Submitted:
02 January 2024
Posted:
03 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
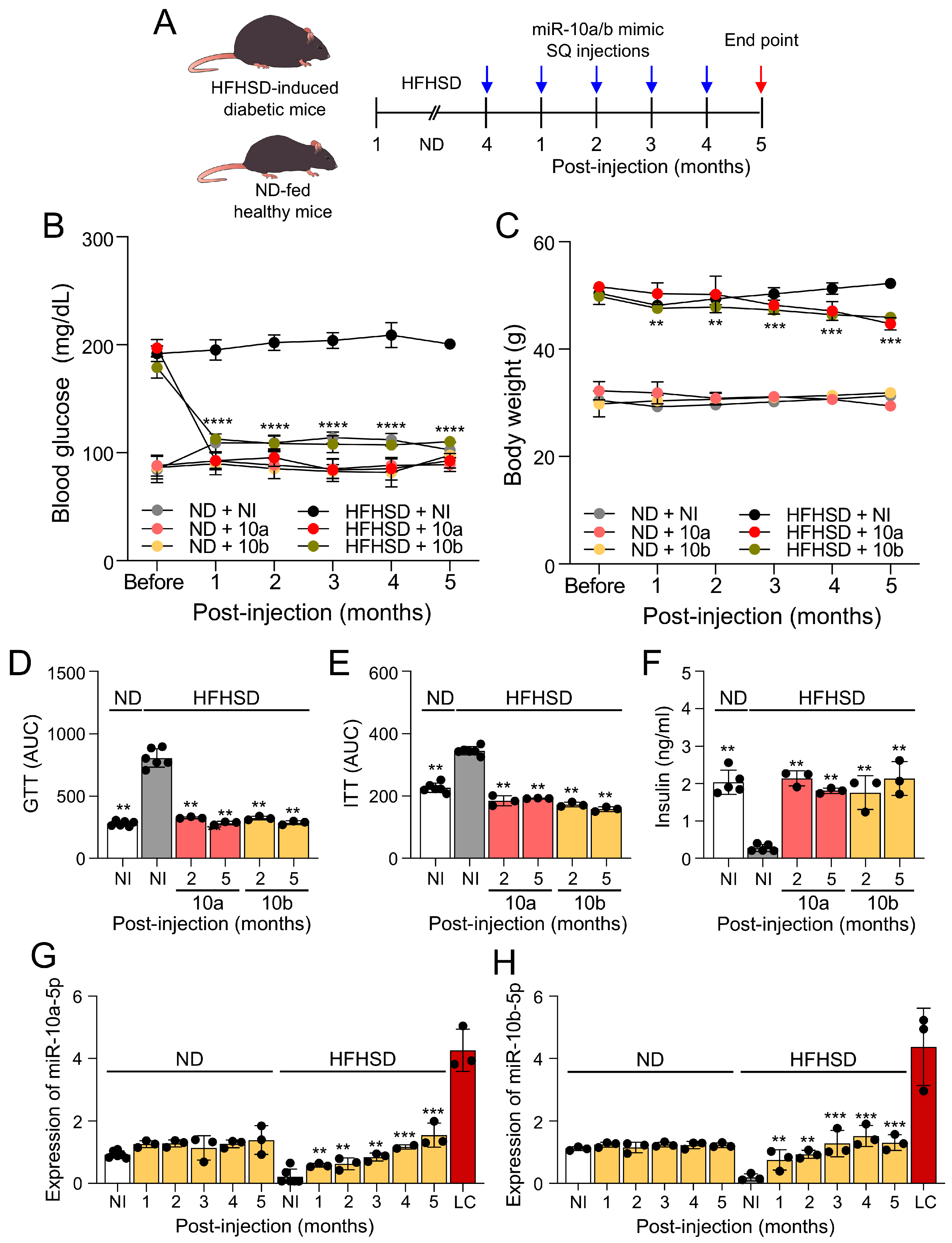
2.1. Long-term treatment of miR-10a/b mimics rescues diabetes in HFHSD-induced diabetic mice without excessive miR-10a/b-5p
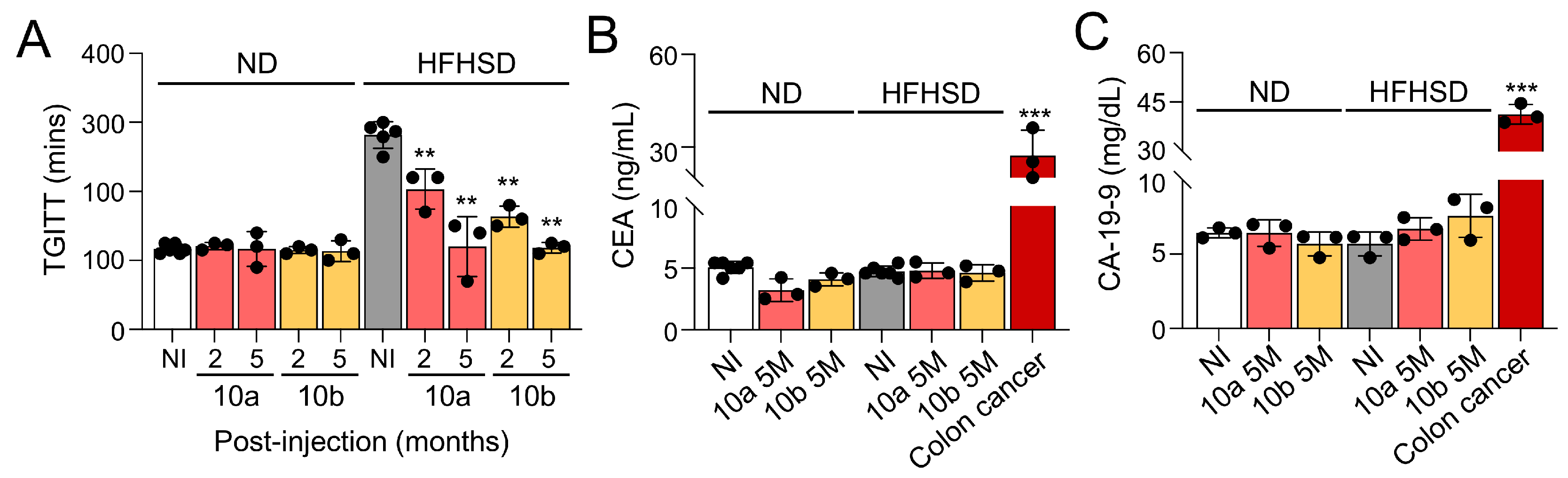
2.2. Long-term treatment of miR-10a/b mimics rescues GI dysmotility in HFHSD-induced diabetic mice without indication of risk for colon cancer
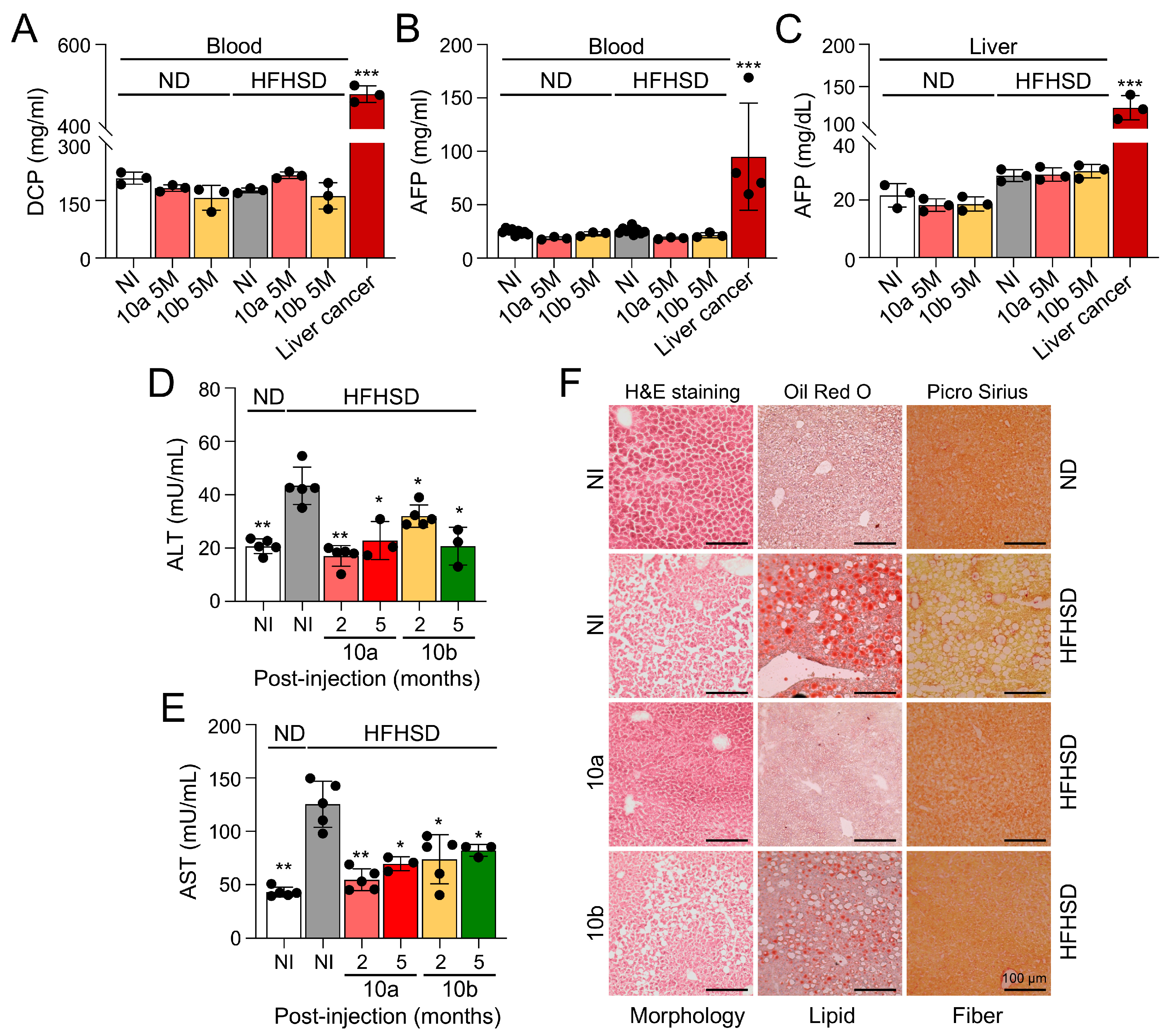
2.3. Long-term treatment of miR-10a/b mimics in HFHSD-induced diabetic mice indicates no risk for liver cancer
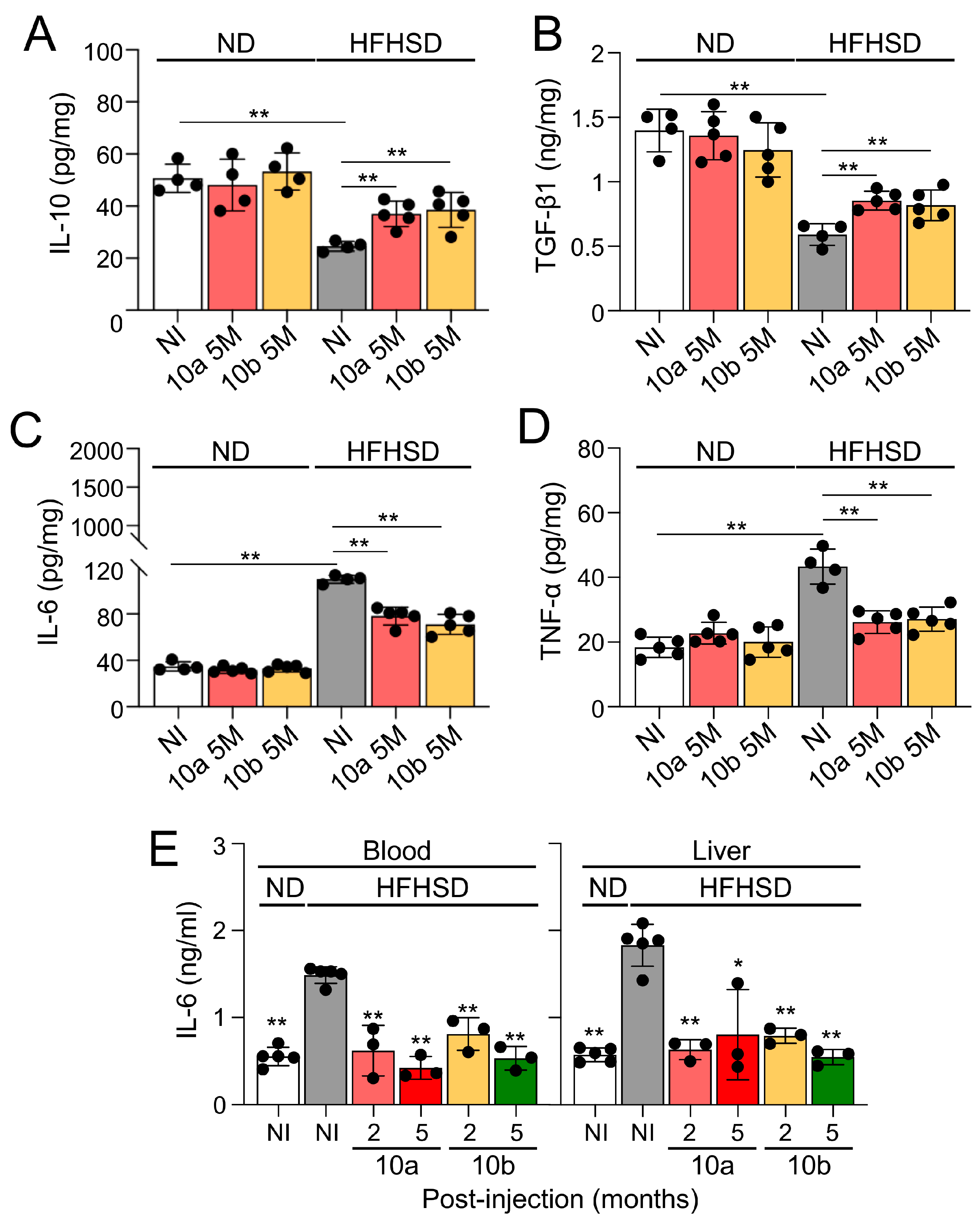
2.4. Long-term treatment of miR-10a/b mimics in HFHSD-induced diabetic mice indicates no risk for inflammation in colon and liver
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Mice
4.2. Diet
4.3. miR-10a/b mimics intervention
4.4. Metabolic procedures
4.5. Total gastrointestinal transit time test
4.6. Reverse Transcription Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction
4.7. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
4.8. Immunohistochemical and confocal microscopy analysis
4.9. Hematoxylin and eosin, Oil Red O, and Picro Sirius staining
4.10. Statistical analyses
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ogurtsova, K.; Guariguata, L.; Barengo, N.C.; Ruiz, P.L.; Sacre, J.W.; Karuranga, S.; Sun, H.; Boyko, E.J.; Magliano, D.J. IDF diabetes Atlas: Global estimates of undiagnosed diabetes in adults for 2021. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2022, 183, 109118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Zogg, H.; Wei, L.; Bartlett, A.; Ghoshal, U.C.; Rajender, S.; Ro, S. Gut Microbial Dysbiosis in the Pathogenesis of Gastrointestinal Dysmotility and Metabolic Disorders. J Neurogastroenterol Motil 2021, 27, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camilleri, M.; Chedid, V.; Ford, A.C.; Haruma, K.; Horowitz, M.; Jones, K.L.; Low, P.A.; Park, S.Y.; Parkman, H.P.; Stanghellini, V. Gastroparesis. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2018, 4, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camilleri, M.; Kuo, B.; Nguyen, L.; Vaughn, V.M.; Petrey, J.; Greer, K.; Yadlapati, R.; Abell, T.L. ACG Clinical Guideline: Gastroparesis. Am J Gastroenterol 2022, 117, 1197–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Zogg, H.; Ghoshal, U.C.; Ro, S. Current Treatment Options and Therapeutic Insights for Gastrointestinal Dysmotility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders. Front Pharmacol 2022, 13, 808195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eizirik, D.L.; Pasquali, L.; Cnop, M. Pancreatic beta-cells in type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus: different pathways to failure. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2020, 16, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, K.M.; Ward, S.M.; Koh, S.D. Interstitial cells: regulators of smooth muscle function. Physiol Rev 2014, 94, 859–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ro, S.; Park, C.; Jin, J.; Zheng, H.; Blair, P.J.; Redelman, D.; Ward, S.M.; Yan, W.; Sanders, K.M. A model to study the phenotypic changes of interstitial cells of Cajal in gastrointestinal diseases. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 1068–1078.e1061-1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrovatin, K.; Bastidas-Ponce, A.; Bakhti, M.; Zappia, L.; Buttner, M.; Salinno, C.; Sterr, M.; Bottcher, A.; Migliorini, A.; Lickert, H.; et al. Delineating mouse beta-cell identity during lifetime and in diabetes with a single cell atlas. Nat Metab 2023, 5, 1615–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudish, L.I.; Reusch, J.E.; Sussel, L. beta Cell dysfunction during progression of metabolic syndrome to type 2 diabetes. J Clin Invest 2019, 129, 4001–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, M.; Bernard, C.E.; Pasricha, P.J.; Lurken, M.S.; Faussone-Pellegrini, M.S.; Smyrk, T.C.; Parkman, H.P.; Abell, T.L.; Snape, W.J.; Hasler, W.L.; et al. Clinical-histological associations in gastroparesis: results from the Gastroparesis Clinical Research Consortium. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2012, 24, 531–539.e249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Zogg, H.; Ro, S. Role of microRNAs in Disorders of Gut-Brain Interactions: Clinical Insights and Therapeutic Alternatives. J Pers Med 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zogg, H.; Singh, R.; Ro, S. Current Advances in RNA Therapeutics for Human Diseases. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poy, M.N.; Eliasson, L.; Krutzfeldt, J.; Kuwajima, S.; Ma, X.; Macdonald, P.E.; Pfeffer, S.; Tuschl, T.; Rajewsky, N.; Rorsman, P.; et al. A pancreatic islet-specific microRNA regulates insulin secretion. Nature 2004, 432, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belgardt, B.F.; Ahmed, K.; Spranger, M.; Latreille, M.; Denzler, R.; Kondratiuk, N.; von Meyenn, F.; Villena, F.N.; Herrmanns, K.; Bosco, D.; et al. The microRNA-200 family regulates pancreatic beta cell survival in type 2 diabetes. Nat Med 2015, 21, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, A.H. Cells choose their words wisely. Cell 2022, 185, 1114–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Ha, S.E.; Wei, L.; Jin, B.; Zogg, H.; Poudrier, S.M.; Jorgensen, B.G.; Park, C.; Ronkon, C.F.; Bartlett, A.; et al. miR-10b-5p Rescues Diabetes and Gastrointestinal Dysmotility. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 1662–1678.e1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zogg, H.; Singh, R.; Ha, S.E.; Wang, Z.; Jin, B.; Ha, M.; Dafinone, M.; Batalon, T.; Hoberg, N.; Poudrier, S.; et al. miR-10b-5p rescues leaky gut linked with gastrointestinal dysmotility and diabetes. United European Gastroenterol J 2023, 11, 750–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheedy, P.; Medarova, Z. The fundamental role of miR-10b in metastatic cancer. Am J Cancer Res 2018, 8, 1674–1688. [Google Scholar]
- Guessous, F.; Alvarado-Velez, M.; Marcinkiewicz, L.; Zhang, Y.; Kim, J.; Heister, S.; Kefas, B.; Godlewski, J.; Schiff, D.; Purow, B.; et al. Oncogenic effects of miR-10b in glioblastoma stem cells. J Neurooncol 2013, 112, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Cheung, H.H.; Lu, G.; Chen, Z.; Chan, W.Y. MicroRNA-10a promotes granulosa cells tumor development via PTEN-AKT/Wnt regulatory axis. Cell Death Dis 2018, 9, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, G.; Huang, H.; Feng, M.; Yang, G.; Zheng, S.; You, L.; Zheng, L.