Submitted:
02 January 2024
Posted:
03 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
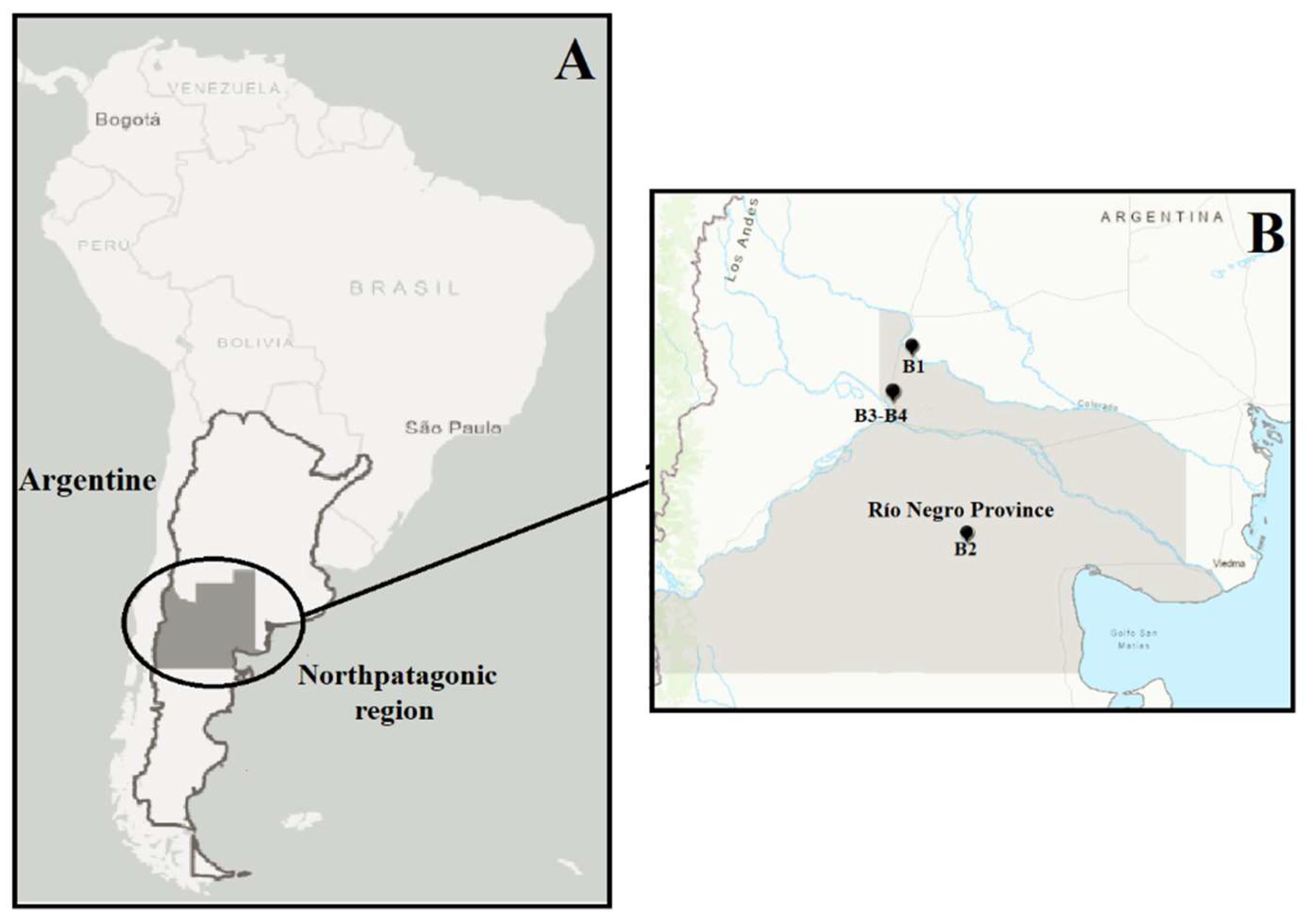
2.1. Bentonite samples
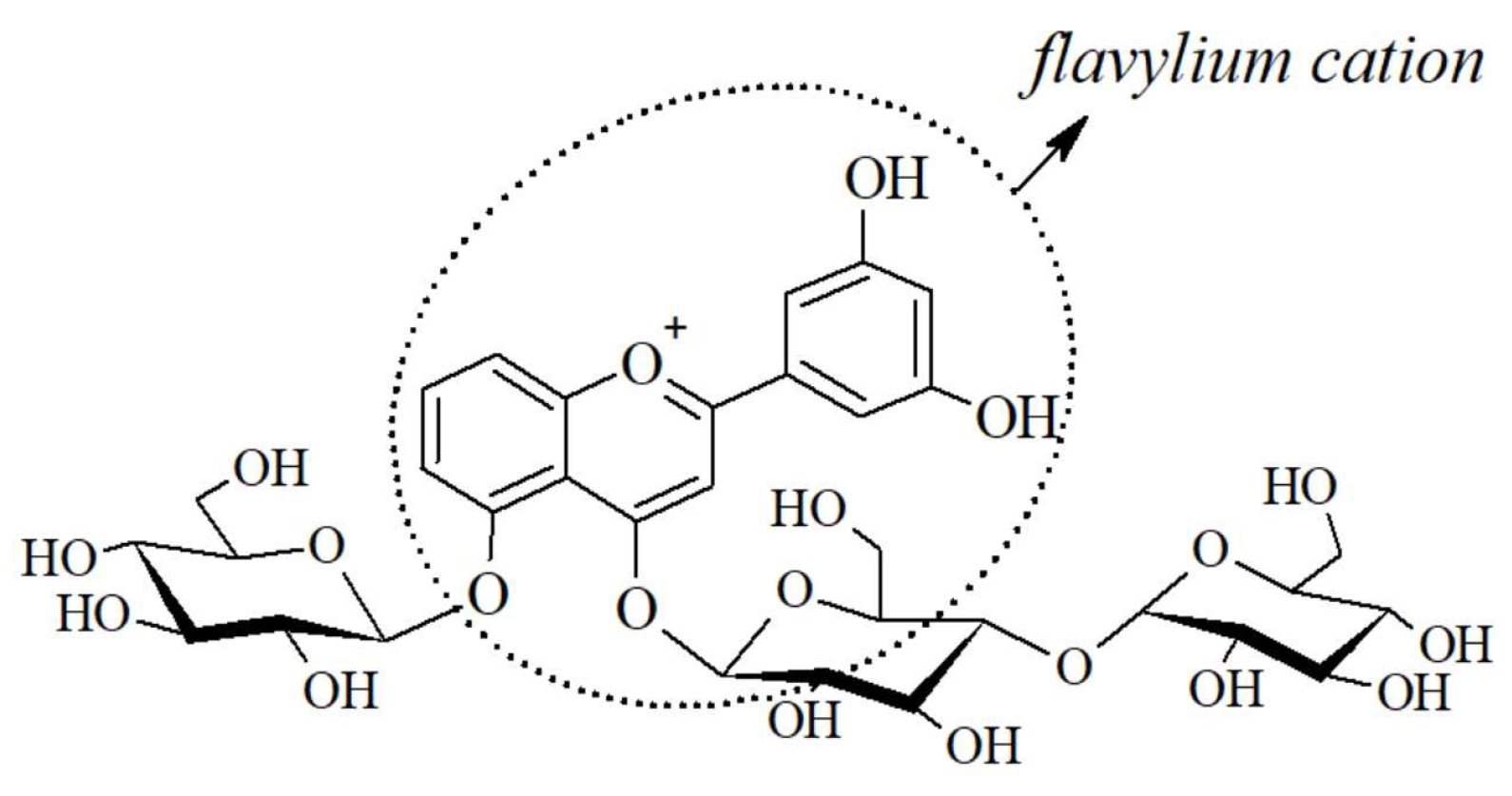
2.2. Anthocyanis properties and extraction
2.3. Characterization of bentonite samples
2.3.1. Mineralogical, chemical and structural characterization
2.3.2. Physical and physicochemical properties
2.4. Anthocyanins adsorption assays
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Material characterization
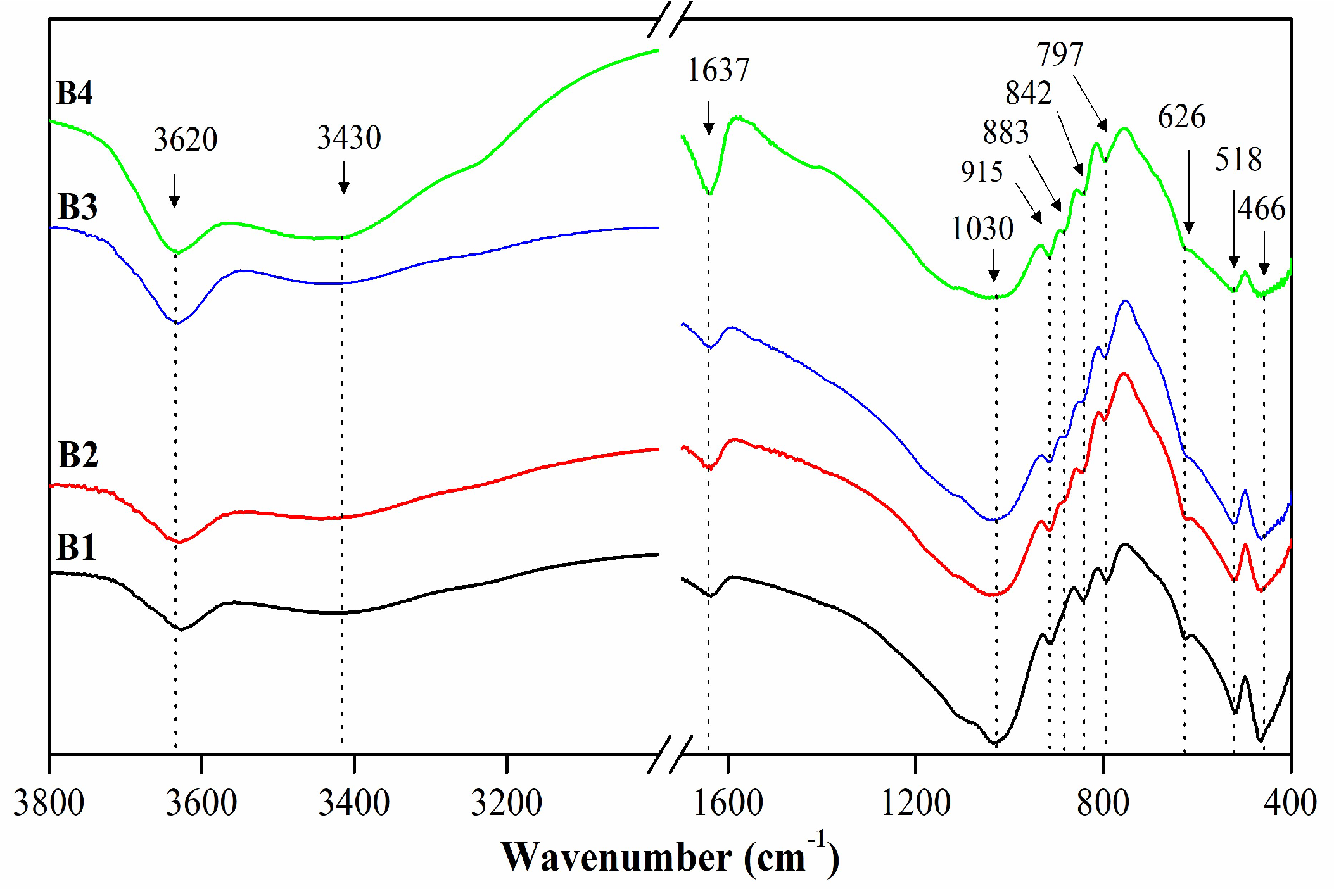
3.1.1. Mineralogical, chemical and structural characterization
3.1.2. Physical and physicochemical properties
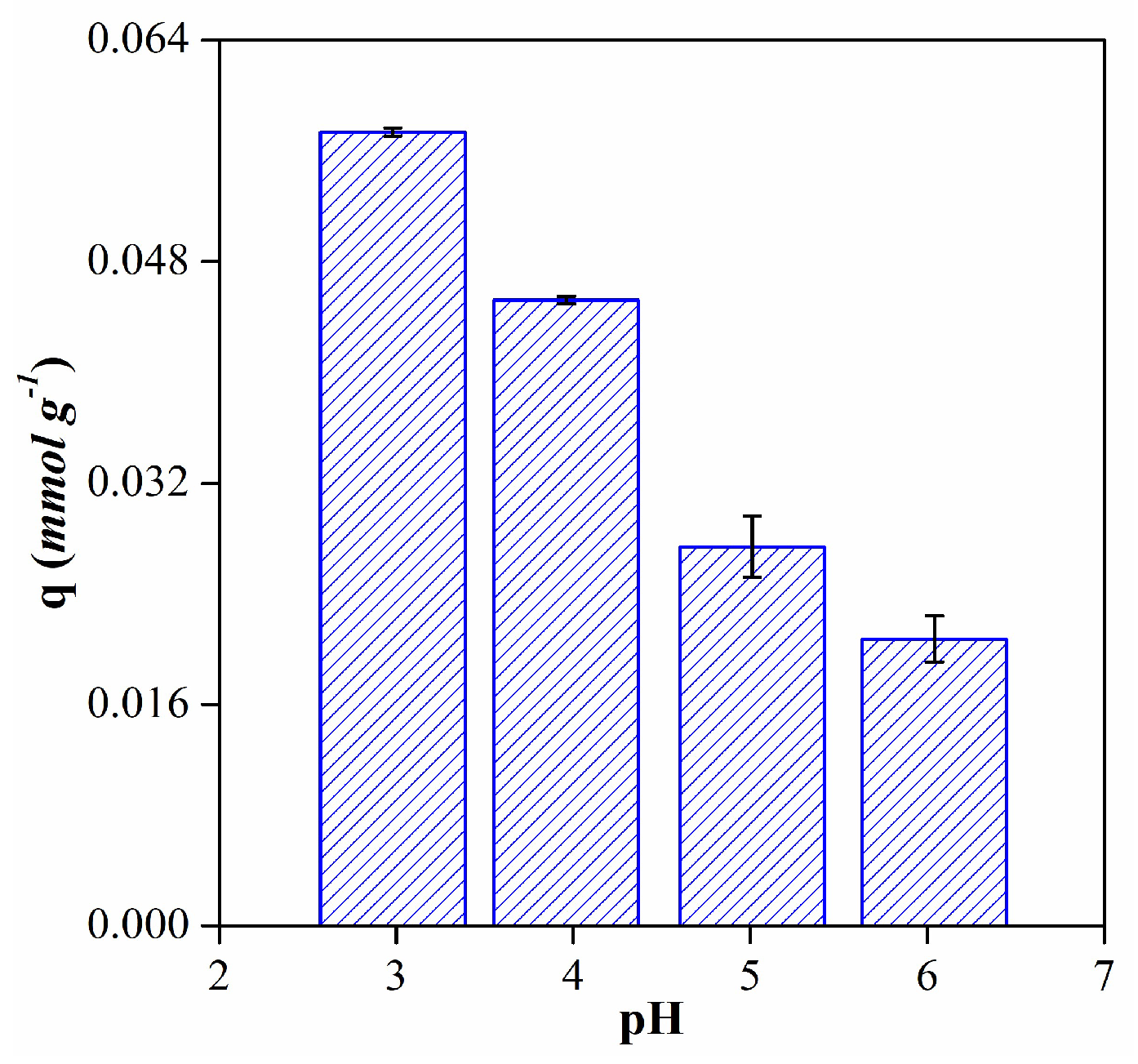
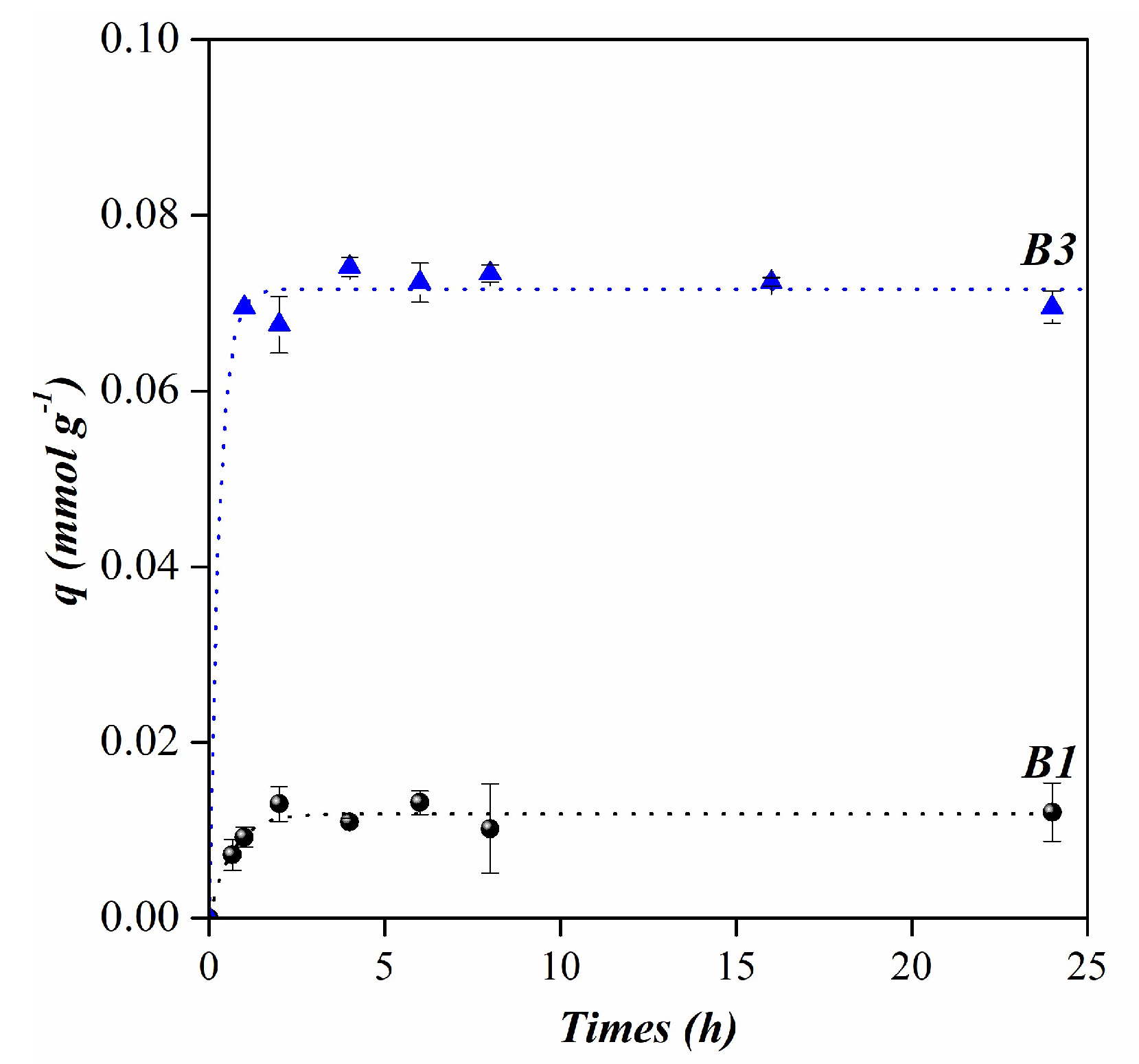
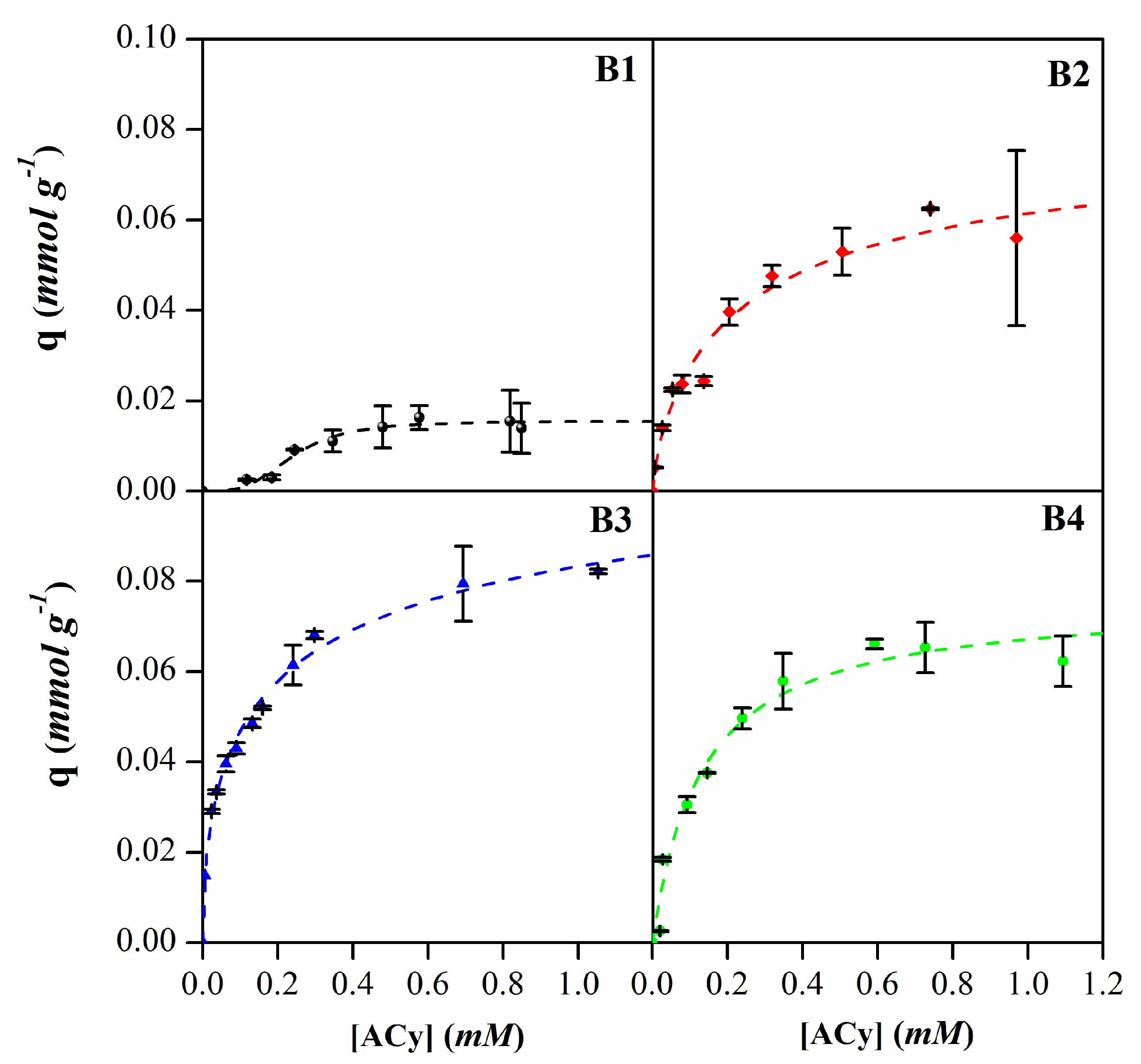
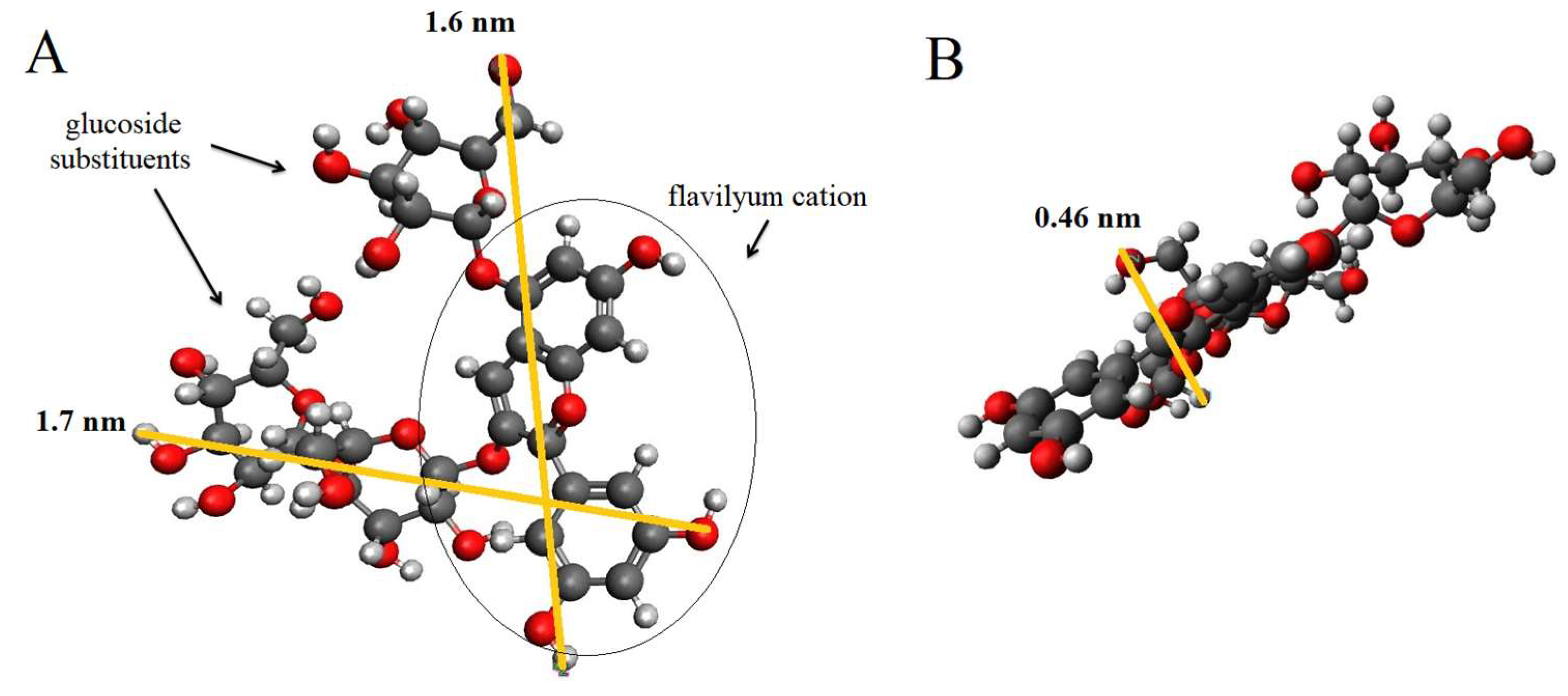
3.2. Anthocyanins adsorption
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, T.J.; Idoine, N.E.; Raycraft, E.R.; Shaw, R.A.; Hobbs, S.F.; Everett, P.; Deady, E.A.; Bide, T. World Mineral Production 2012 - 2016. Br. Geol. Surv. 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Musso, T.B.; Roehl, K.E.; Pettinari, G.; Vallés, J.M. Assessment of smectite-rich claystones from Northpatagonia for their use as liner materials in landfills. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 48, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, B.; Baschini, M.; Torres Sánchez, R.M. Bentonite deposits of Northern Patagonia. Appl. Clay Sci. 2003, 22, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parolo, M.E.; Avena, M.J.; Pettinari, G.R.; Baschini, M.T. Influence of Ca2+ on tetracycline adsorption on montmorillonite. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2012, 368, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parolo, M.E.; Savini, M.C.; Vallés, J.M.; Baschini, M.T.; Avena, M.J. Tetracycline adsorption on montmorillonite: pH and ionic strength effects. Appl. Clay Sci. 2008, 40, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parolo, M.E.; Avena, M.J.; Pettinari, G.; Zajonkovsky, I.; Valles, J.M.; Baschini, M.T. Antimicrobial properties of tetracycline and minocycline-montmorillonites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 49, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca Jalil, M.E.; Baschini, M.; Sapag, K. Influence of pH and antibiotic solubility on the removal of ciprofloxacin from aqueous media using montmorillonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 114, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca Jalil, M.E.; Vieira, R.S.; Azevedo, D.; Baschini, M.; Sapag, K. Improvement in the adsorption of thiabendazole by using aluminum pillared clays. Appl. Clay Sci. 2013, 71, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, B.; Baschini, M.; Torres Sánchez, R.M. Optimization of parameters and adsorption mechanism of thiabendazole fungicide by a montmorillonite of North Patagonia, Argentina. Appl. Clay Sci. 2003, 24, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretero, M.I.; Pozo, M. Clay and non-clay minerals in the pharmaceutical industry. Part I. Excipients and medical applications. Appl. Clay Sci. 2009, 46, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretero, M.I.; Pozo, M. Clay and non-clay minerals in the pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries Part II. Active ingredients. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 47, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, J.D.D.; Bertolino, S.R.A.; Cuffini, S.L.; Ducart, D.F.; Bretzke, P.E.; Leonardi, G.R. Clay minerals: Properties and applications to dermocosmetic products and perspectives of natural raw materials for therapeutic purposes—A review. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 534, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca Jalil, M.E.; Sanchez, M.; Pozo, M.; Soria, C.; Vela, L.; Gurnik, N.; Baschini, M. Assessment of natural and enhanced peloids from the Copahue thermal system (Argentina): Effects of the drying procedure on lidocaine adsorption. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iborra Viseras, C.; Cultrone, G.; Cerezo, P.; Aguzzi, C.; Baschini, M.T.; Vallés, J.; López-Galindo, A. Characterisation of northern Patagonian bentonites for pharmaceutical uses. Appl. Clay Sci. 2006, 31, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourjavaher, S.; Almasi, H.; Meshkini, S.; Pirsa, S.; Parandi, E. Development of a colorimetric pH indicator based on bacterial cellulose nanofibers and red cabbage (Brassica oleraceae) extract. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 156, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghareaghajlou, N.; Hallaj-Nezhadi, S.; Ghasempour, Z. Red cabbage anthocyanins: Stability, extraction, biological activities and applications in food systems. Food Chem. 2021, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDougall, G.J.; Fyffe, S.; Dobson, P.; Stewart, D. Anthocyanins from red cabbage - stability to simulated gastrointestinal digestion. Phytochemistry 2007, 68, 1285–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saluk, J.; Bijak, M.; Kołodziejczyk-Czepas, J.; Posmyk, M.M.; Janas, K.M.; Wachowicz, B. Anthocyanins from red cabbage extract - evidence of protective effects on blood platelets. Cent. Eur. J. Biol. 2012, 7, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benvenuti, S.; Bortolotti, E.; Maggini, R. Antioxidant power, anthocyanin content and organoleptic performance of edible flowers. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 199, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiczkowski, W.; Szawara-Nowak, D.; Topolska, J. Red cabbage anthocyanins: Profile, isolation, identification, and antioxidant activity. Food Res. Int. 2013, 51, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S. E.; Mu, B.; Ding, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.W.; Wang, A.Q. Fabrication of anthocyanin/ montmorillonite hybrid pigments to enhance their environmental stability and application in allochroic composite films. Clays Clay Min. 2021, 69, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amogne, N.Y.; Ayele, D.W.; Tsigie, Y.A. Recent advances in anthocyanin dyes extracted from plants for dye sensitized solar cell. Mater. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohno, Y.; Yasushi, K.; Shibata, M.; Fukuhara, C.; Maeda, Y.; Tomita, Y.; Kobayashi, K. Enhanced stability of natural anthocyanin incorporated in Fe-containing mesoporous silica. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015, 203, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohno, Y.; Haga, E.; Yoda, K.; Shibata, M.; Fukuhara, C.; Tomita, Y.; Maeda, Y.; Kobayashi, K. Adsorption behavior of natural anthocyanin dye on mesoporous silica. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2014, 75, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohno, Y.; Kinoshita, R.; Ikoma, S.; Yoda, K.; Shibata, M.; Matsushima, R.; Tomita, Y.; Maeda, Y.; Kobayashi, K. Stabilization of natural anthocyanin by intercalation into montmorillonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2009, 42, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, G.T.M.; Silva, C.P.; Gehlen, M.H.; Oake, J.; Bohne, C.; Quina, F.H. Organic/inorganic hybrid pigments from flavylium cations and palygorskite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 162, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohno, Y.; Hoshino, R.; Matsushima, R.; Tomita, Y.; Kobayashi, K. Stabilization of Flavylium Dyes by Incorporation in the Clay Interlayer. J. Jpn. Soc. Colour. Mater. 2007, 80, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caminos, R.; Chernicoff, C.J.; Fauqué, L.; Franchi, M. Hoja Geológica 4166-I Valcheta. 2001.
- Johanis, P.; Dalponte, M.; Juárez, P.; Giacosa, R. Recursos minerales industriales, rocas de aplicación y gemas de la provincia de Río Negro. Ser. Contrib. Técnicas Recur. Miner. N° 2022, 49, 1–97. [Google Scholar]
- Giusti, M.; Wrolstad, R. Characterization and Measurement of Anthocyanins by UV-Visible Spectroscopy. Food Anal. Chem. 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, L.G. Quantitative Interpretation of Mineralogical Composition from X-ray and Chemical Data for the Pierre Shale. Geol. Surv. Prof. Pap. 1964.
- Moore, D.M.; Reynolds, R.C. X-Ray Diffraction and the Identification and Analysis of Clay Minerals, Second Edition. Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1997, pp. 378.
- Massiot, D.; Bessada, C.; Coutures, J.P.; Taulelle, F. A quantitative study of 27Al MAS NMR in crystalline YAG. J. Magn. Reson. 1990, 2, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, L.P.; Kahr, G. Determination of the Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC) of Clay Minerals Using the Complexes of Copper (II) Ion with Triethylenetetramine and Tetraethylenepentamine. Clays Clay Min. 1999, 47, 386–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd, P.; Khan, A.; Farooqui, M. Analytical Applications of Plant Extract as Natural pH Indicator: A Review. 2011.
