Submitted:
02 January 2024
Posted:
03 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. General Study Characteristics
2.2. Exosomes Structure and Function
2.3. Exosome Role in Tumorigenesis
2.4. Exosomes as Therapeutic Targets in cSCC
2.4.1. Circ-CYP24A1
2.4.2. Desmoglein 2 (Dsg2)
2.5. Prospects for Exosomes in NMSC Anticancer Therapy
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
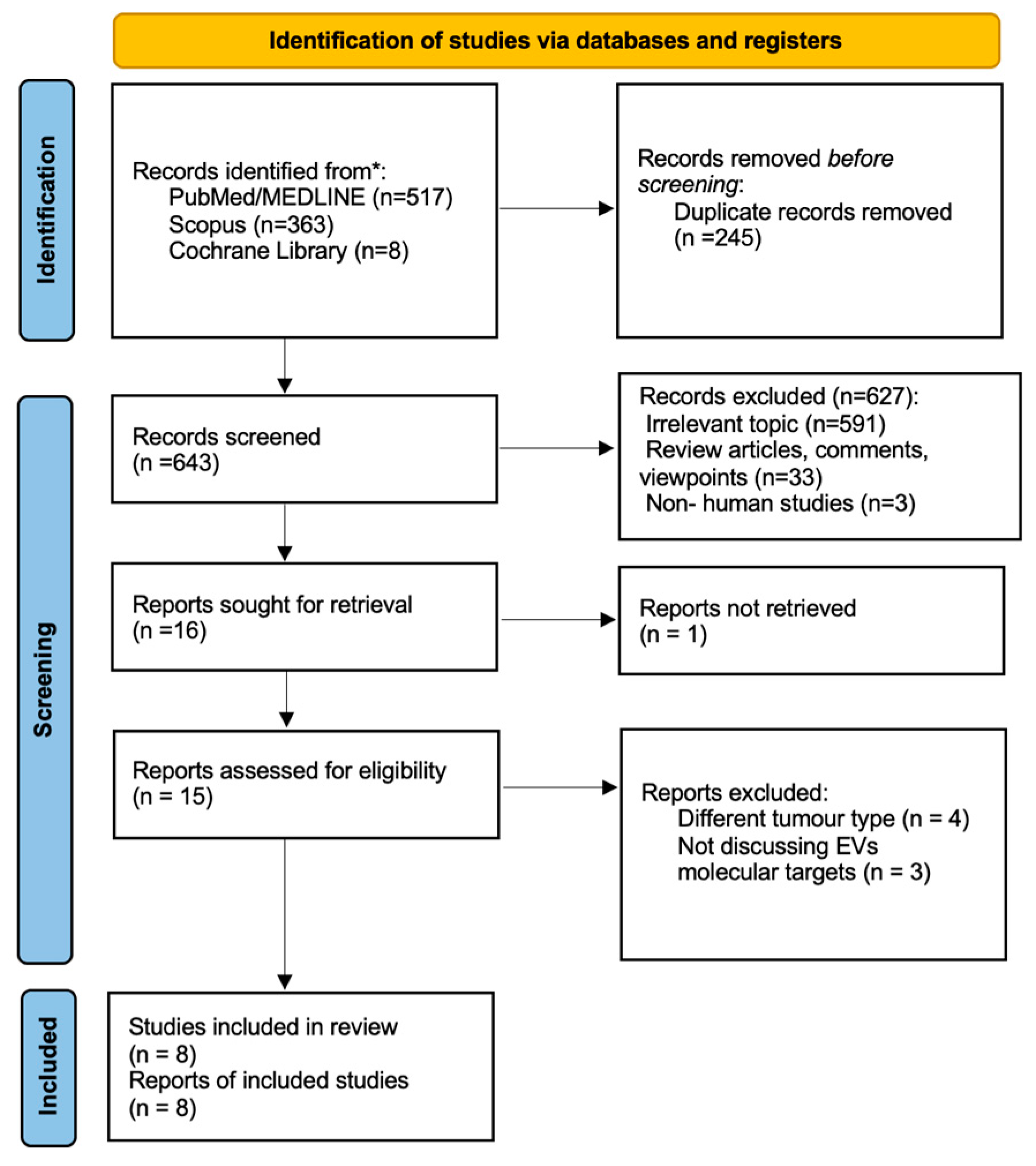
4.1. Study Protocol
4.2. Search Strategy
4.3. Eligibility of Relevant Studies
4.4. Study Selection
4.5. Data Collection and Risk of Bias Assessment
4.5. Data Synthesis and Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zelin, E.; Maronese, C.A.; Dri, A.; Toffoli, L.; Di Meo, N.; Nazzaro, G.; Zalaudek, I. Identifying Candidates for Immunotherapy among Patients with Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer: A Review of the Potential Predictors of Response. J Clin Med 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, S.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.-B.; Zheng, X.-H.; Li, H.-R.; Wen, J. Identification of CDK1 as a Candidate Marker in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis. Transl Cancer Res 2021, 10, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Guo, H.; Yang, W.; Li, J. Exosomal Circular RNA RNA-Seq Profiling and the Carcinogenic Role of Exosomal Circ-CYP24A1 in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Front Med (Lausanne) 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalhout, S.Z.; Emerick, K.S.; Kaufman, H.L.; Miller, D.M. Immunotherapy for Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer. Curr Oncol Rep 2021, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.Q.; Akhtar, S.; Prabhu, K.S.; Zarif, L.; Khan, R.; Alam, M.; Buddenkotte, J.; Ahmad, A.; Steinhoff, M.; Uddin, S. Exosomes: Emerging Diagnostic and Therapeutic Targets in Cutaneous Diseases. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.; Gao, L.; Loveless, R.; Rodrigo, J.P.; Strojan, P.; Willems, S.M.; Nathan, C.A.; Mäkitie, A.A.; Saba, N.F.; Ferlito, A. The Hidden Link of Exosomes to Head and Neck Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overmiller, A.M.; Pierluissi, J.A.; Wermuth, P.J.; Sauma, S.; Martinez-Outschoorn, U.; Tuluc, M.; Luginbuhl, A.; Curry, J.; Harshyne, L.A.; Wahl, J.K.; et al. Desmoglein 2 Modulates Extracellular Vesicle Release from Squamous Cell Carcinoma Keratinocytes. FASEB Journal 2017, 31, 3412–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Zhao, J.; Yan, M.; He, H.; Yu, S. Exosomes: Potential Biomarkers and Functions in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Front Mol Biosci 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-M.; Wu, C.; Jin, H.-Z. Exosomes in Chronic Inflammatory Skin Diseases and Skin Tumors. Exp Dermatol 2019, 28, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Tang, F.; Li, J.; Yu, H.; Wu, M.; Wu, Y.; Zeng, H.; Hou, K.; Zhang, Q. Tumor-Derived Exosomes: The Emerging Orchestrators in Melanoma. Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy 2022, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, P.; Zhang, G.; Ji, J.; Li, M.; Shen, S.; Wang, X. Exosomes from 5-Aminolevulinic Acid Photodynamic Therapy-Treated Squamous Carcinoma Cells Promote Dendritic Cell Maturation. