Submitted:
02 January 2024
Posted:
03 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
3. Diabetic Retinopathy
| Study | Equipment | Number of eyes and study design | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boile et al. 2023 [15] | UWF-FA Optos® 200Tx versus OCTA with montage of 12 × 12 mm fields of several visual fixations using the PLEX Elite 9000® (field of 24 x 24 mm) | 51 severe NPDR and PDR eyes, treatment-naïve; analysis of the utility of the non-perfusion index (NPI) | The NPI was significantly higher in eyes with PDR (18.94% vs. 7.51%; P<0.01). Measurement of NPI on the whole wide-field OCTA image was not sensitive enough to replace the detection of NV for the diagnosis of PDR. UWF-FA detected NV foci outside the range of WF-OCTA. |
| Bajka et al. 2023 [16] | Xephilio OCT-S1 (23 x 20 mm OCTA scan) versus Optos California UWF-FA | 15 eyes; evaluation of the retinal NP and NV; calculation of the ischemic index and VD | Both UWF-FA and WF-OCTA detected NP in 11 eyes (73%); NV was detected in four eyes by UWF-FA and in three eyes by WF-OCTA. |
| Hamada et al. 2023 [17] | UWF-FA (Optos) versus Canon Xephilio OCT-S1 (23 x 20 mm) OCTA scan | 108 gradable images; NV detection | With UWF-FA, 175 NV lesions were detected in 40 eyes; with WF-OCTA, 156 NV lesions were detected, with 118 of them confirmed by UWF-FA (true positive). Of 57 false negative lesions, the primary causes were being outside the scan range (26 lesions) and segmentation errors (21 lesions). WF-OCTA achieved a sensitivity of 95% and specificity of 88% in detecting eyes with NV. |
| Hirano et al. 2023 [18] | Xephilio OCT-S1 (23 x 20 mm OCTA scan) versus conventional FA | 64 eyes; NV detection in PDR patients | WF-OCTA revealed 96% (162) of NV sites when the scan was fovea-centered and 99% (166) when it was disc-centered compared to conventional FA (168 sites). With a mosaic of these two fields, all NVs were visualized by WF-OCTA. |
| Cui et al. 2021 [19] | UWF-FA Optos® 200Tx versus OCTA with montage of 12 × 12 mm fields of several visual fixations using the PLEX Elite 9000® | 152 eyes of 101 patients; comparing WF- OCTA with UWF-CP and UWF-FA in detection of DR lesions | WF-OCTA was superior to UWF-CP in detecting IRMAs (P<0.001) and NVE/NVD (P=0.007). The detection rates for microaneurysms, IRMAs, NVE/NVD, and NPs with WF-OCTA were comparable with those of UWF-FA (P>0.05). A comparison of UWF-OCTA plus UWF-CP with UWF-FA showed identical detection rates for microaneurysms, IRMAs, NVE/NVD, and NP areas (P>0.005). There was high agreement (κ=0.916) between WF-OCTA and UWF-FA in classifying DR. |
| Picchi et al. 2020 [20] | UWF-FA Optos® 200Tx versus OCTA with 12 × 12 mm fields of five visual fixations using the PLEX Elite 9000® | 82 eyes; NV detection in PDR patients | NVD was detected in 13 eyes by UWF-CP, 35 eyes by UWF-FA, and 37 eyes by WF-OCTA. Upon review of the 2500 OCT B-scans with superimposed flow overlay, NVD was confirmed in 37 eyes. UWF-CP analysis detected 62 foci of NVE out of the 196 confirmed by B-scan (31.6% detection rate). An additional 11 foci of NVE seen on UWF-CP were not confirmed by B-Scan (15% false positive rate). UWF-FA identified 182 foci of NVE (detection rate 91.3%); WF-OCTA detected 196 NVE (detection rate 100%). The rate of false positives for both UWF-FA and WF-OCTA was < 2%. Respectively, the sensitivity and specificity of NVD detection were 35.1% and 97.8% for UWF-CP, 94.6% and 100% for UWF-FA, and 100% and 100% for WF-OCTA. |