- Vareda, J.P. On validity, physical meaning, mechanism insights and regression of adsorption kinetic models. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X. Adsorption isotherm models: Classification, physical meaning, application and solving method. Chemosphere 2020, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene-Kelly, R. The identification of montmorillonoids in clays. Journal of soil science 1953, 4, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabak, A.; Afsin, B.; Aygun, S.F.; Koksal, E. Structural characteristics of organo-modified bentonites of different origin. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2007, 87, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komadel, P.; Madejová, J. Chapter 7.1 Acid Activation of Clay Minerals. Dev. Clay Sci. 2006, 1, 263–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madejová, J. FTIR techniques in clay mineral studies. Vib. Spectrosc. 2003, 31, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guggenheim, S.; Koster van Groos, A.F. Baseline studies of the clay minerals society source clays: Thermal analysis. Clays Clay Min. 2001, 49, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorieul, S.; Allard, T.; Wang, L.; Grambin-Lapeyre, C.; Lian, J.; Calas, G.; Ewing, R. Radiation-stability of smectite. Env. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 8407–8411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Önal, M.; Sarıkaya, Y. Thermal behavior of a bentonite. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2007, 90, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woessner, D.E. Characterization of clay minerals by 27 Al nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Am. Mineral. 1989, 74, 203–215. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, H.H. Chapter 2: Structure and Composition of the Clay Minerals and their Physical and Chemical Properties. Developments in Clay Science 2006, 2, 7–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sette, P.; Fernandez, A.; Soria, J.; Rodriguez, R.; Salvatori, D.; Mazza, G. Integral valorization of fruit waste from wine and cider industries. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, C.H.; Smith, D. A General Treatment and Classification of the Solute Adsorption Isotherm. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 1974, 47, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limousin, G.; Gaudet, J.P.; Charlet, L.; Szenknect, S.; Barthès, V.; Krimissa, M. Sorption isotherms: A review on physical bases, modeling and measurement. Appl. Geochem. 2007, 22, 249–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadi, R.; Saadi, Z.; Fazaeli, R.; Fard, N.E. Monolayer and multilayer adsorption isotherm models for sorption from aqueous media. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 32, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigatti, M.F.; Galán, E.; Theng, B.K.G. Structure and Mineralogy of Clay Minerals. Dev. Clay Sci. 2013, 5, 21–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, R.; Trigueiro, P.; Orta-Cuevas, M.; Medina-Carrasco, S.; Duarte, T.; Honório, L.; Damacena, D.; Fonseca, M.G.; da Silva-Filho, E.; Osajima, J. The Stability of Anthocyanins and Their Derivatives through Clay Minerals: Revising the Current Literature. Minerals 2023, 13, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhalifah, A.; Murugesan, T.; Azmi-Bustam, M. Characterization of different cationic forms of montmorillonite by FTIR, XRD and TGA techniques. Natl. Postgrad. Conf. 2011, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein, R.M.; Bassler, G.C. Spectrometric identification of organic compounds, 1962, 39.
- Chigurupati, N.; Saiki, L.; Gayser, C.; Dash, A.K. Evaluation of red cabbage dye as a potential natural color for pharmaceutical use. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 241, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenger, J.A.; Moloney, M.; Robbins, R.J.; Collins, T.M.; Dangles, O. The influence of acylation, metal binding and natural antioxidants on the thermal stability of red cabbage anthocyanins in neutral solution. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 6740–6751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, E.; Martínez-Ortiz, M.J.; Fregoso, E.; Méndez-Vivar, J. Capturing natural chromophores on natural and synthetic aluminosilicates. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 2007, 170, 2110–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chigurupati, N.; Saiki, L.; Gayser, C.; Dash, A.K. Evaluation of red cabbage dye as a potential natural color for pharmaceutical use. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 241, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