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther 2020, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panvongsa, W.; Pegtel, D.M.; Voortman, J. More than a Bubble: Extracellular Vesicle MicroRNAs in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers (Basel) 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flemming, J.P.; Hill, B.L.; Haque, M.W.; Raad, J.; Bonder, C.S.; Harshyne, L.A.; Rodeck, U.; Luginbuhl, A.; Wahl, J.K.; Tsai, K.Y.; et al. MiRNA- and Cytokine-Associated Extracellular Vesicles Mediate Squamous Cell Carcinomas. J Extracell Vesicles 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Ma, J.; Sun, T.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, W.; Wang, G.; Wu, P.; Wang, H.; Jiang, L.; et al. Exosomal CircRNAs: Biogenesis, Effect and Application in Human Diseases. Mol Cancer 2019, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.T.-L.; Shen, C.-H.; Tsai, F.-C.; Chen, C.-B.; Ma, K.S.-K. Cancer-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Biomarkers for Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review. Cancers (Basel) 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Zhou, X.; Yin, J.; Zhou, Y. Lnc-PICSAR Contributes to Cisplatin Resistance by MiR-485-5p/REV3L Axis in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Open Life Sci 2020, 15, 488–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesnik, J.; Antes, T.; Kim, J.; Griner, E.; Pedro, L. Registered Report: Melanoma Exosomes Educate Bone Marrow Progenitor Cells toward a pro-Metastatic Phenotype through MET. Elife 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Modica, M.; Regondi, V.; Sandri, M.; Iorio, M. V.; Zanetti, A.; Tagliabue, E.; Casalini, P.; Triulzi, T. Breast Cancer-Secreted MiR-939 Downregulates VE-Cadherin and Destroys the Barrier Function of Endothelial Monolayers. Cancer Lett 2017, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morello, M.; Minciacchi, V.R.; De Candia, P.; Yang, J.; Posadas, E.; Kim, H.; Griffiths, D.; Bhowmick, N.; Chung, L.W.K.; Gandellini, P.; et al. Large Oncosomes Mediate Intercellular Transfer of Functional MicroRNA. Cell Cycle 2013, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazzoli, R.; Buttitta, F.; Di Nicola, M.; Malatesta, S.; Marchetti, A.; Rom, W.N.; Pass, H.I. MicroRNAs Derived from Circulating Exosomes as Noninvasive Biomarkers for Screening and Diagnosing Lung Cancer. Journal of Thoracic Oncology 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Tran, D.C.; Zhu, G.A.; Li, R.; Whitson, R.; Kim, Y.H.; Gupta, A.; Afshari, A.; Antes, T.; Spitale, R.C.; et al. Initial in Vitro Functional Characterization of Serum Exosomal MicroRNAs from Patients with Metastatic Basal Cell Carcinoma. British Journal of Dermatology 2017, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, E.; Ren, N.; Shi, X.; Zhang, R.; Yu, H.; Yu, F.; Qin, S.; Xue, J. Extracellular Vesicle Biomarkers for Pancreatic Cancer Diagnosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Cancer 2022, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, M.; Silva, J.; López-Alfonso, A.; López-Muñiz, M.B.; Peña, C.; Domínguez, G.; García, J.M.; López-Gónzalez, A.; Méndez, M.; Provencio, M.; et al. Different Exosome Cargo from Plasma/Bronchoalveolar Lavage in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2014, 53, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Woess, K.; Kienzl, M.; Leb-Reichl, V.M.; Feinle, A.; Wimmer, M.; Zauner, R.; Wally, V.; Luetz-Meindl, U.; Mellerio, J.E.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles as Biomarkers for the Detection of a Tumor Marker Gene in Epidermolysis Bullosa-Associated Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2018, 138, 1197–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zauner, R.; Wimmer, M.; Atzmueller, S.; Proell, J.; Niklas, N.; Ablinger, M.; Reisenberger, M.; Lettner, T.; Illmer, J.; Dorfer, S.; et al. Biomarker Discovery in Rare Malignancies: Development of a MiRNA Signature for RDEB-CSCC. Cancers (Basel) 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodoraki, M.