| Pellegrini et al. 2019 [21] | 55-degree FA (Spectralis Heidelberg Engineering) versus standard OCTA Plex Elite OCTA (Carl Zeiss) 12 x 12 mm and the same OCTA with prototype +20.0 D lens | 43 eyes (32 DR, 8 RVO, 2 RVO with radiation retinopathy, 1 Coats disease); comparison of field of view, NP areas, NV, and vessel density | The extension of NP areas was significantly larger with extended field imaging OCTA versus standard OCTA and FA (34.22 vs 20.46 vs 27.56 mm2). No differences were found between the devices with respect to the detection of NV. The mean vessel density was significantly lower with extended field imaging OCTA. Nevertheless, FA gave more details of the perfusion status of the retina; in some cases, OCTA erroneously imagined hypoperfused areas that were not confirmed by FA. |
| Russell et al. 2019 [22] | UWF-FA Optos® 200Tx versus PLEX Elite 9000® OCTA with 12 × 12 mm fields of five visual fixations | 20 eyes of 15 patients; observation of NV after panretinal photocoagulation (PRP) at one week, one month, and three months |
The en-face SS-OCTA 12 × 12 mm vitreoretinal interface slab images showed NV at baseline in 18 of 20 eyes (90%). Concerning the remaining two eyes, the posterior pole montage captured peripheral NV in one eye; in the other eye, no evidence of NV was detected with either UWF FA or SS-OCTA. Based on UWF-FA, eight eyes (47%) progressed and nine eyes (53%) regressed. Identical conclusions were reached from SS-OCTA scans. SS-OCTA provided a more detailed visualization of the vascular changes. |
| Sawada et al. 2018 [23] | UWF-FA Optos® panoramic 200Tx versus OCTA with 12 × 12 mm fields of five visual fixations using the PLEX Elite 9000® | 58 eyes; detection of NP areas or NV | NP areas were detected in 47 eyes by UWF-FA versus 48 eyes by OCTA; NV was detected in 25 eyes by UWF-FA versus 26 by OCTA. The sensitivity for the detection of NP areas using OCTA was 0.98 and the specificity was 0.82; the sensitivity for the detection of NV was 1.0 and the specificity was 0.97. |
| Zhang et al. 2018 [24] | OCTA PLEX Elite 9000® montage of 16 images 6 x 6 mm (100 degrees) versus traditional 50-degree FA | Three PDR patients; comparison of montage UWF OCTA to 50-degree FA | More details regarding the capillary network and visualization of NVs were missing in standard FA. |

4. Retinal Vein Occlusion
| Study | Equipment | Number of eyes | Study design and results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Siying et al. 2022 [37] | UWF-FA Optos 200Tx versus a single capture of 24 x 20 mm wide-field SS-OCTA scan using BM400K (Bmizar, TowardPi Medical Technology Co., Ltd, Beijing, China) |
32 treatment-naïve eyes | Comparison of the FAZ area, FAZ perimeter, and NP areas (measurements at SCP); the measurements were performed manually. The median FAZ area was 0.373 mm2 (range 0.277–0.48) on SS-OCTA and 0.370 mm2 (range 0.277–0.48) on UWF-FA. The median FAZ perimeter was 2.480 mm (range 2.011–2.998) and 2.330 mm (range 2.027–2.807) on the SS-OCTA and UWF-FA images, respectively. No significant difference was noted (P=0.818 and P=0.536, respectively). The mean NP area was larger on SS-OCTA than on UWF-FA (89.977 ± 78.805 vs. 87.944 ± 77.444 mm2, P=0.037) at corresponding images; SS-OCTA was superior in visualizing capillary changes and collateral vessels. |
| Glacet-Bernard et al. 2021 [38] | WF-OCTA (PLEX Elite, Carl Zeiss Meditec, Dublin, CA) with a montage of five 12 × 12 mm images versus UWF-FA (Optos, 200 degrees) | 43 eyes | The ischemic index on UWF-FA and the vascular density in the superficial and deep plexus correlated significantly (P=0.019, r=0.357 and P<0.013, r=0.375, respectively). The qualitative classification on wide-field OCTA and the ischemic index on UWF-FA correlated significantly (P<0.001, r=0.618). For the detection of marked non-perfusion (ischemic index ≥ 25%), wide-field OCTA had a sensitivity of 100% and a specificity of 64.9%. |
| Kadamodo et al. 2021 [39] | Plex Elite 9000 (Carl Zeiss) montage of five 12 x 12 mm scans versus single OCTA scan and UWF-FA, Optos 200TX |