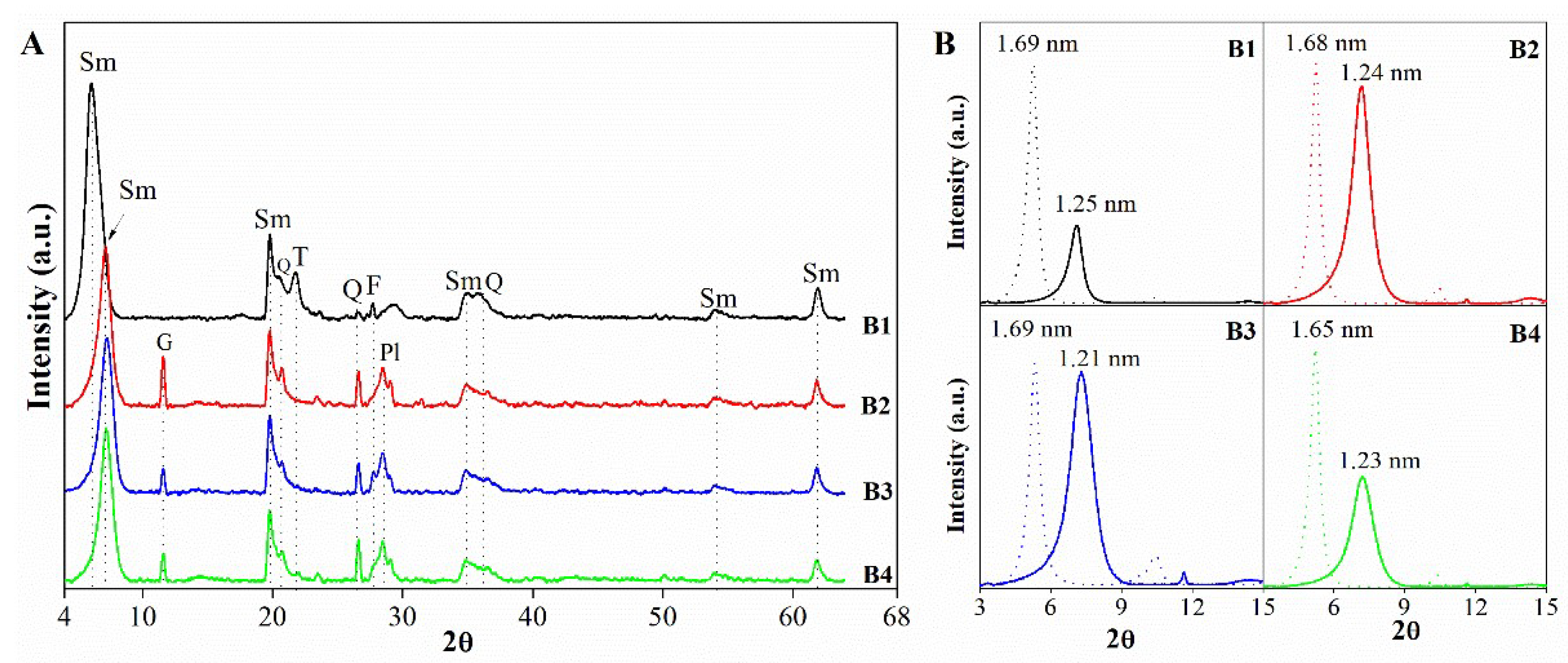
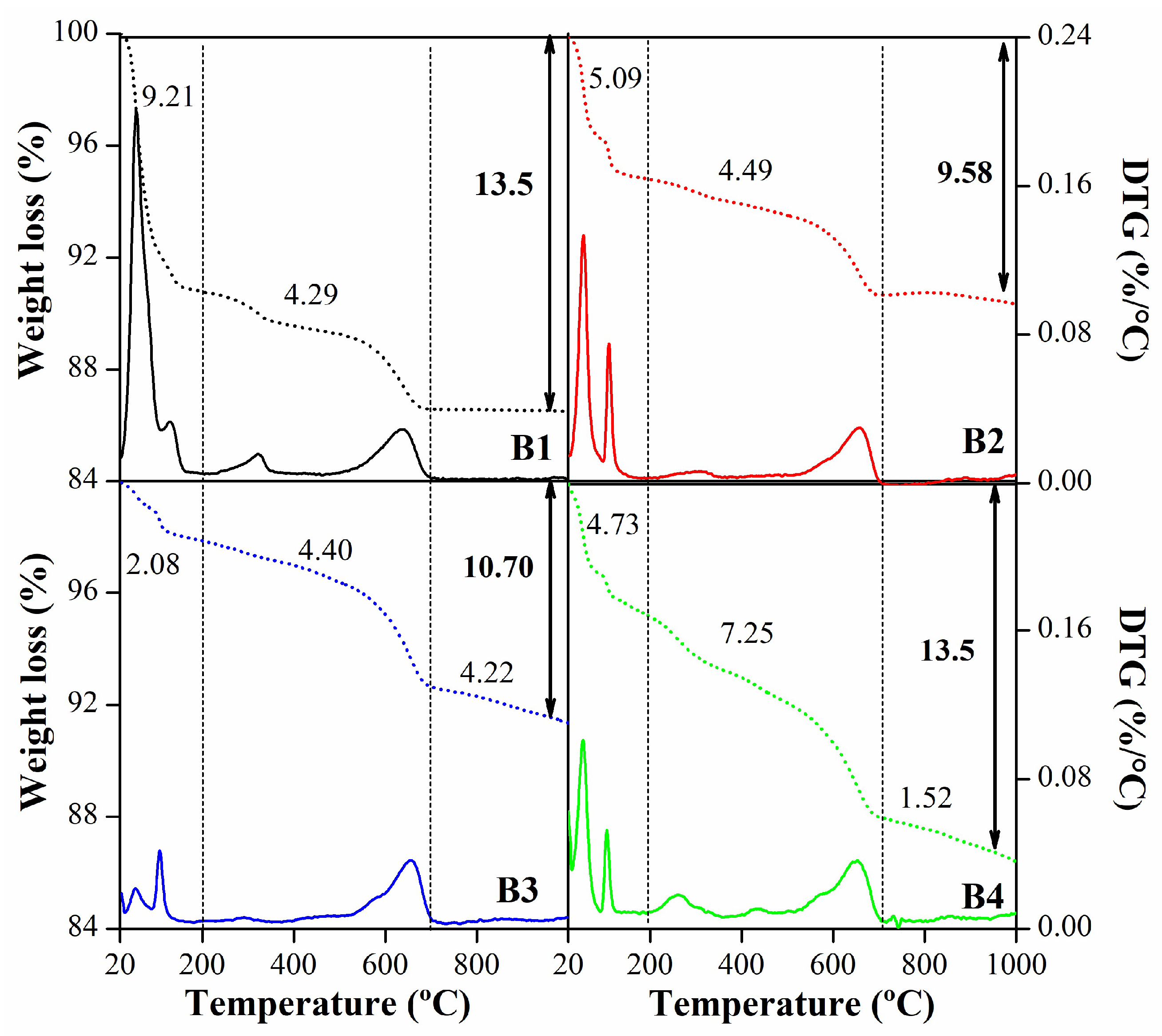
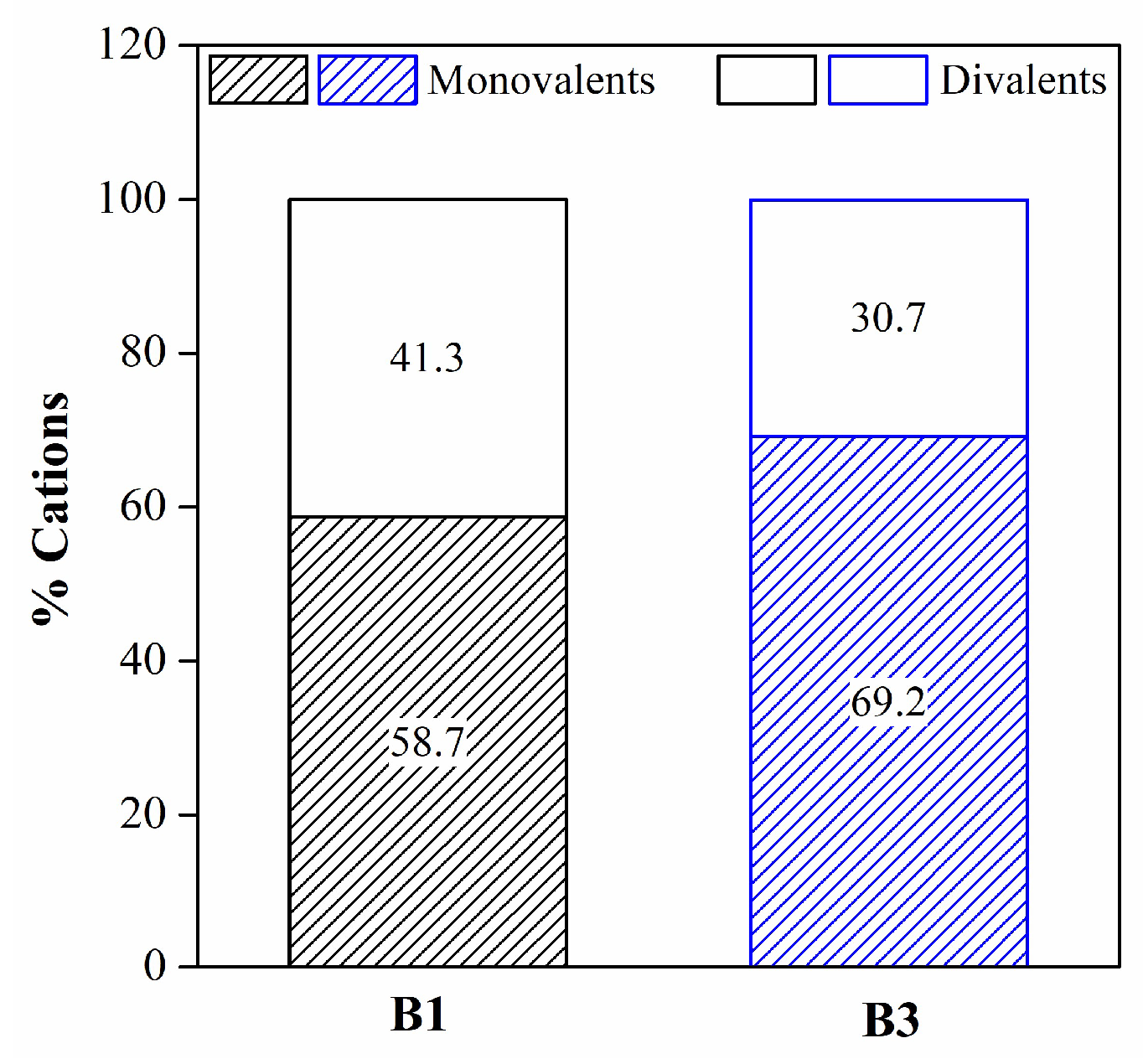
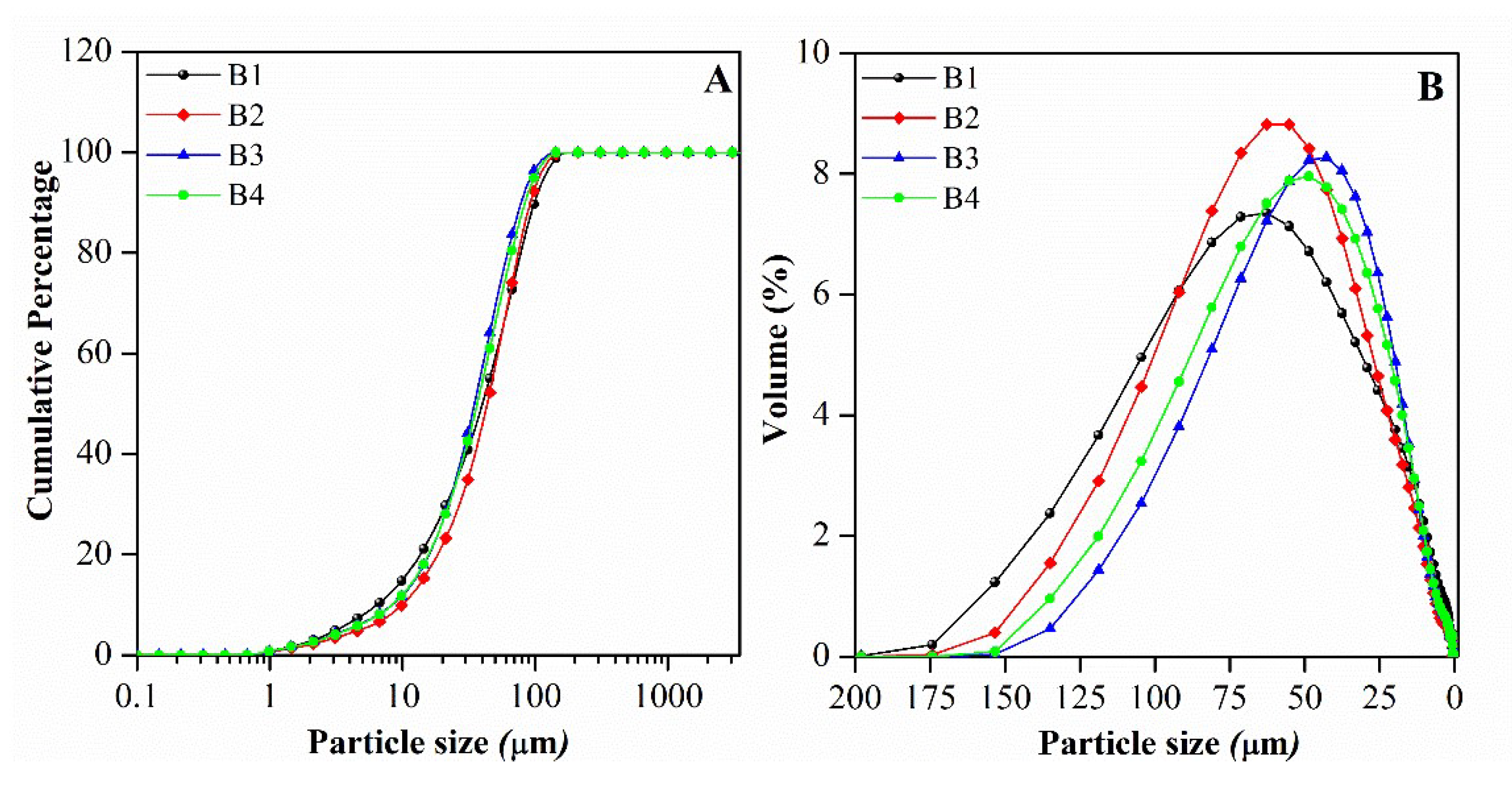
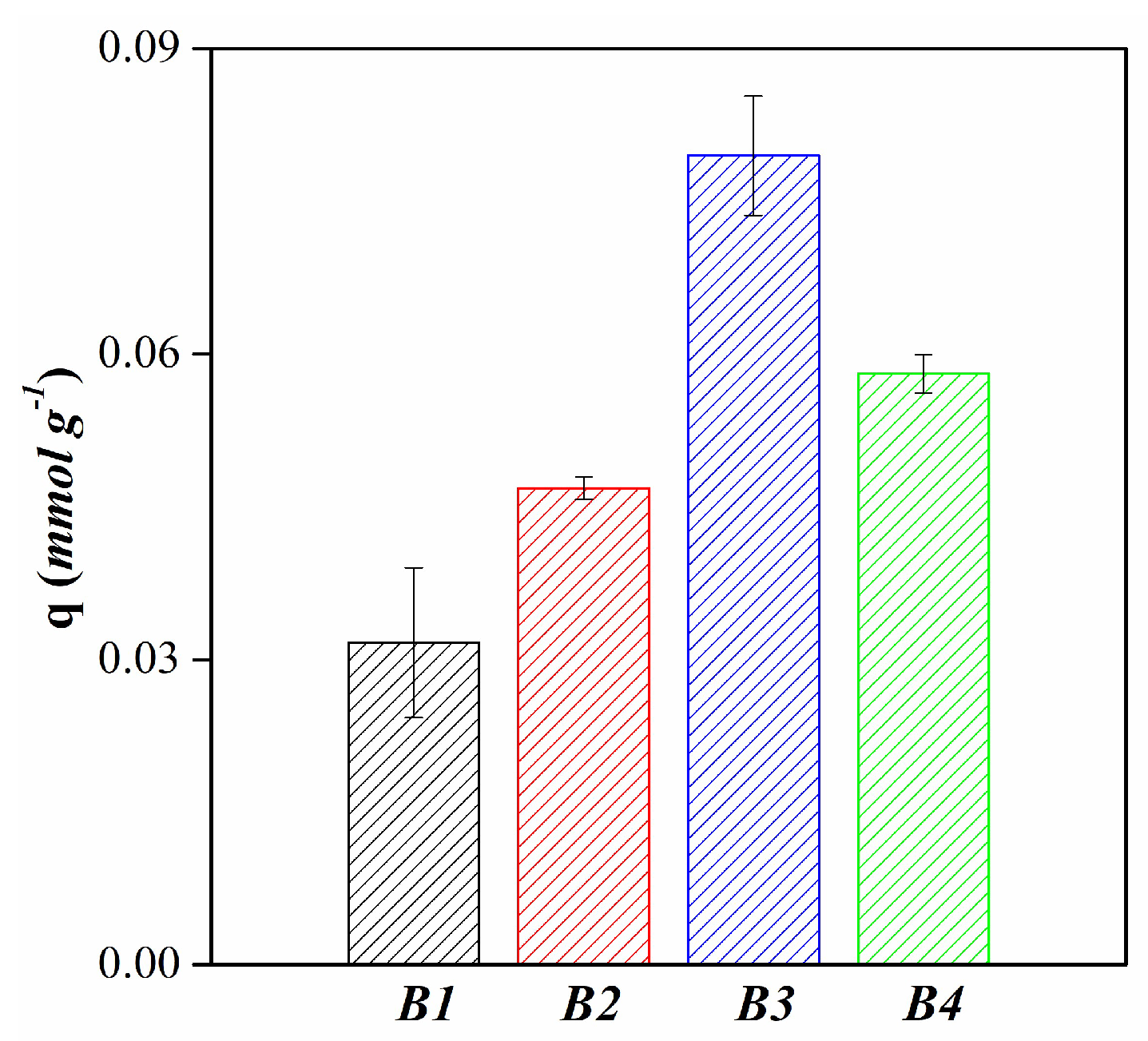

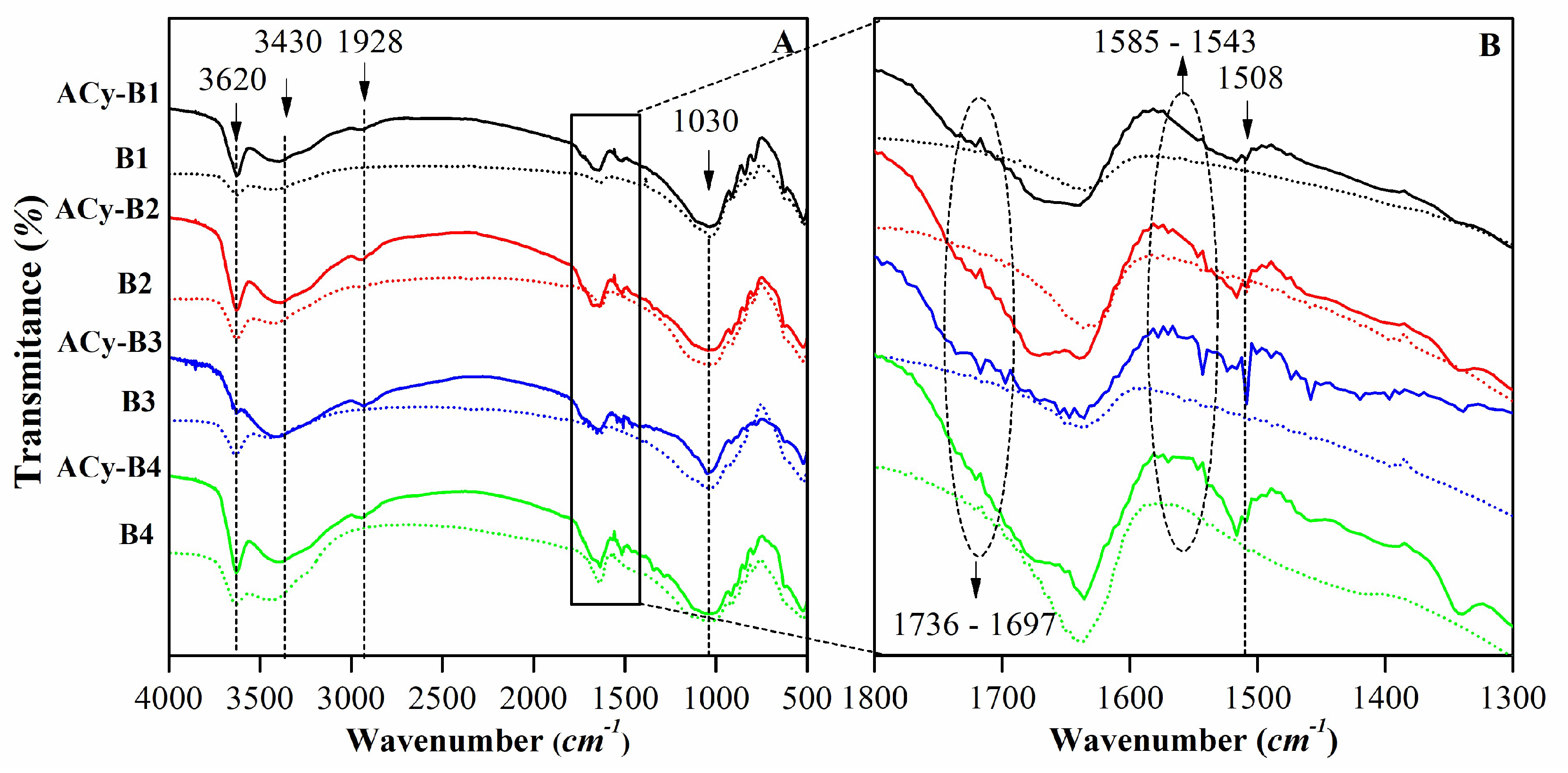
| Mineralogy (%w/w) | Basal d-spacing (nm) | Smectite crystallinity | Weight loss (%) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sm | Gy | Qz | Try | F | d001 | d060 | FWHM | Cr | 20-200°C | 200-1000°C | Total | |||
| B1 | 88 | 0 | Tr. | 10 | 2 | 1.456 | 0.1498 | 0.47 | 18 | 9.21 | 4.20 | 13.42 | ||
| B2 | 94 | 4 | 2 | 0 | Tr. | 1.247 | 0.1499 | 0.40 | 20 | 5.01 | 4.50 | 9.51 | ||
| B3 | 95 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1.224 | 0.1498 | 0.49 | 17 | 1.97 | 6.31 | 8.28 | ||
| B4 | 95 | 2 | 3 | 0 | Tr. | 1.224 | 0.1498 | 0.44 | 18 | 4.19 | 9.00 | 13.20 | ||
| % Sample |
SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | TiO2 | P2O5 | LOI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 | 58.49 | 14.58 | 1.09 | 0.031 | 4.19 | 1.09 | 1.28 | 0.26 | 0.158 | < 0.01 | 17.41 |
| B2 | 54.14 | 16.78 | 4.38 | 0.017 | 2.78 | 1.79 | 2.21 | 0.36 | 0.526 | 0.19 | 15.42 |
| B3 | 55.29 | 17.62 | 4.18 | 0.043 | 2.67 | 1.11 | 2.68 | 0.28 | 0.198 | 0.06 | 15.15 |
| B4 | 54.56 | 16.99 | 4.26 | 0.044 | 2.59 | 2.21 | 2.67 | 0.30 | 0.257 | 0.08 | 14.76 |
| B1 (Si8)IV(Al2.80Fe0.14Mg1.10Mn0.005Ti0.02)VIO20(OH)4,M+0.96 B2(Si7.92 Al0.08)IV(Al2.81Fe0.48Mg0.61Mn0.002Ti0.06)VIO20(OH)4 M+0.72 B3(Si7.93 Al0.07)IV(Al2.88Fe0.46Mg0.51Mn0.005Ti0.02)VIO20(OH)4M+0.79 B4(Si7.87Al0.13)IV(Al2.76Fe0.46Mg0.56Mn0.005Ti0.03)VIO20(OH)4 M+1.02 | |||||||||||
| Assignment | Sample (cm-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 | B2 | B3 | B4 | Wy | |
| υ Al(or Mg)-O-H | 3623 | 3620 | 3620 | 3620 | 3631 |
| υ H-O-H | 3430 | 3430 | 3430 | 3430 | 3442 |
| δ H-O-H | 1637 | 1637 | 1637 | 1637 | 1640 |
| υ Si-O | 1030 | 1030 | 1030 | 1030 | 1045 |
| δ Al-Mg-OH | 915 | 915 | 915 | 915 | 919 |