-N.; Laban, S.; Jackson, E.K.; Lotfi, R.; Schuler, P.J.; Brunner, C.; Hoffmann, T.K.; Whiteside, T.L.; Hofmann, L. Changes in Circulating Exosome Molecular Profiles Following Surgery/(Chemo)Radiotherapy: Early Detection of Response in Head and Neck Cancer Patients. Br J Cancer 2021, 125, 1677–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massey, A.E.; Malik, S.; Sikander, M.; Doxtater, K.A.; Tripathi, M.K.; Khan, S.; Yallapu, M.M.; Jaggi, M.; Chauhan, S.C.; Hafeez, B.B. Clinical Implications of Exosomes: Targeted Drug Delivery for Cancer Treatment. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Zhu, Y.; Ali, D.J.; Tian, T.; Xu, H.; Si, K.; Sun, B.; Chen, B.; Xiao, Z. Engineered Exosomes for Targeted Co-Delivery of MiR-21 Inhibitor and Chemotherapeutics to Reverse Drug Resistance in Colon Cancer. J Nanobiotechnology 2020, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, W.; Wen, Z.; Chen, H.; Duan, Y. Exosomes as Carriers for Drug Delivery in Cancer Therapy. Pharm Res 2023, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, S.I.; Takanashi, M.; Sudo, K.; Ueda, S.; Ishikawa, A.; Matsuyama, N.; Fujita, K.; Mizutani, T.; Ohgi, T.; Ochiya, T.; et al. Systemically Injected Exosomes Targeted to EGFR Deliver Antitumor Microrna to Breast Cancer Cells. Molecular Therapy 2013, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmults, C.D.; Blitzblau, R.; Aasi, S.Z.; Alam, M.; Andersen, J.S.; Baumann, B.C.; Bordeaux, J.; Chen, P.-L.; Chin, R.; Contreras, C.M.; et al. NCCN Guidelines® Insights: Squamous Cell Skin Cancer, Version 1.2022. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2021, 19, 1382–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stratigos, A.J.; Garbe, C.; Dessinioti, C.; Lebbe, C.; Bataille, V.; Bastholt, L.; Dreno, B.; Fargnoli, M.C.; Forsea, A.M.; Frenard, C.; et al. European Interdisciplinary Guideline on Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Skin: Part 1. Epidemiology, Diagnostics and Prevention. European Journal of Cancer 2020, 128, 60–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seretis, K.; Thomaidis, V.; Karpouzis, A.; Tamiolakis, D.; Tsamis, I. Epidemiology of Surgical Treatment of Nonmelanoma Skin Cancer of the Head and Neck in Greece. Dermatol Surg 2010, 36, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seretis, K.; Bounas, N.; Lykoudis, E.G. An Algorithmic Approach for the Reconstruction of Extended Upper-Third Auricular Soft Tissue Defects. J Craniofac Surg 2022, 33, e452–e453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomaidis, V.; Seretis, K.; Fiska, A.; Tamiolakis, D.; Karpouzis, A.; Tsamis, I. The Scalping Forehead Flap in Nasal Reconstruction: Report of 2 Cases. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 2007, 65, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seretis, K.; Boptsi, A.; Boptsi, E.; Lykoudis, E.G. The “Facelift” Flap Revisited. J Craniofac Surg 2023, 34, 1015–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seretis, K.; Bounas, N.; Lykoudis, E.G. Repair of a Large Defect Involving the Cheek and Ear. Dermatol Surg 2023, 49, 197–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumpston M, Chandler J. Chapter IV: Updating a Review. In: Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA (Editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 6.3 (Updated February 2022). Cochrane, 2022.
