schulman BA, Phillips LA, Tasian SK, Loh ML, Su X, Liu W, Devidas M, Atlas SR, Chen IM, Clifford RJ, Gerhard DS, Carroll WL, Reaman GH, Smith M, Downing JR, Hunger SP & Willman CL (2009) JAK mutations in high-risk childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106, 9414-9418. [CrossRef]
- Kaplan HG, Jin R, Bifulco CB, Scanlan JM & Corwin DR (2022) PCM1-JAK2 Fusion Tyrosine Kinase Gene-Related Neoplasia: A Systematic Review of the Clinical Literature. Oncologist 27, e661-e670. [CrossRef]
- Elnaggar MM, Agersborg S, Sahoo T, Girgin A, Ma W, Rakkhit R, Zorrilla I & Leal A (2012) BCR-JAK2 fusion as a result of a translocation (9;22)(p24;q11.2) in a patient with CML-like myeloproliferative disease. Mol Cytogenet 5, 23. [CrossRef]
- Richardson PG, Mitsiades CS, Laubach JP, Lonial S, Chanan-Khan AA & Anderson KC (2011) Inhibition of heat shock protein 90 (HSP90) as a therapeutic strategy for the treatment of myeloma and other cancers. Br J Haematol 152, 367-379. [CrossRef]
- von Bubnoff N, Gorantla SP, Engh RA, Oliveira TM, Thone S, Aberg E, Peschel C & Duyster J (2011) The low frequency of clinical resistance to PDGFR inhibitors in myeloid neoplasms with abnormalities of PDGFRA might be related to the limited repertoire of possible PDGFRA kinase domain mutations in vitro. Oncogene 30, 933-943. [CrossRef]
- Duyster J, Baskaran R & Wang JY (1995) Src homology 2 domain as a specificity determinant in the c-Abl-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation of the RNA polymerase II carboxyl-terminal repeated domain. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 92, 1555-1559. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