26 treatment-naive eyes | The retinal areas of NP measured using single OCTA and panoramic OCTA were compatible with those measured using UWF-FA (P<0.001 for both). Retinal neovascularization lesions were observed in four (15.4%) of 26 eyes. For patients with accompanying neovascularization, the retinal NP measured using UWF-FA, single OCTA, and panoramic OCTA were 187.9 ± 39.5 mm2 (disc area 109.9 ± 21.4), 34.3 ± 13.7 mm2 (disc area 19.9 ± 7.7), and 106.6 ± 24.5 mm2 (disc area 62.4 ± 13.6), respectively, and were larger than for those without neovascularization (P<0.001, P<0.014, and P<0.001, respectively). |
| Huemer et al. 2021 [40] | Plex Elite 9000 (Carl Zeiss) montage of five 12 x 12 mm scans versus standard examination and UWF-FA, Optos 200TX if available |
39 eyes with ischemic RVO | Retrospective study. NVE was detected in 41% of eyes by WF-OCTA versus 10.3% via standard examination; in one case, NVE detected by OCTA was not revealed by UWF-FA. WF-OCTA provided sea-fan and nodular morphological characteristics of NVE vessels. UWF-OCT images provided details on the location of NV in reference to the posterior hyaloid (sea-fan growing along the posterior hyaloid and nodular close to the retinal surface). Nodular vessels were not detected during standard examinations but only via UWF exams. Sea-fan vessels were detected in all cases during standard exams. |
| Shiraki 2019 [41] | Plex Elite 9000 (Carl Zeiss), a mosaic of five 12 x 12 mm scans versus UWF-FA Optos 200TX | 23 eyes | The mean area of NP in the OCTA images was 81.0 ± 66.8 mm2 (range 0.0–188.8) versus 84.7 ± 72.5 mm2 (range 0.0–221.9) on FA (for corresponding examined retinal areas in both tests). The total area of NP on FA had a mean of 184.1 ± 167.7 mm2. The mean VD was 27.6 ± 3.5% (range 19.6–33.7); the mean VL was 12.4 ± 8.5% (range 5.4–31.3). Separate regression analysis of the areas of retinal non-perfusion in FA (p=0.0004, R2=0.4627) and the total FA (p=0.0008, R2=0.4214) images showed a significant association with the VL. |
| Kakihara et al. 2018 [42] | Plex Elite 9000 SS-OCTA with EFI (+20 D lens); 12 x 12 mm scans versus standard FA | 23 eyes of 22 patients | The average extension rate of EFI-SS-OCTA over SS-OCTA was 1.39 ± 0.06 and the average scanning area was enlarged by 76.4%. There was a moderate concordance to FA images in reference to NP areas (Cohen’s unweighted Kappa coefficient = 0.60). The OCTA images showed a larger extent of NP compared to FA, as the authors note, due to a lack of masking by the leakage from retinal vessels present in FA. |
| Kimura et al. 2016 [43] | RTVue Avanti with extended field imaging (+20 D lens), basic 8 x 8 mm scan versus standard FA (Heidelberg Retina Angiograph 2) with 30 degrees of field of view | 10 eyes of nine patients | Enlargement of 188.5% of the standard field with +20 D lens; good definition of NP areas in SCP. The average area of NP determined by EFI OCTA was 18.3 mm2 versus 16.8 mm2 using fluorescein angiography. |
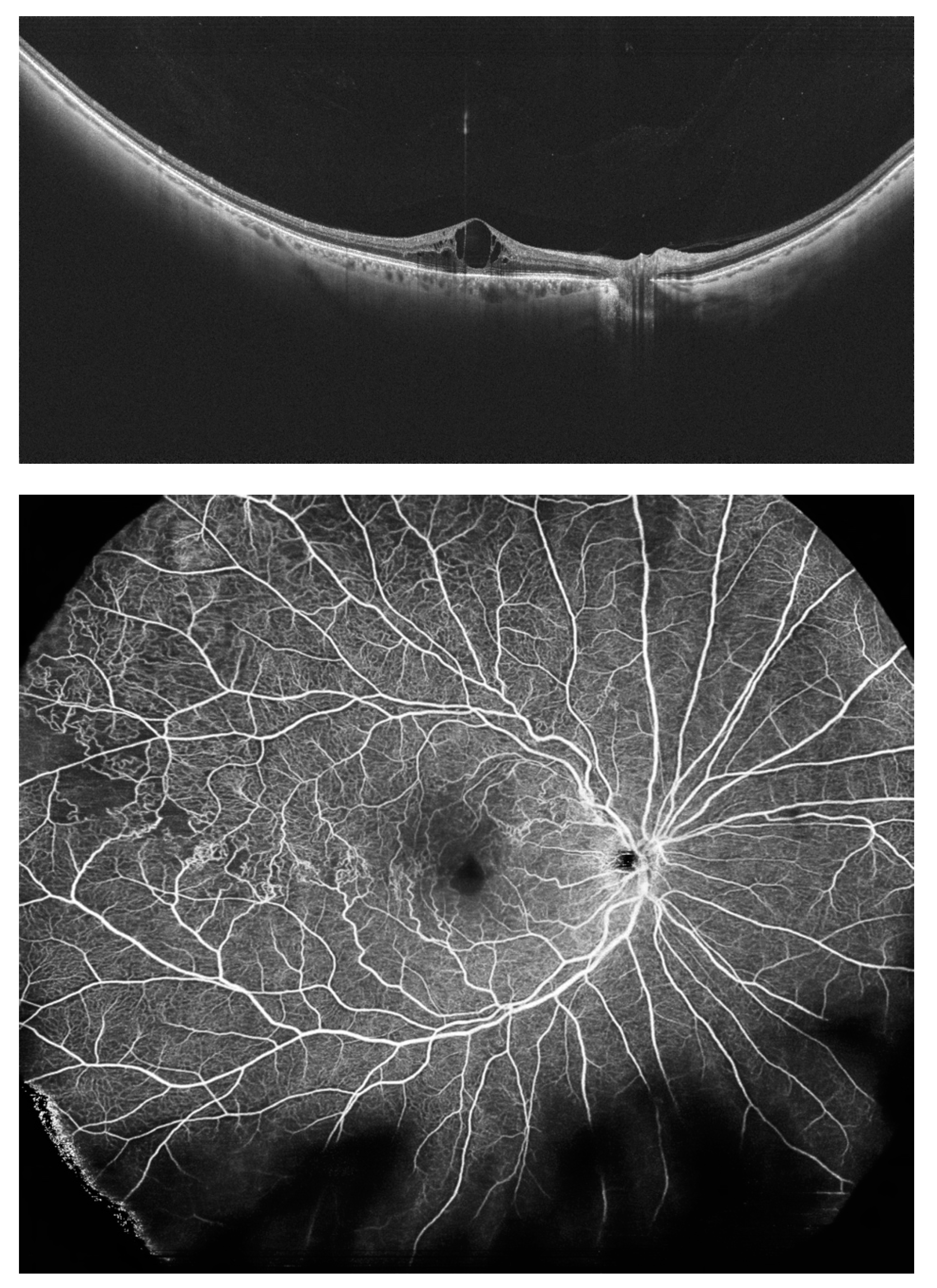
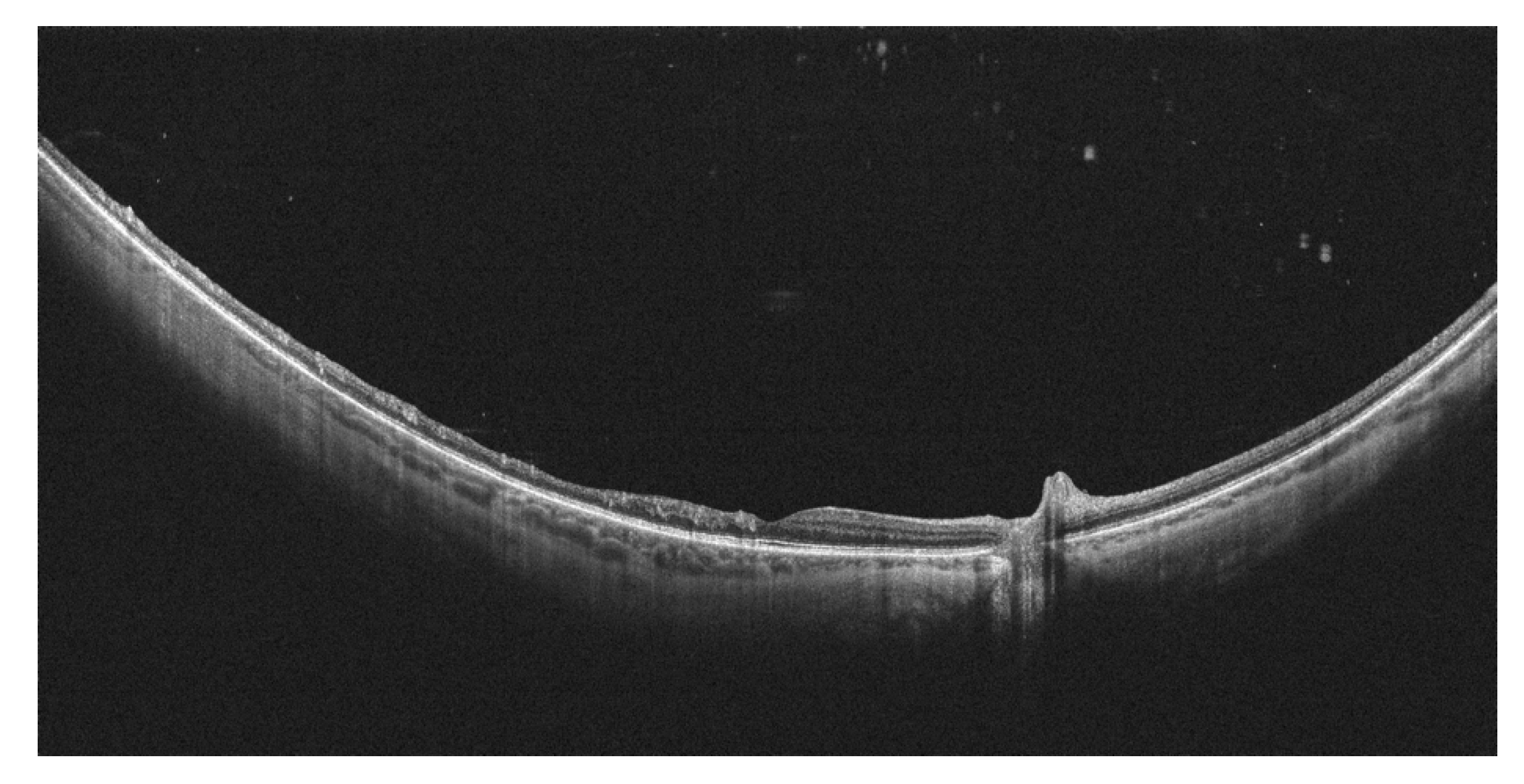
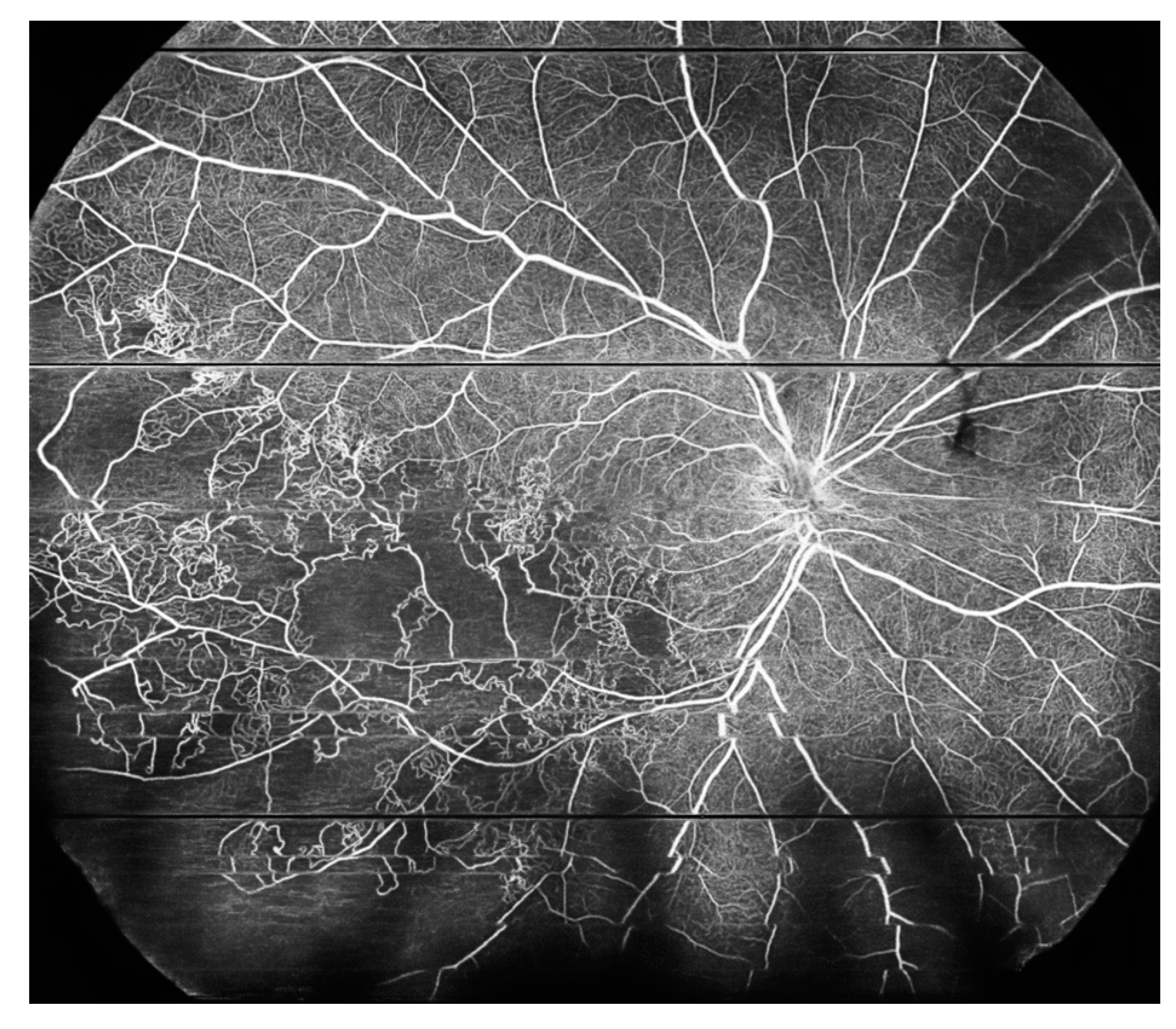
5. Peripheral Retinal Telangiectasia and Coats Disease
6. Peripheral Retinal Degeneration
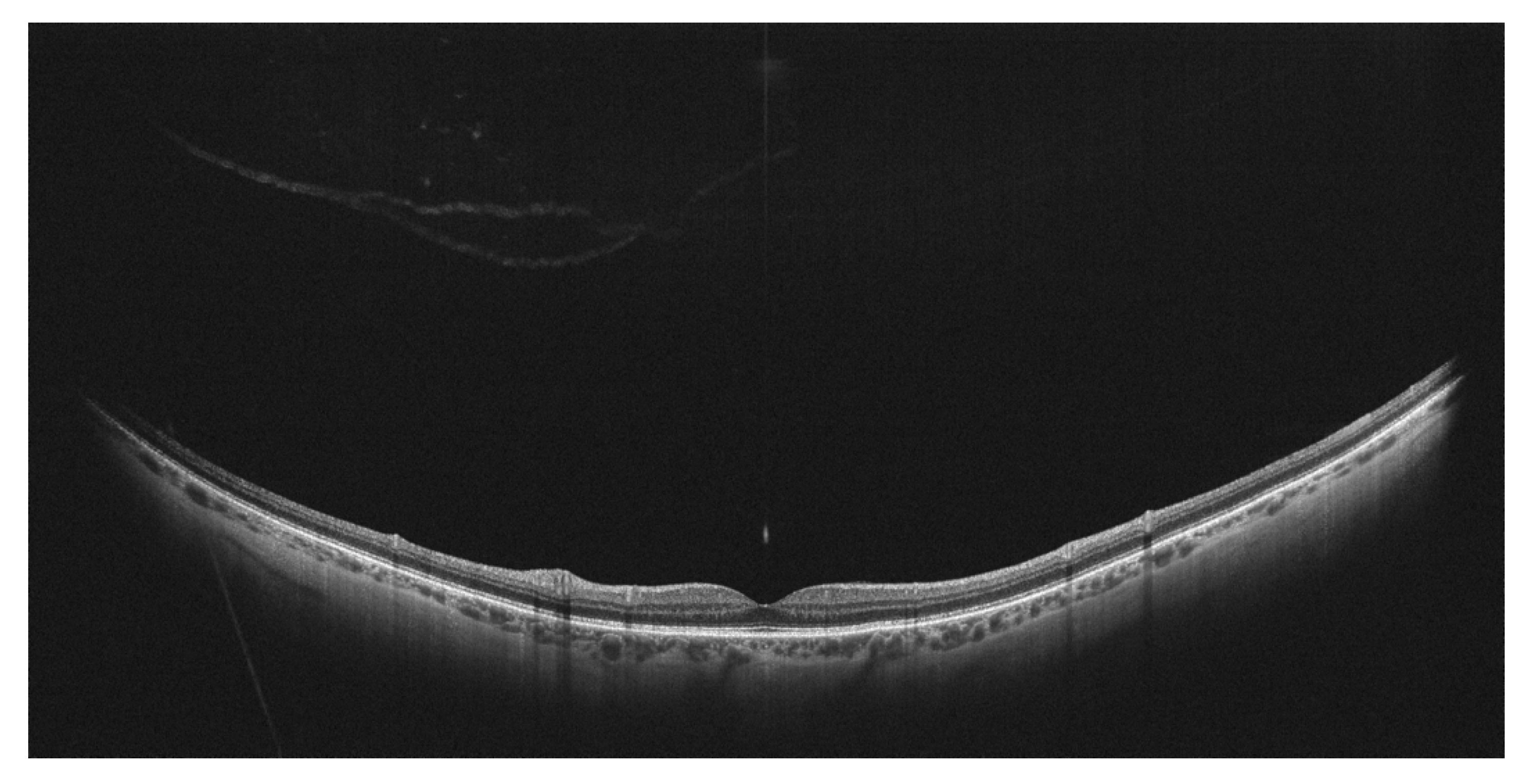
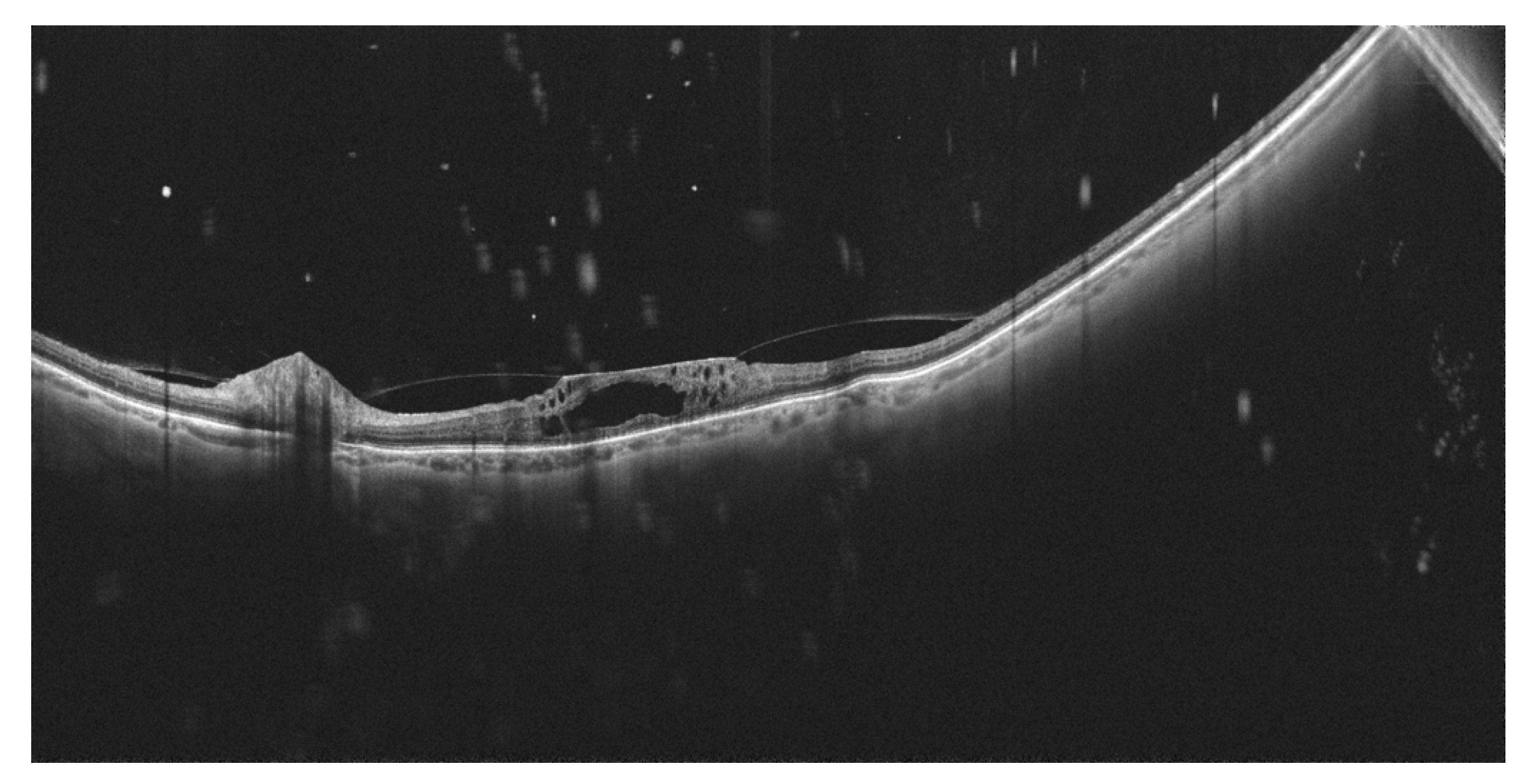
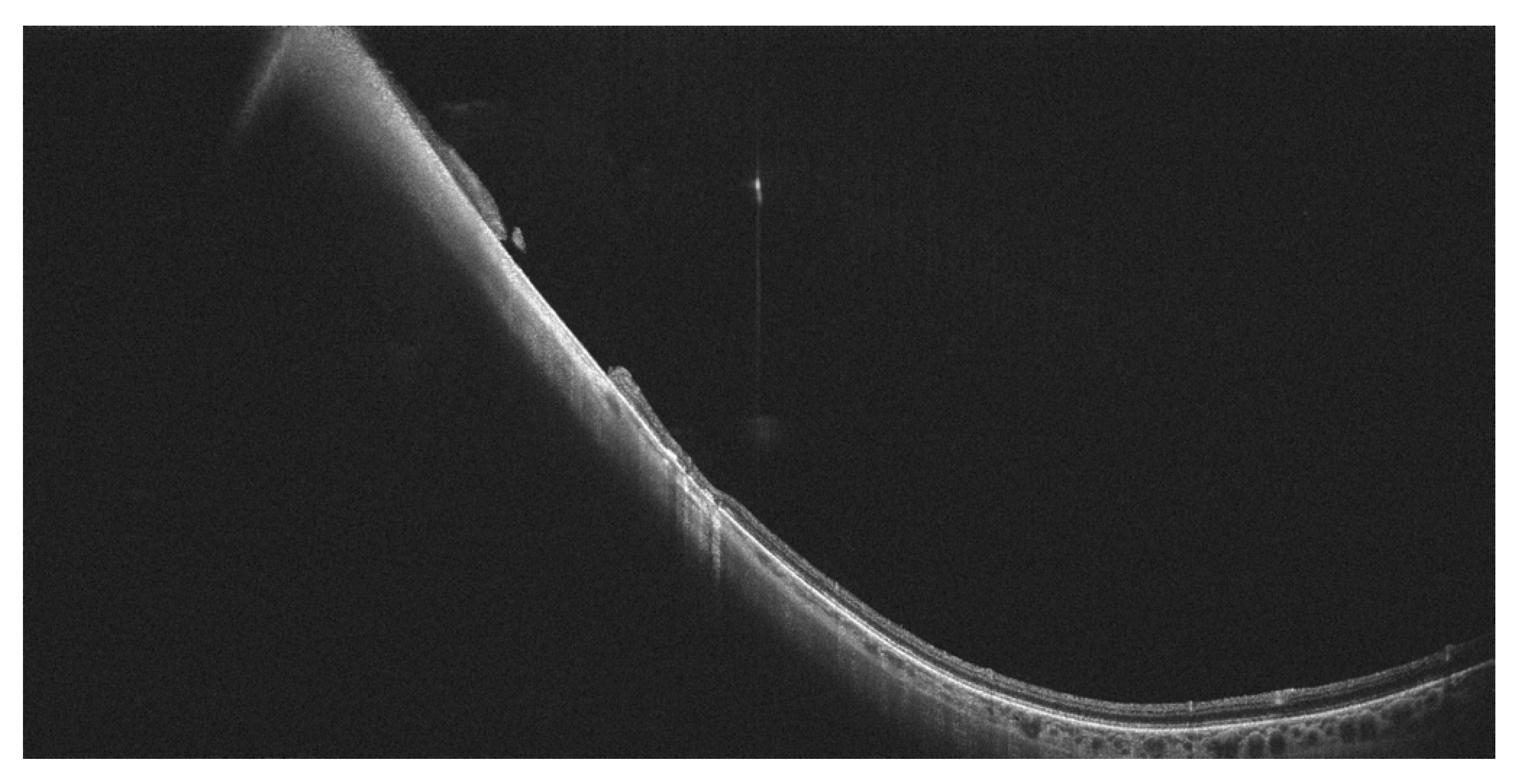
7. Other Clinical Entities
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shah, P.N.; Mishra, D.K.; Falahat, P.; Fischer, L.; Guzman, G.; Terheyden, J.H.; Holz, F.G.; Krohne, T.U.; Finger, R.P.; Wintergerst, M.W.M. Inter-Rater Reliability of Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy Assessment on Wide-Field OCT-Angiography and Fluorescein Angiography. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2023, 12, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaal, K.B.; Munk, M.R.; Wyssmueller, I.; Berger, L.E.; Zinkernagel, M.S.; Wolf, S. Vascular abnormalities in diabetic retinopathy assessed with swept-source optical coherence tomography angiography Widefield Imaging. Retina 2019, 39, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastline, M.; Munk, M.R.; Wolf, S.; Schaal, K.B.; Ebneter, A.; Tian, M.; Giannakaki-Zimmermann, H.; Zinkernagel, M.S. Repeatability of Wide-field Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography in Normal Retina. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2019, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munk, M.R.; Kashani, A.H.; Tadayoni, R.; Korobelnik, J.F.; Wolf, S.; Pichi, F.; Koh, A.; Ishibazawa, A.; Gaudric, A.; Loewenstein, A.; Lumbroso, B.; Ferrara, D.; Sarraf, D.; Wong, D.T.; Skondra, D.; Rodriguez, F.J.; Staurenghi, G.; Pearce, I.; Kim, J.E.; Freund, K.B.; Parodi, M.B.; Waheed, N.K.; Rosen, R.; Spaide, R.F.; Nakao, S.; Sadda, S.; Vujosevic, S.; Wong, T.Y.; Murata, T.; Chakravarthy, U.; Ogura, Y.; Huf, W.; Tian, M. Recommendations for OCT Angiography Reporting in Retinal Vascular Disease: A Delphi Approach by International Experts. Ophthalmol. Retina. 2022, 6, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhry, N.; Duker, J.S.; Freund, K.B.; Kiss, S.; Querques, G.; Rosen, R.; Sarraf, D.; Souied, E.H.; Stanga, P.E.; Staurenghi, G.; Sadda, S.R. Classification and Guidelines for Widefield Imaging: Recommendations from the International Widefield Imaging Study Group. Ophthalmol. Retina. 2019, 3, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, L.D.; Au, S.; Chong, N.V. Optomap ultrawide field imaging identifies additional retinal abnormalities in patients with diabetic retinopathy. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2015, 9, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.S.; Horton, M.B.; Clary, D.; Lewis, D.G.; Sun, J.K.; Cavallerano, J.D.; Aiello, L.P. Identification of Diabetic Retinopathy and Ungradable Image Rate with Ultrawide Field Imaging in a National Teleophthalmology Program. Ophthalmology 2016, 123, 1360–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemi Falavarjani, K.; Wang, K.; Khadamy, J.; Sadda, S.R. Ultra-wide-field imaging in diabetic retinopathy; an overview. J. Curr. Ophthalmol. 2016, 28, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talks, S.J.; Manjunath, V.; Steel, D.H.; Peto, T.; Taylor, R. New vessels detected on wide-field imaging compared to two-field and seven-field imaging: implications for diabetic retinopathy screening image analysis. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 99, 1606–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.S.; Cavallerano, J.D.; Haddad, N.M.; Kwak, H.; Dyer, K.H.; Omar, A.F.; Shikari, H.; Aiello, L.M.; Sun, J.K.; Aiello, L.P. Peripheral Lesions Identified on Ultrawide Field Imaging Predict Increased Risk of Diabetic Retinopathy Progression over 4 Years. Ophthalmology 2015, 122, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, D.M.; Silva, P.S.; et al. Liu DRCR Retina Network. Association of Predominantly Peripheral Lesions on Ultra-Widefield Imaging and the Risk of Diabetic Retinopathy Worsening Over Time. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2022, 140, 946–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, P.S.; Marcus, D.M.; et al. DRCR Retina Network. Association of Ultra-Widefield Fluorescein Angiography-Identified Retinal Nonperfusion and the Risk of Diabetic Retinopathy Worsening Over Time. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2022, 140, 936–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wessel, M.M.; Nair, N.; Aaker, G.D.; Ehrlich, J.R.; D'Amico, D.J.; Kiss, S. Peripheral retinal ischaemia, as evaluated by ultra-widefield fluorescein angiography, is associated with diabetic macular oedema. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 96, 694–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikkhah, H.; et al. Extended targeted retinal photocoagulation versus conventional pan-retinal photocoagulation for proliferative diabetic retinopathy in a randomized clinical trial. Int. Ophthalmol. 