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, Y. MiR-10a-5p targets TFAP2C to promote gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2018, 37, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vukobrat-Bijedic, Z.; Husic-Selimovic, A.; Sofic, A.; Bijedic, N.; Bjelogrlic, I.; Gogov, B.; Mehmedovic, A. Cancer Antigens (CEA and CA 19-9) as Markers of Advanced Stage of Colorectal Carcinoma. Med Arch 2013, 67, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.J.; Ju, Q.; Li, G.C. Tumor markers for hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Clin Oncol 2013, 1, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalas, M.A.; Chavez, L.; Leon, M.; Taweesedt, P.T.; Surani, S. Abnormal liver enzymes: A review for clinicians. World J Hepatol 2021, 13, 1688–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zhu, X.; Lv, X.; Han, X.; Xu, Y.; Huang, J.; Chen, X.; Yu, Z. Recent Updates on the Role of the MicroRNA-10 Family in Gynecological Malignancies. J Oncol 2022, 2022, 1544648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Shi, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Xu, W. The emerging role of miR-10 family in gastric cancer. Cell Cycle 2021, 20, 1468–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Yang, X.; Zhang, H.; Yu, M.; Long, J.; Yang, T. Inhibition of miR-10a-5p suppresses cholangiocarcinoma cell growth through downregulation of Akt pathway. Onco Targets Ther 2018, 11, 6981–6994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, D.; Zhao, H.Y.; Gu, A.D.; Wu, Y.W.; Weng, Y.H.; Li, S.J.; Song, J.Y.; Gu, X.F.; Qiu, J.; Zhao, W. miRNA-10a-5p inhibits cell metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma via targeting SKA1. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 2021, 37, 784–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, R.; Wang, D.; Lu, J. MicroRNA-10b inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion in cervical cancer cells via direct targeting of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor. Oncol Lett 2017, 13, 5009–5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, Z.B.; Wichmann, B.; Kalmar, A.; Galamb, O.; Bartak, B.K.; Spisak, S.; Tulassay, Z.; Molnar, B. Colorectal adenoma and carcinoma