| δ Fe-Al-OH | --- | 883 | 883 | 883 | --- |
| δ Al-Al-OH | 845 | 845 | 849 | 845 | 843 |
| υ Si-O | 791 | 797 | 797 | 797 | 798 |
| δSi-O and Al-O | 626 | 626 | 626 | 626 | --- |
| δ Al-O-Si | 525 | 525 | 525 | 525 | --- |
| δ Si-O-Si | 463 | 463 | 463 | 463 | 463 |
|
CEC (cmol kg-1) |
Swelling (mL g-1) | Water content (%) | Color parameters | Silt (%) | Clay (%) | Dv50 (m) | Dv90 (m) | D[4,3] (m) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L* | a* | b* | |||||||||
| B1 | 99.56 | < 5.00 | 7.16 | 79.44 | 0.36 | 7.18 | 83.70 | 3.60 | 40.30 | 99.00 | 47.30 |
| B2 | 92.83 | 6.75 | 7.43 | 88.95 | 0.55 | 3.96 | 86.10 | 2.70 | 43.60 | 92.50 | 47.90 |
| B3 | 98.16 | 15.00 | 6.93 | 80.40 | -0.39 | 11.1 | 97.10 | 3.20 | 35.00 | 78.50 | 39.90 |
| B4 | 94.79 | 15.75 | 6.50 | 78.53 | 0.14 | 12.9 | 93.40 | 3.10 | 36.60 | 84.00 | 42.10 |
| B1 | B3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo- first order | qe (mmol g-1) | 0.01 | 0.07 |
| k1 (min-1) | 0.03 | 0.06 | |
| R2 | 0.92 | 0.99 | |
| Pseudo- second order | qe (mmol g-1) | 0.01 | 0.07 |
| k2 (g⸳(mmol min)-1) | 3.86 | 3.35 | |
| R2 | 0.89 | 0.99 |
| B1 | B2 | B3 | B4 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | qm (mmol g-1) | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.07 |
| k (L mmol-1) | 1.64 | 6.53 | 14.32 | 7.60 | |
| R2 | 0.87 | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.97 | |
| Freundlich | kf (L g-1) | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.07 |
| n | 1.62 | 2.61 | 3.53 | 2.82 | |
| R2 | 0.83 | 0.95 | 0.98 | 0.89 | |
| Sips | qm (mmol g-1) | 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.12 | 0.07 |
| b (L mmol-1)1/n | 4.17 | 3.90 | 3.96 | 8.67 | |
| n | 0.29 | 1.32 | 1.88 | 0.84 | |
| R2 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.99 | 0.97 |
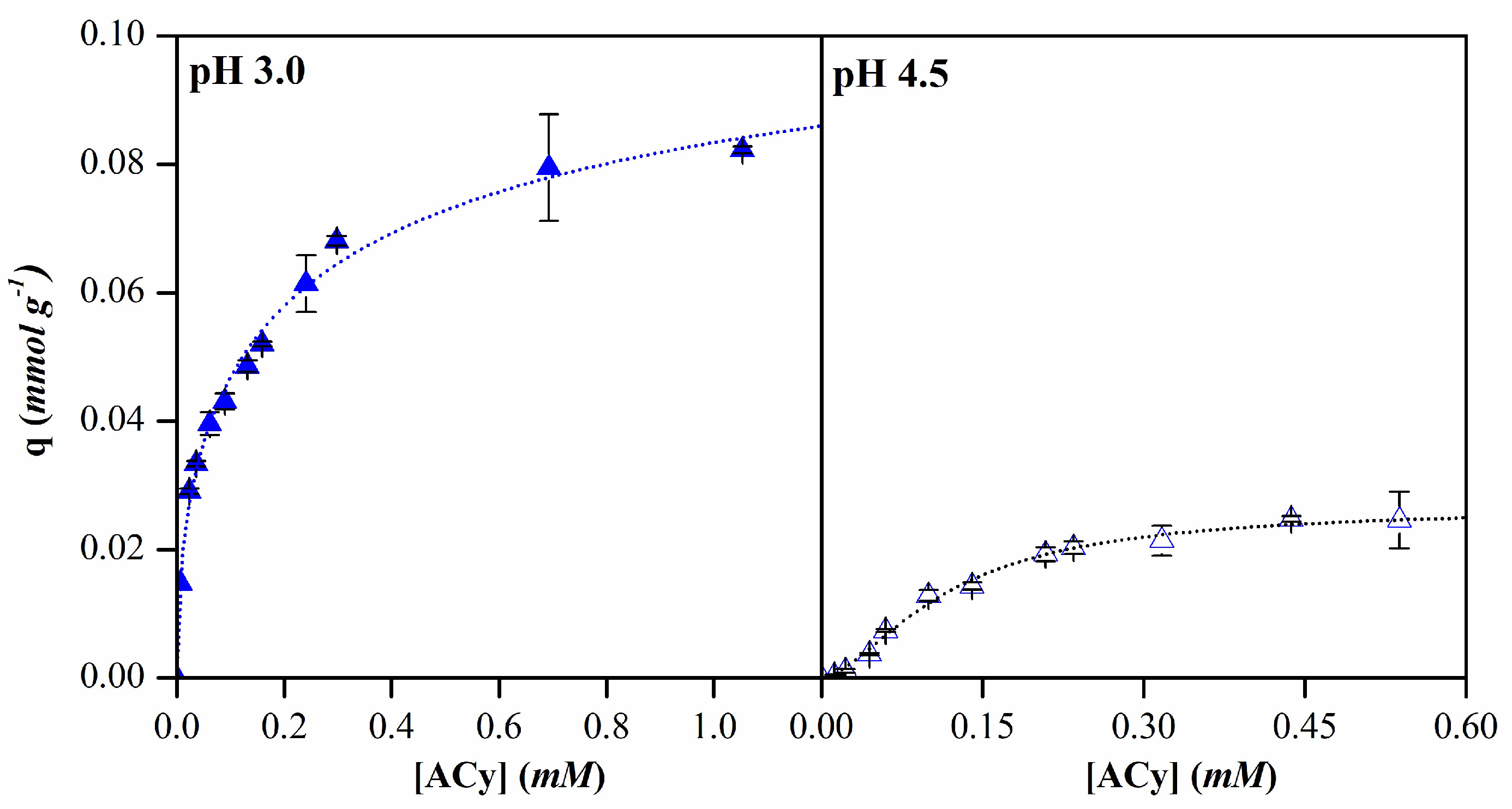
| pH 3.0 | pH 4.5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | qm (mmol g-1) | 0.08 | 0.04 |
| k (L mmol-1) | 14.32 | 4.51 | |
| R2 | 0.95 | 0.98 | |
| Freundlich | kf (L g-1) | 0.09 | 0.04 |
| n | 3.53 | 1.76 | |
| R2 | 0.98 | 0.93 | |
| Sips | qm (mmol g-1) | 0.12 | 0.03 |
| b (L mmol-1)1/n | 3.96 | 8.57 | |
| n | 1.88 | 0.61 | |
| R2 | 0.99 | 0.99 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