2018, 38, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Boité, H.; Gaudric, A.; Erginay, A.; Tadayoni, R.; Couturier, A. Is There a Nonperfusion Threshold on OCT Angiography Associated With New Vessels Detected on Ultra-Wide-Field Imaging in Diabetic Retinopathy? Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2023, 12, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajka, A.; Bacci, T.; Wiest, M.R.J.; Brinkmann, M.; Hamann, T.; Toro, M.; Zweifel, S.A. Feasibility and Clinical Utility of Wide-Field Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography Compared to Ultrawide-Field Fluorescein Angiography in Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy. Klin. Monbl Augenheilkd. 2023, 240, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, M.; Hirai, K.; Wakabayashi, T.; Ishida, Y.; Fukushima, M.; Kamei, M.; Tsuboi, K. Real-world utility of wide-field OCT angiography to detect retinal neovascularization in eyes with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Ophthalmol. Retina. 2023 Nov 24:S2468-6530(23)00617-6.
- Hirano, T.; Hoshiyama, K.; Takahashi, Y.; Murata, T. Wide-field swept-source OCT angiography (23 × 20 mm) for detecting retinal neovascularization in eyes with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2023, 261, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, J.C.; Lu, Y.; Zeng, R.; Katz, R.; Vingopoulos, F.; Le, R.; Laíns, I.; Wu, D.M.; Eliott, D.; Vavvas, D.G.; Husain, D.; Miller, J.W.; Kim, L.A.; Miller, J.B. Comparison of widefield swept-source optical coherence tomography angiography with ultra-widefield colour fundus photography and fluorescein angiography for detection of lesions in diabetic retinopathy. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 105, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichi, F.; Smith, S.D.; Abboud, E.B.; Neri, P.; Woodstock, E.; Hay, S.; Levine, E.; Baumal, C.R. Wide-field optical coherence tomography angiography for the detection of proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2020, 258, 1901–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, M.; Cozzi, M.; Staurenghi, G.; Corvi, F. Comparison of wide field optical coherence tomography angiography with extended field imaging and fluorescein angiography in retinal vascular disorders. PLoS One. 2019, 14, e0214892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, J.F.; Shi, Y.; Hinkle, J.W.; Scott, N.L.; Fan, K.C.; Lyu, C.; Gregori, G.; Rosenfeld, P.J. Longitudinal Wide-Field Swept-Source OCT Angiography of Neovascularization in Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy after Panretinal Photocoagulation. Ophthalmol. Retina. 2019, 3, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawada, O.; Ichiyama, Y.; Obata, S.; Ito, Y.; Kakinoki, M.; Sawada, T.; Saishin, Y.; Ohji, M. Comparison between wide-angle OCT angiography and ultra-wide field fluorescein angiography for detecting non-perfusion areas and retinal neovascularization in eyes with diabetic retinopathy. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2018, 256, 1275–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Rezaei, K.A.; Saraf, S.S.; Chu, Z.; Wang, F.; Wang, R.K. Ultra-wide optical coherence tomography angiography in diabetic retinopathy. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2018, 8, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Mao, M.; Wei, D.; Liu, M.; Liu, X.; Leng, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, R.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, J.; Zhong, J. Different scan areas affect the detection rates of diabetic retinopathy lesions by high-speed ultra-widefield swept-source optical coherence tomography angiography. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023, 14, 1111360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stino, H.; Huber, K.L.; Niederleithner, M.; Mahnert, N.; Sedova, A.; Schlegl, T.; Steiner, I.; Sacu, S.; Drexler, W.; Schmoll, T.; Leitgeb, R.; Schmidt-Erfurth, U.; Pollreisz, A. Association of Diabetic Lesions and Retinal Nonperfusion Using Widefield Multimodal Imaging. Ophthalmol. Retina. 2023, 7, 1042–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, M.; Wei, D.; Mao, M.; Liu, X.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Chen, B.; Yang, L.; Liu, S.; Qiao, L.; Zhang, R.; Li, J.; Dong, W.; Zhong, J. Early changes to retinal structure in patients with diabetic retinopathy as determined by ultrawide swept-source optical coherence tomography-angiography. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023, 14, 1143535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, B.; Wang, E.; et al. Ultra-wide field swept-source optical coherence tomography angiography in patients with diabetes without clinically detectable retinopathy. BMC Ophthalmol. 2021, 21, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, P.H.; Khalid, H.; Keane, P.A. The utility of wide-field optical coherence tomography angiography in diagnosis and monitoring of proliferative diabetic retinopathy in pregnancy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. Case Rep. 2022, 25, 101280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.; Sun, J.K.; Silva, P.S.; Aiello, L.P. Using Ultrawide Field-Directed Optical Coherence Tomography for Differentiating Nonproliferative and Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2023, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turczyńska, M.J.; Krajewski, P.; Brydak-Godowska, J.E. Wide-Field Fluorescein Angiography in the Diagnosis and Management of Retinal Vein Occlusion: A Retrospective Single-Center Study. Med. Sci. Monit. 2021, 27, e927782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Ghasemi Falavarjani, K.; Nittala, M.G.; Sagong, M.; Wykoff, C.C.; van Hemert, J.; Ip, M.; Sadda, S.R. Ultra-Wide-Field Fluorescein Angiography-Guided Normalization of Ischemic Index Calculation in Eyes With Retinal Vein Occlusion. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2018, 59, 3278–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-Cardenas, V.; Shah, S.U.; Apap, D.; Joseph, A.; Heilweil, G.; Zutis, K.; Trucco, E.; Hubschman, J.P. Assessment of Ischemic Index in Retinal Vascular Diseases Using Ultra-Wide-Field Fluorescein Angiography: Single Versus Summarized Image. Semin. Ophthalmol. 2017, 32, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, I.; Williams, B.K., Jr.; Kok, Y.O.; Heilweil, G.; Schwartz, S.D. Reliability of Ischemic Index Grading in Common Retinal Vascular Diseases. Ophthalmic Surg. Lasers Imaging Retina. 2015, 46, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.E.; Ibrahim, F.; Chandrasekaran, P.R.; Teo, K.Y.C. Clinical utility of ultra-widefield fluorescein angiography and optical coherence tomography angiography for retinal vein occlusions. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023, 10, 1110166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, I.; Kaines, A.; Havunjian, M.A.; Hubschman, S.; Heilweil, G.; Prasad, P.S.; Oliver, S.C.; Yu, F.; Bitrian, E.; Hubschman, J.P.; Friberg, T.; Schwartz, S.D. Ischemic index and neovascularization in central retinal vein occlusion. Retina 2011, 31, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siying, L.; Qiaozhu, Z.; Xinyao, H.; et al. Comparison of widefield swept-source optical coherence tomography angiography with ultra-widefield fluorescein angiography for the evaluation of lesions in retinal vein occlusion. BMC Ophthalmol. 