specific miRNA profiles in biopsy and their expression in plasma specimens. Clin Epigenetics 2017, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Tang, H. miR-10a suppresses colorectal cancer metastasis by modulating the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and anoikis. Cell Death Dis 2017, 8, e2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, K.; Lou, T. MicroRNA-10a suppresses breast cancer progression via PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Oncol Lett 2017, 14, 5994–6000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, A.H. miR-10 in development and cancer. Cell Death Differ 2010, 17, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, R.; Hunter, K.; Pandha, H.S. Downstream of the HOX genes: Explaining conflicting tumour suppressor and oncogenic functions in cancer. Int J Cancer 2022, 150, 1919–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Mahner, S.; Jeschke, U.; Hester, A. The Distinct Roles of Transcriptional Factor KLF11 in Normal Cell Growth Regulation and Cancer as a Mediator of TGF-beta Signaling Pathway. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Boussouar, A.; Mazelin, L.; Tauszig-Delamasure, S.; Sun, Y.; Goldschneider, D.; Paradisi, A.; Mehlen, P. The Proto-oncogene c-Kit Inhibits Tumor Growth by Behaving as a Dependence Receptor. Mol Cell 2018, 72, 413–425.e415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, H.; Kazi, J.U.; Zhao, H.; Sun, J. Germline mutations of KIT in gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) and mastocytosis. Cell Biosci 2016, 6, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Hui, T.; Wang, G.; Zhang, X.; Xue, X.; Kang, J.; Feng, G. Deficiency of microRNA-10b promotes DSS-induced inflammatory response via impairing intestinal barrier function. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2022, 636, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Oh, H.J.; Han, J.; Hong, S.H.; Park, W.; Song, H. Liposome-mediated small RNA delivery to convert the macrophage polarity: A novel therapeutic approach to treat inflammatory uterine disease. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 2022, 30, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, M.; Nie, S.; Zhou, M.