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372. [Google Scholar]
- Hooijmans, C.R.; Rovers, M.M.; De Vries, R.B.M.; Leenaars, M.; Ritskes-Hoitinga, M.; Langendam, M.W. SYRCLE’s Risk of Bias Tool for Animal Studies. BMC Med Res Methodol 2014, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne JAC, Savović J, Page MJ, Elbers RG, Blencowe NS, Boutron I, Cates CJ, Cheng H-Y, Corbett MS, Eldridge SM, Hernán MA, Hopewell S, Hróbjartsson A, Junqueira DR, Jüni P, Kirkham JJ, Lasserson T, Li T, McAleenan A, Reeves BC, Shepperd S, Shrier I, Stewart LA, Tilling K, White IR, Whiting PF, Higgins JPT. RoB 2: A Revised Tool for Assessing Risk of Bias in Randomised Trials. BMJ 2019, 366(L4898).
| Author, Year | Target Molecule | Source | Study group | Control group | Incubation | Exp. method | Analysis method | Outcome | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overmiller A. et al. (2017) | Dsg-2-CTF | Cell lines | - | - | A431/GFP, A431-Dsg2/GFP, HaCaT/GFP, HaCaT-Dsg2/GFP, primary NHK | In vitro | Western blot | Overexpression in SCC-derived EVs resulted in increased EVs secretion; inhibition of proteolysis of Dsg2 resulted in reduced EVs secretion | Therapeutic target |
| Chang et al. (2017) | miR197 |
Serum | 9 MBCC patients | 9 non MBCC patients | NHK, human skin fibroblasts | In vitro | PCR | SS upregulation in MBCC patients; no impact on proliferation noted in fibroblasts and keratinocytes | Therapeutic target, prognostic biomarker |
| Sun et al. (2017) | Ct-SLCO1B3 | Tissue |
RDEB-SCC patients | - | RDEB, RDEB-SCC, NHK |
In vitro and in vivo | PCR | Expression of Ct-SLCO1B3 only in RDEB-SCC derived EVs | Diagnostic biomarker |
| Zhao Z. et al. (2020) | ALA-PDT exosomes | Cell lines | - | - | SCCs (human A431, mouse PECA, primary mice SCCs), fibroblasts 3T3, DCs | In vitro | Western blot | Stimulation of DCs maturation and fibroblasts’ TGF-β1 secretion, leading to an anti-tumor immune response | Treatment |
| Wang et al. (2020) | lnc-PICSAR | Serum | 30 cSCC patients | 30 healthy patients | NHEK, A431, HSC-5 cells | In vitro and in vivo | PCR | Elevated in cSCC cells and DDP-resistant cSCC cells | Prognostic biomarker, therapeutic target |
| Flemming J. et al. (2020) | Dsg-2 | Cell lines | - | - | A431/GFP, A431-Dsg2/GFP, A432-Dsg2cacs/GFP | In vitro and in vivo | Western blot | Inhibited palmitoylation of Dsg-2 corellates with reduced sEVs secretion and attenuated tumor development | Therapeutic target |
| Zhang Z. et al. (2021) | circ-CYP24A1 | Serum |
5 cSCC patients | 5 healty patients | A431, SCL-1 cells | In vitro | PCR | Upregulated in cSCC EVs; inhibition leads to attenuation of the tumor’s metastatic dynamic | Therapeutic target, diagnostic biomarker |
| Zauner R et al. (2023) | miRNA (expr. profile) | Tissue | 6 RDEB-cSCC | 4 healthy patients, 5 RDEB | - | In vitro | PCR | 51 miRNAS found significantly up-regulated and 74 down-regulated in RDEB-cSCC compared to RDEB | Diagnostic biomarker |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