2022, 22, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glacet-Bernard, A.; Miere, A.; Houmane, B.; Tilleul, J.; Souied, E. NONPERFUSION ASSESSMENT IN RETINAL VEIN OCCLUSION: Comparison Between Ultra-widefield Fluorescein Angiography and Widefield Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography. Retina 2021, 41, 1202–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadomoto, S.; Muraoka, Y.; Uji, A.; Tamiya, R.; Oritani, Y.; Kawai, K.; Ooto, S.; Murakami, T.; Iida-Miwa, Y.; Tsujikawa, A. NONPERFUSION AREA QUANTIFICATION IN BRANCH RETINAL VEIN OCCLUSION: A Widefield Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography Study. Retina 2021, 41, 1210–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huemer, J.; Khalid, H.; Wagner, S.K.; Nicholson, L.; Fu, D.J.; Sim, D.A.; Patel, P.J.; Balaskas, K.; Rajendram, R.; Keane, P.A. Phenotyping of retinal neovascularization in ischemic retinal vein occlusion using wide field OCT angiography. Eye (Lond) 2021, 35, 2812–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiraki, A.; Sakimoto, S.; Tsuboi, K.; Wakabayashi, T.; Hara, C.; Fukushima, Y.; Sayanagi, K.; Nishida, K.; Sakaguchi, H.; Nishida, K. Evaluation of retinal nonperfusion in branch retinal vein occlusion using wide-field optical coherence tomography angiography. Acta Ophthalmol. 2019, 97, e913–e918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakihara, S.; Hirano, T.; Iesato, Y.; Imai, A.; Toriyama, Y.; Murata, T. Extended field imaging using swept-source optical coherence tomography angiography in retinal vein occlusion. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 62, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M.; Nozaki, M.; Yoshida, M.; Ogura, Y. Wide-field optical coherence tomography angiography using extended field imaging technique to evaluate the nonperfusion area in retinal vein occlusion. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2016, 10, 1291–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Liu, W.; Guo, J.; Zhang, L.; Xu, G.; Wang, K.; Chang, Q. Wide-field swept-source OCT angiography of the periarterial capillary-free zone before and after anti-VEGF therapy for branch retinal vein occlusion. Eye Vis (Lond). 2022, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Kumar, V. Vitrectomy for epiretinal membrane in adult-onset Coats' disease. Indian. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 65, 1046–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Chandra, P.; Kumar, A. Ultra-wide field imaging in the diagnosis and management of adult-onset Coats' disease. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2017, 100, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.G.; Park, Y.H. Quantitative analysis of retinal microvascular changes in macular telangiectasia type 2 using optical coherence tomography angiography. PLoS One 2020, 15, e0232255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breazzano, M.P.; Yannuzzi, L.A.; Spaide, R.F. GENESIS OF RETINAL-CHOROIDAL ANASTOMOSIS IN MACULAR TELANGIECTASIA TYPE 2: A Longitudinal Analysis. Retina 2021, 41, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Van Dijk, E.H.C.; Borrelli, E.; Fragiotta, S.; Breazzano, M.P. OCT and OCT Angiography Update: Clinical Application to Age-Related Macular Degeneration, Central Serous Chorioretinopathy, Macular Telangiectasia, and Diabetic Retinopathy. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirafici, P.; Musolino, M.; Saccheggiani, M.; Traverso, C.E.; Nicolò, M. Multimodal Imaging Findings and Treatment with Dexamethasone Implant in Three Cases of Idiopathic Macular Telangiectasia Type 1. Case Rep. Ophthalmol. 2021, 12, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorusso, M.; Zito, R.; Nikolopoulou, E.; Ferrari, L.M.; Cicinelli, M.V.; Querques, G.; Ferrari, T.M. Progression of retinal ischemia in a case of macular telangiectasia type 1 after ranibizumab injection: optical coherence tomography angiography findings. Retin. Cases Brief. Rep. 2020, 14, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govetto, A.; Sebag, J.; Lucchini, S.; Ballabio, C.; Matteucci, M.; Ranno, S.; Carini, E.; Virgili, G.; Bacherini, D.; Radice, P. Imaging rhegmatogenous retinal lesions and peripheral vitreo-retinal interface with wide-field optical coherence tomography. Retina. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurobe, R.; Hirano, Y.; Ogura, S.; Yasukawa, T.; Ogura, Y. Ultra-Widefield Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography Findings of Peripheral Retinal Degenerations and Breaks. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2021, 15, 4739–4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanga, P.E.; Pastor-Idoate, S.; Reinstein, U.; Vatas, P.; Patel, U.; Dubovy, S.; Reinstein, D.Z.; Zahavi, O. Navigated single-capture 3D and cross-sectional wide-field OCT of the mid and peripheral retina and vitreoretinal interface. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 32, 1642–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukahara, M.; Mori, K.; Gehlbach, P.L.; Mori, K. Posterior Vitreous Detachment as Observed by Wide-Angle OCT Imaging. Ophthalmology. 2018, 125, 1372–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, Z.; Sun, L.; Li, S.; Huang, L.; Liu, C.; Chen, C.; Luo, X.; Yu, B.; Ding, X. Ultra-wide-field scanning laser ophthalmoscopy and optical coherence tomography in FEVR: findings and its diagnostic ability. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 105, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lai, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, T.; Sun, L.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, L.; Li, S.; Ding, X. Ultra-wide-field optical coherence tomography angiography in mild familial exudative vitreoretinopathy. Retina 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitamura, M.; Noda, K.; Kase, S.; Hirooka, K.; Ishida, S. Retinal hypoperfusion detected by wide-field optical coherence tomographic angiography in a case of retinal racemose hemangioma. Retin. Cases Brief. Rep. 2023, 17, 723–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNabb, R.P.; Grewal, D.S.; Mehta, R.; Schuman, S.G.; Izatt, J.A.; Mahmoud, T.H.; Jaffe, G.J.; Mruthyunjaya, P.; Kuo, A.N. Wide field of view swept-source optical coherence tomography for peripheral retinal disease. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 100, 1377–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preziosa, C.; Corvi, F.; Staurenghi, G.; Pellegrini, M. Extended field imaging optical coherence tomography angiography for the study of retinal and choroidal changes after radiation therapy for choroidal melanoma: comparison with wide-field angiography. Retina 2021, 41, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, P.; Rajesh, R.; Shanmugam, M.; Konana, V.K.; Mishra, D. Comparison of optical coherence tomography angiography and fundus fluorescein angiography features of retinal capillary hemangioblastoma. Indian. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 66, 872–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansfield Smith, S.; Makam, R.; Sullivan, L.; Sandford, R.; Allen, L. Is ultra wide-field retinal imaging alone appropriate for retinal angioma screening in lower risk subjects attending Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) clinics? Ophthalmic Genet. 2019, 40, 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alba-Linero, C.; Liscombe-Sepúlveda, J.P.; Llorenç, V.; GiraltJosa, J.; Adán, A. Use of ultra-wide field retinal imaging and optical coherence tomography angiography in the diagnosis of incomplete Susac syndrome. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 31, 3238–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
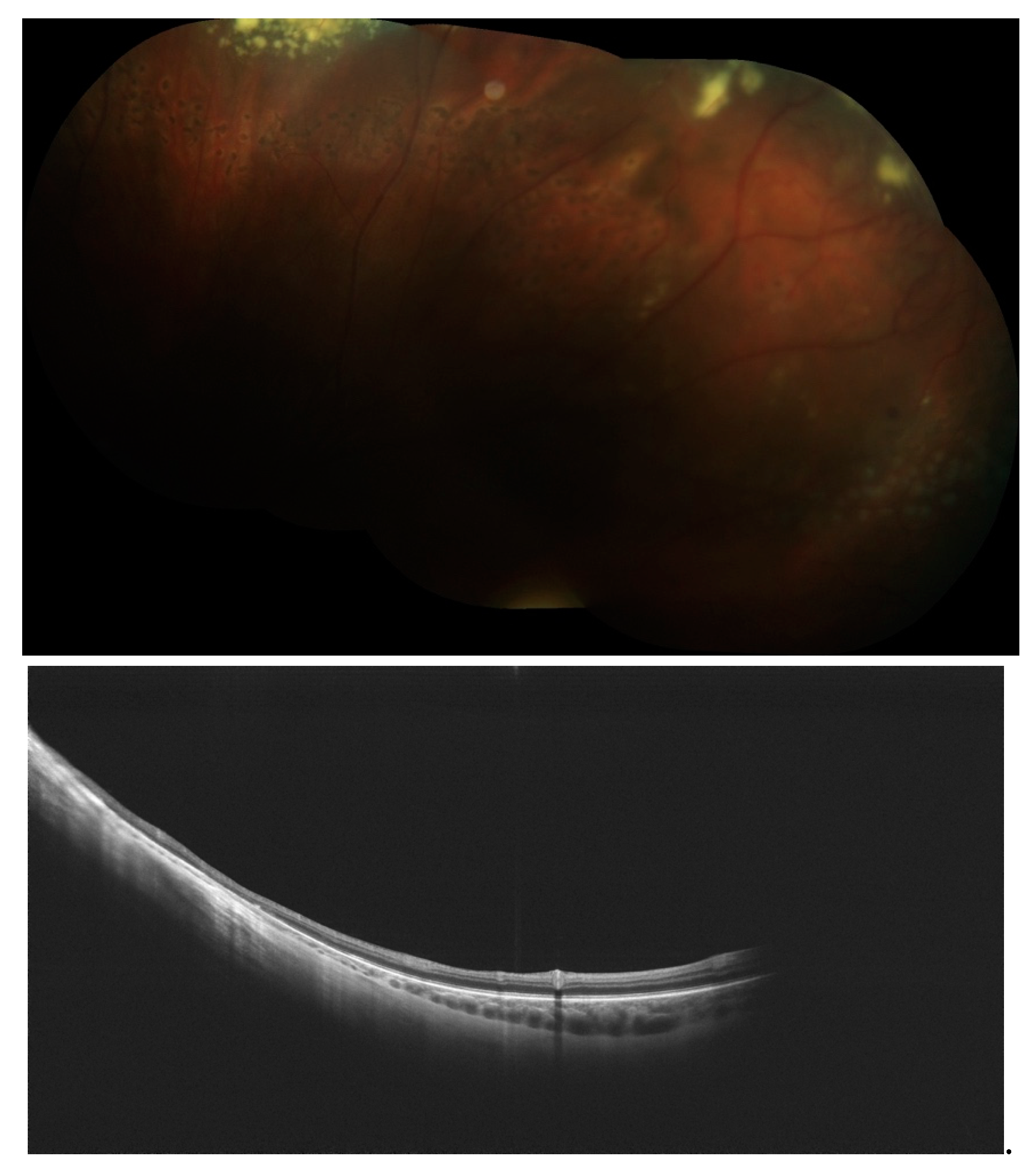
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