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Hou, F.F. MicroRNA-10 negatively regulates inflammation in diabetic kidney via targeting activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Mol Ther 2021, 29, 2308–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valmiki, S.; Ahuja, V.; Paul, J. MicroRNA exhibit altered expression in the inflamed colonic mucosa of ulcerative colitis patients. World J Gastroenterol 2017, 23, 5324–5332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wohnhaas, C.T.; Schmid, R.; Rolser, M.; Kaaru, E.; Langgartner, D.; Rieber, K.; Strobel, B.; Eisele, C.; Wiech, F.; Jakob, I.; et al. Fecal MicroRNAs Show Promise as Noninvasive Crohn's Disease Biomarkers. Crohns Colitis 360 2020, 2, otaa003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altaf-Ul-Amin, M.; Karim, M.B.; Hu, P.; Ono, N.; Kanaya, S. Discovery of inflammatory bowel disease-associated miRNAs using a novel bipartite clustering approach. BMC Med Genomics 2020, 13, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.K.; Son, Y.; Kim, S.N.; Song, H.D.; Kim, M.; Park, J.H.; Jung, Y.S.; Ahn, S.Y.; Saha, A.; Granneman, J.G.; et al. MicroRNA-10a-5p regulates macrophage polarization and promotes therapeutic adipose tissue remodeling. Mol Metab 2019, 29, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Yang, C.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, H.; Qi, B. Hypoxic glioma-derived extracellular vesicles harboring MicroRNA-10b-5p enhance M2 polarization of macrophages to promote the development of glioma. CNS Neurosci Ther 2022, 28, 1733–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauck, M.A.; Quast, D.R.; Wefers, J.; Meier, J.J. GLP-1 receptor agonists in the treatment of type 2 diabetes - state-of-the-art. Mol Metab 2021, 46, 101102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamborlane, W.V.; Barrientos-Perez, M.; Fainberg, U.; Frimer-Larsen, H.; Hafez, M.; Hale, P.M.; Jalaludin, M.Y.; Kovarenko, M.; Libman, I.; Lynch, J.L.; et al. Liraglutide in Children and Adolescents with Type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med 2019, 381, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




